Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Understanding the Fundamentals of Physical Geography
Caricato da
mjDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Understanding the Fundamentals of Physical Geography
Caricato da
mjCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PAMANTASAN NG LUNGSOD NG VALENZUELA
COLLEGE OF EDUATION, ARTS & SCIENCES
Thinking Geographically:
A Module in Physical Geography GEOG1 Physical Geography
Course Code: GEO1
MARY JOY B. EDURIA
Unit I: Looking at the World
1
FOREWORD
Thinking like a geographer is describe as a person who studies the earth and its people. One way
to learn Geography is to know some basic concepts and skills in analyzing its content.
Geography is more than studying facts and figures but it also means doing your own exploration
of the earth. With Physical Geography as a subject and specialization in Geography, it deals with
the understanding of the earth’s function, its system and environment.
This module in Geo1 Physical Geography is an attempt to come up with instructional material
that can be utilized by college students to facilitate the teaching and learning process in a self-
paced learning approach. Each of the topic is accompanied by suggested independent learning
activities, essential questions, suggested readings for the development of skills that will aid the
learning objectives of this module. Evaluative measures are also designed in the end of this
module to assess and monitor the student’s learning progress.
“Man is born on the earth’s surface where he makes his living and where he eventually dies”
(Duka, 2001). Therefore, after going through this module, students can be crucial for making
informed decision about the use and preservation of Earth’s resources and environmental
awareness that can benefit or endanger the future generations.
GEOG1 Physical Geography
Unit I: Looking at the World
2
CONTENTS
UNIT I – Looking at the World
PART 1: Introduction to Geography
Diagnostic Assessment
Five Themes of Geography
Geography and Other Disciplines
Scope of Geography as Physical and Human Geography
Elements of Physical Geography
Summative Assessment
PART 2: Representation, Movement and Knowledge of the Earth
Diagnostic Assessment
Cartography
Maps
Remote Sensing
Locational Knowledge
Time zones
Absolute and Relative Location
Earth rotation and Movement GEOG1 Physical Geography
Summative Assessment
PART 3: The Earth System
Diagnostic Assessment
Atmosphere
Hydrosphere
Lithosphere
Biosphere
Human sphere
Summative Assessment
PART 4: The Impact of Resources
Diagnostic Assessment
The Consumption of resources
Alternative Energy Resources
The Environment: Population, Pollution, Climate Change
Summative Assessment
Unit I: Looking at the World
3
UNIT II – The Physical Geography of Philippines
PART 5: Philippines, the Pearl of the Orient Seas
Diagnostic Assessment
Place
Physical features
Size
Shape
Environment
Climate
Weather
Landforms
Waterforms
Natural resource
Forest
Agricultural
Mineral
Industrial
Regionalization Resources
Northern and Central Luzon
NCR and Southern Luzon
The Visayan Island
GEOG1 Physical Geography
Mindanao
Sulu Island
Summative Assessment
Formative Assessment
Unit I: Looking at the World
4
DIAGNOSTIC ASSESSMENT
Multiple Choice: Write the letter of the correct answer.
_____1. The five themes of geography are
a. landscape, water forms, climate, weather, biosphere
b. latitude, longitude, absolute, relative, technology
c. location, place, human interaction, movement, regions *
d. science, history, environment, technology, earth
_____2. The theme ____ is concerned with the question “Where is it”?
a. location *
b. place
c. human interaction
d. movement
_____3. It can be described in terms of land, water, weather, soil, and plant and animal life.
a. location
b. place *
c. human interaction
d. movement
_____4. To make sense of all the complex things in the world, geographers often group places or
areas into ________. GEOG1 Physical Geography
a. location
b. regions *
c. human interaction
d. movement
_____5. This theme relates to the question “How are people and places connected?”
a. place
b. regions
c. human interaction
d. movement *
_____6. The word geography comes from the Greek word geographia,, which means
a. a report of land and people
b. a description of the earth *
c. account of physical and human
d. study of creatures
_____7. _______ are people who study the Earth
a. Scientist
b. Geographers *
c. Astronaut
d. Environmentalist
Unit I: Looking at the World
5
_____8. Geo refers to _____ and graphic refers to picture or writing
a. World
b. Globe
c. Earth
d. Universe
_____9. Which aspect of Geography is consists of the systematic study of the origin, distribution,
and significance of the major physical features of the earth such as landforms, climates, the
oceans and natural resources?
a. Cultural Geography
b. Human Geography
c. Physical Geography
d. World Geography
_____10. _________ was not only the “Father of History” but also of geography because of his
role in historic events in their geographic setting.
a. Aristotle
b. Socrates
c. Herodotus
d. Plato
_____11. The primary concern is man and his works that is closely allied with other social
sciences. GEOG1 Physical Geography
a. Cultural Geography
b. Human Geography
c. Physical Geography
d. World Geography
_____ 12. Climate, topography, the geographic arrangement of people illustrate the physical
elements as the backdrop of human behavior. The things he uses to change the physical
environment to serve his needs are called ________.
