Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Final Exam 1018
Caricato da
HayaAhmedTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Final Exam 1018
Caricato da
HayaAhmedCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1Dr.
Ramakrishna NAME:
BUAD631 Final Exam
(100 points)
Instructions:
READ (and FOLLOW) THE INSTRUCTIONS
1. Please make sure you put your name in the space provided at the top right corner of this
page.
2. Please insure that your copy of the exam has a total of 10 numbered pages that includes
14 questions and two computer printouts.
3. For essay questions, I have provided just enough space for you to write your answers.
Please do not write too much beyond the space provided (otherwise, you will run out of
time).
4. You can use the one-page notes sheet on this exam. You are not permitted to use any
other notes, class materials, books, or other sources of information.
5. This is a timed exam. You will have a maximum of 75 minutes to complete the exam.
6. Assume an = .05 whenever necessary.
GRADE SUMMARY
Problems Partial 36
Full 34
Short essays 12
Multiple choice 18
Extra credit 4
Total 100
Good Luck
Final Exam Page 1 of 10
Problems -- Partial
For the next four problems just do the following:
(Answer any three of the four questions. If you answer a fourth question and identify that as an
extra-credit question, it will be graded for four extra credit points)
A. Identify the independent variable(s) – if any (and define them precisely and indicate they
are qualitative or quantitative)
B. Identify the dependent variable – if any (and define them precisely and indicate they are
qualitative or quantitative)
C. Identify the type of analysis that is appropriate (Chi-Square test of independence, ANOVA,
Regression, or Correlation)
D. Justify why the analysis you identified in part C is correct.
(3 + 3 + 3 + 3 points)
1. Your firm is having quality problem with the production of plastic automotive parts: there are too
many defectives. One of your engineers thinks that it’s because the temperature of the process is
not controlled carefully enough. Another engineer is sure that it’s because the assembly line is
being shut down too often for unrelated reasons. You have decided to analyze the problem and
have come up with figures for the percent defective each day recently, the standard deviation of
temperature measured hourly each day (as a measure of temperature control), and the number of
assembly line stoppages each day. You are interested in finding out which engineer is right.
A.
B.
C.
D.
2. Some critics of big business argue that CEOs are overpaid and that their compensation is not
related the performance of their company. To test this theory, data on executive’s total pay and
company’s performance was collected from a randomly selected set of fifty companies.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Final Exam Page 2 of 10
3. Many companies use well-known celebrities in their ads, while other companies create their own
spokespersons (such as Maytag repairman). A marketing researcher is interested in investigating
the relationship between gender of the spokesperson and brand awareness. Three hundred
television viewers were asked to identify the products advertised by celebrity spokespersons.
A.
B.
C.
D.
4. To test whether the mean time needed to mix a batch of material is the same for machines produced
by three manufacturers, Jacob’s Chemical Company obtained the data on the mixing times from ten
batches for each of the machines. What can we conclude?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Final Exam Page 3 of 10
Problems -- Full
For the next two problems just do the following:
A. Set up the appropriate hypotheses (in plain English)
B. Draw appropriate statistical conclusions (based on the printout provided). In your
conclusions, make sure to indicate what values you specifically used from the printout
(i.e., highlight/mark/circle the relevant values you need from the printout and then use
them in your discussion/conclusions).
C. Present proper conclusions for the business problem.
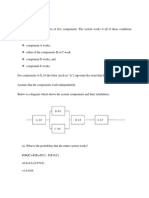
5. As a consulting industrial engineer you are hired to perform a "human factors experiment"
at Burstinter & Lobel, a large law firm. A pool of 30 typists of similar ability and
experience is selected to participate. Groups of 10 typists each are randomly assigned to
one of three working conditions—very noisy atmosphere (90 Db constant), somewhat
noisy atmosphere (65 Db constant), and pleasant atmosphere (40 Db constant). The
subjects are then asked to type a technical manuscript. The following data represent the
number of mistakes on the manuscript make by the typists under the various working
conditions.
Groups
Very Noisy Somewhat Noisy Pleasant
(90 Db) (65 Db) (40 Db)
14 2 2
12 5 6
13 8 6
13 5 2
16 7 4
18 6 3
19 9 2
11 4 1
10 10 7
13 9 5
At the .01 level of significance, is there evidence of a difference in the average number of
errors between the three groups?
