Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
A Throat Culture or Strep Test Is Performed by Using A Throat Swab To Detect The Presence of Group A Streptococcus Bacteria
Caricato da
Keij AranetaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
A Throat Culture or Strep Test Is Performed by Using A Throat Swab To Detect The Presence of Group A Streptococcus Bacteria
Caricato da
Keij AranetaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
A throat culture or strep test is performed by using a throat swab to detect the presence of group A streptococcus
bacteria, the most common cause of strep throat. Group A streptococcus bacteria also can cause other infections, including
pneumonia, tonsillitis, and meningitis.
A sample swabbed from the back of the throat is put on a special plate (culture) that enables bacteria to grow. The specific type
of infection is determined using chemical tests. If bacteria don't grow, the culture is negative and the person doesn't have a strep
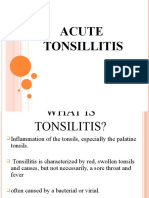
throat infection.Strep throat is a bacterial infection that affects the back of the throat and the tonsils, which become irritated and
swell, causing a sore throat that's especially bothersome when swallowing. White or yellow spots or a coating on the throat and
tonsils also might be present, and the lymph nodes in the neck may swell.Strep throat is most common among school-age
children. The infection may cause headaches, stomachaches, nausea, vomiting, and listlessness. Strep throat infections don't
usually include cold symptoms such as sneezing, coughing, or a runny or stuffy nose.While symptoms of strep throat usually go
away within a few days without direct treatment, doctors will prescribe antibiotics to help prevent related complications such as
rheumatic fever.
Why It's Done
The throat culture test can help determine the cause of a sore throat. Often, a sore throat is caused by a virus, but a throat culture
will determine if it's definitely caused by strep bacteria so doctors can provide proper treatment.
What are the causes and risks of the infection?
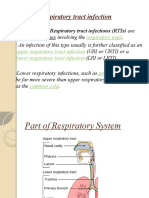
There are many different types of upper respiratory infections, including:
the common cold, usually due to a virus
the flu, or influenza virus infection, which causes more severe symptoms than a cold
acute sinusitis or chronic sinusitis, which involve the nasal sinuses
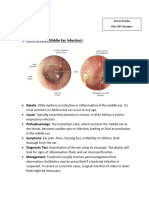
otitis externa, or infection of the outer ear
acute otitis media, or infection of the middle ear behind the eardrum
pharyngitis, or sore throat
acute bronchitis, an infection in the lower windpipes
croup, which is a viral infection of the main windpipe that is usually only seen in children
epiglottitis, a bacterial infection of the main windpipe that is more commonly seen in children
Other types of URI may also occur, but they are less common. A decongestant called
phenylpropanolamine
Symptoms & Signs
What are the signs and symptoms of the infection?