a. environmental elements
b. science elements
c. cultural elements
d. technology elements
_____ 13. Analyzes the differences and similarities in climate from place to place
a. Geomorphology
b. Oceanography
c. Climatology
d. Biogeography
_____ 14. Another kinds of human geography that deals with the study of cities with the
important roles cities play in the life of a nation.
a. Cultural geography
Unit I: Looking at the World
6
b. Population geography
c. Political geography
d. Urban geography
_____ 15. Which of the following illustrates geography with other disciplines in social science?
a. Primarily concerned with human occupancy of the Earth
b. Unique position in the field of knowledge of the Earth
c. Common ground for physical features of the Earth
d. Studies nature and other surface of the Earth
GEOG1 Physical Geography
Unit I: Looking at the World
7
1
Introduction to
Physical Geography
This unit begins with geographic terms, nature, scope and elements of Physical Geography and
other disciplines as a major part of the field of geography.
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
1. What are the five themes of Geography?
2. Why is Geography considered both as a Physical Science and a Social Science?
3. What is Physical Geography and how significant is this branch of Social Science?
INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES
1. Discuss the concept of Geography and other geographical terms
2. Define and explain the relations of Physical Geography and the Social Sciences
3. Enumerate the elements of Physical Geography
4. Determine the scope of Physical Geography
GEOG1 Physical Geography
What is Geography?
One of the most fascinating studies known to man is the study of the earth and its inhabitants
which later called as geography. The word Geography comes from the Greek language
“geographia” which means “earth description”. Geo refers to Earth and graphy means writing or
picture. Everything you see, touch, use and even hear is related to geography. Historically,
geography remains to be broad which includes the examination, description, and explanation of
cultural as well as physical features of the Earth. To further understand the term geography,
Geography Education Standards Project of Geography for Life defines it as :
an integrative discipline that brings together the physical and human dimensions of
the world in the study of peoples, places, environment. Its subject matter is the
Earth’s surface and the processes that shape it, the relationship between people and
environment, and the connections between people and places.
Geographers study the processes that influenced Earth’s physical and cultural landscapes in the
past, today and in the future and how it changes over space and time. Geographers are people
who study geography. According to Webster, it defines geography as the science of the earth and
its life, the description of land, sea, air and the distribution of plants, animals including man and
his industries with reference to mutual relation of diverse elements. In some textbooks,
geography indicates the physical environment of the earth and how it is related to its inhabitants.
Unit I: Looking at the World
8
In a nutshell, while man changes the landscape, his actions are influenced by the environment
which means geography is a study of the earth as the home of man.
Climate, topography, water, land, soils, weather, natural plant and animal life and numerous
other factors illustrate the role of physical elements as the backdrop of human behavior. There
are some limitations that man has to accept certain physical elements but also either to control or
modify some of them. And the things he uses to change the physical environment to serve his
needs make up what are called cultural elements or the elements that result from his presence.
Under cultural elements are population, cultural heritage, economic activities, and major works
or accomplishments.
Historically, it has been a concerned with the nature how man is curious with his homeland and
known world, but not until the Golden Age of Greece that the science of geography was
established. Herodotus who was the Father of History of 485-425 BC and also of geography
because of the historic events he placed in their geographic setting. Herodotus observed the Delta
of the Nile which has a rich black soil and explained the result of river deposition. Herodotus
pointed out that the riches of the delta contributed to making the place one of the cradles of
ancient civilization. He found the relationship of the physical environment importance to the
activities of man which became the very essence of geography.
Activity 1- Study Questions
Direction: Write the definition of the following concepts:
GEOG1 Physical Geography
1. What is geography?
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
2. What is the significance of studying geography?
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
3. What do you mean by geographers?
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
4. What is the difference of physical elements to cultural elements?
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
5. What is the role of Herodotus in the field of geography?
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
Unit I: Looking at the World
9
Five Themes of Geography
In studying geography, it is important to have a basic understanding of geographic terms. The
study of geography can be organized around five themes: location, place, human/environment
interaction, movement, and region. The purpose of five themes offer a structured way of thinking
about the world and can be used to study all kinds of geographic issues at local, national and
global levels.
Location
This theme concerned with the question “Where is it?”. Geographers first take a look at where
place is located. Knowing the location of places helps you to orient yourself in space and to
develop an awareness of the world around you.
Place
Geographers also look at places and regions. Place is concerned with “What is it like there?”
Place includes those features and characteristics that give an area its own identity or personality.
For instance, landforms, climates, plants and animals are considered as physical characteristics
while language, religion, architecture, music, politics, and way of life are human characteristics.
