Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
38untitled Extract Pages
Caricato da
qc_531040655Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
38untitled Extract Pages
Caricato da
qc_531040655Copyright:
Formati disponibili
AISC_PART 16_A_Prelims_15th Ed.
_2016 2016-11-15 11:23 AM Page xlii (Black plate)
16.1-xlii GLOSSARY
Braced frame†. Essentially vertical truss system that provides resistance to lateral forces and
provides stability for the structural system.
Bracing. Member or system that provides stiffness and strength to limit the out-of-plane
movement of another member at a brace point.
Branch member. In an HSS connection, member that terminates at a chord member or main
member.
Buckling†. Limit state of sudden change in the geometry of a structure or any of its elements
under a critical loading condition.
Buckling strength. Strength for instability limit states.
Built-up member, cross section, section, shape. Member, cross section, section or shape fab-
ricated from structural steel elements that are welded or bolted together.
Camber. Curvature fabricated into a beam or truss so as to compensate for deflection in-
duced by loads.
Charpy V-notch impact test. Standard dynamic test measuring notch toughness of a specimen.
Chord member. In an HSS connection, primary member that extends through a truss connection.
Cladding. Exterior covering of structure.
Cold-formed steel structural member†. Shape manufactured by press-braking blanks sheared
from sheets, cut lengths of coils or plates, or by roll forming cold- or hot-rolled coils or
sheets; both forming operations being performed at ambient room temperature, that is,
without manifest addition of heat such as would be required for hot forming.
Collector. Also known as drag strut; member that serves to transfer loads between floor
diaphragms and the members of the lateral force-resisting system.
Column. Nominally vertical structural member that has the primary function of resisting
axial compressive force.
Column base. Assemblage of structural shapes, plates, connectors, bolts and rods at the base
of a column used to transmit forces between the steel superstructure and the foundation.
Compact section. Section capable of developing a fully plastic stress distribution and pos-
sessing a rotation capacity of approximately three before the onset of local buckling.
Compartmentation. Enclosure of a building space with elements that have a specific fire
endurance.
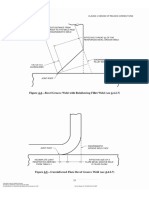
Complete-joint-penetration (CJP) groove weld. Groove weld in which weld metal extends
through the joint thickness, except as permitted for HSS connections.
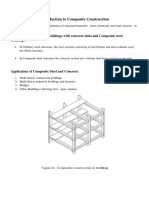
Composite. Condition in which steel and concrete elements and members work as a unit in
the distribution of internal forces.
Composite beam. Structural steel beam in contact with and acting compositely with a rein-
forced concrete slab.
Composite component. Member, connecting element or assemblage in which steel and con-
crete elements work as a unit in the distribution of internal forces, with the exception of
the special case of composite beams where steel anchors are embedded in a solid concrete
slab or in a slab cast on formed steel deck.
Concrete breakout surface. The surface delineating a volume of concrete surrounding a steel
headed stud anchor that separates from the remaining concrete.
Specification for Structural Steel Buildings, July 7, 2016
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF STEEL CONSTRUCTION
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Composite Steel and Concrete Structural Members: Composite Steel and Concrete Structures: Fundamental Behaviour (Second Edition)Da EverandComposite Steel and Concrete Structural Members: Composite Steel and Concrete Structures: Fundamental Behaviour (Second Edition)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Dimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyDa EverandDimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyNessuna valutazione finora
- CV0054 Design of Structures: Structural Steel Part 2: GlossaryDocumento12 pagineCV0054 Design of Structures: Structural Steel Part 2: GlossaryVajindra WijewickramaNessuna valutazione finora
- 39untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina39untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 40untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina40untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 130 DrawingsDocumento22 pagine130 DrawingsJustin GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anchor Roads:: Steel GlossaryDocumento3 pagineAnchor Roads:: Steel Glossaryusman aslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 09Documento48 paginePresentation 09engsamim.walizadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Columns Beams SlabsDocumento48 pagineColumns Beams SlabsWilson Muguro100% (1)
