Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
4-Vitamins 2015 PDF
Caricato da
Fariz AzizTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
4-Vitamins 2015 PDF
Caricato da
Fariz AzizCopyright:
Formati disponibili
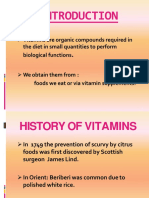
I – fat soluble vitamins
1-Vitamin A (Retinol)
*precursor: B caroten
* uses :
A-psoriasis
b- Acne vulgaris (retinoic acid)
c- Night blindness
d- Skin disease
N.B: vit A does not cross the placenta & it is essential for mucous epithelial cell
production (Category X in pregnancy)
*deficiency:
a- night blindness
b- Keratinization of the epithelial cells of the cornea & all mucous membrane
c- Loss of appetite
*toxicity:
-hyperstoses (bone hypertrophy) in children
- peeling of the skin
- Headache
- Lymph node enlargement
*daily requirements: orally or IM
Child 1300- 2600 IU
Adults 3000 IU
N.B:- Zn is essential for 1- maintenance of vit A in plasma
2-mobilization of vit A from the liver
- Administration of vit E with vit A increase absorption & tissue storage
- vit A must not exceed 10000 iu
- vit A is imp for vision , growth & reproduction
2-VIT D: (calciferol)
*precursor: 7- dehydro ergosterol U.V cholecalciferol D3
Ergosterol u.v calciferol VIT D2
*uses:
Has parathyroid hormone like action
1 Edition 2015 Cell phone: +1(571)699 4550
-increase GIT absorption of Ca++
-increase tubular reabsorption of Ca++
- decrease mobilization of Ca++ from bone to blood
*deficiency: due to diet deficiency or inadequate exposure to sun light
In children rickets
In adults osteomalacia "soft bone"
Hyperparathyroidism
*toxicity:
-hypercalcaemia -myocardial infarction
-Mental retardation - deposition of Ca in soft tissue
-Increase digitalis toxicity - constipation
- stop the growth
*uses: Treatment of hyperparathyroidism & rickets
*daily req: 400 IU &for rickets 4000-40000
N.B: + Vit D is completely absorbed from GIT & depend on hepatic & biliary function, so drug
that increase hepatic microsomal enz (e.g. anticoagulants, barbiturates, rifampicin &
antidepressants ) cause vit D deficiency
+ lasix (furosemide) is contra indicated in vit D deficiency because it cause hypocalcaemia
(decrease Ca++)
3-VIT E : alpha -tocopherol
*present naturally in green vegetables, eggs & meat
* uses:
-increase absorption of vit A
- Anti oxidant for oily solution
- Carried in plasma by B- lipoprotein
*deficiency:
a- anemia b- muscular dystrophy
2 Edition 2015 Cell phone: +1(571)699 4550
c- Male sterility d- habitual abortion in females
*toxicity:
Safe in very high doses
*daily req: 5-10 IU/day
NB: contraindicated with minerals as Ca++ & iron
4-VIT K : K1 phyto quinone plant origin
K2 mena quinone bacteria origin in GIT
K3 mena dione synthetic origin (H2O sol)
*Uses:
Essential for production of prothrombin in the liver
* Deficiency:
- In infant: hemorrhagic anemia & kernicterus (increase bilirubin)
- In adult: decrease liver function jaundice
N.B: .Antidote of vit K is coumarine (dicoumarol)
. xss Ab use decrease normal flora decrease vit K synthesis
deficiency of vit k
II-water soluble vitamins
1-vit B1 (thiamine)
Co enz in CHO metabolism, present naturally in yeast & liver. It is thermo labile
* Deficiency:
Cause Beri –Beri disease (peripheral neuritis) its symptoms:
- Mental disorder - fatigue
- Tachycardia -heart edema
-Low conc of HCL
3 Edition 2015 Cell phone: +1(571)699 4550
*toxicity: not marked (safe)
*daily Req : adult >0.6mg 4,5mg
Child 0.4mg
*uses:
1-Beri Beri treatment 2-diabetes mellitus (peripheral neuritis)
3-Neuralgia 4 -Mental disorder
2-vit B2 (Riboflavin )
An H+ carrier which play imp role in energy metabolism in respiratory chain.