a runny nose or stuffy nose
sore throat fever
headache cough
malaise, or vague feeling of illness
muscle aches loss of appetite ear pain
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Sinus Problems Stop!: The Complete Guide on Sinus Infection, Sinusitis Symptoms, Sinusitis Treatment, & Secrets to Natural Sinus Relief without Harsh DrugsDa EverandSinus Problems Stop!: The Complete Guide on Sinus Infection, Sinusitis Symptoms, Sinusitis Treatment, & Secrets to Natural Sinus Relief without Harsh DrugsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharyngitis TonsilitisDocumento23 paginePharyngitis TonsilitisJessa BorreNessuna valutazione finora
- Causes of Pharyngitis: Pharyngitis: A Case StudyDocumento2 pagineCauses of Pharyngitis: Pharyngitis: A Case StudyRiadi riadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ear Infection Essentials Understanding, Treating, and PreventingDa EverandEar Infection Essentials Understanding, Treating, and PreventingNessuna valutazione finora
- PharyngitisDocumento6 paginePharyngitisJeriel DelavinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 73Documento88 pagineChapter 73Julian TaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Viral Disease of The Upper RSDocumento19 pagineViral Disease of The Upper RSAries Gonzales CaraganNessuna valutazione finora
- PHARYNGITISDocumento8 paginePHARYNGITISWàrìs Ràfìqùé ßàlòçhNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory and CirculatoryDocumento35 pagineRespiratory and CirculatoryTumabangNessuna valutazione finora
- Larynx Cartilage Mucus Tension Lungs: Picture of The Larynx and TracheaDocumento22 pagineLarynx Cartilage Mucus Tension Lungs: Picture of The Larynx and TracheaRamesh Emraan DassNessuna valutazione finora
- Epiglottitis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorsDocumento5 pagineEpiglottitis: Causes, Incidence, and Risk FactorscnvNessuna valutazione finora
- Respi SDG Cluster3Documento45 pagineRespi SDG Cluster3faye kimNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Notes On UrtiDocumento9 pagineLesson Notes On UrtiNeethupaulNessuna valutazione finora
- SorethroatDocumento2 pagineSorethroatAntaraaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tonsillitis FACT SheetDocumento3 pagineTonsillitis FACT SheetSiska SitumorangNessuna valutazione finora
- Tonsillitis PDFDocumento7 pagineTonsillitis PDFUmar FarooqNessuna valutazione finora
- Laryngitis and PericarditisDocumento17 pagineLaryngitis and Pericarditis2B-4- TUNAC, Avvy Charlotte R.Nessuna valutazione finora
- TonsilitisDocumento9 pagineTonsilitisDeepak patelNessuna valutazione finora
- Throat Diseases and SepsisDocumento15 pagineThroat Diseases and SepsisOlga GoryachevaNessuna valutazione finora
- All About TonsillitisDocumento4 pagineAll About TonsillitisJennifer AsistidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory Tract InfectionDocumento30 pagineRespiratory Tract InfectionNaresh JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- TonsillitisDocumento3 pagineTonsillitisVina MuspitaNessuna valutazione finora
- PneumoniaDocumento13 paginePneumoniaRobelNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding TonsillitisDocumento2 pagineUnderstanding TonsillitisMarjun JacosalemNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatrics: Acute PharyngitisDocumento16 paginePediatrics: Acute PharyngitisÄfťæb AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharyngitis PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaPharyngitis Pathophysiologychristine louise bernardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Signs and Symptoms: MicroorganismsDocumento11 pagineSigns and Symptoms: MicroorganismsReni April AnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Signs and Symptoms: MicroorganismsDocumento4 pagineSigns and Symptoms: MicroorganismsNikki P. NarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Management of Children With Respiratory System DysfunctionsDocumento27 pagineNursing Management of Children With Respiratory System DysfunctionsDody ZainNessuna valutazione finora
- Sore TroatDocumento2 pagineSore TroatD'Say P'alaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Otitis Media I. Overview/DefinitionDocumento10 pagineOtitis Media I. Overview/DefinitionBiancaGabatinoAbarcaNessuna valutazione finora