People’s activities change the way a place looks. Thus, a place may look quite different
depending on whether it is used for hunting and fishing, herding, farming, manufacturing, or
shopping. Geographers often group places or areas into regions which are united by one or more
common characteristics. For example, the regions of Asia: Central Asia, Eastern
GEOG1 Asia,
Physical Southern
Geography
Asia, South-Eastern Asia, Western Asia and Northern Asia.
Human/Environment Interaction
The study of geography includes looking at human and environmental interaction, or how and
why people change their surroundings. It answers the question “What is the relationship between
people and their environment?” Geographers strive to understand the relationship of places on
the earth to people and to other places. All places have some desirable and undesirable features.
Places attract people for various reasons. For such, people may be attracted to a place by an
ocean, a river or a lake. They may be attracted to a place by the amount of sunshine it receives.
Different groups of people may use the features of a place in different ways. Some people are
interested in warm, sunny places for growing crops while other people are interested in the same
places for recreational activities.
Geographers are interested in how people adapt to their environment and how people change
their environment. For example, some people wear light clothing in hot places and warm clothing
in cold places. Some people considered deserts ay undesirable places to live but today people use
irrigation to change desert land into farmland. Lastly, geographers are also concerned with how
people created problems with their environment. Among the problems are air pollution, water
pollution, and waste material, which consider hazardous to living things.
Unit I: Looking at the World
10
Movement
Another important theme in geography is movement. This theme relates to the question “How are
people and places connected?” there have been movements of larger groups of people from one
place to another throughout history. People moved from different reasons such as better land,
religious freedom, a chance to earn a better living. Movement can be part of our lives. For
instance, people use automobiles, buses, subways, and commuter trains to move from one place
to another. There are also movement of goods, information and ideas which people become
interdependent that relies on each other for goods and services. Geographers help us to
understand the importance of movement.
Activity 2: Like a Geographer
Direction: Using the 5 Themes of Geography, complete a study of your home
town. You can choose to present your information as a poster, story, essay, map
or comic. Choose ONE from the following:
a. Story: Write a story with you as the main character. The story should take place around where
you live. Be sure that you IDENTIFY and EXPLAIN all of the 5 Themes of Geography that can
be found around your home.
b. Essay: Write a 7 paragraph essay IDENTIFYING and EXPLAINING all of the 5 Themes of
Geography. The essay will included an intro and conclusion paragraph andPhysical
GEOG1 one paragraph for
Geography
each of the 5 Themes.
c. Map: Make a map of where you live. Make sure to LABEL and EXPLAIN each of the 5
Themes of Geography that you can find near your home. Your map should be neat and have
color.
d. Comic: Make a comic that has at least 5 Panels. Each panel should show one of the 5 Themes
of Geography that can be found around where you live. Make sure to add words to help
EXPLAIN your understanding of each of the themes.
e. Poster: Create a collage poster with pictures and maps to describe the 5Themes of Geography
around your town. Be sure to LABEL and EXPLAIN all of the 5 themes.
Geography and Other Disciplines
Geographers study both physical and human features of the earth and analyze patterns and
relationship of each. In the process, these areas of geographic study are linked to other subjects
including natural sciences, social sciences, and humanities.
Geography belongs to the field of natural science because of its physical features of studying the
earth as a central theme. You will notice that this module will comprise topics about nature such
as the water, landforms, minerals, soil, climate, and flora and fauna on the surface of the earth. It
Unit I: Looking at the World
11
will also discuss some common ground with geology, biology, astronomy, and oceanography,
science and technology among other things.
Geography also deals with social science that focus on man as the architect of the earth’s surface.
It will explain in the latter discussion about man’s political and economic system, religious and
educational institutions, man’s cultural values, mores and folkways and beliefs. Geography also
included in the field of humanities for it studies artistic works. Lastly, geography is linked with
history, economics, political, science, anthropology, sociology and demography. Hence,
geography provides the blending of the natural science, social science and humanities.
Scope of Physical and Human Geography
Geographers organize their study of the earth in many ways. They also classify the branches of
geography according to whether they deal with the physical or with human activity.
Physical Geography
Physical geography deals with the location of such earth features as land, water, and climate and
their relationship to one another and to human activities. Physical geographers study all
processes and characteristics of the natural environment in which they cannot exclude the human
element because people affect and otherwise affected by natural processes and features. It is also
concerned with the forces that create and change them. Physical geography is further categorized
into the following: GEOG1 Physical Geography
Geomorpholog Climatology Mathematica Oceanograph Biogeograph Medical
y and l y y geography
Meteorology Geography
Studies land Climatolog Deals with Studies the Studies Deals
and water forms y studies accurate ocean and its geographical with the
as well as the wind measurement phenomena, distribution relationship
development of movements of the earth current wave of plants between
irregularities in , cloud and activity, which related disease-
the surface of formation, calculation of temperature to ecology causing
the earth. temperature the exact differences that studies organisms
changes, location of and tides. the and their
and points on the relationship physical
precipitatio earth’s between environment
n of all surface such plants and .
kinds while as the exact animals and
meteorolog location of a their habitat
y consider city in latitude or natural
the and longitude environment.
processes
that affect
daily
weather
and
Unit I: Looking at the World
12
forecast
weather
conditions.
