Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Types of Pathogens: Anna Beth Reardon KINS 2041
Caricato da
Elisa Kustiyaningsih0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
15 visualizzazioni12 pagineannabeth-typesofpathogens-140228191244-phpapp01
Titolo originale
annabeth-typesofpathogens-140228191244-phpapp01
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoannabeth-typesofpathogens-140228191244-phpapp01
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
15 visualizzazioni12 pagineTypes of Pathogens: Anna Beth Reardon KINS 2041
Caricato da
Elisa Kustiyaningsihannabeth-typesofpathogens-140228191244-phpapp01
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 12
Types of Pathogens
Anna Beth Reardon KINS 2041
Pathogens
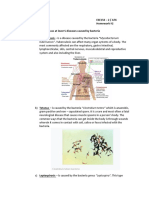
Pathogen – A microorganism that causes disease.
Reservoir – A natural environment in which a pathogen
typically lives.
- A human
- An animal
-An environmental component like soil or water
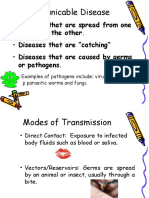
How do pathogens spread?
Pathogens must leave the reservoir through some portal of
exit.
Pathogens
Human Portals of exit:
-Saliva for mumps
-Mucous membranes for sexually transmitted diseases
-Blood for HIV and hepatitis
-Feces for intestinal infections
-Nose and throat discharges for colds and influenza
Pathogens can be transmitted directly or indirectly.
Directly transmitted – pathogens are passed from one person to another
without an intermediary.
-Sneezing
-Coughing
-Sexual contact
-Blood
-Mosquitoes
Types of Pathogens
Indirectly transmitted – animals or insects serve as vectors carrying the
pathogens from one host to the next.
-Ticks
-Mosquitoes
Different types of pathogens may include:
-Bacteria
-Viruses
-Fungi
-Protozoa
-Parasitic worms
-Prions
Bacteria
Bacteria – single-celled organism that usually reproduce by splitting in two
to create a pair of identical cells.
-Most abundant living things on earth
-Helpful and harmful bacteria
-Helpful bacteria: produce vitamins
help digest nutrients
keep harmful bacteria in check by competing for
food and resources
secreting substances toxic to pathogenic
bacteria
Diseases associated with bacteria:
Pneumonia – inflammation of the lungs
-Symptoms: fever, chills, shortness of breath, cough
-Leading infectious cause of death worldwide
-Vaccinations are recommended for adults 65 and older
.
Bacteria cont.
Meningitis – infection of the membranes covering the brain and
spinal cord
-Symptoms: fever, headache, stiff neck, confusion
-Usually mild and goes away on its own
-Vaccinations are recommended for children 11-18.
Strep throat – red, sore throat with white patches on the tonsils
-Symptoms: swollen lymph nodes, fever, headache
Tuberculosis – chronic bacterial infection that usually affects the
lungs
-Symptoms: coughing, fatigue, night sweats, weight loss
-10- 15 billion Americans have been infected and carry
Ulcers – 25 million Americans suffer
-Symptoms: pain in abdomen, nausea, loss of appetite
Virus
Virus – a very small infectious agent composed of nucleic acid
surrounded by a protein coat; lacks an independent metabolism and
reproduces only within a host cell.
-Inside the host cell, it sheds its protein covering,
and its genetic material takes control of the cell
and creates more viruses.
-Most common form of contagious disease
Diseases associated with viruses:
Common cold – lasts 1-2 weeks
-Almost always transmitted by hand-to-hand contact
-Reduce risks by washing hands frequently and avoid
touching face
-Avoid multi-symptom cold remedies
Virus cont.
Influenza – infection of the respiratory tract
-Commonly called the flu
-Symptoms: fever and extreme fatigue
-Recover within 1-2 weeks but can develop pneumonia
-Highest rates occur in children
Herpesvirus- a family of viruses responsible for cold sores,
mononucleosis, chickenpox, and herpes.
-Once infected, the host is never free of the virus
-Virus lies latent within cells and become active periodically
-Two herpesviruses can cause severe infections in people
with suppressed immune system which infects the lungs,
brain, colon, and eyes
Virus cont.
