Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Area and Geometry Formulas
Caricato da
sandeepTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Area and Geometry Formulas
Caricato da
sandeepCopyright:
Formati disponibili
24.
AREA
FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS
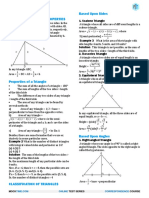
Resulte on Triangles
th angles of a triangle is 180
Sum ofthe
Sum of
1
wo sides of a
2. The
of
sum
triangle is greater than the third side.
3. ythagoras Theorem: In a right-angled triangle,
(Hypotenuse) = (Base) +(Heightt2
The line joining the mid-point of a side of a triangle to the opposite vertex is called
the mediana.
here
whe the three medians of a
5. The point triangle : 1. is called
rentroid divides each of the medians in the ratio 2meet, centroid., The
cIn an isosceles triangle, the altitude from the vertex
bisects the base.
The median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of the same area.
of the triangle
& The area
formed by joining the
is one-fourth of the area of the
mid-points of the sides of a given
triangle given triangle.
Rerulte on Quadrilaterals:
. The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
2. Each diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into twotriangles of the same area.
3. The diagonals of a rectangle are equl and bisect each other.
4. The diagonals of a square are equal and bisect each other at
right angle8
5. The diagonals of a rhombus are unequal and bisect each other at
right angles.
6. A parallelogram anda rectangle on
the same base and between the same parallels
are equal in area.
1. Of all the parallelogram of given sides, the parallelogram which is rectangle has a
the greatest area.
IMPORTANT FORMULAE
L1 Area of a rectangle (Length x Breadth).
=
Area Area
Length =
and Breadth =
(Breadth) Length
.
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2 (Length + Breadth).
Areaof a square = (side* =(diagonal)
Area
of 4 walls of a room 2 (Length + Breadth) x
Height.
Area of a triangle =xBase xHeight.
2. rea of a triangle = ys(s-a)(s - b) (s - c), where a, b, c are the sides of the
triangle and s =
(a t+b+ c).
499
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Geometry For Dummies Cheat SheetDocumento1 paginaGeometry For Dummies Cheat SheetfdjNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry: Triangles and Their Properties Based Upon SidesDocumento34 pagineGeometry: Triangles and Their Properties Based Upon SidesVaseem Raza Mirza100% (1)
- Adjustment and Impulse Control DisordersDocumento19 pagineAdjustment and Impulse Control DisordersArchana50% (4)
- Benokraitis, Benokraitis Nijole Vaicaitis - Marriages & Families - Changes, Choices, and Constraints-Pearson (2015)Documento617 pagineBenokraitis, Benokraitis Nijole Vaicaitis - Marriages & Families - Changes, Choices, and Constraints-Pearson (2015)colleen100% (1)
- Birds, Bees and Burgers: Puzzling Geometry from EnigMathsDa EverandBirds, Bees and Burgers: Puzzling Geometry from EnigMathsNessuna valutazione finora
- ScreenwritingDocumento432 pagineScreenwritingkunalt09100% (4)
- M13 - Solution of TrianglesDocumento5 pagineM13 - Solution of Triangles9703693564Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aligning With New Digital Strategy A Dynamic CapabilitiesDocumento16 pagineAligning With New Digital Strategy A Dynamic Capabilitiesyasit10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Synergetics in The PlaneDocumento27 pagineSynergetics in The PlaneIan BeardsleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lim vs. CA DigestDocumento2 pagineLim vs. CA Digestsamme1010100% (1)
- ERICO Surge Protection Products CatalogDocumento60 pagineERICO Surge Protection Products Catalogcyelectrocontrolll35Nessuna valutazione finora
- Strategicmanagement Finalpaper 2ndtrisem 1819Documento25 pagineStrategicmanagement Finalpaper 2ndtrisem 1819Alyanna Parafina Uy100% (1)
- Working Capital Management at Padmavathi Co-operative BankDocumento53 pagineWorking Capital Management at Padmavathi Co-operative BankMamidishetty Manasa67% (3)
