Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Duty Cycle: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Caricato da
Madhu BediguthuTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Duty Cycle: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Caricato da
Madhu BediguthuCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Duty cycle
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A duty cycle is the percent of time that an entity spends in an active state as a fraction of the total time under
consideration.[1][2] The term is often used pertaining to electrical devices, e.g., switching power supplies. It is
also sometimes used pertaining to living systems such as the firing of action potentials byneurons. In an
electrical device, a 60% duty cycle means the power is on 60% of the time and off 40% of the time. The "on
time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second – or for say, irrigation pumps, days – depending on
how long the device's period is. Here one period is the length of time it takes for the device to go through a
complete on/off cycle. The term "duty cycle" has no agreed meaning for aperiodic devices. [citation needed]
Contents
[hide]
1 Definition
2 Examples
o 2.1 Electronics and digital signal processing
o 2.2 Electrical devices
o 2.3 Biological systems
3 References
Definition[edit]
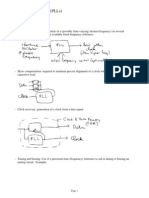
The duty cycle is defined as the ratio between the pulse duration ( ) and the period ( ) of a rectangular waveform
In a periodic event, duty cycle is the ratio of the duration of the event to the total period of a signal.
[3]
duty cycle
where
is the duration that the function is active.
is the period of the function.
Examples[edit]
Electronics and digital signal processing[edit]
In an ideal pulse train (one having rectangular pulses), the duty cycle is the pulse duration divided
by the pulse period.[4] For example, a pulse train in which the pulse duration is 1 μs and the pulse
period is 4 μs has a duty cycle of 25%. The pulse duration is normally calculated for positive
pulses unless "negative duty cycle" is specified.
The duty cycle of a non-rectangular waveform, such as a sine or triangle wave, is defined as the
fraction of the period the waveform spends above 0.[5]
In a continuously variable slope delta (CVSD) modulation converter, the mean proportion
of binary "1" digits at the converter output in which each "1" indicates a run of a specified number
of consecutive bits of the same polarity in the digital output signal.
Electrical devices[edit]
Electrical motors typically use less than a 100% duty cycle. For example, if a motor runs for one
out of 100 seconds, or 1/100 of the time, then, its duty cycle is 1/100, or 1 percent. [6]
In electronic music, music synthesizers vary the duty cycle of their audio-frequency oscillators to
obtain a subtle effect on the tone colors. This technique is known as pulse-width
modulation (PWM).
In the printer / copier industry, the duty cycle specification refers to the rated throughput (that is,
printed pages) of a device per month.
In a welding power supply, the maximum duty cycle is defined as the percentage of time in a 10
minute period that it can be operated continuously before overheating. [7]
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Technology Procurement HandbookDocumento329 pagineThe Technology Procurement HandbookAlexander Jose Chacin NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- 1988 Mazda 323 Workshop Manual V1.0 (Turbo Only)Documento880 pagine1988 Mazda 323 Workshop Manual V1.0 (Turbo Only)Mike Marquez100% (2)
- NGCP - Procedures and Requirements For Energy ProjectsDocumento17 pagineNGCP - Procedures and Requirements For Energy ProjectspurplebasketNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulse Width Modulation HelpDocumento4 paginePulse Width Modulation Helpapi-19667371Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muhammad Sohaib Ali Fa20-Bee-2C-241Documento3 pagineMuhammad Sohaib Ali Fa20-Bee-2C-241Souban JavedNessuna valutazione finora
