Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Additional Notes in Pedia Neuro2
Caricato da
Geraldine Marie SalvoDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Additional Notes in Pedia Neuro2
Caricato da
Geraldine Marie SalvoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
[HOUSE STARK] 2017
INFRATENTORIAL TUMORS
ADDITIONAL NOTES IN PEDIA NEURO (PART 2)
DR. DIAZ Incoordination
Ataxia
Nystagmus
CLASSIFICATION AND GRADING OF INTRACRANIAL NEOPLASM Diplopia
(WH0) Blurred Vision
Torticollis
HISTOLOGICAL GROUPS Cerebellar Dysfunction
Neuroepithelial
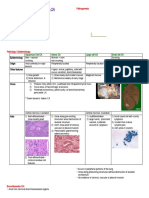
Meningeal CEREBELLAR ASTROCYTOMAS
Sellar Region
Germ Cell Most common primary CNS tumor
Lymphoid-Hematopoeitic Juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma in cerebellum
Cranial/ Spinal Nerve (Grade 1); fibrillary diffuse (Grade 2); anaplastic
(Grade 3); Gliobalstoma mulitforme (Grade 4)
WHO GRADING Peak age 5-9 years
GRADE 1 – slow growing, non-malignant, with long- RADIOLOGIC FUNCTION: neuromedium enhancing
term survival nodule within the wall of as cystic mass
GRADE 2 – relatively slow-growing, recurrent, MICROSCOPY: presence of Rosenthal bodies help
progress to higher grade establish the diagnosis
GRADE 3 – malignant, recur as higher grade Low metastatic potential, rarely spread
GRADE 4 – very aggressive Complete surgical resection = 80-100% cure
MEDULLOBLASTOMA
Most common malignant tumor
Accounts for 90% of PNET or embryonal tumor
Most common cytogenic abnormality is
chromosome 17p deletions
Median age of 5-7 years, mostly males
Occurs in the midline cerebellar vermis
Children , 4 years have poo outcome because of
incidence of dissemination
Radiosensitive and chemotherapy sensitive
WINTER IS COMING. |AMCA 1
[HOUSE STARK] 2017
The tumor may spread contagiously, to the Dense cellularity, high mitotic index, microvesicular
cerebellar peduncle and/or the floor of the fourth proliferation, foci of tumor necrosis
ventricle Over expression of P53 is a poor prognostic sign
Anteriorly, to the brainstem
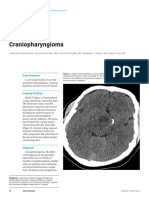
Inferiorly, to the cervical spine CRANIOPHARYNGIOMA
Superiorly, above the tentorium
It may also spread via the CSF intra-cranially or to WHO Grade 1, histologically benign neuroepithelial
the leptomeninges and spinal cord tumor
Peak age incidence 5-10 years
BRAINSTEM GLIOMA Remnant of Rathke’s Pouch – Pituitary Gland
Minimally invasive, adheres to brain parenchyma,
Peak age 7-9 years engulf brain tissues
Accounts for 80% of brainstem tumors RADIOLOGIC FUNCTION: calcifications with solid and
Constitute 10-20% of childhood primary CNS cystic wall components
tumors Surgery + radiotherapy, chemotherapy has no role
Classic triad – motor weakness, lower cranial
nerve deficits, ataxia PINEAL GLAND TUMORS
4 Types – focal, dorsally exophytic,
cervicomedullary, diffuse intrinsic tumor 2ND most common malignancies after germ cell
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy, no role for tumor in pineal area
surgery PINEOCYTOMA – benign, young adults, present as
hydrocephalus
SUPRATENTORIAL TUMORS PINEOBLASTOMA – most malignant variant, PNET in
pineal area, young children; associated with
Motor weakness retinoblastoma, CSF seeding
Sensory changes Multimodal therapy
Speech disorders
Seizures
Change in hand preference
Hemiparesis
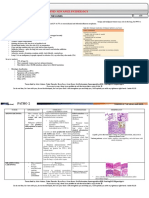
EPENDYMOMA
Third most common primary CNS tumor
Tumor of the ependymal lining of the ventricles –
glial cell differentiated along glial lines
70% in the posterior fossa, in the 4th ventricle
Mean age is 6 years
Younger children have poorer outcome
Multimodal treatment – sensitive to chemotherapy,
surgery
GLIOBALSTOMA MULTIFORME
Subcortical white matter of the cerebral
hemisphere
May infiltrate adjacent cortex, basal ganglia and
contralateral hemisphere
WHO Grade 4
WINTER IS COMING. |AMCA 2
[HOUSE STARK] 2017
NEURODIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES TEMPORAL LOBECTOMY & HEMISPHERECTOMY
EEG
Skull X-ray
Cranial CT Scan
Cranial MRI
MANAGEMENT
Close Observation
Multimodal:
Surgery
Radiotherapy
Chemotherapy
SURGERY
1. Surgery also may help: RADIOTHERAPY
1. Reduce the size of the tumor
2. Relieve symptoms, such as headaches, and 1. EXTERNAL BEAM RADIATION THERAPY (EBRT) –
