Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
BITS Pilani Electrical Engineering Mid-Semester Test
Caricato da
dharmendra_kanthariaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BITS Pilani Electrical Engineering Mid-Semester Test
Caricato da
dharmendra_kanthariaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani
Work-Integrated Learning Programmes Division
Second Semester 2018-2019
Mid-Semester Test
(EC-2 Makeup)
Course No. : ENGG ZC112
Course Title : ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS TECHNOLOGY
Nature of Exam : Closed Book
Weightage : 30% No. of Pages =2
Duration : 2 Hours No. of Questions = 6
Date of Exam : 24/03/2019 (AN)
Note:
1. Please follow all the Instructions to Candidates given on the cover page of the answer book.
2. All parts of a question should be answered consecutively. Each answer should start from a fresh page.
3. Assumptions made if any, should be stated clearly at the beginning of your answer.
Q.1. An electrical load consists of three resistors R1, R2, and R3, connected in parallel across
terminals A and B. The three resistors R1, R2, and R3 are having resistance of 10 ohm, 15
ohm and 6 ohm, respectively. This load is connected to a DC voltage source having an
internal resistance of 0.5 ohm. The total load current is 4 A.
(a) Calculate the voltage of the DC voltage source. [1]
(b) Calculate the terminal voltage (VAB) across the load terminals. [1]
(c) Calculate the current through the resistor R1. [1]
(d) Calculate the power dissipated in resistor R2. [1]
(e) Calculate the energy dissipated in the resistor R3 in one minute. [1]
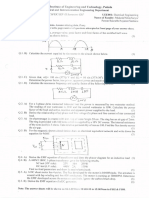
Q.2. Consider the circuit shown in Figure Q2.
Figure Q2
(a) Write the equations for mesh analysis of the given circuit. [2]
(b) Calculate the mesh currents I1, I2 and I3 using mesh analysis. [2]
(c) Calculate the voltage across 3 ohm resistor. [1]
Q.3. Consider the circuit shown in Figure Q3. A load resistance of 10 ohm is connected across the
load terminals A and B.
ENGG ZC112 (EC-2 Make-up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 1 of 2
Figure Q3
(a) Calculate Norton’s equivalent resistance and Norton’s equivalent current for the circuit
as seen from the load terminals A and B. [2]
(b) Calculate the load current using Norton’s equivalent circuit. [1]
(c) If an additional resistor of 15 ohm is connected across the load terminals A and B,
calculate the load current through the 15 ohm resistor using Norton’s equivalent circuit.
[1]
(d) Using Norton’s equivalent circuit obtained above, draw Thevenin’s equivalent circuit. [1]
Q.4. A series combination of a resistor R and a 150 μF capacitor is connected to a 220 V DC
supply through a switch. Initially the switch is open and the voltage across the capacitor is 0
V. The switch is closed at time, t=0. The circuit has a time constant of 1.5 s.
(a) Calculate the value of the resistor R. [1]
(b) Write down the expressions for the capacitor voltage and capacitor current using the
numerical values given. [1]
(c) Calculate the voltage across the capacitor and the current flowing through the circuit at
time t = 4.5 s. [2]
(d) Calculate the voltage across the resistor at time, t = 3 s. [1]
Q.5. A coil of 150 Ω resistance and 1 H inductance is connected in parallel with a 120 μF
capacitor. This parallel combination is connected to a 230 V, 50 Hz, single phase AC supply.
(a) Calculate the total impedance of the parallel combination. [1]
(b) Calculate the current through the coil. [1]
(c) Calculate the current delivered by the supply. [1]
(d) Calculate the active power delivered by the supply. [1]
(e) Draw the phasor diagram showing the current through the coil, current through the
capacitor, the total current and the supply voltage [1]
Q.6. A single phase, 250 V/500 V, 2.5 kVA, 50 Hz ideal transformer has 75 turns on low voltage
winding. A load of (0.25 + j 0.4) kΩ is connected to the low voltage side of the transformer.
