Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Number Theory Worksheet
Caricato da
Keri-ann MillarCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Number Theory Worksheet
Caricato da
Keri-ann MillarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
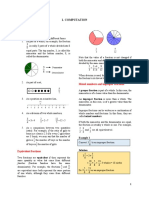
CSEC Mathematics
SECTION 1 – Number Theory and Computation
Number Theory
What is a number?
A number is an arithmetical value, expressed by a word, symbol, or figure, representing a particular
quantity and used in counting and making calculations.
Numbers are a fascinating part of our lives. They are much more a part of our everyday life than we
might realize and would affect many things you might not realize.
Consider your daily routine.
What would life be without numbers?
How would you be affected if no numbers existed?
Types of Numbers
real numbers, factors, even numbers, prime numbers, complex numbers, whole numbers,
irrational numbers, natural numbers, rational numbers, odd numbers, integers, multiples,
composite numbers
Exercise
Use the list of words or phrases above to fill in the blanks for each question below. You are allowed to
use each only once.
1. The set of ____________ is another name given to the set of counting numbers. It is represented by
the symbol N. N = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, …}.
2. The set of ______________ is the set of natural or counting numbers and zero. It is represented by
the symbol W. W = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …}.
3. The set of _______________is the set of numbers that is exactly divisible by two. For example, {2,
4, 6, 8, 10, 12, …}.
4. The set of ______________is the set of numbers which cannot be exactly divided by two. For
example, {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, …}.
5. The set of _______________ is the set of numbers which have only two factors, one and itself. For
example, {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, …}
6. The set of ________________ is the set of numbers which have more than two factors. For
example, {4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15, 16, 18, …}.
7. The set of __________ of a number is the set of numbers which can divide another number
without leaving a remainder. For example, the set of factors of 15 is {1, 3, 5, 15} and
the set of factors of 18 is {1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18}.
8. The set of _____________ of a number is the set of numbers which can be divided by another
number without leaving a remainder. For example, the set of multiples of 3 is
{3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, …} and the set of multiples of 7 is {7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, …}.
9. The set of ______________ consist of zero, positive and negative natural numbers. It is
represented by the symbol Z. Z = {…, - 6, - 5, - 4, - 3, - 2, - 1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …}.
10. The set of ________________ is the set of numbers which can be written as a fraction. For
3 1 3 2
, , ,
example, 4 2 9 7 . It is represented by the symbol Q.
11. The set of _______________ is the set of numbers that cannot be written as a fraction. For
5 2
3, 7,
example, 4 9 . It is represented by the symbol Q1 or I.
12. The set of ____ is the set of both the rational and irrational numbers. It is represented by the
symbol R.
We note N W Z Q R and Q1 R. So R = Q Q1. The Venn diagram representing the
set of real numbers is as follows: U=R
N W Z Q
Q1 = I
Square Numbers
Square numbers are as follows: 12, 22, 32, 42, 52, 62, 72, 82, 92, 102, 112, 122, …
That is, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121, 144, 169, 225, …
NOTE: Square roots 1 1, 4 2, 9 3, 16 4, 25 5, 36 6 , and so on.
Cube Numbers
Cube numbers: 13, 23, 33, 43, 53, 63, 73, 83, 93, 103, 113, 123, … That is,
1, 8, 27, 64, 125, 216, 343, …
NOTE: Cube roots 1 1, 8 2, 27 3, 64 4, 125 5, 3 216 6
3 3 3 3 3
and so.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Section 1 - Number Theory and ComputationDocumento79 pagineSection 1 - Number Theory and ComputationAntwayne Youcantstopmaprogress Hardie100% (1)
- Practice P2 Higher Edexcel 2Documento23 paginePractice P2 Higher Edexcel 2rsendhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Sba GuidelinesDocumento2 pagineSba GuidelinesBrianna BaileyNessuna valutazione finora
- Factor by Grouping Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineFactor by Grouping Lesson Planapi-246371537Nessuna valutazione finora
- Linear ProgrammingDocumento5 pagineLinear ProgrammingMichael HarrichandsinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Sets QuestionsDocumento6 pagineSets QuestionsVynash Bhagaloo0% (2)
- Transformations - SPQDocumento10 pagineTransformations - SPQAnthony BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Factors AND MultiplesDocumento15 pagineFactors AND MultiplessharonNessuna valutazione finora
