Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Redwan Ahmed Miazee - HW - 2
Caricato da
REDWAN AHMED MIAZEEDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Redwan Ahmed Miazee - HW - 2
Caricato da
REDWAN AHMED MIAZEECopyright:
Formati disponibili
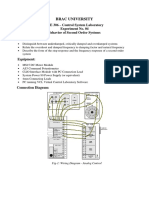
EEE 207 / ECE 207: Electronic Devices and Circuits II
Home Work – 2
Summer 2020 Due: 9 Aug, 2020
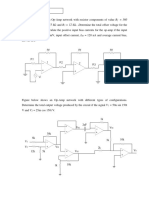
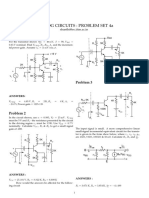
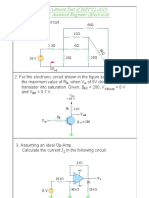
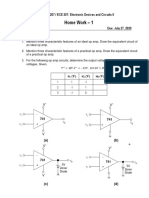
1. For the following amplifier circuit, determine the output voltage: Show the relevant calculations.
Given Rf = 100 kΩ, R1 = 10 kΩ and R2 = 20 kΩ. v1 = -100 mV and v2 = 200 mV.
Rf
Rf
R
R1 -
v1
R2 +
- v2 +
vo
OA1
vo
v2 + R1 -
R2 v1
Circuit for Question 1 Circuit for Question 2
2. For the following amplifier circuit, determine the output voltage: Show the relevant calculations.
Given Rf = 90 kΩ, R = R1 = 10 kΩ and R2 = 30 kΩ, v1 = 4 V and v2 = -8 V.
3. Design an adder circuit that will provide an output voltage, 𝑣0 = 2𝑣1 + 3𝑣2 − 5𝑣3 , where
v1, v2 and v3 are the three input voltages. Choose resistor values not less than 10k.
4. Mention three modes of operation of VCC
Transistors. What are the conditions required
for each mode of operation? IC
5. Which two modes of operations are used for
switching application of a transistor? Mention RC
the state of the transistor voltages VBE and VCE,
during these two modes of operations. VC
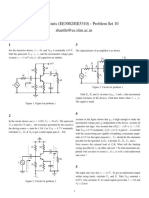
6. For the BJT circuit shown, RB = 100k, RC = RB VB
Vi
2.2k, VCC = 15V and Vi = 5V. Determine the +
currents and voltages as indicated on the IB VBE
circuit. Assume VBE = 0.7 V and = 100. Also, -
determine the mode of operation of the
transistor.
7. It is required to operate the transistor in the above problem (Q. 6) in saturation mode.
Determine the value of RB that will bring the transistor at the edge of saturation mode.
Assume VBE = 0.7 V, = 100 and VCEsat = 0.2V.
8. For the circuit shown, determine the close loop voltage gains (vA/vi), (vB/vi), and (vo/vi). If
the input voltage vi = 1.2 V, determine the output voltages vA, vB, and vo.
100 kΩ
10 kΩ
- vA
+ +
100 kΩ
vo
vi
10 kΩ
- - vB
+
9. Draw the circuit diagram of a difference amplifier. Mention three limitations of a difference
amplifier.
10. For the following multistage amplifier, identify the amplifier configuration and determine the
gain of the each of the stages and the overall gain. Also determine the voltages v01, v02,
and vo. Given vi = 100 mV.
