Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Furosemide: Online Audio
Caricato da
Dani Philip0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
20 visualizzazioni4 pagineHui
Titolo originale
Furosemide
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoHui
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
20 visualizzazioni4 pagineFurosemide: Online Audio
Caricato da
Dani PhilipHui
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 4
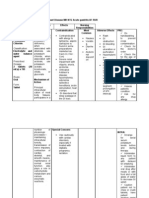
Furosemide
Pronunciation:
fur-oh-se-mide
Online audio
Trade Name(s)
• Lasix
Pregnancy Category
CategorY. C
Ther. Class.
diuretics
Pharm. Class.
loop di u reties
• Edema due to heart failure, hepatic impairment or
renal disease.
• Hypertension.
• Inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and chloride
from the loop of Henle and distal renal tubule.
• Increases renal excretion of water, sodium, chloride,
magnesium, potassium , and calcium.
• Effectiveness persists in impaired renal function .
Therapeutic Effect( s):
• Diuresis and subsequent mobilization of excess
fluid (edema, pleural effusions).
• Decreased BP.
Absorption: 60-67°/o absorbed after oral
administration (1 in acute HF and in renal failure); also
absorbed from IM sites.
Distribution: Crosses placenta, enters breast milk.
Protein Binding: 91-99°/o.
Metabolism and Excretion: Minimally metabolized
by liver, some nonhepatic metabolism, some renal
excretion as unchanged drug.
Half-life: 30-60 min (i in renal impairment).
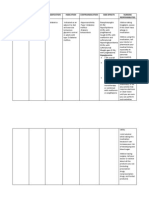
TIME/ACTION PROFILE (diuretic effect)
ROUTE ONSET PEAK DURATION
PO 30- 60 min 1- 2 hr 6- 8 hr
IM 10-30 min unknown 4-8 hr
IV 5 min 30 min 2 hr
Contraindicated in:
• Hypersensitivity;
• Cross-sensitivity with thiazides and sulfonamides
may occur;
• Hepatic coma or anuria;
• Some liquid products may contain alcohol, avoid in
patients with alcohol intolerance.
Use Cautiously in:
• Severe liver disease (may precipitate hepatic coma;
concurrent use with potassium-sparing diuretics
may be necessary);
• Electrolyte depletion;
• Diabetes mellitus;
• Hypoprotei nemia (j risk of ototoxicity);
• Severe renal impairment (j risk of ototoxicity);
• OB: Lactation: Safety not established;
• Pedi: j risk for renal calculi and patent ductus
arteriosis in premature neonates;
• Geri: May have j risk of side effects, especially
hypotension and electrolyte imbalance, at usual
doses.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
CNS: blurred vision, dizziness, headache, vertigo
EENT: hearing loss, tinnitus
CV: hypotension
GI: anorexia, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth,
dyspepsia, j liver enzymes, nausea, pancreatitis,
vomiting
GU: j BUN, excessive urination, nephrocalcinosis
Derm: ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME , STEVENS -
JOHNSON SYNDROME , TOXIC EPIDERMAL
NECROLYSIS , photosensitivity, pruritis, rash, urticaria
Endo: hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia,
hypertriglyceridemia, hyperuricemia
F and E: dehydration, hypocalcemia, hypochloremia,
hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hyponatremia,
hypovolemia, metabolic alkalosis
Hemat: APLASTIC ANEMIA , AGRANULOCYTOSIS ,
hemolytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
MS: muscle cramps
Neuro: paresthesia
Misc: fever
* CAPITALS indicate life-threatening.
Italics indicate most frequent.
• Instruct patient to take furosemide as directed. Take
missed doses as soon as possible; do not double
doses.
o Caution patient to change positions slowly to
minimize orthostatic hypotension. Caution
patient that the use of alcohol, exercise during
hot weather, or standing for long periods during
therapy may enhance orthostatic hypotension .
o Instruct patient to consult health care
professional regarding a diet high in potassium
(see food sources for SRecific nutrients ).
o Advise patient to contact health care
professional of weight gain more than 3 lbs in 1
day.
o Instruct patient to notify health care professional
of all Rx or OTC medications, vitamins, or herbal
products being taken and to consult health care
professional before taking any OTC medications
concurrently with this therapy.
o Instruct patient to notify health care professional
of medication regimen before treatment or
surgery.
o Caution patient to use sunscreen and protective
clothing to prevent photosensitivity reactions.
o Advise patient to contact health care
professional immediately if rash, muscle
weakness, cramps, nausea, dizziness,
numbness , or tingling of extremities occurs.
o Advise diabetic patients to monitor blood
glucose closely; may cause increased blood
glucose levels.
o Emphasize the importance of routine follow-up
examinations.
o Geri: Caution older patients or their caregivers
about increased risk for falls. Suggest strategies
for fall prevention.