nausea focus from the source outside the body
3. Place a shunt to drain excess CSF, which may
cause including headaches and blurred vision 2. THREE-DIMENSIONAL CONFORMAL RADIATION
(3D-CRT) – 3D-CRT uses the results of imaging
VENTRICULOPERITONEAL SHUNT tests such as MRI and special computers; radiation
beams are then shaped and aimed at the tumor
from different conditions
3. INTENSITY MODULATED RADIATION THERAPY
(IMRT) – advanced form of 3D therapy; shaping the
beams and aiming them at the tumor from several
angles, the intensity (strength) of the beams can be
adjusted to limit the dose reaching the most
sensitive normal tissues
4. CONFORMAL PROTON BEAM RADIATION THERAPY:
Proton beam therapy is related to 3D-CRT; proton
beams on the tumor; less damage
5. STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY/ STEREOTACTIC
RADIOTHERAPY: delivers a large, precise radiation
dose to the tumor area in a single session
(radiosurgery) or in a few session (radiotherapy)
6. BRACHYTHERAPY (INTERNAL RADIOTHERAPY):
Unlike the external radiation approaches above in
brachytherapy a radiation source is put directly
into or near the tumor; most often used along with
external radiation. It provides a high dose of
WINTER IS COMING. |AMCA 3
[HOUSE STARK] 2017
radiation at the tumor site, while the external
radiation treats nearby areas with a lower dose.
7. WHOLE BRAIN AND SPINAL CORD RADIATION
THERAPY (CRANIOSPINAL RADIATION): is tests,
such as MRI scan or lumbar puncture, show the
tumor has spread along the covering od the spinal
cord (meninges) or into the surrounding
cerebrospinal fluid, then radiation may be given to
the whole brain and spinal cord
8. GAMMA KNIFE RADIOSURGERY: delivers a pinpoint
dose of radiation to the tumor from hundreds of
angles. It may be used if the tumor’s location makes
it impossible to remove of if the child is not healthy
CHEMOTHERAPY
Chemotherapy is used for many types of brain
tumors including aggressive, high-grade tumors
Chemotherapy can be administered as pills (orally),
intravenously (IV, by vein), injected directly into the
cerebrospinal fluid, or injected directly into the
cavity left after surgical removal of the brain tumor
– Carboplatin, Carmustine (BCNU), Cisplatin,
Cyclophosphamide, Etoposide, Lomustine (CCNU),
Methotrexate, Temozolomide, Thiotepa, Vincristine
WINTER IS COMING. |AMCA 4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Cncy 21537Documento16 pagineCncy 21537Rizki Amalia JuwitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Peadiatric Brain Tumour: Wong Ann Cheng MD (Ukm) MRCPCH (Uk)Documento48 paginePeadiatric Brain Tumour: Wong Ann Cheng MD (Ukm) MRCPCH (Uk)An Zheng100% (4)
- Brain Tumour: Histological Type Common Site Malignancy AgeDocumento4 pagineBrain Tumour: Histological Type Common Site Malignancy AgeyandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Klasifikasi Tumor Otak Div NeuroonkoDocumento30 pagineKlasifikasi Tumor Otak Div Neuroonkonovy rosalia chandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumours of The Central Nervous System: FM Brett MD., FrcpathDocumento57 pagineTumours of The Central Nervous System: FM Brett MD., FrcpathRerendhutNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumours of The Central Nervous System: FM Brett MD., FrcpathDocumento57 pagineTumours of The Central Nervous System: FM Brett MD., FrcpathDrGasnasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Brain TumorDocumento49 paginePediatric Brain TumorJessica Victoria SudanawidjajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical Pathology - CNSDocumento2 pagineSurgical Pathology - CNSIsabel CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumor: Essential Neurosurgery For Medical StudentsDocumento26 pagineTumor: Essential Neurosurgery For Medical StudentsMaria JanticNessuna valutazione finora
- Trypanosoma-SppDocumento4 pagineTrypanosoma-SppVE NI CENessuna valutazione finora
- Neurooncology of Familial Cancer SyndromesDocumento10 pagineNeurooncology of Familial Cancer SyndromesMădălina SimionNessuna valutazione finora
