Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Mock Net - Chemistry: For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams
Caricato da
Geeta WatalDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mock Net - Chemistry: For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams
Caricato da
Geeta WatalCopyright:
Formati disponibili
For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams
MOCK NET – CHEMISTRY
1. No. of P – O bonds in solid phosphorous trioxide
(A) 9 (B) 12 (C) 15 (D) 3
2. Product of the reaction 3NaBH4 + 2BF3 ---
(A) B2H6 + NaBF4 (B) BH2F + H2 (C) B2H6 + H2 (D) H2 + BH3
3. Which of the following is best Fluorinating agent
(A) XeF2 (B) XeF4 (C) XeF6 (D) XeO2F2
4. Perxenate ion can be represented as
(A) [XeO6]–4 (B) [XeO4]–2 (C) [XeO3]–3 (D) [XeOF4]–2
5. The octahedral crystal field splitting energy ( ∆ 0 ) of d orditals of the following metal ions decreases in the order
(A) Co2+ > Co3+ > Rh3+ (B) Rh3+ > Co3+ > Co2+
(C) Rh3+ > Co2+ > Co3+ (D) Co3+ > Co2+ > Rh3+
6. The unit of the wave function ψ of a hydrogen atom is :
(A) L3 (B) L–3 (C) L–3, 2 (D) dimensionless
Here, L represents length.
7. The orbital angular momentum (in units of h/2π; where h is the Planck’s constant) of an electron in the 3d orbital
is
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 21/2 (D) 61/2
8. The result of the reduction of either (R) or (S) 2-methylcycyclohexanone, in separate reactions, using LiAlH4 is
that the reduction of
(A) the R enantiomer is stereoselective (B) the R enantiomer is sterespecific
(C) the S enantiomer is stereospecific (D) both the R and S enantiomers is stereoselective
9. Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) In living organism, circulation of 14C from atmosphere is high so that carbon content is constant in organism.
(B) Carbon dating can be made to find out the age of earth curst and rocks.
(C) Radioactive absorption due to cosmic radiation is equal to the rate of radioactive decay, hence the carbon
content remains constant in organism.
(D) Carbon dating can not be used to determine concentration of 14C in dead being.
10. The activity of a radioactive substance is R0 at t = 0; R1 at t = t and R2 at t = 2t. The decay constant of this
species cannot be given by
loge R1 − logR2 loge R0 − loge R1
(A) (B)
t t
loge R2 − loge R1 loge R0 − loge R2
(C) (D)
2t 2t
11. What is left if chloroplast is burnt?
(A) Mg (B) Mn (C) Fe (D) S
12. Mo deficiency causes
(A) Wilting (B) Increase in growth (C) Chlorosis (D) Necrosis and molting
Website: www.vpmclasses.com Phone: 0744-2429714 Mobile: 09950679922 Email:
vpmclasses@yahoo.com Address: 1-C-8, SFS, TALWANDI, KOTA, RAJASTHAN
For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams
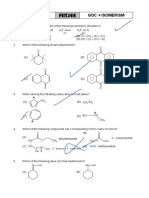
13. The molecules (s) that exist as meso structure (s)
(K) (L) (M)
is/are
(A) only M (B) both K and L (C) only L (D) only K
14. The compound is known by which of the following names:-
(A) Bicyclo-[2, 2, 2] octane (B) Bicyclo-[2, 2, 1] octane
(C) Bicyclo-[1, 2, 1] octane (D) Bicyclo-[1, 1, 1] octane
15. The number of stereo isomers that are possible for the following compound is
+
H C O O C N –: – – – C -H X
5 2 6 5
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
16. The hydrogen atoms Ha and Hb in the given allene are
H b
H
––
C = C = C
––
C 3H
H 3 C
(A) Enantiotopic (B) Homotopic (C) Diastereotopic (D) None
17. Huckel’s rule for aromaticity is followed by
(1) C10H10 (2) C12H12 (3) C12H12–2 (D) C12H12+2
(A) 1, 3 (B) 1, 4 (C) 3, 4 (D) 2, 3
18. The aromatic species are
(1) C20H20 (2) C20H20– (3) C20H20–2 (4) C20H20+ (5) C20H20+2
(A) 3, 5 (B) 2, 4 (C) 2, 3, 4 (D) 1, 3, 5
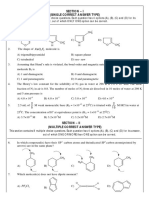
19. Consider the 1H NMR spectrum of the following substance, which set of protons appears farthest downfield
relative to TMS ?
