Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
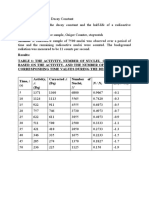
Rav 1586
Caricato da
ravinderTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Rav 1586
Caricato da
ravinderCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Index I-13
Mutual inductance, 990–993 rotational analog of, 307, 313–315 parent, 1452
Myopia, 1140–1143 statement of, 111 properties of, 1440–1441
weight and, 110, 114–116 radius of, 1441
N Newton’s third law of motion, 116–119 shell model of, 1449–1450
Nanometer, 5 action–reaction pairs and, 116–119 structure of, 1445
Nanoparticles, 944f application of, 117–118, 120 volume of, 1441
Nanosecond, 5 fluid resistance and, 147–150 Nuclides, 1442
Natural angular frequency, 455–456 momentum and, 243 decay of, 1452–1461. See also Radioactive decay
Natural light, 1092 statement of, 116 odd-odd, 1451
Natural line width, 1310 tension and, 119 radioactive, 1452–1457. See also Radioactivity
Near point, of eye, 1140 Noble gases, 1388 stable, 1450–1451
Near-field diffraction, 1187 Nodal curves, 1163 synthesis of, 1514–1515
Nearsightedness, 1140–1143 Nodal planes, 1069
Neddermeyer, Seth, 1485 Nodes, 487 O
Ne’eman, Yu’val, 1498 displacement, 518–519 object distance, 1112
Negative ions, 686 pressure, 519 object, in optics, 1111
Negative work, 175–176, 178 Noise, 510 object point, 1112
Neon, 1388 Noise control, wave interference in, 526 objective, microscope, 1145
Nerve cells, 738f, 822f, 880 Nonconservative forces, 218–220 occhialini, Guiseppe, 1265
Net force, 103–104, 243–244 Nonelectrostatic fields, 957, 971 ocean thermal energy conversion, 681
acceleration and, 108–113 Nonlinear conductors, 821 oculars, 1145
center-of-mass motion and, 256–258 Nonreflective coatings, 1175–1176 odd-odd nuclides, 1451
circular motion and, 109 Nonuniform circular motion, 85, 155 oersted, Hans Christian, 883
momentum and, 238–240 Normal force, 102, 142 ohm, 824
Newton’s first law and, 105–107, 108 Normal mode, 492 ohmic conductors, 821
Newton’s second law and, 108–112 Normalization condition, 1335, 1361 ohmmeters, 861
torque and, 306, 317, 318 North (N) pole, 882 ohm’s law, 820, 823–824
zero, 106–107, 108 n-type semiconductors, 1426 1 newton per coulomb, 696
Net torque, 316 Nuclear accidents, 1470 onnes, Heike Kamerlingh, 822
Neutral side of line, 867, 869 Nuclear angular momentum, 1443 open circuits, 868
Neutrino(s), 1453–1454, 1492 Nuclear binding, 1446–1450 open orbits, 408
mass of, 1502 Nuclear fission, 1242, 1466–1470 operational definition, 4
Neutrino detectors, 1490 chain reactions in, 1468 optic axis, of mirror, 1115
Neutrino oscillations, 1502 liquid-drop model of, 1467 optical fibers, 1088
Neutron(s) reaction dynamics in, 1466–1467 optics, 1078. See also Light
absorption of, 1465–1466 in reactors, 1468–1470 geometric. See Geometric optics
discovery of, 1482 tunneling in, 1467 image in, 1112
magnetic moment of, 1443–1444, 1498 Nuclear force, 1447–1448 object in, 1111
mass of, 685, 1441 mesons and, 1485 physical, 1080, 1160
spin angular momentum of, 1443 potential-energy function for, 1450, 1491 orbit(s)
Neutron activation analysis, 1466 Nuclear fusion, 1470–1472 center of mass and, 414
Neutron number, 1441 heat of, 560 circular, 408–410, 412
Neutron-proton pair binding, 1448 helium, 1515 closed, 408
Newton (N), 6, 105, 110 solar, 1502 of Comet Halley, 413
Newton, Isaac, 1078 tunneling in, 1342–1343 elliptical, 411–412
Newtonian mechanics, 101 Nuclear magnetic moment, 1444 open, 408
Newtonian synthesis, 414 Nuclear magnetic resonance, 1445 satellite, 407–410
Newton-meter, 173, 304 Nuclear magneton, 1444 sector velocity and, 411