Absorbed from upper GIT & never given alone but in combination with other Vit B cplx
* Deficiency:
1-chelosis (cracks in the corner of the mouth)
2-Glossitis (tongue inflammation)
3-photophobia (due to corneal vascularization)
4-Keratitis
5-embryo toxicity in pregnant female
*Daily Req. child > 0.6 adult >1mg oraly ,IM ,SC
3- vit B3 (Nicotinic acid or Niacin)
Nicotinic acid
Occur in 2 forms Nicotinamide
It is H+ carrier coenz for protein metabolism &production of energy ATP (in resp . chain)
*side effect of Vit B3 :
-Flushing -vasodilatation -hyperuricemia
-Hyperglycemia -hypocholesterolemia
* Deficiency:
Mainly cause pellagra characterized by:-
4 Edition 2015 Cell phone: +1(571)699 4550
1-dermatitis 2-weakness 3-Neuritis
4-CNS confusion 5-photosensitivity 6-GIT irritation
7-schizophrenia sub clinical pellagra
*Daily Req.: child > 4mg adult > 6mg 45mg
4-Vit B6 (pyridoxine)
1-for amino acid metabolism: tryptophan vit B6 Nicotinic acid
2-Co enz essential for GABA production in the brain which is the main neurotransmitter
inhibitor to prevent convulsion
* Deficiency:
+epileptic convulsion +peripheral neuritis +Dermatitis
+ iron deficiency anemia
*Drug interaction with Vit B6
-oral contraceptive: deplete B6 should be supplied
-pregnancy : deplete B6
-Hydralazine, INH, penecillamine: decrease tryptophan metabolism
-L-Dopa: increase metabolism of vit B6 by increase synth of decarboxylase enz
(convert L-Dopa dopamine)
5-VIT B12 (cyanocobolamin)
- Maintenance of myelin sheath in the nervous tissue (its deficiency neurological signs)
-imp for synthesis of epithelial cells & normal growth
-It needs an intrinsic factor for its absorption from GIT, it is a glycoprotein in nature
(Its deficiency is called pernicious anemia)
- How to differentiate if pernicious anemia is due to either
a) Deficiency of intrinsic factor
Or b) deficiency of B12 by
5 Edition 2015 Cell phone: +1(571)699 4550
Schilling test: take vit B12 + Co57 or Co58
1-if Co57 appear in feaces: (not absorbed)
So pernicious anemia due to lack of intrinsic factor
Vit B12
2- If Co57 appear in urine (absorbed)
So anemia due to lack of vit B12 alone
Pernicious anemia (addison's pernicious anemia)
-due to decrease in intrinsic factor in GIT
- lead to peripheral gastric mucosal atrophy, glotitis, achlorohydria (decrease HCL
secretion) &lead to megaloplastic anemia
- III by vit B12 IM or SC inj (depovit B12)
NB: * oral preparation are of no value
6-Folic acid :
- Essential for synthesis of pyrine &pyrimidine bases
- used in megaloplastic anemia beside B12
*not use folic acid because it mask signs of vit B12 deficiency
*folic acid anti metabolite (methotrexate) used as anticancer
7-Biotine:-
*synthesized by bacterial flora or taken with food
*involved in some fatty acid synthesis & many carboxylation reactions
*consumption of egg white only deficiency
8-Choline:-
*synthesized in the body from Methionine amino acid
* Essential for phosphatidyl Choline synthesis which is involved in lipid transport
&Ach synthesis
6 Edition 2015 Cell phone: +1(571)699 4550
9-Pantothenic acid:- (panthenol)
Converted to co A enz which is essential for A Ch . synthesis
Used locally to heal wounds F.A. metabolism
10-Vit C: Ascorbic acid
Present in green veg. & citrus fruits
Level in female > male & smoking decrease vit C in blood
Importance: 1-essential for collagen synthesis in the connective tissue
2-imp in oxidation – reduction reaction (redox) & cellular respiration
3-as a reducing agent: - used in III of Meth Heamoglobinemia
4-antidote for alcohol over dose bec – it activate alc. Dehydrogenase
enz. Which is essential for alc metabolism
NB: vit C give false +ve result with clinitest depends on cuso4 reduction by glucose in urine
Defficiency:
Scurvy disease:- Gum bleeding- lesion in teeth, bones & blood vessels
Toxicity:
1-stones in urinary tract
2-diarhea
3-ingesion of 10 gm daily then withdrawal frank symptom or scurvy
NB: scurvy appears in new bornes whom mothers ingest high amount of vit C
Dose: child >20mg/day
Adult >150mg/ day
7 Edition 2015 Cell phone: +1(571)699 4550
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Assignment No. 01 SEMESTER: Spring 2020 CS403-Database Management System Question StatementDocumento3 pagineAssignment No. 01 SEMESTER: Spring 2020 CS403-Database Management System Question StatementMarrayam MarrayamNessuna valutazione finora