(a) Calculate the value of the maximum flux in the core. [1]
(b) Calculate the current rating of both the windings. [1]
(c) Calculate the load current in the low voltage winding. [1]
(d) Calculate the load impedance referred to the high voltage winding. [1]
(e) Calculate the load current referred to the high voltage side. [1]
***********
ENGG ZC112 (EC-2 Make-up) Second Semester 2018-2019 Page 2 of 2
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- SQL commands cheat sheetDocumento1 paginaSQL commands cheat sheetBhushan80% (5)
- Drawings Configuration Practice Labs - 2011 R1Documento118 pagineDrawings Configuration Practice Labs - 2011 R1dharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- E3d-Module Equipment in Aveva E3d PDFDocumento12 pagineE3d-Module Equipment in Aveva E3d PDFRobles Dresch71% (7)
- Matlab TutorialDocumento243 pagineMatlab TutorialPinaki Mishra100% (4)
- SP3D2011 Equipment Tutorial PDFDocumento145 pagineSP3D2011 Equipment Tutorial PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisDa EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNessuna valutazione finora
- 88 Free Hand Picked Resources PDFDocumento20 pagine88 Free Hand Picked Resources PDFBADRIRAM SISTLANessuna valutazione finora
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Documento147 pagineCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drawings Creation Practice Labs - 2011R1Documento78 pagineDrawings Creation Practice Labs - 2011R1dharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 10 PDFDocumento3 pagineWorksheet 10 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Pipe SupportsDocumento87 paginePipe SupportsVeeramanikandanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Generation and Distribution On Cargo ShipDocumento10 pagineElectrical Generation and Distribution On Cargo ShipDavid Ella Inalegwu100% (2)
- Electricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science - Learn CBSEDocumento39 pagineElectricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science - Learn CBSEAmitChopraNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Fields and Circuits Study GuideDocumento22 pagineElectric Fields and Circuits Study GuideLawrence Onthuga100% (1)
- Tubos de CalorDocumento7 pagineTubos de CalorChristo AcostaNessuna valutazione finora
- Try Out The Interactive: Window Functions Partition by Order by Aggregate Functions vs. Window FunctionsDocumento2 pagineTry Out The Interactive: Window Functions Partition by Order by Aggregate Functions vs. Window FunctionsalbNessuna valutazione finora
- BITS Pilani EC-2 Mid-Semester TestDocumento2 pagineBITS Pilani EC-2 Mid-Semester Testdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Birla Institute Electrical Exam QuestionsDocumento3 pagineBirla Institute Electrical Exam Questionsdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enggzc112 May05 An PDFDocumento3 pagineEnggzc112 May05 An PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 10Documento3 pagineWorksheet 10JunLi CaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Assignment - Elevate Classes 11095472 2022 09-20-07 47Documento134 pagineElectronics Assignment - Elevate Classes 11095472 2022 09-20-07 47dixitratan68Nessuna valutazione finora
- C.S.E.-(Mains)-1992 Electrical Engineering Paper AnalysisDocumento147 pagineC.S.E.-(Mains)-1992 Electrical Engineering Paper Analysisvenki3236Nessuna valutazione finora
- Civil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007Documento147 pagineCivil Service - Electrical Engineering Main Paper I & II - 1992 - 2007venki3236Nessuna valutazione finora
- BEE Model Paper 1Documento7 pagineBEE Model Paper 1Nikhil SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- DPP 3Documento11 pagineDPP 3mstudy1009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Leb30303-Electro Technique 2Documento7 pagineLeb30303-Electro Technique 2Alif AkmalNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Bee4113 Sem 2 200809Documento8 pagineFinal Exam Bee4113 Sem 2 200809Kung ChinHanNessuna valutazione finora
- Eoc Det20033 QuestionDocumento3 pagineEoc Det20033 Questiondanialhaziq60Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ee307 2016 06Documento3 pagineEe307 2016 06Simbarashe UsaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Current 1Documento4 pagineCurrent 1Devansh DuhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Exercises 0: The Basics: E1001 Electronic Circuits Prof P BayvelDocumento7 pagineTutorial Exercises 0: The Basics: E1001 Electronic Circuits Prof P BayvelraihanserajNessuna valutazione finora
- Bangladesh University Textile Engineering EEE-1 Course OverviewDocumento30 pagineBangladesh University Textile Engineering EEE-1 Course OverviewMdAsaduz-ZamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Elec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564Documento6 pagineElec2091st Semester Ex - 1705355554564family7482pleaseNessuna valutazione finora
- BML University Exam Covers Electrical Engineering ConceptsDocumento2 pagineBML University Exam Covers Electrical Engineering ConceptsVikash ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Systems EC1021Documento5 pagineElectrical Systems EC1021Sulaksha WimalasenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid Sem 19-20Documento2 pagineMid Sem 19-20Soumya Ranjan NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- MST 2 P1 (Ex-502)Documento36 pagineMST 2 P1 (Ex-502)ASHISH SINGH SENGARNessuna valutazione finora