Newton’s first law of motion, 101, 105–108 Nuclear medicine, 1463 semi-major axis of, 411, 412
application of, 120 Nuclear physics, 1440–1473 orbital angular momentum
equilibrium and, 106 Nuclear power plants, 1242, 1468–1470 quantization of, 1369–1370, 1380–1381
inertia and, 105, 107–108 Nuclear reactions, 1464–1472 spin angular momentum and, 1383–1385
net force and, 105–107 chain, 1468 orbital eccentricity, 411
statement of, 105 endoergic, 1464 orbital magnetic quantum number, 1370
Newton’s law of gravitation, 398–402 endothermic, 1464 orbital period, 412
Newton’s laws of motion, 101–158 exoergic, 1464 orbital quantum number, 1369
application of, 120 exothermic, 1464 orbital speed, 412
first law, 101, 105–108. See also Newton’s first law fission, 1242, 1466–1470 order-of-magnitude estimates, 10
of motion fusion, 1470–1472 organ pipes, 520–522
free-body diagrams for, 120 neutron absorption in, 1465–1466 oscillation, 433–438
inertial frame of reference and, 107–108 reaction energy for, 1464–1465 amplitude of, 434
Kepler’s laws and, 411–413, 414 thermonuclear, 1472 damped, 453–455
particle model and, 1267–1268 threshold energy for, 1464 displacement in, 434
relativity and, 1238–1240, 1244–1245 Nuclear reactors, 1242, 1468–1470 driven, 455–456
second law, 108–116. See also Newton’s second law Nuclear spin, 1443–1444 electrical, 1004–1008
of motion Nuclear stability, 1450–1452 forced, 455–456, 522
third law, 116–119. See also Newton’s third law of Nucleon number, 1441 frequency of, 434–435
motion Nucleons, 1440–1441 in harmonic oscillators. See Harmonic oscillators
uncertainty and, 1267–1268 Nucleosynthesis, 1514–1515 molecular vibration and, 447–449
Newton’s second law of motion, 108–116 Nucleus, 1440–1473 neutrino, 1502
acceleration and, 108–112 atomic, 685, 1288 overview of, 433–435
application of, 111–112, 120 daughter, 1452 of pendulum, 450–453
component equations for, 111–112 density of, 1441 of periodic waves, 470–472
entropy and, 670, 673 in excited states, 1455 resonance and, 456–457, 522–524
fluid resistance and, 148–150 formation of, 1514–1515 simple harmonic motion and, 435–450. See also
inertial reference frames and, 112 in ground state, 1455 Simple harmonic motion
mass and, 110, 112, 114–116 half-life of, 1458 in spring, 433–434
momentum and, 238 lifetime of, 1458 oscillation cycle, 434
net force and, 108–112 liquid-drop model of, 1448–1449 oscillation period, 434
relativity and, 1238–1240, 1244–1245 mass of, 1441 otto cycle, 652–653
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Rav 10Documento1 paginaRav 10ravinderNessuna valutazione finora
- Rav 9Documento1 paginaRav 9ravinderNessuna valutazione finora
- Rav 7Documento1 paginaRav 7ravinderNessuna valutazione finora
- Rav 8Documento1 paginaRav 8ravinderNessuna valutazione finora
- Rav 6Documento1 paginaRav 6ravinderNessuna valutazione finora
- Rav 5Documento1 paginaRav 5ravinderNessuna valutazione finora
- Rav 4Documento1 paginaRav 4ravinderNessuna valutazione finora
- Rav 1587Documento1 paginaRav 1587ravinderNessuna valutazione finora
- Rav 1Documento1 paginaRav 1ravinderNessuna valutazione finora
- Rav 1593Documento1 paginaRav 1593ravinderNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure Mark Scheme: Science Exams SortedDocumento8 pagineAtomic Structure Mark Scheme: Science Exams SortedSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNessuna valutazione finora
- Chernobyl Thesis StatementDocumento4 pagineChernobyl Thesis Statementroxyrobertssavannah100% (2)
