Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Clarisa Report
Caricato da
JC0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
13 visualizzazioni5 pagineTitolo originale
CLARISA-REPORT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
13 visualizzazioni5 pagineClarisa Report
Caricato da
JCCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 5
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Energy from the sun enters the planet in a continuous flow as
it is transferred from one organism to the next through food
chains and food webs.
Photosynthesis
Requires sunlight, carbon dioxide and water that needed in
the chemical reaction.
Once the process is complete, the plant release oxygen and
the carbohydrate molecule known as glucose, which that is used
as component for energy production.
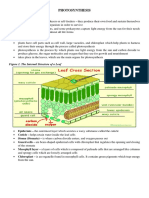
The process takes place in the plant leaves which contain many
cell layers.
Mesophyll - when photosynthesis occur in the middle layer,
which contains tiny openings called stomata where gases enter
and exit the leaves.
Chloroplast - have a double inner and outer membrane.
Thylakoids - are tiny disc-shaped structures stacked up on top
of each other.
Granum - stack of thylakoids in which is surrounded by a space
known as stroma.
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages:
LIGHT-DEPENDENT STAGE
Occurs in the thylakoids membrane of the chloroplasts where the
chlorophyll pigments absorbs the light energy from the sun and converts
it into chemical energy together with water. Oxygen is also released by
product.
Organisms such as green plants, algae, and cyanobacteria contain the
pigment chlorophyll a that allows photosynthesis.
The reaction begins in a group of pigments and proteins known as
photosystem.
Photosystem
Are located in the membranes of the thylakoids.
Exist as photosystem II and photosystem I in eukaryotes and some
prokaryotes.
Photon- the pigment molecule absorbs one at a time, one packet of light.
Photosystem II transfers the free electrons along a series of protein
called the electron transport chain.
Energy from the electron fuels membrane pumps that move hydrogen
ion against the concentration gradient from the stroma to the thylakoid
space, As the energy is used, the electron will be accepted by another
pigment molecule in photosynthesis.
I. This causes the electrons to be break away
from the atom of the chlorophyll molecule
As more energy is absorbed, it is absorbed by two carrier molecules:
ATP (adenosine triphosphate and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide phosphate).
The movements of hydrogen ions through ATP synthase is also
known as chemiosmosis.
Aside from ATP, another function of the light-dependent stage is the
generation of another energy carrier, NADPH.
The energy carried by these electrons fuels the formation of NADPH
from NADP+ and hydrogen ions.
LIGHT-DEPENDENT STAGE
Also known as the calvin cycle or calvin- benson cycle,
occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast.
Calvin Cycle is also known as the ‘’dark reaction’’ because it
does not require the presence of light to produce glucose.
Inside the chloroplast, carbon dioxide diffuses into the stroma.
An enzyme called ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCo)
catalyzes the reaction and combines carbon dioxide with a five-
carbon sugar molecule called ribulose biphosphate (RuBP). This
results in an unstable six-carbon compound, which is
immediately broken down into two three carbon (3-C)
compounds. This process is called carbon fixation.