Human Geography
Human geography is primarily concern with man and his works that is closely allied with other
social sciences such as economics, political science, history, sociology, anthropology. Human
geography is further subdivided into the following: (a) cultural geography, (b) population
geography, (c) political geography, (d) historical geography and (e) urban geography.
Cultural Population Political Historical Urban
Geography Geography Geography Geography geography
Studies the Deals with Studies Studies the Deals with
distribution of numbers and the patterns of cities with
cultural traits distribution relationship man and his significant
such as of people. It between works roles cities
customs, is related to political change play in the
traditions, demography, units such as through life of a
taboos, the statistical provinces or time; may nation, site
religions, study of states, place of a city, the
dialects, population. nations, or emphasis of type and
customs and unions of a small direction of
dwellings. . nations, how region at aGEOG1 Physical Geography
its growth,
boundaries certain time. function of a
are drawn city and
and probable strong
problems or commercial
disputes may ties.
create.
Elements of Physical Geography
Spatial Science Perspective
In physical geography, they use scientific method to study variations over space which is called
spatial science. There are five spatial topics- location, characteristics of places, spatial
distribution and pattern, spatial interaction, and change over space and time. These illustrate
factors that geographers consider in understanding the field of study.
It is important for geographers’ to begin with locational information that describes a location
with two methods: absolute location and relative location. Absolute location explained by a
coordinate system while relative location identifies where a feature lies in relation to something
else. Typical questions for spatial science involving location were include the following: Where
are Volcanoes found? (or other type of Earth feature) Why are volcanoes located where they are?
What method can we use for to locate Volcanoes?
Unit I: Looking at the World
13
Another spatial topics is the characteristics of places which focus on environmental features and
processes that make a place unique with shared or similar characteristics. Example questions are
How does Sahara desert compare to Australian desert? What environmental conditions make one
country more agriculturally productive? How does the climate of Africa differ from America?
And Why?
In terms of the describing extent of the area or areas where feature of interest exist is called
spatial distribution. For example tropical rainforest which cover particular expanses of Earth’s
surface that is spatially distributed. While spatial pattern refers to how multiple individuals of the
same type of feature or event are arrange on Earth’s surface. For spatial distribution and spatial
pattern relevant questions are: Where are certain features abundant, and where are they rare?
What processes are responsible for these distributions or patterns? If a spatial pattern exists, what
does it signify?
Spatial Interaction differ from spatial distribution and pattern because of areas in our planet are
interconnected in which they are linked elsewhere on Earth. In other words spatial interaction is a
process in one place that has impact on other places. For example, excessive rainfall from one
place may lead to flooding with the other place. Spatial interaction exists so physical geographers
consider problem such as: What are the important interconnections link the ocean to the
atmosphere and the atmosphere to the land surface? What will the effect of stricter pollution?
How spatially interacting variables affect each other?
Earth’s feature and landscapes change continually. Changes in storms conditions, landslides,
GEOG1
volcanic eruptions and floods of different types modify the landscape Physical Geography
at different rates. As a
result, geographers ask questions such as: How are Earth features changing in ways? What
processes contributed to those changes? Do all places on Earth experience the same level of
change or is there spatial variation?
Physical Science Perspective
Like other scientist, physical geographers use the scientific method in their investigations of the
characteristics and processes acting on Earth’s surface. They observe the phenomena, collect and
analyze the data, answer questions, and find solution to problems related to natural processes,
draw and contribute to larger body of knowledge and results of their research. There are physical
geographers who are specializing in different field such as climatology or meteorology,
geomorphology and soil geographers. The geographers tend to take a holistic approach to their
studies.
Environmental Science Perspective
The physical environment or the environment itself is our surroundings consisting of social,
cultural and physical aspects of the world that affect our growth, health, and the way we live.
Physical geography in a holistic approach enhances the ability for geographers to study the
environment because of the important factors and processes not only individually but also as
integral parts of a function environmental system. The geographic distribution of human
Unit I: Looking at the World
14
population densities around the world, varying from uninhabited to dense settlements that reflects
the environmental disparity.
Physical geography contribution
Every day in our lives we are affected by our physical environment, the principles and
perspectives of physical geography help us to be aware environmentally, assess the situation of
our environment from the past, present, and for the future, analyzed the factors involved, and
make informed decisions about courses of action. Physical geographers make major
contributions to human well-being and to the environment.
Geography is a way of looking at the world and observing and analyzing its features.
Appreciating the beauty and complexity of the nature involves asking questions. With greater
awareness and deeper understanding, you will have learned to observe Earth differently.
Activity 3: Study questions
Direction: Answer the following questions.