Viral Hepatitis- inflammation of the liver
-Caused by Hepatitis A, B, or C
-Symptoms: fatigue, jaundice, abdominal pain, loss of
appetite, and nausea
-Recover in one month
-5-10% of people infected with Hepatitis B and 85-90% of
Hepatitis C become chronic carriers of the virus
-500 million people worldwide may be carriers
-People who should get checked are people who had injected
drugs, received blood transfusion, have tattoos or piercings
Fungi & Protozoa
Fungus- an organism that absorbs food from organic matter
-Usually restricted to the skin, mucous membrane, and lungs
-Athlete’s foot, jock itch, and ringwom are common
-Can be deadly in people with an impaired immune system
Protozoa- a microscopic single-celled organism that often produces
recurrent, cyclical attacks of disease
-Malaria is a major killer worldwide
-Mostly among infants and children
-Giardiasis- parasite that lives in the intestines of humans
-Symptoms: nausea, diarrhea, bloating, abdominal cramp
Parasitic Worms &Prions
Parasitic Worms- a pathogen that causes intestinal and other infections
-Examples include: tapeworms, hookworms, and pinworms
-Tapeworms can grow many feet
-Pinworms are most common in United States
-Originate from contaminated food or drink
Prions- responsible for degenerative disorders of the central nervous system
-Lack DNA or RNA and consist of only protein
-Sponge-like holes in the brain
-Symptoms: loss of coordination, weakness, dementia, and death
-Examples include: Mad Cow Disease
Reference
Insel, Paul M., and Walton T. Roth. "Immunity And Infection." Connect Core
Concepts in Health. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2010. Print.
"Bacteria." American Museum of Natural History. Web. 03 Apr. 2011.
<http://
www.amnh.org/nationalcenter/youngnaturalistawards/1998/bacteria.h
tml>
"Viruses and Bacteria." NetDoctor.co.uk -The UK's Leading Independent
Health Website. Web. 03 Apr. 2011. <http://www.netdoctor.co.uk/
health_advice/facts/virusbacteria.htm>.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A New Model For Mental Health at WorkDocumento24 pagineA New Model For Mental Health at WorkJOSE100% (1)
- Aging and Its Socio Medical Implication PPT SajDocumento38 pagineAging and Its Socio Medical Implication PPT SajAsif Khan100% (1)
- II ME NRP B SS 26. Human Health and DiseaseDocumento9 pagineII ME NRP B SS 26. Human Health and DiseaseAmit RavindhraNessuna valutazione finora
- Infectious Disease NotesDocumento19 pagineInfectious Disease Notesshwetlana rampureNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of InfectionDocumento27 paginePrinciples of InfectionShella WidiyastutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-8 Human Health and Diseases ContinuationDocumento9 pagineChapter-8 Human Health and Diseases ContinuationKeerthana D SNessuna valutazione finora
- Health GR 7 Third QuarterDocumento60 pagineHealth GR 7 Third QuarterMeloueen Tolentino Osillos-AcdalNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Health and DiseaseDocumento6 pagineHuman Health and DiseaseSunil GargNessuna valutazione finora
- 10.1 PathogensDocumento8 pagine10.1 Pathogenselena farahNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogens & Microbiological Risk Assessment: CEGE2008 - Environmental PollutionDocumento43 paginePathogens & Microbiological Risk Assessment: CEGE2008 - Environmental PollutionmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Infection: Nevada Health ScienceDocumento26 paginePrinciples of Infection: Nevada Health Sciencejustin_saneNessuna valutazione finora
- 19 Chapter 22 PathogensDocumento29 pagine19 Chapter 22 Pathogenshoria96Nessuna valutazione finora
- Family: Picornaviridae (Enteroviruses)Documento35 pagineFamily: Picornaviridae (Enteroviruses)sky rainNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Human Health and Diseases PPT - (13 Feb 2022) (Repaired)Documento55 pagine8 Human Health and Diseases PPT - (13 Feb 2022) (Repaired)ssatechies62Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio - Human Health & DiseaseDocumento14 pagineBio - Human Health & Diseasea34146525Nessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 4222-265 Cause and Spread of InfectionDocumento3 pagineUNIT 4222-265 Cause and Spread of Infectionamacovei_3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 7 - Infectious Disease NotesDocumento12 pagineModule 7 - Infectious Disease NotesHSC CoachNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio InvestigatoryDocumento15 pagineBio InvestigatoryShrilata EruguralaNessuna valutazione finora