- Vibrations Eoliennes Intro PDFDocumento26 pagineVibrations Eoliennes Intro PDFkolombo1776Nessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding SYSCLK JitterDocumento10 pagineUnderstanding SYSCLK Jitterxiaokang.liuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ring Oscillators: Characteristics and Applications: M K Mandal & B C SarkarDocumento10 pagineRing Oscillators: Characteristics and Applications: M K Mandal & B C SarkarIdk RebollosNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 02-Physical Layer-Transmission Terminology-1920Documento80 pagineLecture 02-Physical Layer-Transmission Terminology-1920Arvin 97Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vibrations Eoliennes IntroDocumento26 pagineVibrations Eoliennes Intromacjosmanuel5453Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rise Time 3dB Bandwidth Relationship Lab FactDocumento26 pagineRise Time 3dB Bandwidth Relationship Lab Factvotasugs756Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Set Three-Wave GeneratorDocumento10 pagineLecture Set Three-Wave GeneratorNasa McAikenNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Systems Protection Course: Al-Balqa Applied UniversityDocumento37 paginePower Systems Protection Course: Al-Balqa Applied UniversityNitesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Signal Transfer Functions and Mathematical Model of The Boost Power ConverterDocumento6 pagineSmall Signal Transfer Functions and Mathematical Model of The Boost Power ConverterNtokozo HlatshwayoNessuna valutazione finora
- A Model of A QCW Diode Pumped Passively Q-Switched Solid State LaserDocumento6 pagineA Model of A QCW Diode Pumped Passively Q-Switched Solid State LaserAishum1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Razavi PLL TutorialDocumento39 pagineRazavi PLL TutorialbsrathorNessuna valutazione finora
- Telecommunications AssignmentDocumento17 pagineTelecommunications AssignmentKai DetsunNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Control Methods Sharing Synchronous Converter: For Current of Interleaved Buck AndreassenDocumento7 pagineDigital Control Methods Sharing Synchronous Converter: For Current of Interleaved Buck Andreassenrmsharma1970Nessuna valutazione finora
- Razavi Monolithic Phase-Locked Loops and Clock Recovery CircuitsDocumento39 pagineRazavi Monolithic Phase-Locked Loops and Clock Recovery CircuitsAhmedEssa89Nessuna valutazione finora
- A 230ns Settling Time Type-I PLL With 0.96mW TDC Power and Simple T Calculation AlgorithmDocumento4 pagineA 230ns Settling Time Type-I PLL With 0.96mW TDC Power and Simple T Calculation AlgorithmNguyen Van ToanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulse Width ModulationDocumento7 paginePulse Width ModulationAnonymous E4Rbo2sNessuna valutazione finora
- Application Note: Lifetime of OptocouplersDocumento5 pagineApplication Note: Lifetime of OptocouplersRM MódulosNessuna valutazione finora
- Fault Resistance, Location and Inception Angle Effects On DC Offset of The Fault CurrentsDocumento6 pagineFault Resistance, Location and Inception Angle Effects On DC Offset of The Fault CurrentsItalo ChiarellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Space Vector PWM - 2Documento6 pagineSpace Vector PWM - 2guanitouNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsDa EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNessuna valutazione finora
- PSPS - Module 1 - Part 1 PDFDocumento14 paginePSPS - Module 1 - Part 1 PDFOmkar GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Time ConstantDocumento9 pagineTime Constantmoise adrianNessuna valutazione finora
- Considerations For Notch Simulation - JCDocumento1 paginaConsiderations For Notch Simulation - JCjoacocnNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 03Documento64 pagineCH 03rabeea malikNessuna valutazione finora
- UCK304E ElectricalExperiments Experiment2 Lab FileDocumento7 pagineUCK304E ElectricalExperiments Experiment2 Lab Filey.komurcu921Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bhandari GuruDocumento38 pagineBhandari GuruNam NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 3 Data and SignalsDocumento80 pagineWeek 3 Data and SignalsMuneebNessuna valutazione finora
- Rectangular To Circular Waveguide Converter For Microwave Devices CharacterizationDocumento10 pagineRectangular To Circular Waveguide Converter For Microwave Devices Characterizationjalmeida88Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1Documento1 pagina1DharanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Dual-Slope Conversion Improvement: Radojle Radetić, Marijana Pavlov-Kagadejev, Nikola MilivojevićDocumento13 pagineThe Dual-Slope Conversion Improvement: Radojle Radetić, Marijana Pavlov-Kagadejev, Nikola MilivojevićasprillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Iceei 2011 6021720Documento5 pagineIceei 2011 6021720Janyss. MMNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 9: Natural Response of An RC Circuit: Muhammad Ahmed Minhas FA20-BEE-2C-112Documento3 pagineLab 9: Natural Response of An RC Circuit: Muhammad Ahmed Minhas FA20-BEE-2C-112Souban JavedNessuna valutazione finora