- Sol IntracranialDocumento76 pagineSol IntracranialPanduRespatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Epilepsy Imaging: Approaches and ProtocolsDocumento9 pagineEpilepsy Imaging: Approaches and ProtocolsNatalia E PenagosNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory 03 - Bronchiogenic CA: 1) Smoking/industrial Hazards/air Pollution 2) Molecular Genetic MutationDocumento2 pagineRespiratory 03 - Bronchiogenic CA: 1) Smoking/industrial Hazards/air Pollution 2) Molecular Genetic Mutationkamil malikNessuna valutazione finora
- Adult Brainstem Gliomas: Sylvia C. Eisele, MD and David A. Reardon, MDDocumento11 pagineAdult Brainstem Gliomas: Sylvia C. Eisele, MD and David A. Reardon, MDJuan Diego Martinez LemusNessuna valutazione finora
- Nonvestibular Schwannoma Tumors in The CPA GgodDocumento12 pagineNonvestibular Schwannoma Tumors in The CPA GgodnabilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Benitez - 2018 - Chemotherapy of Brainstem GliomasDocumento12 pagineBenitez - 2018 - Chemotherapy of Brainstem GliomasMatheus FreitasNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain TumorDocumento61 pagineBrain TumorRima Artika Mayanda0% (1)
- Clinical Therapeutics Case No.16: Presented By: Maria Cristina CastroDocumento65 pagineClinical Therapeutics Case No.16: Presented By: Maria Cristina CastroMichelle Vera GabunNessuna valutazione finora
- 3504-Article Text-11497-1-10-20200318Documento3 pagine3504-Article Text-11497-1-10-20200318Ade Puji AstutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Peripheral Primitive Neuro-Ectodermal Tumor of The Pleura About A Rare Caser, With Literature ReviewDocumento4 paginePeripheral Primitive Neuro-Ectodermal Tumor of The Pleura About A Rare Caser, With Literature ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Intramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors: Clinical PresentationDocumento15 pagineIntramedullary Spinal Cord Tumors: Clinical Presentationmetasoniko81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tumors of CNSDocumento30 pagineTumors of CNSShweta Ann SureshNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumours of The Central Nervous System: FM Brett MD., FrcpathDocumento57 pagineTumours of The Central Nervous System: FM Brett MD., FrcpathDaniela Vilches PérezNessuna valutazione finora
- SNP Envolvimento em Doentes Com Neoplasia Lancet 2007Documento12 pagineSNP Envolvimento em Doentes Com Neoplasia Lancet 2007Gonçalo CabralNessuna valutazione finora
- Curr Diag Pathol-2006-12 - Sinonasal CarcinomasDocumento14 pagineCurr Diag Pathol-2006-12 - Sinonasal Carcinomasdarmayanti ibnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ganglioneuroma: O Adam, ES Boia, Rodica Ilie, Ramona MandruscaDocumento4 pagineGanglioneuroma: O Adam, ES Boia, Rodica Ilie, Ramona MandruscaRaluca BolboaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Intradural Extramedullary TumorsDocumento10 pagineIntradural Extramedullary TumorsFaizyab AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Internal Medicine,: Prof WBP Matuja Muhas/MnhDocumento31 pagineDepartment of Internal Medicine,: Prof WBP Matuja Muhas/MnhDanyu KibuguluNessuna valutazione finora
- Shekdar2017Documento15 pagineShekdar2017FarhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented by Dr. Shamim Rima M.Phil Radiology & Imaging BsmmuDocumento113 paginePresented by Dr. Shamim Rima M.Phil Radiology & Imaging Bsmmudr_shamimrNessuna valutazione finora
- Lungs Benign and MalignantDocumento7 pagineLungs Benign and MalignantNestley TiongsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain TumorsDocumento43 pagineBrain TumorsDanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Tumors in Pediatrics: Resident Education Lecture SeriesDocumento28 pagineBrain Tumors in Pediatrics: Resident Education Lecture SeriesFetinuhan97Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brain TumorsDocumento72 pagineBrain Tumorsmo_mibNessuna valutazione finora
- Intracranial Pressure: Concepts and ManagementDocumento16 pagineIntracranial Pressure: Concepts and Managementyanuar andaniNessuna valutazione finora
- EPOSTER PABI Dr. Defri HeryadiDocumento1 paginaEPOSTER PABI Dr. Defri HeryadiSeptia Pristi RahmahNessuna valutazione finora
