Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Basic Genetics For Blood Bankers
Caricato da
cyrelleTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Basic Genetics For Blood Bankers
Caricato da
cyrelleCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BASIC GENETICS FOR BLOOD BANKERS
GENOTYPE
- the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual (i.e, the specific allele makeup of the
individual usually with reference to a specific character under consideration.
PHENOTYPE
- it is defined as an organisms expressed physical traits. Phenotype is determined by an
individuals genotype and expressed genes, random genetic variation and environmental
influences.
MENDEL’S LAW OF INHERITANCE
1. One of two principles of heredity first formulated by Gregor Mendel, founded on his
experiements wih pea plants and stating that the members of a pair of homologous
chromosomes segregate during meiosis and are distributed to different gametes. Also called law
ug segregation.
HARDY-WEINBERG PRINCIPLE
o Formula: p = q = 1
p equals the gene frequency of the dominant allele
q equals the gene frequency of the recessive allele
o p2 + 2pq+ q2 = 1
in this equation p2 is the predicted frequency of homozygous dominant (AA) people in a
population. 2pq is the predicted frequency of heterozygous (Aa) people, and q2 is the
predicted frequency of homozygous recessive (aa) ones.
CRITERIA FOR USE OF THE HARDY-WEINBERG FORMULA
Population studied must be large
Mating among all individuals must be random
Mutations must not occur in parents or offspring
No migration, differential fertility or mortality of genotypes studied
INHERITANCE PATTERNS
It trace the transmission of genetically encoded traits, conditions or diseases to offspring.
There are four types of Mendelian inheritance patterns:
Autosomal dominant
Autosomal recessive
X-linked recessive
X-linked dominant
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT
- Dominant conditions are expressed in individuals who have just one copy of the mutant allele.
- Affected males and females have an equal probability of passing on the trait to offspring.
Affected individuals have one normal copy of the gene and one mutant copy of the gene thus
each offspring has a 50% chance on inheriting the mutant allele.
Autosomal dominant conditions:
Huntington Diseasae
a condroplasia (short-limbed dwarfism)
polycystic kidney disease
AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE
- Recessive conditions are clinically manifest only when an individual has two copies of the
mutant allele.
- When just one copy of the mutant allele is present, an individual is a carrier of the mutation, but
does not develop the condition.
- Females and males are affected equally by traits transmitted by autosomal recessive
inheritance. When two carriers mate, each child has a 25% chance of being homozygous wild
type (unaffected): a mutant (affected): or a 50% chance of being heterozygous (unaffected
carrier).
Autosomal recessive diseases:
Cystic fibrosis
Tay-Sachs
hemochromatosis
phenylketonuria (PKU)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Printable Iphone Case Template Everydaydishes - Com 5 PDFDocumento1 paginaPrintable Iphone Case Template Everydaydishes - Com 5 PDFcyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Ingredients:: Wedding CakeDocumento2 pagineIngredients:: Wedding CakecyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Eggshell As A Chalk - Docx IP NAMO AYAW IDELETE IMPORTANTE NI!!!!Documento4 pagineEggshell As A Chalk - Docx IP NAMO AYAW IDELETE IMPORTANTE NI!!!!cyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- The Problem and Its Scope: Liceo de Cagayan University College of Medical Laboratory ScienceDocumento53 pagineThe Problem and Its Scope: Liceo de Cagayan University College of Medical Laboratory SciencecyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- July 11Documento1 paginaJuly 11cyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Ip2018 Final (Original) Ayaw I Delete!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Documento21 pagineIp2018 Final (Original) Ayaw I Delete!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!cyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Ascaris Lumbricoides Among Children of Barangay Iponan,"Documento11 pagineAscaris Lumbricoides Among Children of Barangay Iponan,"cyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- ExhibitDocumento1 paginaExhibitcyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical TechniqueDocumento1 paginaStatistical TechniquecyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity1science Ayaw I Delete!!!Documento2 pagineActivity1science Ayaw I Delete!!!cyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- BrazilDocumento3 pagineBrazilcyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Requirements Ayaw Idelete!!!!!!!!!!!Documento8 pagineAP Requirements Ayaw Idelete!!!!!!!!!!!cyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Ingredients:: Wedding CakeDocumento2 pagineIngredients:: Wedding CakecyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflective Essay: 1. Marrying at A Very Young AgeDocumento3 pagineReflective Essay: 1. Marrying at A Very Young AgecyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Kelompok 1 Design MediaDocumento2 pagineKelompok 1 Design MediaVira NurmilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Testimonio Rosa HensonDocumento1 paginaTestimonio Rosa HensoncyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- The Problem and Its Scope: Liceo de Cagayan University College of Medical Laboratory ScienceDocumento51 pagineThe Problem and Its Scope: Liceo de Cagayan University College of Medical Laboratory SciencecyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Cryoprecipitate Is Prepared From Plasma and Contains FibrinogenDocumento2 pagineCryoprecipitate Is Prepared From Plasma and Contains FibrinogencyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Requirements Ayaw Idelete!!!!!!!!!!!Documento8 pagineAP