- ch03 Comm Network Lecture 3 LIU Fall 2021Documento64 paginech03 Comm Network Lecture 3 LIU Fall 2021salahrafeek231Nessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Aeolian Vibration On Transmission LineDocumento7 pagineAnalysis of Aeolian Vibration On Transmission LineameypnNessuna valutazione finora
- RC Time Constant: Cutoff Frequency Delay See Also References External LinksDocumento3 pagineRC Time Constant: Cutoff Frequency Delay See Also References External LinksPralay MaitiNessuna valutazione finora
- UT Question and AnswersDocumento11 pagineUT Question and Answersrzajadgs50% (2)
- Water Level Indicator - HBRP PublicationDocumento5 pagineWater Level Indicator - HBRP PublicationsdevanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Control of A Four Stroke Internal CombuDocumento7 pagineElectronic Control of A Four Stroke Internal CombuSB ZouheyrNessuna valutazione finora
- A 148 Fs Rms Integrated Noise 4 MHZ Bandwidth Second-Order DS Time-To-Digital Converter With Gated Switched-Ring OscillatorDocumento9 pagineA 148 Fs Rms Integrated Noise 4 MHZ Bandwidth Second-Order DS Time-To-Digital Converter With Gated Switched-Ring Oscillatornucleur_13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unique Concepts of Power ElectronicsDocumento4 pagineUnique Concepts of Power Electronicsegaupc2123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dokumen Tanpa JudulDocumento54 pagineDokumen Tanpa JudulKimriyahrfk 999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Closed Loop Control Design of Two Inductor Current-Fed Isolated DC-DC Converter For Fuel Cells To Utility Interface ApplicationDocumento8 pagineClosed Loop Control Design of Two Inductor Current-Fed Isolated DC-DC Converter For Fuel Cells To Utility Interface ApplicationNagababuMutyalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 13Documento13 pagineLecture 13Mohd FaridNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement System For Transformer Inrush Current Higher Harmonics DeterminationDocumento6 pagineMeasurement System For Transformer Inrush Current Higher Harmonics DeterminationnmulyonoNessuna valutazione finora
- ModulationDocumento10 pagineModulationgeofrey fungoNessuna valutazione finora
- Actuators and WaveformsDocumento55 pagineActuators and WaveformsdsenpenNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical EngineeringDocumento20 pagineElectrical EngineeringLuke WangNessuna valutazione finora
- Power System ProtectionDocumento37 paginePower System ProtectionKarthick Rathinasamy100% (1)
- Power Systems Protection Course: Al-Balqa Applied UniversityDocumento37 paginePower Systems Protection Course: Al-Balqa Applied Universityrodruren01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Astable Multivibrators: Astable Multivibrator Free-Running ClockDocumento4 pagineAstable Multivibrators: Astable Multivibrator Free-Running ClockJohn Brix BalisterosNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Dead-Time in Interleaved PWM For Two Parallel-Connected InvertersDocumento8 pagineEffect of Dead-Time in Interleaved PWM For Two Parallel-Connected Invertersnaseer m a abdul khadarNessuna valutazione finora
- Jitter, Noise, and Signal Integrity at High-Speed: A Tutorial - Part IIDocumento4 pagineJitter, Noise, and Signal Integrity at High-Speed: A Tutorial - Part IIMarcos PerdomoNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective Questions or Mcqs On Circuit Theory: Back To Main Mcqs PageDocumento8 pagineObjective Questions or Mcqs On Circuit Theory: Back To Main Mcqs PageRahul SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Fully Digital Hysteretic Modulator For DC-DC Switching ConvertersDocumento8 pagineFully Digital Hysteretic Modulator For DC-DC Switching ConvertersAnand RamamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessDa EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlDa EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Greek AlphabetDocumento2 pagineGreek AlphabetMadhu BediguthuNessuna valutazione finora
- Rules For Plant LayoutDocumento8 pagineRules For Plant LayoutMadhu Bediguthu100% (1)
- Cooling Tower RecommedationDocumento1 paginaCooling Tower RecommedationMadhu BediguthuNessuna valutazione finora
- PG Test Procedure For ACCDocumento3 paginePG Test Procedure For ACCMadhu BediguthuNessuna valutazione finora
- A Feasibility Study On Adopting Sliding Pressure Operation For Drum Type BoilerDocumento5 pagineA Feasibility Study On Adopting Sliding Pressure Operation For Drum Type BoilerMadhu BediguthuNessuna valutazione finora
