Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Assignment 1
Caricato da
Tahsan Kabir100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
607 visualizzazioni2 pagineThis document contains instructions for 5 assignments related to economics and development. The first assignment involves drawing and explaining graphs showing the impact of a price increase on consumption of coffee and tea. The second asks students to determine market demand and supply curves, plot the equilibrium point, and solve for equilibrium price and quantity. The third builds on this by introducing a new supply curve and asking students to graph it and solve for the new equilibrium. The fourth considers the impact of a sales tax on equilibrium price and quantity. The fifth involves illustrating the impact of various events on oil price and quantity demanded.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis document contains instructions for 5 assignments related to economics and development. The first assignment involves drawing and explaining graphs showing the impact of a price increase on consumption of coffee and tea. The second asks students to determine market demand and supply curves, plot the equilibrium point, and solve for equilibrium price and quantity. The third builds on this by introducing a new supply curve and asking students to graph it and solve for the new equilibrium. The fourth considers the impact of a sales tax on equilibrium price and quantity. The fifth involves illustrating the impact of various events on oil price and quantity demanded.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(1)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (1 voto)
607 visualizzazioni2 pagineAssignment 1
Caricato da
Tahsan KabirThis document contains instructions for 5 assignments related to economics and development. The first assignment involves drawing and explaining graphs showing the impact of a price increase on consumption of coffee and tea. The second asks students to determine market demand and supply curves, plot the equilibrium point, and solve for equilibrium price and quantity. The third builds on this by introducing a new supply curve and asking students to graph it and solve for the new equilibrium. The fourth considers the impact of a sales tax on equilibrium price and quantity. The fifth involves illustrating the impact of various events on oil price and quantity demanded.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOC, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
DEV 300: Economics and Development
Fall 2008
BRAC University
Assignment 1
Due at the beginning of the class 15th October 2008
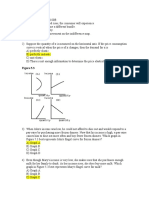
1. The values in the Table refer to the change in an individual’s
consumption of coffee and tea at home when the prices of coffee rises
(everything else, including the price of tea, remains the same). (a)
Draw a figure showing these changes and (b) explain the figure drawn.
Before After
Price Quantity Price Quantity
(cents/c (cups/mon (cents/c (cups/mon
up) th) up) th)
Coffe 40 50 60 30
e
Tea 20 40 20 50
[Hints: Draw two figures, one is for Coffee and another is for
Tea. Put price in the vertical axis and Quantity in the horizontal axis.
Accuracy doesn’t matter but need to understand the concept.]
2. There are 10,000 identical individuals in the market for
commodity X, each with a demand function given by Qdx = 12 – 2Px
and 1000 identical producers of commodity X, each with a function
given by Qsx = 20Px. (a) Find the market demand function and market
supply function for commodity X. (b) Plot, on one set of axes, the
market demand curve and market supply curve for commodity X and
show the equilibrium point. (c) Obtain the equilibrium price and the
equilibrium quantity mathematically.
[Hints: Market demand or supply is found by adding all quantity
demanded and quantity supplied by each individual at each price.]
3. Suppose that from the condition of equilibrium in the previous
problem, there is an improvement in the technology of producing
commodity X (ceteris paribus) so that a new market supply curve is
given by QSx’ = 40000 + 20000Px. (a) show the new market supply
curve (SX’) on the graph of the previous problem and (c) state the new
equilibrium price and the new equilibrium quantity for commodity X.
4. Suppose that from the condition of equilibrium in the previous
problem, the government decides to collect a sales tax of $2 per unit
sold from each of the 1000 identical sellers of commodity X. (a) What
effect does this have on the equilibrium price and quantity of
commodity X? (b) Who actually pays the tax? (c) What is the total
amount of taxes collected by the government?
[Hints: The supply curve does shift upward by $2 and consider
that the demand for the commodity X is relatively price inelastic.]
5. Illustrate the impact of each of the following on price and
quantity demanded:
a. Improvements in transportation lower the costs of importing
oil into the United States in the 1960s.
b. After the 1973 war, oil producers cut oil production sharply.
c. After 1980, smaller automobiles get more miles per gallon.
d. A record-breaking cold winter in1995-1996 unexpectedly
raises the demand for heating oil.
e. A global economic recovery in 1999-2000 leads to a sharp
upturn in oil prices.
