Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Biology 2 Plant Morphology and Biotechnology Plant Systems
Caricato da
larraTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Biology 2 Plant Morphology and Biotechnology Plant Systems
Caricato da
larraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
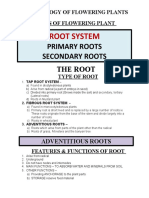
BIOLOGY 2
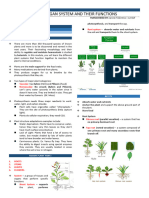
2. SHOOT SYSTEM
PLANT MORPHOLOGY AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
Leaves
PLANT SYSTEMS o Organ for photosynthesis
o Reproduction (i.e. spores of
Shoot System – leaves, stem, flowers ferns)
(accessory) o Stomata – structure of leaves
Root System – roots; vegetative organs below that allow exchange of gases,
the ground opening and closing are
Vascular System – xylem and phloem controlled by structures called
as guard cells
1. ROOT SYSTEM – absorption of nutrients,
anchorage to the ground, reproduction
Stem
o Main axis of plant that
elongates and produces leaves
o Has vascular system inside
Root hairs – increase surface area for
absorption of nutrients
Area of Cell Differentiation – cells differentiate
into different plant cells and tissues
Area of Cell Elongation – allows the root to go
deeper in the soil
Area of Cell Division – undifferentiated cells are
located and rapid cell division occurs
Root Cap – prevents the root from rock and
mechanical injury
Lenticel – provides medium for the direct
exchange of gases vetween the internal tissues
and atmosphere
Terminal bud – main area of growth in most
plants
MS. LARISA MAE C. AGTAY, LPT (GENERAL BIOLOGY 2)
Lateral bud – capable of growing into a branch PROCESS OF FERTILIZATION AMONG FLOWERING
shoot or flower cluster PLANTS
Leaf scar – mark left on a stem after a leaf falls
1. Pollen and Egg Formation
off
a. Anther – pollen – pollen grain tube –
Node – areas here side branches and leaves
sperm
develop
b. Ovary – ovules
Internode – area between nodes
2. Pollination
a. Transfer of pollen grains from stamen
to the stigma
i. Self pollination – same plant
ii. Cross pollination – other plant
of the same species
3. Fertilization
a. Pollen lands on stigma – pollen tube –
style – ovary
b. Zygote – fruit
4. Seed Dispersal
Aside from classifying plants (through the a. Different fruits deploy various strategies
number of cotyledons) as monocot and dicot, to disperse their population
one can determine it by observing its physical 5. Seed Germination
structures of the root and shoot system. a. Seed breaks through the seed coat and
grows new plant from seeds
b. A seed may germinate if it has enough
ACCESORY PART water, oxygen and warmth
PLANT TRANSPORT SYSTEM (Vascular System)
Xylem
o Transport of water through adhesion
and capillary action (from roots going
up)
PISTIL/CARPEL
Stigma – top of the pistil, sticky surface for
pollen to stick to
Style – conncects the stigma to the ovary
Ovary – contains ovules (eggs) Vessel Elements – hollow tube
Tracheids – narrower tube with end walls
Parenchyma cells – store absorbed substances
STAMEN
Phloem – carry products of photosynthesis in a
Anther – produces sperm nuclei by meiosis and bidirectional movement
sperm nuclei are enclosed in pollen grains
Filament – holds the anther up
ACCESORY PARTS OF A FLOWER
Sepals – green leaf protecting the bud, calyx
Petal – makes flowers attractive; corolla
Receptacle
MS. LARISA MAE C. AGTAY, LPT (GENERAL BIOLOGY 2)
Sieve tube – no nucleus but with few organelles - Fired to targets that include embryonic cells,
Sieve plate – makes cytoplasmic connections intact leaves and soft seed kernels
between cells 4. Chloroplast Engineering
- DNA of chloroplast can accept several new
genes at once
TROPISMS OF PLANTS
Plant growth toward (positive) or away
(negative) from a unidirectional stimulus - Genes inserted into the chloroplast will remain
Phototropism – light active when the plant matures
Gravitropism – gravitational pull
5. Anti sense technology
Thigmotropism – touch
- A gene that encodes for a specific trait is
PLANT HORMONES
removed from plant cells used to produce a
1. Ethylene - ripening of fruits complementary copy of itself and transferred
2. Gibberellins – elongation of stem back to the original cells using Agrobacter as a
3. Auxin – cell elongation in shaded area of shoot
tip that results in bending of shoots towards
light
4. Abcissic acid – inhibits growth and causes
wilting of leaves
PLANT BIOTECHNOLOGY
Plant Transgenesis
