Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Long Term - Answer Key: REVISON TEST (28.07.2020)
Caricato da
sachin saku0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
38 visualizzazioni17 pagineNeet
Titolo originale
BOT532GVC_jhds_ANS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoNeet
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
38 visualizzazioni17 pagineLong Term - Answer Key: REVISON TEST (28.07.2020)
Caricato da
sachin sakuNeet
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 17
Test ID : 532
E- mail : gpccnamakkal@gmail.com Website : www.gpccnamakkal.com
REVISON TEST (28.07.2020)
LONG TERM – ANSWER KEY
Choose the correct answer: 180 x 4 = 720
1. 3) Internal description of specimen 6. 2) Alternaria – Sexual reproduction absent –
Explanation : Deuteromycetes
Chapter: 1 Explanation :
* Internal description is anatomy of the Chapter: 2
specimen. Herbarium is a collection of plant 1. Phytophthora – septate mycelium
specimens which are dried pressed and 2. Alternaria – sexual reproduction -
preserved on sheets. The sheet provides
Deuteromycetes
information which is listed in (1), (2) and (4)
3. Albugo – aseptate and coenocytic hyphae -
option but does not describe the internal
Phycomycetes
structure of the specimens.
4. Neurospora – extensively used in genetic
2. Chapter: 2
work - Ascomycetes
2) Heterotrophic bacteria
Explanation : 7. 3) a single leaf arises at each node in alternate
* Most primitive group of microbes belonging manner
to Eubacteria as compared to blue green Explanation :
algae, diatoms and gymnosperms which are Chapter: 5
photosynthetic. All the three plants show alternate phylotaxy.
3. 3) A-(iii), B-(i), c-(iv), d-(ii) Statement 1 – Wrong as Chinarose has twisted
Chapter:3 aestivation
4. 1) free central placentation
Option – 2 – Wrong as
Chapter: 5
Chinarose – monodeiphous stamens
5. 3) only ‘b’
Chapter: 1 Mustard – tetradynamous stamens
Explanation : Sunflower – syngeneous anthers
a) from inside means intrinsic growth i.e. 8. 4) differential action of hormones
increase in size due to increase in number
Chapter: 6
of cells.
9. 4) Metabolic reactions invitrio are living
b) by accumulation of material on surface –
things but surely not living reactions
observed during formation of boulders,
sand mounds, etc Explanation :
c) localised and definite growth – growth in Chapter: 1
animals Metabolic reactions invitrio are not living
d) diffused and indefinite – plant growth things but surely living reactions.
2 Test ID : 532
10. 3) power of adaptability in diverse habitat 3. Perigynous flower ovary-half superior and
Explanation : half inferior G – Plum, rose, peach. e.g.
Chapter: 3 given mustard is wrong
* They have power of adaptability in diverse 4. Epigynous flower – Superior ovary –
habitat because of development of seed G Mustard, China rose, Brinjal. e.g. given
habit. rose is wrong
* The seeds have ability to survive under 13. 2) B and D only
adverse due to dormancy. The seeds can be Explanation :
dispersed to far off places, where they can Chapter: 5
germinate and produce new plants under B-Chysanthemum – Suckers as modification
favourable conditions. of stem for vegetative propagation
11. 1) Dicot stem, monocot root D- Citrus – axillary bud modified into thorns
Explanation : for protection against browsing animals
Chapter: 6 (Spines are modification of leaves)
In Roots: 14. 3) only a
Pith is well developed in monocot root and Explanation :
small or inconspicuous in dicot root Chapter: 6
In stem: b – Primary phloem and secondary phloem
The VBs in dicot stem are arranged in a ring gets gradually crushed due to continued
towards the periphery with the central portion formation and accumulation of secondary
occupied by large number of rounded xylem.
parenchymatous cells with large intercellular
c – formation of phellogen occurs in extra
spaces called pith. Monocot stem – shows
stellar region
atactostele (stele – absent) VBS are scattered
in the ground tissue and are not surrounded by 15. 4) Morels and truffles are edible mushrooms
pericycle and endodermis. Pith is absent. Explanation :
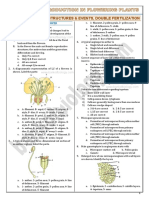
12. Chapter: 2
1. Morels and truffles are edible members of
Ascomycetes fungi and they are not
G Cucumber mushrooms.
Mushrooms belong to the group of
Basidiomycetes.
Explanation :
16. 3) Four
Chapter: 5
Diagram Explanation :
1. represents epigynous flower – ovary is Chapter: 3
Vegetative plant body of moss is haploid
inferior G – examples guava and
which represents gametophytic generation.
cucumber
2. Perigynous flower – ovary-half superior Fusion of antheroid and egg in archegonia
and half inferior G – Plum, rose,peach. e.g. forms a diploid zygote which germinates to
given is wrong produce sporophyte.
3 Test ID : 532
The saprophyte is diploid and consists of a (3) Indicates perianth with 6 tepals
foot, setae and capsule which are dependent P3+3 arranged in 2 rows. Characteristic
on gametophyte. feature of Family : Liliaceae.
zygote of fern → diploid structure Therefore, Belladona is a wrong
17. 2) formation of endosperm before fertilization example as it belongs to family
Explanation : Solanaceae
Chapter: 3 (4) Indiogofera belongs to Family :
Conifers are gymnosperms where endosperm G(2) Fabaceae which has
is formed before fertilization and hence is a monocarpellary gynoecium with
prefertilizea tissue. Grasses are angiosperms, superior ovary.
they exhibit double fertilization hence G – stands for gynoecium – 2
endosperm is a post fertilized tissue. indicates the number of carpels and
18. 3) pericycle G – indicates superior ovary. For
Explanation : Indigofera, it is G1
Chapter: 6 G(2) – describes gynoecium of
Cells of pericycle undergo dedifferentiation solanaceae.
producing vascular cambium along with
20. 3) Enables lateral movement of proteins
conjuctive tissue forming a cambium ring.
Since pericycle and conjunctive tissue both are Explanation :
differentiated tissues which de-differentiate to Chapter: 8
Labelled part A is bilayer of phospholipids.
form cambium ring, it is completely secondary
in origin. 1. Proteins – act as carrier molecules for to
19. 1) C1+2+(2) – Arachis facilitate the transport of polar molecules
across the membrane.
Explanation :
Chapter: 5 2. Glycolipids – found attached to the outer
surface of the membrane which provides
(1) Describes the characteristic corolla
membrane stability.
C1+2+(2) of flowers belonging to family.