(A) a (B) b (C) c (D) bc
20. Which of the following substance does not give a 1H NMR spectrum consisting of only two peaks?
Website: www.vpmclasses.com Phone: 0744-2429714 Mobile: 09950679922 Email:
vpmclasses@yahoo.com Address: 1-C-8, SFS, TALWANDI, KOTA, RAJASTHAN
For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams
(A) (B)
(C) (D) None of these (all satisfy the spectrum)
21. The multiplicity of the protons in the 1H NMR spectrum of the following substance is
(A) Singlet (B) Doublet (C) Triplet (D) Quartet
22. For a free radical polymerisation reaction, the kinetic chain length ‘γ’, is defined as the ratio
propagation rate initiation rate initiation rate propagation rate
(A) initiation rate (B) propagation rate (C) ter mination rate (D) ter mination rate
23. How many signals are expected in the 13C NMR spectrum of the following substance ?
(A) 5 (B) 6 (C) 8 (D) 10
24. The major product formed in the reaction of cyclopentadiene with a mixture of dichloroacetyl chloride and
triethylamine is
(A) (B) (C) (D)
NaNH2
→
25. lip.NH3 +
The above reaction is an example of
(A) nucleophilic substitution of addition-elimination mechanism
(B) electrophilic substitution by addition-elimination mechanism
(C) radical substitution reaction
(D) nucleophilic substitution involving benzyne intermediate
Website: www.vpmclasses.com Phone: 0744-2429714 Mobile: 09950679922 Email:
vpmclasses@yahoo.com Address: 1-C-8, SFS, TALWANDI, KOTA, RAJASTHAN
For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams
26. undergoes electrophilic substitution reaction preferentially
(A) at position 2 (B) at position 3 (C) at position 4 (D) at positions 2 and 4
27. Oxymercuration-demercuration reaction of 1-methylcyclohexene gives
(A) cis-2-methylcyclohexanol (B) trans-2-methylcyclohexanol
(C) 1-methylcyclohexanol (D) mixture of cis and trans-2-methylcyclohexanol
28. Sodium metal crystallizes in the body centered cubic lattice with cell edge a. The radius of the sodium atom is
a a 3 a 3 a
(A) 2 (B) 2 (C) 4 (D) 2 2
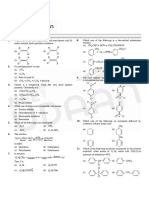
29. Which carbons of 1-chloro-4-fluorobenzene are the most shielded ?
(A) C - 1 (B) C - 3 and C - 5 (C) C - 2 and C - 6 (D) C - 4
30. A chlorinated derivative of benzene had only two peaks for aromatic carbons in its 13
C NMR spectrum. Of the
following, which compound can be eliminated on the basis of this information ?
C I
C I C I C I C I
C I C IC I C I C I C I
(A) (B) (C) (D)
31. The 13 C NMR spectrum of a C7H7CIO isomer has peaks for a methyl carbons. Which compound can you
exclude based solely on the number of peaks ?
O C3 H O C 3 CH I O C3 H
C I C I
(A) (B) (C)
32. A compound of molecular formula C6 H9 NO2 had peaks for its benzene ring carbons at δ 113.8, 119.3, 131.6,
and 151.4. No other peaks for benzene ring carbons were present. Which compound is most consistent with this
13
C NMR data?
(A) (B) (C) (D)
33. A compound of molecular formula C8 H2 CIO2 had peaks for its benzene ring carbons at δ 114.3, 125.3, 134.0,
and 165.5. other peaks for benzene ring carbons were present. Which compound is most consistent with the 13C
NMR data ?