- Area and VolumesDocumento3 pagineArea and VolumesSharon MantodeNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Formulas for Area and Perimeter CalculationsDocumento3 pagineImportant Formulas for Area and Perimeter CalculationsGopal PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental ConceptsDocumento2 pagineFundamental ConceptsmahepNessuna valutazione finora
- Area Wiki PDFDocumento6 pagineArea Wiki PDFgooglepleckNessuna valutazione finora
- Math TipsDocumento5 pagineMath TipsDolly KumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Anchor Chart TrianglesDocumento2 pagineAnchor Chart TrianglesMiddle Scoool MathNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Team 10 - Bip-2Documento23 pagineGeometry Team 10 - Bip-2Rosiana RamadhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Mensuration: Basic Concepts and Important Formulas Equilateral TriangleDocumento5 pagineMensuration: Basic Concepts and Important Formulas Equilateral TriangleSrinu MaddikuntlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Area, Surface Area, VolumeDocumento11 pagineArea, Surface Area, VolumeSankaran Arumugam100% (1)
- Triangle geometry SOLMEN 113Documento7 pagineTriangle geometry SOLMEN 113CyndelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Area of A Circle: R Is The Radius of The Circle (Any LineDocumento6 pagineArea of A Circle: R Is The Radius of The Circle (Any LineAndrea Chellsea Abejero LaguraNessuna valutazione finora
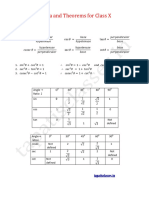
- Formula and Theorems For Class XDocumento12 pagineFormula and Theorems For Class XPraneel .SNessuna valutazione finora
- A About Area and PerimeterDocumento11 pagineA About Area and PerimeterAmiel ColanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mensuration 1st ChapterDocumento23 pagineMensuration 1st ChaptersanthoshNessuna valutazione finora
- SOLMEN 112 - Module 1-Introduction and TrianglesDocumento6 pagineSOLMEN 112 - Module 1-Introduction and TrianglesFlores, Allyssa Mae M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Important Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasDocumento10 pagineImportant Formulas - Area: 3. Geometric Shapes, Solids and Important Formulas Geometric Shape Description FormulasAmey GudigarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastering The Basics of TrigonometryDocumento8 pagineMastering The Basics of TrigonometryKarthik RNessuna valutazione finora
- GeometryDocumento12 pagineGeometryJose Marviel JesoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 (H1N1 Remediation)Documento3 pagineLesson 1 (H1N1 Remediation)nateiddeNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Formulas for Mensuration Chapter 11Documento4 pagineImportant Formulas for Mensuration Chapter 11mekala deevena kumariNessuna valutazione finora
- A KM/HR Ax: Problem On Trains KM/HR To M/s ConversionDocumento7 pagineA KM/HR Ax: Problem On Trains KM/HR To M/s ConversionShiva RokaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometry - PresentationDocumento99 pagineTrigonometry - PresentationsaifullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid Geometry ExplainedDocumento9 pagineSolid Geometry Explainedfachira_humairaNessuna valutazione finora
- Volume and Surface Area - Pyramids, Cones, and SphereDocumento16 pagineVolume and Surface Area - Pyramids, Cones, and Sphereʀᴇᴀ ꜰᴏɴᴅNessuna valutazione finora
- Right TrianglesDocumento13 pagineRight TrianglesMHARLOU TORINGNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathe Formula Grade 8Documento6 pagineMathe Formula Grade 8hasan alaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Formulae GuideDocumento1 paginaMathematical Formulae GuideNORHAYATI BINTI SALLEH MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11Documento4 pagineChapter 11Preetham RaajNessuna valutazione finora
- S (S A) (S B) (S C) A+b+ CDocumento3 pagineS (S A) (S B) (S C) A+b+ CSaideep AryalNessuna valutazione finora
- Encyclipedia of Trignometry - Andrew BarnesDocumento140 pagineEncyclipedia of Trignometry - Andrew Barnessaka1977Nessuna valutazione finora
- Triangle NotesDocumento3 pagineTriangle NotesSriharsha PidaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- LABOR REQUIREMENT calculationDocumento3 pagineLABOR REQUIREMENT calculationvee propagandaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFDocumento1 pagina6 Geometry 01apr2009 PDFNarenNessuna valutazione finora