• Hypertension: Advise patients on antihypertensive
regimen to continue taking medication even if
feeling better. Furosemide controls but does not
cure hypertension .
o Reinforce the need to continue additional
therapies for hypertension (weight loss ,
exercise, restricted sodium intake, stress
reduction, regular exercise, moderation of
alcohol consumption, cessation of smoking).
• Decrease in edema.
o Decrease in abdominal girth and weight.
o Increase in urinary output.
• Decrease in BP.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsDocumento5 pagineGeneric Name: Brand Name: Lasix Classification: Loop DiureticsKat ZNessuna valutazione finora
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesDa EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Drug Study (MS)Documento9 pagineDrug Study (MS)Kristine GallardoNessuna valutazione finora
- HydrochlorothiazideDocumento3 pagineHydrochlorothiazideapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcDa EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento44 pagineDrug StudyLohrhen Lheighh CahreeniyowNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento8 pagineDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetic Cooking for One and TwoDa EverandDiabetic Cooking for One and TwoValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- ANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Documento5 pagineANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Rhanne BolanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Bumetanide (Drug Study)Documento2 pagineBumetanide (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse68880% (1)
- Oral meds: Drug dosages, mechanisms, effectsDocumento15 pagineOral meds: Drug dosages, mechanisms, effectsitsmechachaNessuna valutazione finora
- CVA Drug StudyDocumento51 pagineCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNessuna valutazione finora
- IrbesartanDocumento3 pagineIrbesartanapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Medication ListDocumento181 pagineClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Drugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcDocumento12 pagineDrugs Study of Omeprazole, Metoclopramide EtcMargaret Cortinas75% (4)
- FurosemideDocumento4 pagineFurosemideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Pravastatin SodiumDocumento3 paginePravastatin Sodiumapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- Losartan PotassiumDocumento3 pagineLosartan Potassiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- Pharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardDocumento7 paginePharmacological: Drug Features Therapeutic Effects Nursing Responsibilities Indication Contraindication Desired UntowardyannahmaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento10 pagineDrug StudyHelen ReonalNessuna valutazione finora
- GemfibrozilDocumento3 pagineGemfibrozilapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- PALMARES Drug StudyDocumento13 paginePALMARES Drug StudyIvan Jules P. PALMARESNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study ICUDocumento4 pagineDrug Study ICUArthadian De PeraltaNessuna valutazione finora
- Doxazosin MesylateDocumento2 pagineDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento17 pagineDrug StudyJoan RabeNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento11 pagineDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Valproic AcidDocumento4 pagineValproic Acidapi-3797941100% (2)
- Diuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEDocumento12 pagineDiuretics: Generic Name: FUROSEMIDEJR BetonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesDocumento11 pagineDrug Classificat ION Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing Considerations Sodium Chloride DosagesBernie Evan Oidem ForlajeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyclophospha mide, Cisplastin, Doxorubicin Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento4 pagineCyclophospha mide, Cisplastin, Doxorubicin Nursing ResponsibilitiesAlexis Abigail de LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- FurosemideDocumento2 pagineFurosemideJm RomancapNessuna valutazione finora
- DrugsDocumento20 pagineDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- BumetanideDocumento3 pagineBumetanideapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- LithiumDocumento4 pagineLithiumapi-3797941100% (1)
- CVS PART 1 DiureticsDocumento31 pagineCVS PART 1 Diureticshishamasmaa5Nessuna valutazione finora
- ValsartanDocumento3 pagineValsartanapi-3797941100% (1)
- LasixDocumento1 paginaLasixKatie McPeek100% (2)
- Ix. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDocumento21 pagineIx. Pharmacologic Management Brand Name Classification Indication Mechanism of Action Dosage and Frequency Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationDizerine Mirafuentes RolidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento12 pagineDrug Dosage, Classification, Indications, and Nursing ResponsibilitiesCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Name of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocumento11 pagineName of Drug Action Indication Contra-Indication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMalou SanNessuna valutazione finora
- CNS: GI: Assessment & Drug Effects: Generic Name Brand Name Indications Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento4 pagineCNS: GI: Assessment & Drug Effects: Generic Name Brand Name Indications Action Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJon Adam Bermudez SamatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ditropan Drug CardDocumento2 pagineDitropan Drug CardBenNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento9 pagineDrug StudyOdarp PradzNessuna valutazione finora
- TriamtereneDocumento2 pagineTriamtereneapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- FenofibrateDocumento3 pagineFenofibrateapi-3797941100% (1)