Website: www.vpmclasses.com Phone: 0744-2429714 Mobile: 09950679922 Email:
vpmclasses@yahoo.com Address: 1-C-8, SFS, TALWANDI, KOTA, RAJASTHAN
For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams
O O O O
C I C O 3 C H C 3 H O C C I C O 3 C H C C I
C I C 3 H O
(A) (B) (C) (D)
34. If the shortest wavelength of H atom in Lyman series is a then longest wavelength in balmer series of He+ is
9 36 a 5a
(A) a (B) a (C) (D)
5 5 4 9
35. Given than
2 – r – aor 1
∝ e
a
ψn, l, m(r, θ, φ) = Rnl (r) Ylm(θ, φ); R20 (r) 0 ; Y0, 0(θ, φ) = 4π
The position of radial node in the 2s orbital is at
a0 a0
(A) r = a 0
(B) r = 2a 0
(C) r = 2 (D) r = 4
36. Which of the following relates to photons both as wave motion and as a stream of particles ?
(A) Interference (B) E = mc2 (C) Diffraction (D) E = hv
37. If the slope and intercept values for a Langmuir absorption process are 0.55 Pa cm–3 and 0.525 × 10–3 cm–1,
respectively, the value of adsorption coefficient (Pa–1) is
(A) 1,904 (B) 1.818 (C) 1 × 10–3 (D) 1.047 × 103
38. The absorption isotherm is defined as the dependence of
(A) surface coverage on the temperature at a fixed pressure
(B) surface coverage on the pressure at a fixed temperature
(C) surface coverage on the oxidation state of the surface material
(D) rate of a surface reaction on the pressure at a fixed temperature
39. Which option represent the general form of an equation of state
(A) P = f(T, V, n) (B) V = f(P, T, n) (C) T = f(P, V, n) (D) n = f(P, V, T)
40. For the reaction PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) → PCl5(g), if Kc at 250ºC is 26, Kp at 250ºC will be –
(A) 0.57 (B) 0.4 6 (C) 0.33 (D) 0.61
41. Steam reacts with iron at high temperature to give hydrogen gas and Fe 3O4(s). The correct expression for the
equilibrium constant is –
PH22 (PH 2 )4 (PH2 )4 [Fe3 O 4 ] [Fe3 O4 ]
(A) 2 (B) 4 (C) 4 (D)
PH2O (PH2 O ) (PH2 O ) [Fe] [Fe]
42. In a reaction A + B C + D, , the initial concentrations of A and B were 0.9 mol. dm–3 each. At equilibrium the
concentration of D was found to be 0.6 mol dm–3. What is the value of equilibrium constant for the reaction ?
(A) 8 (B) 4 (C) 9 (D) 3
43. Which of the following option is true about isothermal Joule-Thomson coefficient ?
−1 ∂H ∂H
(1) µ T = − CP µ (2) µ T = − CP µ (3) µ T = (4) µ T =
∂P T ∂P H
( µ = Joule -momentum coefficient; µ T = Isothermal Joule -Thomson coefficient)
Website: www.vpmclasses.com Phone: 0744-2429714 Mobile: 09950679922 Email:
vpmclasses@yahoo.com Address: 1-C-8, SFS, TALWANDI, KOTA, RAJASTHAN
For IIT-JAM, JNU, GATE, NET, NIMCET and Other Entrance Exams
(A) 1, 3 (B) 2, 4 (C) 1, 4 (D) 2, 3
44. Which of the following options are true about Joule -Thomson coefficient (µ)
(1) Positive value of µ implies that gas cools on expansion
(2) Real gases have non-zero value of µ
(3) Positive value of µ imples that gas heats-up on expansion.
