Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pages From AV15 - L9-5
Caricato da
msTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pages From AV15 - L9-5
Caricato da
msCopyright:
Formati disponibili
ISS0065 Control Instrumentation Lecture 9
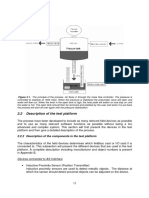
2. After the secondary loop is tuned, the primary loop is tuned with the secondary loop in
automatic.
When the loops are tuned, careful attention should be paid to the response to set point changes.
Without doubt cascade control can bring about substantial improvements in the quality of con-
trol. However, the benefits are critically dependant upon proper implementation. The control
scheme should be designed to target specific disturbances [6, 4].
Benefits:
• Compensates for specific disturbances at source;
• Improves dynamics;
• Linearizes model.
1.3 Override control
When there are more controlled variables than manipulated variables, a common solution to this
problem is to use a selector to choose the appropriate process variable from among a number of
available measurements. Selectors can be based on multiple measurement points, multiple final
control elements, or multiple controllers, as discussed below. Selectors are used to improve the
control system performance as well as to protect equipment from unsafe operating conditions [1].
An “override” control strategy involves a selection between two or more controller output signals,
where only one controller at a time gets the opportunity to exert control over a process.
A very important consideration for any override control strategy is how to manage integral
windup. If a controller with integral action is de-selected by the selector function, the integral term
of the controller will have the tendency to wind up (or wind down) over time. As controller was
overridden, it can have no effect on the process variable. Thus, integral control action will work in
vain to eliminate an error it cannot influence. Then control is handed back to that controller, the
integral action will have to spend time to un-do what it did while it was de-selected. Thus, override
controls demand some form of integral windup limits that engage when a controller is de-selected
[3].
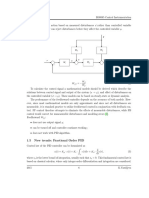
1.4 Feedforward
If the process exhibits slow dynamic response and disturbances are frequent, then the application
of feedforward control may be advantageous. Feedforward (FF) control differs from feedback (FB)
control in that the primary disturbance or load (D) is measured via a sensor and the manipulated
variable (U) is adjusted so that deviations in the controlled variable from the set point are minimized
or eliminated.
K.Vassiljeva 5 2015
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Untitled 4pagesDocumento1 paginaUntitled 4pagesmsNessuna valutazione finora
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Tank Management Made Easy Your GuideDocumento1 paginaTank Management Made Easy Your GuidemsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Find The Right Solutions For Your Tanks: Click On The Below Buttons To Find Out MoreDocumento1 paginaFind The Right Solutions For Your Tanks: Click On The Below Buttons To Find Out MoremsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Leak Detection: How Can Leaks Be Detected?Documento1 paginaLeak Detection: How Can Leaks Be Detected?msNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Untitled 2pagesDocumento1 paginaUntitled 2pagesmsNessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Chart That Makes The Different Parts of The Process Work in A Specified OrderDocumento2 pagineChart That Makes The Different Parts of The Process Work in A Specified OrdermsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- 2.2.2 Description of The Components in The Test PlatformDocumento3 pagine2.2.2 Description of The Components in The Test PlatformmsNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Untitled Extract Pages8Documento2 pagineUntitled Extract Pages8msNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled Extract Pages5Documento3 pagineUntitled Extract Pages5msNessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Untitled Extract Pages1Documento5 pagineUntitled Extract Pages1msNessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Pages From AV15 - L9-3Documento1 paginaPages From AV15 - L9-3msNessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- 1 Continuous Controllers: Seadesuurus Hetke (Juhitav) V Artus JuhtsignalDocumento1 pagina1 Continuous Controllers: Seadesuurus Hetke (Juhitav) V Artus JuhtsignalmsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Pages From AV15 - L9-4Documento1 paginaPages From AV15 - L9-4msNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- 1 Advanced Control Methods: 1.1 LinearizationDocumento1 pagina1 Advanced Control Methods: 1.1 LinearizationmsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Pages From AV15 - L9-qsdDocumento1 paginaPages From AV15 - L9-qsdmsNessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- 1.1 Proportional Control Mode (P) : V OimendustegurDocumento1 pagina1.1 Proportional Control Mode (P) : V OimendustegurmsNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Gregory K. Mcmillan: N A D KDocumento3 pagine6 Gregory K. Mcmillan: N A D KmsNessuna valutazione finora
