Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Protection Example and General Concepts: Table I - Failure Rates, Ref. 1
Caricato da
alvin me0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
8 visualizzazioni1 paginaTitolo originale
Failure Statistics
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
8 visualizzazioni1 paginaProtection Example and General Concepts: Table I - Failure Rates, Ref. 1
Caricato da
alvin meCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 1
external bus and cable, and faults in these zones 2.
Protection Example and General Concepts
may expose personnel to arc flash hazards. Slow The reader interested in additional information,
clearing protection schemes may be unaccept- advanced or unusual application advice, and
able from an arc flash exposure perspective. detailed settings guidance should refer to Ref. 1.
Fires in an indoor transformer may have high risk This document includes extensive references and
of catastrophic facility damage and even higher bibliographies. Also, Ref. 2 and 3, textbooks on
personnel safety risks, increasing the need for protective relaying, contain chapters on trans-
advanced high speed protection. The proximity former protection, and Ref. 4, another IEEE
of flammable process chemicals increases a standard, includes good overall protection
need for protection schemes that reduce the risk schemes where a transformer is the interface
of a tank fire. The failure of a transformer used in point between a utility and an industrial customer.
a large base load unit-connected generator may
cause extended generation-replacement costs; There are three general categories of protective
even the loss of a small station service trans- relay technology that arise in the discussions to
former can cause a notable disruption of genera- follow:
tion and high economic consequences. Similar • Electromechanical: uses magnetic flux
economic impacts may also exist at industrial created from current and voltage to create
sites. Some transformers are custom designs torques on movable disks and relays, which
that may have long lead times, increasing the is the source of the term “relay.” Usually
need for advanced protection schemes. single device number functionality.
• Solid State: uses low voltage analog signals
1. Failure Statistics created from sensed currents and voltages;
uses discrete electronics and basic logic
Table I lists failures for six categories of faults
circuits; may contain a basic microprocessor
(IEEE C37.90, “Guide for Protective Relay
for logic and some math. Usually single or
Applications to Power Transformers, Ref. 1).
dual device number functionality.
Winding and tap changers account for 70% of
• Numeric: a multifunction, programmable
failures. Loose connections are included as the
logic relay; digitizes sensed current and
initiating event, as well as insulation failures. The
voltage, then calculates an RMS or phasor
miscellaneous category includes CT failure,
equivalent value; uses a high-end micropro-
external faults, overloads, and damage in
cessor. Usually incorporates many device
shipment. An undisclosed number of failures
number functions.
starts as incipient insulation breakdown prob-
All Basler Electric relays are solid state or
lems. These failures can be detected by sophis-
numeric.
ticated online monitoring devices (e.g. gas-in-oil
analyzer) before a serious event occurs.
1955-1965 1975-1982 1983-1988
Percent of Percent of Percent of
Number Total Number Total Number Total
Winding failures 134 51 615 55 144 37
Tap changer failures 49 19 231 21 85 22
Bushing failures 41 15 114 10 42 11
Terminal board failures 19 7 71 6 13 3
Core failures 7 3 24 2 4 1
Miscellaneous failures 12 5 72 6 101 26
TOTAL 262 100 1127 100 389 100
Table I - Failure Rates, Ref. 1.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Basler Transformer Protection Application Guide PDFDocumento33 pagineBasler Transformer Protection Application Guide PDFAbrakain69Nessuna valutazione finora
- 09 - Transformer Protection Guide PDFDocumento33 pagine09 - Transformer Protection Guide PDFseshatsNessuna valutazione finora
- WRK PDFDocumento5 pagineWRK PDFRaghul RamasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- A Literature Review: Traditional and Advanced Protection Schemes of Power TransformerDocumento15 pagineA Literature Review: Traditional and Advanced Protection Schemes of Power TransformerFLORENS CAROLINENessuna valutazione finora
- Littelfuse Protection Relay Protection Relays White Paper PDFDocumento6 pagineLittelfuse Protection Relay Protection Relays White Paper PDFRamphani NunnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ijirt147770 Paper PDFDocumento2 pagineIjirt147770 Paper PDFSHRINGERI ACADEMYNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter One: Overview of Protective RelaysDocumento51 pagineChapter One: Overview of Protective RelaysyasinNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDa EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDa EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionNessuna valutazione finora