3. Phospholipids – they have quasi-fluid
Fabaceae. Papilionaceous corolla
nature (fluidity) which permits lateral
with 5 petals consisting of a
movement of proteins.
posterior standard, two lateral wing
4. Glycoproteins and glycoplipids : they form
petals, two anterior keel petals
specific antigens or function as surface
(fused). Mulaithi is medicinal plant
receptors which are unique to different
of the same family.
cells. Hence, aide in cell recognition / cell
(2) Describes the petals and identification.
androecium of flowers of family 21. 3) They help in dissolving egg membrane
Solanaceae. The representation as during fertilization
well as the example given are
Explanation :
wrong. Gloriosa belongs to family- Chapter: 8
Liliaceae. Lysosomes are single membrane bounded cell
organelles which contain hydrolytic enzymes
4 Test ID : 532
best functioning in acidic pH. They exhibit 25. 4) a, b, c, d, e
substrate specificity and functions Explanation :
extracellularly as well as intracellularly. They Chapter: 8
are involved in various cell processes like Cell being thick and rigid
apoptosis, cell signaling, secretion, plasma a) gives a definite shape to the cell.
membrane repairs. b) provides protection to the cell
22. 3) Oxidation of organic substrates in TCA c) helps in cell to cell interaction through
cycle plasmodesmata.
Explanation : d) does not allow the passage of large
Chapter: 8 molecules
Mitochondria has F1 particles which are e) helps in imbibition of water due to
components of ETS present in the inner presence of colloidal substances –
mitochondrial membrane. The reduced co- Cellulose, hemicellulose.
enzymes (FADH2, NADH2) are formed by 26. 2) mesosome
oxidation of organic substrates during Kreb’s Explanation :
cycle occurring in mitochondrial matrix. 34 Chapter: 8
The special membraneous structure which is
ATPs are generated from one molecule of
formed by the extensions of plasma membrane
glucose in mitochondria.
into the cell is called mesosome. They are in
23. 2) Polysome the form of vesicles, tubules and lamellae
Explanation : which help in cell wall formation, DNA
Chapter: 8 replication, helps in respiration, secretion
Inclusion bodies are reserved materials in processes and increases the surface area of
prokaryotes that are stored in the cytoplasm. plasma membrane and enzyme content.
The lie free in the cytoplasm as they are not 27. 4) A and D only
bounded by any membrane system. Explanation :
Eg: 1, 3, 4 options Chapter: 8
Polysome is a chain of several ribosomes 1. Polysomes – Polyribsomes are present in
attached to a single mRNA. These ribosomes cytoplasm
translate the mRNA code into proteins. 2. Chloroplast – absent in animal cell.
24. 3. Mitochondria – Present in animal cell but
of 70 S type.
3)
amoeboid movement 4. At surface of ER – 80S type on ER forms
rough ER.
Explanation : 5. Inner nuclear membrane – no ribosome
Chapter: 8 present
RBCs are round, disc shaped biconcave cells 28. 2) Golgi body
in (human body). Explanation :
Amoeboid shape is exhibited by WBCs. Chapter: 2
A large number of proteins synthesized by
ribosomes on the endoplasmic reticulum are
packed and transported to cisternae of Golgi
5 Test ID : 532
bodies for modification before they are 34. 3) Systems of classification
released for functioning. Golgi apparatus is the Chapter: Biological classification
important site of formation of glycosylation of 35. 3) Monera
lipids and proteins (glycoproteins and glyco Explanation :
lipids). Chapter: Biological classification
29. 2) They help in replication of nucleoid Protista and Plantae have photo autotrophs.
Explanation : 36. 2) Monera, Fungi, Plantae
Chapter: 8 Chapter: Biological classification
The nucleoid (circular DNA) replicates 37. 2) Acetobacter
because of its own origin of replication. Explanation :
Plasmids are extra chromosomal molecules of Chapter: Biological classification
circular DNA, which are autonomously * Mycoplasma is pleomorphic but do not
replicating mini chromosomes having their possess cell wall.
own ori. Streptomyces is not pleomorphic.
30. 2) II and IV 38. 3) Most of the chrysophytes are
photosynthetic
Explanation :
Explanation :
Chapter: The Living world
Chapter: Biological classification
* II. Reproduction is not a defining property
* 1) Histones are present in all eukaryotes –
of all living organisms. Ex: Infertile humun
Dinoflagellates do not have histones
couple
2) Euglinoids exhibit a protein rich cell wall
* IV. Callus formation in invitro culture is
– cell wall is absent.
consider as growth / reproduction
4) all bacterial cells are aerobic - anaerobic
31. 1) Growth bacteria like clostridium also present.
Explanation : 39. 1) Three
Chapter: The Living world Explanation :
* Metabolism- observed only in living, Chapter: Biological classification
Reproduction – observed in living, Alternaria, Trichoderma, Colletotrichum
Irritability-living character only. 40. 4) I, II, III & IV
32. 2) Diptera Explanation :
Explanation : Chapter: Plant kingdom
Chapter: The Living world I) Primitive embryophytes - bryophyte
* a) Hominidae, c) Anacardiaceae, d) Poaceae II) Primitive tracheophytes - Pteridophytes
–are families. III) Advanced archegoniates- Gymnosperms
33. 3) Manuals provide information of habitat and IV) Advanced embryophytes- Angiosperms
distribution of plants of a given area. 41. 1) iii ii i iv
Explanation : Chapter: Plant kingdom
Chapter: The Living world 42. 4) Both 1 and 2
* Manuals – provide identification of names Chapter: Plant kingdom
of species found in an area. Bryophytes
6 Test ID : 532
43. 4) All the above 48. 4) Meristematic activity
Explanation : Chapter: Anatomy of flowering plants
Chapter: Plant kingdom 49. 2) adaxial epidermis of grass leaf
1) Algae & Bryophytes Explanation :
2) Bryophytes & Pteridophytes Chapter: Anatomy of flowering plants
3) Gymnosperms & Angiosperms * adaxial means, upper epidermis. In stems,
44. 4) photoautotroph roots and dicot leaves, bulliform cells are
absent.
Explanation :
R
Chapter: Plant kingdom 50. 4) |
−
Because, gametophyte is independent and H 2 N − CH − COO
photosynthetic Explanation :
45. 2) Functions of companion cells are controlled Chapter: Biomolecules
by nucleus of sieve tubes * Aminoacid is in the zwitter ion form in
Explanation : solution with pH 7.
Chapter: Anatomy of flowering plants * pH of the solution is 9 means it is basic
Functions of sieve tube elements are solution.
controlled by the nucleus of companion cells * Basic solution contains more OH- ions. OH-
ions react with hydrogen of NH3+ group of
46. 2) different types of cells that perform single
amino acid.
function.
* As a result, NH3 group becomes NH2.
Explanation : OH- ion cannot react with COO-.
Chapter: Anatomy of flowering plants
Therefore ans is 4.
* Complexes tissues are Xylem and Phloem.
51. 4) Paper chromatography
They consist of many components. For
Explanation :
instance, xylem has tracheids, vessels,
Chapter: Biomolecules
Parenchyma and fibres. All these elements * Agarose gel electrophoresis is used for
are involved in conduction of water. Like separation of nucleic acids.
xylem, phloem also has sieve tube elements, * Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is used
companion cells, parenchyma and fibres. for sepation of proteins.