- Middle Ear Infections: Buy The BookDocumento6 pagineMiddle Ear Infections: Buy The BookAndi Astrid AgustinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Upper Respiratory Infection Definition and FactsDocumento2 pagineUpper Respiratory Infection Definition and FactsBerlian PurnamasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Strep ThroatDocumento11 pagineStrep ThroatJenifer C. BangunanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharyngitis BING BARUDocumento5 paginePharyngitis BING BARUAndini RizkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute TonsillitisDocumento22 pagineAcute Tonsillitisg0ldz21100% (10)
- Upper Respiratory Infection (URI/Common Cold) : Kathly M. Jean-Gilles, MSN, RN, RRT-NPS, FNP Gregory A. Wagoner, MD, MBADocumento4 pagineUpper Respiratory Infection (URI/Common Cold) : Kathly M. Jean-Gilles, MSN, RN, RRT-NPS, FNP Gregory A. Wagoner, MD, MBAadhiztinenNessuna valutazione finora
- Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis Sinusitis,: Symptom Allergy URI InfluenzaDocumento4 pagineGroup A Streptococcal Pharyngitis Sinusitis,: Symptom Allergy URI InfluenzaAron Tianchon CatalanNessuna valutazione finora
- CroupDocumento40 pagineCroupAbigail Basco100% (1)
- Ear Infection (Otitis Media)Documento14 pagineEar Infection (Otitis Media)matushenko.n14Nessuna valutazione finora
- Who Gets Tonsillitis?Documento3 pagineWho Gets Tonsillitis?Mounir ChadliNessuna valutazione finora
- TonsillitisDocumento19 pagineTonsillitisrosejoseph0777Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ent OralDocumento34 pagineEnt OralDrashti kamodiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clearing The Throat: Coughs Affected PartDocumento6 pagineClearing The Throat: Coughs Affected Partkarla callejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Define EpiglottisDocumento10 pagineDefine EpiglottisAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNessuna valutazione finora
- Escherichia Coli, A Diarrheal Disease That Is OftenDocumento9 pagineEscherichia Coli, A Diarrheal Disease That Is OftenassetoNessuna valutazione finora
- CoughDocumento6 pagineCoughaigoooNessuna valutazione finora
- Sinusitis DefinitionDocumento7 pagineSinusitis Definitionfaye kimNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonia in Children What Is Pneumonia in Children?Documento7 paginePneumonia in Children What Is Pneumonia in Children?Sandra GabasNessuna valutazione finora
- Rhino PharyngitisDocumento27 pagineRhino PharyngitisinriantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Otitis MediaDocumento11 pagineOtitis MediajessyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cold, Flu, & Cough Health Center: Coughs - Topic OverviewDocumento7 pagineCold, Flu, & Cough Health Center: Coughs - Topic OverviewJune DumdumayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nasal Discharge - Symptom EvaluationDocumento2 pagineNasal Discharge - Symptom EvaluationUjwal NarayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory System DisordersDocumento9 pagineRespiratory System Disordersasop06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ear InfectionDocumento1 paginaEar InfectionDerly Yerson OlazabalNessuna valutazione finora
- Select Your Child's Date of BirthDocumento9 pagineSelect Your Child's Date of BirthProperty ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Finalterm (9th Sem)Documento52 pagineClinical Finalterm (9th Sem)sarwar sonsNessuna valutazione finora
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infections Group 1 BSN 2.3Documento57 pagineUpper Respiratory Tract Infections Group 1 BSN 2.3Joedelynne Diane Endaya GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 17Documento19 pagineChapter 17Patricia VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- RisperidoneDocumento2 pagineRisperidoneKeij Araneta0% (1)
- Insulin Drug StudyDocumento7 pagineInsulin Drug StudyKeij AranetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseKeij AranetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Pediatric Community Acquired PneumoniaDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Pediatric Community Acquired PneumoniaKeij AranetaNessuna valutazione finora
- NLEDocumento18 pagineNLEKeij AranetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study (Ceftriaxone)Documento2 pagineDrug Study (Ceftriaxone)Keij Araneta93% (15)
- Drug Study (Ceftriaxone)Documento2 pagineDrug Study (Ceftriaxone)Keij Araneta93% (15)
- Health Teaching: Activity: "Operation Feeding" Audience: Children of Greenside and LowlandersDocumento2 pagineHealth Teaching: Activity: "Operation Feeding" Audience: Children of Greenside and LowlandersKeij AranetaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHN-NLE Practice QuestionDocumento40 pagineCHN-NLE Practice QuestionKeij Araneta100% (5)
