Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
The Easy Guide To The McKinsey 7S Model
Caricato da
Rose Dumayac0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
86 visualizzazioni4 pagineMANAGEMENT
Titolo originale
The Easy Guide to the McKinsey 7S Model
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoMANAGEMENT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
86 visualizzazioni4 pagineThe Easy Guide To The McKinsey 7S Model
Caricato da
Rose DumayacMANAGEMENT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 4
The Easy Guide to the McKinsey 7S Model
Updated on: 13 November 2019
Although invented in the late 1970s, the McKinsey 7S model still helps businesses of all
sizes succeed. A conceptual framework to guide the execution of strategy.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the 7S of the McKinsey Framework and how to
apply it to evaluate and improve performance.
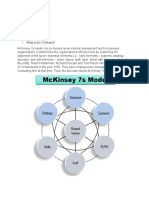
McKinsey 7S Model Definition
The McKinsey 7S model is one of the most popular strategic planning tools.
Businesses commonly use it to analyze internal elements that affect organizational
success.
The model recognizes 7 of these elements and considers them to be interlinked,
therefore it’s difficult to make significant progress in one area without making progress
in other areas as well. Accordingly, to be successful, the organization should ensure
that all these elements are aligned and reinforced.
The model divides these 7 elements into two categories;
Hard elements – Strategy, Structure, Systems (these are easier to be identified and
defined and can be directly influenced by the management)
Soft elements – Shared Values, Skills, Style, Staff (these are harder to be defined
because they are less tangible, but are just as important as the hard elements)
You can use the framework
To successfully execute new strategies
To analyze how different key parts of your organization work together
To facilitate changes in the organization
To help align processes during a merger or acquisition
To support management thinking during strategy implementation and change
management
The 7 Elements of the McKinsey 7S Framework
Let’s dig into these elements in more detail.
Strategy
A strategy is a plan the company develops to maintain its competitive advantage in the
market. It consists of a set of decisions and action steps that need to be taken in
response to the changes in the company’s external environment which includes its
customers and competitors.
An effective strategy would find external opportunities and develop the necessary
resources and capabilities to convert the environmental changes into sources of new
competitive advantage.
Structure
The structure is the organizational chart of the company. It represents how the different
units and divisions of the company are organized, who reports to whom and the division
and integration of tasks. The structure of a company could be hierarchical or flat,
centralized or decentralized, autonomous or outsourced, or specialized or integrated.
Compared to most other elements, this one is more visible and easier to change.
Organizational Chart (Click on the template to edit it online)
Systems
These are the primary and secondary activities that are part of the company’s daily
functioning. Systems include core processes such as product development and support
activities such as human resources or accounting.
Skills
Skills are the skill set and capabilities of the organization’s human resources. Core
competencies or skills of employees are intangible but they a major role in attaining
sustainable competitive advantage.
Staff
The most valuable strategic asset of an organization is its staff or human resources.
This element focuses on the number of employees, recruitment, development of
employees, remuneration and other motivational considerations.
Style
This refers to the management style of the company leadership. It includes the actions
they take, the way they behave, and how they interact.
Shared Values
Shared values are also referred to as superordinate goals and are the element that is in
the core of the model. It is the collective value system that is central to the
organizational culture and represents the company’s standards and norms, attitudes,
and beliefs. It’s regarded as the organization’s most fundamental building block that
provides a foundation for the other six elements.
How to Use the McKinsey 7S Model
The model can be used to do a gap analysis or to determine the gap between what the
company is currently doing and what it needs to do to successfully execute the
strategy.
Step 1: Analyze the current situation of your organization
This is where you need to understand the current situation of the organization with
regard to the 7 elements. Analyzing them closely will give you a chance to see if they
are aligned effectively.
The following checklist questions will help you explore your situation.
Strategy
What’s the objective of your company strategy?
How do you use your resources and capabilities to achieve that?
What makes you stand out from your competitors?
How do you compete in the market?
How do you plan to adapt in the face of changing market conditions?
Structure
What’s your organizational structure?
Who makes the decisions? Who reports to whom?
Is decision-making centralized or decentralized?
How do the employees align themselves to the strategy?
How is information shared across the organization?
Sytems
What are the primary processes and systems of the organization?
What are the system controls and where are they?
How do you track progress?
What are the processes and rules the team sticks with to keep on track?