These all components work together for * Spectrophotometer is used for qualitative
food conduction in plants. and quantitative analysis of proteins, nucleic
47. 1) roots of all vascular plants acids etc.
Explanation : * Paper chromatography is used for separation
Chapter: Anatomy of flowering plants of amino acids.
* Exarch and endarch xylem is mainly based Therefore answer is 4.
52. 3) 1
on the position of protoxylem.
* Exarch xylem- protoxylem lies towards Explanation :
outside of the root. Whereas Metaxylem Chapter: Biomolecules
* The given structure is diglyceride. As a
towards inside (Centrifugal protoxylem). In
result, it can esterify with only one fatty
stems it is endarch (centripetal xylem).
acid.
7 Test ID : 532
53. 4) Protein 59. 1) inner
Explanation : Chapter: The unit of life
Chapter: Biomolecules * Direct NCERT book line.
* Acid insoluble pool contains proteins, 60. 3) A, C, D, E only correct
lipids, nucleic acids and carbohydrates Explanation :
(macromolecules). Chapter: The unit of life
* When separation technique is used, proteins * A – Both are involved in ATP synthesis -
will be separated.
correct
* Therefore answer is proteins but not
* B - Only chloroplast synthesizes glucose but
micromolecules such as glucose, amino acid
not mitochondria - wrong
and nucleotide.
* C – Both involve in metabolism – Correct
54. 2) A, B, C and F
* D – Both contain dsDNA – Correct
Explanation :
* E – Both do not have 80S ribosomes –
Chapter: Biomolecules
Correct
* Nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. They
* F – Mitochondria involve in oxidative
consist of nucleotides.Nucleotides are
composed of nitrogen base (mono or phosphorylation but not chloroplast -
bicyclic heterocyclic aromatic rings), Wrong.
pentose (ribose or deoxyribose) sugar, 61. 4) IV III I II
phosphate. Glutamic acid and glucose are Chapter: The unit of life
not components of nucleic acids. Single membrane bound
55. 2) sequence of amino acids. Endomembrane
cell organelles – ER, GA,
Explanation : system
Lysosome, Vacuole
Chapter: Biomolecules
Active transport –
*Intercellular ground substance is collagen. It Vacuole
Tonoplast
contains a sequence of amino acids.
56. 3) Statement I is incorrect and statement II is Primary cell
Meristematic cell
correct wall
Chapter: Biomolecules Amembranous
Direct NCERT book statements 80S ribosomes
cell organelle
57. 2) 0.1 – 0.3 µm 62. 1) A and B
Explanation : Explanation :
Chapter: The unit of life
Chapter: The unit of life
* Smallest living organisms are mycoplasmas.
* Acrocentric, metacenric chromosomes have
Their size is ranging from 0.1 to 0.3
1 centromere and 2 kinetochores.
micrometers.
* Acrocentric chromosome has 1 very large
58. 3) Mesosomes
arm and 1 very short arm whereas
Explanation :
metacentric chromosome has 2 equal arms.
Chapter: The unit of life
* Therefore length of arms and number of
* In prokaryotes, DNA replication and
genes are not same.
secretion occur with the help of mesosomes.
8 Test ID : 532
63. 3) Mo, Mg, Fe 70. 4) T.W. Engelmann –The first absorption
Chapter: Mineral Nutrition spectrum was constructed.
* Direct NCERT book concepts. Explanation :
64. 1) Ca, > 10 mM Chapter: Photosynthesis in higher plants
* Engelmann constructed first action spectrum
Chapter: Mineral Nutrition
of photosynthesis.
* Deficiency symptoms of immobile elements
71. 3) Single molecule of chlorophyll a
first appear in young leaves. Ex : Ca, it is a
Explanation :
macro nutrient. ∴ its concentration is more
Chapter: Photosynthesis in higher plants
than 10 mM/ kg of dry matter. * The single molecule of chlorophyll a, forms
65. 4) Mg the reaction centre.
Chapter: Mineral Nutrition 72. 4) beyond 680 nm, ATP
* Direct NCERT book concepts. Explanation :
66. 2) S, K, Mo, N Chapter: Photosynthesis in higher plants
Chapter: Mineral nutrition * Cyclic flow of electrons in light reaction
* Direct NCERT book concepts. occurs beyond 680 nm wavelength of light
67. 3) produce nodules on the roots of legume, for synthesis of ATP.
73. 3) 2 : 2
non legume plants respectively
Explanation :
Chapter: Mineral nutrition
Chapter: Photosynthesis in higher plants
* Direct NCERT book concepts.
* During reduction step of Calvin cycle, for
68. 4) 80 ATP, 5 N2 each CO2 two ATP and two NADPH are
Explanation : required.
Chapter: Mineral nutrition 74. 3) C4 plants and C3 plants
* Formation of one NH3 requires 8 ATP and 1 Explanation :
N atom. Chapter: Photosynthesis in higher plants
Therefore, 10 NH3 require * Phosphoenolpyruvate and RUBP are
10 x 8 ATP = 80 ATP primary CO2 acceptor in C4 plants and C3
10 x1N = 5 N2. plants respectively.
69. 3) 28 S rRNA 75. 3) > 450 µlL-1
Explanation :
Explanation :
Chapter: Photosynthesis in higher plants
Chapter: The unit of life
* CO2 saturation point for C3 plants is at
* Centrioles are present in eukaryotic animal
about 450 µlL-1 and C4 plants is at about 360
cells.
µlL-1.
* In eukaryotic cell, larger sub-unit of
76. 4) the formation of OAA by the carboxylation
ribosome contains 28S rRNA, 5S rRNA,
of PEP in mesophyll cells.
5.8S rRNA.
Explanation :
* Among these, 28S rRNA acts as catalyst Chapter: Photosynthesis in higher plants
and commonly called ribozyme. * The first step of CO2 fixation in C4 pathway
* 18S rRNA, 16S rRNA, 5S rRNA are not occurs in mesophyll cells and forms OAA
acting as catalysts. by the carboxylation of PEP.
9 Test ID : 532
77. 4) Three 84. 4) A – 1, B – 4, C – 2, D – 3
Explanation : Chapter: Respiration in plants
Chapter: Photosynthesis in higher plants 85. 1) Acetaldehyde to Ethanol
* Ethylene is a plant growth regulator, it does Explanation :
not involve in production of new leaves and Chapter: Respiration in plants
chloroplast and xylem differentiation. * In alcoholic ferementation by yeast cells
78. 1) Promotion of flowering in pineapple – utilize NADH2, which is produced during
Auxin and Ethylene glycolysis to reduce acetaldehyde to ethanol
Explanation : 86. 2) 2NADH + H+ + 2ATP + 2 pyruvic acid
Chapter: Plant growth and development Explanation :
* Promotion of flowering in pineapple by Chapter: Respiration in plants
Auxin and Ethylene is synergistic function. * The net gain of Glycolysis from 1 molecule
79. 2) Wheat of glucose is 2NADH + H+ + 2ATP + 2
Explanation : Pyruvic acid molecules.