(A) 1, 2 (B) 2, 3 (C) Only 2 (D) Only 1
45. Internal energy and pressure of a gas of unit volume are related as :
2 3 E
(A) P = E (B) P = E (C) P = (D) P = 2E
3 2 2
46. The rate of reaction A + B → Pr oducts is given by the equation r = k[A] [B]. If B is taken in large excess, the
order of the reaction would be
(A) 2 (B) 1 (C) 0 (D) unpredictable
47. For an endothermic reaction where ∆H represents the enthalpy of the reaction in kJ/ mol, the minimum value
for the energy of activation will be
(A) less than ∆H (B) zero (C) more than ∆H (D) equal to ∆H
48. The conductivity of 0.01 mol/dm3 aqueous acetic acid at 300K is 19.5 × 10 -5 ohm-1cm-1 and the limiting molar
conductivity of acetic acid at the same temperature is 390 ohm -1cm2mol-1. The degree of dissociation of acetic
acid
(A) 0.5 (B) 0.05 (C) 5 × 10-3 (D) 5 × 10-7
49. The standard reduction potentials, E0, for the half reactions are
Zn2+ + 2e − → Zn, E 0 = −0.76 V
Fe2 + + 2e − → Fe, E 0 = −0.41 V
The EMF for the cell reaction
Fe2 + + Zn → Zn 2+ + Fe is
(A) – 0.35 V (B) + 0.35 V (C) + 1.17 V (D) – 1.17 V
50. The ionization constant of a weak electrolyte is 25 × 10-6 while the equivalent conductance of its 0.01M solution
is 19.6 S cm2eq-1. The equivalent conductance of the electrolyte at infinite dilution (in S cm2eq-1) will be
(A) 250 (B) 196 (C) 392 (D) 384
Answer key
Question. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
Answer. B A C A B C D D C C A D D A B B C A A B
Question. 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
Answer. A A C A D B C C C D C A A A B D D B A D
Question. 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
Answer. B D D A A B C B B C
Website: www.vpmclasses.com Phone: 0744-2429714 Mobile: 09950679922 Email:
vpmclasses@yahoo.com Address: 1-C-8, SFS, TALWANDI, KOTA, RAJASTHAN
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Solution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringDa EverandSolution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Chemistry BITSAT Question BankDocumento26 pagineChemistry BITSAT Question Bankaayushdoshi20210041Nessuna valutazione finora
- Net Paper With Solution June 2017 Chemical SciencesDocumento40 pagineNet Paper With Solution June 2017 Chemical SciencesDeeksha KumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper: Csir-Ugc-Net/Jrf June 2017: Part-BDocumento19 paginePaper: Csir-Ugc-Net/Jrf June 2017: Part-BBaban BaidyaNessuna valutazione finora
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - M.Sc. Chemistry HyderabadDocumento22 pagine(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - M.Sc. Chemistry HyderabadYocobSamandrewsNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.GOC & IsomerismDocumento37 pagine9.GOC & IsomerismVinod AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordination CompoundDocumento9 pagineCoordination CompoundRetroNessuna valutazione finora
- 21CYB101J Jan 2023Documento3 pagine21CYB101J Jan 2023learncoursegrbNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 GATE-CY 2003 Question PaperDocumento15 pagine1 GATE-CY 2003 Question PaperKARTIK RANANessuna valutazione finora
- GOC (13th)Documento34 pagineGOC (13th)Raju SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Brain Storm Chemistry Med FinalDocumento7 pagine1 Brain Storm Chemistry Med FinalShudhanshu KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Goc + IsomerismDocumento5 pagineGoc + IsomerismRohail HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Cat 8Documento3 pagineCat 8Ravi Kiran KoduriNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Chemical BondingDocumento3 pagineTest Chemical Bondingdevansh dewanNessuna valutazione finora
- 13FINALSHEET06STEREOISOMERDocumento23 pagine13FINALSHEET06STEREOISOMERarryan keshanNessuna valutazione finora
- 48 Paper: Iit-Jam 2011Documento8 pagine48 Paper: Iit-Jam 2011prakhar vishwakarma100% (1)
- MOCK TEST - I, JEEM Shift-II, 4-11-2023Documento3 pagineMOCK TEST - I, JEEM Shift-II, 4-11-2023shashwat.gupta.707Nessuna valutazione finora
- Co OrdinateDocumento72 pagineCo OrdinateMotivational BabaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2010 PDFDocumento8 pagine2010 PDFprakhar vishwakarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical BondingDocumento22 pagineChemical BondingAbhishek KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- LPP-Transition Elements and Coordination Compounds: Te Te Te EtDocumento4 pagineLPP-Transition Elements and Coordination Compounds: Te Te Te EtYash TandonNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordination CompoundsDocumento3 pagineCoordination CompoundsDisha ChawlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic+Dpps A1-A14 PDFDocumento43 pagineOrganic+Dpps A1-A14 PDFAditya ChakraniNessuna valutazione finora