- Beam, Frame TrussDocumento3 pagineBeam, Frame TrussKrishna MyakalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mkae1033 1Documento5 pagineMkae1033 1omed muhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel DesignDocumento5 pagineSteel DesignKutty MansoorNessuna valutazione finora
- FlangeDocumento3 pagineFlangeCabsNessuna valutazione finora
- Rigid Frame Systems, Also Called Moment Frame Systems, Are Used in Steel and ReinforcedDocumento1 paginaRigid Frame Systems, Also Called Moment Frame Systems, Are Used in Steel and Reinforcedyedida viswanadhNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel and Timber ReviewerDocumento4 pagineSteel and Timber ReviewerGlaiza Marie MasbateNessuna valutazione finora
- Students' Reinforced Concrete Thesaurus: (With Due Reverence To MR Roget)Documento5 pagineStudents' Reinforced Concrete Thesaurus: (With Due Reverence To MR Roget)KWUPASENANessuna valutazione finora
- Theory - Introjoist and Structural Glossary 4Documento29 pagineTheory - Introjoist and Structural Glossary 4Christina De MesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Construction MethoddDocumento13 pagineComposite Construction MethoddEditha BaniquedNessuna valutazione finora
- Shear ConnectorDocumento2 pagineShear ConnectorDhanush SNessuna valutazione finora
- Research PsteelDocumento13 pagineResearch PsteelAira NunagNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Behavior of Steel Building With Concentric and Eccentric BracingDocumento8 pagineStructural Behavior of Steel Building With Concentric and Eccentric BracingNazim Uddin RahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Push Over Analysis of Unstiffened Steel Plate Shear Wall: Abhishek Verma, P. R. MaitiDocumento9 paginePush Over Analysis of Unstiffened Steel Plate Shear Wall: Abhishek Verma, P. R. MaitiIJERDNessuna valutazione finora
- Beam To Beam ConnectionsDocumento9 pagineBeam To Beam ConnectionskarthiksampNessuna valutazione finora
- Reinforcing Steel Bars and TendonsDocumento31 pagineReinforcing Steel Bars and TendonsJebone Stein Web JuarbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Construction MethodsDocumento33 pagineComposite Construction Methodscristian santillanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Behavior of Concrete and Steel StructuresDocumento11 pagineIntroduction To Behavior of Concrete and Steel StructuresLopez ReyNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of RC Structure and Composite Strucutre Based On Literature ReviewDocumento20 pagineComparison of RC Structure and Composite Strucutre Based On Literature ReviewAngela100% (1)
- Ass Unit 2Documento17 pagineAss Unit 2Samreen Khan100% (1)
- Introduction To Reinforced Concrete Design PrinciplesDocumento13 pagineIntroduction To Reinforced Concrete Design PrinciplesMagsino, Jubillee SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Steel Structures BS 5950: Eng. Chamara Yapa Arachchi Civil EngineerDocumento60 pagineDesign of Steel Structures BS 5950: Eng. Chamara Yapa Arachchi Civil Engineerpareen9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Residential Steel Frame Building Case StudyDocumento29 pagineResidential Steel Frame Building Case Studyprajoshi62Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prestressed Concrete: BT AR Joseph ReaDocumento4 paginePrestressed Concrete: BT AR Joseph ReaDaryl AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Design Basic ConceptsDocumento3 pagineSteel Design Basic ConceptsmithunNessuna valutazione finora
- 2022Documento2 pagine2022medNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 7 & 8Documento59 pagineLesson 7 & 8Jay-r MiñozaNessuna valutazione finora
- PSD Test NotesDocumento21 paginePSD Test Notesmuhfil MuhfilNessuna valutazione finora
- Wither3d Lateral Forces Study Guide VimprotantDocumento12 pagineWither3d Lateral Forces Study Guide VimprotantthewodrosNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Bracing in Braced Multi-Storey FramesDocumento12 pagineSteel Bracing in Braced Multi-Storey FramesVictor OmotoriogunNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 7. Structural Steel Assemblies & ConnectionsDocumento22 pagineLesson 7. Structural Steel Assemblies & Connectionsarkidiots2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Joist and Structural GlossaryDocumento473 pagineJoist and Structural GlossaryPolo EspondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Beam (Structure) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento3 pagineBeam (Structure) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadonodoni0008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Composite ConstructionDocumento16 pagineIntroduction To Composite Constructionabdelrahman emadNessuna valutazione finora
- 37untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina37untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Self-Centering Moment Resisting Frame and Experimental Loading SystemDocumento17 pagineDesign of Self-Centering Moment Resisting Frame and Experimental Loading SystemAshwini TeegalaNessuna valutazione finora