1. How spatial science differ from physical science perspective?
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
GEOG1 Physical Geography
2. Why is the study of geography important to man?
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
3. Differentiate physical geography from human geography?
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
4. How is geography related to other discipline?
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
5. As a social science major, how would you relate the importance of geography in your practical
life?
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Unit I: Looking at the World
15
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT
IDENTIFICATION
Direction: Identify the following subdivisions of Geography.
_________ 1. It deals with the location of such earth features as land, water, and climate and
their relationship to one another and to human activities.
_________ 2. It is concerned with the study of distribution of cultural traits such as customs,
traditions, taboos, religions, dialects, customs and dwellings.
_________ 3. It studies the land and water forms as well as the development of irregularities in
the surface of the earth.
_________ 4. It deals with cities with significant roles cities play in the life of a nation and site
of a city.
_________ 5. It studies the patterns of man and his works change through time; may place
emphasis of a small region at a certain time.
__________6. It studies the relationship between political units such as provinces, states and
nations GEOG1 Physical Geography
__________7. It deals with numbers and distribution of people. It is related to demography, the
statistical study of population.
__________8. It studies the ocean and its phenomena, current wave activity, temperature
differences and tides.
__________9. It is concerned with man and his works that is closely allied with other social
sciences
__________10. It deals with the relationship between disease-causing organisms and their
physical environment
Unit I: Looking at the World
16
Diagnostic Assessment Answer Key:
1. C 6. B 11. B
2. A 7. B 12.C
3. B 8. C 13. C
4. B 9. C 14. D
5. D 10. C 15. A
Summative Assessment Answer Key:
1. Physical geography 6. Political geography
2. Cultural geography 7. Population geography
3. Geomorphology 8. Oceanography
4. Urban geography 9. Human geography
5. Historical geography 10. Medical geography GEOG1 Physical Geography
References
Boehm, R. G., (2000). World Geography. Glencoe Mc Graw Hill. Columbus, Ohio, United Staes
of America.
Duka, C. D., (2001) World Geography. Rex Printing Company. Quezon City, Philippines.
Petersen, J.F., et al (2017) Physical geography, Eleventh Edition. Cengage Learning. Boston,
USA.
Unit I: Looking at the World
17
Study Questions Clip art https://www.google.com/search?
q=STUDY+QUESTIONS+CLIP+ART&sxsrf=ALeKk02LKnXVgeFQR4_0UVPiGiFR0GjRSQ:1593442558318&tbm
=isch&source=iu&ictx=1&fir=WMf0P0Tmjftk5M%252CJxG47tsQzgOL7M%252C_&vet=1&usg=AI4_-
kRQZJt_KukE6BMegKPLFXoPKPyDXA&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwj24qGNpKfqAhWKfd4KHYNdA4cQ9QEwDnoE
CAkQLg&biw=1242&bih=597#imgrc=7hzW9kvJa84Z7M
GEOG1 Physical Geography
Unit I: Looking at the World
18
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Geog 1 - Geog As A DisciplineDocumento2 pagineGeog 1 - Geog As A DisciplineHanaKaz100% (1)
- Physical GeoDocumento36 paginePhysical GeoLalaine Marie BianzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth As A SystemDocumento15 pagineEarth As A SystemDondon TayabanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson PlanDocumento9 pagineLesson PlanBernadette DispoNessuna valutazione finora
- Places and LandscapesDocumento77 paginePlaces and LandscapesRhe Ya100% (1)
- Places and Landscape in A Changing World - AsiaDocumento7 paginePlaces and Landscape in A Changing World - Asiajohn diolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Recognizing The Importance of Teaching Social Sciences in Philippine Schools1Documento35 pagineRecognizing The Importance of Teaching Social Sciences in Philippine Schools1Ramie SenarosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 Physical Geography 2.Documento15 pagineModule 1 Physical Geography 2.marvsNessuna valutazione finora
- Commission On Higher Education Bago City College: Module in Ss4-2 Year Bsed - Social StudiesDocumento7 pagineCommission On Higher Education Bago City College: Module in Ss4-2 Year Bsed - Social StudiesEduardo QuidtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geography 3 Week 1&2 ActivityDocumento2 pagineGeography 3 Week 1&2 ActivityJun Mark Balasico YaboNessuna valutazione finora
- Places and Landscape ModuleDocumento5 paginePlaces and Landscape ModuleQueenby MelalabsNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Part I Asian StudiesDocumento2 pagineFinal Exam Part I Asian StudiesAlma Mae CalivoNessuna valutazione finora
