Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
1.12.2.1 Adding A Parallel Pipe Example: Dr. Burhan S. Abdulrazzaq
Caricato da
aramDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1.12.2.1 Adding A Parallel Pipe Example: Dr. Burhan S. Abdulrazzaq
Caricato da
aramCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Dr. Burhan S.
Abdulrazzaq
1.12.2 Other Pipe Flow Examples
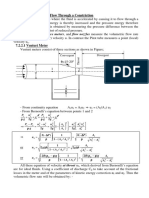
1.12.2.1 Adding a parallel pipe example
A pipe joins two reservoirs whose head difference is 10m. The pipe is 0.2 m diameter, 1000m in length
and has a f value of 0.008.
a) What is the flow in the pipeline?
b) It is required to increase the flow to the downstream reservoir by 30%. This is to be done
adding a second pipe of the same diameter that connects at some point along the old pipe and runs
down to the lower reservoir. Assuming the diameter and the friction factor are the same as the old
pipe, how long should the new pipe be?
10m
Original pipe
New pipe
100
0m
a)
fLQ 2
hf =
3d 5
0.008 × 1000Q 2
10 =
3 × 0.25
Q = 0.0346 m 3 / s
Q = 34.6 litres / s
b)
H = 10 = h f 1 + h f 2 = h f 1 + h f 3
∴
hf 2 = hf 3
2 2
f 2 L2Q2 f LQ
5
= 3 3 53
3d 2 3d 3
as the pipes 2 and 3 are the same f, same length and the same diameter then Q2 = Q3.
By continuity Q1 = Q2 + Q3 = 2Q2 = 2Q3
So
Q1
Q2 =
2
and
L2 = 1000 -L1
Then
Dr. Burhan S. Abdulrazzaq
10 = h f 1 + h f 2
f1 L1Q12 f 2 L2Q22
10 = +
2d12 2d 22
f1 L1Q12 f 2 (1000 − L1 )(Q1 / 2)
2
10 = +
2d12 2d 22
As f1 = f2, d1 = d2
10 =
f1Q12 ⎛
L +
(1000 − L1 ) ⎞
2 ⎜ 1 ⎟
3d1 ⎝ 4 ⎠
The new Q1 is to be 30% greater than before so Q1 = 1.3 × 0.034 = 0.442 m3/s
Solve for L to give
L1 = 455.6m
L2 = 1000 – 455.6 = 544.4 m
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Problems On Pipe Flow-Lectures 31-32Documento7 pagineProblems On Pipe Flow-Lectures 31-32ujjancricketNessuna valutazione finora
- Summer2014 203 Quiz 7 PDFDocumento2 pagineSummer2014 203 Quiz 7 PDFSeljen AceNessuna valutazione finora
- Final 2015Documento13 pagineFinal 2015Julia CNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec4b-Multiple Pipe SystemsDocumento18 pagineLec4b-Multiple Pipe SystemsJesselyn EstopitoNessuna valutazione finora
- UTS 2010/2011 reaction rates and thermodynamicsDocumento2 pagineUTS 2010/2011 reaction rates and thermodynamicsRIMA AMIRA DARMAWANTI -Nessuna valutazione finora
- BREB Recruitment Question ME (8th June 2018) 'S Solution As On 26.06.2018Documento6 pagineBREB Recruitment Question ME (8th June 2018) 'S Solution As On 26.06.2018Shahriar AlamNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulics - Quiz 3 Sol. - 12 Sept. 2022Documento7 pagineHydraulics - Quiz 3 Sol. - 12 Sept. 2022Crestine Lily DongosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Four Reservoir ProblemsDocumento36 pagineFour Reservoir ProblemsMhorien Macatangay0% (1)
- Some Past Paper Answers CIVL2103Documento7 pagineSome Past Paper Answers CIVL2103Chan Yui HinNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluids - IIIDocumento9 pagineFluids - IIIPOONAM RANINessuna valutazione finora
- ASS 2 and 3 SolutionsDocumento23 pagineASS 2 and 3 SolutionsShaun Dash Nemakhavhani100% (1)
- Ans Problem Set - Complex PipingDocumento5 pagineAns Problem Set - Complex PipingChua Jenzer100% (1)
- Study Problems 1Documento10 pagineStudy Problems 1Alejandro Arismendy SalasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 BDocumento50 pagineChapter 4 BZahidahNessuna valutazione finora
- Contoh Soal Radiasi Dan KonveksiDocumento5 pagineContoh Soal Radiasi Dan Konveksi038 - ahmad sidikNessuna valutazione finora