- .CDC For Nurses 1 - 1663860790000Documento57 pagine.CDC For Nurses 1 - 1663860790000Birhanu AbebeNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbial Diseases of The Respiratory SystemDocumento9 pagineMicrobial Diseases of The Respiratory SystemAnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infection: Meenal Jain MPT (Ortho and Manual)Documento18 pagineInfection: Meenal Jain MPT (Ortho and Manual)Rahul YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Health q3 ReviewerDocumento3 pagineHealth q3 Reviewerjoyceannmaglanoc123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Communicable DiseaseDocumento64 pagineCommunicable DiseaseMorris AngelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapeh ReviewerDocumento12 pagineMapeh ReviewerShane Marie TabulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Resuento - MIDTERM BIOSTATDocumento13 pagineResuento - MIDTERM BIOSTATKristine Joy Abellar ResuentoNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento5 pagineUntitledKanike ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 8 - Human Health and Diseases - NottesDocumento61 pagineCH 8 - Human Health and Diseases - NottesGopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Bilogy Class 12 Practical ProjectDocumento21 pagineBilogy Class 12 Practical Projectjoelpaul devrajNessuna valutazione finora
- Infection, Chain of Infection, and Infection Control NotesDocumento10 pagineInfection, Chain of Infection, and Infection Control NotesVerba LegisNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Infection ControlDocumento26 pagineBasic Infection ControlRayzl GacayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Eukaryotic Diseases - 06Documento33 pagineEukaryotic Diseases - 06Vien WhitlockNessuna valutazione finora
- Name:-Class: - Roll No.: - Subject:-: Rajbeer Malhotra Ix-D 24 BiologyDocumento15 pagineName:-Class: - Roll No.: - Subject:-: Rajbeer Malhotra Ix-D 24 BiologyKrish AggrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Project by Mohini SagarDocumento14 pagineBiology Project by Mohini Sagarsagarankit9977762Nessuna valutazione finora
- Infectious Diseases and Immunity: Set By: Mrs. Emebet Mohammed Mr. Solomon Taddesse Dr. Amir AlelignDocumento32 pagineInfectious Diseases and Immunity: Set By: Mrs. Emebet Mohammed Mr. Solomon Taddesse Dr. Amir AlelignTsegaye YalewNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Biology Notes Ch08 Human Health and DiseaseDocumento4 pagine12 Biology Notes Ch08 Human Health and DiseaseWali Pramod100% (1)
- DemoDocumento37 pagineDemoRhenevoi Bastiero NonatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Hand in 1Documento14 pagineFinal Hand in 1lauraNessuna valutazione finora
- VirusesDocumento13 pagineVirusesblakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report On Human Diseases: PathogenDocumento8 pagineProject Report On Human Diseases: PathogenPandit Shikhar TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes of CH 13 Why Do We Fall Ill Class 9Th Science: Topics in The ChapterDocumento7 pagineNotes of CH 13 Why Do We Fall Ill Class 9Th Science: Topics in The ChaptermallikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Health and DiseasesDocumento15 pagineHuman Health and DiseasesHarshith HachhuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Causes and Spread of InfectionDocumento7 pagineThe Causes and Spread of InfectionRamona LazurcaNessuna valutazione finora
- HW2 Ese150 GiananDocumento9 pagineHW2 Ese150 GiananTyrone GiananNessuna valutazione finora
- Aged 410 Presentation PathogensDocumento10 pagineAged 410 Presentation Pathogensapi-731088203Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCB 405 Dr. M-1-1Documento6 pagineMCB 405 Dr. M-1-1ejohn8340Nessuna valutazione finora
- Human Health NotesDocumento17 pagineHuman Health NotesGayathri Nandana M.SNessuna valutazione finora
- Giardia: PROTOZOA Is A Group of Phyla That Comprises The Single-Celled Microscopic Animals, WhichDocumento5 pagineGiardia: PROTOZOA Is A Group of Phyla That Comprises The Single-Celled Microscopic Animals, WhichAilah OtaganNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12Documento17 pagineClass 12Jitendra Kumar SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 156 Chapter 15 Powerpoint PP07Documento26 pagineBIO 156 Chapter 15 Powerpoint PP07DrPearcyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture No. 4 Biosci VirusDocumento3 pagineLecture No. 4 Biosci VirusJenny MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 14 EpidemiologyDocumento33 pagineCH 14 EpidemiologyCangelkween Krixen BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Health and Disease-1Documento18 pagineHuman Health and Disease-1debasmitabera5947Nessuna valutazione finora
- Human Health & DiseasesDocumento62 pagineHuman Health & DiseasesSumiNessuna valutazione finora
- Communicable DiseaseDocumento32 pagineCommunicable DiseaseRaquel M. MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 10Documento29 pagineLec 10api-27080431Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Project RDocumento20 pagineBio Project RSanjukth100% (1)
- Summary Science Unit 5, Lesson 1Documento3 pagineSummary Science Unit 5, Lesson 1Yohana ChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Viral Diseases - 06Documento51 pagineViral Diseases - 06HIMANSHU SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- 46 Infectious DiseasesDocumento36 pagine46 Infectious DiseasesRam NarayanaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Big Book of Infectious Disease Trivia: Everything You Ever Wanted to Know about the World's Worst Pandemics, Epidemics and DiseasesDa EverandThe Big Book of Infectious Disease Trivia: Everything You Ever Wanted to Know about the World's Worst Pandemics, Epidemics and DiseasesNessuna valutazione finora
