Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Finite Element 2 PDF
Caricato da
rip111176Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Finite Element 2 PDF
Caricato da
rip111176Copyright:
Formati disponibili
RAYLEIGH –RITZ METHOD
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
In the Rayleigh-Ritz method
A single trial function is applied throughout the entire region
Trial functions of increasing complexity are required to model all but the simplest
problems
The FE approach
uses comparatively simple trial functions that are applied piece-wise to parts of
the region
These subsections of the region are then the finite elements
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
Consider the problem of 1-D heat flow, the functional to be extremised is
where the integral over W corresponds to the length of the region and Neumann
boundary conditions are specified at one end, G,of the region
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
The length over which the solution is required, is divided up into finite elements
In each element the value of f is found at certain points called nodes
Two nodes will mark the extremities of the element
Other nodes may occur inside the element
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
Let the unknown temperatures at the nodes of the element e be
where n+1 is the number of nodes in each element.
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
The temperature at any other position in the element is represented in terms of the nodal
values {f}e and shape functions associated with each node
where Nb is the shape function associated with the node b and b=i ... i+n and [N]
is the corresponding row matrix.
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
Let us write the trial function f over the entire region Ω in the form
where the summation is over all the nodes in W.
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
The global shape functions have been used to take into account the contribution
from fa to f over the entire region W
The global shape functions over much of W will be zero
For interior nodes of an element will be non-zero only within that element
End nodes of an element will have non-zero values over the two elements sharing the
node.
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
For example :
is non-zero only in elements e and e+1.
will be non-zero only in
element e.
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
Neglecting for the moment, consideration of the first and last elements of the region
Write the Rayleigh-Ritz statement in which the nodal values are the adjustable
parameters.
Consider the nodes i...i+n belonging to element e
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
where for example òelement e stands for
over the element e
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
Let us
focus on the terms containing an integral over the element e
Drop the superscript g on the shape functions
Suppose that the element extends from x=xe to x=xe+h
No loss in generality is incurred if we
Shift the origin to x=xe
Take the element to extend rather from 0 to h
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
The function can be written as,
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
Also, noting
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
So, differentiating under the integral sign, we have
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
This equation is one in the set of n+1 simultaneous equations obtained by letting a run
through the values i...i+n :
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
where
and
In the end elements, where Neumann boundary conditions may have to be considered,
there is an additional term
where Nar is the value of Na on the boundary G
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
If there are two 2-noded elements, labelled m and n, with nodes i, i+1 and i+2,
assembly of the element matrices is as before. Then
for the first element m
and similarly for element n
FE Modification of the Rayleigh-Ritz Method
By combining these two matrix equations
The global assembly matrix is built up in this way
The boundary conditions on the extreme elements are inserted
The set of equations is solved for the unknown values of f
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 10 Rayleigh Ritz Method-1Documento19 pagine10 Rayleigh Ritz Method-1rashmitha chigullapallyNessuna valutazione finora