100 kΩ
- 10 kΩ
20 kΩ
OA1 - vo1
vi + OA2
+ 10 kΩ
-
OA4
100 kΩ + +
10 kΩ 10 kΩ vo
- vo2 -
OA3 20 kΩ
+
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- DC Week 3 Circuit Analysis ProblemsDocumento9 pagineDC Week 3 Circuit Analysis ProblemsAbel CarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec ltm1160 5 1Documento475 pagineLec ltm1160 5 1mohamed Abd ElhafeezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Global Semiconductor IndustryDocumento76 pagineThe Global Semiconductor IndustryAnanth Kumar100% (1)
- Modeling Communication Networks and Protocols: Paweł GburzyńskiDocumento499 pagineModeling Communication Networks and Protocols: Paweł Gburzyńskimaxwell_eulerNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Solutions PDFDocumento41 pagineChapter 5 Solutions PDFREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Work Book - Opamp - Analog Sid SirDocumento12 pagineWork Book - Opamp - Analog Sid Sirawsmpranav4698Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment OpampDocumento3 pagineAssignment OpampRamNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Problems: 40 k Ω 4 kΩ Vo +Documento16 pagineReview Problems: 40 k Ω 4 kΩ Vo +NajmoAdenNessuna valutazione finora
- BJT Inverter Circuit AnalysisDocumento1 paginaBJT Inverter Circuit Analysisharlem shakeNessuna valutazione finora
- PBL1Documento6 paginePBL1Muhammad Shafiq Bin Abdul KarimNessuna valutazione finora
- Differential Amplifier Numericals PDFDocumento13 pagineDifferential Amplifier Numericals PDFShibin Kuthirummal KNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 6: 1 2 C CE BEDocumento4 pagineTutorial 6: 1 2 C CE BEAadarshPotluruNessuna valutazione finora
- EEN-205 Electronic Circuits Tutorial Sheet 2 Amplifier AnalysisDocumento2 pagineEEN-205 Electronic Circuits Tutorial Sheet 2 Amplifier Analysisguddu guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE 311 Power Point FinalDocumento4 pagineEEE 311 Power Point FinalAnik Saha Toni 1912619643Nessuna valutazione finora
- Active FiltersDocumento102 pagineActive FiltersnhnhnhNessuna valutazione finora
- 305 Tutorial QuesDocumento5 pagine305 Tutorial QuesUti MichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- EEN-205 Circuit Design TutorialDocumento1 paginaEEN-205 Circuit Design Tutorialguddu guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- EE3115 Exam Review ProblemsDocumento9 pagineEE3115 Exam Review ProblemsNajmoAdenNessuna valutazione finora
- Op amp circuits homework problemsDocumento5 pagineOp amp circuits homework problemsDavidRubeomNessuna valutazione finora
- Op-Amp Circuits Testing Understanding Feedback Gain CMRRDocumento2 pagineOp-Amp Circuits Testing Understanding Feedback Gain CMRRgebretsadkan abrhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aec Lab ManualDocumento33 pagineAec Lab Manualganga_ch1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial5Documento16 pagineTutorial5Sayam SanchetiNessuna valutazione finora
- Divisor de Tensión SimpleDocumento18 pagineDivisor de Tensión SimpleAlfre OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm 11 2022Documento4 pagineMidterm 11 2022kunghsiangyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 31 Tutorial5 PDFDocumento7 pagineLecture 31 Tutorial5 PDFAkhendra KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 04 (07022019)Documento9 pagineTutorial 04 (07022019)Devansh GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Communication Lab ManualDocumento59 pagineAnalog Communication Lab Manualsasa_sag100% (2)
- Tutorial 10Documento4 pagineTutorial 10Abhijith ASNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 5 f2016Documento6 pagineAssignment 5 f2016phoebezzNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems Theme 3 (BJT)Documento11 pagineProblems Theme 3 (BJT)erosceleste17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sboa 221 ADocumento4 pagineSboa 221 Anupoorhit2126Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lec Digital Multimeters 120520 PDFDocumento2 pagineLec Digital Multimeters 120520 PDFMunazza TanvirNessuna valutazione finora
- 300-02 - Op Amp-IIDocumento18 pagine300-02 - Op Amp-IIJade Jumao-asNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronic Circuits - IIITPDocumento13 pagineAnalog Electronic Circuits - IIITPpriyanshu raneNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec0122 Electric Circuits LaboratoryDocumento37 pagineEc0122 Electric Circuits LaboratorybhavanimurugaramalinNessuna valutazione finora
- BIFPCL 2019 Electrical Engineer Recruitment Test QuestionsDocumento3 pagineBIFPCL 2019 Electrical Engineer Recruitment Test QuestionsA One ShoppersNessuna valutazione finora
- Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) : Dr. Mustafa Kemal UyguroğluDocumento36 pagineOperational Amplifiers (Op Amps) : Dr. Mustafa Kemal UyguroğluY BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter V - Problem Set P5.1Documento15 pagineChapter V - Problem Set P5.1Aaron MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- HW 2Documento3 pagineHW 2Emir OmerdicNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions of Homework ProblemsDocumento21 pagineSolutions of Homework ProblemsHusni MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog ElectronicsDocumento166 pagineAnalog ElectronicsSSE OHE 1Nessuna valutazione finora