- Direct transfer of genes that permits
innovations but is impossible to be achieved
with the conventional methods
- E.g. Polyploidy – multiple chromosome sets
greater than normal have been used for many
years as means to increase desirable traits, esp
size of many crops including watermelon, sweet
potatoes, bananas, strawberries and wheat
1. Protoplast Fusion vector organism
- Protoplast of plant A is fused with plant B to PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS
produce a hybrid plant
- Obtained specimen is put into a dish containing 1. Genetic Pesticides
cellulose, sugar and salts to break down its cell a. BT Corn (Bacillus thuringienensis)
wall 2. Herbicide Resistance
- Protoplast is obtained through centrifugation 3. Enhanced Nutrition
and then injected into the protoplast of another
2. Leaf Fragment Technique
- Small discs are
cut from the
leaf
- Cultured briefly
in a medium
containing
genetically
modified
Agrobacter
3. Gene guns
- The bullets of
gene guns are
tungsten beads (1 micrometer in diameter)
- DNA is coated on the surfaces of the beads and
fired from guns with the velocities of 430 m/s
MS. LARISA MAE C. AGTAY, LPT (GENERAL BIOLOGY 2)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Plant and Animal BiologyDocumento4 paginePlant and Animal BiologyGina Liza CanamaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Botlec ReviewerDocumento7 pagine1 Botlec ReviewerKamille PobleteNessuna valutazione finora
- Botany Module 2.1Documento11 pagineBotany Module 2.1Yaz VergaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure: Plant Form and FunctionDocumento12 pagineStructure: Plant Form and FunctionPhilippines QatarNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant VS Animal ReprductionDocumento9 paginePlant VS Animal ReprductionHanna Hazel Donaire IlaidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7Documento4 pagineLecture 7김j.kNessuna valutazione finora
- NMAT Review 2018 Module - BiologyDocumento34 pagineNMAT Review 2018 Module - BiologyRaf Lin DrawsNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Sheet 1 in General Biology - 02Documento4 pagineActivity Sheet 1 in General Biology - 02Julianne Maxine FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Morphology and Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocumento3 pagineMorphology and Anatomy of Flowering PlantsAyako HayashidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Core CH 19 BiodiversityDocumento8 pagineCore CH 19 Biodiversitystudy.stkgNessuna valutazione finora
- ELS - Plant ReproductionDocumento1 paginaELS - Plant ReproductionRaymond BunsoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Plants Morphology & PhysiologyDocumento5 paginePlants Morphology & PhysiologyDonna Mae AbonalNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Sheet 1 GenBio2Documento4 pagineActivity Sheet 1 GenBio2Sean MatuguinasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDocumento8 pagineChapter 2: Biology of Agricultural CropsDwight Luciano T MendezNessuna valutazione finora
- Dizon - Module 5Documento9 pagineDizon - Module 5Penelopy DizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 - Gen Bot LecDocumento3 pagineLesson 1 - Gen Bot LecYoko DeangNessuna valutazione finora
- Share The Following CharacteristicsDocumento6 pagineShare The Following CharacteristicsJeshrael CabrigasNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Diversity A) How The Plant Kingdom EvolvedDocumento15 paginePlant Diversity A) How The Plant Kingdom EvolvedAkhmad AkhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocumento13 pagineMorphology of Flowering PlantsTanishq AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Notes Module 5 DetailedDocumento30 pagineBiology Notes Module 5 DetailedMohannad OdahNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 11.1 LE 2 NotesDocumento7 pagineBio 11.1 LE 2 NotesCode BlueNessuna valutazione finora
- Dokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyDocumento11 pagineDokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyAin SufizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Bio 2 - Chapter 1Documento79 pagineGen Bio 2 - Chapter 1Samantha AcostaNessuna valutazione finora
- VegetationDocumento14 pagineVegetationChris P. BeaconNessuna valutazione finora