- Diversity and Spatial Differentiation in The CityDocumento2 pagineDiversity and Spatial Differentiation in The CityZephyrine MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Coseptualizing Social StudiesDocumento2 pagineCoseptualizing Social StudiesDexter Malonzo TuazonNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 AnswersDocumento5 pagineModule 2 AnswersmarvsNessuna valutazione finora
- Philisophy of Ss EduDocumento11 paginePhilisophy of Ss Eduapi-317882869Nessuna valutazione finora
- Asian Hist Prelim LMDocumento36 pagineAsian Hist Prelim LMAlleah Mae NavalNessuna valutazione finora
- The National Capital Region (NCR) : PopulationDocumento36 pagineThe National Capital Region (NCR) : PopulationNynNessuna valutazione finora
- Group5 Summary of Report (Places and Landscapes)Documento21 pagineGroup5 Summary of Report (Places and Landscapes)Rowela NimNessuna valutazione finora
- SSE 101foundation of Social StudiesDocumento2 pagineSSE 101foundation of Social StudiesEdwin SamisNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1Documento10 pagineLesson 1Rhea amor SabuitoNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 1 - Lesson 1Documento10 pagineUNIT 1 - Lesson 1Dianne Mae LlantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rizal Technological University: ObjectivesDocumento2 pagineRizal Technological University: ObjectivesShynah Jane Viaña TinaligaNessuna valutazione finora
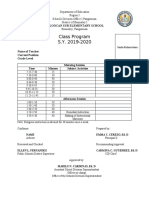
- Class Program S.Y. 2019-2020: Caloocan Sur Elementary SchoolDocumento1 paginaClass Program S.Y. 2019-2020: Caloocan Sur Elementary SchoolShikinah Glory PadillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Studies Notes 1Documento9 pagineSocial Studies Notes 1Joryl Shane Matero RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation of Social Studies (SSED-113)Documento23 pagineFoundation of Social Studies (SSED-113)Via OctosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Social Studies in Elementary Grades BEED 2Documento27 pagineTeaching Social Studies in Elementary Grades BEED 2Arcelita Aninon MagbanuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Emphasis of Social StudiesDocumento12 pagineEmphasis of Social StudiesDan GregoriousNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 in Foundation of Social StudiesDocumento17 pagineModule 2 in Foundation of Social StudiesRomar M. DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Places - Threats To NatureDocumento6 paginePlaces - Threats To NatureJEEHAN DELA CRUZNessuna valutazione finora
- Theoretical Perspectives in Social Anthropology and Material CultureDocumento4 pagineTheoretical Perspectives in Social Anthropology and Material CultureMarilouSabaterNessuna valutazione finora
- Bachelor of Secondary Education Major in Social StudiesDocumento4 pagineBachelor of Secondary Education Major in Social StudiesChristine Joy MarcelNessuna valutazione finora
- Module I: Introduction To The Study of HistoryDocumento4 pagineModule I: Introduction To The Study of Historyever existenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Instructional StrategiesDocumento19 pagineEffective Instructional StrategiesSheryl Ann Tumacder DionicioNessuna valutazione finora
- Objectives of Teaching Social StudiesDocumento22 pagineObjectives of Teaching Social StudiesRizza SandoyNessuna valutazione finora
- AsianStudies Syllabus-First Semester To Third QuarterDocumento7 pagineAsianStudies Syllabus-First Semester To Third Quarterlklklklk8908Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3Documento11 pagineModule 3marvsNessuna valutazione finora
- SST 101 I. History of Geography HGDocumento10 pagineSST 101 I. History of Geography HGJomar CatacutanNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 AnswerDocumento26 pagineModule 3 AnswermarvsNessuna valutazione finora
- UCSP Notes 1st GradingDocumento30 pagineUCSP Notes 1st GradingKhassie B. GrandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Geography is the study of Earth and humansDocumento46 pagineGeography is the study of Earth and humansIanBiagtan100% (1)
- Social Studies Teaching MethodologyDocumento4 pagineSocial Studies Teaching MethodologyArvind Ranganathan100% (1)
- Foundation OF: The Great Plebeian College College Department Alaminos City, Pangasinan Term: 1 SemesterDocumento20 pagineFoundation OF: The Great Plebeian College College Department Alaminos City, Pangasinan Term: 1 SemesterJessa GallardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson-Plan-Do42 2016 Social StudiesDocumento8 pagineLesson-Plan-Do42 2016 Social StudiesAubry joy MacasoNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippine Popular Culture Course OutlineDocumento2 paginePhilippine Popular Culture Course OutlineJustin SanchoNessuna valutazione finora