- 9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocumento8 pagine9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Semester-1 - Chemistry Stream - Mid+end PaperDocumento15 pagineSemester-1 - Chemistry Stream - Mid+end PaperGopiNessuna valutazione finora
- Short Ans CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (181 Marks)Documento36 pagineShort Ans CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (181 Marks)Hiya ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- U20EE201 - CT - Model QPDocumento4 pagineU20EE201 - CT - Model QPvinothkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- EE101 BASICS OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (END_SP23)Documento2 pagineEE101 BASICS OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (END_SP23)soronaj532Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 3 - Ac CircuitDocumento3 pagineAssignment 3 - Ac CircuitDiptiben GanatraNessuna valutazione finora
- r7100206 Electrical Circuit AnalysisDocumento4 paginer7100206 Electrical Circuit AnalysissivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee1 HW 2Documento3 pagineEee1 HW 2Averly Jerryl EscotoNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics Circuit QuestionsDocumento8 pagineElectrostatics Circuit Questions6C09 FUNG CHI LAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 28 PDFDocumento2 pagineWorksheet 28 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- ch11 Sci Practice SheetDocumento6 paginech11 Sci Practice SheetMeetNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2015 Supplementary Exams for Electrical CircuitsDocumento2 pagineJune 2015 Supplementary Exams for Electrical CircuitsKhajavali ShaikNessuna valutazione finora
- ELEC201 Practice L02Documento25 pagineELEC201 Practice L02MilNessuna valutazione finora
- JNTU Network Theory Exam QuestionsDocumento3 pagineJNTU Network Theory Exam Questions2BL20EC096spoorti NidoniNessuna valutazione finora
- UEE001Documento1 paginaUEE001ishuNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems Chptrs1 18Documento46 pagineProblems Chptrs1 18celeritas81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ut - 1 Xii PhyDocumento2 pagineUt - 1 Xii PhyRitik Kumar NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Electricity - Objective WorksheetDocumento7 pagineCurrent Electricity - Objective Worksheetansh1510Nessuna valutazione finora
- Elec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568Documento7 pagineElec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568family7482pleaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Electricity Test1Documento10 pagineCurrent Electricity Test1Harsh RuhalNessuna valutazione finora
- Seat No.: - F.E. (First Semester) EXAMINATION, 2023 Basic Electrical Engineering (2019 PATTERN) TimeDocumento7 pagineSeat No.: - F.E. (First Semester) EXAMINATION, 2023 Basic Electrical Engineering (2019 PATTERN) TimeNikhil SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1371 Analog ElectronicsDocumento1 paginaQ1371 Analog ElectronicsDivyanshu BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- EE181107Documento4 pagineEE181107Sumit ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Faculty of Engineering Electronic and Computer EngineeringDocumento4 pagineFaculty of Engineering Electronic and Computer EngineeringSamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- EST QuestionDocumento3 pagineEST QuestionashNessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity LaunchDocumento18 pagineElectricity LaunchPhone experimentsNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Electricity - CC - E - WADocumento12 pagineCurrent Electricity - CC - E - WAHussain Ali PioneerNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY2 June 2005Documento2 paginePHY2 June 2005api-3726022Nessuna valutazione finora
- DJJ2022 - Jun 16 PDFDocumento7 pagineDJJ2022 - Jun 16 PDFZiqmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFDocumento11 pagineRevision DPP - JEE Advance - DPP-3 - P - DPP-3 - DPP - 03 PDFvijay kakarlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics XII Sample Paper 1 UnsolvedDocumento6 paginePhysics XII Sample Paper 1 UnsolvedRyn RkNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE307 Mid 1 ModeratedDocumento1 paginaEEE307 Mid 1 ModeratedMasud SarkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesDa EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Example Fa-Class 4-Feb 3 2024-Solution With Class NotesDocumento14 pagineBasic Example Fa-Class 4-Feb 3 2024-Solution With Class Notesdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Example Fa-Class 4-Feb 3 2024-Solution With Class NotesDocumento14 pagineBasic Example Fa-Class 4-Feb 3 2024-Solution With Class Notesdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping Interview QuestionDocumento10 paginePiping Interview Questiondharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Matlab Command FunctionsDocumento17 pagineMatlab Command FunctionsbehroozfNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 4Documento6 pagineQuiz 4dharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 2Documento6 pagineQuiz 2dharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 2 MatlabDocumento3 pagineQuiz 2 Matlabdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 3Documento6 pagineQuiz 3dharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid Term - EEEDocumento10 pagineMid Term - EEEdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- SlidesDocumento36 pagineSlidesdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Reference Manual - Utilities PDFDocumento86 pagineDesign Reference Manual - Utilities PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Administrator Command Reference ManualDocumento207 pagineAdministrator Command Reference ManualhgolestaniNessuna valutazione finora