- Voltage Sag Detection Using 8051 Microcontroller IJERTV3IS21294Documento6 pagineVoltage Sag Detection Using 8051 Microcontroller IJERTV3IS21294nouhailaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ijert Ijert: Voltage Sag Detection Using 8051 MicrocontrollerDocumento6 pagineIjert Ijert: Voltage Sag Detection Using 8051 MicrocontrollernouhailaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Selection of MV Public Distribution NetworksDocumento24 pagineBasic Selection of MV Public Distribution NetworksBanyar AungNessuna valutazione finora
- Multifunction Digital Relays For Generator ProtectionDocumento10 pagineMultifunction Digital Relays For Generator Protectionfreddy riveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Over Current Protection of Transmission Line Using GSM and ArduinoDocumento5 pagineOver Current Protection of Transmission Line Using GSM and ArduinoFasika NibretuNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformer Protection Application GuideDocumento33 pagineTransformer Protection Application GuideDulon40100% (2)
- Embedded Control With Predictive Diagnostics Algorithm of The Induction Machine Drive SystemDocumento6 pagineEmbedded Control With Predictive Diagnostics Algorithm of The Induction Machine Drive SystemStephano Saucedo ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Transformer ProtectionDocumento70 paginePower Transformer ProtectionKavuri Sai PradeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Cmozina Generator Protection PDFDocumento18 pagineCmozina Generator Protection PDFEzequiel GregolinNessuna valutazione finora
- Protection and Commissioning of Multifunction Digital Transformer RelaysDocumento13 pagineProtection and Commissioning of Multifunction Digital Transformer Relaysrobertovm2002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Elnet GR User Manual PDFDocumento85 pagineElnet GR User Manual PDFStyler2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Breaker Maintenance, Sentinels On GuardDocumento4 pagineCircuit Breaker Maintenance, Sentinels On GuardНаталья ЕфименкоNessuna valutazione finora
- Schneider Electric - Electronic Trip Circuit Breaker BasicsDocumento20 pagineSchneider Electric - Electronic Trip Circuit Breaker BasicsJohn100% (3)
- Integrati On Ensí G Timing, Etc.: 1.2 Typical Protective Relays and Relay SystemsDocumento3 pagineIntegrati On Ensí G Timing, Etc.: 1.2 Typical Protective Relays and Relay Systemsbryan eduardo villegas carrascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Yalla UpgradeDocumento10 pagineYalla UpgradeBrett HendricksNessuna valutazione finora
- Rahnamaye Nasbe 110EM - en PDFDocumento17 pagineRahnamaye Nasbe 110EM - en PDFsenooooooNessuna valutazione finora
- Arduino Based Multifunctional Relay For Protection of Induction MotorDocumento6 pagineArduino Based Multifunctional Relay For Protection of Induction MotordaNessuna valutazione finora
- 18 PDFDocumento6 pagine18 PDFSunayana NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- 28 35 Talha Ali Qasmi PDocumento9 pagine28 35 Talha Ali Qasmi PbrightmoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Breaker BasicsDocumento20 pagineCircuit Breaker BasicsMarco Antonio Romero Acosta100% (1)
- Overload NotesDocumento20 pagineOverload NotesMisango EmmanuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter One: Introduction 1.1 Background of The StudyDocumento30 pagineChapter One: Introduction 1.1 Background of The StudyUzoma FrancisNessuna valutazione finora
- Easun Reyrolle Limited: Application and Commissioning Manual Mit161 RelayDocumento24 pagineEasun Reyrolle Limited: Application and Commissioning Manual Mit161 RelaySumonto MajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mit 161Documento24 pagineMit 161Santosh Gairhe100% (1)
- Commissioning and Maintenance Testing of Multifunction Digital RelaysDocumento10 pagineCommissioning and Maintenance Testing of Multifunction Digital RelaysASHOK KUMAR MUWALNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotor Earth Fault Protection of GeneratorDocumento31 pagineRotor Earth Fault Protection of GeneratorRoger IlachoqueNessuna valutazione finora
- An Online Technique For Monitoring The InsulationDocumento9 pagineAn Online Technique For Monitoring The InsulationMonthly ImogenNessuna valutazione finora
- Protection of Power Systems With Distributed GenerationDocumento35 pagineProtection of Power Systems With Distributed GenerationTrường ArsenalNessuna valutazione finora
- ESD User ManualDocumento58 pagineESD User ManualRamesh darwin100% (1)
- Voltage Sags: Effects, Mitigation and PredictionDocumento7 pagineVoltage Sags: Effects, Mitigation and PredictionHigor SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformer Fault Detection Using Zigbee and GSMDocumento46 pagineTransformer Fault Detection Using Zigbee and GSMIrfan Baig100% (1)