The organic molecule is further modified into a simple sugar
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate(G3P) using the energy from ATP
and NADPH.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideDa EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Sleep Smarter Book SummaryDocumento6 pagineSleep Smarter Book SummaryEthanSong100% (18)
- Deer, Timothy R. - Pope, Jason E - Treatment of Chronic Pain Conditions - A Comprehensive Handbook-Springer (2017)Documento319 pagineDeer, Timothy R. - Pope, Jason E - Treatment of Chronic Pain Conditions - A Comprehensive Handbook-Springer (2017)paticex241100% (2)
- Circulatory - Respiratory Systems MCQDocumento6 pagineCirculatory - Respiratory Systems MCQFake Gamer100% (1)
- ADHD Circadian Dysfunction and ChronotherapyDocumento19 pagineADHD Circadian Dysfunction and ChronotherapyPAULANessuna valutazione finora
- Sinus ArrhythmiaDocumento6 pagineSinus ArrhythmiaVincent Maralit MaterialNessuna valutazione finora
- Bab 12 - Muscular SystemDocumento73 pagineBab 12 - Muscular SystemDaeng FarahnazNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 Science Reviewer Quarter 1 PDFDocumento16 pagineGrade 9 Science Reviewer Quarter 1 PDFDane Gian Angelo TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocumento4 paginePhotosynthesis and RespirationChristian BaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Psychology Kalat 12th Edition Solutions ManualDocumento12 pagineBiological Psychology Kalat 12th Edition Solutions ManualJames Pennington100% (35)
- Photosynthesis: Leaves and Leaf StructureDocumento11 paginePhotosynthesis: Leaves and Leaf StructureMatthew BetinolNessuna valutazione finora
- Hotosynthesis: Big PictureDocumento3 pagineHotosynthesis: Big Picturehomamunfat100% (1)
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocumento8 paginePhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationFatima DariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atlas of Sleep MedicineDocumento362 pagineAtlas of Sleep MedicinekattbattNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 - Heart-1Documento63 pagineChapter 12 - Heart-1Thania IslaNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy TransformationDocumento14 pagineEnergy TransformationJoaquine ArateaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology 1: MODULE 3 and 4Documento12 pagineGeneral Biology 1: MODULE 3 and 4Theworld MagicNessuna valutazione finora
- Chloroplast Photosynthesis-FileDocumento17 pagineChloroplast Photosynthesis-Filesiguro hwahahahNessuna valutazione finora
- PhotosynthesisDocumento3 paginePhotosynthesisCristina MaquintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis (Handouts)Documento5 paginePhotosynthesis (Handouts)Jelea MagallanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis Cell Biology FileDocumento16 paginePhotosynthesis Cell Biology FileRei KaplanNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis Cell Biology FileDocumento16 paginePhotosynthesis Cell Biology FileRei KaplanNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 PhotosynthesisDocumento10 pagine15 PhotosynthesisEarl Adam LambacoNessuna valutazione finora
- PhotosynthesisDocumento2 paginePhotosynthesistanaythegreat999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chloroplasts UpdatedDocumento4 pagineChloroplasts Updateddrug123addict25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Report Group 11Documento5 pagineReport Group 11Boyd benson kayomboNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis Converts Light to Food in 37 CharactersDocumento2 paginePhotosynthesis Converts Light to Food in 37 CharactersLorena DizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Form Carbohydrate That Is Usable by The BodyDocumento5 pagineForm Carbohydrate That Is Usable by The BodyEmman RevillaNessuna valutazione finora
- PhotosynthesisDocumento3 paginePhotosynthesisDarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio HWDocumento9 pagineBio HWedgar batotoNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis, Process by Which Green Plants and Certain Other OrganismsDocumento3 paginePhotosynthesis, Process by Which Green Plants and Certain Other OrganismsAbhinavNessuna valutazione finora
- How Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Work TogetherDocumento5 pagineHow Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Work TogetherKhyla Grace DijenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis: Light-Dependent and Light-Independent ReactionsDocumento12 paginePhotosynthesis: Light-Dependent and Light-Independent ReactionsMalinda GreeneNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDocumento8 pagineWhat Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDiana Jean Alo-adNessuna valutazione finora