- IIT Kanpur Homework on Oscillators and Bistable CircuitsDocumento1 paginaIIT Kanpur Homework on Oscillators and Bistable CircuitsAditya TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- ASD Sessional I Answer Scheme-1Documento10 pagineASD Sessional I Answer Scheme-1Gaurav KhandelwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Homewrok 1 BJTDocumento2 pagineHomewrok 1 BJTersahinmert63Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 4 Title: Basic Op-Amp Application Objectives: Vo R R V R R V .... EtcDocumento3 pagineExperiment 4 Title: Basic Op-Amp Application Objectives: Vo R R V R R V .... EtcHasmizar Abd Halim (KTN)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 5 18022020Documento6 pagineTutorial 5 18022020Parekh Prashil BhaveshbhaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Verify Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's LawsDocumento5 pagineVerify Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's LawsjoebrislinNessuna valutazione finora
- Lic Combined SlidesDocumento288 pagineLic Combined SlidesMadhuNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE2280 Homework #1 Fall 2011: Use: Ignore R - V - 0.7, V 20+0.001sin (20t) I VXDocumento11 pagineECE2280 Homework #1 Fall 2011: Use: Ignore R - V - 0.7, V 20+0.001sin (20t) I VXXxx CccNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE2280 Homework #1 Fall 2011: Use: Ignore R - V - 0.7, V 20+0.001sin (20t) I VXDocumento11 pagineECE2280 Homework #1 Fall 2011: Use: Ignore R - V - 0.7, V 20+0.001sin (20t) I VXXxx CccNessuna valutazione finora
- 04-MB-4 Version Anglaise - Mai 2014Documento4 pagine04-MB-4 Version Anglaise - Mai 2014LuisAranaNessuna valutazione finora
- Load Line and Q-PointDocumento3 pagineLoad Line and Q-PointRavi Kanth M NNessuna valutazione finora
- KNR1723 2122Tutorial02SolutionwrewrweDocumento18 pagineKNR1723 2122Tutorial02SolutionwrewrweSebastianNessuna valutazione finora
- RF Circuit AnalysisDocumento18 pagineRF Circuit Analysismd7mdNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4Documento2 pagineLab 4soniakhiNessuna valutazione finora
- (0825 - 2) P BM PSPICE-6 (Schematic)Documento6 pagine(0825 - 2) P BM PSPICE-6 (Schematic)ayanavakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 4-1Documento4 pagineSheet 4-1bodesaid2002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronics Lab. - Tarun - 05616412820Documento38 pagineAnalog Electronics Lab. - Tarun - 05616412820TarunNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 03Documento5 pagineAssignment 03Akshay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Diode Circuit - DPP 03 (Of Lec 09)Documento3 pagineDiode Circuit - DPP 03 (Of Lec 09)devdipika992434Nessuna valutazione finora
- P08 BJTAmplifierCircuits SolDocumento9 pagineP08 BJTAmplifierCircuits SolkahinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Control System Labsheet Exp5Documento5 pagineControl System Labsheet Exp5REDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- FDFDFDDocumento8 pagineFDFDFDREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Labsheet Exp4Documento6 pagineLabsheet Exp4REDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Shortened PointsDocumento4 pagineShortened PointsREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Labsheet Exp2Documento5 pagineLabsheet Exp2REDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 10 HighlightsDocumento6 pagineLec 10 HighlightsREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Control System Labsheet Exp4Documento8 pagineControl System Labsheet Exp4REDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Control Systems Lab: Root Locus and Stability AnalysisDocumento12 pagineControl Systems Lab: Root Locus and Stability AnalysisREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Control System Labsheet Exp1Documento9 pagineControl System Labsheet Exp1REDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- CERT NO: MV/MC/CERT-41304/07/2020: Name of The Insured & AddressDocumento1 paginaCERT NO: MV/MC/CERT-41304/07/2020: Name of The Insured & AddressREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Summer 2020 MAT 216 Problem Sheet: Solve The Following ProblemsDocumento3 pagineSummer 2020 MAT 216 Problem Sheet: Solve The Following ProblemsREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Summer 2020 MAT 216 Problem Sheet: Solve The Following ProblemsDocumento3 pagineSummer 2020 MAT 216 Problem Sheet: Solve The Following ProblemsREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- 4.6 Null Space, Column Space, Row SpaceDocumento10 pagine4.6 Null Space, Column Space, Row SpaceSceptic GrannyNessuna valutazione finora
- Summer 2020 Mat 216 Solutions (Problem Sheet) : Ia Iia Iii ADocumento12 pagineSummer 2020 Mat 216 Solutions (Problem Sheet) : Ia Iia Iii AREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Academic Calendar - 2020 - RevisedDocumento1 paginaAcademic Calendar - 2020 - RevisedMohammed RiyadhNessuna valutazione finora