[Hints: This particular problem is taken from Samuelson’s book,
chapter 3. You can review figure 3.1 (Gasoline prices move with
demand and supply changes) to get an insight about the problem.]
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ECON1000B: Principles of Microeconomics Midterm Test #1: October 8, 2010Documento6 pagineECON1000B: Principles of Microeconomics Midterm Test #1: October 8, 2010examkillerNessuna valutazione finora
- The Process of Capitalist Production as a Whole (Capital Vol. III)Da EverandThe Process of Capitalist Production as a Whole (Capital Vol. III)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice (One Point Each)Documento4 pagineMultiple Choice (One Point Each)Mulugeta GirmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento4 pagineAssignment 1raheelNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento4 pagineAssignment 1raheelNessuna valutazione finora
- Individual and Group Assignment On EconomicsDocumento2 pagineIndividual and Group Assignment On EconomicsnegussieteklemariamNessuna valutazione finora
- EconomicsDocumento69 pagineEconomicsNikithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics INDERJIT SINGHDocumento9 pagineMicroeconomics INDERJIT SINGHJennifer KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- MBA OUM Demo Lecture QuestionsDocumento15 pagineMBA OUM Demo Lecture Questionsmup100% (2)
- Intro Micro UTS EssayDocumento3 pagineIntro Micro UTS EssaynaylaNessuna valutazione finora
- ECO 3108 - Tutorial 2: The Basics of Supply and Demand Name: - Student ID: - DateDocumento5 pagineECO 3108 - Tutorial 2: The Basics of Supply and Demand Name: - Student ID: - DateLEE SHXIA YAN MoeNessuna valutazione finora
- List 2Documento3 pagineList 2agnessNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid Term RevisionDocumento9 pagineMid Term RevisionRabie HarounNessuna valutazione finora
- Guia Micro II Parcial II Pac 2017Documento16 pagineGuia Micro II Parcial II Pac 2017Anthony Yemil Guerrero100% (2)
- Introduction To Economics Exercise Chapter TwoDocumento5 pagineIntroduction To Economics Exercise Chapter TwoNebiyu NegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 2Documento5 pagineTutorial 2Tasneemah HossenallyNessuna valutazione finora
- HW Microeconomics)Documento3 pagineHW Microeconomics)tutorsbizNessuna valutazione finora
- Economics TutorialsDocumento17 pagineEconomics TutorialsMukul ParasharNessuna valutazione finora
- Government PoliciesDocumento7 pagineGovernment Policies28122004zhNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Homew OrkDocumento32 pagineMicroeconomics Homew OrkTấn Lộc LouisNessuna valutazione finora
- COMM 220 Practice Problems 2 2Documento11 pagineCOMM 220 Practice Problems 2 2Saurabh SaoNessuna valutazione finora
- GE273 Homework Week3Documento3 pagineGE273 Homework Week3MrDiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet CH - 2Documento2 pagineWorksheet CH - 2Bekele FufaNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics Problem Set 2Documento8 pagineMicroeconomics Problem Set 2Thăng Nguyễn BáNessuna valutazione finora
- ECON 201 - Problem Set 1Documento5 pagineECON 201 - Problem Set 1KemalNessuna valutazione finora
- Econ-Hw 2Documento3 pagineEcon-Hw 2юрий локтионовNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1ADocumento5 pagineAssignment 1Agreatguy_070% (1)
- Tutorial 8-10 Q - EconomicsDocumento4 pagineTutorial 8-10 Q - EconomicsJing ZeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cond EnsiveDocumento5 pagineCond EnsiveRabie HarounNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Assessment For ECO120 Principles of Economics (Oct 2021 To Feb 2022)Documento9 pagineOnline Assessment For ECO120 Principles of Economics (Oct 2021 To Feb 2022)AIN ZULLAIKHANessuna valutazione finora
- Ch4 - HomeworkDocumento3 pagineCh4 - Homeworknour.benamorNessuna valutazione finora
- EconomicsDocumento5 pagineEconomicssharathk916Nessuna valutazione finora
- Competitive Markets MEDocumento24 pagineCompetitive Markets MEdheerajm880% (1)
- BACore1-Activity #4Documento5 pagineBACore1-Activity #4Arnold Quachin TanayNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento18 pagineChapter 7dheerajm88Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment2 Machenical PDFDocumento2 pagineAssignment2 Machenical PDFSahil KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter #1 - IntroductionDocumento2 pagineChapter #1 - IntroductionmaximeNessuna valutazione finora
- 2024 Tutorial 8Documento2 pagine2024 Tutorial 8ksfksfdsfNessuna valutazione finora
- ProbleSet Eco1Documento6 pagineProbleSet Eco1souha mhamdiNessuna valutazione finora
- ECON 446 First AssinmentDocumento2 pagineECON 446 First AssinmentFrancisco WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 2 - Micro1Documento8 pagineAssignment 2 - Micro1Teak Tattee0% (1)
