Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Carbonates, Air and Water PDF
Caricato da
Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Carbonates, Air and Water PDF
Caricato da
Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Carbonates, Air and Water
Specification Points
Air and Water
Understand the importance of water:
• know a chemical test for water and how water is purified by filtration and chlorination
• name some uses of water in the home and some uses of water in industry
• discuss the implications of an inadequate supply of water, limited to safe water for
drinking and water for irrigating crops
Understand the importance of clean air:
• clean air is a mixture containing approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen
• oxygen is used in oxygen tents in hospitals and (with the hydrocarbon acetylene) in
welding
• there are small amounts of noble gases, carbon dioxide and water vapour in the air
• carbon dioxide is formed by the complete combustion of carbon compounds
• carbon dioxide is a product of respiration
• carbon dioxide and methane are greenhouse gases and be able to explain how they
contribute to climate change
• carbon dioxide is given off when an acid reacts with a carbonate
• pollutants in the air include carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen and
lead compounds and state the adverse effects of these common pollutants on building
and health and discuss why these pollutants are of global concern
• the carbon monoxide is formed by incomplete combustion of carbon compounds and is
poisonous
• the sulphur dioxide is formed from the combustion of fossil fuels containing sulphur
• sulphur dioxide contributes to acid rain which corrodes buildings and damages fish and
plants
• the lead compounds and nitrogen oxides are found in car exhausts
• nitrogen oxides contribute to acid rain and irritate the nose and throat
• lead compounds damage the nervous system
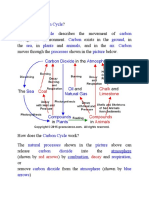
• describe the carbon cycle in simple terms to include the processes of combustion,
respiration and photosynthesis
• describe how nitrogen and oxygen are separated from liquid air by fractional distillation
• explain how nitrogen oxides are formed in the car engine and are removed by the
catalytic converter
Describe methods of rust prevention:
• paints and other coatings prevent rust by stopping oxygen getting to the iron
• sacrificial protection (by placing a metal higher in the reactivity series in contact with the
iron) and galvanizing iron with a layer of zinc
Carbonates
Describe the reactions and uses of calcium carbonate:
• how lime (calcium oxide) is made from calcium carbonate by heating
• the chemical reaction involved in making lime is thermal decomposition
• lime is used to neutralise acidic soils
• slaked lime is used to neutralise acidic industrial waste
• calcium carbonate is used in the manufacture of iron and of cement
Independent Study suggestions
1. Look at the specification points above – use the textbook pages (210-241) or the revision guide
pages (123-129,132-136) to make a few notes/spider diagram/revision cards
2. Have a go at the questions in the revision guide on pages 130-131, 137-138 and mark yourself –
answer in the back
3. Watch the Fuse School short 3-4 minute explanation videos for any topic you are unsure about.
Reactions of iron: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/973
Iron alloys: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/327
Corrosion and rusting: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/367
Rust prevention: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/328
The atmosphere: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/1026
Properties of hydrogen: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/1212
Properties of oxygen: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/969
Properties of nitrogen: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/968
Nitrogen cycle: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/1107
Air Pollution: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/838
Acid rain: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/331
Reducing acid rain: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/332
Global warming: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/332
Effects of global warming: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/1053
Burning fossil fuels and global warming: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/1082
Evaluating the evidence for global warming: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/837
Ozone layer 1: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/1083
Ozone layer 2: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/1019
Catalytic converters: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/967
Biofuels: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/1061
Biofuels – economic costs: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/391
Carbon cycle 1: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/1051
Carbon cycle 2: https://www.fuseschool.org/topics/65/contents/1052
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Earth and Life Science ReviewerDocumento46 pagineEarth and Life Science ReviewerMalou San81% (27)
- Nebosh EnvironmentDocumento192 pagineNebosh EnvironmentSelva Ganapathi86% (49)
- Cambridge - Science - WB9Documento192 pagineCambridge - Science - WB9Nguyen Minh Anh90% (10)
- S9 Unit 1 WorksheetsDocumento10 pagineS9 Unit 1 Worksheetsasmaa hussienNessuna valutazione finora
- Forest Carbon Stock Assessment - ManualDocumento74 pagineForest Carbon Stock Assessment - ManualHana DejasmineNessuna valutazione finora