- Coronavirus Covid-19. Defend Yourself. Avoid Contagion. Protect Your Home, Your Family, Your Work. Updated Fourth Edition.Da EverandCoronavirus Covid-19. Defend Yourself. Avoid Contagion. Protect Your Home, Your Family, Your Work. Updated Fourth Edition.Nessuna valutazione finora
- InterimGuidelines AHduringCOVID19Documento10 pagineInterimGuidelines AHduringCOVID19Shardin Labawan-Juen,RNNessuna valutazione finora
- Коспект лекційDocumento51 pagineКоспект лекційМарія МайорчакNessuna valutazione finora
- Australian Indigenous People - EditedDocumento8 pagineAustralian Indigenous People - EditedApril CliffordNessuna valutazione finora
- MCN Oral Surgery Referral Guidelines For Gdps Jan 2019 v1Documento23 pagineMCN Oral Surgery Referral Guidelines For Gdps Jan 2019 v1Smriti VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Infinity Fitness: A Gym and Wellness CenterDocumento24 pagineInfinity Fitness: A Gym and Wellness CenterAbygail MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing CS Acute-Kidney-Injury 04Documento1 paginaNursing CS Acute-Kidney-Injury 04Mahdia akterNessuna valutazione finora
- Hivi Hardtack Innovation Fish Scale Cookies Made From Fish Scales To Optimally Increase NutritionDocumento1 paginaHivi Hardtack Innovation Fish Scale Cookies Made From Fish Scales To Optimally Increase Nutritionapriyandi akNessuna valutazione finora
- Mood Disorders 1Documento54 pagineMood Disorders 1sijixoNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Plan MiloDocumento20 pagineMarketing Plan MiloSpear HenryNessuna valutazione finora
- Academic Sessions: Date Topic Speaker Designation DepartmentDocumento6 pagineAcademic Sessions: Date Topic Speaker Designation Departmentgoutham valapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quarter1 Module 1-2 and 3-4 DRRM SummativeDocumento3 pagineQuarter1 Module 1-2 and 3-4 DRRM SummativeGabriel Cabansag100% (1)
- Follow UpDocumento36 pagineFollow UpAlegria03Nessuna valutazione finora
- Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio As A Prognostic Indicator in Dengue Fever Patients at Tertiary Care Hospital in Northwest-MaharashtraDocumento5 pagineNeutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio As A Prognostic Indicator in Dengue Fever Patients at Tertiary Care Hospital in Northwest-MaharashtraIJAR JOURNALNessuna valutazione finora
- Scalp Acupuncture Treatment For Children With Autism and AdhdDocumento13 pagineScalp Acupuncture Treatment For Children With Autism and AdhdJujun100% (1)
- Clinic Director Operations Healthcare in Chicago IL Resume Kivaughn SheltonDocumento3 pagineClinic Director Operations Healthcare in Chicago IL Resume Kivaughn SheltonKivaughnSheltonNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 3 How A Clinical Psychologist ThinksDocumento7 pagineLesson 3 How A Clinical Psychologist Thinksjericho anchetaNessuna valutazione finora
- "Sin Taxes" and Health Financing in The Philippines - Case StudyDocumento10 pagine"Sin Taxes" and Health Financing in The Philippines - Case StudyMack ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- Gpas 2015 10 PaediatricsDocumento14 pagineGpas 2015 10 PaediatricsZack TaylorNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-Ii Role of The Nurse in Health Care: By: Farzana Nursing InstructorDocumento26 pagineUnit-Ii Role of The Nurse in Health Care: By: Farzana Nursing InstructorFara ZamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Miami Beach Police Jacobo Chigin Arrest FormDocumento4 pagineMiami Beach Police Jacobo Chigin Arrest FormRandom Pixels blogNessuna valutazione finora
- Three Treasures Manual With Tongue Pictures PDFDocumento214 pagineThree Treasures Manual With Tongue Pictures PDFspiraldao100% (4)
- Clinical States of Cirrhosis and Competing RisksDocumento14 pagineClinical States of Cirrhosis and Competing RisksmaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Libs 2804 Assignment 1 Fall 2021Documento2 pagineLibs 2804 Assignment 1 Fall 2021api-537166164Nessuna valutazione finora
- NEW Periodontal ClassificationDocumento7 pagineNEW Periodontal ClassificationCarlos MikaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Residents Self Assessment FormDocumento5 pagineResidents Self Assessment Formapi-245673459Nessuna valutazione finora
- Za Del Pací Co y Cuáles Son Sus Principales Bene Cios?Documento18 pagineZa Del Pací Co y Cuáles Son Sus Principales Bene Cios?SCA-Partners Export ConsultingNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurological Reorganization For Brain Injury by Sargent L. Goodchild, Jr.Documento6 pagineNeurological Reorganization For Brain Injury by Sargent L. Goodchild, Jr.autismoneNessuna valutazione finora