Skills
What are the core competencies of the organization? Are these skills sufficiently
available?
Are there any skill gaps?
Are the employees aptly skilled to do their job?
What do you do to monitor, evaluate and improve skills?
What is it that the company is known for doing well?
Staff
How many employees are there?
What are the current staffing requirements?
Are there any gaps in the required resources?
What needs to be done to address them?
Style
What is the management style like?
How do the employees respond to this style?
Are employees competitive, collaborative or cooperative?
What kind of tasks, behaviors, and deliverables does the leadership reward?
What kind of teams are there in the organization? Are there real teams or are
they just nominal groups?
Shared Values
What are the mission and vision of the organization?
What are your ideal and real values?
What are the core values the organization was founded upon?
How does the company incorporate these values in daily life?
Step 2: Determine the ideal situation of the organization
Specify where you ideally want to be and the optimal organizational design you want to
achieve, with the help of the senior management. This will make it easier to set your
goals and come up with a solid action plan to implement the strategy.
Since the optimal position you want to be in is still not known to you, you will have to
collect data and insight through research on the organizational designs of competitors
and how they coped with organizational change. Answering the questions above are
just the starting point.
Step 3: Develop your action plan
Here you will identify which areas need to be realigned and how you would do that. The
result of this step should be a detailed action plan listing the individual steps you need
to take to get to your desired situation, along with other important details such as task
owners, timeframes, precautions and so on.
Step 4: Implement the action plan
Successfully executing the action plan is depended on who executes it. Therefore you
need to make sure that you assign the tasks to the right people in your organization.
Additionally, you can also hire consultants to guide the process.
Step 5: Review the seven elements from time to time
Since the seven elements are subjected to constant change, reviewing them
periodically is essential. A change in one element will affect all the others, which will
require you to implement a new organization design. Review the situation frequently to
stay aware of the remedial action you might want to take.
Advantages and Disadvantages of McKinsey 7S Model
Advantages
Considers 7 elements of strategic fit, which is more effective than the traditional
model that only focuses on strategy and structure
It helps align the processes, systems, people, and values of an organization
Since it analyzes each element and the relationship between them in detail, it
ensures that you miss no gaps caused by changed strategies
Helps organizations identify how they should align the different key parts of the
organization to achieve their goals
Disadvantages
It requires the organization to do a lot of research and benchmarking, which
makes it time-consuming
It only focuses on internal elements, while paying no attention to the external
elements that may affect organizational performance.
It requires the help of senior management which may not be readily available
depending on how busy they are
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Mckinsey 7 Dimensions and Hofstede SMMDocumento18 pagineMckinsey 7 Dimensions and Hofstede SMMLyna EvaNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7s ModelDocumento11 pagineMcKinsey 7s ModelAnilKotthur0% (1)
- Mcckinsey 7s Short SummaryDocumento7 pagineMcckinsey 7s Short SummaryBarış TunçbilekNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7s Mode1Documento4 pagineMcKinsey 7s Mode1Rose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- The McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocumento6 pagineThe McKinsey 7S FrameworkMathan Raj75% (4)
- The Seven Elements: Hard Elements Soft ElementsDocumento5 pagineThe Seven Elements: Hard Elements Soft ElementsVineet KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Tool: Mckinsey 7S ModelDocumento9 pagineUnderstanding Tool: Mckinsey 7S ModelMajid HashimNessuna valutazione finora
- The McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocumento17 pagineThe McKinsey 7S FrameworkDanna Denise MalotoNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7SDocumento14 pagineMcKinsey 7SVijay HalalliNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocumento7 pagineMcKinsey 7S FrameworkRara AlonzoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Mckinsey 7-S Framework: Ensuring That All Parts of Your Organization Work in HarmonyDocumento6 pagineThe Mckinsey 7-S Framework: Ensuring That All Parts of Your Organization Work in HarmonychanukyaNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7S ModelDocumento9 pagineMcKinsey 7S ModelMohd SajidNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 S MoodelDocumento15 pagine7 S MoodelvasudevprasadNessuna valutazione finora