- Area Perimeter and Surface Area of ObjectsDocumento9 pagineArea Perimeter and Surface Area of ObjectsElioz BatungwanayoNessuna valutazione finora
- L2 Fsolimon - TriangleDocumento20 pagineL2 Fsolimon - Trianglepaulrestar777Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plane Geometry 1 & 3Documento2 paginePlane Geometry 1 & 3AhllyNessuna valutazione finora
- Session 9 Area Volume and SurfaceDocumento12 pagineSession 9 Area Volume and SurfaceRamnarayan MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- AMC Club Geometry Cram CourseDocumento8 pagineAMC Club Geometry Cram CourseJames WigtonNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Sheets Geometry MATH 097: A Summary of Concepts Needed To Be Successful in MathematicsDocumento10 pagineReview Sheets Geometry MATH 097: A Summary of Concepts Needed To Be Successful in Mathematicsyus accNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Matematik f1f2f3Documento5 pagineFormula Matematik f1f2f3Christina MathewNessuna valutazione finora
- AreaDocumento15 pagineAreanavyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Revcards Adam SSMDocumento12 pagineRevcards Adam SSMHannah YeungNessuna valutazione finora
- Plane Trigonometry - by TrockersDocumento59 paginePlane Trigonometry - by Trockersnigeltinashe56Nessuna valutazione finora
- CentroidsDocumento6 pagineCentroidsLaquando YoungNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento16 pagineChapter 7Pyae Sone KyawNessuna valutazione finora
- The Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaDocumento12 pagineThe Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaMolla DerbewNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 103 Lecture Notes: Leah Keshet January 9, 2005Documento28 pagineMath 103 Lecture Notes: Leah Keshet January 9, 2005nagaraj108Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics 10 DLS 26-27Documento6 pagineMathematics 10 DLS 26-27Ivan Miguel MariNessuna valutazione finora
- Four-Side Plane FiguresDocumento26 pagineFour-Side Plane FiguresFajrin Maulana Kingwijati100% (1)
- Find The Angle - Choice Board ScaffoldedDocumento3 pagineFind The Angle - Choice Board Scaffoldedapi-474129066Nessuna valutazione finora
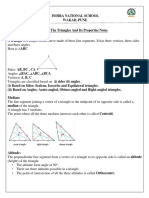
- Notes of The Triangles and Its PropertiesDocumento3 pagineNotes of The Triangles and Its PropertiesIshanviNessuna valutazione finora
- Rumus PrimoidalDocumento7 pagineRumus PrimoidaltsipilNessuna valutazione finora
- Relationship Between Perimeter and AreaDocumento3 pagineRelationship Between Perimeter and Areaharyani husnizanNessuna valutazione finora
- SAT Math - Plane and Solid GeometryDocumento8 pagineSAT Math - Plane and Solid GeometryΜάριος Α. ΠαππάςNessuna valutazione finora
- 2023.workbook - Maths Literacy Grade 12Documento12 pagine2023.workbook - Maths Literacy Grade 12tinashe chirukaNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Aug 19, 2020Documento1 paginaScan Aug 19, 2020sandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar: A Book of Grammar and CompositionDocumento1 paginaGrammar: A Book of Grammar and CompositionsandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Aug 19, 2020Documento2 pagineScan Aug 19, 2020sandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Average Speed and Weight FormulaeDocumento1 paginaAverage Speed and Weight FormulaesandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Aug 19, 2020Documento2 pagineScan Aug 19, 2020sandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Aug 19, 2020 PDFDocumento2 pagineScan Aug 19, 2020 PDFsandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Arithmetic ability section on operations with numbersDocumento1 paginaArithmetic ability section on operations with numberssandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Epass Manual For JharkhandDocumento8 pagineEpass Manual For JharkhandManmohan SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- PROLEC BASIC Lightning Counter PDFDocumento1 paginaPROLEC BASIC Lightning Counter PDFsandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Scan Aug 19, 2020 PDFDocumento2 pagineScan Aug 19, 2020 PDFsandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- LCF78 