- Cahier Technique by SchneiderDocumento30 pagineCahier Technique by SchneiderKS CheeNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Paper (New 1)Documento5 pagineResearch Paper (New 1)Mahesh ShendeNessuna valutazione finora
- Protection Relays: Noornabi ShaikhDocumento47 pagineProtection Relays: Noornabi ShaikhSyeda TanzilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principle of Arc Fault Detection For Solid State Power ControllerDocumento7 paginePrinciple of Arc Fault Detection For Solid State Power ControllerwilliamNessuna valutazione finora
- CT185 Dynamic Stability of Industrial NetworkDocumento28 pagineCT185 Dynamic Stability of Industrial NetworkEdsonHenriqueFerreiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical ProtectionDocumento94 pagineElectrical ProtectionNeil Summer100% (7)
- Numerical RelaysDocumento38 pagineNumerical Relaysashutosh2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- MOZINA - Upgrading The Protection of Industrialsized Generators Using DigDocumento8 pagineMOZINA - Upgrading The Protection of Industrialsized Generators Using DigAngel De la CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophy of Protective RelayingDocumento20 paginePhilosophy of Protective RelayingSasquatchCornNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 A.) - Various Types of IED SDocumento4 pagine8 A.) - Various Types of IED SIfiifNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics Design Handbook: Low-Power Components and ApplicationsDa EverandPower Electronics Design Handbook: Low-Power Components and ApplicationsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageDa EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageNessuna valutazione finora
- Transistor Electronics: Use of Semiconductor Components in Switching OperationsDa EverandTransistor Electronics: Use of Semiconductor Components in Switching OperationsValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Aerox Stop and Start SystemDocumento1 paginaAerox Stop and Start Systemalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerox Seat Opening and ClosingDocumento1 paginaAerox Seat Opening and Closingalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerox Restarting The EngineDocumento1 paginaAerox Restarting The Enginealvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Systems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application PapersDocumento1 paginaSystems With The DC Mid-Point Grounded: Technical Application Papersalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Aerox Smart Key SystemDocumento1 paginaAerox Smart Key Systemalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocumento1 paginaTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocumento1 pagina2.5 2 1.41 Iconv: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- High Fault ResistanceDocumento1 paginaHigh Fault Resistancealvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocumento1 paginaTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Systems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2Documento1 paginaSystems With The DC Negative Pole Grounded: dc1 DC/R Convdc2alvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G GDocumento1 paginaFaults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Converters: G G DCN G G Galvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- High Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application PapersDocumento1 paginaHigh Fault Resistance R With ESS (S1 OFF, S2 ON) : Technical Application Papersalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution SystemsDocumento1 paginaAdvantages of Low Voltage DC Distribution Systemsalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Hazard of Direct CurrentDocumento1 paginaHazard of Direct Currentalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavior With PV PlantDocumento1 paginaBehavior With PV Plantalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Waveform of The AC CurrentDocumento1 paginaWaveform of The AC Currentalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Maximum AC Current AbsorptionDocumento1 paginaMaximum AC Current Absorptionalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- LVDC Microgrid BehaviorDocumento1 paginaLVDC Microgrid Behavioralvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Case 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6Documento1 paginaCase 2a: Sin Sin (6.3) 106.6alvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Ground Fault AnalysisDocumento1 paginaDC Ground Fault Analysisalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
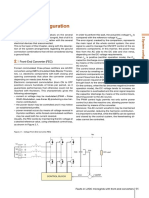