- 202003291621085882smitasingh McKinsey 7s ModelDocumento6 pagine202003291621085882smitasingh McKinsey 7s ModelJanice MkhizeNessuna valutazione finora
- SM II-handout 05-Mckinsey 7s ModelDocumento6 pagineSM II-handout 05-Mckinsey 7s ModelAkshay sachanNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Unit Supervision (McKinsey 7S Model)Documento4 pagineSmall Unit Supervision (McKinsey 7S Model)PEMS Ivan Theodore P LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7s ModelDocumento7 pagineMcKinsey 7s ModelMuhammad Imran KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7-S FrameworkDocumento4 pagineMcKinsey 7-S FrameworkSOHEB TADVINessuna valutazione finora
- 7s ModelDocumento6 pagine7s ModelRaymond Diaz0% (1)
- McKinsey 7S ModelDocumento12 pagineMcKinsey 7S Modelmahmoud elsrogyNessuna valutazione finora
- Demystifying Strategic Planning: People-Centered Leadership, #2Da EverandDemystifying Strategic Planning: People-Centered Leadership, #2Nessuna valutazione finora
- AmulDocumento9 pagineAmulAshik NavasNessuna valutazione finora
- 7s ModelDocumento11 pagine7s ModelABA DBA JBANessuna valutazione finora
- Lewin's Three-Step Model For Implementing Change: UnfreezingDocumento21 pagineLewin's Three-Step Model For Implementing Change: UnfreezingnidhiviniNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7 S FrameworkDocumento6 pagineMcKinsey 7 S FrameworkDeepank GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Essential Business Strategy ToolsDocumento30 pagine5 Essential Business Strategy ToolsrlwersalNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7s ModelDocumento5 pagineMcKinsey 7s Model2K20DMBA158 Prabhakar MallikNessuna valutazione finora
- 7S FrameworkDocumento10 pagine7S FrameworkAshwini SudheerNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 McKinsey 7SDocumento7 pagine04 McKinsey 7Ssunshine4u5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Strategic ManagementDocumento18 pagineUnit 4 Strategic ManagementMadhu ShrivastavNessuna valutazione finora
- The McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocumento7 pagineThe McKinsey 7S FrameworkShruti VinyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ge9 CellDocumento8 pagineGe9 Cellsneha bhongadeNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 SDocumento5 pagine7 Sregine bacabagNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7S Framework of Nestle LTD ScribdDocumento2 pagineMcKinsey 7S Framework of Nestle LTD Scribdsreeya50% (6)
- MC Kinsey ModelDocumento9 pagineMC Kinsey ModelJuhika SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7S ModelDocumento15 pagine7S ModelRupashi GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- The McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocumento5 pagineThe McKinsey 7S FrameworkSmriti KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - The McKinsey 7SDocumento6 pagine3 - The McKinsey 7SAlex SimmonsNessuna valutazione finora
- MC Kinsey 7S Model Its Implementation in InfosysDocumento24 pagineMC Kinsey 7S Model Its Implementation in InfosysAbdul Halim JoharNessuna valutazione finora
- Mckinsey 7-S Framework: Making Every Part of Your Organization Work in HarmonyDocumento10 pagineMckinsey 7-S Framework: Making Every Part of Your Organization Work in HarmonyDaiserie Mae AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- The McKinsey 7S FrameworkDocumento2 pagineThe McKinsey 7S FrameworkKarl Joseph PaladaNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsDa EverandBuilding Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsNessuna valutazione finora
- 7S Model Of: MckinseyDocumento23 pagine7S Model Of: MckinseyShuchi Prashant SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- The McKinsey 7S Framework - Strategy Skills FromDocumento7 pagineThe McKinsey 7S Framework - Strategy Skills Frommanish PatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7sDocumento2 pagineMcKinsey 7sSunil BawaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7S FrameworkDocumento2 pagine7S FrameworkSanjay GhodadraNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic ImplementationDocumento8 pagineStrategic ImplementationAnjali KedareNessuna valutazione finora
- Organisational TheoryDocumento4 pagineOrganisational TheoryIvan DanielNessuna valutazione finora
- The McKinsey 7S Framework - Strategy Skills From MindToolsDocumento7 pagineThe McKinsey 7S Framework - Strategy Skills From MindToolstani100% (1)