- Vascular and Nonvascular PDFDocumento55 pagineVascular and Nonvascular PDFMiedy Corazon TabangNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Lesson 6 To 9 Botany LecDocumento23 pagineNotes Lesson 6 To 9 Botany LecMohamidin MamalapatNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts and Functiond of PlantsDocumento5 pagineParts and Functiond of PlantsCjoy MañiboNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories of The Origin of Solar SystemDocumento18 pagineTheories of The Origin of Solar SystemGWYNETH REIN CARI�ONessuna valutazione finora
- B8.2 Revision Notes 1q0d1tjDocumento4 pagineB8.2 Revision Notes 1q0d1tjStudy AccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Land Ho: Plants and Arthropods!Documento58 pagineLand Ho: Plants and Arthropods!BarbNessuna valutazione finora
- Ustet ReviewerDocumento16 pagineUstet ReviewerVinzynt Isler Carmona100% (19)
- Chapter-2.Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocumento49 pagineChapter-2.Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsravillamuni007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Form and FunctionsDocumento2 paginePlant Form and FunctionsJason TaburnalNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Form, Eco, Aqua, BiologicalDocumento17 paginePlant Form, Eco, Aqua, BiologicalPolee SheaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 6 (A) BiologyDocumento5 pagineWeek 6 (A) BiologyBeyonce SkekelNessuna valutazione finora
- A Plant's Organ Systems and Their FunctionsDocumento1 paginaA Plant's Organ Systems and Their FunctionsMariel KhoNessuna valutazione finora
- GS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsDocumento9 pagineGS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsChary Johanne MenesesNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 - Plant TissuesDocumento23 pagine02 - Plant Tissuestri hastutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Structure, Form and Function: Fall 2014Documento22 paginePlant Structure, Form and Function: Fall 2014SA JWNessuna valutazione finora
- CASNS 1a Module 4.2Documento13 pagineCASNS 1a Module 4.2Maxi VellasNessuna valutazione finora
- BotaDocumento15 pagineBotaMichelle Angelie DinoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Tissues and Organs Plant Tissues: Tracheary Elements Tracheids TracheidsDocumento2 paginePlant Tissues and Organs Plant Tissues: Tracheary Elements Tracheids TracheidsNathaniel John AlcoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Morphology of Flowering Plants 1Documento45 pagineMorphology of Flowering Plants 1suresh yadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology EndOfSpringDocumento12 pagineBiology EndOfSpringBryanNessuna valutazione finora
- PK Notes Ncert Detail ExplnDocumento33 paginePK Notes Ncert Detail Explnarjun shindeNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology II Midterms PDFDocumento16 pagineGeneral Biology II Midterms PDFantonio louise anjella monNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants: Ii Pu Biology Target 70 - Question Bank - 3 MarksDocumento18 pagineReproduction in Flowering Plants: Ii Pu Biology Target 70 - Question Bank - 3 MarksSRS status kingNessuna valutazione finora
- Stomata and Others (Bakita Bujhe Nis)Documento8 pagineStomata and Others (Bakita Bujhe Nis)PukuNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Structure and GrowthDocumento3 paginePlant Structure and GrowthCielo PulmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Term Science 5 Modules 5-8Documento18 pagineSecond Term Science 5 Modules 5-8Kathleen FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Roots Written ReportDocumento3 paginePlant Roots Written ReportAshlee JornadalNessuna valutazione finora
- TISSUES (Prashant Kirad)Documento9 pagineTISSUES (Prashant Kirad)abhijotsinghas83Nessuna valutazione finora
- Main Functions of Roots:: and Produces Branch Roots Called Lateral RootsDocumento4 pagineMain Functions of Roots:: and Produces Branch Roots Called Lateral RootsAleczandra QuesadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 (Part 1) - Plant Anatomy & Physiology PDFDocumento89 pagineChapter 1 (Part 1) - Plant Anatomy & Physiology PDFMohammed Ridzuwan94% (16)
- Chapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Documento180 pagineChapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)FITRINESSA IBOLNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 05Documento21 pagineCH 05ispasNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Permanent Tissues Three Major Types of Root SystemDocumento4 pagineSimple Permanent Tissues Three Major Types of Root SystemAleczandra QuesadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio2 Module 1Documento4 pagineBio2 Module 1jaylordyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport in Plants and Animals.Documento135 pagineTransport in Plants and Animals.Kiprono Mathew100% (11)