- Math SBA OutlineDocumento3 pagineMath SBA OutlineDontaeTheRealOne100% (1)
- Number Theory & ComputationDocumento66 pagineNumber Theory & ComputationShannon Smith100% (1)
- Vectors Tutorial PDFDocumento8 pagineVectors Tutorial PDFCarl Agape DavisNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Documento12 pagineCSEC Mathematics - Graphs - (2015-2010)Anthony BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Matrices - Lessons - Part 4Documento6 pagineMatrices - Lessons - Part 4Anthony BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Sets - SPQDocumento10 pagineSets - SPQAnthony BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- Credit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsDocumento28 pagineCredit Past Paper Questions - SolutionsknoxmathsNessuna valutazione finora
- FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS WorksheetDocumento2 pagineFRACTIONS AND DECIMALS WorksheetKeri-ann Millar0% (1)
- CCSLC BookletDocumento20 pagineCCSLC BookletLuis VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- (Template) CXC Questions On FunctionsDocumento2 pagine(Template) CXC Questions On FunctionsAshleigh JarrettNessuna valutazione finora
- Fourth Form Mathematics Module 5Documento85 pagineFourth Form Mathematics Module 5Chet Ack100% (1)
- CSEC Maths Geometry & TrignometryDocumento10 pagineCSEC Maths Geometry & TrignometryDwayne DixonNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebraic FractionsDocumento35 pagineAlgebraic FractionsAntwayne Youcantstopmaprogress Hardie100% (1)
- Circle Theorem Booklet PDFDocumento16 pagineCircle Theorem Booklet PDFPerry Sin100% (1)
- CSEC Math Lesson 1 To 2 - Introduction To Sets and Sub-SetsDocumento31 pagineCSEC Math Lesson 1 To 2 - Introduction To Sets and Sub-SetsTaariq Abdul-Majeed100% (1)
- Additional Mathematics SBADocumento13 pagineAdditional Mathematics SBABritneyDNessuna valutazione finora
- O Level Additional Mathematics Past QuestionsDocumento16 pagineO Level Additional Mathematics Past QuestionsnurlNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Programming Jan 2017Documento4 pagineLinear Programming Jan 2017melissa100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Topics Math CXCDocumento2 pagineLesson Plan Topics Math CXCKembla1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 17 CSEC ConciseComplete January BrochureDocumento5 pagine17 CSEC ConciseComplete January BrochureAWNessuna valutazione finora
- Write and Read NumbersDocumento10 pagineWrite and Read NumbersZachrylahok LahokNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Ideas and LinksDocumento5 pagineProject Ideas and LinksKeston Winston Jr Mikaelson50% (2)
- Canadian School of Arts and Science Easter Term Exam - March 2020 Mathematics - Paper 2 (Total 100 Marks) Grade 11 2 Hours 30 MinutesDocumento20 pagineCanadian School of Arts and Science Easter Term Exam - March 2020 Mathematics - Paper 2 (Total 100 Marks) Grade 11 2 Hours 30 MinutesTrevor G. SamarooNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC Mathematics SBA Guideline - MR Conlloyd GumbsDocumento8 pagineCSEC Mathematics SBA Guideline - MR Conlloyd GumbsLyshii BooNessuna valutazione finora
- Csec Add Maths 2015 Paper2 PDFDocumento11 pagineCsec Add Maths 2015 Paper2 PDFSabrina PowellNessuna valutazione finora
- Mensuration ChapterDocumento41 pagineMensuration ChapterBhumika DNessuna valutazione finora
- Add Math Sba!!!Documento24 pagineAdd Math Sba!!!Aarti BalkaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra, Relations, Functions and Graphs IIDocumento27 pagineAlgebra, Relations, Functions and Graphs IIAnthony Benson100% (2)
- 25.csec Maths June 2016Documento49 pagine25.csec Maths June 2016Gregory Lewis100% (1)
- 4 Simultaneous EquationsDocumento9 pagine4 Simultaneous EquationsTANG PEI PEINessuna valutazione finora
- Order of Operations ExponentsDocumento6 pagineOrder of Operations ExponentsJ AvilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Add Maths Jun 07, 2022Documento19 pagineAdd Maths Jun 07, 2022Amarah MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 1 Matrices (1) Grade 10Documento3 pagineWorksheet 1 Matrices (1) Grade 10Diana Frills100% (1)
- Form Four Term Two Worksheet Three Consumer Arithmetic PDFDocumento2 pagineForm Four Term Two Worksheet Three Consumer Arithmetic PDFmissy100% (1)
- Trigonometry-Edexcel GCSEDocumento16 pagineTrigonometry-Edexcel GCSEMoli CaoNessuna valutazione finora
- C XCC Sec Maths Must Know ListDocumento1 paginaC XCC Sec Maths Must Know ListSwayne JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths MCDocumento5 pagineMaths MCADrian ZeeGreatNessuna valutazione finora
- B T X X: Geometry Name - Similarity Review Sheet Date - SolveDocumento3 pagineB T X X: Geometry Name - Similarity Review Sheet Date - Solve王珊珊Nessuna valutazione finora