- McKinsey 7-S Framework - Making Every Part of Your Organization Work in HarmonyDocumento1 paginaMcKinsey 7-S Framework - Making Every Part of Your Organization Work in HarmonyVikas RupareliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management AssignmentDocumento17 pagineStrategic Management Assignmentshiv mehraNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey 7s ModelDocumento9 pagineMcKinsey 7s ModelriteshNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Resources Management: A Guide on How to Implement HR Best Practices Includes Ready Structured Procedures and FormsDa EverandHuman Resources Management: A Guide on How to Implement HR Best Practices Includes Ready Structured Procedures and FormsNessuna valutazione finora
- Strat Bus Analysis Lecture2Documento15 pagineStrat Bus Analysis Lecture2Hannahbea LindoNessuna valutazione finora
- McKinsey Framework2Documento4 pagineMcKinsey Framework2Enna L LebarimNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract:: 7S FrameworkDocumento5 pagineAbstract:: 7S FrameworkTuba AkbarNessuna valutazione finora
- Strat Management Chap2Documento4 pagineStrat Management Chap2kim zamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- HR NeedsDocumento6 pagineHR NeedsRABBI PAGUNSANNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQs For Preparation of FPSC TeachingDocumento94 pagineMCQs For Preparation of FPSC TeachingRose Dumayac100% (1)
- Curriculum DevelopmentDocumento71 pagineCurriculum DevelopmentRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Multiple IntelligencesDocumento4 pagineTheory of Multiple IntelligencesRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis of Philippine History Pre-Spanish TimesDocumento50 pagineSynopsis of Philippine History Pre-Spanish TimesRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Crafting The CurriculumDocumento62 pagineCrafting The CurriculumRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum MappingDocumento20 pagineCurriculum MappingRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- The Effects of Union On WagesDocumento5 pagineThe Effects of Union On WagesRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- The Industrial Revolution During Renaissance PeriodDocumento2 pagineThe Industrial Revolution During Renaissance PeriodRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 22 The Larger World OpenDocumento75 pagineChapter 22 The Larger World OpenRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Digging Deeper Into CyberspaceDocumento18 pagineDigging Deeper Into CyberspaceRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- The Benefits of Teenage Curfew LawsDocumento5 pagineThe Benefits of Teenage Curfew LawsRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Special Topic (Mother Tongue Based Education)Documento32 pagineSpecial Topic (Mother Tongue Based Education)Rose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Rubrics: Useful Assessment ToolsDocumento3 pagineRubrics: Useful Assessment ToolsRose Dumayac100% (1)
- Chapter 3: Understanding Test Quality-Concepts of Reliability and ValidityDocumento10 pagineChapter 3: Understanding Test Quality-Concepts of Reliability and ValidityRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Graphic OrganizersDocumento36 pagineGraphic OrganizersRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 Reasons Why Filipino Children Learn Better While Using Their Mother TongueDocumento34 pagine21 Reasons Why Filipino Children Learn Better While Using Their Mother TongueRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory of Multiple IntelligencesDocumento4 pagineTheory of Multiple IntelligencesRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- The Secret To Becoming More ConfidentDocumento8 pagineThe Secret To Becoming More ConfidentRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Situational Leadership TheoryDocumento2 pagineSituational Leadership TheoryRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Blooms InfoDocumento12 pagineRevised Blooms Infoapi-232411650Nessuna valutazione finora
- Society and Culture With Family PlanningDocumento7 pagineSociety and Culture With Family PlanningRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Dressing and Bandaging With ProcedureDocumento4 pagineDressing and Bandaging With ProcedureRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Imperyong Ghana Mali at SonghaiDocumento26 pagineImperyong Ghana Mali at SonghaiRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Curriculum and InstructionDocumento29 pagineManagement of Curriculum and InstructionRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Historyof Phil CostitutionDocumento7 pagineHistoryof Phil CostitutionRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 7 Managing Change For Organizational Improvement: E838 Effective Leadership and Management in EducationDocumento12 pagineSection 7 Managing Change For Organizational Improvement: E838 Effective Leadership and Management in EducationRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 7 Managing Change For Organizational Improvement: E838 Effective Leadership and Management in EducationDocumento12 pagineSection 7 Managing Change For Organizational Improvement: E838 Effective Leadership and Management in EducationRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 8 Strategic Management: E838 Effective Leadership and Management in EducationDocumento10 pagineSection 8 Strategic Management: E838 Effective Leadership and Management in EducationJeremiah Miko LepasanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adaptive Leaders Are Effective LeadersDocumento3 pagineAdaptive Leaders Are Effective LeadersRose DumayacNessuna valutazione finora