- I - Fat Soluble Vitamins: 1-Vitamin A (Retinol)Documento7 pagineI - Fat Soluble Vitamins: 1-Vitamin A (Retinol)Zehra KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins & NutritionDocumento56 pagineVitamins & Nutritionahmed abd elazizNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins: Dr. Babiker Mohamed Ali RahamtallaDocumento52 pagineVitamins: Dr. Babiker Mohamed Ali Rahamtallaعوض الكريمNessuna valutazione finora
- The Eldoret National Polytechnic, Diploma in Pharmaceutical TechnologyDocumento20 pagineThe Eldoret National Polytechnic, Diploma in Pharmaceutical TechnologyGerald Limo Arap ChebiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Soluble VitaminsDocumento33 pagineWater Soluble VitaminsRhomizal MazaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Acting On Nutrition and PainDocumento96 pagineDrugs Acting On Nutrition and Painhanna caballoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bridge Vitamins and HaematinicsDocumento22 pagineBridge Vitamins and HaematinicsHamss AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry: SMASHUSMLE Biochemistry Lecture NotesDocumento40 pagineBiochemistry: SMASHUSMLE Biochemistry Lecture NotesRaju NiraulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Defisiensi VitaminDocumento30 pagineDefisiensi VitaminRulianis ApriantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry "Vitamins"Documento7 pagineBiochemistry "Vitamins"HERONessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins: Lec.1: Dr. NahidaDocumento11 pagineVitamins: Lec.1: Dr. NahidaxxxdarknessNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin SlidesCarnivalDocumento29 pagineVitamin SlidesCarnivalBibek GajmerNessuna valutazione finora
- VITAMINSDocumento58 pagineVITAMINSRazvan DinuNessuna valutazione finora
- VitaminsDocumento15 pagineVitaminsSAURABH PRAJAPATINessuna valutazione finora
- VitaminsDocumento29 pagineVitaminsVijay KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin EDocumento29 pagineVitamin ESiva Krishna NeppaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Soluble Vitamin: Dept. of Nutrition Medical School Universitas PadjadjaranDocumento49 pagineWater Soluble Vitamin: Dept. of Nutrition Medical School Universitas PadjadjaranHadiyatussalamah Pusfa KencanasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin-A: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDocumento42 pagineVitamin-A: M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, PH.DDr. M. Prasad NaiduNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry and Source Vitamin A Occurs in Nature in Several Forms. RetinolDocumento6 pagineChemistry and Source Vitamin A Occurs in Nature in Several Forms. RetinolElly NurlaelyNessuna valutazione finora
- VITAMINS - StomDocumento45 pagineVITAMINS - StomMihalachi-Anghel MariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry of VitaminsDocumento64 pagineBiochemistry of VitaminsConrado CatimbangNessuna valutazione finora
- "Vita" - Life, + AmineDocumento91 pagine"Vita" - Life, + AmineMaureen Chavez Kinney100% (1)
- Vitamins: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman Ph.D. M.D Medical BiochemistryDocumento20 pagineVitamins: Dr. Lotfi S. Bin Dahman Ph.D. M.D Medical BiochemistryHUAWEI HUAWEINessuna valutazione finora
- Defisiensi VitaminDocumento30 pagineDefisiensi VitaminnawriirwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Defisiensi VitaminDocumento30 pagineDefisiensi VitaminayuNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin Deficiencies & Excesses: Dr. Shirley L A, Sp.ADocumento32 pagineVitamin Deficiencies & Excesses: Dr. Shirley L A, Sp.ADiana Fadly MatondangNessuna valutazione finora
- Night BlindnessDocumento18 pagineNight BlindnessNicholas RedlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Watersolublevit Vasundhara 150819084407 Lva1 App6891Documento52 pagineWatersolublevit Vasundhara 150819084407 Lva1 App6891Abdur RafeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin Larut Lemak 2016Documento30 pagineVitamin Larut Lemak 2016Arum KunarniNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins BUC PDFDocumento40 pagineVitamins BUC PDFThe Egy NerdNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition and Vitamins PreseDocumento52 pagineNutrition and Vitamins PreseRuchie Ann Pono BaraquilNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins Are Organic Compounds Required in The Diet in Small Quantities To Perform Biological FunctionsDocumento70 pagineVitamins Are Organic Compounds Required in The Diet in Small Quantities To Perform Biological FunctionsRose LiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin: Course Title: Medicinal Chemistry-I Course Code: BPH 2203Documento9 pagineVitamin: Course Title: Medicinal