Chapter: Plant growth and development 87. 2) Oxalosuccinic acid
* Wheat is an annual plant and influenced by Explanation :
vernalization. Chapter: Respiration in plants
80. 3) bolting in plants * In Kreb’s cycle, final 6C tricarboxylic acid
Explanation : is Oxalosuccinic acid.
Chapter: Plant growth and development 88. 3) cyt – a3
* In most of the situations ABA act
Explanation :
antagonistic to GA (Bolting in plants is
Chapter: Respiration in plants
under control of GA)
* In ETS molecular oxygen receives electrons
81. 1) Both statement I and statement II are
from copper centre present in cyt-a3
correct
89. 4) Proteins and fats
Explanation :
Explanation :
Chapter: Plant growth and development
Chapter: Respiration in plants
82. 1) One daughter cell remain meristematic,
* RQ values of proteins is 0.9 and Fats (tri
other differentiates and matures
palmitin) is 0.7.
Explanation :
90. 3) interphase
Chapter: Plant growth and development
* Arithmetic growth curve is linear because Explanation :
out of two daughter cells formed one retain Chapter: Cell cycle and cell division
meristematic activity, the other differentiate * During cell cycle, more than 95% of time is
and mature. lost for interphase
83. 2) CO2, H2O as end products and heat as 91. 1) G1 phase
major form of energy. Explanation :
Explanation : Chapter: Cell cycle and cell division
Chapter: Respiration in plants * In interphase two growth periods are
* Complete combustion of glucose yield CO2, present such as growth period 1 (G1) and
H2O and yield heat as major form of energy. growth period 2 (G2). G1 occurs prior to S
phase
10 Test ID : 532
92. 2) Centriole 99. 4) thistle funnel, semi permeable membrane
Explanation : and beaker
Chapter: Cell cycle and cell division Explanation :
NCERT lines from Pg.No.163 Chapter: Transport in plants
93. 4) Microtubules are key players only in * Osmometer can be constructed by a thistle
chromosomal movement . funnel, egg membrane a semi permeable
Explanation : membrane and beaker
Chapter: Cell cycle and cell division 100. 1) osmotic pressure
* Microtubules not only play an important Explanation :
role in chromosomal moment but also in cell Chapter: Transport in plants
plate formation, cell movement etc. * The pressure that has to be applied to a pure
94. 3) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I solvent to prevent it from passing into a
Chapter: Cell cycle and cell division given solution by osmosis is known as
95. 3) G2 phase osmotic pressure. Often used to express the
concentration of the solution
Explanation :
101. 1) Statement I is true and statement II is false
Chapter: Cell cycle and cell division
* Tubulin synthesis occurs prior to prophase Explanation :
i.e. G2 phase Chapter: Transport in plants
* Proteins that are completely embedded in
96. 4) late telophase
the membrane are called intrinsic protein
Explanation :
and they can act as porins
Chapter: Cell cycle and cell division
* Porins are absent in mitochondrial inner
* Event necessary for the transition from
membrane
mitosis to interphase is cytokinesis. This
102. 1) mutualism
process initiated in the late telophase
Explanation :
97. 2) pachytene
Chapter: Transport in plants
Explanation :
* Significant associations between roots of
Chapter: Cell cycle and cell division
plants and a wide variety of soil fungi are
* Mutual exchange of hereditary material
called as mycorrhiza, in which both the
between homologous chromosomes occur
partners are benefited so it is mutualism
through crossing over. It takes place in
103. 1) c, a, d, b
pachytene
Explanation :
98. 1) unpairing of homologous chromosomes
Chapter: Microbes in human welfare
Explanation : * Antibiotics are most important therapeutics
Chapter: Cell cycle and cell division in human society. Biogas commonly used as
* Desynapsis is the process of separation of fuel in rural India. Citric acid used as
paired homologous chromosomes. It begins flavoring agent in food industry. Curd is
in diplotene common fermented food.
11 Test ID : 532
104. 1) Oscillatoria 109. 4) Blood cholesterol lowering agent is
Explanation : produced by an unicellular eukaryote
Chapter: Microbes in human welfare Explanation :
* Oscillatoria is a BGA. It can perform Chapter: Microbes in human welfare
photosynthesis as well as N2 fixation. * Toddy is a traditional drink and is made by
105. 4)
Trichoderma Bacterial biocontrol agent of fermenting the phloem sap from palms
several plant pathogens * Cryopreservation used to store germplasm
not to store fermented fish.
Explanation :
Chapter: Microbes in human welfare * Distillation is the process used to remove
excess of water. Filtration is the process
* Trichoderma is free living soil fungi. It
used to the remove yeast debris from
control several root born diseases.
fermented broth.
106. 1)Roquefort cheese is ripened by using
* Blood cholesterol lowering agent is
Propionibacterium
produced by Monascus
Explanation :
110. 4) oxygen consumed by microbes
Chapter: Microbes in human welfare
Chapter: Microbes in human welfare
* Roquefort cheese ripend by Penicillium
* Direct NCERT Book
Roquefort.
111. 1) mitosis
107. 3) A – IV, B – III, C- II, D - I
Explanation :
Explanation : Chapter: Sexual reproduction in flowering
Chapter: Microbes in human welfare plants
* Yeast – End product of alcoholic NCERT XII – Pg.No (21 and 22)
fermentation i.e. ethyl alcohol inhibits the microsporogenesis – Moderate
yeast metabolism by exhibiting feedback * Microspores are haploid cells they produce
inhibition, when its concentration exceeds mature make gametophyte or pollengrain
13%. by two successive mitosis.
* Statin – It hibits the HMG CoA reductase 112. 3) dehiscence
activity by exhibiting competitive inhibition Explanation :
against mevalonic acid. Chapter: Sexual reproduction in flowering
* Cyclosporin A – Trichoderma – plants
Deuteromycetes * Cell of endothecium have fibrous
thickening of cellwall , which is unevenly
* clot buster – Streptococus – Bacteria.
distributed. It become hygroscopic in nature
108. 2) Statement I is false and statement II is true
and helps in dehiscence of anther.
Explanation : 113. 3) Pollengrain, Embryo sac
Chapter: Microbes in human welfare
Explanation :
* Ampicillin is a semi-synthetic broad spectrum
Chapter: Sexual reproduction n flowering
antibiotic. plants
* LAB play an important role in checking the * Except pollen grain and Embryosac which
disease causing microbes in stomach are gametophyte (Haploid) remaining all are
Diploid (Sporophytic bodies)
12 Test ID : 532
114. 3) It does not require pollinators 118. 4) Both (2) and (3)
Explanation : Explanation :
Chapter: Sexual reproduction in flowering Chapter: Sexual reproduction in flowering
plants plants
* Cleistogamous flowers are always closed, * Seed are not required for vegetative
invariably autogamous hence they do not reproduction
require pollinators. Since it is autogamy * Fertilization is not required for both
genetic variations are not possible vegetative reproduction and Apomixis
115. 2) 16, 8, 8, 8, 16 * Both process produce clones
Explanation : 119. 1) A, B
Chapter: Sexual reproduction in flowering Explanation :
plants Chapter: Sexual reproduction in flowering
* Root apical meristem is diploid ovary is plants
diploid – 16 * Direct lines from NCERT Pg.No. 32, 33
* Embryosac is haploid gametophyte – 8 120. 1) Formation of male gametes
* Generative cell haploid – 8 Explanation :
* Polar nuclei haploid – 8 (Two haploid Chapter: Sexual reproduction in flowering
nuclei) plants
* remaining of nucellus perisperm diploid - * Formation of two male gametes from
16 generative cell is a equational division.