- SSGBIO1 - CM Week 7Documento61 pagineSSGBIO1 - CM Week 7christine ManuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Notes 14/09: PhotoexcitationDocumento2 pagineBio Notes 14/09: PhotoexcitationDaniel RoopchandNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis ReadingDocumento11 paginePhotosynthesis ReadingLogan ParkisonNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Description-Final DraftDocumento3 pagineTechnical Description-Final Draftapi-295061687Nessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis Interactive Part 1Documento2 paginePhotosynthesis Interactive Part 1api-522847737Nessuna valutazione finora
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS - Light and Dark ReactionDocumento4 paginePHOTOSYNTHESIS - Light and Dark ReactionJeaña Despi DaguismolNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Unit 2 SummaryDocumento43 pagineBiology Unit 2 SummaryYuh moddaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio2 91156 PhotosynrespirationDocumento1 paginaBio2 91156 Photosynrespirationapi-277699810Nessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis Is A Series of Chemical Reactions TDocumento12 paginePhotosynthesis Is A Series of Chemical Reactions Tmacalinabdiwali007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Notes Unit TwoDocumento158 pagineBiology Notes Unit TwoBlohsh KeenenNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosyntheis and RespirationDocumento37 paginePhotosyntheis and Respirationfelisilda.136571140273Nessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis: 6CO2+6H2O+light Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2Documento3 paginePhotosynthesis: 6CO2+6H2O+light Energy C6H12O6 + 6O2louNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy to Chemical EnergyDocumento13 paginePhotosynthesis Converts Light Energy to Chemical EnergyMina IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocumento45 pagineEnergy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationlovepugsNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis: Using Light To Make Food: UsuallyDocumento12 paginePhotosynthesis: Using Light To Make Food: UsuallyMARCO ANTONIO CONDOR CHAVEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 13 14 BiologyDocumento22 pagineWeek 13 14 BiologyPark RiRinNessuna valutazione finora
- LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION - Discussrion Ni MaamDocumento3 pagineLIGHT DEPENDENT REACTION - Discussrion Ni MaamAiejeoff JordanNessuna valutazione finora
- Light-Dependent and Light-Independent ReactionsDocumento20 pagineLight-Dependent and Light-Independent ReactionsMOSIGAN, Vince EmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Condensed VersionDocumento3 pagineCondensed Versiondrug123addict25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis-WPS OfficeDocumento5 paginePhotosynthesis-WPS Officeimaan buttNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Quarter - Gen. Bio.1Documento38 pagine2nd Quarter - Gen. Bio.1Reylyn SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Utilizing Energy For LifeDocumento41 pagineUtilizing Energy For LifeJOHN PAUL MACALLINGNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis (Reviewer) - JMDPDocumento2 paginePhotosynthesis (Reviewer) - JMDPJhianne Mylz ParañalNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis: How Plants Use Light Energy to Produce FoodDocumento4 paginePhotosynthesis: How Plants Use Light Energy to Produce FoodmarimoryNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hill reaction, spectrophotometry, chloroplasts, and electron transport in photosynthesisDocumento2 pagineThe Hill reaction, spectrophotometry, chloroplasts, and electron transport in photosynthesishernys NietoNessuna valutazione finora
- PhotosynthesisDocumento1 paginaPhotosynthesisPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- PhotosynthesisDocumento1 paginaPhotosynthesisHatdog Ka BaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Light and Dark ReactionDocumento1 paginaWhat Is Light and Dark ReactionSheharyar The PRONessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis: Study Guide Photosynthesis Equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O - C6H12O6 + 6O2Documento4 paginePhotosynthesis: Study Guide Photosynthesis Equation: 6CO2 + 6H2O - C6H12O6 + 6O2vscolegit shoppeNessuna valutazione finora
- Week - 3 - Lectures 1-1Documento74 pagineWeek - 3 - Lectures 1-1Benjamin SamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is PhotosynthesisDocumento10 pagineWhat Is PhotosynthesisGenie SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis Powers Life on EarthDocumento4 paginePhotosynthesis Powers Life on EarthBlair CaguioaNessuna valutazione finora