- 50 Expected QuestionsDocumento6 pagine50 Expected QuestionsShadhasanNessuna valutazione finora
- GOC & EAS CPP-II - PMDDocumento14 pagineGOC & EAS CPP-II - PMDVansh sareenNessuna valutazione finora
- Objectives: CH - OHDocumento18 pagineObjectives: CH - OHHarsh TyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- XL 2018Documento25 pagineXL 2018PARAB ROHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Q. 1 - Q. 5 Carry One Mark EachDocumento5 pagineQ. 1 - Q. 5 Carry One Mark EachSai MungalNessuna valutazione finora
- UnitTest - D09 Mar 2024Documento28 pagineUnitTest - D09 Mar 2024NamraNessuna valutazione finora
- GUJCET - D22 Mar 2024Documento17 pagineGUJCET - D22 Mar 2024aadityabhagchandaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-7) - PaperDocumento13 pagineChemistry Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-7) - PaperNitin SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rits-21 1Documento13 pagineRits-21 1Muhammad HamzaNessuna valutazione finora
- GOC Sheet PDFDocumento55 pagineGOC Sheet PDFAayush KharbandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gurukul Classes: Wagh's ChemistryDocumento3 pagineGurukul Classes: Wagh's ChemistryJagdish WaghNessuna valutazione finora
- Dec - 2012Documento20 pagineDec - 2012Sumanta- 14Nessuna valutazione finora
- Question - 123Documento3 pagineQuestion - 123bazith.azasoftNessuna valutazione finora
- Dec. 2017 Chemical Sciences Paper With SolutionDocumento42 pagineDec. 2017 Chemical Sciences Paper With SolutionSoumya Ganguly50% (2)
- Adobe Scan 05-Jan-2023Documento7 pagineAdobe Scan 05-Jan-2023sachinmzp033Nessuna valutazione finora
- 09 Jan 2019 Shift 1 English ChemistryDocumento9 pagine09 Jan 2019 Shift 1 English ChemistryAsharani MahapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Prof Shekhar ChemistryDocumento9 pagineProf Shekhar Chemistryveer_sNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2011Documento17 pagineJune 2011Anonymous BdarBSg5c3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Coordination Compounds 1Documento5 pagineCoordination Compounds 1Nikhar MalooNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 5Documento3 pagineChemistry 5Ronak JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Adobe Scan 27-Dec-2022Documento8 pagineAdobe Scan 27-Dec-2022Krishnanjali MajumderNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz - Coordination Compounds PDFDocumento2 pagineQuiz - Coordination Compounds PDFAman JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cu NH PTCLDocumento3 pagineCu NH PTCLSonu KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 24 Hydrocarbon Set Test Final EDocumento3 pagine24 Hydrocarbon Set Test Final EKumar kartikeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry DPPDocumento4 pagineChemistry DPPTapan MajumdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Du Entrance Chemistry 2017Documento15 pagineDu Entrance Chemistry 2017Arnav ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Target: Jee (Advanced) 2015Documento8 pagineTarget: Jee (Advanced) 2015Prince SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- IIT-JEE 2007 Sample Test Paper: Cooh CL HDocumento7 pagineIIT-JEE 2007 Sample Test Paper: Cooh CL HRanjit Raj RNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry (Full Test) Mains - Paper 2Documento5 pagineChemistry (Full Test) Mains - Paper 2Ravi Kiran KoduriNessuna valutazione finora
- Isomerism Level Wise Practice Sheet by Mr. Dhirendra Kumar For Class 11th ChemistryDocumento7 pagineIsomerism Level Wise Practice Sheet by Mr. Dhirendra Kumar For Class 11th ChemistryManoj SisodiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dec 2016 Chemistry PaperDocumento24 pagineDec 2016 Chemistry PaperDaniella MendoncaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper 3: ChemistryDocumento13 pagineSample Paper 3: ChemistryPr SathishNessuna valutazione finora
- D and F Block Elements - AssignmentDocumento9 pagineD and F Block Elements - AssignmentlavenyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dec Chem 2015Documento26 pagineDec Chem 2015maheshNessuna valutazione finora