- OPAL ReactorDocumento21 pagineOPAL ReactorbenshtanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Lab - Half Life and The Decay ConstantDocumento7 paginePhysics Lab - Half Life and The Decay ConstantGiovanni SlackNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7 Lesson 1 DennyDocumento6 pagineCH 7 Lesson 1 Dennyapi-254594631Nessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Study GuideDocumento8 pagineMidterm Study GuideAustin TroutNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Science Third Quarter ExamDocumento4 paginePhysical Science Third Quarter ExamMelanie Miranda100% (3)
- Physics CLIL: Nuclear Physics - Prof - Samuele PetinoDocumento11 paginePhysics CLIL: Nuclear Physics - Prof - Samuele Petinoperry7grineNessuna valutazione finora
- Status of Innovative Small and Medium Sized Reactor Designs 2005Documento712 pagineStatus of Innovative Small and Medium Sized Reactor Designs 2005Myo ThihaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario Capitulo 23 Paul e TippensDocumento22 pagineSolucionario Capitulo 23 Paul e TippensAxel Gutiérrez VillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Symbol (Chemistry) : Symbol Is A Code For A ChemicalDocumento47 pagineSymbol (Chemistry) : Symbol Is A Code For A ChemicalCATHERINE D. ANDALNessuna valutazione finora
- Pms Optional PapersDocumento148 paginePms Optional PapersZaheer Ahmed MughalNessuna valutazione finora
- Inti Atom Dan Iptek NuklirDocumento26 pagineInti Atom Dan Iptek NuklirAnggy N100% (1)
- Biological Effects of RadiationDocumento6 pagineBiological Effects of RadiationZain Ul AbidinNessuna valutazione finora
- En 19Documento6 pagineEn 19AntonellaNessuna valutazione finora
- All PhysicalDocumento326 pagineAll PhysicalsfkwongNessuna valutazione finora
- M.Sc. (Part-II) (Chemistry) (For Colleges) - 18.082020Documento120 pagineM.Sc. (Part-II) (Chemistry) (For Colleges) - 18.082020KuNdAn DeOrENessuna valutazione finora
- SLG 5.2.2 Atomic StructureDocumento5 pagineSLG 5.2.2 Atomic StructurePaul CustodioNessuna valutazione finora
- Probalistic Risk Assessment API1000Documento19 pagineProbalistic Risk Assessment API1000micaziv4786Nessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Hots Physics XII 2009Documento57 pagineCBSE Hots Physics XII 2009jagannivas100% (1)
- Apex Learning - Practice AssignmentDocumento12 pagineApex Learning - Practice AssignmentYOLIAZ يوليازNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear PhysicsDocumento26 pagineNuclear PhysicsraviNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of The Atom NotesDocumento3 pagineStructure of The Atom NotesMayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice WorksheetDocumento3 pagineProtons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice WorksheetMelerose Dela SernaNessuna valutazione finora
- Isotope Dilution AnalysisDocumento5 pagineIsotope Dilution AnalysisUsman GhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure WKSHTDocumento9 pagineAtomic Structure WKSHTDennis Limosnero MayorNessuna valutazione finora
- Gamma-Ray Anisotropy ThermometersDocumento4 pagineGamma-Ray Anisotropy ThermometersSameh AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- JEE Main 2023-24 Atoms and Nuclei Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocumento18 pagineJEE Main 2023-24 Atoms and Nuclei Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadPAARTH DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Chemistry Practice TestDocumento5 pagineNuclear Chemistry Practice TestSwiss PabloNessuna valutazione finora
- History of The Evolution of Light Water Reactor Safety in The USDocumento1.116 pagineHistory of The Evolution of Light Water Reactor Safety in The USFairewinds Energy EducationNessuna valutazione finora