- Paraneoplastic Syndrome of CNSDocumento71 pagineParaneoplastic Syndrome of CNSpreeti sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Craniopharyngioma: Case SummaryDocumento3 pagineCraniopharyngioma: Case SummaryeugeniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Referat Genomics Brain TumorDocumento51 pagineReferat Genomics Brain TumorAlessia Wyneini TirzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sarcomas: Bone Sarcoma Soft Tissue SarcomasDocumento3 pagineSarcomas: Bone Sarcoma Soft Tissue SarcomasCharlie65129Nessuna valutazione finora
- EncephalitisDocumento17 pagineEncephalitiseko andryNessuna valutazione finora
- BRAIN Tumors PDFDocumento44 pagineBRAIN Tumors PDFHalima Assi100% (1)
- Foaie de CoptDocumento105 pagineFoaie de CoptVlad Octavian BolocanNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento2 pagineUntitledVin TagenNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumori Mozga (Prof. Stevic) PDFDocumento14 pagineTumori Mozga (Prof. Stevic) PDFБогдан ЛажетићNessuna valutazione finora
- Retinopathy of Prematurity & Retinoblastoma: Salinas & EstellaDocumento23 pagineRetinopathy of Prematurity & Retinoblastoma: Salinas & Estellaallenh016Nessuna valutazione finora
- Neurologicemergenciesin Pediatricpatients Includingaccidentaland NonaccidentaltraumaDocumento18 pagineNeurologicemergenciesin Pediatricpatients Includingaccidentaland NonaccidentaltraumaAvrilMontNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain Cancer by A4Documento122 pagineBrain Cancer by A4pauchanmnlNessuna valutazione finora
- Acoustic NeuromaDocumento31 pagineAcoustic NeuromaHreem FarrakhNessuna valutazione finora
- Middle Ear Tumors - Dr. Shivendra PandeyDocumento60 pagineMiddle Ear Tumors - Dr. Shivendra PandeyNupur GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumor OtakDocumento61 pagineTumor OtakHelena Kartika UtamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Round Cell TumorsDocumento131 pagineSmall Round Cell TumorschinnnababuNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain & Spinal Cord Tumor: Miss.S.Krishana Lecturer (Prob) SHS, FHCS, EuslDocumento24 pagineBrain & Spinal Cord Tumor: Miss.S.Krishana Lecturer (Prob) SHS, FHCS, EuslSalman SalmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Acoustic NeuromaDocumento14 pagineAcoustic NeuromaNeshanth SurendranNessuna valutazione finora
- Laporan Dutch Foundation CourseDocumento4 pagineLaporan Dutch Foundation CourserimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcfaline Figueroa2018Documento9 pagineMcfaline Figueroa2018Kang LimbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroblastoma Cerebral: Diagnóstico y Tratamiento: R. Prat, I. Galeano, F.J. Conde, P. Febles, S. CortésDocumento3 pagineNeuroblastoma Cerebral: Diagnóstico y Tratamiento: R. Prat, I. Galeano, F.J. Conde, P. Febles, S. CortésjoaquinNessuna valutazione finora
- Embryology, Anatomy and Physiology & Disease of The LarynxDocumento83 pagineEmbryology, Anatomy and Physiology & Disease of The LarynxGeraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mental HealthDocumento59 pagineMental HealthGeraldine Marie Salvo97% (29)
- LEGALMED DEception DetectionDocumento9 pagineLEGALMED DEception DetectionGeraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Stages of LaborDocumento5 pagineStages of LaborGeraldine Marie Salvo100% (4)
- Chest TraumaDocumento27 pagineChest TraumaGeraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1: Histology Case #3Documento19 pagineGroup 1: Histology Case #3Geraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1 Enzyme Chemistry Part 1Documento7 pagine4.1 Enzyme Chemistry Part 1Geraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.2 Enzyme Chemistry Part 2Documento6 pagine4.2 Enzyme Chemistry Part 2Geraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro Case Report DinerevisedDocumento12 pagineIntro Case Report DinerevisedGeraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- With Important Actions On Smooth MuscleDocumento90 pagineWith Important Actions On Smooth MuscleGeraldine Marie Salvo100% (1)