(3 + 8 + 6 points)
Please refer to Printout #1 for this problem
A. H0:
H1:
B.
C.
Final Exam Page 4 of 10
6. A list of best selling cars for 1987 is shown in the table. The 1988 suggested retail price
and the total number sold are given in the table below..
MODEL 1988 Price Number sold
(in thousands) (in thousands)
Hyundai 5.4 264
Oldsmobile Cierra 11.4 245
Nissan Sentra 6.4 236
Ford Tempo 9.1 219
Chev. Corsica 10.0 214
Pontiac Grand Am 10.3 211
Toyota Camry 11.2 187
Chev. Caprice 12.5 177
At = .05, is there evidence of relationship between the two variables?
(3 + 8 + 6 points)
Please refer to Printout #2 for this problem
A H0:
H1:
B.
C.
Final Exam Page 5 of 10
Essay Questions
7. What is Post-ANOVA test? Why is it necessary? When? Explain with an example.
(4 + 2 + 2 points)
8. The heights of a sample of husbands and wives in the Heightlands are given below. Write
down an equation (i.e., the regression equation) predicting the height of a husband (Y)
from the height of his wife (X). What is the correlation coefficient for this equation? (2 + 2
points)
Height of husband Height of wife
72 67
68 63
63 58
59 54
___________________________________________________________
Final Exam Page 6 of 10
Printout #1
One-way ANOVA: Mistakes versus NoiseLevel
Method
Null hypothesis All means are equal
Alternative Not all means are equal
hypothesis
Significance level α = 0.05
Equal variances were assumed for the analysis.
Factor Information
Factor Levels Values
NoiseLeve 3 1, 2, 3
l
Analysis of Variance
Adj
Source DF SS Adj MS F-Value P-Value
NoiseLeve 2 546.9 273.433 42.19 0.000
l
Error 27 175.0 6.481
Total 29 721.9
Model Summary
R-
S R-sq sq(adj) R-sq(pred)
2.5458 75.76% 73.96% 70.07%
8
Means
NoiseLeve StDe
l N Mean v 95% CI
1 1 13.900 2.923 (12.248, 15.552)
0
2 1 6.500 2.550 (4.848, 8.152)
0
3 1 3.800 2.098 (2.148, 5.452)
0
Pooled StDev = 2.54588
Final Exam Page 7 of 10
Interval Plot of Mistakes vs NoiseLevel
95% CI for the Mean
16
14
12
Mistakes
10
2
1 2 3
NoiseLevel
The pooled standard deviation is used to calculate the intervals.
Final Exam Page 8 of 10
Printout #2
Regression Analysis: Number versus Price
Analysis of Variance
Adj
Source DF Adj SS MS F-Value P-Value
Regressio 1 3311 3310.9 7.77 0.032
n
Price 1 3311 3310.9 7.77 0.032
Error 6 2556 426.0
Total 7 5867
Model Summary
R-
S R-sq sq(adj) R-sq(pred)
20.639 56.43% 49.17% 23.44%
6
Coefficients
SE T-
Term Coef Coef Value P-Value VIF
Constan 302.9 30.9 9.80 0.000
t
Price -8.78 3.15 -2.79 0.032 1.00
Regression Equation
Numbe = 302.9 - 8.78 Price
r
Fits and Diagnostics for Unusual Observations
Ob Std
s Number Fit Resid Resid
2 245.0 202.8 42.2 2.30 R
R Large residual
Final Exam Page 9 of 10
Scatterplot of Number vs Price
270
260
250
240
230
Number
220
210
200
190
180
5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
Price
Final Exam Page 10 of 10
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Double Bottom Line: Profit and Social BenefitDocumento10 pagineThe Double Bottom Line: Profit and Social BenefitjennyxzxzNessuna valutazione finora
- Adjective Clause Worksheet EslDocumento4 pagineAdjective Clause Worksheet Eslmali MalekNessuna valutazione finora
- Acrostic PoemDocumento1 paginaAcrostic Poemapi-332962221Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis Statement PracticDocumento36 pagineThesis Statement PracticHanna HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Making Inferences 2Documento2 pagineMaking Inferences 2Arsha AsimNessuna valutazione finora
- Character Analysis EssayDocumento7 pagineCharacter Analysis EssayKeizsha Leyma100% (1)
- Cases of PronounsDocumento19 pagineCases of PronounsMaki Acedo0% (1)
- Haze: A Danger To Health - Sample Essay: Directed WritingDocumento8 pagineHaze: A Danger To Health - Sample Essay: Directed WritingYazid HaronNessuna valutazione finora
- Participial Phrases: Looking at The Recent Issue of CosmoDocumento3 pagineParticipial Phrases: Looking at The Recent Issue of CosmoFernanda MarangielloNessuna valutazione finora