- Code Conversion FEM - XFEMDocumento6 pagineCode Conversion FEM - XFEMjacobessNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundation of Computational Fluid Dynamics Dr. S. Vengadesan Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 12Documento14 pagineFoundation of Computational Fluid Dynamics Dr. S. Vengadesan Department of Applied Mechanics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 12mahesh dNessuna valutazione finora
- Fea ImpDocumento14 pagineFea ImpC61 Mahesh RathodNessuna valutazione finora
- Fem PresentationDocumento33 pagineFem PresentationAditya UpadhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis For Handwriting Analysis: N. Vincent, A. Seropian, G. StamonDocumento9 pagineSynthesis For Handwriting Analysis: N. Vincent, A. Seropian, G. StamonFilmor MalnegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Functions Used in AnalysisDocumento7 pagineCommon Functions Used in AnalysisCarl Andrew PimentelNessuna valutazione finora
- An - Algorithm - For - Computing - Fekete - Points - in - The - TRDocumento15 pagineAn - Algorithm - For - Computing - Fekete - Points - in - The - TRThiago NobreNessuna valutazione finora
- 2d Enriched ElementsDocumento11 pagine2d Enriched ElementsAngshuman SinghaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Concepts of The Finite Element MethodDocumento2 pagineBasic Concepts of The Finite Element MethodRajesh PerumalNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Numerical Laplace InversionDocumento5 pagineNotes On Numerical Laplace InversiondjfwalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The Best Mathematical Language For Discrete Geometry?Documento78 pagineWhat Is The Best Mathematical Language For Discrete Geometry?api-316318749Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lovely School of Engineering: Term PaperDocumento11 pagineLovely School of Engineering: Term PaperThakur AbhinavNessuna valutazione finora
- FEA BasicsDocumento43 pagineFEA Basicsmayuresh_6767Nessuna valutazione finora
- Section 4.2. Lebesgue Integration of A Bounded Measurable Function Over A Set of Finite MeasureDocumento8 pagineSection 4.2. Lebesgue Integration of A Bounded Measurable Function Over A Set of Finite MeasureLakshmi NarayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Finite Element Methods Applied To Solve PDE: Lecture NotesDocumento19 pagineFinite Element Methods Applied To Solve PDE: Lecture NotesMohammad Rizwan MalikNessuna valutazione finora
- FEM Method in 2D Heat Conduction PDFDocumento52 pagineFEM Method in 2D Heat Conduction PDFAhmadreza AminianNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculus III Study GuideDocumento23 pagineCalculus III Study Guideasipasi7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bartle On Riemann IntegralDocumento8 pagineBartle On Riemann IntegralEleutherosNessuna valutazione finora
- TD N°4: Finite Element Method: 1 First PartDocumento2 pagineTD N°4: Finite Element Method: 1 First PartabbeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Laplace Transform - Aminul Haque, 2224EEE00222Documento25 pagineLaplace Transform - Aminul Haque, 2224EEE00222Ãmîñûł Hãqûê AHNessuna valutazione finora
- Radon TransformDocumento9 pagineRadon TransformUmi HikariNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Integration 1DDocumento7 pagineMath Integration 1Dమత్సా చంద్ర శేఖర్Nessuna valutazione finora
- High Order Differential Form-Based Elements For The Computation of Electromagnetic FieldDocumento7 pagineHigh Order Differential Form-Based Elements For The Computation of Electromagnetic FieldMaxim ShvetsovNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Solutions of Laplacian Problem PDFDocumento10 pagineNumerical Solutions of Laplacian Problem PDFKetan RsNessuna valutazione finora
- 123FEADocumento56 pagine123FEAkhalil alhatabNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Interpolation Functions For Finite Element FormulationDocumento32 pagine05 Interpolation Functions For Finite Element FormulationAnamolNessuna valutazione finora
- In Place Merge SortDocumento9 pagineIn Place Merge Sortcipher12345677718Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computation of Determinants Using Contour IntegralsDocumento12 pagineComputation of Determinants Using Contour Integrals123chessNessuna valutazione finora
- Laplace Transform - Aminul Haque, 2224EEE00222Documento25 pagineLaplace Transform - Aminul Haque, 2224EEE00222Ãmîñûł Hãqûê AHNessuna valutazione finora
