Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Chapter - 6 History Peasants and Farmers
Caricato da
bharath pachipenta0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
12 visualizzazioni2 pagineTitolo originale
his_6.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
12 visualizzazioni2 pagineChapter - 6 History Peasants and Farmers
Caricato da
bharath pachipentaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
Chapter – 6 History
Peasants and Farmers
OPEN FIELDS AND COMMON LAND
• Peasants cultivated open fields which were strips of land near their villages. These strips
were of varying quality. This was a measure to ensure that everyone had a mix of good and
bad land. Beyond these strips lay common land which was used by all to graze cattle, gather
fruits and berries and firewood.
This began to change from the 16th century. Wool became important. Farmers began to
enclose fields to improve sheep breeds and ensure good feed. With enclosed fields there was
no concept of common land. This changed the entire landscape of England.
• Thrust in Grain Cultivation: From the mid-18th century onwards enclosures became
different. They were now for grain cultivation. English population was expanding and Britain
was industrialising. People moved to urban areas. Lesser people had to produce more grains.
The market for foodgrain expanded. Foodgrain prices rose. This encouraged landowner to
enclose lands and enlarge the area under grain cultivation.
• Enclosures: Foodgrain production increased as much as population. England was producing
almost 80% of the foodgrain the population consumed. Crop production received a boost
through various crop rotation techniques. Enclosures allowed landowners to expand the land
under their control and produce more for the market.
• The Farmers — The Poor: The poor no longer had access to the commons. They were
displaced from their lands and found their customary rights disappearing. Work became
uncertain, insecure and income unstable.
• Dependency on Machines — The Thresher: During the Napoleonic wars the threshing
machine was introduced to lessen dependency on labour and increase production. After the
Napoleonic wars ended soldiers returned home but found no work. At the same time an
agricultural depression set in. There was agricultural surplus and labourers without work.
BREAD BASKET AND DUST BOWL
• America the Land of Promises: During the time of enclosed fields in England, in the USA, the
white American settlers were confined to a small narrow strip in the east. By early 20th
century, these Americans moved westward. America was seen as a land of promises. The
American Indians were forced to give up their land and move westward. The white
Americans now moved westward, cleared land and cultivated wheat.
• The Demand for Wheat: From the late 19th century onwards there was a population
increase. Export market in wheat was also becoming bigger. Demand for wheat increased.
Wheat supply from Russia was cut off. During the First World War the wheat market boomed.
• The Introduction of Inventions: New technology was introduced which aimed at increasing
production. Tractors, disk ploughs, mechanical reapers, combine harvesters, etc., began to be
used.
• The Poor: The machines spelt misery for the poor farmers. Many bought machines on loan
which they could not pay later. Jobs were difficult to find. Production expanded and soon
there was surplus. Wheat prices fell and export markets were adversely affected. The Great
American Depression ruined the farmers in the 1930s.
• Dust Bowl: In the 1930s, great dust storms were experienced. These killed cattle and
destroyed land. Farmers had cleared land of grass which rendered large areas of land
coverless and dry. The sod was broken into dust.
THE INDIAN FARMER AND OPIUM PRODUCTION
• Trade with China: Opium production in India is directly linked to the British trade with
China. The western merchants wanted to balance their trade with China and hence searched
for a commodity that could sell in China. The English bought tea from China and the Chinese
bought opium from them.
• The Opium — Its Source — India: The Indian peasants were forced to grow opium. The
British government bought this opium from them at nominal rates.
• Unwilling Cultivators: The cultivators were unwilling to produce opium for various reasons:
• opium required fertile land
• rates paid by the British were very low
• it required looking after
The British discovered that opium produced in British territories was declining whereas in
territories not under British rule the production was increasing. Traders were selling opium
directly to China. This forced the British to establish its monopoly over this trade.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Exam Form 2Documento23 pagineExam Form 2Didi Gump EddieNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Colonization of AmericaDocumento52 pagine1 Colonization of Americamarinusm100% (1)
- Complete Saas PresentationDocumento36 pagineComplete Saas PresentationDavid BandaNessuna valutazione finora
- EndorsementsDocumento16 pagineEndorsementsHarish Kapoor50% (2)
- An Edible History of Humanity NotesDocumento4 pagineAn Edible History of Humanity NotesPeter Wilson38% (21)
- Powerpoint On The PeasantryDocumento29 paginePowerpoint On The Peasantrymausernameaintunique80% (10)
- Starving the South: How the North Won the Civil WarDa EverandStarving the South: How the North Won the Civil WarValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (12)