- Organization EffectivenessDocumento11 pagineOrganization EffectivenessSofi KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Fundamentals of ManagementDocumento38 pagineChapter 1 - Fundamentals of ManagementabdulfetahNessuna valutazione finora
- InvestmentDocumento3 pagineInvestmentAngelica PagaduanNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum Vitae: Dr. Bidhu Kanti DasDocumento22 pagineCurriculum Vitae: Dr. Bidhu Kanti DasTanuj DeyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Foreign Exchange MarketDocumento3 pagineThe Foreign Exchange MarketDavina AzaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Royal Enfield Project 36 Organisation StudyDocumento45 pagineRoyal Enfield Project 36 Organisation StudyVijay AravindNessuna valutazione finora
- Investor Presentation MARCH 2011: A Global Leader in Integrated Clean Air Solutions For IndustryDocumento33 pagineInvestor Presentation MARCH 2011: A Global Leader in Integrated Clean Air Solutions For IndustrymynameisvinnNessuna valutazione finora
- Hotel Resevation System - Database ProjectDocumento9 pagineHotel Resevation System - Database ProjectMero Hmd100% (1)
- IMS Brochure NewDocumento4 pagineIMS Brochure NewCoCgamer ProNessuna valutazione finora
- TDS - 1K RAL 9005 Black-ZFDocumento4 pagineTDS - 1K RAL 9005 Black-ZFBharath OXYNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Marketing Master FileDocumento30 pagineDigital Marketing Master Filejinal patadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bullying Behaviour in Corporate: What Is Workplace Bullying?Documento5 pagineBullying Behaviour in Corporate: What Is Workplace Bullying?prabhuhateNessuna valutazione finora
- Intan Larasati 2A English For Syariah Banking Islamic Banking and Finance ContextDocumento7 pagineIntan Larasati 2A English For Syariah Banking Islamic Banking and Finance ContextMauLana IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- WadsfDocumento2 pagineWadsfHuy LeNessuna valutazione finora
- Culinarian CookwareDocumento8 pagineCulinarian CookwarePratip BeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Navistar Capacity Verification: Supplier / Part InformationDocumento4 pagineNavistar Capacity Verification: Supplier / Part InformationAnurag TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistic OptimizationDocumento34 pagineLogistic OptimizationYudie Andre SiswantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Agreement of Sale Cum General Power of AttorneyDocumento7 pagineAgreement of Sale Cum General Power of AttorneyNitipal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Connecting Strategy To ExecutionDocumento13 pagineConnecting Strategy To ExecutionrpreidNessuna valutazione finora
- COA CIRCULAR NO. 2023-003 June 14 2023Documento14 pagineCOA CIRCULAR NO. 2023-003 June 14 2023Jennifer Go100% (2)
- ALARP - Demonstration STD - AUSDocumento24 pagineALARP - Demonstration STD - AUSMahfoodh Al AsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Measurement in Decentralized Organizations-1Documento84 paginePerformance Measurement in Decentralized Organizations-1Ashar IsmailNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.3 Planeacion de Requirimientos de RecursosDocumento22 pagine2.3 Planeacion de Requirimientos de RecursosYenifer PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership of Woman President in The Philippine State Universities and CollegesDocumento14 pagineLeadership of Woman President in The Philippine State Universities and CollegesAPJAET JournalNessuna valutazione finora
- Bill of Lading AustriaDocumento2 pagineBill of Lading AustriaTitik KurniyatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Deed of Assignment With AssumptionDocumento3 pagineDeed of Assignment With AssumptionJecky Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- To Update Your Contact Details, Kindly Call 1800-103-2292 (Toll Free)Documento9 pagineTo Update Your Contact Details, Kindly Call 1800-103-2292 (Toll Free)Rajesh RamaswamyNessuna valutazione finora
- International Accounting Standard With ExamplesDocumento15 pagineInternational Accounting Standard With ExamplesAmna MirzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dkeff Guarantor FormDocumento2 pagineDkeff Guarantor FormDallas SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Finance Lecturers by Course and Size UNSWDocumento2 pagineFinance Lecturers by Course and Size UNSWhello248Nessuna valutazione finora
- Infosys-A Case Study Decision SheetDocumento3 pagineInfosys-A Case Study Decision SheetRAW STARNessuna valutazione finora