Chemistry-I Course Code: BPH 2203raisul razaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins Deficiencies and ToxicitiesDocumento76 pagineVitamins Deficiencies and ToxicitieszeeshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins: IntroductionDocumento16 pagineVitamins: IntroductionDarshan MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin StudentDocumento63 pagineVitamin Studentlethigialinhlop11a4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Calories, Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrition - Finals Lesson 12Documento12 pagineCalories, Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrition - Finals Lesson 12yoonie catNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin I & II - Noor WaseemDocumento49 pagineVitamin I & II - Noor Waseemqueenmasa191Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of VitaminsDocumento26 pagineClassification of VitaminsRajesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy AY 2020-2021: VitaminsDocumento3 pagineNutrition and Diet Therapy AY 2020-2021: VitaminsToyour EternityNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 MICRONUTRIENTSDocumento12 pagineChapter 4 MICRONUTRIENTSSami InglesNessuna valutazione finora
- Amino Acids and VitaminsDocumento3 pagineAmino Acids and Vitaminscathlynjoy.marsamoloNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin B ComplexDocumento15 pagineVitamin B ComplexMemoona AfzaalNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin B Complex: By, Dr. Priyanga. P (Part I) Department of PaediatricsDocumento41 pagineVitamin B Complex: By, Dr. Priyanga. P (Part I) Department of PaediatricsPRIYANGA. PNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins For BSC Nursing Students (PHARMACOLOGY) - By: BINI P SAMUEL, ASSISTANT PROFESSORDocumento17 pagineVitamins For BSC Nursing Students (PHARMACOLOGY) - By: BINI P SAMUEL, ASSISTANT PROFESSORbinipsamuel25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins PowerpointDocumento37 pagineVitamins Powerpointerika paduaNessuna valutazione finora
- VITAMINS-are Subs That Your Body Needs To Grow and DevelopDocumento28 pagineVITAMINS-are Subs That Your Body Needs To Grow and DevelopMary Faith MadayagNessuna valutazione finora
- 17.vit AdekDocumento16 pagine17.vit AdekRosyida OktavianiNessuna valutazione finora
- FinalDocumento101 pagineFinalVimal ChauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Notes On Vitamins: Vitamin-D (Calciferol)Documento3 pagineShort Notes On Vitamins: Vitamin-D (Calciferol)Aastha WankhadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamins: Presented By: BSN II-2 Group 1Documento32 pagineVitamins: Presented By: BSN II-2 Group 1vorcuseNessuna valutazione finora
- MICRONUTRIENTS - Vitamins - CompleteDocumento33 pagineMICRONUTRIENTS - Vitamins - CompleteAlex BotosanNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 A Vitamins - Water Soluble Ed F17-2Documento57 pagine12 A Vitamins - Water Soluble Ed F17-2Thomas GavertNessuna valutazione finora
- VitaminsDocumento8 pagineVitaminsbananakyuNessuna valutazione finora
- VitaminsDocumento32 pagineVitaminsdivya100% (5)
- 1.4. VITAMINS, Minerals and WaterDocumento45 pagine1.4. VITAMINS, Minerals and Waterashenafihailemariam43Nessuna valutazione finora
- 12 - Vitamins Students BICH 200Documento18 pagine12 - Vitamins Students BICH 200DR. ANUPAMA NAGARAJNessuna valutazione finora
- Vitamin B3 Deficiency, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Its Treatment and Related DiseasesDa EverandVitamin B3 Deficiency, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Its Treatment and Related DiseasesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Vitamin B1 Deficiency, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandVitamin B1 Deficiency, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- 6-Pharma Table 2015Documento4 pagine6-Pharma Table 2015Fariz AzizNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry: Edition 2015 Cell:+1 (571) 699 4550Documento2 pagineBiochemistry: Edition 2015 Cell:+1 (571) 699 4550Fariz AzizNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-Organic Chemistry 2015 PDFDocumento6 pagine1-Organic Chemistry 2015 PDFFariz AzizNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - Microbiology 2015Documento7 pagine3 - Microbiology 2015Fariz AzizNessuna valutazione finora
- Al Mustaqeem Pharmacy: Bill No Insurance/Company Name Date Form NoDocumento1 paginaAl Mustaqeem Pharmacy: Bill No Insurance/Company Name Date Form NoFariz AzizNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Development FunnelDocumento2 pagineDrug Development FunnelSALEHA HASSANNessuna valutazione finora