- Mikhailov1994-Finite Difference Method by Using MathematicsDocumento5 pagineMikhailov1994-Finite Difference Method by Using MathematicsRenato Santos de SouzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heaviside Operational Calculus by J R CarsonDocumento26 pagineHeaviside Operational Calculus by J R CarsonGeraldo Carvalho Brito Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ottosen and Peterrsson - Introduction of FEM - 17 ChaptersDocumento175 pagineOttosen and Peterrsson - Introduction of FEM - 17 ChaptersatankasalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Syntax-Directed TranslationDocumento38 pagineSyntax-Directed TranslationKristy SotoNessuna valutazione finora
- Syntax Directed TranslationDocumento12 pagineSyntax Directed TranslationShyjutestingShyjuNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is FEM?: FEM (Finite Element Method)Documento2 pagineWhat Is FEM?: FEM (Finite Element Method)Anonymous DbDOldj0Nessuna valutazione finora
- Talk 4Documento11 pagineTalk 4MikeNessuna valutazione finora
- Finite-Element Methods in Semiconductor Device SimulationDocumento8 pagineFinite-Element Methods in Semiconductor Device SimulationMaxim KomarNessuna valutazione finora
- You Only Live OnceDocumento13 pagineYou Only Live OnceSaket AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelling & Simulation 3 - (3 Year) (Unit Code: MACE 30051)Documento19 pagineModelling & Simulation 3 - (3 Year) (Unit Code: MACE 30051)Jason YangNessuna valutazione finora
- Ps1 Solution (VERY IMP)Documento6 paginePs1 Solution (VERY IMP)Omega ManNessuna valutazione finora
- Regularization of Feynman IntegralsDocumento28 pagineRegularization of Feynman IntegralsRonaldo Rêgo100% (1)
- 6th Lecture FEM 2022Documento12 pagine6th Lecture FEM 2022hudasaadNessuna valutazione finora
- The Daubechies D4 Wavelet TransformDocumento4 pagineThe Daubechies D4 Wavelet Transformavi0341Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2: Renormalization Groups (Continued) David Gross 2.1. Finite RenormalizationDocumento9 pagineLecture 2: Renormalization Groups (Continued) David Gross 2.1. Finite RenormalizationluisdanielNessuna valutazione finora
- A Top-Down Approach To Fundamental InteractionsDocumento27 pagineA Top-Down Approach To Fundamental InteractionsShivraj ThoratNessuna valutazione finora
- Meshless Element Free Galerkin Method For Unsteady Nonlinear Heat Transfer ProblemsDocumento8 pagineMeshless Element Free Galerkin Method For Unsteady Nonlinear Heat Transfer ProblemschrissbansNessuna valutazione finora
- l3 IntegrationDocumento5 paginel3 Integrationapi-287224366Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shape FuncDocumento33 pagineShape FuncSAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Institute For Theoretical Physics, University of Utrecht, P. O. Box 80.006, 3508 TA Utrecht, The NetherlandsDocumento17 pagineInstitute For Theoretical Physics, University of Utrecht, P. O. Box 80.006, 3508 TA Utrecht, The NetherlandsMaiman LatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Two Dimensional ProblemsDocumento33 pagineTwo Dimensional Problemsbalajeemech2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment#2: Dilawar Fa18-Epe-130Documento16 pagineAssignment#2: Dilawar Fa18-Epe-130Esmatullah BegzadNessuna valutazione finora
- Daa R20 Unit 1Documento21 pagineDaa R20 Unit 1A Raghava Chowdary maddipatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Algorithms: Process of Translating A Problem Into An AlgorithmDocumento17 pagineIntroduction To Algorithms: Process of Translating A Problem Into An AlgorithmMutheviAnilkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 - L2 - Review of Laplace TransformDocumento39 pagineWeek 2 - L2 - Review of Laplace TransformOlerile AnaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4.....Documento30 pagineLecture 4.....GooftilaaAniJiraachuunkooYesusiinNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Finite Element Method: Zelalem ZDocumento15 pagineIntroduction To Finite Element Method: Zelalem Zabegaz yeshanehNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction to Lebesgue Integration and Fourier SeriesDa EverandAn Introduction to Lebesgue Integration and Fourier SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- GEMC-511687720852142 Invoice PDFDocumento2 pagineGEMC-511687720852142 Invoice PDFrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gemc 