- NLEDocumento18 pagineNLEKeij AranetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diabetes MellitusDocumento5 pagineDiabetes MellitusKeij AranetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chi SquareDocumento1 paginaChi SquareKeij AranetaNessuna valutazione finora
- NASA ISS Expedition 2 Press KitDocumento27 pagineNASA ISS Expedition 2 Press KitOrion2015Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Way Out of Alcoholism by Jack BolandDocumento38 pagineThe Way Out of Alcoholism by Jack BolandIma AardvarkNessuna valutazione finora
- ATRT66Documento10 pagineATRT66luunhauyen.pisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Intellectual Disability: Definition, Classification, Causes and CharacteristicsDocumento12 pagineIntellectual Disability: Definition, Classification, Causes and CharacteristicsRyan RV ViloriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Starbucks Reconciliation Template & Instructions v20231 - tcm137-84960Documento3 pagineStarbucks Reconciliation Template & Instructions v20231 - tcm137-84960spaljeni1411Nessuna valutazione finora
- Persyaratan COMA KP 241 TAHUN 2019 (SI 65-01 Rev 3)Documento3 paginePersyaratan COMA KP 241 TAHUN 2019 (SI 65-01 Rev 3)Hafiz ZachariNessuna valutazione finora
- RCMaDocumento18 pagineRCMaAnonymous ffje1rpaNessuna valutazione finora
- PL00002949Documento5 paginePL00002949Nino AlicNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q4 - Lessons 7 and 8) Electrochemical ReactionsDocumento11 pagineLearning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q4 - Lessons 7 and 8) Electrochemical Reactionsprincess3canlasNessuna valutazione finora
- Content of An Investigational New Drug Application (IND)Documento13 pagineContent of An Investigational New Drug Application (IND)Prathamesh MaliNessuna valutazione finora
- PMEGP Revised Projects (Mfg. & Service) Vol 1Documento260 paginePMEGP Revised Projects (Mfg. & Service) Vol 1Santosh BasnetNessuna valutazione finora
- EHEDG Guidelines by Topics 04 2013Documento2 pagineEHEDG Guidelines by Topics 04 2013renzolonardi100% (1)
- Intraocular Pressure and Aqueous Humor DynamicsDocumento36 pagineIntraocular Pressure and Aqueous Humor DynamicsIntan EkarulitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tryout Consent Form - 2014 - Sign and ReturnDocumento2 pagineTryout Consent Form - 2014 - Sign and ReturnSanjeevan BaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Bartos P. J., Glassfibre Reinforced Concrete - Principles, Production, Properties and Applications, 2017Documento209 pagineBartos P. J., Glassfibre Reinforced Concrete - Principles, Production, Properties and Applications, 2017Esmerald100% (3)
- Fawad Hussain, Feedback On Industrial Visit To Sahiwal Coal Power PlantDocumento2 pagineFawad Hussain, Feedback On Industrial Visit To Sahiwal Coal Power PlantSyed Fawad MarwatNessuna valutazione finora
- Indirect Current Control of LCL Based Shunt Active Power FilterDocumento10 pagineIndirect Current Control of LCL Based Shunt Active Power FilterArsham5033Nessuna valutazione finora
- OM Mannual FOsDocumento38 pagineOM Mannual FOsAbdulmuqtadetr AhmadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ne XT ProtDocumento2 pagineNe XT Protwilliam919Nessuna valutazione finora
- 5000mah Mi Power Bank 2 - PDFDocumento6 pagine5000mah Mi Power Bank 2 - PDFManuel Jesús Fernández lavadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Meng Mammogram JulDocumento4 pagineMeng Mammogram JulLivia MillNessuna valutazione finora
- This Is No Way To Treat An Aorta.: Edwards EZ Glide Aortic CannulaDocumento5 pagineThis Is No Way To Treat An Aorta.: Edwards EZ Glide Aortic CannulaAhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- RNW Position PaperDocumento2 pagineRNW Position PaperGeraldene AcebedoNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic As Soil StabilizerDocumento28 paginePlastic As Soil StabilizerKhald Adel KhaldNessuna valutazione finora
- EESC 111 Worksheets Module 5Documento5 pagineEESC 111 Worksheets Module 5Keira O'HowNessuna valutazione finora
- Margarita ForesDocumento20 pagineMargarita ForesKlarisse YoungNessuna valutazione finora
- Silage Sampling and AnalysisDocumento5 pagineSilage Sampling and AnalysisG_ASantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Phoenix Contact DATA SHEETDocumento16 paginePhoenix Contact DATA SHEETShivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformers ConnectionsDocumento6 pagineTransformers Connectionsgeorgel1980Nessuna valutazione finora
