Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Poster of Master Thesis
Caricato da
Marat KhodzhaievDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Poster of Master Thesis
Caricato da
Marat KhodzhaievCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Fakultät Bauingenieurwesen Fakultätsrechenzentrum
Topology, shape, and size optimization of transmission towers
Author: Marat Khodzhaiev
WS 2019/20
Supervisor: Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. Uwe Reuter, Fakultätsrechenzentrum Fakultät Bauingenieurwesen
Goals: • Investigation of suitable optimization and design approaches of transmission towers
• Developing an approach to design optimization of transmission tower with aiming at
the practical application of its implementation.
• Implementation of the developed approach in the form of a computer program.
Problem: Designing a transmission tower requires considerable time in order to find efficient form in terms of cost. In order
to find the optimum design in a given time, an efficient approach to topology, shape, and size optimization is
needed. For the approach to be applicable, a resultant transmission tower geometry should conform industry
limitations and structural verifications to be performed according to EN 50341-1:2012.
Solution: An approach to topology, shape, and size design optimization of a transmission tower based on a genetic
algorithm was developed in this research. The proposed approach performs topology and shape optimization by
varying number and heights of tower panels. Size optimization is performed by a search for the most optimal
combination of cross-sectional and material parameters of the tower members. Lower tower cost is considered as
a design objective. Feasible tower geometry configurations conform to conventional layouts of a lattice steel
tower with continuous cross bracing. The proposed approach was implemented in the form of a computer
program written in the Python programming language. Computer program FEAPpv is utilized for structural
calculation by the finite element method.
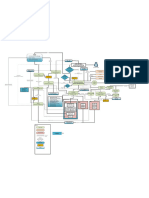
Layout optimization Geometry
Start
Problem subdividing input
Set
Generation
Layout initial parent
population
Design Input optimization genome
FALSE Wind load
Subproblem 1 Size generation
optimization IF For each
Problem subdividing TRUE the number of individual:
generation exceeds an Structural
Layout upper limit Size calculation by
optimization Freeze optimization FEAPpv
Next
optimal
Size subproblem Sizing
geometry
optimization optimization of
Setting fittest members
Search for
individual a
FALSE the fittest
new parent
Output IF next individual Evaluation
subproblem IF
optimal TRUE available the objective of cost
geometry of the fittest is smaller
TRUE of the parent
FALSE
Cost
Finish output
Example: Topology, shape and size optimization of 110 kV double circuit transmission tower.
Master Thesis
Genetic algorithm parameters: 10 generations of 300 population size.
Subproblem 2 Subproblem 4
Initial Optimized
Results:
Sub Initial Final Cost
problem cost cost reduction Initial
1 89.0 78.3 12.1%
2 98.4 98.3 0.1%
3 226.2 215.4 4.8%
4 410.4 367.0 10.6%
5 590.8 507.0 14.2%
TOTAL 1414.8 1265.9 10.5%
Optimized
Subproblem 2 Subproblem 4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Old Ossetic Inscription From The River Zelenčuk,: Achtung!Documento4 pagineThe Old Ossetic Inscription From The River Zelenčuk,: Achtung!gippertNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5.0.2018 - Retaining WallDocumento36 pagineChapter 5.0.2018 - Retaining WallHawaiiChongNessuna valutazione finora
- Twu GeneralMotors 5152012Documento16 pagineTwu GeneralMotors 5152012Milton Encalada100% (1)
- Geometry Modeling For Automated Finite-Element Analysis of Aircraft Conceptual DesignDocumento21 pagineGeometry Modeling For Automated Finite-Element Analysis of Aircraft Conceptual DesignHassanNessuna valutazione finora
- FEM Techniques in Structural Analysis: Gfem LoadsDocumento1 paginaFEM Techniques in Structural Analysis: Gfem LoadsBala KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 - The Design Process - NASA PDFDocumento42 pagine01 - The Design Process - NASA PDFrafael ricardo molina navarroNessuna valutazione finora
- AI StrategyDocumento31 pagineAI StrategyHans CasteelsNessuna valutazione finora