- MAT216 Cosine Similarity Shopping HabitsDocumento10 pagineMAT216 Cosine Similarity Shopping HabitsREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Term Project 2: Must Be Submitted by The Due Date. 20% Deduction For Each Day Late. No ExceptionDocumento3 pagineTerm Project 2: Must Be Submitted by The Due Date. 20% Deduction For Each Day Late. No ExceptionREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- BRAC University ECE230&EEE209 Semiconductor Materials and Devices Summer 2020 Assignment 1Documento1 paginaBRAC University ECE230&EEE209 Semiconductor Materials and Devices Summer 2020 Assignment 1REDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Week5HW S15 Solutions PDFDocumento14 pagineWeek5HW S15 Solutions PDFPranjal MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Work - 3: EEE 207 / ECE 207: Electronic Devices and Circuits IIDocumento3 pagineHome Work - 3: EEE 207 / ECE 207: Electronic Devices and Circuits IIREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Bandpass filter design and analysisDocumento3 pagineBandpass filter design and analysisREDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Travel Crop Design: Energy Conversion-I EEE 221 Lecture-09Documento12 pagineTravel Crop Design: Energy Conversion-I EEE 221 Lecture-09REDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Redwan Ahmed Miazee - HW - 1Documento3 pagineRedwan Ahmed Miazee - HW - 1REDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 3: ECE209&EEE209 (Semiconductor Materials and Devices) Summer 2020Documento1 paginaAssignment 3: ECE209&EEE209 (Semiconductor Materials and Devices) Summer 2020REDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- BRAC University: ECE230 & EEE209 (Semiconductor Materials and Devices) Summer 2020Documento2 pagineBRAC University: ECE230 & EEE209 (Semiconductor Materials and Devices) Summer 2020REDWAN AHMED MIAZEENessuna valutazione finora
- G6S User Manual PDFDocumento72 pagineG6S User Manual PDFMarco CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Fpga Motor Control Reference Design: Spartan™-3 Microblaze™Documento15 pagineFpga Motor Control Reference Design: Spartan™-3 Microblaze™ASOCIACION ATECUBONessuna valutazione finora
- Iotega Installer ManualDocumento72 pagineIotega Installer ManualjhuenupNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverter Family-220615Documento18 pagineInverter Family-220615حلواني حلوانيNessuna valutazione finora
- Type LFCB Digital Current Differential Relay: FeaturesDocumento14 pagineType LFCB Digital Current Differential Relay: FeaturesFredrikNessuna valutazione finora
- HT82M99A HoltekSemiconductorDocumento50 pagineHT82M99A HoltekSemiconductorLama AmalNessuna valutazione finora
- PN Junction Diode OperationDocumento8 paginePN Junction Diode OperationAyush NinaweNessuna valutazione finora
- Intel Desktop Board d945gcnl blkd945gcnl Manual de UsuarioDocumento4 pagineIntel Desktop Board d945gcnl blkd945gcnl Manual de UsuarioCarlos RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- B1/B1z/HB1 Model List: Module Name SpecificationDocumento2 pagineB1/B1z/HB1 Model List: Module Name SpecificationAmmar Al-KindyNessuna valutazione finora
- Semi ConverterDocumento5 pagineSemi ConverteremanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bahria University Digital Logic Design Lab Report on Decoder CircuitsDocumento5 pagineBahria University Digital Logic Design Lab Report on Decoder CircuitsAbdul BasitNessuna valutazione finora
- 19 10 28 Arm Pluto 8-Michael Hennerich PDFDocumento40 pagine19 10 28 Arm Pluto 8-Michael Hennerich PDFnaujNessuna valutazione finora
- Is 2032-8Documento17 pagineIs 2032-8suresh kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Custom PC Issue 215Documento116 pagineCustom PC Issue 215Eleodor Paul CirlugeaNessuna valutazione finora
- COA MCQsDocumento168 pagineCOA MCQsb krishna vamsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment IictDocumento11 pagineAssignment IictZohaib JoyiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Audio Broadcasting and Digital TV ReplacementDocumento2 pagineDigital Audio Broadcasting and Digital TV ReplacementAmin sanNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract View of System ComponentsDocumento21 pagineAbstract View of System ComponentsXhéhzÂda saleem zehriNessuna valutazione finora
- CS 356 Cache Exercises SolutionsDocumento4 pagineCS 356 Cache Exercises SolutionsNguyễn Trọng NhânNessuna valutazione finora
- FMB 26L SankenelectricDocumento2 pagineFMB 26L SankenelectricEdu EduNessuna valutazione finora
- 2023 弹道InSe晶体管 NatureDocumento22 pagine2023 弹道InSe晶体管 NatureXingxia SunNessuna valutazione finora
- Pasternack Accessories RF 2009 PDFDocumento241 paginePasternack Accessories RF 2009 PDFVlad LecherNessuna valutazione finora
- Egg or Naya Phone - Realme C67Documento2 pagineEgg or Naya Phone - Realme C67abhishekchouhab123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sec III, L 5-7: Wafer Preparation: MEL G611: Ic Fabrication TechnologyDocumento33 pagineSec III, L 5-7: Wafer Preparation: MEL G611: Ic Fabrication TechnologyUdai ValluruNessuna valutazione finora
- VLSI Design and TestingDocumento2 pagineVLSI Design and TestingsirapuNessuna valutazione finora
- A Novel Equivalent Circuit and Modeling Method For Defected Ground Structure and Its Application To Optimization of A DGS Lowpass FilterDocumento4 pagineA Novel Equivalent Circuit and Modeling Method For Defected Ground Structure and Its Application To Optimization of A DGS Lowpass FilterRajNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE 4dDocumento37 pagineEEE 4dAisha JainNessuna valutazione finora