- HEAS 1000 Health Assessment: Reflection of PracticeDocumento4 pagineHEAS 1000 Health Assessment: Reflection of PracticePreet ChahalNessuna valutazione finora
- Do You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineDa EverandDo You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineNessuna valutazione finora
- The Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsDa EverandThe Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (6)
- Uncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicDa EverandUncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (9)
- Fatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthDa EverandFatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (7)
- The Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthDa EverandThe Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthNessuna valutazione finora
- Deaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismDa EverandDeaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (30)
- Summary: The Real Anthony Fauci: Bill Gates, Big Pharma, and the Global War on Democracy and Public Health by Robert F. Kennedy Jr: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDa EverandSummary: The Real Anthony Fauci: Bill Gates, Big Pharma, and the Global War on Democracy and Public Health by Robert F. Kennedy Jr: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedNessuna valutazione finora
- The Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryDa EverandThe Truth about Wuhan: How I Uncovered the Biggest Lie in HistoryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Sickening: How Big Pharma Broke American Health Care and How We Can Repair ItDa EverandSickening: How Big Pharma Broke American Health Care and How We Can Repair ItValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (9)
- The Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomeDa EverandThe Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomeValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (7)
- The Inescapable Immune Escape PandemicDa EverandThe Inescapable Immune Escape PandemicValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- War on Ivermectin: The Medicine that Saved Millions and Could Have Ended the PandemicDa EverandWar on Ivermectin: The Medicine that Saved Millions and Could Have Ended the PandemicValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (7)
- Microbiological Quality of FoodsDa EverandMicrobiological Quality of FoodsL SlanetzNessuna valutazione finora
- Profiles of the Vaccine-Injured: "A Lifetime Price to Pay"Da EverandProfiles of the Vaccine-Injured: "A Lifetime Price to Pay"Valutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceDa EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (15)
- Generic Drugs: A Consumer’S Self-Defense GuideDa EverandGeneric Drugs: A Consumer’S Self-Defense GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccines Did Not Cause Rachel's Autism: My Journey as a Vaccine Scientist, Pediatrician, and Autism DadDa EverandVaccines Did Not Cause Rachel's Autism: My Journey as a Vaccine Scientist, Pediatrician, and Autism DadValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Epidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentDa EverandEpidemics and Society: From the Black Death to the PresentValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (9)
- Arthritis Diet: Anti-inflammatory Diet for Arthritis Pain ReliefDa EverandArthritis Diet: Anti-inflammatory Diet for Arthritis Pain ReliefNessuna valutazione finora
- Make America Healthy Again: How Bad Behavior and Big Government Caused a Trillion-Dollar CrisisDa EverandMake America Healthy Again: How Bad Behavior and Big Government Caused a Trillion-Dollar CrisisNessuna valutazione finora
- The Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusDa EverandThe Atlas of Disease: Mapping Deadly Epidemics and Contagion from the Plague to the CoronavirusValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (10)
- The Gut-loving Cookbook: Over 65 deliciously simple, gut-friendly recipes from The Gut StuffDa EverandThe Gut-loving Cookbook: Over 65 deliciously simple, gut-friendly recipes from The Gut StuffNessuna valutazione finora
- Panic Attack: Playing Politics with Science in the Fight Against COVID-19Da EverandPanic Attack: Playing Politics with Science in the Fight Against COVID-19Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (10)