- Microservice PatternDocumento1 paginaMicroservice PatternHari Haran M100% (1)
- Monorail DesignDocumento12 pagineMonorail DesignCong Thu PhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 1 1 55 4078 PDFDocumento33 pagine10 1 1 55 4078 PDFpatilhitzNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization of Composite: Recent Advances and ApplicationDocumento18 pagineOptimization of Composite: Recent Advances and Applicationjunjie yiNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Article: Robust Design Optimization of An Aerospace Vehicle Prolusion SystemDocumento19 pagineResearch Article: Robust Design Optimization of An Aerospace Vehicle Prolusion SystemPrashanth DalawaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ga11 2019Documento5 pagineGa11 2019haval.alsofiNessuna valutazione finora
- First Presentation BESS ProjectDocumento14 pagineFirst Presentation BESS ProjecthuamanahuiNessuna valutazione finora
- Engine Structure Poster 18x24Documento1 paginaEngine Structure Poster 18x24Алексей Гончаров100% (1)
- Casting Brochure 0Documento12 pagineCasting Brochure 0makdangNessuna valutazione finora
- Geo Workflow Geo Workflow: Create / Open ProjectDocumento2 pagineGeo Workflow Geo Workflow: Create / Open ProjectFriska AyundaNessuna valutazione finora
- Casting Brochure 1 PDFDocumento12 pagineCasting Brochure 1 PDFAkshayNessuna valutazione finora
- Parameter Tuning - Prediction of Supply Chain Parameters Such As Lead Time and YieldDocumento1 paginaParameter Tuning - Prediction of Supply Chain Parameters Such As Lead Time and YieldPriyam DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Seven PillarsDocumento2 pagineSeven PillarsparkmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison Between Xgboost, Lightgbm and Catboost Using A Home Credit DatasetDocumento5 pagineComparison Between Xgboost, Lightgbm and Catboost Using A Home Credit DatasetEduardo Miguel Vásquez SoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Everything You Need To Know About Moving From Maximo EAM To Maximo Application SuiteDocumento22 pagineEverything You Need To Know About Moving From Maximo EAM To Maximo Application SuiteWSNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 DistQueryOptimizationDocumento14 pagine10 DistQueryOptimizationRonaldMartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- Petrel TutoriorDocumento177 paginePetrel TutoriorAlfian AminNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Javascript: Interpreter/ Compiler/ JIT CompilerDocumento1 paginaAdvanced Javascript: Interpreter/ Compiler/ JIT CompilerJamshid AzizovNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced JavascriptDocumento1 paginaAdvanced Javascriptsttv2727Nessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Javascript: Interpreter/ Compiler/ JIT Compiler Writing Optimized CodeDocumento1 paginaAdvanced Javascript: Interpreter/ Compiler/ JIT Compiler Writing Optimized CodeRonNessuna valutazione finora
- AutoForm Distributor MeetingDocumento56 pagineAutoForm Distributor MeetingLeandro SoaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Software CMG HighlightsDocumento16 pagineSoftware CMG HighlightsAndyPaezNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Estimating in BIMDocumento16 pagineUnderstanding Estimating in BIMKAushik KaRavadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Expert NW PlanningDocumento2 pagineExpert NW Planninganat17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Article 2Documento1 paginaArticle 2bhagat103Nessuna valutazione finora
- Strategy in Business Context: People Motivation InteractionDocumento1 paginaStrategy in Business Context: People Motivation InteractionBaher WilliamNessuna valutazione finora
- Proposal Thesis - Thesis FrameworkDocumento2 pagineProposal Thesis - Thesis Frameworkarrizky ayu faradila purnamaNessuna valutazione finora
- QFD TesisDocumento1 paginaQFD TesisGabriel VazquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluent Meshing 18.2 Module03 CFDSurf ImportDocumento65 pagineFluent Meshing 18.2 Module03 CFDSurf ImportcansuyusNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Systems: Educati On Smart Gover NanceDocumento2 pagineStrategic Systems: Educati On Smart Gover NanceRavindra JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- A3 Estandarización Del ArmadoDocumento1 paginaA3 Estandarización Del ArmadoVictorNessuna valutazione finora