116. 2) I, III, IV, V * Generative and vegetative cell formation is
Explanation : unequal division
Chapter: Sexual reproduction in flowering * Zygote produce one base cell one
plants suspended cell by unequal division.
* Zastera : release pollengrains in water 121. 2) Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophyte
(Epihydrophily) Explanation :
* Maize : Pollinated by wind (Anemophily) Chapter: Sexual reproduction in flowering
* Vallisneria : release pollengrains on surface plants
of water hence (epihydrophily) * Lower plants group such as algae,
* Rice is a grass it pollinated by wind Bryophytes and Pteridophytes male gametes
(Anemophily) transported by water.
* Yucca: Pollinated by moth (entamophely) 122. 1) fertilization
117. 1)synchronized pollen release and stigma Explanation :
receptivity. Chapter: Sexual reproduction in flowering
Explanation : plants
Chapter: Sexual reproduction in flowering * Edible part of groundnut is cotyledons
plants coming from embryo. Embryo is a product
* Unsynchronised pollen release and stigma of fertilization.
receptivities promote cross pollination.
13 Test ID : 532
123. 4)
restriction fragments length polymorphism 128. 3) activation of amino acid
(RFLP) Explanation :
Explanation : Chapter: Molecular Biology
Chapter: Molecular Biology * In the first phase of translation, Amino
* DNA of an individual carries specific acids are activated by using ATP in the
presence of Aminoacyl synthetase enzyme.
sequences of nucleotides which are repeated
Activated amino acids later transferred to
many times throughout the length of DNA.
concern
This reveals polymorphism in DNA. These
t-RNA.
are inherited. Each individual inherits these
129. 1) repressor
repeats from his/her parents which are used
Explanation :
as genetic markers in personal identity test.
Chapter: Molecular Biology
124. 1) the DNA is complexed with histones
* The regulation gene product is regulation
Explanation : protein, that can act both positively
Chapter: Molecular Biology (Activators) and negatively (repressor)
* DNA is complexed with histones in 130. 4)
A codon in mRNA is read in a non -
eukaryotes. contiguous manner
125. 4) (ii) and (iv) are correct Explanation :
Explanation : Chapter: Molecular Biology
* The genetic code consists of 64 triplets of
Chapter: Molecular Biology
nucleotides. These triplets are called codons.
* mRNA provides the template for synthesis
With three exceptions, each codon encodes
of proteins. A segment of DNA coding for
for one of the 20 amino acids used in the
polypeptide is called exon. synthesis of proteins that produces some
126. 4)DNA fingerprinting involves identifying redundancy in the code. Most of the amino
similarities in repetitive DNA. acids are encoded by more than one codon.
Explanation : The genetic code can be expressed as either
Chapter: Molecular Biology RNA codons or DNA codons.
* DNA fingerprinting involves identifying 131. 3) Frame shift mutation
differences in repetitive DNA. Since the DNA Explanation :
from every tissue of an individual show the Chapter: Molecular Biology
same degree of polymorphism, they become * Frame shift mutation is a type of gene
mutation where the reading of codons is
very useful identification tool in forensic
changed due to insertion or deletion of
application.
nucleotide due to which amino acids
127. 1) protein sequence of the protein change and become
Explanation : non functional.
Chapter: Molecular Biology 132. 2) 5′ capping
* Exons are the coding part of mRNA. Chapter: Molecular Biology
14 Test ID : 532
133. 4)
It is correlated with the complexity and 138. 3) mutation breeding
habit of plants Chapter: Strategies for enhancement in
Explanation : food production
Chapter: Reproduction in organisms * NCERT
* Life spans of organisms are not necessarily 139. 3) high aspartic acid and low nitrogen content
correlated with their sizes. Chapter: Strategies for enhancement in
* Death of every individual organisms is a food production
certainly. i.e., no individual is immortal, NCERT
except single called organisms. 140. 4) Chilli Pusa sadabahar leaf curl
134. 2)Is used for building up resources for next Chapter: Strategies for enhancement in
flowering food production
Explanation : NCERT
Chapter: Reproduction in organisms 141. 1) 2
* In polycarpic plants, the period between Explanation :
two consecutive flowering phases is called Chapter: Molecular basis of inheritance
inter flowering period. It is not the Juvenile * In a dinucleotide, 1 phosphodiester bond
phase but is a part of the mature phase and is (or) 2 phosphoester bonds are formed
also called recovery phase. between 2 nucleotides.
142. 3) 10
* During which the plant prepares itself for
Explanation :
next flowering structurally and
Chapter: Molecular basis of inheritance
physiologically.
34Ao ds DNA has 20 nucleotides. Each strand
135. 1)
Embryo = 1260, Prothallus = 630,
has 10 nucleotides. If one strand is labelled
Oosphere = 630
with 32P , all the 10 nucleotides is this strand
Explanation : are with 32P.
Chapter: Reproduction in organisms This DNA is allowed to undergo replication in
* Ophioglossum chromosome number in 15
N medium for three generations.
embryo 2n = 1260 After three generations 8 ds DNA molecules
Prothallus n = 630 are formed. The total strands are 16 out of
Oosphere n (egg cell) = 630 which only one strand is with 32P (10
136. 4) More than one option is correct nucleotides) and the remaining 15 strands are
Explanation : with 15N.
Chapter: Reproduction in organisms A+G
143. 1)
* Penicillium has branched conidiophores, T+C
produce exogenous asexual spores Explanation :
(mitospores) in basipetal manner called Chapter: Molecular basis of inheritance
conidia * According to Chargaff’s rule purines are
137. 2) Tissue culture and somatic hybridization equal to pyrimidines and hence A + G are
Chapter: Strategies for enhancement in purines and T + C are pyrimidines.
food production A+G
=1
NCERT T+C
15 Test ID : 532
144. 2) Remove 3′ OH group in deoxyribose 150. 2) 90
Explanation : Explanation :
Chapter: Molecular basis of inheritance Chapter: Molecular basis of inheritance
* To continue the synthesis of new strand * 10.2 nm dsDNA has 3 coils.
3 OH group is essential. When you remove * 3 coils of DNA has 60 nucleotides
this group, the synthesis of DNA strand is
* out of 60 nucleotides, 30 nucleotides are
inhibited.
purines and 30 are pyrimidines.