- MA3006 Tutorial 9 Solution Guideline April 2020Documento4 pagineMA3006 Tutorial 9 Solution Guideline April 2020clarence limNessuna valutazione finora
- Pump problem set solutions and calculationsDocumento10 paginePump problem set solutions and calculationsJames Nevin GoNessuna valutazione finora
- LecturesNotes (MEE122) 89Documento1 paginaLecturesNotes (MEE122) 89mhd slmnNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample ProblemsDocumento9 pagineSample ProblemsPaul Justin MangatNessuna valutazione finora
- JEE Main 2019 Mock Test SolutionsDocumento10 pagineJEE Main 2019 Mock Test SolutionsHemendra PrasannaNessuna valutazione finora
- CE141 2 M3 Exam Part 2Documento3 pagineCE141 2 M3 Exam Part 2Sittie Ainna A. UnteNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 7 Exercises Problem No. 1Documento3 pagineModule 7 Exercises Problem No. 1Ariel Gamboa100% (1)
- Module 7 Exercises Problem No. 1Documento3 pagineModule 7 Exercises Problem No. 1Ariel GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 7 Exercises Problem No. 1Documento3 pagineModule 7 Exercises Problem No. 1Ariel GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- HW3 - Solutions (Sec 21)Documento3 pagineHW3 - Solutions (Sec 21)Joichiro NishiNessuna valutazione finora
- Point: Electric Current in Conductors Chapter - 32Documento20 paginePoint: Electric Current in Conductors Chapter - 32Jaynandan KushwahaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 Fluids Solutions PDFDocumento5 pagine2013 Fluids Solutions PDFBakheit Layli100% (1)
- Design of Reactive Muffler For Study On The Noise Level and Performance of A Two Cylinder Four Stroke 16 H.P Diesel EngineDocumento12 pagineDesign of Reactive Muffler For Study On The Noise Level and Performance of A Two Cylinder Four Stroke 16 H.P Diesel EngineSuseel Jai Krishnan100% (1)
- Heat load and log mean temperature difference calculationDocumento3 pagineHeat load and log mean temperature difference calculationElzubair EljaaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Aits 2122 FT Vii Jeea Paper 2 Sol PDFDocumento12 pagineAits 2122 FT Vii Jeea Paper 2 Sol PDFSantanu SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cengel Fluid Mechanics 6 Edition PDFDocumento7 pagineCengel Fluid Mechanics 6 Edition PDFVenkat MacharlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Success Magnet-Solutions (Part-IDocumento2 pagineHeat Success Magnet-Solutions (Part-IRAGINI AGARWALNessuna valutazione finora
- Lgtrung - MO - HW#1+2+3Documento3 pagineLgtrung - MO - HW#1+2+3Trung SnowboyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - TutorialDocumento5 pagineChapter 4 - TutorialDavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3, Solution 97CDocumento6 pagineChapter 3, Solution 97CkarenNessuna valutazione finora
- CHE 511A Compilation 2 3 M F PDFDocumento164 pagineCHE 511A Compilation 2 3 M F PDFMaame Efua NeizerNessuna valutazione finora
- Minggu 07 Contoh Soal: Mohammad Farid S.T., M.T., PH.DDocumento18 pagineMinggu 07 Contoh Soal: Mohammad Farid S.T., M.T., PH.DJessica PrimaulyNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Exchanger design parametersDocumento5 pagineHeat Exchanger design parametersUmme Laila JatoiNessuna valutazione finora
- ProblemsDocumento83 pagineProblemsShiva SanthojuNessuna valutazione finora
- BESA Hydraulics Geotechnical Preboard Solutions 18 Feb. 2022Documento35 pagineBESA Hydraulics Geotechnical Preboard Solutions 18 Feb. 2022Chaythina Corteza100% (1)