- International Journal of Civil and Structural EngineeringDocumento11 pagineInternational Journal of Civil and Structural EngineeringstlebeNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 - Structural Steel Frame Construction (B)Documento33 pagine7 - Structural Steel Frame Construction (B)Dennis NjorogeNessuna valutazione finora
- INtro To SteelDocumento29 pagineINtro To SteelAnima PNessuna valutazione finora
- Thin-Walled Structures: Kim J.R. Rasmussen, Mani Khezri, Benjamin W. Schafer, Hao ZhangDocumento42 pagineThin-Walled Structures: Kim J.R. Rasmussen, Mani Khezri, Benjamin W. Schafer, Hao ZhangJavedNessuna valutazione finora
- Mod 3 - Tos V NotesDocumento6 pagineMod 3 - Tos V NotesAysha FarialNessuna valutazione finora
- Fleischman Et Al Connections VIII 2016Documento11 pagineFleischman Et Al Connections VIII 2016AlirezaNessuna valutazione finora
- 20eucv038 - Ocle 1 (1) - 20eucv038 - Saran KDocumento24 pagine20eucv038 - Ocle 1 (1) - 20eucv038 - Saran KkirthickNessuna valutazione finora
- Reinforced Concrete BeamsDocumento28 pagineReinforced Concrete BeamsEdriane Jude MalemNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Action in BeamsDocumento21 pagineComposite Action in BeamsAlemayehu DargeNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Construction MethodsDocumento4 pagineComposite Construction Methodskimobar34Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2.4 Related LiteratureDocumento2 pagine2.4 Related LiteratureqdalquiambaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Seismic DesignDocumento24 pagineSteel Seismic DesignsenthilcivilNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Theory Chapter 1Documento12 pagineStructural Theory Chapter 1MAGNI FICATNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel Member DefinitionDocumento2 pagineSteel Member DefinitionVeereshNessuna valutazione finora
- Braced Frames: From Steelconstruction - InfoDocumento18 pagineBraced Frames: From Steelconstruction - Infojohnsmith1980Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionDa EverandStructural Concrete: The Commonwealth and International Library: Structures and Solid Body Mechanics DivisionNessuna valutazione finora
- Intercure 99 Application Guidelines UkDocumento14 pagineIntercure 99 Application Guidelines Ukqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Qulified JointsDocumento6 paginePre Qulified Jointsqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bolt Torque - Astm & IsoDocumento2 pagineBolt Torque - Astm & Isoqc_53104065550% (4)
- ASTM D1621 Compression Testing of Expanded Plastics and FoamsDocumento2 pagineASTM D1621 Compression Testing of Expanded Plastics and Foamsqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- Root Cause Techniques PresentationDocumento17 pagineRoot Cause Techniques Presentationqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bolt Torque - Astm & IsoDocumento2 pagineBolt Torque - Astm & Isoqc_531040655100% (1)
- Flowtech Company Profile Full Line Catalogue 2018Documento16 pagineFlowtech Company Profile Full Line Catalogue 2018qc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Test-Consent FormDocumento1 paginaRevision Test-Consent Formqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- Flowtech Company Profile Full Line Catalogue 2018Documento16 pagineFlowtech Company Profile Full Line Catalogue 2018qc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 30untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina30untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 37untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina37untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 33untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina33untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 31untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina31untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- Project: EXPO 2020 - OV016 - USA PAVILION Inspection and Test Plan (Itp)Documento5 pagineProject: EXPO 2020 - OV016 - USA PAVILION Inspection and Test Plan (Itp)qc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- Symbol Section: Merican Nstitute of Teel OnstructionDocumento1 paginaSymbol Section: Merican Nstitute of Teel Onstructionqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 26untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina26untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 28untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina28untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 22untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina22untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 24untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina24untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 27untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina27untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 23extract PagesDocumento1 pagina23extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 21untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina21untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 16untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina16untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 19untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina19untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- 15untitled Extract PagesDocumento1 pagina15untitled Extract Pagesqc_531040655Nessuna valutazione finora