- Seismic Safety, Risk Reduction and Performance-Based Design Aimed at Nuclear Facility StructuresDocumento46 pagineSeismic Safety, Risk Reduction and Performance-Based Design Aimed at Nuclear Facility StructuresZeeshaan BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- Reconstructing Genome-Scale Metabolic Models With MerlinDocumento1 paginaReconstructing Genome-Scale Metabolic Models With MerlinSemana de Engenharia '2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9m Investigating Mind MapDocumento1 pagina9m Investigating Mind MapMayra SamaNessuna valutazione finora
- SAFe Glossary EN PDFDocumento16 pagineSAFe Glossary EN PDFBharat Vyas100% (2)
- Optimisation of A Three-Dimensional Axial Pump Using An Artificial Neural Network, A Genetic Algorithm and A Navier-Stokes SolverDocumento1 paginaOptimisation of A Three-Dimensional Axial Pump Using An Artificial Neural Network, A Genetic Algorithm and A Navier-Stokes SolveravinashpatilNessuna valutazione finora
- GTS NX FabeDocumento10 pagineGTS NX FabeJose Luis Nava HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Computerized Optimiza-Tion in Die Casting ProcessesDocumento8 pagineAutomatic Computerized Optimiza-Tion in Die Casting ProcessesmuktahansNessuna valutazione finora
- Framework Profitability Smarthveer Sidana 1Documento1 paginaFramework Profitability Smarthveer Sidana 1adityaNessuna valutazione finora
- J OCTA Brochure (201403)Documento4 pagineJ OCTA Brochure (201403)SrashmiNessuna valutazione finora
- ReservoirDocumento1 paginaReservoirDeepak ChandranNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart br002 - en PDocumento14 pagineSmart br002 - en PjeyakaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Product Development Process For Suspension Component Aided by Numerical SimulationsDocumento9 pagineProduct Development Process For Suspension Component Aided by Numerical SimulationsLuis Alberto Garrido MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tivoli Overview - Future IncludedDocumento1 paginaTivoli Overview - Future Includedknokturnal839Nessuna valutazione finora
- Parallel Computing ChallangesDocumento7 pagineParallel Computing ChallangesmuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- SWAN Tutorial Slot Model Design AnalysisDocumento7 pagineSWAN Tutorial Slot Model Design AnalysisSyed Nazim ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- V12 1 EngDocumento8 pagineV12 1 EngAnonymous a4Jwz14WNessuna valutazione finora
- 3DP SAMKIT Brouchure 002 OnlineDocumento2 pagine3DP SAMKIT Brouchure 002 OnlineNoor MalakNessuna valutazione finora
- Copernicus Programme - InfrastructureDocumento1 paginaCopernicus Programme - InfrastructureGemmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Enr2017 Top500Documento66 pagineEnr2017 Top500Ahmed AlnagarNessuna valutazione finora
- FlutterDocumento1 paginaFluttermouchrif.hadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Short-Term Analysis in Energy ManagementDocumento1 paginaShort-Term Analysis in Energy ManagementlupoderiNessuna valutazione finora
- HOLOS: Free-Form Curved Surface Measuring Program (Option)Documento4 pagineHOLOS: Free-Form Curved Surface Measuring Program (Option)김병곤Nessuna valutazione finora
- Template WFP-Expenditure Form 2024Documento22 pagineTemplate WFP-Expenditure Form 2024Joey Simba Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computational Geometry: Exploring Geometric Insights for Computer VisionDa EverandComputational Geometry: Exploring Geometric Insights for Computer VisionNessuna valutazione finora
- Master Thesis PresentationDocumento66 pagineMaster Thesis PresentationMarat KhodzhaievNessuna valutazione finora
- Precast Balanced Cantilever ConstructionDocumento146 paginePrecast Balanced Cantilever ConstructionMarat KhodzhaievNessuna valutazione finora
- Topology, Shape, and Size Optimization of Transmission TowersDocumento66 pagineTopology, Shape, and Size Optimization of Transmission TowersMarat KhodzhaievNessuna valutazione finora