- Cycling of Materials in EcosystemsDocumento25 pagineCycling of Materials in EcosystemsAyesha SarwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Cycle PresentationDocumento14 pagineCarbon Cycle Presentationapi-282480169Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 11 CHAPTER-3 Physics Motion in A Straight LineDocumento11 pagineClass 11 CHAPTER-3 Physics Motion in A Straight LineHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Worksheet (HKM)Documento1 paginaCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Worksheet (HKM)Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry WorksheetDocumento1 paginaCBSE Class 11 Chemistry WorksheetHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz-1.1 Element, Compound and MixtureDocumento2 pagineQuiz-1.1 Element, Compound and MixtureHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Made By-Samiran Ghosh Class - Xi "A"Documento88 pagineMade By-Samiran Ghosh Class - Xi "A"Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Units and Measurement Test Paper IIIDocumento2 pagineUnits and Measurement Test Paper IIIHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Structure of AtomDocumento16 pagineChapter 2 - Structure of AtomHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hakim-Phy-lesson-Chapter-2 Units and MeasurementDocumento28 pagineHakim-Phy-lesson-Chapter-2 Units and MeasurementHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Made By-Samiran Ghosh Class - Xi "A"Documento88 pagineMade By-Samiran Ghosh Class - Xi "A"Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1.3 Law of Chemical Combination-HakimDocumento37 pagineChapter-1.3 Law of Chemical Combination-HakimHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Documento18 pagineStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Projectiles Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Documento6 pagineProjectiles Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - Motion in A PlaneDocumento30 pagineChapter 4 - Motion in A PlaneHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1.3 Law of Chemical Combination-HakimDocumento38 pagineChapter-1.3 Law of Chemical Combination-HakimHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Density Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Documento1 paginaDensity Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2.1 - Structure of Atom 2Documento60 pagineChapter 2.1 - Structure of Atom 2Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2.1 - Structure of AtomDocumento46 pagineChapter 2.1 - Structure of AtomHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Scalar/Vector Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Documento6 pagineScalar/Vector Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Resolving Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Documento15 pagineResolving Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009David AllenNessuna valutazione finora
- F Ma Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Documento13 pagineF Ma Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.2.2 Hooke's Law PDFDocumento2 pagine2.2.2 Hooke's Law PDFRobert EdwardsNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Documento8 pagineEnergy Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1.6 Work Done & PowerDocumento10 pagine2.1.6 Work Done & PowerHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion Graph Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Documento14 pagineMotion Graph Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Young's Modulus Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Documento32 pagineYoung's Modulus Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- SUVAT Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Documento7 pagineSUVAT Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminal Velocity Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Documento6 pagineTerminal Velocity Past Paper Questions Jan 2002 To Jan 2009Hakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.5 Atomic Structure and PeriodicityDocumento13 pagine1.5 Atomic Structure and PeriodicitychwalidNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4 EnergeticsDocumento10 pagine1.4 EnergeticsMahmoud TahaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4 EnergeticsDocumento12 pagine1.4 EnergeticschwalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Factsheet Klimawandel 1.1 EN WebDocumento32 pagineFactsheet Klimawandel 1.1 EN WebRefat NafiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Earths Cycles (Lecture 06) - Part 02Documento39 pagineEarths Cycles (Lecture 06) - Part 02Binthan RamzeeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Cycle SEDocumento7 pagineCarbon Cycle SEAlex0% (3)
- Phytoplankton Population Drops 40 Percent Since 1950 - Scientific AmericanDocumento9 paginePhytoplankton Population Drops 40 Percent Since 1950 - Scientific AmericanMichael Drew PriorNessuna valutazione finora
- Sci11 q1 Mod1 IntroductionToEarth v2 ForprintDocumento9 pagineSci11 q1 Mod1 IntroductionToEarth v2 ForprintChloe Elysse AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbon Sequestration in SoilsDocumento4 pagineCarbon Sequestration in SoilsDee875Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical CyclesDocumento4 pagineChemical CyclesRoscela Mae D. ArizoNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is BiodiversityDocumento78 pagineWhat Is BiodiversityAnonymous XXENB3eONessuna valutazione finora
- Potential of Carbon Sequestration and Storage by TreesDocumento6 paginePotential of Carbon Sequestration and Storage by TreesMichael HeongNessuna valutazione finora
- What Humans Contribute To Atmospheric CO: Comparison of Carbon Cycle Models With ObservationsDocumento21 pagineWhat Humans Contribute To Atmospheric CO: Comparison of Carbon Cycle Models With ObservationsTolga KaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Living in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFDocumento35 pagineDwnload Full Living in The Environment 19th Edition Miller Solutions Manual PDFemicant.pintosfe9soe100% (10)
- What Is The Carbon CycleDocumento7 pagineWhat Is The Carbon CycleAnonymous wf0U20MMqxNessuna valutazione finora
- World Atmospheric CO2, Its 14C Specific Activity,.2Documento15 pagineWorld Atmospheric CO2, Its 14C Specific Activity,.2Anonymous yE2LIYBNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods To Estimate Above Ground BiomassDocumento7 pagineMethods To Estimate Above Ground BiomassMiguel ParejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Combinepdf PDFDocumento417 pagineCombinepdf PDFmasterindNessuna valutazione finora
- Prairie To CornDocumento7 paginePrairie To CornLorrieNessuna valutazione finora
- Despiite Pandemic Earths Co2 Levels at HighestDocumento4 pagineDespiite Pandemic Earths Co2 Levels at Highestapi-537816221Nessuna valutazione finora
- IPCC Fifth Assessment Report, Climate Change 2013-The Physical Science Basis IPCC 2013Documento18 pagineIPCC Fifth Assessment Report, Climate Change 2013-The Physical Science Basis IPCC 2013Pyke MainNessuna valutazione finora
- MCB 410Documento33 pagineMCB 410oluwaleye victorNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Change A Silent ThreatDocumento229 pagineClimate Change A Silent ThreatCHRISTOS KALOUDISNessuna valutazione finora
- Env Law End TermDocumento13 pagineEnv Law End TermSadhvi SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cycling of Materials in EcosystemsDocumento39 pagineThe Cycling of Materials in Ecosystemsmely marconNessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON PLAN Carbon CycleDocumento6 pagineLESSON PLAN Carbon CycleGemay DanglayNessuna valutazione finora