- An Essay About The Nature of CurriculumDocumento4 pagineAn Essay About The Nature of CurriculumvhergraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Secondary Education Development ProgramDocumento8 pagineSecondary Education Development ProgramBrose CathieNessuna valutazione finora
- SSE 107 Macroeconomics SG 5Documento8 pagineSSE 107 Macroeconomics SG 5Aila Erika EgrosNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 Physical Geography 2.Documento9 pagineModule 2 Physical Geography 2.marvsNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Syllabus Socsci 211Documento7 pagineCourse Syllabus Socsci 211IreneNessuna valutazione finora
- Folk and Popular CultureDocumento4 pagineFolk and Popular CultureElla Mae Gapi DagsaanNessuna valutazione finora
- FSSE-104-PLACES-and-LANDSCAPE-FINALS CHEYEN29Documento6 pagineFSSE-104-PLACES-and-LANDSCAPE-FINALS CHEYEN29French Che'yen Viloria CortelNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Outline On Places and LandscapesDocumento12 pagineCourse Outline On Places and LandscapesMicheleNessuna valutazione finora
- Readings in Philippine HistoryDocumento40 pagineReadings in Philippine HistoryRod de CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Japan, Industrial Giant of Asia: Geography. The Japanese Call Their Nation Nippon, Which Means "Land of The RisingDocumento15 pagineJapan, Industrial Giant of Asia: Geography. The Japanese Call Their Nation Nippon, Which Means "Land of The RisingJerome EncinaresNessuna valutazione finora
- (Template) Pink Module 2.0Documento98 pagine(Template) Pink Module 2.0Mia Mones Lunsayan BrionesNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Guide For Module No. 3: Rocks and MineralsDocumento5 pagineStudy Guide For Module No. 3: Rocks and MineralsMaia Gabriela100% (1)
- Critique New Elementary School Curriculum (Nesc) and K To 12 CurriculumDocumento4 pagineCritique New Elementary School Curriculum (Nesc) and K To 12 CurriculumAlyLiwagNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit I: The Elementary Social Studies CurriculumDocumento12 pagineUnit I: The Elementary Social Studies CurriculumShiela Jane Langga SanghidNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 5 Nov 5-6 History, Historical Sources, Historical Criticism PDFDocumento33 pagineWeek 5 Nov 5-6 History, Historical Sources, Historical Criticism PDFmj0% (1)
- First Mass WorksheetDocumento2 pagineFirst Mass WorksheetmjNessuna valutazione finora
- Local HistoryDocumento24 pagineLocal HistorymjNessuna valutazione finora
- PNHS Ap Dept Action Plan Sy 2021-2022Documento10 paginePNHS Ap Dept Action Plan Sy 2021-2022mjNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 4 Did Rizal RetractDocumento2 pagineActivity 4 Did Rizal RetractmjNessuna valutazione finora
- SF 1 School RegisterDocumento215 pagineSF 1 School RegistermjNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Education: Individual Workweek Accomplishment ReportDocumento2 pagineDepartment of Education: Individual Workweek Accomplishment ReportmjNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus Redesigning Outline FormDocumento14 pagineSyllabus Redesigning Outline FormmjNessuna valutazione finora
- DepEd Workweek Report TemplateDocumento2 pagineDepEd Workweek Report TemplatemjNessuna valutazione finora
- PHD Notes ReportDocumento12 paginePHD Notes ReportmjNessuna valutazione finora
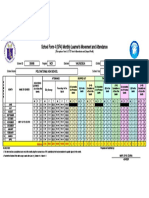
- School Form 4 (SF4) Monthly Learner's Movement and AttendanceDocumento1 paginaSchool Form 4 (SF4) Monthly Learner's Movement and AttendancemjNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 3 First MassDocumento2 pagineActivity 3 First MassmjNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Education: National Capital Region Division of City Schools - Valenzuela Polo National High SchoolDocumento3 pagineDepartment of Education: National Capital Region Division of City Schools - Valenzuela Polo National High SchoolmjNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto-SF2: InstructionsDocumento34 pagineAuto-SF2: InstructionsmjNessuna valutazione finora
- PHD Notes ReportDocumento12 paginePHD Notes ReportmjNessuna valutazione finora
- W10 Controversial Issues Debate TopicDocumento1 paginaW10 Controversial Issues Debate TopicmjNessuna valutazione finora
- Polo National High School Student Class Excuse FormDocumento1 paginaPolo National High School Student Class Excuse FormmjNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm 19-20 Answer Sheet in LongDocumento1 paginaMidterm 19-20 Answer Sheet in LongmjNessuna valutazione finora
- The Misunderstood Patriot: Pio ValenzuelaDocumento4 pagineThe Misunderstood Patriot: Pio ValenzuelamjNessuna valutazione finora
- PHILIPPINEHISTORY Pre Colonial Period PDFDocumento87 paginePHILIPPINEHISTORY Pre Colonial Period PDFJi Yu75% (4)
- Group Activity Case AnalysisDocumento3 pagineGroup Activity Case AnalysismjNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Intro RPHDocumento21 pagineCourse Intro RPHmjNessuna valutazione finora