- Febuxostat lowers uric acid for goutDocumento2 pagineFebuxostat lowers uric acid for goutJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- ValdecoxibDocumento3 pagineValdecoxibapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lascuna-Drug StudyDocumento8 pagineLascuna-Drug StudyAiza Pearl LascuñaNessuna valutazione finora
- CarbamazepineDocumento5 pagineCarbamazepineapi-3797941100% (2)
- SpironolactoneDocumento3 pagineSpironolactoneapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- C C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentDocumento12 pagineC C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentEarl Tony TrinidadNessuna valutazione finora
- DrugsDocumento17 pagineDrugsRenzkie GeronimoNessuna valutazione finora
- Meperidine Hydro ChlorideDocumento4 pagineMeperidine Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chlorpheniramine MaleateDocumento3 pagineChlorpheniramine Maleateapi-3797941100% (1)
- NCP DrugDocumento13 pagineNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento14 pagineDrug StudyTin BernardezNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Mechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento31 pagineDrug Mechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesiamjenivicNessuna valutazione finora
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Childhood Obesity in IndiaDocumento34 paginePrevalence and Risk Factors of Childhood Obesity in IndiaDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Holistic care model for hospitalized preschoolersDocumento8 pagineHolistic care model for hospitalized preschoolersDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Accurate Assessment of Patient Weight - Nursing TimesDocumento7 pagineAccurate Assessment of Patient Weight - Nursing TimesDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendices Appendices Appendices AppendicesDocumento21 pagineAppendices Appendices Appendices AppendicesDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Records and Registers To Be Maintained at School Level Related To RmsaDocumento6 pagineRecords and Registers To Be Maintained at School Level Related To RmsaDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- CPR Questionnaire - Essential First Aid StepsDocumento1 paginaCPR Questionnaire - Essential First Aid StepsDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Vit StaDocumento6 pagineVit StaDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Article 03Documento8 pagineArticle 03Dani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Ob PDFDocumento25 pagineOb PDFDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Sharda Hospital Clinical Material Report for October 2016Documento1 paginaSharda Hospital Clinical Material Report for October 2016Dani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Research TopicsDocumento1 paginaResearch TopicsDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- UpdateRequestFormV2 PDFDocumento2 pagineUpdateRequestFormV2 PDFeceprinceNessuna valutazione finora
- A.P.J Abdul Kalam The Visionary of India) On 15: Time Venue: Block - 4, 3Documento1 paginaA.P.J Abdul Kalam The Visionary of India) On 15: Time Venue: Block - 4, 3Dani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 N235 33824Documento22 pagine05 N235 33824Dani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- CPR Questionnaire - Essential First Aid StepsDocumento1 paginaCPR Questionnaire - Essential First Aid StepsDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- May 2016Documento18 pagineMay 2016Dani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Codeofethicsppt 150907030516 Lva1 App6892Documento57 pagineCodeofethicsppt 150907030516 Lva1 App6892Dani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Dosage and IV Rates Calculations PDFDocumento6 pagineDrug Dosage and IV Rates Calculations PDFvarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix DDocumento5 pagineAppendix DcerisimNessuna valutazione finora
- Care Plan Criteria For Evlauation NOWDocumento1 paginaCare Plan Criteria For Evlauation NOWDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix I Faculty Evaluation System General InformationDocumento11 pagineAppendix I Faculty Evaluation System General InformationDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical RubricDocumento5 pagineClinical RubricDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical RubricDocumento5 pagineClinical RubricDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Trendsandissuesinnursingcompatibilitymode 120712052718 Phpapp01Documento24 pagineTrendsandissuesinnursingcompatibilitymode 120712052718 Phpapp01Dani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- STEAM INHALATION RELIEFDocumento4 pagineSTEAM INHALATION RELIEFDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Transportation For ResearchDocumento2 pagineTransportation For ResearchDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- School Stock Register TemplatesDocumento10 pagineSchool Stock Register TemplatesDebasis SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Article Wjpps 1417425593Documento10 pagineArticle Wjpps 1417425593Dani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Records and Registers To Be Maintained at School Level Related To RmsaDocumento6 pagineRecords and Registers To Be Maintained at School Level Related To RmsaDani PhilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem SetDocumento2 pagineProblem Sethlc34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gingival Periodontal IndexDocumento23 pagineGingival Periodontal Indexxodia_04100% (3)
- PASSIVE MOVEMENT TECHNIQUESDocumento58 paginePASSIVE MOVEMENT TECHNIQUESabdulahNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Injury Fact SheetDocumento1 paginaBrain Injury Fact SheetAnonymous NUidh1TiuNessuna valutazione finora