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersDa EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNessuna valutazione finora
- Report in Evolec 1st PartDocumento3 pagineReport in Evolec 1st PartlarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 - Bending - Shear & Moment in Beams - Lecture - Markup - Part1Documento39 pagineChapter 6 - Bending - Shear & Moment in Beams - Lecture - Markup - Part1larraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Artists Journey (Steven Pressfield (Pressfield, Steven) )Documento167 pagineThe Artists Journey (Steven Pressfield (Pressfield, Steven) )larra100% (1)
- Lesson 3 - Respiratory SystemDocumento6 pagineLesson 3 - Respiratory SystemlarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 302L - Activity 1Documento5 pagineBio 302L - Activity 1larraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 - Stresses in Beams - Part 2 - Mark Ups LectureDocumento35 pagineChapter 7 - Stresses in Beams - Part 2 - Mark Ups LecturelarraNessuna valutazione finora
- 4-Molecular Basis of HeredityDocumento4 pagine4-Molecular Basis of HereditylarraNessuna valutazione finora
- BatStateU-FO-REG-12 - Application Form For Shifter, Transferee - Rev. 03Documento3 pagineBatStateU-FO-REG-12 - Application Form For Shifter, Transferee - Rev. 03larraNessuna valutazione finora
- Econ c3Documento51 pagineEcon c3larra100% (1)
- Situation of The Philippines On The Area of EnergyDocumento10 pagineSituation of The Philippines On The Area of EnergylarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 - Stresses in Beams - Part 1 - Mark Ups LectureDocumento58 pagineChapter 7 - Stresses in Beams - Part 1 - Mark Ups LecturelarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Jamaela Pagcaliwagan - Performance Task Module 13-14Documento2 pagineJamaela Pagcaliwagan - Performance Task Module 13-14larraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ese Module 1Documento100 pagineEse Module 1larraNessuna valutazione finora
- Road Classifications & Considerations For Highway PlanningDocumento17 pagineRoad Classifications & Considerations For Highway PlanningJanina Matanguihan100% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines Batangas State University: Ñoso JRDocumento6 pagineRepublic of The Philippines Batangas State University: Ñoso JRlarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Inclined Stadia SightsDocumento4 pagineInclined Stadia SightsSchChrScaLavNessuna valutazione finora
- CE 2201 - Pagcaliwagan, Larra Marie J.Documento15 pagineCE 2201 - Pagcaliwagan, Larra Marie J.larraNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - CEE 401 (Topic 1)Documento13 pagineModule 1 - CEE 401 (Topic 1)larraNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Questions pc2Documento7 pagineReview Questions pc2larraNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Surveying: Civil and Sanitary Engineering DepartmentDocumento9 pagineFundamentals of Surveying: Civil and Sanitary Engineering DepartmentlarraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Competency of Batangas State University Junior High School Students in Utilization of English Language in Comprehensive Reading and WritingDocumento3 pagineThe Competency of Batangas State University Junior High School Students in Utilization of English Language in Comprehensive Reading and WritinglarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Research DesignDocumento5 pagineResearch DesignlarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Research DesignDocumento5 pagineResearch DesignlarraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocumento12 pagineThe Problem and Its BackgroundlarraNessuna valutazione finora
- (Pornwasin, A (2014) - On-Demand Cab Service at Your Fingertips. Retrieved December 9, 2014 FromDocumento2 pagine(Pornwasin, A (2014) - On-Demand Cab Service at Your Fingertips. Retrieved December 9, 2014 FromlarraNessuna valutazione finora
- RRL Foreign Mahasaraswati UniversityJ DenpasarJ Bali J IndonesiaDocumento2 pagineRRL Foreign Mahasaraswati UniversityJ DenpasarJ Bali J IndonesialarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3Documento8 pagineChapter 3larra100% (2)