- BECO100 1314 Fall Assignment2Documento4 pagineBECO100 1314 Fall Assignment2PriceNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Exam 2Documento7 pagineSample Exam 2Kateryna TernovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Session-Numerical Problems With CalculusDocumento42 pagineExtra Session-Numerical Problems With CalculusAnit DattaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam 10Documento15 pagineFinal Exam 10Nadira RoslanNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculating Exercises For Chapter 2+3 Exercise 1: Suppose The Market For Good A Has Supply and Demand Function As FollowDocumento3 pagineCalculating Exercises For Chapter 2+3 Exercise 1: Suppose The Market For Good A Has Supply and Demand Function As FollowTrần Xuân NgọcNessuna valutazione finora
- ECO101: Introduction To Economics (Summer Semester, 2019) Tutorial Problem Set - 02Documento3 pagineECO101: Introduction To Economics (Summer Semester, 2019) Tutorial Problem Set - 02Shubham KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ExerciseDocumento6 pagineExerciseNurul Farhan IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Equations in Economic ProblemsDocumento4 pagineLinear Equations in Economic ProblemsDan CeresauNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Questions 2014Documento15 paginePractice Questions 2014Ankit Sahu0% (1)
- Calculus For Bus and Econ Sample PDFDocumento5 pagineCalculus For Bus and Econ Sample PDFWade GrayNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set 5Documento6 pagineProblem Set 5Thulasi 2036Nessuna valutazione finora
- PS 7Documento9 paginePS 7Gülten Ece BelginNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 2 Review 2Documento13 pagineTest 2 Review 2caitlin1593Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 ReviewDocumento14 pagineChapter 3 ReviewMateo NogueraNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 ECO 213Documento5 pagineAssignment 1 ECO 213khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Review1answers - Microeconomic AnalysisDocumento4 pagineReview1answers - Microeconomic AnalysisSalsa FaniaNessuna valutazione finora
- PS1 QuestionsDocumento5 paginePS1 QuestionsHussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Due Diligence Planning, Questions, IssuesDocumento224 pagineDue Diligence Planning, Questions, IssueshowierdNessuna valutazione finora
- PT Wahana Ottomitra Multiartha TBKDocumento97 paginePT Wahana Ottomitra Multiartha TBKHellcurtNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Risk Measurement MethodsDocumento2 pagineBusiness Risk Measurement MethodsSahaa NandhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk N ReturnDocumento6 pagineRisk N ReturnRakesh Kr RouniyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Question 591541Documento7 pagineQuestion 591541sehajleen randhawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Presentationon SharekhanDocumento15 pagineFinal Presentationon SharekhanRajat SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Account Activity: Transaction Date Value Date Reference Description Debit Credit BalanceDocumento9 pagineAccount Activity: Transaction Date Value Date Reference Description Debit Credit BalanceAmin KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Auditing Gray 2015 CH 13 Final Work Spesific Problems Related To Inventories Contruction Contract Trade Payables Financial LiabilitiesDocumento29 pagineAuditing Gray 2015 CH 13 Final Work Spesific Problems Related To Inventories Contruction Contract Trade Payables Financial LiabilitiesSani AuroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Wonders of ExcelDocumento45 pagineWonders of ExceloscarhasibuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Assignment - IUB - MBA - Managerial EconomicsDocumento12 pagineFinal Assignment - IUB - MBA - Managerial EconomicsMohammed Iqbal HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- 01.12 Posting RestrictionsDocumento14 pagine01.12 Posting Restrictionsmevrick_guyNessuna valutazione finora
- Broker Business PlanDocumento18 pagineBroker Business PlanJulie FlanaganNessuna valutazione finora
- The Business Plan, Creating and Starting The VentureDocumento24 pagineThe Business Plan, Creating and Starting The VentureE Kay Mutemi100% (1)
- Period Cash Flow Future Value: Investment 2Documento2 paginePeriod Cash Flow Future Value: Investment 2Kim FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- MainMenuEnglishLevel-3 RLD2014016Documento291 pagineMainMenuEnglishLevel-3 RLD2014016Asif RafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Security Valuation G3 730AMDocumento3 pagineSecurity Valuation G3 730AMKearn CercadoNessuna valutazione finora
- ch03 Test ACCT 512 Financial Accounting Theory and IssuesDocumento12 paginech03 Test ACCT 512 Financial Accounting Theory and IssuesSonny MaciasNessuna valutazione finora
- Invoice Original 1882427818115Documento1 paginaInvoice Original 1882427818115Anno DominiNessuna valutazione finora
- BSBFIM601 Manage FinancesDocumento5 pagineBSBFIM601 Manage FinancesCindy Huang0% (2)
- Problems On Internal ReconstructionDocumento24 pagineProblems On Internal ReconstructionYashodhan Mithare100% (4)