- KVPY SA 2017 Chemistry Question Answerkey SolutionsDocumento11 pagineKVPY SA 2017 Chemistry Question Answerkey SolutionsPRITHISH HAZRANessuna valutazione finora
- Time: 1 Hrs Max. Marks: 87 Single Correct: OH OH OH OHDocumento5 pagineTime: 1 Hrs Max. Marks: 87 Single Correct: OH OH OH OHlakshmi.vedanarayanan7785Nessuna valutazione finora
- HPMPeikko Group 001 TMAWebDocumento36 pagineHPMPeikko Group 001 TMAWebMukesh ShettyNessuna valutazione finora
- General Principles of Measurement SystemsDocumento21 pagineGeneral Principles of Measurement SystemsChelseaNessuna valutazione finora
- Expansion Model Test of Expansive Soil in Different Stress State BDocumento11 pagineExpansion Model Test of Expansive Soil in Different Stress State BHuang BenNessuna valutazione finora
- On P-Groups of Maximal Class: August 2019Documento9 pagineOn P-Groups of Maximal Class: August 2019JodeNessuna valutazione finora
- Overlap 2Documento22 pagineOverlap 2Anonymous fFl3xgWNessuna valutazione finora
- Advances in Motor Torque Control PDFDocumento122 pagineAdvances in Motor Torque Control PDFTasos PoteasNessuna valutazione finora
- Drmos Specifications: November 2004 Revision 1.0Documento17 pagineDrmos Specifications: November 2004 Revision 1.0Tran Xuan NamNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross ArmsDocumento46 pagineCross Armshalel111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Interactive Powerpoint Presentation On QuadrilateralsDocumento3 pagineInteractive Powerpoint Presentation On QuadrilateralsSkoochh KooNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Chemistry Basic ConceptsDocumento12 pagineAnalytical Chemistry Basic ConceptsNino Jay FabrosNessuna valutazione finora
- MKN Hansdampf Cge12 eDocumento2 pagineMKN Hansdampf Cge12 eRumen PavlovNessuna valutazione finora
- WEEK 5 Dot Product and WorkDocumento10 pagineWEEK 5 Dot Product and Workmaria1345Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tachi e 2004Documento12 pagineTachi e 2004Ahsan Habib TanimNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42Documento20 pagineCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/42spotifysubs250Nessuna valutazione finora
- PVC& CPVC SCH 80 Technical CatalogueDocumento49 paginePVC& CPVC SCH 80 Technical CataloguekailashNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling and Response Prediction in Performance-Based Seismic Evaluation: Case Studies of Instrumented Steel Moment-Frame BuildingsDocumento33 pagineModeling and Response Prediction in Performance-Based Seismic Evaluation: Case Studies of Instrumented Steel Moment-Frame BuildingsAshish ɐʇoʞdɐsNessuna valutazione finora
- LG Lx-U250a Lxs-U250Documento55 pagineLG Lx-U250a Lxs-U250remanuel18Nessuna valutazione finora
- ReiewDocumento19 pagineReiewcullen bohannonNessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 Shear Strength of Brick Masonry Walls Assembled With Different Types of MortarDocumento8 pagine2013 Shear Strength of Brick Masonry Walls Assembled With Different Types of MortarCatherineNessuna valutazione finora
- Bab 8 Notes and Latihan Form 3 PtsiDocumento15 pagineBab 8 Notes and Latihan Form 3 PtsiShanti Guna0% (1)
- Neon Genesis Evangelion ANIMA Vol. 4Documento262 pagineNeon Genesis Evangelion ANIMA Vol. 4jojo100% (2)
- Complete Notes On 9th Physics by Asif RasheedDocumento82 pagineComplete Notes On 9th Physics by Asif RasheedAsif Rasheed Rajput75% (28)
- BroombastickDocumento3 pagineBroombastickAllen SornitNessuna valutazione finora
- The Interpretation of Incomplete Piezocone Dissipation TestsDocumento358 pagineThe Interpretation of Incomplete Piezocone Dissipation Testsmaroof nahinNessuna valutazione finora
- MeasurementsDocumento8 pagineMeasurementsSethu Naidu0% (1)
- Antenna Radiation Electromagnetic Electrical Resistance Ohm MeterDocumento6 pagineAntenna Radiation Electromagnetic Electrical Resistance Ohm Meterbiswa217Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Sciences PDFDocumento51 paginePhysical Sciences PDFfarooqi111Nessuna valutazione finora
- CG Industrial Product OverviewDocumento12 pagineCG Industrial Product Overviewvanessa quispeNessuna valutazione finora
- RDM-chapter 1Documento35 pagineRDM-chapter 1Mat MatttNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Specimen Thickness and Stress Ratio On Fatigue Crack Growth After A Single Overload Cycle On Structural SteelDocumento8 pagineEffect of Specimen Thickness and Stress Ratio On Fatigue Crack Growth After A Single Overload Cycle On Structural SteelKamal MankariNessuna valutazione finora