- British Agricultural RevolutionDocumento8 pagineBritish Agricultural RevolutionviahulNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Data Analytics Methods and Applications Jovan PehcevskiDocumento430 pagineBig Data Analytics Methods and Applications Jovan Pehcevskihizem chaima100% (2)
- CBSE Class 10 History Notes Chapter 3 - The Making of A Global WorldDocumento8 pagineCBSE Class 10 History Notes Chapter 3 - The Making of A Global WorldGitika DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Audit and Assurance Paper p7 UpdatedDocumento172 pagineAdvanced Audit and Assurance Paper p7 UpdatedAdelodun Tesleem AladeNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampel For CAT 2022Documento15 pagineSampel For CAT 2022Vidhi ChoithaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Direct MarketingDocumento14 pagineIntroduction To Direct Marketingvishal_shekhar2416Nessuna valutazione finora
- Euro Chapter 19 Study GuideDocumento3 pagineEuro Chapter 19 Study GuideLili PengNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes of CH 6 Peasants and Farmers Class 9th HistoryDocumento9 pagineNotes of CH 6 Peasants and Farmers Class 9th Historynareshpolai07Nessuna valutazione finora
- How Did The World Go From That?Documento76 pagineHow Did The World Go From That?saxapilNessuna valutazione finora
- Economic SystemDocumento8 pagineEconomic SystemAparupa RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Making of A Global World Part 2Documento18 pagineThe Making of A Global World Part 2amulyajadhav119Nessuna valutazione finora
- Agrarian RevolutionDocumento33 pagineAgrarian Revolutionkwezi kennedyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Industrial RevolutionDocumento5 pagineThe Industrial RevolutionStefania SchmidtNessuna valutazione finora
- INDUSTRIALREVDocumento16 pagineINDUSTRIALREVIshana DasguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Agricultural Development in The British-North American ColoniesDocumento22 pagineAgricultural Development in The British-North American ColoniesCoté PizarroNessuna valutazione finora
- The Making of A Global WorldDocumento26 pagineThe Making of A Global Worldatanush619Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Making of A Global WorldDocumento21 pagineThe Making of A Global WorldKeerthana AdarshNessuna valutazione finora
- The Agrarian Revolution PPT 2023 (New)Documento9 pagineThe Agrarian Revolution PPT 2023 (New)renaebroomfield43Nessuna valutazione finora
- Colonialism and The Countryside: Exploring Official ArchivesDocumento47 pagineColonialism and The Countryside: Exploring Official Archivesmonika singh100% (3)
- European Rule (1760AD - 1947AD)Documento12 pagineEuropean Rule (1760AD - 1947AD)Oyon Nur newazNessuna valutazione finora
- Jesse Braden - NHD PaperDocumento8 pagineJesse Braden - NHD Paperapi-445711360Nessuna valutazione finora
- Deterioration of AgricultureDocumento3 pagineDeterioration of AgricultureMadhavan SeenivasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Revolution 1750 1850Documento25 pagineIndustrial Revolution 1750 1850Ryan KeeneyNessuna valutazione finora
- History - LS - 3 - Ruling Our CountrysideDocumento12 pagineHistory - LS - 3 - Ruling Our CountrysideTanviNessuna valutazione finora
- The Agrarian Revolution in BritainDocumento4 pagineThe Agrarian Revolution in BritainTaaboNessuna valutazione finora
- Agriculture 2Documento30 pagineAgriculture 2Jomar CasolNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pre Modern World: InstagramDocumento10 pagineThe Pre Modern World: InstagramHarsh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Novel and Its HistoryDocumento26 pagineNovel and Its HistoryDhruv Singh ShekhawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes For U.S. HistoryDocumento13 pagineNotes For U.S. Historyisabella.collins.03Nessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Baking-Wps OfficeDocumento18 pagineAdvanced Baking-Wps OfficeJoshua LatoyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Industrial Revolution Notes 2022Documento14 pagineThe Industrial Revolution Notes 2022MichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- The Establishment of The Peasantry 1838 To 1900Documento4 pagineThe Establishment of The Peasantry 1838 To 1900Aswani HarrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Revolution-Arg PlantationDocumento4 pagineIndustrial Revolution-Arg Plantationapi-250076624Nessuna valutazione finora
- ESD Module2011Documento112 pagineESD Module2011backtrxNessuna valutazione finora
- Wk2 - BritishColony and SlaveryDocumento28 pagineWk2 - BritishColony and SlaveryTempleton KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Growth OF Agriculture During British RuleDocumento11 pagineGrowth OF Agriculture During British RulehasratsandhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ruling The Country SideDocumento4 pagineRuling The Country SideAnonymous S1YCc9GNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Science Class-XDocumento22 pagineSocial Science Class-Xdhdahanuwala100% (1)
- THE WAY WEST (Chapter 13 Notes.)Documento5 pagineTHE WAY WEST (Chapter 13 Notes.)swampfsNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 3 HistoryDocumento5 pagineCH 3 HistoryDev BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- Popular Resistance To The British Rule: Module - 1Documento22 paginePopular Resistance To The British Rule: Module - 1SatyajitMohapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- 10-18th Century Economy and SocietyDocumento26 pagine10-18th Century Economy and SocietyThatKidNessuna valutazione finora
- ESD Module2011Documento109 pagineESD Module2011MetroNation808Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10agriculture2Documento33 pagineChapter 10agriculture2venki420Nessuna valutazione finora