145. 3) 1.33
* Each purine has 2 – C – N rings and hence
Explanation :
30 x 2 = 60 C – N rings.
Chapter: Molecular basis of inheritance
* In one of the strand of DNA ratio * Each pyrimidine has 1 C – N ring and hence
i.e 5 → 3′ is 0.75 30 x 1 = 30.
3 * Total number of dicyclic and heterocyclic
0.75 = . rings (C – N rings) are 60 + 30 = 90
4
* In the opposite complementary strand 151. 1) Watson
4 Chapter: Principles of Inheritance and
3′ → 5′ is = 1.33
3 Variation
146. 4) 2 and 3 152. 2) recessive
Explanation : Chapter: Principles of Inheritance and
Chapter: Molecular basis of inheritance Variation
* Deoxy ribonucleoside triphosphates are 153. 3) A and B
playing double role during the synthesis of Explanation :
novel DNA strand. They provide energy and Chapter: Principles of Inheritance and
also play role in providing nucleotides for Variation
the synthesis of new strand.
* ¼ : ½ : ¼ or 1:2:1 represents the genotypic
* RNA primer is essential for the initiation of ratio of monohybrid cross. This ratio is
new strand of DNA. It is made of
similar to the genotypic ratio ( 1:2:1) of
ribonucleoside triphosphates. Therefore,
incomplete dominance and co-dominance.
both 2 and 3 options are correct.
154. 1) Statement I and II are correct
147. 1) A – IV, B – II, C – I, D – III, E - V
Chapter: Molecular basis of inheritance Chapter: Principles of Inheritance and
148. 4) 3 Variation
155. 2) Law of dominance
Explanation :
Chapter: Molecular basis of inheritance Chapter: Principles of Inheritance and
* a, b and e are correct and hence 3 Variation
statements are correct 156. 4) 12.5 %
149. 3) 4 Explanation :
Explanation : Chapter: Principles of Inheritance and
Chapter: Molecular basis of inheritance Variation
* QB bacteriophage has RNA and it has 4 * Percentage of gametes formed = 2n
types of nucleotides. n= 3 hybrids
16 Test ID : 532
2 x 2 x 2 = 8 gametes are formed. 161. 3) i and iv
ABC ABc Explanation :
Abc Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications
AbC * Agrochemicals are too expensive for the
aBC farmer in developing world and got success
abC in tripling of food production and supply.
aBc
162. 3) enhanced nutritional value
abc
Percentage of dominant alleles (gametes) Explanation :
– ABC Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications
* Vitamin–A enriched rice is developed to
1
x 100 = 12.5% enhance nutritional values.
8
157. 3) 1:1:1:1 163. 4) > 8 of the gut
Explanation : Explanation :
Chapter: Principles of Inheritance and Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications
Variation * Inactive toxin is converted in to an active
Ttrr x Rrtt form of toxin due to alkaline pH of the gut,
Rt rt which solubilize the crystals.
Tr 1TtRr 1Ttrr 164. 4) 3
tr 1ttRr 1ttrr Explanation :
1TtRr (tall, red) : 1Ttrr (tall, green): 1ttRr
Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications
(dwarf, red) : 1ttrr (dwarf, green)
* Pro-Insulin has a polypeptide chain with
9 1 three segments in it A - Peptide, B - peptide
158. 1) :
16 16 and C - peptide. On maturation, C- peptide
Explanation : get separated and A, B peptides combined
Chapter: Principles of Inheritance and by creating disulphide bridges.
Variation
165. 2)
Recombinant therapeutics induce unwanted
The phenotypic ratio of F2 generation
immunological responses.
dihybrid cross is
9//16: 3/16 : 3/16 : 1//16 or Explanation :
9 (dominant parent characters): Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications
3 (recombinants) : * Recombinant therapeutics do not induce
3 (recombinants): unwanted immunological responses.
1 (recessive parent characters) 166. 4) A – IV, B – III, C – I, D – II
Therefore answer is 9/16:1/16 Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications
159. 3) AB and ab 167. 3) US patent and Trademark office
Chapter: Principles of Inheritance and Explanation :
Variation Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications
160. 3) Pairing of chromosomes would not lead to * An American company got patent rights on
the segregation of factors they carried. Basmati rice through US patent and Trade
Chapter: Principles of Inheritance and mark office.
Variation
17 Test ID : 532
168. 2) A – II, B – V, C – I, D – IV * Then it should be converted into permeable
Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications by treating with calcium chloride followed
169. 3) Statement I is correct and statement II is by heat and cold shocks. Then the pores in
incorrect bacterial cell wall become more wider and
Explanation : Penetrates foreign DNA into host.
Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications 174. 3) Endonucleases
* Genetic modifications have been used to Explanation :
create tailor – made plants as resources to Chapter: Biotechnology principles and
industries in the form of starches, fuels and process.
pharmaceuticals. * Generally most of the restriction enzymes
* RNA interference takes place in all or endonucleases form sticky ends. These
eukaryotes as a method of cellular defense. are essential for rDNA technology and can
170. 3) Introduction of ADA by introducing into be ligated easily by ligase.
cells at early embryonic stages. 175. 2) air bubbles obstruct the actual flow of
Explanation : digested DNA fragments
Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications Chapter: Biotechnology principles and
* Adenosine deaminase deficiency can be process.
cured permanently by introducing ADA in 176. 1) 1972
to cells at early embryonic stages. Chapter: Biotechnology principles and
171. 3) I and II process.
Explanation : 177. 2) 1 : 1
Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications Explanation :
* The Indian parliament has recently cleared Chapter: Biotechnology principles and
the second amendment of the Indian patents process.
bill, that take issues including patent terms * The recognition sequence of EcoRI is
emergency provisions and research and GAATTC in 5′ to 3′ direction and it will be
development initiatives. same in opposite direction. In this sequence
172. 4) All of the above 6 purines and 6 pyrimidines are present.
Explanation : 178. 1) 120 kDa
Chapter: Biotechnology and its applications Explanation :
* The Indian government has set up Chapter: Biotechnology principles and
organizations such as GEAC, which will process.
make decisions regarding the validity of GM * Smaller DNA fragments move fastly than
research and safety of introducing GMO for larger molecules.
public services. 179. 4) Ethidium bromide
173. 3) Calcium Chapter: Biotechnology principles and
Explanation : process.