511687729107385 20012022 PDFDocumento4 pagineGemc 511687729107385 20012022 PDFrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gemc 511687728136292 17092022Documento3 pagineGemc 511687728136292 17092022rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- GeM Bidding 3656858 PDFDocumento4 pagineGeM Bidding 3656858 PDFrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gemc 511687737438095 25032022 PDFDocumento3 pagineGemc 511687737438095 25032022 PDFrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- AMD Tutorial ME CADCAM 2022-23Documento6 pagineAMD Tutorial ME CADCAM 2022-23rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- GeM Bidding 3152874 PDFDocumento4 pagineGeM Bidding 3152874 PDFrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- ME SEM 2 CADCAM 3720821 OT Presentation MAY 2020Documento1 paginaME SEM 2 CADCAM 3720821 OT Presentation MAY 2020rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial: Optimization Techniques 1Documento6 pagineTutorial: Optimization Techniques 1rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Statement Ledger PDFDocumento1 paginaStatement Ledger PDFrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6-Interest Payable by The TaxpayerDocumento13 pagine6-Interest Payable by The Taxpayerrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial MD II 2015 3Documento1 paginaTutorial MD II 2015 3rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prepared by - Vedant Vyas. (150180708011) M.E. Cad/Cam. Guided by - Prof. R. I. Patel. Place-GEC - DahodDocumento33 paginePrepared by - Vedant Vyas. (150180708011) M.E. Cad/Cam. Guided by - Prof. R. I. Patel. Place-GEC - Dahodrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- 77-9 Design of CranesDocumento10 pagine77-9 Design of Cranesrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial MD II 2015 1Documento1 paginaTutorial MD II 2015 1rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- ME SEM 2 CADCAM FEA Presentation MAY 2020 PDFDocumento1 paginaME SEM 2 CADCAM FEA Presentation MAY 2020 PDFrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial MD II 2015 4Documento1 paginaTutorial MD II 2015 4rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial MD II 2015 2Documento1 paginaTutorial MD II 2015 2rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial MD II 2015 5Documento1 paginaTutorial MD II 2015 5rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Design of Cranes 2017Documento2 pagineTutorial Design of Cranes 2017rip11117633% (3)
- Subject: Machine Design Be Sem Vii Mechanical Tutorial:02 (Helical Gear)Documento1 paginaSubject: Machine Design Be Sem Vii Mechanical Tutorial:02 (Helical Gear)rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- AMD Tutorial Stress StrainDocumento3 pagineAMD Tutorial Stress Strainrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amd Tutorial Me Cadcam 2017Documento5 pagineAmd Tutorial Me Cadcam 2017rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- A PPT On Worm Gear: Presented byDocumento19 pagineA PPT On Worm Gear: Presented byrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- TUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and CouplingDocumento2 pagineTUTORIAL 3 Design of Shaft Key and Couplingrip111176100% (1)
- Recent Advancements in Rapid Prototyping For Bio Medical ModelsDocumento19 pagineRecent Advancements in Rapid Prototyping For Bio Medical Modelsrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Recent Advancements in Rapid Prototyping For Bio Medical ModelsDocumento19 pagineRecent Advancements in Rapid Prototyping For Bio Medical Modelsrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Enginering Department: Sub:-Machine Design CODE:-2171903 Topic:-Design of Helical GearsDocumento18 pagineMechanical Enginering Department: Sub:-Machine Design CODE:-2171903 Topic:-Design of Helical Gearsrip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- MD PPT 150183119005,06Documento28 pagineMD PPT 150183119005,06rip111176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Formulation For OptimizationDocumento5 pagineProblem Formulation For OptimizationabrhshNessuna valutazione finora
- Gaussian Elimination: 1 Linear EquationDocumento4 pagineGaussian Elimination: 1 Linear EquationPankaj SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Numerical Analysis 10th Edition Burden Solutions Manual PDFDocumento35 pagineDwnload Full Numerical Analysis 10th Edition Burden Solutions Manual PDFmclauglinnelida100% (12)