Requirements Ayaw Idelete!!!!!!!!!!!cyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- CATEGORY II. Tasks That Involve NODocumento5 pagineCATEGORY II. Tasks That Involve NOcyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials and Methods: Liceo de Cagayan University College of Medical Laboratory ScienceDocumento3 pagineMaterials and Methods: Liceo de Cagayan University College of Medical Laboratory SciencecyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Cryoprecipitate Is Prepared From Plasma and Contains FibrinogenDocumento2 pagineCryoprecipitate Is Prepared From Plasma and Contains FibrinogencyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Histo-Biographical Criticism: "Footnote To Youth" by Jose Garcia VillaDocumento2 pagineHisto-Biographical Criticism: "Footnote To Youth" by Jose Garcia VillacyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Define: Gaucher's Disease: AnemiaDocumento7 pagineDefine: Gaucher's Disease: AnemiacyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Parasitology A Practical Approach, 2E LEDocumento3 pagineClinical Parasitology A Practical Approach, 2E LEcyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Cestodes and ArthropodsDocumento7 pagineCestodes and ArthropodscyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Requirements Ayaw Idelete!!!!!!!!!!!Documento8 pagineAP Requirements Ayaw Idelete!!!!!!!!!!!cyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Colonial Authors of The PhilippinesDocumento1 paginaColonial Authors of The PhilippinescyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Cestodes and ArthropodsDocumento7 pagineCestodes and ArthropodscyrelleNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Mod 2 MC - GSM, GPRSDocumento61 pagineMod 2 MC - GSM, GPRSIrene JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- Saeed Sentence Relation and Truth (Summary)Documento11 pagineSaeed Sentence Relation and Truth (Summary)Mohammad Hassan100% (1)
- Synopsis SsDocumento14 pagineSynopsis SsJYOTI KATIYAR SVUNessuna valutazione finora
- COE301 Lab 2 Introduction MIPS AssemblyDocumento7 pagineCOE301 Lab 2 Introduction MIPS AssemblyItz Sami UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Maintaining Godly Spirituality in The Face of ChallengesDocumento3 pagineMaintaining Godly Spirituality in The Face of ChallengesDavid OmoniyiNessuna valutazione finora
- DCNF Vs Hhs Nov 2020Documento302 pagineDCNF Vs Hhs Nov 2020SY LodhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Classroom Activty Rubrics Classroom Activty Rubrics: Total TotalDocumento1 paginaClassroom Activty Rubrics Classroom Activty Rubrics: Total TotalMay Almerez- WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis Statement On Lionel MessiDocumento4 pagineThesis Statement On Lionel Messidwham6h1100% (2)
- Guide For Sustainable Design of NEOM CityDocumento76 pagineGuide For Sustainable Design of NEOM Cityxiaowei tuNessuna valutazione finora
- 555 TimerDocumento25 pagine555 TimerDr-Muhammad Aqeel AslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Stress InterventionsDocumento5 pagineJob Stress InterventionscocaralucamihaelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Probset 3 KeyDocumento7 pagineProbset 3 KeyhoneyschuNessuna valutazione finora
- MICRF230Documento20 pagineMICRF230Amador Garcia IIINessuna valutazione finora
- Weather Prediction Using Machine Learning TechniquessDocumento53 pagineWeather Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniquessbakiz89Nessuna valutazione finora
- ARMY - Chapter Eight Explosive BreachingDocumento25 pagineARMY - Chapter Eight Explosive Breachingrsreeth100% (1)
- Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education. Academic Monitoring Department ProfileDocumento14 pagineMaharashtra State Board of Technical Education. Academic Monitoring Department Profilevspd2010Nessuna valutazione finora
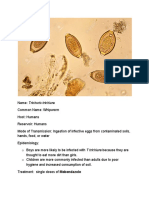
- Instruction Manual Il-Obct-R1: Slip-Over Current Transformer ObctDocumento2 pagineInstruction Manual Il-Obct-R1: Slip-Over Current Transformer Obctبوحميدة كمالNessuna valutazione finora
- Forlong - Rivers of LifeDocumento618 pagineForlong - Rivers of LifeCelephaïs Press / Unspeakable Press (Leng)100% (15)
- Capacitor Trip Device CTD-4Documento2 pagineCapacitor Trip Device CTD-4DAS1300Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5: Current and Resistance: 5.1 The Motion of Electric ChargeDocumento11 pagineChapter 5: Current and Resistance: 5.1 The Motion of Electric Chargeayunna ayunniNessuna valutazione finora
- ELS 15 Maret 2022 REVDocumento14 pagineELS 15 Maret 2022 REVhelto perdanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rizal Noli Me TangereDocumento35 pagineRizal Noli Me TangereKristine Cantilero100% (2)
- Quiz EditedDocumento6 pagineQuiz EditedAbigail LeronNessuna valutazione finora
- PNP Loan Application Form February 2021 16Documento6 paginePNP Loan Application Form February 2021 16Wilhelm RegaladoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulics Sheet 5 Energy ADocumento19 pagineHydraulics Sheet 5 Energy AMohamed H AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypoglycemia After Gastric Bypass Surgery. Current Concepts and Controversies 2018Documento12 pagineHypoglycemia After Gastric Bypass Surgery. Current Concepts and Controversies 2018Rio RomaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1941 Iraq and The IlluminatiDocumento4 pagine1941 Iraq and The IlluminatiZaneWeltonNessuna valutazione finora
- On The Margins - A Study of The Experiences of Transgender College StudentsDocumento14 pagineOn The Margins - A Study of The Experiences of Transgender College StudentsRory J. BlankNessuna valutazione finora
- Competent Testing Requirements As Per Factory ActDocumento3 pagineCompetent Testing Requirements As Per Factory Actamit_lunia100% (1)
- Symmetrir and Order. Reasons To Live According The LodgeDocumento6 pagineSymmetrir and Order. Reasons To Live According The LodgeAnonymous zfNrN9NdNessuna valutazione finora