- A Long, Circular Aluminium Rod Attached at One End ToDocumento6 pagineA Long, Circular Aluminium Rod Attached at One End TocaptainhassNessuna valutazione finora
- Fme 431 Revision Questions Jan23Documento5 pagineFme 431 Revision Questions Jan23Ti SavageNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter02 03 SJDocumento5 pagineChapter02 03 SJkaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Palli MercadoDocumento22 paginePalli MercadoAudberto Millones ChafloqueNessuna valutazione finora
- GATE 2023 ME Answer Key & Solutions Memory Based QuestionsDocumento45 pagineGATE 2023 ME Answer Key & Solutions Memory Based QuestionsascvbtfcNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 16B Quiz 6 SolutionsDocumento2 pagineMath 16B Quiz 6 SolutionsKaren Keith TengcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipeflow ExampleDocumento19 paginePipeflow ExampleRick WongNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 ME331 Fluid MechanicsDocumento10 pagineModule 5 ME331 Fluid MechanicsGr MacopiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 7Documento19 pagineTutorial 7clarence limNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem 13.147: Given: Find: SolutionDocumento2 pagineProblem 13.147: Given: Find: SolutionLucas Baldo CardosoNessuna valutazione finora
- CED Lab Tuto5 DecantDocumento3 pagineCED Lab Tuto5 Decantyaseen sheikhNessuna valutazione finora
- AY2010 CE2134 Hydraulics E04 First Law of Thermodynamics Frictional Losses in Pipe FlowsDocumento18 pagineAY2010 CE2134 Hydraulics E04 First Law of Thermodynamics Frictional Losses in Pipe FlowsEmily ShumNessuna valutazione finora
- Exer 3Documento3 pagineExer 3V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pumps Sheet-1-SolutionDocumento12 paginePumps Sheet-1-Solutionamrahmes123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ejemplo 2Documento2 pagineEjemplo 2Romano MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsDa EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ion Beams for Materials AnalysisDa EverandIon Beams for Materials AnalysisR. Curtis BirdNessuna valutazione finora
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterDa EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion Questions - 2Documento2 pagineCorrosion Questions - 2aramNessuna valutazione finora
- Viscosity and Wettability of Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) Solutions and Artificial SalivaDocumento9 pagineViscosity and Wettability of Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) Solutions and Artificial SalivaaramNessuna valutazione finora
- D Q K D Q G K Ga Q K G U K H: 1.11.2 An Alternative MethodDocumento2 pagineD Q K D Q G K Ga Q K G U K H: 1.11.2 An Alternative MethodaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Venturi Meters, Orifice Meters, and Flow Nozzles Measure The Volumetric Flow RateDocumento2 pagineVenturi Meters, Orifice Meters, and Flow Nozzles Measure The Volumetric Flow RatearamNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.2.4 The Notch or Weir: H H B H DH HDocumento2 pagine7.2.4 The Notch or Weir: H H B H DH HaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Burhan S. AbdulrazzaqDocumento3 pagineDr. Burhan S. AbdulrazzaqaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Analysis With The Finite Element Method. Linear StaticsDocumento1 paginaStructural Analysis With The Finite Element Method. Linear StaticsluchogilmourNessuna valutazione finora