- Ran CadDocumento6 pagineRan CadSameer JadhavNessuna valutazione finora
- MK Notes by YournursingspaceDocumento60 pagineMK Notes by Yournursingspaceezinne obinna-umaNessuna valutazione finora
- Patofisiologi Malaria PDFDocumento11 paginePatofisiologi Malaria PDFMeylinda LinNessuna valutazione finora
- Siddha Marine Drug Palagarai (Cypraea Moneta Linn.) - A ReviewDocumento3 pagineSiddha Marine Drug Palagarai (Cypraea Moneta Linn.) - A ReviewLucasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell SignalingDocumento1 paginaCell SignalingNathan Stuart The Retarded idiotNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study, NCP, and Concept MapDocumento8 pagineDrug Study, NCP, and Concept MapMj BollenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Naprex Drug StudyDocumento3 pagineNaprex Drug StudyAngelica shane NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Toc CBTDocumento9 pagineToc CBTRaquel IsahíNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology and Toxicology Mcqs PDF DownloadDocumento7 paginePharmacology and Toxicology Mcqs PDF DownloadSanjy KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Tubular Acidosis: ObjectivesDocumento11 pagineRenal Tubular Acidosis: Objectivesms khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vesicular Systems An OverviewDocumento13 pagineVesicular Systems An OverviewdianNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs of Abuse: Reymark C. Adorada MAPEH TeacherDocumento40 pagineDrugs of Abuse: Reymark C. Adorada MAPEH Teacherreymark adoradaNessuna valutazione finora
- Behandlingstudier - Overblik Over Planlagte Og Igangværende Studier Af Lægemidler Til Behandling Af COVID-19Documento217 pagineBehandlingstudier - Overblik Over Planlagte Og Igangværende Studier Af Lægemidler Til Behandling Af COVID-19Ishan ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 - Practical Guide - Overview EBM - Dr. Jarir at Thobari, PhD.,D.Pharm (2020)Documento13 pagineLecture 3 - Practical Guide - Overview EBM - Dr. Jarir at Thobari, PhD.,D.Pharm (2020)Lily LiestiowatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Changes in The Mucoadhesion of Powder Formulations After Drug Application Investigated With A Simplified Method - 2007Documento10 pagineChanges in The Mucoadhesion of Powder Formulations After Drug Application Investigated With A Simplified Method - 2007Evelyn de OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral CorticosteroidsDocumento29 pagineOral CorticosteroidsloraNessuna valutazione finora
- My PosterDocumento1 paginaMy PosterLucky HutapeaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Liver in Times of COVID-19 What Hepatologists Should KnowDocumento6 pagineThe Liver in Times of COVID-19 What Hepatologists Should KnowFita FitriantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Malaysia Variation Guideline For Pharmaceutical Products 2013 - Edition 1 (April 2013) 080513Documento52 pagineMalaysia Variation Guideline For Pharmaceutical Products 2013 - Edition 1 (April 2013) 080513NikNurShafiqahNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 - Text Book of Clinical Pharmacognosy Dr. Mansoor Ahmad Karachi UiversityDocumento600 pagine2016 - Text Book of Clinical Pharmacognosy Dr. Mansoor Ahmad Karachi UiversityAmini Mohammad Humayoon100% (1)
- 1388 Cardiovascular Drugs: Interactions Units Adverse Effects, Treatment, and PrecautionsDocumento2 pagine1388 Cardiovascular Drugs: Interactions Units Adverse Effects, Treatment, and PrecautionsPopov VictorNessuna valutazione finora
- Atypical Antidepressants - Pharmacology, Administration, and Side Effects - UpToDateDocumento16 pagineAtypical Antidepressants - Pharmacology, Administration, and Side Effects - UpToDateMelissandreNessuna valutazione finora
- Macrocytosis - Macrocytic Anemia - UpToDateDocumento36 pagineMacrocytosis - Macrocytic Anemia - UpToDateMarvin VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 - Kidney and NephronDocumento30 pagineUnit 5 - Kidney and NephronAbdullah MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Promotional LiteratureDocumento17 pagineDrug Promotional LiteratureKaruna Sree PNessuna valutazione finora
- Vox Sanguin Februari 2021Documento116 pagineVox Sanguin Februari 2021rsdarsono labNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento8 pagineUntitledPrakash SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- HomeostasisDocumento8 pagineHomeostasisLely SharmaNessuna valutazione finora