- Graphs and Variations IDocumento34 pagineGraphs and Variations IA.BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- 28-Trigonometry Paper 2Documento6 pagine28-Trigonometry Paper 2iyaad MubarakNessuna valutazione finora
- Vectors - Lessons - Part ADocumento14 pagineVectors - Lessons - Part AAnthony Benson100% (1)
- Copy and Fill in The Gaps Using The Words BelowDocumento10 pagineCopy and Fill in The Gaps Using The Words BelowMeena RajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Factors and MultiplesDocumento4 pagineChapter 2 Factors and MultiplesJiajia Lau100% (1)
- Circle Theorem Unit 1Documento8 pagineCircle Theorem Unit 1Chet AckNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebraic Fractions Exam Questions-SolutionsDocumento2 pagineAlgebraic Fractions Exam Questions-SolutionsAntwayne Youcantstopmaprogress HardieNessuna valutazione finora
- MSG.03.Consumer Arithmetic PDFDocumento9 pagineMSG.03.Consumer Arithmetic PDFIkram Ullah100% (1)
- Csec Add Maths May 2016Documento29 pagineCsec Add Maths May 2016Joshua JagroopNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC 06-UpDocumento132 pagineCSEC 06-UpA.Benson100% (1)
- Mathematics 1202 Overtime Worksheet: M T W T F S SDocumento4 pagineMathematics 1202 Overtime Worksheet: M T W T F S SKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet - MatricesDocumento12 pagineWorksheet - MatricesChadymon EllisNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 Sept. 2016Documento2 pagineAssignment 1 Sept. 2016Keri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Work 1 - September 4, 2017Documento2 pagineClass Work 1 - September 4, 2017Keri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- SBA Mark AllocationDocumento2 pagineSBA Mark AllocationKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC Mathematics OutlineDocumento2 pagineCSEC Mathematics OutlineKeri-ann Millar67% (3)
- FRACTIONS AND DECIMALS WorksheetDocumento2 pagineFRACTIONS AND DECIMALS WorksheetKeri-ann Millar0% (1)
- 7) Matrix TransformationsDocumento10 pagine7) Matrix TransformationsKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC MATHEMATICS Assignment 1Documento2 pagineCSEC MATHEMATICS Assignment 1Keri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pure Mathematics C4-WorksheetDocumento1 paginaPure Mathematics C4-WorksheetKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- 6) Matrix TransformationsDocumento8 pagine6) Matrix TransformationsKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Circle TheoremDocumento5 pagineCircle TheoremKeri-ann Millar100% (1)
- 6) Matrix TransformationsDocumento8 pagine6) Matrix TransformationsKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sequences, Mathematical Induction, and Recursion Sequences, Mathematical Induction, and RecursionDocumento49 pagineSequences, Mathematical Induction, and Recursion Sequences, Mathematical Induction, and RecursionKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Positive and Negative Coordinates - ALLDocumento20 paginePositive and Negative Coordinates - ALLKeri-ann Millar0% (2)
- Task 1: Draw A Set of Axes, Using 1 Square Task 1: Draw A Set of Axes, Using 1 SquareDocumento1 paginaTask 1: Draw A Set of Axes, Using 1 Square Task 1: Draw A Set of Axes, Using 1 SquareKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 21. Draw and Interpret Bar ChartsDocumento37 pagine20 21. Draw and Interpret Bar ChartsKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Drawing Bar Charts: Starter QuestionsDocumento1 paginaDrawing Bar Charts: Starter QuestionsKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Draw A Frequency Table For This Pictogram: VauxhallDocumento11 pagineDraw A Frequency Table For This Pictogram: VauxhallKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordinates All Quadrant 2Documento8 pagineCoordinates All Quadrant 2Keri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Drawing Bar ChartsDocumento2 pagineDrawing Bar ChartsKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Plotting CoordinatesDocumento6 paginePlotting CoordinatesKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dot To Dot ADocumento3 pagineDot To Dot AKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet On Surds PDFDocumento2 pagineWorksheet On Surds PDFKeri-ann Millar50% (4)
- Unit 8: Area Between CurvesDocumento15 pagineUnit 8: Area Between CurvesKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Matrix Determinants Inverses and Triangle Area WorksheetDocumento2 pagineMatrix Determinants Inverses and Triangle Area WorksheetKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Plotting Co-Ordinates in Four QuadrantsDocumento2 paginePlotting Co-Ordinates in Four QuadrantsKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading Points - ALLDocumento30 pagineReading Points - ALLKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Coordinates Halloween Bat PDFDocumento3 pagineCoordinates Halloween Bat PDFKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Determinants: Determinant of An NDocumento22 pagineDeterminants: Determinant of An NKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- LG LZ 1: Algebra Determinants of 4-6inverseDocumento2 pagineLG LZ 1: Algebra Determinants of 4-6inverseKeri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Real-World Applications 3x3Documento13 pagineReal-World Applications 3x3Keri-ann MillarNessuna valutazione finora