- Have A Nice Day, Dude: The First Which You Need To Say Yourself in The MorningDocumento1 paginaHave A Nice Day, Dude: The First Which You Need To Say Yourself in The MorningMarat KhodzhaievNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 4063-2010 RU Welding and Allied Processes - Nomenclature of Processes and Reference NumbersDocumento16 pagineISO 4063-2010 RU Welding and Allied Processes - Nomenclature of Processes and Reference NumbersMarat KhodzhaievNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Welded Connections PDFDocumento37 pagineDesign of Welded Connections PDFMarat Khodzhaiev100% (1)
- Safety PledgeDocumento3 pagineSafety Pledgeapi-268778235100% (1)
- Bahria University (Karachi Campus) : Department of Electrical Engineering Assignment # 03Documento11 pagineBahria University (Karachi Campus) : Department of Electrical Engineering Assignment # 03rizwan ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Sec D CH 12 Regression Part 2Documento66 pagineSec D CH 12 Regression Part 2Ranga SriNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts Catalogue YAMAHA ET-1Documento18 pagineParts Catalogue YAMAHA ET-1walterfrano6523Nessuna valutazione finora
- Canon Ts5000 (Impressora) MANUALDocumento441 pagineCanon Ts5000 (Impressora) MANUALMiguel DinisNessuna valutazione finora
- Q4 TLE AFA Horticulture 9 Week3Documento4 pagineQ4 TLE AFA Horticulture 9 Week3Dash Bello100% (1)
- High Pressure Hazard Safety AwarenessDocumento57 pagineHigh Pressure Hazard Safety AwarenessPurnomo JarodNessuna valutazione finora
- ENaresh BossBabu GRahul 33Documento6 pagineENaresh BossBabu GRahul 33anthonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Attitude Summary MFDocumento8 pagineAttitude Summary MFAraz YagubluNessuna valutazione finora
- Examples V4.1 PDFDocumento39 pagineExamples V4.1 PDFgerNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet: TV10S 335-11Z-M20Documento6 pagineDatasheet: TV10S 335-11Z-M20Dayglis CostaNessuna valutazione finora
- AVR Studio TutorialDocumento8 pagineAVR Studio Tutorialtio2903Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit1 Topic1 Digital Logic IntroductionDocumento33 pagineUnit1 Topic1 Digital Logic IntroductionHari Kumar N CNessuna valutazione finora
- ISD1820 Voice Recorder Module User Guide: Rev 1.0, Oct 2012Documento5 pagineISD1820 Voice Recorder Module User Guide: Rev 1.0, Oct 2012HARFA industriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Gkournelos Triantafillou 2023 Out of Plane Behavior of in Plane Damaged Masonry Infills Retrofitted With TRM andDocumento14 pagineGkournelos Triantafillou 2023 Out of Plane Behavior of in Plane Damaged Masonry Infills Retrofitted With TRM andN.prem kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Flutter WidgetsDocumento43 pagineFlutter WidgetsSangakkara WarriorsNessuna valutazione finora
- Danik Bhaskar Jaipur 05-24-2014Documento28 pagineDanik Bhaskar Jaipur 05-24-2014bhaskar_newsNessuna valutazione finora
- HP-AN200-2 - Fundamentals of Quartz OscillatorsDocumento28 pagineHP-AN200-2 - Fundamentals of Quartz Oscillatorssirjole7584100% (1)
- 2010 Summer SchoolDocumento31 pagine2010 Summer SchoolAlbanita MendesNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Symbolic Frame Worksheet 1Documento3 pagine5 Symbolic Frame Worksheet 1api-529132129Nessuna valutazione finora
- PHY11L E201: Work, Energy, and PowerDocumento16 paginePHY11L E201: Work, Energy, and PowerMikaella TambisNessuna valutazione finora
- LR Chapter 5 - Input and OutputDocumento6 pagineLR Chapter 5 - Input and OutputAakash KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 20.29 147192 (CM9383)Documento10 pagine20.29 147192 (CM9383)marcelo sampaioNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Gas Conditioning and ProcessingDocumento14 pagineOverview of Gas Conditioning and ProcessingJOSE GONZALEZ VALERONessuna valutazione finora
- About The ProjectDocumento5 pagineAbout The Projectanand kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- JLG 860SJ Parts - Global - English PDFDocumento294 pagineJLG 860SJ Parts - Global - English PDFfater esmandarNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Transfer Lines: UNIT-3 Automation Manufracturing PvpsitDocumento14 pagineAnalysis of Transfer Lines: UNIT-3 Automation Manufracturing PvpsitSravanth KondetiNessuna valutazione finora
- Curl (Mathematics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento13 pagineCurl (Mathematics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediasoumyanitcNessuna valutazione finora