- Chap 3Documento3 pagineChap 3larra0% (1)
- Thermodynamics Problem Set With SolutionsDocumento66 pagineThermodynamics Problem Set With Solutionslarra100% (2)
- Stadia Survey Lab ReportDocumento7 pagineStadia Survey Lab ReportlarraNessuna valutazione finora
- 11th STD Botany One MarksDocumento24 pagine11th STD Botany One Marksjac100% (2)
- HOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE ExerciseDocumento10 pagineHOW DO ORGANISMS REPRODUCE ExerciseShreyansh DugarNessuna valutazione finora
- Oladokun Et Al-2019-Plant PathologyDocumento8 pagineOladokun Et Al-2019-Plant PathologyJim EspinosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Akasia HibridDocumento24 pagineAkasia HibridAida HusnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Garden Farming ManualDocumento16 pagineGarden Farming ManualMónica EspitiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trees of Our Life BookDocumento200 pagineTrees of Our Life BookSANTHAN PONNUTHEERTHAGIRINessuna valutazione finora
- Al-Yamamah Palace - Riyadh: Daily Landscape & Irrigation Activity ReportDocumento1 paginaAl-Yamamah Palace - Riyadh: Daily Landscape & Irrigation Activity Reportjags_raibag007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Broccoli Juan Nastor SR., Rafael Cachin and Vivian V. ReyesDocumento18 pagineBroccoli Juan Nastor SR., Rafael Cachin and Vivian V. ReyespandaypiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Bussiness PlanDocumento37 pagineBussiness PlanBopzilla Reddy0% (1)
- ARACEAE History5Documento206 pagineARACEAE History5Manu MandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Herbicides ClassificationDocumento6 pagineHerbicides ClassificationSahely KanthalNessuna valutazione finora
- EPPO StandardsDocumento11 pagineEPPO StandardsIrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Uptake and Movement of Water in Plants: Exercise 13Documento24 pagineUptake and Movement of Water in Plants: Exercise 13pikachuzingungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign LiteratureDocumento5 pagineForeign LiteratureDeckster DeveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Response of Intercropping and Different Row Ratios On Growth and Yield of Wheat (Triticum Aestivum) Under Rainfed Condition of Kaymore PlateauDocumento5 pagineResponse of Intercropping and Different Row Ratios On Growth and Yield of Wheat (Triticum Aestivum) Under Rainfed Condition of Kaymore PlateautheijesNessuna valutazione finora
- @ Infosys Bangalore: Mirah Hospitality & Food Solutions PVT - LTDDocumento5 pagine@ Infosys Bangalore: Mirah Hospitality & Food Solutions PVT - LTDVijay PerumalsamyNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Make A Dwarf Mango TreeDocumento5 pagineHow To Make A Dwarf Mango TreegildesenganioNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant Hormones - AnswersDocumento2 paginePlant Hormones - AnswersRoya ParsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Forests: Our Life Line: Biology ActivityDocumento10 pagineForests: Our Life Line: Biology Activityad9iNessuna valutazione finora
- The Stem and LeavesDocumento2 pagineThe Stem and LeavesMaria Vanessa SagarioNessuna valutazione finora
- The Potential of South African Indigenous Plants For Flower TradeDocumento13 pagineThe Potential of South African Indigenous Plants For Flower TradeKNessuna valutazione finora
- US Department of Agriculture - Seeds ImportedDocumento1.053 pagineUS Department of Agriculture - Seeds ImportedTaylorMooreNessuna valutazione finora
- Plants Unit Goals and ObjectivesDocumento2 paginePlants Unit Goals and Objectivesapi-545952718Nessuna valutazione finora
- Passiflora Longifilamentosa A K Koch A CDocumento6 paginePassiflora Longifilamentosa A K Koch A ClucianobotanicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacterial Wilt Management in Tomato - South Asia PDFDocumento18 pagineBacterial Wilt Management in Tomato - South Asia PDFYanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Botha 1988Documento4 pagineBotha 1988Sonia BalintNessuna valutazione finora
- Agro Techniques of Selected Medicinal Plants Vol-II PDFDocumento138 pagineAgro Techniques of Selected Medicinal Plants Vol-II PDFNiwut LaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Epsom SaltsDocumento5 pagineEpsom SaltsthendralNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 ChapterDocumento28 pagine1 ChapterMarilyn BuscatoNessuna valutazione finora