- TSMP1003 - SmartPlant3D Grid-Structure Labs V2011R1 PDFDocumento436 pagineTSMP1003 - SmartPlant3D Grid-Structure Labs V2011R1 PDFdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping and Pipe Support SystemsDocumento178 paginePiping and Pipe Support Systemssaisssms9116Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pipe Support PDFDocumento111 paginePipe Support PDFm2110Nessuna valutazione finora
- SP3D H&S TutorialDocumento44 pagineSP3D H&S Tutorialdharmendra_kanthariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Piping 1Documento3 pagineAdvanced Piping 1IrHerryAbdillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Discussed QuestionsDocumento7 pagineDiscussed Questionsnafish sams souravNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY 504 - Advanced Mechanics Assignment 2: (Dated: August 28, 2020)Documento2 paginePHY 504 - Advanced Mechanics Assignment 2: (Dated: August 28, 2020)santosh thapaNessuna valutazione finora
- 06837093Documento20 pagine06837093sivasankarmeaeNessuna valutazione finora
- GP 1 Module 4Documento91 pagineGP 1 Module 4Raymund EspinoNessuna valutazione finora
- IC6003-Principles of RoboticsDocumento15 pagineIC6003-Principles of Roboticsrajemtech100% (1)
- 10 Aberration Theory Part IDocumento42 pagine10 Aberration Theory Part IxbNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-IV - Voli. 2 Polyphase TransformersDocumento74 pagineUnit-IV - Voli. 2 Polyphase Transformersvasu_koneti5124Nessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Sheet 3Documento2 pagineProblem Sheet 3balochfrahan.2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rectilinear and rotational kinematics problemsDocumento5 pagineRectilinear and rotational kinematics problemsAljay Dungao40% (5)
- GVSU Segway Design Project Exec SummaryDocumento53 pagineGVSU Segway Design Project Exec SummaryAnonymous L9fB0XU100% (4)
- 1st Year Chemistry All MCQS Short Questions For Federal Board Punjab BoardDocumento8 pagine1st Year Chemistry All MCQS Short Questions For Federal Board Punjab BoardDaniyal yousaf100% (1)
- Module6 - Ideal Gas ProcessesApplicationDocumento20 pagineModule6 - Ideal Gas ProcessesApplicationJohn Dalton ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cooling Strategies, Summer Comfort and Energy Performance of A Rehabilitated Passive Standard Office Building PDFDocumento9 pagineCooling Strategies, Summer Comfort and Energy Performance of A Rehabilitated Passive Standard Office Building PDFIkutegbe CharlesNessuna valutazione finora
- Universal Dataset Number 58Documento17 pagineUniversal Dataset Number 58Palazzo345Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Description of PlasmaDocumento10 pagineFluid Description of PlasmaDaniel HikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Microwave Solvothermal Synthesis and Characterization of Manganese-Doped Zno NanoparticlesDocumento12 pagineMicrowave Solvothermal Synthesis and Characterization of Manganese-Doped Zno NanoparticlesTamilan TamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Cau Truc To HopDocumento1.258 pagineCau Truc To Hopkhôi trươngNessuna valutazione finora
- Sec. 6.7 Peak Structural Response From The Response SpectrumDocumento2 pagineSec. 6.7 Peak Structural Response From The Response SpectrumIt'x PathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rohini 46645264742Documento5 pagineRohini 46645264742Faheem aktharNessuna valutazione finora
- Particle Image VelocimetryDocumento16 pagineParticle Image VelocimetrySiamakNessuna valutazione finora
- Photoluminescence and Photocatalytic Activity of Spin Coated Ag+ Doped Anatase TiO2 Thin FilmsDocumento14 paginePhotoluminescence and Photocatalytic Activity of Spin Coated Ag+ Doped Anatase TiO2 Thin FilmsJasielRuizDesalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce 6306 Som Part A AnswersDocumento21 pagineCe 6306 Som Part A Answersommech2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Dynamics CourseDocumento5 pagineGas Dynamics CourseBalveer CLNessuna valutazione finora
- Nikolas TeslaDocumento4 pagineNikolas TeslaJamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrodynamics of Foaming Systems in Packed TowersDocumento9 pagineHydrodynamics of Foaming Systems in Packed TowersdoufethiNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of PlasticityDocumento110 pagineTheory of Plasticitytayyeb803Nessuna valutazione finora
- (William L. Kruer) The Physics of Laser Plasma IntDocumento29 pagine(William L. Kruer) The Physics of Laser Plasma IntVijay SinghNessuna valutazione finora