50JL PDFDocumento2 pagineLCF78 50JL PDFsandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- LCF78 50JL PDFDocumento2 pagineLCF78 50JL PDFsandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-5/8" CELLFLEX Premium Attenuation Low-Loss Foam-Dielectric Coaxial CableDocumento2 pagine1-5/8" CELLFLEX Premium Attenuation Low-Loss Foam-Dielectric Coaxial CablesandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- IRCTC e-ticket for travel from BKSC to NDLSDocumento2 pagineIRCTC e-ticket for travel from BKSC to NDLSsandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- BXT Bas 920300Documento1 paginaBXT Bas 920300sandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Rdso-Spn 165-2012Documento2 pagineRdso-Spn 165-2012sandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Booklet English 2016Documento17 pagineBooklet English 2016Noranita ZakariaNessuna valutazione finora
- X TensoqaDocumento2 pagineX TensoqaLeo CabelosNessuna valutazione finora
- IELTS Writing Task 2/ IELTS EssayDocumento2 pagineIELTS Writing Task 2/ IELTS EssayOlya HerasiyNessuna valutazione finora
- Fixed Prosthodontics Provisional Materials: Making The Right Selection.Documento7 pagineFixed Prosthodontics Provisional Materials: Making The Right Selection.veloso.rossana0% (1)
- Beuys Begleitheft en ScreenDocumento18 pagineBeuys Begleitheft en Screensofijawt0% (1)
- Srimanta Shankardev: Early LifeDocumento3 pagineSrimanta Shankardev: Early LifeAnusuya BaruahNessuna valutazione finora
- CFC KIDS FOR CHRIST 2020 FINAL EXAMDocumento13 pagineCFC KIDS FOR CHRIST 2020 FINAL EXAMKaisser John Pura AcuñaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Leaders of The NationDocumento3 pagineThe Leaders of The NationMark Dave RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- A. Rationale: Paulin Tomasuow, Cross Cultural Understanding, (Jakarta: Karunika, 1986), First Edition, p.1Documento12 pagineA. Rationale: Paulin Tomasuow, Cross Cultural Understanding, (Jakarta: Karunika, 1986), First Edition, p.1Nur HaeniNessuna valutazione finora
- SPH3U Formula SheetDocumento2 pagineSPH3U Formula SheetJSNessuna valutazione finora
- Database Case Study Mountain View HospitalDocumento6 pagineDatabase Case Study Mountain View HospitalNicole Tulagan57% (7)
- AESCSF Framework Overview 2020-21Documento30 pagineAESCSF Framework Overview 2020-21Sandeep SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Split Plot Design GuideDocumento25 pagineSplit Plot Design GuidefrawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Female and Male Hacker Conferences Attendees: Their Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) Scores and Self-Reported Adulthood ExperiencesDocumento25 pagineFemale and Male Hacker Conferences Attendees: Their Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) Scores and Self-Reported Adulthood Experiencesanon_9874302Nessuna valutazione finora
- Advancements in Organic Rankine Cycle System Optimisation For Combined Heat and Power Applications Components Sizing and Thermoeconomic ConsiderationsDocumento14 pagineAdvancements in Organic Rankine Cycle System Optimisation For Combined Heat and Power Applications Components Sizing and Thermoeconomic ConsiderationsGuadalupe Abigail Rueda AguileraNessuna valutazione finora
- Enbrighten Scoring Rubric - Five ScoresDocumento1 paginaEnbrighten Scoring Rubric - Five Scoresapi-256301743Nessuna valutazione finora
- BH Tif03Documento21 pagineBH Tif03Andres R. OlguinNessuna valutazione finora
- ARTS 9 Q4 Week 1Documento3 pagineARTS 9 Q4 Week 1Elaissa MaglanqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Culture and Traditions PaperDocumento7 pagineFamily Culture and Traditions PaperAmit JindalNessuna valutazione finora
- Advisory Circular: Aircraft Maintenance Engineer Licence - Examination Subject 2 Aircraft Engineering KnowledgeDocumento44 pagineAdvisory Circular: Aircraft Maintenance Engineer Licence - Examination Subject 2 Aircraft Engineering KnowledgejashkahhNessuna valutazione finora
- School newspaper report teaches Present PerfectDocumento2 pagineSchool newspaper report teaches Present PerfectMiro MiroNessuna valutazione finora
- 4439 Chap01Documento28 pagine4439 Chap01bouthaina otNessuna valutazione finora