- IEPH All SlidesDocumento13 pagineIEPH All SlidesKaushik SomaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 19 Study GuideDocumento8 pagineChapter 19 Study GuideAlice LiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Failed Colonies and Early Successful English Settlements in North AmericaDocumento49 pagineFailed Colonies and Early Successful English Settlements in North AmericaLucas AccastelloNessuna valutazione finora
- AgeofIndustrialisation-StudyMaterial 7692Documento10 pagineAgeofIndustrialisation-StudyMaterial 7692Roopa UNessuna valutazione finora
- Changes in AgricultureDocumento26 pagineChanges in AgricultureDwight Jr GibbsNessuna valutazione finora
- 10th HistoryDocumento117 pagine10th HistoryDhiraj Kumar SarafNessuna valutazione finora
- British Colonialism and War of Independence 1857Documento11 pagineBritish Colonialism and War of Independence 1857abdullah shahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Dust BowlDocumento3 pagineDust Bowlapi-629862469Nessuna valutazione finora
- ESD Module2011Documento109 pagineESD Module2011Tafadzwa ChikombaNessuna valutazione finora
- Food, Land & People in A Changing America: The Story of American AgricultureDocumento22 pagineFood, Land & People in A Changing America: The Story of American AgriculturehanskokoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ied CH.1Documento11 pagineIed CH.1Tanya AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 History PPT Grade 9 Term 1Documento137 pagine2020 History PPT Grade 9 Term 1Chloe van der MerweNessuna valutazione finora
- A Short History of English AgricultureDa EverandA Short History of English AgricultureNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-7 History History and Sport: The Story of Cricket: ConceptsDocumento3 pagineChapter-7 History History and Sport: The Story of Cricket: Conceptsbharath pachipentaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 4 History Forest Society and ColonialismDocumento3 pagineChapter - 4 History Forest Society and Colonialismbharath pachipentaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-8 History Clothing: A Social HistoryDocumento2 pagineChapter-8 History Clothing: A Social Historybharath pachipentaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 10 History The Changing World of Visual Arts: New Forms of Imperial ArtDocumento3 pagineChapter - 10 History The Changing World of Visual Arts: New Forms of Imperial Artbharath pachipentaNessuna valutazione finora
- Soyouwanttobean Economics Journalist?Documento357 pagineSoyouwanttobean Economics Journalist?l 0Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formulaire Accepteur Agrege Marchand English VERSIONDocumento2 pagineFormulaire Accepteur Agrege Marchand English VERSIONGerald NONDIANessuna valutazione finora
- MD - Lutful MamunDocumento47 pagineMD - Lutful MamunNafiz FahimNessuna valutazione finora
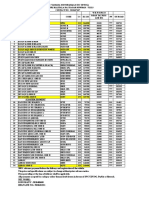
- Account StatementDocumento7 pagineAccount Statementbilieber.billieNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Management Term PaperDocumento18 pagineMarketing Management Term PaperSamiraNessuna valutazione finora
- NATO STO CPoW 2021Documento71 pagineNATO STO CPoW 2021iagaruNessuna valutazione finora
- April 202 FdA Business Environment Assignment 2 L4 AmendedDocumento5 pagineApril 202 FdA Business Environment Assignment 2 L4 AmendedHussein MubasshirNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento1 paginaUntitledReplacement AccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Simulation Assigment 2Documento8 pagineBusiness Simulation Assigment 2steven msusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Innovation in Nursing: A Concept Analysis: January 2016Documento5 pagineInnovation in Nursing: A Concept Analysis: January 2016shejila c hNessuna valutazione finora
- DownloadDocumento2 pagineDownloadJOCKEY 2908Nessuna valutazione finora
- ECO 210 - MacroeconomicsDocumento5 pagineECO 210 - MacroeconomicsRahul raj SahNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Economics (Banking and Financial Markets) Online MSCDocumento2 pagineApplied Economics (Banking and Financial Markets) Online MSCSami GulemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mahalwari Abd Ryotwari SystemDocumento10 pagineMahalwari Abd Ryotwari SystemHarper companyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1e1 S4hana2022 BPD en UsDocumento60 pagine1e1 S4hana2022 BPD en UsprajeethNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Teacher ContractDocumento3 pagineForeign Teacher ContractMuntana Tewpaingam100% (1)
- LAW485Documento4 pagineLAW485Rabiatul AdawiyahNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Studies Grade 9 PDFDocumento9 pagineSocial Studies Grade 9 PDFJudith BandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mishbahul AzmanDocumento4 pagineMishbahul AzmanHarlis NasutionNessuna valutazione finora
- Nov-Dec 2011Documento9 pagineNov-Dec 2011Usuf JabedNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit Program Licensing TermsDocumento8 pagineAudit Program Licensing TermsPrem Prakash PoddarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mooe School Forms 2020Documento48 pagineMooe School Forms 2020KrisPaulineSantuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Increasing Financial Literacy Among Senior High School Non Abm Students Through Interactive MultimediaDocumento11 pagineIncreasing Financial Literacy Among Senior High School Non Abm Students Through Interactive MultimediaTcherKamilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Massey & Gail Fee Petition - LTLDocumento74 pagineMassey & Gail Fee Petition - LTLKirk HartleyNessuna valutazione finora