- When A SIL Rating Is Not Enough PDFDocumento2 pagineWhen A SIL Rating Is Not Enough PDFmsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Support PlanningDocumento4 pagineSupport Planningd_shivarajNessuna valutazione finora
- NEBOSH HSE Certificate in Process Safety Management - NEBOSHDocumento8 pagineNEBOSH HSE Certificate in Process Safety Management - NEBOSHamra_41Nessuna valutazione finora
- Combat Aircraft 2020 09 SepDocumento100 pagineCombat Aircraft 2020 09 SepSérgio SantanaNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Oposa v. Factoran (G.R. No. 101083 July 30, 1993)Documento12 pagineOposa v. Factoran (G.R. No. 101083 July 30, 1993)Claire CaceresNessuna valutazione finora
- Reliable and Unreliable SourcesDocumento10 pagineReliable and Unreliable SourcesSherlyn L. YaunNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effect of Monolingual and Bilingual Dictionary On The Foreign Language Learners' AcquisitionDocumento4 pagineThe Effect of Monolingual and Bilingual Dictionary On The Foreign Language Learners' AcquisitionLong NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Flight Management Computer System FMC Update 13.0 Reference GuideDocumento558 pagineFlight Management Computer System FMC Update 13.0 Reference GuideSHIJKNessuna valutazione finora
- Fighting Cartels in Europe and The US: Different Systems, Common GoalsDocumento7 pagineFighting Cartels in Europe and The US: Different Systems, Common GoalsAndrea AndreeaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Examples of Codes:: What Is Code ?Documento5 pagineExamples of Codes:: What Is Code ?Hiraya ManawariNessuna valutazione finora
- Yibltal Tsegaw MSC Thesis Proposal EditedDocumento35 pagineYibltal Tsegaw MSC Thesis Proposal EditedYibeltalNessuna valutazione finora
- Island Cruise NegotiationDocumento1 paginaIsland Cruise Negotiationphd2313100% (1)
- Proposal Argument (FINAL)Documento10 pagineProposal Argument (FINAL)NgoziNessuna valutazione finora
- Agricultural Literacy: Clarifying A Vision For Practical ApplicationDocumento15 pagineAgricultural Literacy: Clarifying A Vision For Practical ApplicationSubba RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Arms Rules 1924 PDFDocumento88 pagineArms Rules 1924 PDFshoaib87% (23)
- 3 Background: Coffee Production in Papua New GuineaDocumento10 pagine3 Background: Coffee Production in Papua New GuineamiriamNessuna valutazione finora
- Verified Complaint - Ball & Chain Case - 1st Amendment ViolationsDocumento48 pagineVerified Complaint - Ball & Chain Case - 1st Amendment ViolationsMichael PancierNessuna valutazione finora
- Skill Development Programme: Presented byDocumento12 pagineSkill Development Programme: Presented byamit chavariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Brochure EricksonDocumento3 pagineBrochure Ericksonpunchline7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Letters, Memo, and E-MailsDocumento4 pagineLetters, Memo, and E-MailsMarielle PanolleraNessuna valutazione finora
- Example Off LettersDocumento3 pagineExample Off Lettersnina monicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Proposal CFW Lean MonthsDocumento2 pagineProject Proposal CFW Lean MonthskapeatbutasNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction PaperDocumento34 pagineReaction PaperHarriane Mae GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Learning Styles Tips and StrategiesDocumento2 pagineLearning Styles Tips and Strategiestitobej377Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 Risk and Opportunities Register PDFDocumento3 pagine2015 Risk and Opportunities Register PDFdachoko8782% (11)
- Lotte Department StoreDocumento8 pagineLotte Department StoreRebecca ViolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Production Layout Improvement For Steel Fabrication WorksDocumento5 pagineProduction Layout Improvement For Steel Fabrication WorksyemNessuna valutazione finora
- Manpower PlanningDocumento8 pagineManpower PlanningfabyunaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional Values PPTDocumento12 pagineProfessional Values PPTJudge NumberFiveNessuna valutazione finora
- Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman (Utar) : Faculty of Accountancy and Management (Fam)Documento12 pagineUniversiti Tunku Abdul Rahman (Utar) : Faculty of Accountancy and Management (Fam)Wanqi LooNessuna valutazione finora
- MRRD 2020 LVRRGuidelineandStandards Vol2GeometricDesign AsCAP AFG2155A 200831 CompressedDocumento206 pagineMRRD 2020 LVRRGuidelineandStandards Vol2GeometricDesign AsCAP AFG2155A 200831 CompressedMichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Beginning AutoCAD® 2022 Exercise Workbook: For Windows®Da EverandBeginning AutoCAD® 2022 Exercise Workbook: For Windows®Nessuna valutazione finora
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationDa EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Weldments Exam PreparationValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)