- 2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)Documento1 pagina2 System Configuration: Front-End Converter (FEC)alvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Elimination of SynchronizationDocumento1 paginaElimination of Synchronizationalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensitive Electronic LoadsDocumento1 paginaSensitive Electronic Loadsalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Ambient Temperature Around The Miniature Circuit BreakerDocumento1 paginaAmbient Temperature Around The Miniature Circuit Breakeralvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End ConvertersDocumento1 paginaTechnical Application Papers: Faults in LVDC Microgrids With Front-End Convertersalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Distribution NetworksDocumento1 paginaElectrical Distribution Networksalvin meNessuna valutazione finora
- Introducing The Hybrid Method of Moments/Finite Element Method (Mom/Fem)Documento4 pagineIntroducing The Hybrid Method of Moments/Finite Element Method (Mom/Fem)Edy JjNessuna valutazione finora
- TESAR - TransformersDocumento4 pagineTESAR - TransformersIvan HandjievNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectricityDocumento9 pagineElectricityTwinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Sheet 6ES7232-4HD32-0XB0: General InformationDocumento3 pagineData Sheet 6ES7232-4HD32-0XB0: General InformationafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Gemini 15 Laser SystemDocumento72 pagineGemini 15 Laser Systemt8e7w2koNessuna valutazione finora
- UFS 15-22-40-110 UFS15J-22J-40J: Braking UnitDocumento21 pagineUFS 15-22-40-110 UFS15J-22J-40J: Braking UnitnayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Snap-On Multimeter ManualDocumento15 pagineSnap-On Multimeter ManualAdrianna ColonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutsheet5 SolutionsDocumento5 pagineTutsheet5 SolutionsDevendra Singhaniya90% (10)
- 012-1Z5T (Rele)Documento3 pagine012-1Z5T (Rele)el_george0079491Nessuna valutazione finora
- Leece Neville 4000 Series Alternator Service ManualDocumento21 pagineLeece Neville 4000 Series Alternator Service ManualOneil Campbell100% (1)
- EasyPact CVS Trip CurvesDocumento7 pagineEasyPact CVS Trip CurvesKS CheeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Actuator Head 227sol: DescriptionDocumento2 pagineElectrical Actuator Head 227sol: DescriptionIVAN DE LA CRUZNessuna valutazione finora
- Admmodule s11 12ps Iiia 1Documento27 pagineAdmmodule s11 12ps Iiia 1Lebz Ricaram100% (2)
- O Level Physics Formula SheetDocumento2 pagineO Level Physics Formula SheetMomin BabarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.dynamics of Electrical DrivesDocumento47 pagine2.dynamics of Electrical DrivesSimbarashe ChitsungeNessuna valutazione finora
- Allied PhysicsDocumento9 pagineAllied PhysicsJostin Punnassery50% (4)
- Engineering Sciences 151. Electromagnetic Communication LaboratoryDocumento5 pagineEngineering Sciences 151. Electromagnetic Communication LaboratorybaymanNessuna valutazione finora
- HV Porcelain Bushing: IS2099 Galvanization: IS2633 Primary Terminals: IS 10601Documento9 pagineHV Porcelain Bushing: IS2099 Galvanization: IS2633 Primary Terminals: IS 10601AnilNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms & Isotopes 1 QPDocumento17 pagineAtoms & Isotopes 1 QPMagd OsamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Right Side View Panel Front View: C13, C15 and C18 Generator Set Electrical System With EMCP 4.1/4.2Documento2 pagineRight Side View Panel Front View: C13, C15 and C18 Generator Set Electrical System With EMCP 4.1/4.2Rachmad BuntoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas Fisika - 2Documento4 pagineTugas Fisika - 2bellina yunitasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock Test Code-BDocumento18 pagineMock Test Code-BKomal VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Generator Stator Assembly Inspection Sheet PDFDocumento32 pagineGenerator Stator Assembly Inspection Sheet PDFPradip RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Self InductanceDocumento3 pagineSelf Inductancesuhayb100% (1)
- With Monitor Bio-Uv MiiiDocumento93 pagineWith Monitor Bio-Uv MiiiCarlos PinellNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics LectureDocumento23 paginePhysics LectureDenji HimenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Order in Nanoparticles A XMCD SDocumento12 pagineMagnetic Order in Nanoparticles A XMCD STobiasNessuna valutazione finora
- ERRORLESS Unit ND DimensionsDocumento25 pagineERRORLESS Unit ND DimensionsMoon KnightNessuna valutazione finora
- LS Medium Voltage Vacuum Contactors: Tri-MECDocumento36 pagineLS Medium Voltage Vacuum Contactors: Tri-MECEkanit ChuaykoedNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnetic Integration For Interleaved Converters: P. Zumel, O. García, J. A. Cobos and J. UcedaDocumento7 pagineMagnetic Integration For Interleaved Converters: P. Zumel, O. García, J. A. Cobos and J. Ucedaraza239Nessuna valutazione finora