- Friction in OrthodonticsDocumento9 pagineFriction in Orthodonticsaa bbNessuna valutazione finora
- EC6302 - Digital ElectronicsDocumento6 pagineEC6302 - Digital ElectronicsAdal ArasuNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminal Blocks: KasugaDocumento6 pagineTerminal Blocks: KasugaKs MuraliNessuna valutazione finora
- Reconfigurable Vivaldi Antenna With Improved Gain For Uwb ApplicationsDocumento5 pagineReconfigurable Vivaldi Antenna With Improved Gain For Uwb ApplicationsSubhanjali MyneniNessuna valutazione finora
- Jsa-Wif-9 Pulling CableDocumento12 pagineJsa-Wif-9 Pulling CableY a n i. A h m e dNessuna valutazione finora
- Hex Head AVD 780 Installation Manual WEB PDFDocumento77 pagineHex Head AVD 780 Installation Manual WEB PDFdasdsaNessuna valutazione finora
- CD 74 HCT 164 MDocumento16 pagineCD 74 HCT 164 MfabriziocasNessuna valutazione finora
- Et200s Im151 1 Standard Manual en-US en-USDocumento66 pagineEt200s Im151 1 Standard Manual en-US en-USJesús Zacarías ZapataNessuna valutazione finora
- STG SiemensDocumento2 pagineSTG SiemensjoncperezNessuna valutazione finora
- THE William Francis Galvin, Secretary of The Commonwealth State Publications and RegulationsDocumento54 pagineTHE William Francis Galvin, Secretary of The Commonwealth State Publications and Regulationsbubbo07Nessuna valutazione finora
- VENTILADOR INDUSTRIAL enDocumento4 pagineVENTILADOR INDUSTRIAL enFelipe BarrientosNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec7 WallapDocumento20 pagineEc7 WallapJack DoverNessuna valutazione finora
- U2000 Oss NmsDocumento27 pagineU2000 Oss Nmschandan100% (1)
- Paes 217 1Documento18 paginePaes 217 1Czarina Mae MacaraegNessuna valutazione finora
- Hands-On Exercise Oracle 10g PL SQL - v1 0Documento24 pagineHands-On Exercise Oracle 10g PL SQL - v1 0pavanNessuna valutazione finora
- SEREP System Equivalent ReductionDocumento2 pagineSEREP System Equivalent ReductiondogusNessuna valutazione finora
- Comment To RTDocumento32 pagineComment To RTLim Wee BengNessuna valutazione finora
- School Data Management System ReportDocumento122 pagineSchool Data Management System ReportshekharyadawNessuna valutazione finora
- LV SWBDQualityInspectionGuideDocumento72 pagineLV SWBDQualityInspectionGuiderajap2737Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tiny House MovementDocumento51 pagineTiny House MovementAngelique Lucille PumanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Analysis Bitupan LastDocumento25 pagineSoil Analysis Bitupan Lastbitupon boraNessuna valutazione finora
- Crompton ProjectDocumento110 pagineCrompton Projectarunkcmt0% (2)
- CalibrationDocumento7 pagineCalibrationstolen mechieducNessuna valutazione finora
- GNB Absoltye IIPDocumento18 pagineGNB Absoltye IIPFederico Tellez QNessuna valutazione finora
- Low-Power Digital Signal Processor Architecture For Wireless Sensor NodesDocumento9 pagineLow-Power Digital Signal Processor Architecture For Wireless Sensor NodesGayathri K MNessuna valutazione finora
- 4Ms of Production FactorsDocumento31 pagine4Ms of Production FactorsMaryann Mojica GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- FiberHome Introduction (07.12.2015)Documento13 pagineFiberHome Introduction (07.12.2015)Sandeep SheetalNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 12Documento3 pagineQuiz 12mwende faiyuuNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Extinguisher Location and Placement: Fact SheetDocumento2 pagineFire Extinguisher Location and Placement: Fact SheetEli NaguitNessuna valutazione finora