- Persuasive Essay Graphic OrganizerDocumento3 paginePersuasive Essay Graphic Organizerapi-400072597Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analogies WorksheetsDocumento4 pagineAnalogies WorksheetsowaeisNessuna valutazione finora
- 508 WWCPG SecondaryWriting 122719Documento97 pagine508 WWCPG SecondaryWriting 122719Rose Mc CollinNessuna valutazione finora
- ES1103 Rubric For Problem Solution Essay - Student Version - FINALDocumento2 pagineES1103 Rubric For Problem Solution Essay - Student Version - FINALSimon Warui100% (2)
- Persuasive Writing Unit: Name: - DateDocumento23 paginePersuasive Writing Unit: Name: - Dateapi-300074215Nessuna valutazione finora
- Argumentative EssayDocumento2 pagineArgumentative EssayJulie Basbas-CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Fast-Cars Co. Rim Study Exam I Version ADocumento7 pagineFast-Cars Co. Rim Study Exam I Version AKoe Chien ThongNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploits University Exam Paper Covers Research Methods TopicsDocumento5 pagineExploits University Exam Paper Covers Research Methods TopicsVincent KamangaNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT 2601 Final Exam Extra Practice QuestionsDocumento9 pagineSTAT 2601 Final Exam Extra Practice Questionssubui613Nessuna valutazione finora
- BBA OM PreboardDocumento2 pagineBBA OM PreboardJabed MansuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt ExamDocumento6 pagineLean Six Sigma Black Belt ExamMarlon0% (3)
- Problem 1Documento12 pagineProblem 1Hafiz MunirNessuna valutazione finora
- HBC 2210 Operations ResearchDocumento7 pagineHBC 2210 Operations Researchmwakoja saidNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical Methods and Inference: Toaxyz - Raphaellee - T1923161 (Omit D/O, S/O)Documento7 pagineStatistical Methods and Inference: Toaxyz - Raphaellee - T1923161 (Omit D/O, S/O)Suwandi LieNessuna valutazione finora
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: B.Tech Ii Year Ii Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017Documento2 pagineWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: B.Tech Ii Year Ii Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017Tameem AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- ST131: Introduction To Statistics Assignment, Semester 1, 2020Documento2 pagineST131: Introduction To Statistics Assignment, Semester 1, 2020TeratabuNessuna valutazione finora
- MG311 ExamDocumento4 pagineMG311 ExamTetzNessuna valutazione finora
- Show Your Work Wherever Possible.: STAT 305 Section B Spring 2012 Exam I Version ADocumento9 pagineShow Your Work Wherever Possible.: STAT 305 Section B Spring 2012 Exam I Version AKoe Chien ThongNessuna valutazione finora
- FPMA1054 Business Statistics Coursework AssignmentDocumento9 pagineFPMA1054 Business Statistics Coursework Assignmentyenhui613Nessuna valutazione finora
- EG110 (Spring 2021) Exam #2 Pelayo MartinezDocumento6 pagineEG110 (Spring 2021) Exam #2 Pelayo MartinezPelayo MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- GATE-2018: All India Mock GATE Test SeriesDocumento16 pagineGATE-2018: All India Mock GATE Test SeriesRohit SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 QM II End Term FinalDocumento4 pagine2020 QM II End Term FinalSIRSHA PATTANAYAKNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam questions on computer simulationDocumento4 pagineExam questions on computer simulationMark MumbaNessuna valutazione finora
- BEN2203 MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2019 SYNCHRONISEDDocumento7 pagineBEN2203 MID SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2019 SYNCHRONISEDAgang KanyaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Production and Operations Management Practice SetDocumento7 pagineProduction and Operations Management Practice SetArup Kumar SenNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiplication and Division: Learning From HomeDocumento38 pagineMultiplication and Division: Learning From HomeShane RajapakshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Operation Research Exam 2020Documento14 pagineOperation Research Exam 2020林芷帆Nessuna valutazione finora