- English Assessment Physiotherapy & History Taking Dialogue EnglishDocumento4 pagineEnglish Assessment Physiotherapy & History Taking Dialogue EnglishRobby FahrezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Review - Bio 172Documento21 pagineFinal Exam Review - Bio 172Erin McElhaney QuirkNessuna valutazione finora
- TCM Patent-Study Guide - FinalDocumento9 pagineTCM Patent-Study Guide - FinalpranajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Cardiac Patients: History TakingDocumento31 paginePediatric Cardiac Patients: History TakingnovylatifahNessuna valutazione finora
- Prevalence of Gestational Diabetes and Contributing Factors Among Pregnant Jordanian Women Attending Jordan University HospitalDocumento8 paginePrevalence of Gestational Diabetes and Contributing Factors Among Pregnant Jordanian Women Attending Jordan University HospitalManar ShamielhNessuna valutazione finora
- Combination of Lisinopril and Nifedipine GITS.10Documento7 pagineCombination of Lisinopril and Nifedipine GITS.10Andi PermanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Renr Practice Test 9 FinalDocumento12 pagineRenr Practice Test 9 FinalTk100% (2)
- Clinical Practice Guideline for Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic InsomniaDocumento43 pagineClinical Practice Guideline for Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic InsomniaAna Cristina BrazNessuna valutazione finora
- Merged Document 14 PDFDocumento9 pagineMerged Document 14 PDFMurali SmatNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrients: Anemia of Chronic Diseases: Wider Diagnostics-Better Treatment?Documento17 pagineNutrients: Anemia of Chronic Diseases: Wider Diagnostics-Better Treatment?Gufront MustofaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Fermentation of Dairy ProductsDocumento4 pagineAdvantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Fermentation of Dairy ProductsEkoh EnduranceNessuna valutazione finora
- CL (Mr. Von) Mathematics (Mr. Ryan) : Trivia QuestionsDocumento2 pagineCL (Mr. Von) Mathematics (Mr. Ryan) : Trivia QuestionsRichard Andrew Abratique DandanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry Importance for NursesDocumento15 pagineBiochemistry Importance for NursesJulius Memeg PanayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Peds Shelf NotesDocumento88 paginePeds Shelf Notesskeebs23100% (8)
- Kala-Azar (Leishmaniasis) Symptoms, Signs, DiagnosisDocumento36 pagineKala-Azar (Leishmaniasis) Symptoms, Signs, Diagnosisatulbd2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic/Nephritic Syndrome: AK. Soyibo Department of Medicine Review ClassDocumento143 pagineNephrotic/Nephritic Syndrome: AK. Soyibo Department of Medicine Review ClassKay BristolNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecart Medications and EquipmentDocumento9 pagineEcart Medications and EquipmentJan Philippe BelandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Postpartum Hemorrhage Nursing CareDocumento3 paginePostpartum Hemorrhage Nursing CareClaire Canapi BattadNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Hygene and SanitationDocumento22 pagine1 Hygene and SanitationJammil Ud-ulonNessuna valutazione finora
- CHC Jawa Hub: Jawa, Rewa, Madhya Pradesh Rewa Madhya Pradesh - 486223 Phone No.Documento2 pagineCHC Jawa Hub: Jawa, Rewa, Madhya Pradesh Rewa Madhya Pradesh - 486223 Phone No.MAHESH GAUTAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Bailey's Othorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck SurgeryDocumento3.775 pagineBailey's Othorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck SurgeryDr. Christian Dimitrov92% (12)
- Head Eyes: Head To Toe AssessmentDocumento2 pagineHead Eyes: Head To Toe AssessmentVijungco88% (8)
- Advances and Challenges in Stroke RehabilitationDocumento13 pagineAdvances and Challenges in Stroke Rehabilitationarif 2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Toxins: Use of Botulinum Toxin in Orofacial Clinical PracticeDocumento16 pagineToxins: Use of Botulinum Toxin in Orofacial Clinical PracticeAfiliado LendárioNessuna valutazione finora
- Hyper-Reflexia in Guillain - Barré Syndrome: Systematic ReviewDocumento7 pagineHyper-Reflexia in Guillain - Barré Syndrome: Systematic ReviewVladimir BasurtoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dan Gelber Letter To Gov. Ron DeSantisDocumento2 pagineDan Gelber Letter To Gov. Ron DeSantisPeterBurkeNessuna valutazione finora
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDa EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (402)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDa EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (327)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDa EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (13)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesDa EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementDa EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDa EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDa EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDa EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDa EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDa EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingDa EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDa EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDa EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (31)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDa EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (169)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDa EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsDa EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (41)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossDa EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Da EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)