- AdrenocorticosteroidsDocumento64 pagineAdrenocorticosteroidsGeraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Case Presentation: Abat FamilyDocumento80 pagineFamily Case Presentation: Abat FamilyGeraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- EPIDEMIOLOGY & GEOGRAPHIC DistributionDocumento2 pagineEPIDEMIOLOGY & GEOGRAPHIC DistributionGeraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Medication List For PregnancyDocumento1 paginaMedication List For PregnancyGeraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life SupportDocumento43 pagineAdvanced Cardiovascular Life SupportGeraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 Physical Injury Part 2Documento8 pagine2015 Physical Injury Part 2Geraldine Marie SalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutramine MenDocumento2 pagineNutramine MenCh Ashish PawaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- (GYNE) Ovarian Neoplasms-Dr. Delos Reyes (MRA)Documento9 pagine(GYNE) Ovarian Neoplasms-Dr. Delos Reyes (MRA)adrian kristopher dela cruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Avon and CSRDocumento4 pagineAvon and CSRrebelious_think100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - VaginaDocumento1 paginaChapter 2 - VaginaalexandrumascanNessuna valutazione finora
- Gastrointestinal Oncology Principles and PracticesDocumento794 pagineGastrointestinal Oncology Principles and Practicesjohny3333Nessuna valutazione finora
- Elyn Jacobs - Hormone BalanceDocumento20 pagineElyn Jacobs - Hormone BalanceMNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Cancer ChemotherapyDocumento9 pagineHistory of Cancer ChemotherapyJoydeep MajumdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study IN Penile CancerDocumento15 pagineCase Study IN Penile CancerPrincess Gutierrez RositaNessuna valutazione finora
- Re-Humanising Health CareDocumento11 pagineRe-Humanising Health CareAltaf MansooriNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento2 pagineAssignment 1Kartik GvrNessuna valutazione finora
- Phytochemical Analysis and in Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Jojoba OilDocumento5 paginePhytochemical Analysis and in Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Jojoba OilRahma SantosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Malignant Struma OvariiDocumento4 pagineMalignant Struma Ovariixwahyu 108Nessuna valutazione finora
- Disease of Immune System: Sharon Hazel Joyce C. Sebastian, RMTDocumento47 pagineDisease of Immune System: Sharon Hazel Joyce C. Sebastian, RMTGilo IlaganNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 Bookmatter BlausteinSPathologyOfTheFemaleDocumento40 pagine2019 Bookmatter BlausteinSPathologyOfTheFemaleKazuto Kath TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- CONCHEM q4 m4 Anticancerdrugs-V3Documento24 pagineCONCHEM q4 m4 Anticancerdrugs-V3NovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Testing of Thyroid NodulesDocumento7 pagineMolecular Testing of Thyroid Nodulesayodeji78Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hospice Care (End of Life Care) For Terminal Illness - Case Study SampleDocumento19 pagineHospice Care (End of Life Care) For Terminal Illness - Case Study Samplepeng kulongNessuna valutazione finora
- Chlorine and Water-A Table ResearchDocumento5 pagineChlorine and Water-A Table ResearchrajaratnaNessuna valutazione finora
- OncologyDocumento19 pagineOncologyLiezel Cauilan0% (1)
- The Atlas of Natural CuresDocumento515 pagineThe Atlas of Natural CuresChristopher Phillips100% (10)
- CapecitabineDocumento13 pagineCapecitabinegd_hbar100% (1)
- Ovarian Cancers Advances Through International Research Cooperation GINECO ENGOT GCIGDocumento288 pagineOvarian Cancers Advances Through International Research Cooperation GINECO ENGOT GCIGCatalin SavinNessuna valutazione finora
- Corilagine PropriétésDocumento8 pagineCorilagine PropriétésAbderrahim Ait OuchaouiNessuna valutazione finora
- Colorectal Cancer Screening: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines)Documento49 pagineColorectal Cancer Screening: NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines)StangPongritNessuna valutazione finora
- Kelime Sorulari 1Documento8 pagineKelime Sorulari 1atalikaciNessuna valutazione finora
- Willms TumorDocumento41 pagineWillms TumorBhardwaj Lokesh100% (2)
- Enagic KW2 PDFDocumento125 pagineEnagic KW2 PDFKS Lee100% (6)
- CramDocumento122 pagineCramHuỳnh Hiển TrươngNessuna valutazione finora
- Recist Criteria - Respon Solid Tumor Pada TerapiDocumento18 pagineRecist Criteria - Respon Solid Tumor Pada TerapiBhayu Dharma SuryanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathway Tumor GinjalDocumento1 paginaPathway Tumor GinjalElizabeth VickiNessuna valutazione finora