- Photosynthesis AND Cellular RespirationDocumento24 paginePhotosynthesis AND Cellular RespirationJennifer ParduchoNessuna valutazione finora
- Light ReactionDocumento2 pagineLight Reactioncjungshook ́Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chloroplast Structure and Function GuideDocumento2 pagineChloroplast Structure and Function GuideSamantha JerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pandan PandaDocumento1 paginaPandan PandaJCNessuna valutazione finora
- Pandan PandaDocumento1 paginaPandan PandaJCNessuna valutazione finora
- My Learnings, Insights in Contemporary Phil. Arts From The Regions"Documento2 pagineMy Learnings, Insights in Contemporary Phil. Arts From The Regions"JCNessuna valutazione finora
- Contemporary ArtDocumento1 paginaContemporary ArtJCNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Saint JudeDocumento3 pagineHistory of Saint JudeJCNessuna valutazione finora
- Couch PotatoDocumento1 paginaCouch PotatoJCNessuna valutazione finora
- Isn ScienceDocumento8 pagineIsn ScienceJCNessuna valutazione finora
- Martial Arts: Martial Arts Refers To The Various Traditional and Modern Combat Systems PracticedDocumento10 pagineMartial Arts: Martial Arts Refers To The Various Traditional and Modern Combat Systems PracticedJCNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide QuestionsDocumento1 paginaGuide QuestionsJCNessuna valutazione finora
- Martial Arts: Martial Arts Refers To The Various Traditional and Modern Combat Systems PracticedDocumento10 pagineMartial Arts: Martial Arts Refers To The Various Traditional and Modern Combat Systems PracticedJCNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Order Costing ActivityDocumento1 paginaJob Order Costing ActivityJCNessuna valutazione finora
- Inflation in Malaysia PDFDocumento16 pagineInflation in Malaysia PDFJashmin CosainNessuna valutazione finora
- The Summary of The Emergence of United States As The World PowerDocumento1 paginaThe Summary of The Emergence of United States As The World PowerJCNessuna valutazione finora
- Sympathomimetics Physical MCQDocumento4 pagineSympathomimetics Physical MCQMohamed MoustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physio Essay #4Documento2 paginePhysio Essay #4Maria Margarita Chon100% (1)
- Blood Circulatory SystemDocumento2 pagineBlood Circulatory SystemSARVESHINI A/P MURUGAN MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading as a Physiological ProcessDocumento2 pagineReading as a Physiological ProcessJee DeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 1424Documento13 pagine1424Caiden HenryNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 - Skin Barrier Immunity and AgeingDocumento11 pagine2019 - Skin Barrier Immunity and AgeingRatih Anindita Rahajeng Ripyono100% (1)
- Cal EcgDocumento7 pagineCal EcgNur Amirah FarhanahNessuna valutazione finora
- BTL Cardiopoint-Abpm: User'S ManualDocumento36 pagineBTL Cardiopoint-Abpm: User'S ManualAlejandro VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensorium.: NiirDocumento6 pagineSensorium.: NiirSundar RajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Arianna Mabunga Bsn-3BDocumento7 pagineArianna Mabunga Bsn-3BArianna Jasmine MabungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Asthma: Section 3: Pulmonary DisordersDocumento36 pagineAsthma: Section 3: Pulmonary Disordersalyssa azzahraNessuna valutazione finora
- Excretion and the Removal of WasteDocumento3 pagineExcretion and the Removal of WasteHn HMSNessuna valutazione finora
- Campugan Jay Patho AssignmentDocumento27 pagineCampugan Jay Patho AssignmentJAY M. CAMPUGANNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Phlebotomy PrinciplesDocumento9 pagineUnderstanding Phlebotomy PrinciplesAlyssa Marielle VillaricoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 5Documento34 pagineBiology - XI - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - MCQs 5SDO BSNL NALAGARHNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Analysis Tool (CAT) Worksheet: Student's NameDocumento7 pagineCase Analysis Tool (CAT) Worksheet: Student's NameDina KristevaNessuna valutazione finora
- L - 28-Composition and Function of Blood. ( (L32) )Documento28 pagineL - 28-Composition and Function of Blood. ( (L32) )Turky TurkyNessuna valutazione finora
- DAMS CBT 2015 Test -1 ReviewDocumento173 pagineDAMS CBT 2015 Test -1 ReviewMitvinder SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Our Senses and Body SystemsDocumento3 pagineOur Senses and Body SystemsNataliaNessuna valutazione finora