- Proof of Goldbach's ConjectureDocumento2 pagineProof of Goldbach's ConjectureMichael GrützmannNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide CardDocumento1 paginaGuide Cardmario buenaventeNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Find The Area of A TriangleDocumento4 pagineHow To Find The Area of A Triangleapi-150547803Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCQs+VSAQs (Determinants)Documento7 pagineMCQs+VSAQs (Determinants)SkNessuna valutazione finora
- Integers and MultiplesDocumento12 pagineIntegers and Multiplesmargaretta yunitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 Unpacking CombiningDocumento6 pagineModule 2 Unpacking Combiningcjade08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computation FractionsDocumento6 pagineComputation Fractionsreeta ramNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations of RAEDocumento1 paginaOperations of RAEMargarette SeguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Book Mathematics Class XDocumento368 pagineNCERT Book Mathematics Class Xrakeshge100% (4)
- Number SystemDocumento11 pagineNumber SystemSoumyajit BagchiNessuna valutazione finora
- Institute of Finance Management (Ifm) Computer Science and Mathematics Department. Mtu 07101:business Mathematics Topic:Review of AlgebraDocumento51 pagineInstitute of Finance Management (Ifm) Computer Science and Mathematics Department. Mtu 07101:business Mathematics Topic:Review of AlgebraCriss JasonNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento77 pagineUnit 1Subarna PoudelNessuna valutazione finora
- MT Yearly Plan Year 6Documento6 pagineMT Yearly Plan Year 6Saiful AsrulNessuna valutazione finora
- Parcial de Operaciones en Los Sistemas NuméricosDocumento2 pagineParcial de Operaciones en Los Sistemas NuméricosDIANA SOFIA ROSERO LÓPEZNessuna valutazione finora
- IIT JEE and AIEEE Maths Solved Problems WWW - IitportalDocumento341 pagineIIT JEE and AIEEE Maths Solved Problems WWW - IitportalSonu Agarwal100% (1)
- Math Properties of Numbers NotesDocumento3 pagineMath Properties of Numbers NotesmathstarNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Maths - Pranav Popat - Full PDFDocumento39 pagineBasics of Maths - Pranav Popat - Full PDFravishukla81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of Exponents-0 PowerpointDocumento19 pagineLaws of Exponents-0 PowerpointLilibeth M. BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Aptitude Book PDFDocumento114 pagineMaths Aptitude Book PDFArjav DesaiNessuna valutazione finora
- A+ Blog-std-9-Mathematics Second Term Exam 2023-Em AnsDocumento8 pagineA+ Blog-std-9-Mathematics Second Term Exam 2023-Em AnsniranjanthuvasseryNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers: Sample Answer: Peter Has 7 Apples. His Sister HasDocumento62 pagineAnswers: Sample Answer: Peter Has 7 Apples. His Sister HasMOEDNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 6: Back of Chapter QuestionsDocumento32 pagineCBSE NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 6: Back of Chapter Questionssangdeep waldeNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 - OperatorsWithAnswers - UpdatedDocumento8 pagine01 - OperatorsWithAnswers - UpdatedTejas Rane100% (1)
- Xor XNor ApplicationsDocumento12 pagineXor XNor ApplicationsPortgas D AceNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematics Techno Solutions (VI - X) 2016 - 17 Final/IX - Class/IX - Part - I/1. TriganometryDocumento14 pagineMathematics Techno Solutions (VI - X) 2016 - 17 Final/IX - Class/IX - Part - I/1. TriganometryMatta GaneshNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To TrigonometryDocumento14 pagineIntroduction To TrigonometryAnil KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Video Math Tutor: Basic Math: Lesson 4 - Properties of NumbersDocumento20 pagineVideo Math Tutor: Basic Math: Lesson 4 - Properties of NumbersThe Video Math Tutor100% (5)
- 04 - Trig Ratios of Any Angle PDFDocumento4 pagine04 - Trig Ratios of Any Angle PDFMark Abion ValladolidNessuna valutazione finora
- Mind Map of Fibonacci in NatureDocumento3 pagineMind Map of Fibonacci in NatureVrine LimNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH 10 Module 4 (Rational Exponents and Radical Expressions)Documento49 pagineMATH 10 Module 4 (Rational Exponents and Radical Expressions)Karla MarasiganNessuna valutazione finora