- Assignment 2 - 228265B - Excel Solver AttachementDocumento4 pagineAssignment 2 - 228265B - Excel Solver AttachementUtpali BhagyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Secant MethodDocumento4 pagineNumerical Secant MethodCaptain DogeNessuna valutazione finora
- Math1414 Dividing PolynomialsDocumento10 pagineMath1414 Dividing PolynomialsErwin AldemitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Integration PDFDocumento56 pagineNumerical Integration PDFNi Mesh100% (1)
- 02 Introduction To OptimizationDocumento14 pagine02 Introduction To Optimizationriya lakhotiaNessuna valutazione finora
- PresentationDocumento15 paginePresentationMuhammad UmerNessuna valutazione finora
- Integer Linear ProgrammingDocumento10 pagineInteger Linear Programminglmsm0% (1)
- Linear Algebra & Optimization: BITS PilaniDocumento26 pagineLinear Algebra & Optimization: BITS Pilanimanoj kumar sethyNessuna valutazione finora
- RS Aggarwal Solution Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise 2BDocumento14 pagineRS Aggarwal Solution Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Exercise 2BThe Time ParadoXNessuna valutazione finora
- (Laurent Lessard) LP DualityDocumento28 pagine(Laurent Lessard) LP DualityLeonardo Gama AssumpçãoNessuna valutazione finora
- CS-6777 Liu AbsDocumento103 pagineCS-6777 Liu AbsILLA PAVAN KUMAR (PA2013003013042)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Economic Dispatch - 2Documento76 pagineEconomic Dispatch - 2Syed Ali RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Division Long Grid 2digit Divisor 4digit Dividend No Remainders All.1496071805Documento20 pagineDivision Long Grid 2digit Divisor 4digit Dividend No Remainders All.1496071805the thirdNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical AnalysisDocumento4 pagineNumerical AnalysissuryanshchauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Na (Lec 3)Documento17 pagineNa (Lec 3)Muhammad AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical MCQS2Documento7 pagineNumerical MCQS2Mian Hasham Azhar AZHARNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization in Operations Research 2nd Edition Rardin Solutions ManualDocumento19 pagineOptimization in Operations Research 2nd Edition Rardin Solutions ManualShannonCampbellwoft100% (44)
- The Hilber-Hughes-Taylor-α (HHT-α) method compared withDocumento14 pagineThe Hilber-Hughes-Taylor-α (HHT-α) method compared withnabin nitNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics: H.Z. Hassan, A.A. Mohamad, G.E. AtteiaDocumento10 pagineJournal of Computational and Applied Mathematics: H.Z. Hassan, A.A. Mohamad, G.E. AtteiaCarlos VelásquezNessuna valutazione finora
- WORKSHEET (SESSION 2022 - 2023) Grade 10 Subject - Mathematics Polynomials S.NO. Questions Section A (1 Mark Questions)Documento2 pagineWORKSHEET (SESSION 2022 - 2023) Grade 10 Subject - Mathematics Polynomials S.NO. Questions Section A (1 Mark Questions)Sonia100% (1)
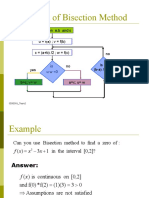
- Flow Chart of Bisection Method: Start: Given a,b and ε u = f (a) ; v = f (b) c = (a+b) /2 ; w = f (c) yes no noDocumento10 pagineFlow Chart of Bisection Method: Start: Given a,b and ε u = f (a) ; v = f (b) c = (a+b) /2 ; w = f (c) yes no noRaisqi Kun HartadiNessuna valutazione finora
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.1Documento20 pagineNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.1anilNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Evaluation of Duhamel's Integral: Undamped SystemDocumento11 pagineNumerical Evaluation of Duhamel's Integral: Undamped SystemFeynmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 1408808410LINEAR PROGRAMMING NotesDocumento4 pagine1408808410LINEAR PROGRAMMING NotesKudakwashe RuzvidzoNessuna valutazione finora
- ChanGreifOLeary2007Milestones in Matrix Computation - GolubPapers - OxfordDocumento578 pagineChanGreifOLeary2007Milestones in Matrix Computation - GolubPapers - OxfordmoisesceniNessuna valutazione finora
- ECN 2115 Lecture 1 - 2Documento6 pagineECN 2115 Lecture 1 - 2GABRIEL CHIKUSELANessuna valutazione finora
- Computation of Gauss-Jacobi, Gauss-Radau-Jacobi and Gauss-Lobatto-Jacobi Quadrature Formulae Using Golub-Welsch MethodDocumento9 pagineComputation of Gauss-Jacobi, Gauss-Radau-Jacobi and Gauss-Lobatto-Jacobi Quadrature Formulae Using Golub-Welsch MethodFlorian Leonard Gozman100% (2)