- LVDH Mechanical Schematic DiagramDocumento1 paginaLVDH Mechanical Schematic DiagramMadhu BediguthuNessuna valutazione finora
- MSS SP Stds Reference ListDocumento1 paginaMSS SP Stds Reference ListMadhu BediguthuNessuna valutazione finora
- Dewatering SolutionsDocumento6 pagineDewatering SolutionsMadhu BediguthuNessuna valutazione finora
- BS 381 Color CodeDocumento4 pagineBS 381 Color CodeMadhu BediguthuNessuna valutazione finora
- 8051 Programs Using Kit: Exp No: Date: Arithmetic Operations Using 8051Documento16 pagine8051 Programs Using Kit: Exp No: Date: Arithmetic Operations Using 8051Gajalakshmi AshokNessuna valutazione finora
- Aectp 300 3Documento284 pagineAectp 300 3AlexNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Frequency AllocationsDocumento1 pagina2011 Frequency Allocationsculeros1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Zener Tester: by MedhatkoDocumento6 pagineZener Tester: by Medhatkosaran gulNessuna valutazione finora
- The 5 Pivotal Paragraphs in A PaperDocumento1 paginaThe 5 Pivotal Paragraphs in A PaperFer Rivas NietoNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept of Lokmitra Kendra in Himachal PradeshDocumento2 pagineConcept of Lokmitra Kendra in Himachal PradeshSureshSharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Use The Analysis ToolPak To Perform Complex Data Analysis - Excel - OfficeDocumento5 pagineUse The Analysis ToolPak To Perform Complex Data Analysis - Excel - OfficedakingNessuna valutazione finora
- Davis A. Acclimating Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus Vannamei, To Inland, Low-Salinity WatersDocumento8 pagineDavis A. Acclimating Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus Vannamei, To Inland, Low-Salinity WatersAngeloNessuna valutazione finora
- SemDocumento583 pagineSemMaria SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Afa Coursework ExamplesDocumento6 pagineAfa Coursework Examplesiuhvgsvcf100% (2)
- EEE301 Digital Electronics Lecture 1 Part 3: Dr. A.S.M. MohsinDocumento6 pagineEEE301 Digital Electronics Lecture 1 Part 3: Dr. A.S.M. MohsinAaa AaaNessuna valutazione finora
- DA-I Question Bank From Module 1-3 of PHY1701 Course, Winter Semester 2020-21Documento6 pagineDA-I Question Bank From Module 1-3 of PHY1701 Course, Winter Semester 2020-21Likith MallipeddiNessuna valutazione finora
- Slup 230Documento24 pagineSlup 230Jelena TodorovicNessuna valutazione finora
- DTS 600 GDO Installation ManualDocumento12 pagineDTS 600 GDO Installation Manualpiesang007Nessuna valutazione finora
- World Trends in Municipal Solid Waste ManagementDocumento11 pagineWorld Trends in Municipal Solid Waste ManagementNeima EndrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Approach To The Audit of Electronically Processed DataDocumento2 pagineBasic Approach To The Audit of Electronically Processed DataJestell Ann ArzagaNessuna valutazione finora
- College of Engineering Cagayan State UniversityDocumento16 pagineCollege of Engineering Cagayan State UniversityErika Antonio GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Bombas KMPDocumento42 pagineBombas KMPReagrinca Ventas80% (5)
- SQL - Day 2: Structured Query LanguageDocumento10 pagineSQL - Day 2: Structured Query LanguageNight KingNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Test - Math As A Language - MATHEMATICS IN THE MODERN WORLDDocumento8 paginePractice Test - Math As A Language - MATHEMATICS IN THE MODERN WORLDMarc Stanley YaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pascal Die Casting Machine SystemDocumento20 paginePascal Die Casting Machine Systemenascimento32Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions of Inverse Geodetic Problem in Navigational Applications PDFDocumento5 pagineSolutions of Inverse Geodetic Problem in Navigational Applications PDFLacci123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Operation and Service 69UG15: Diesel Generator SetDocumento72 pagineOperation and Service 69UG15: Diesel Generator Setluis aguileraNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3Documento5 pagineUnit 3Narasimman DonNessuna valutazione finora
- Shift Registers NotesDocumento146 pagineShift Registers NotesRajat KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Emcee Script For Recognition DayDocumento3 pagineEmcee Script For Recognition DayRomeo Jr. LaguardiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diltoids Numberletter Puzzles Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form - 38486Documento5 pagineDiltoids Numberletter Puzzles Activities Promoting Classroom Dynamics Group Form - 38486sinirsistemiNessuna valutazione finora