- TA112 .BQAF - .L Question CMA January 2022 Examination PDFDocumento7 pagineTA112 .BQAF - .L Question CMA January 2022 Examination PDFMohammed Javed UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- CMA MAY-2022 EXAMINATION: BQA MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONSDocumento8 pagineCMA MAY-2022 EXAMINATION: BQA MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONSMohammed Javed UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Coqt111 Examination B Sem1 June 2017 - UpdatedDocumento9 pagineCoqt111 Examination B Sem1 June 2017 - UpdatedakiduidrissNessuna valutazione finora
- MA3 Sample Exams Plus SolutionsDocumento89 pagineMA3 Sample Exams Plus Solutionsbooks_sumiNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam - Proba - 2022 - Sem01 - v1Documento3 pagineFinal Exam - Proba - 2022 - Sem01 - v1Jay LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Operation Research HomeworkDocumento7 pagineOperation Research HomeworkThuyết Trương DũngNessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 4N4 Final ExamDocumento5 pagine2013 4N4 Final ExamFaishal AushafNessuna valutazione finora
- 15.053 - Optimization Methods in Management Science (Spring 2007)Documento6 pagine15.053 - Optimization Methods in Management Science (Spring 2007)Ehsan SpencerNessuna valutazione finora
- New QA Past PapersDocumento76 pagineNew QA Past PapersAlphayo MonyigisNessuna valutazione finora
- IEORE4101 Midterm Exam Solutions Spring 2021Documento7 pagineIEORE4101 Midterm Exam Solutions Spring 2021Shlok SethiaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10ISL68-Software Testing Lab Triangle Program TestsDocumento47 pagine10ISL68-Software Testing Lab Triangle Program TestsAashish AcharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Statisticshomework f14Documento2 pagineStatisticshomework f14Pooja JainNessuna valutazione finora
- (l5) Decision Making TechniquesDocumento20 pagine(l5) Decision Making TechniquesBruceNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment BRM.2020Documento8 pagineAssignment BRM.2020Athma LalNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative AssignmentDocumento6 pagineQuantitative AssignmentAlemu Muleta KebedeNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 4 - Analysis of Variance PDFDocumento10 pagineTutorial 4 - Analysis of Variance PDFNoorNabilaNessuna valutazione finora
- MGMT PracticeDocumento3 pagineMGMT Practicegmatej09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sonata PlacementPapers PDFDocumento26 pagineSonata PlacementPapers PDFrohit sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mth601 Collection of Old PapersDocumento33 pagineMth601 Collection of Old Paperscs619finalproject.com86% (7)
- MAST 6474 Introduction To Data Analysis I MAST 6478 Data AnalyticsDocumento4 pagineMAST 6474 Introduction To Data Analysis I MAST 6478 Data AnalyticsMygenNessuna valutazione finora
- 0711230652526896Documento307 pagine0711230652526896Sivaram KavetiNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Exam Solution Key and FormulasDocumento10 pagineMidterm Exam Solution Key and FormulasHARSHIT SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- MMS 2022-24 QP Business StatisticsDocumento5 pagineMMS 2022-24 QP Business StatisticsnimeshnarnaNessuna valutazione finora
- MUN 2400 Practice FinalDocumento15 pagineMUN 2400 Practice FinalMallory EnnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Module 1,2,3Documento129 pagineRevision Module 1,2,3jitamitra88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mental AspectDocumento29 pagineMental AspectBenjii CarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 420001 PDFDocumento13 pagineTest 420001 PDFmaria100% (1)