Chapter: Biotechnology principles and 180. 2) Proteins involved in the replication of
process. plasmid
* it is a bivalent cation. The host bacterium is Chapter: Biotechnology principles and
impermeable to receive foreign DNA. process.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Unit-VI: Reproduction in Plants Chapter-1. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants Book Back AnswersDocumento61 pagineUnit-VI: Reproduction in Plants Chapter-1. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants Book Back Answersgokul ganesh DNessuna valutazione finora
- NEET Bot em 1 Mark QADocumento7 pagineNEET Bot em 1 Mark QAbala44014Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Test:: Long TermDocumento17 pagineRevision Test:: Long Termsachin sakuNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Bio - Bot em 2022Documento101 pagine12 Bio - Bot em 2022Abdulkalam AbdulkalamNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Biology All Chapters Important Questions PDFDocumento38 pagineCBSE Class 12 Biology All Chapters Important Questions PDFReuben Thomas100% (1)
- Class 11 Biology Botany em Revised Edition-2020 English Medium Book Back Answers C.kishore KumarDocumento51 pagineClass 11 Biology Botany em Revised Edition-2020 English Medium Book Back Answers C.kishore KumarRagaviNessuna valutazione finora
- NEET 2020 Exam (Covid Re-Exam)Documento23 pagineNEET 2020 Exam (Covid Re-Exam)lilyNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th STD Bio-Botany EM Book Back AnswersDocumento61 pagine12th STD Bio-Botany EM Book Back AnswersNaveen 18Nessuna valutazione finora
- 12th Bio-Botany English Medium Study MaterialDocumento105 pagine12th Bio-Botany English Medium Study MaterialNithiya LakshmiNessuna valutazione finora
- 11th STD BIO-BOTANY Revised English Medium Book Back AnsDocumento51 pagine11th STD BIO-BOTANY Revised English Medium Book Back AnsDeepsha online100% (1)
- Biology Structured AnswersDocumento11 pagineBiology Structured AnswersNelum FernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Wa0005.Documento14 pagineWa0005.nikhilkumar6377311Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-VI: Reproduction in Plants Chapter-1. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants Book Back AnswersDocumento70 pagineUnit-VI: Reproduction in Plants Chapter-1. Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Plants Book Back AnswersTwelegyNessuna valutazione finora
- Namma Kalvi 11th Bio-Botany Study Material English Medium 219431Documento51 pagineNamma Kalvi 11th Bio-Botany Study Material English Medium 219431Prasanth PrasanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Test of Neet 2024Documento24 pagineFull Test of Neet 2024bhavyakhandelwal2302Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test 12 (Class 11) - Type Bio SCANDocumento6 pagineTest 12 (Class 11) - Type Bio SCANSaurav sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Entrance Questions N AnswersDocumento5 pagine2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Entrance Questions N AnswersStreet Dancer9.2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Credits For Neatness and To The Point Answer Will Be ThereDocumento3 pagineExtra Credits For Neatness and To The Point Answer Will Be There10 Harsheeta RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- High Yielding Test Series - Full Test 3: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Documento23 pagineHigh Yielding Test Series - Full Test 3: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Sumukh SG20BCA086Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fungi QuestionsDocumento2 pagineFungi QuestionsAnanda Mutiara AlhakimahNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th STD Bio Botany em Book Back Answers PDFDocumento7 pagine12th STD Bio Botany em Book Back Answers PDFYouth InternetNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th STD Bio Botany em Book Back Answers PDFDocumento7 pagine12th STD Bio Botany em Book Back Answers PDFChinnasamy DurairajNessuna valutazione finora
- Key 2544424 2023-10-1520043A093A31202B0000 PDFDocumento24 pagineKey 2544424 2023-10-1520043A093A31202B0000 PDFrohit19loharNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Worksheet PracticeDocumento4 paginePlant Worksheet PracticesenjicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Xi - Biology - Work Sheet - Competency Based QNSDocumento9 pagineXi - Biology - Work Sheet - Competency Based QNSSudhansu SahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology AssignmentsDocumento4 pagineBiology AssignmentsPritamNessuna valutazione finora
- XI Botany Chapterwise Prvs Questions Hsslive PDFDocumento25 pagineXI Botany Chapterwise Prvs Questions Hsslive PDFJoshua VargheseNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Form 3Documento51 pagineBiology Form 3Mambo SawaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9th New Test DiversityDocumento4 pagine9th New Test DiversityBalmukund KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Namma Kalvi 12th Bio-Botany Chapter 1 To 5 Loyola Ec Guide emDocumento140 pagineNamma Kalvi 12th Bio-Botany Chapter 1 To 5 Loyola Ec Guide em22L149 - SUBASH KARTHICK VNessuna valutazione finora
- GSB Textback ch.7. Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition DR - Phemie FinalDocumento5 pagineGSB Textback ch.7. Plant Growth and Mineral Nutrition DR - Phemie Finalpranavjain558Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wa0003.Documento16 pagineWa0003.nikhilkumar6377311Nessuna valutazione finora
- Origins of Microsporidia: Patrick J. Keeling and Geoff I. McfaddenDocumento5 pagineOrigins of Microsporidia: Patrick J. Keeling and Geoff I. Mcfaddenthamizh555Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 11 Biology NCERT Textbook Chapter 2 Biological ClassificationDocumento5 pagineClass 11 Biology NCERT Textbook Chapter 2 Biological ClassificationTitan 2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nurture Ph-I & Ii - Subjective Test-10-Biology Solutions 17-12-2023Documento11 pagineNurture Ph-I & Ii - Subjective Test-10-Biology Solutions 17-12-2023Subhajit MandalNessuna valutazione finora
- G7 L-1 Nutrition in Plants - Worksheet - 230520 - 115119Documento3 pagineG7 L-1 Nutrition in Plants - Worksheet - 230520 - 115119ohiobossNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento5 pagineSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsBobbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 3 EVOLUTION & DIVERSITY: Plants, Fungi & Animal EvolutionDocumento13 pagineWorksheet 3 EVOLUTION & DIVERSITY: Plants, Fungi & Animal EvolutionMarell Mae CabayaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Botany AssignmentDocumento8 pagineAnatomy of Flowering Plants - Botany Assignmentme vaisakNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2020 Set 3Documento5 pagineCBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2020 Set 3Rajendra Solanki100% (1)
- Soal SMA English VersionDocumento14 pagineSoal SMA English VersionNuni Rismayanti NurQalbiNessuna valutazione finora
- Test # 13 (NEETprep Test Series For NEET 2020)Documento28 pagineTest # 13 (NEETprep Test Series For NEET 2020)AXR AmstaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological ClassificationDocumento4 pagineBiological ClassificationssNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Neet 2014 PaperDocumento26 pagineModel Neet 2014 PaperselvakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ch.25,29,31 QuizDocumento7 paginech.25,29,31 QuizjeksilverstarNessuna valutazione finora