- Risk Management Concepts: January 1998Documento26 pagineRisk Management Concepts: January 1998IonutStanoiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Hedge Funds-Case StudyDocumento20 pagineHedge Funds-Case StudyRohan BurmanNessuna valutazione finora
- f6vnm 2015dec Q PDFDocumento16 paginef6vnm 2015dec Q PDFSinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Title: Financial Markets Course Code: Course DescriptionDocumento6 pagineCourse Title: Financial Markets Course Code: Course Descriptionharon franciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rich Dad's Guide To Becoming Rich... Without Cutting Up Your Credit CardsDocumento101 pagineRich Dad's Guide To Becoming Rich... Without Cutting Up Your Credit CardsYouert RayutNessuna valutazione finora
- Loan Foreclosure LetterDocumento3 pagineLoan Foreclosure LetterBabu BNessuna valutazione finora
- Summer Internship Programme 2018-19: National Aluminum Company Limited NalcoDocumento59 pagineSummer Internship Programme 2018-19: National Aluminum Company Limited Nalcoanon_849519161Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Prentation of ProjectDocumento17 pagineFinal Prentation of ProjectnilphadtareNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Estate TaxationDocumento88 pagineReal Estate TaxationMichelleOgatis89% (9)
- CARO 2020 PresentationDocumento47 pagineCARO 2020 PresentationMuralidharan SNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingDa EverandUniversity of Berkshire Hathaway: 30 Years of Lessons Learned from Warren Buffett & Charlie Munger at the Annual Shareholders MeetingValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (98)
- A History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationDa EverandA History of the United States in Five Crashes: Stock Market Meltdowns That Defined a NationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (11)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassDa EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassNessuna valutazione finora
- The Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityDa EverandThe Meth Lunches: Food and Longing in an American CityValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailDa EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (238)
- Narrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsDa EverandNarrative Economics: How Stories Go Viral and Drive Major Economic EventsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (94)
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesDa EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (8)
- Look Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereDa EverandLook Again: The Power of Noticing What Was Always ThereValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- The Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaDa EverandThe Trillion-Dollar Conspiracy: How the New World Order, Man-Made Diseases, and Zombie Banks Are Destroying AmericaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationDa EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (46)
- Economics 101: How the World WorksDa EverandEconomics 101: How the World WorksValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (34)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyDa EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (229)
- Economics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsDa EverandEconomics 101: From Consumer Behavior to Competitive Markets—Everything You Need to Know About EconomicsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Second Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenDa EverandSecond Class: How the Elites Betrayed America's Working Men and WomenNessuna valutazione finora
- Decolonial Marxism: Essays from the Pan-African RevolutionDa EverandDecolonial Marxism: Essays from the Pan-African RevolutionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (6)
- Vienna: How the City of Ideas Created the Modern WorldDa EverandVienna: How the City of Ideas Created the Modern WorldNessuna valutazione finora
- This Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimateDa EverandThis Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The ClimateValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (349)
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaDa EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (14)
- Vulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomDa EverandVulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomNessuna valutazione finora
- The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and MoneyDa EverandThe General Theory of Employment, Interest, and MoneyNessuna valutazione finora
- The New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyDa EverandThe New Elite: Inside the Minds of the Truly WealthyValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Economics in America: An Immigrant Economist Explores the Land of InequalityDa EverandEconomics in America: An Immigrant Economist Explores the Land of InequalityValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)