- Aw MD700 Manual G10 150706Documento73 pagineAw MD700 Manual G10 150706Heraldo Ulguim Luis OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization Module For Abaqus/CAE Based On Genetic AlgorithmDocumento1 paginaOptimization Module For Abaqus/CAE Based On Genetic AlgorithmSIMULIACorpNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid SemDocumento1 paginaMid SemvidulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analisis Efektivitas Inklusi Keuangan Di BMT Syariah Riyal: PendahuluanDocumento25 pagineAnalisis Efektivitas Inklusi Keuangan Di BMT Syariah Riyal: PendahuluanEma Rina SafitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning Dirty FrameworkDocumento62 paginePlanning Dirty FrameworkHoàng Hoa Dương100% (1)
- Renal Angina Index in Pediatric Septic Patients As A Predictor of Acute Kidney Injury in Remote AreaDocumento9 pagineRenal Angina Index in Pediatric Septic Patients As A Predictor of Acute Kidney Injury in Remote AreaFarhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Nilufer-CaliskanDocumento7 pagine13 Nilufer-Caliskanab theproNessuna valutazione finora
- Report Card of Army Public School StudentDocumento2 pagineReport Card of Army Public School StudentRama KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Audi A3 Injeção DiretaDocumento109 pagineAudi A3 Injeção Diretawesley candido100% (1)
- MD SHAFIUL ISLAM 沙菲 ID;20183290290Documento23 pagineMD SHAFIUL ISLAM 沙菲 ID;20183290290SHAFIUL SETUNessuna valutazione finora
- SECURE ROAD BLOCKERS PREVENT VEHICLE ATTACKSDocumento2 pagineSECURE ROAD BLOCKERS PREVENT VEHICLE ATTACKSMuhammad Tahir QamarNessuna valutazione finora
- Galvanized and Black Malleable Iron Pipe Fittings SpecificationsDocumento24 pagineGalvanized and Black Malleable Iron Pipe Fittings SpecificationsdeniNessuna valutazione finora
- 102DNDocumento2 pagine102DNManuel ZavalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atpl Formula MergedDocumento74 pagineAtpl Formula Mergeddsw78jm2mxNessuna valutazione finora
- Innovations in Drill Stem Safety Valve TechnologyDocumento22 pagineInnovations in Drill Stem Safety Valve Technologymiguel mendoza0% (1)
- Fish HatcheryDocumento14 pagineFish HatcheryYared Mesfin FikaduNessuna valutazione finora
- CBL Training ReportDocumento12 pagineCBL Training ReportSwapnil Modak100% (1)
- Get Started On Creating Your Event Budget:: If You Decide To Build Your Own Start by Creating A Few ColumnsDocumento4 pagineGet Started On Creating Your Event Budget:: If You Decide To Build Your Own Start by Creating A Few ColumnsGeomarkPaalaMortelNessuna valutazione finora
- Attitudes and Practices Related To Sexuality and Sexual BehaviorDocumento35 pagineAttitudes and Practices Related To Sexuality and Sexual BehaviorGalvin LalusinNessuna valutazione finora
- Keynote Proficient End-Of-Course Test BDocumento7 pagineKeynote Proficient End-Of-Course Test Bana maria csalinasNessuna valutazione finora
- 3ADW000379R0301 DCS550 Manual e CDocumento310 pagine3ADW000379R0301 DCS550 Manual e CLaura SelvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Layer:: SwitchingDocumento27 paginePhysical Layer:: SwitchingPKSachanNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Vitae: Name: Mobile: EmailDocumento3 pagineCurriculum Vitae: Name: Mobile: EmailRākesh RakhiNessuna valutazione finora
- PC 4 Product List 2019 - Pc4Documento28 paginePC 4 Product List 2019 - Pc4ShNessuna valutazione finora
- Plyometric Training Programs For Young Soccer Players: A Systematic ReviewDocumento7 paginePlyometric Training Programs For Young Soccer Players: A Systematic ReviewsteNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of SelfDocumento5 pagineTheories of SelfTd Devi AmmacayangNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Education Region IV-A Business Plan GuideDocumento4 pagineDepartment of Education Region IV-A Business Plan GuideSEAN DANIEL AGUARESNessuna valutazione finora