- Readings in Phil HisDocumento12 pagineReadings in Phil HismjNessuna valutazione finora
- Polo National High School Economics Class ScheduleDocumento3 paginePolo National High School Economics Class SchedulemjNessuna valutazione finora
- 4th QtrimsechipspuzzlemapDocumento1 pagina4th QtrimsechipspuzzlemapmjNessuna valutazione finora
- Poke ChipsDocumento5 paginePoke ChipsmjNessuna valutazione finora
- Garnet 2017 Tops 3rd GradingDocumento13 pagineGarnet 2017 Tops 3rd GradingmjNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Diamond Certificate 2016Documento7 pagine10 Diamond Certificate 2016mjNessuna valutazione finora
- #20pesosm Oneychallen Ge Retsel MJ JhaycieDocumento3 pagine#20pesosm Oneychallen Ge Retsel MJ JhayciemjNessuna valutazione finora
- Geography Paper ExamDocumento11 pagineGeography Paper ExamRavi DixitNessuna valutazione finora
- Geography Fact Sheet Chapter 5&6Documento5 pagineGeography Fact Sheet Chapter 5&6Ma Ronielyn Umantod MayolNessuna valutazione finora
- 5CE4-05 WRE Guess Paper PDFDocumento4 pagine5CE4-05 WRE Guess Paper PDFYogesh PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- PortMiami PhaseIII Impact Assessment FinalDocumento52 paginePortMiami PhaseIII Impact Assessment FinalChris GothnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Formative Assessment - Purposive Communication 1Documento6 pagineFormative Assessment - Purposive Communication 1QUILLO DARWIN JOSEPH ABNE, BA POLSCI A1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eft - Makalah Pariwisata Kabupaten EndeDocumento9 pagineEft - Makalah Pariwisata Kabupaten EndeRevening H. D. MauteyNessuna valutazione finora
- 14.1 and 14.2 GeologyDocumento4 pagine14.1 and 14.2 Geologysabri lalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Setting Out a Building Using Total StationDocumento25 pagineSetting Out a Building Using Total Stationaqilah dianaNessuna valutazione finora
- India TopographyandslopeDocumento22 pagineIndia TopographyandslopejoeNessuna valutazione finora
- For EconomicDocumento25 pagineFor EconomicKristen IjacoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1340 The Age of Exploration PDFDocumento8 pagine1340 The Age of Exploration PDFArijana IbricicNessuna valutazione finora
- Lima and Cusco Are Two Great Cities Located in Peru 2Documento2 pagineLima and Cusco Are Two Great Cities Located in Peru 2Anderson Ocampo Cordova100% (1)
- A Manual of The Salem District in The PRDocumento465 pagineA Manual of The Salem District in The PRபூவை ஜெ ரூபன்சார்லஸ்Nessuna valutazione finora
- New Granada, Twenty Months in The Andes - Isaac F. HoltonDocumento599 pagineNew Granada, Twenty Months in The Andes - Isaac F. HoltonAlᴟatrøzNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 7 DrainageDocumento8 pagineLesson 7 DrainageRakoviNessuna valutazione finora
- Silva Et Al. 2023 - Zircon U-Pb-Hf Isotope and Geochemical ConstraintsDocumento29 pagineSilva Et Al. 2023 - Zircon U-Pb-Hf Isotope and Geochemical ConstraintsathirsonrochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mapping Global Wealth Variations & Questionnaire Surveys on TNC ImpactsDocumento6 pagineMapping Global Wealth Variations & Questionnaire Surveys on TNC ImpactsGabriel JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 - Mercator SailingDocumento35 pagineUnit 4 - Mercator SailingUtpal Kant100% (1)
- 1984, Pred1984, Place As Historically Contingent ProcessDocumento19 pagine1984, Pred1984, Place As Historically Contingent ProcessArwa E. YousefNessuna valutazione finora
- Geography HL and SL Paper 1 May 2010Documento5 pagineGeography HL and SL Paper 1 May 2010Asesoría Educativa - Especialistas de la EducaciónNessuna valutazione finora
- GEOGRAPHY 2 Midterm ReviewerDocumento9 pagineGEOGRAPHY 2 Midterm ReviewerMelanie LomperoNessuna valutazione finora
- Kawah Putih: HistoryDocumento3 pagineKawah Putih: HistoryFrederickDionNessuna valutazione finora
- Bible GeographyDocumento206 pagineBible Geographyandrea caphace0% (1)
- Descriptive Is PeterDocumento14 pagineDescriptive Is Peterglobal NetNessuna valutazione finora
- Specification for Topographic & Hydrographic SurveysDocumento5 pagineSpecification for Topographic & Hydrographic Surveysjinwook75Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Historical Facts in The West Philippine SeaDocumento63 pagineThe Historical Facts in The West Philippine SeaVERA Files93% (14)
- Mine Survey RegulationsDocumento11 pagineMine Survey RegulationsAlekkhyya RoySENessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to CartographyDocumento20 pagineIntroduction to CartographyN Azrina Ramlan100% (1)
- Pub 162 BKDocumento348 paginePub 162 BKartemisNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 11 Our Greener WorldDocumento3 pagineUnit 11 Our Greener WorldNgọc BíchNessuna valutazione finora