- Moasser All Tests On Unit Two 2nd TermDocumento17 pagineMoasser All Tests On Unit Two 2nd TermThe LEGENDNessuna valutazione finora
- Class-XII Biology (Theory) Design of The Question Paper: 1. Weightage of Contents / Subject Units Units Content MarkDocumento99 pagineClass-XII Biology (Theory) Design of The Question Paper: 1. Weightage of Contents / Subject Units Units Content MarkMahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Kingdom-Important QuestionsDocumento3 paginePlant Kingdom-Important QuestionsAnirudh KhannaNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 Plant Breeding and PropagationDocumento2 pagine14 Plant Breeding and PropagationqrqewNessuna valutazione finora
- 11th Biology Book Back Questions New BookDocumento27 pagine11th Biology Book Back Questions New BookNaveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 1Q Practice TestDocumento5 pagineScience 1Q Practice TestPinky LaysaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 DiversityDocumento13 pagine7 Diversitytara tuitionNessuna valutazione finora
- ReproductionDocumento30 pagineReproductionAnisha ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 38 Chapter Full Syllabus Test 05 April From MasterclassDocumento11 pagineBiology 38 Chapter Full Syllabus Test 05 April From MasterclassSaurav sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Living World - NCERT Based PYQsDocumento4 pagineThe Living World - NCERT Based PYQscrackneetmay2024Nessuna valutazione finora
- ClassificationDocumento27 pagineClassificationkaziba stephenNessuna valutazione finora
- Interactions Between Non-Pathogenic Soil Microorganisms And PlantsDa EverandInteractions Between Non-Pathogenic Soil Microorganisms And PlantsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecology of Root PathogensDa EverandEcology of Root PathogensS.V. KrupaNessuna valutazione finora
- Volume Test - Ii: Long Term ChemistryDocumento11 pagineVolume Test - Ii: Long Term Chemistrysachin sakuNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 14.03.14Documento61 pagineECE Final Upto 4th Year Syllabus 14.03.14booksNessuna valutazione finora
- LT & CC - Grand Test Schedule PDFDocumento1 paginaLT & CC - Grand Test Schedule PDFsachin sakuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncert Biology Chapter 9Documento20 pagineNcert Biology Chapter 9sai arunNessuna valutazione finora
- Year Test - Ii: (Batch - A)Documento11 pagineYear Test - Ii: (Batch - A)sachin sakuNessuna valutazione finora
- Year Test - Ii: (Batch - A)Documento11 pagineYear Test - Ii: (Batch - A)sachin sakuNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Year Test: STD: Crash Course (Batch - A) Marks: 400 Date: 29.04.2020 Physics Time: 3 HrsDocumento10 pagineSecond Year Test: STD: Crash Course (Batch - A) Marks: 400 Date: 29.04.2020 Physics Time: 3 Hrssachin sakuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pollen Grain: The Pollen Grains Represent The Male GametophytesDocumento6 paginePollen Grain: The Pollen Grains Represent The Male Gametophytessachin sakuNessuna valutazione finora
- Year Test - Ii: (Batch - A)Documento11 pagineYear Test - Ii: (Batch - A)sachin sakuNessuna valutazione finora
- 71st IPC BrochureDocumento28 pagine71st IPC Brochuresachin sakuNessuna valutazione finora
- Football Speed TrainingDocumento6 pagineFootball Speed TrainingTBM607Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kf22Qt Sec4 FRDDocumento21 pagineKf22Qt Sec4 FRDMauro PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Epoxy Plus Pipeline Repai Grout TG - MSDSDocumento5 pagineEpoxy Plus Pipeline Repai Grout TG - MSDSgrimaguilNessuna valutazione finora
- The Relationship Between Date of Birth and IndividDocumento13 pagineThe Relationship Between Date of Birth and IndividAnonymous ktNyZTNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 16 - Bleeding Tendency DiseasesDocumento64 pagineLecture 16 - Bleeding Tendency Diseasesapi-3703352100% (1)
- Introduction To LubricantsDocumento12 pagineIntroduction To Lubricantsrk_gummaluri5334Nessuna valutazione finora
- CoasteeringDocumento1 paginaCoasteeringIrishwavesNessuna valutazione finora
- 1109 KW 1,487 HP: Gross HorsepowerDocumento12 pagine1109 KW 1,487 HP: Gross HorsepowerDedek SukmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento6 pagineChapter 4Aung MyatNessuna valutazione finora
- Whisper 500 Spec SheetDocumento1 paginaWhisper 500 Spec Sheetfranco cuaylaNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEB Korba THERMAL POWER PLANT Mechanical Training ReportDocumento20 pagineCSEB Korba THERMAL POWER PLANT Mechanical Training Reporthaxxo24Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 26 12Documento9 pagine4 26 12stevenscreekNessuna valutazione finora
- SCOPE OF PRACTICE FOR TCAM PRACTITONERS - V - 01Documento22 pagineSCOPE OF PRACTICE FOR TCAM PRACTITONERS - V - 01shakkiryousufNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume PLPDocumento2 pagineResume PLPapi-302180779Nessuna valutazione finora
- VálvulasDocumento44 pagineVálvulasCarlos LópezNessuna valutazione finora
- Healthy and Unhealthy FoodDocumento16 pagineHealthy and Unhealthy FoodGeovanny ValladarezNessuna valutazione finora
- DolphinsDocumento1 paginaDolphinsDebra OkwuziNessuna valutazione finora
- Cleaning Disinfecting School ClassroomsDocumento2 pagineCleaning Disinfecting School ClassroomsFitz JaminitNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Different Immediate Dentin Sealing Techniques On The Microtensile Bond Strength PDFDocumento6 pagineEffect of Different Immediate Dentin Sealing Techniques On The Microtensile Bond Strength PDFclaudiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lean Six Sigma Green BeltDocumento7 pagineLean Six Sigma Green Beltmulpuru sai snehaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4a-Ancient Indian Engineering BotanyDocumento44 pagine4a-Ancient Indian Engineering BotanyAshok NeneNessuna valutazione finora
- wk8 Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Immune Disorders Part 2Documento32 paginewk8 Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Immune Disorders Part 2claire yowsNessuna valutazione finora
- DR - Vyshnavi Ts ResumeDocumento2 pagineDR - Vyshnavi Ts ResumeSuraj SingriNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction Quality Control PlanDocumento35 pagineConstruction Quality Control PlanMalik Riaz100% (4)
- Synergic Antiobesity Effects of Bitter Melon Water Extract and Platycodin-D in Genetically Obese MiceDocumento9 pagineSynergic Antiobesity Effects of Bitter Melon Water Extract and Platycodin-D in Genetically Obese Micegege wpNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Irregular VerbsDocumento8 pagineDaftar Irregular VerbsWawan MarwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Black and Decker Vaporera Electrica RecetarioDocumento17 pagineBlack and Decker Vaporera Electrica RecetarioFabio AtenógenesNessuna valutazione finora
- By Josephine G. Ignacio, MD and Jennifer T. Co, MD, FPOGSDocumento9 pagineBy Josephine G. Ignacio, MD and Jennifer T. Co, MD, FPOGSAngela SaldajenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Calcium Cyanide: Hydrogen Cyanide. CONSULT THE NEW JERSEYDocumento6 pagineCalcium Cyanide: Hydrogen Cyanide. CONSULT THE NEW JERSEYbacabacabacaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xtra ReportDocumento8 pagineXtra ReportTahfeem AsadNessuna valutazione finora