- National Action Plan Implementation Gaps and SuccessesDocumento8 pagineNational Action Plan Implementation Gaps and SuccessesHamza MinhasNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion To DismissDocumento24 pagineMotion To DismisssandyemerNessuna valutazione finora
- Es 590Documento35 pagineEs 590Adnan BeganovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction and Instructions: ForewordDocumento20 pagineIntroduction and Instructions: ForewordDanang WidoyokoNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport StrikeDocumento9 pagineTransport StrikeYsrael Von ArcillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Motion ProblemsDocumento4 pagineCircular Motion ProblemsGheline LexcieNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformative Change at PPLDocumento24 pagineTransformative Change at PPLAli A. KhokhArNessuna valutazione finora
- Sarah Williams CVDocumento2 pagineSarah Williams CVsarahcwilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- MB0048 Operation Research Assignments Feb 11Documento4 pagineMB0048 Operation Research Assignments Feb 11Arvind KNessuna valutazione finora
- Juegos PPCDocumento8 pagineJuegos PPCikro995Nessuna valutazione finora
- Beijing-Michael PageDocumento71 pagineBeijing-Michael Pagejohndavsg8022Nessuna valutazione finora
- Preventive Maintenance Checklist: Tool Room & Production SawsDocumento2 paginePreventive Maintenance Checklist: Tool Room & Production SawsValerio Ambrocio IsmaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation The New Condominium Rules 9 1 2018 PDFDocumento35 paginePresentation The New Condominium Rules 9 1 2018 PDFYe AungNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Questions Mba-Ii Sem Organisational BehaviourDocumento24 pagineImportant Questions Mba-Ii Sem Organisational Behaviourvikas__ccNessuna valutazione finora
- Barnett V Chelsea and Kensington Hospital Management CommitteeDocumento3 pagineBarnett V Chelsea and Kensington Hospital Management CommitteeArpit Soni0% (1)
- Logbook) Industrial Attachment Brief To Students-3Documento6 pagineLogbook) Industrial Attachment Brief To Students-3geybor100% (1)
- BMW Speakers Install BSW Stage 1 E60 Sedan Logic7Documento13 pagineBMW Speakers Install BSW Stage 1 E60 Sedan Logic7StolnicuBogdanNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Cost CompaniesDocumento9 pagineLow Cost CompaniesIvan RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- (The Nineteenth Century Series) Grace Moore - Dickens and Empire - Discourses of Class, Race and Colonialism in The Works of Charles Dickens-Routledge (2004) PDFDocumento223 pagine(The Nineteenth Century Series) Grace Moore - Dickens and Empire - Discourses of Class, Race and Colonialism in The Works of Charles Dickens-Routledge (2004) PDFJesica LengaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wi-Fi Planning and Design Questionnaire 2.0Documento12 pagineWi-Fi Planning and Design Questionnaire 2.0Free Space67% (3)
- County Project Name Cycle Project Address Proj City Proj Zip Applicant/Owner Name HDGP $ Home $ FHTF $ Lihtc9 $ Help $ Oahtc $ Ghap $ HPF $ Lihtc4 $Documento60 pagineCounty Project Name Cycle Project Address Proj City Proj Zip Applicant/Owner Name HDGP $ Home $ FHTF $ Lihtc9 $ Help $ Oahtc $ Ghap $ HPF $ Lihtc4 $Mamello PortiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Ordnance FactoryDocumento2 pagineIndian Ordnance FactoryAniket ChakiNessuna valutazione finora
- Definition of Sustainable Packaging PDFDocumento10 pagineDefinition of Sustainable Packaging PDFProf C.S.PurushothamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pepsico IncDocumento26 paginePepsico IncYKJ VLOGSNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet HFS60Documento3 pagineDatasheet HFS60RajeswaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For New Students - 2022Documento14 pagineGuidelines For New Students - 2022Ria Faye PaderangaNessuna valutazione finora
- CS 148 - Introduction To Computer Graphics and ImagingDocumento3 pagineCS 148 - Introduction To Computer Graphics and ImagingMurtaza TajNessuna valutazione finora
- FinTech RegTech and SupTech - What They Mean For Financial Supervision FINALDocumento19 pagineFinTech RegTech and SupTech - What They Mean For Financial Supervision FINALirvandi syahputraNessuna valutazione finora
- COST v. MMWD Complaint 8.20.19Documento64 pagineCOST v. MMWD Complaint 8.20.19Will HoustonNessuna valutazione finora
- Sinamics gm150 sm150 Catalog d12 02 2020 enDocumento238 pagineSinamics gm150 sm150 Catalog d12 02 2020 enGo andWatchNessuna valutazione finora