Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
1-6 Specifications FDA
Caricato da
Myasser SoubCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1-6 Specifications FDA
Caricato da
Myasser SoubCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1-6 Specifications
Andrew Chemwolo
WHO Prequalification Team – Medicines Assessment
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Outline
Definition
Why are specifications important?
Setting appropriate specifications
PQT-medicines approach
Selected test parameters
Model dossier example
Common deficiencies
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Useful References
PQ Generic Guideline – Quality Part
WHO PQTm Model Dossier QOS
ICH Q6A Specifications: Test procedures and acceptance criteria for
new drug substances and new drug products: Chemical substances
ICH Q3A - Q3D: Impurities
Ph Int, USP, BP, EP, JP (recognized pharmacopoeias in PQTm)
Other regulatory guidelines
PQ internal guidelines
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
What is a specification?
A specification is a list of tests, references to analytical procedures,
and appropriate acceptance criteria, which are numerical limits,
ranges, or other criteria for the tests described. (ICH Q6A)
Section P.5.1 of PQ QOS-PD table Extract:
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
What is a specification?...
A specification establishes the set of criteria or quality
standards to which an API or FPP should conform to be
considered acceptable for its intended use
Implication: the API or FPP when tested according to the listed
analytical procedures, will meet the acceptance criteria
Should be authorized by the responsible personnel, be version
controlled and have an effective date.
Proposed and justified by applicants and approved by NMRAs
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Why are specifications important?
Part of the total control strategy for the API and
FPP designed to ensure product quality and
consistency: at release and during shelf life
In-process specifications at critical steps
Confirm the quality of the API/FPP rather than to
establish full characterization
Focus on quality attributes critical for safety & efficacy
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Setting appropriate specifications
Product specifications should be appropriate to the product
(formulation, route of administration, API, manufacture method etc.)
Reviewers need to be aware of the available literature on the API/FPP
Important to check if the API or FPP has a monograph in a recognized
pharmacopoeia (BP, USP, JP, Ph.Eur., Ph.Int.)
Past experience with the API or FPP. Have there been any
concerns/issues in the past? Is there an accepted DMF for an API?
Applicant must declare the standard to which the product complies
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Setting appropriate specifications…
Considerations:
Method of manufacture: Manufacturing process specific impurities
Potential residual solvents
Inorganic impurities e.g. from catalysts, reagents etc.
Stability results of the API/FPP
Formulation: solid, liquid, dispersible, IR
Microbial limits
Dissolution test
Degradation products e.g. interaction of Isoniazid with lactose
Disintegration test
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Setting appropriate specifications…
Route of administration: oral vs sterile injectable
Sterility/microbial limits
Bacterial endotoxins
Particulate matter
API(s) involved
Degradation products
Polymorphism e.g. low solubility API
Particle size distribution especially for low solubility API
Chirality – presence of chiral centres
Available pharmacopoeial monographs for the API/FPP
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
PQT approach
QOS PD Introduction : Contains a table for the applicant/assessor to
fill in details on the current status of API and FPP
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
PQT approach…
The information collected will assist an applicant or assessor to be
aware of current standards and literature on the API or FPP
Specifications are required to meet the minimum pharmacopoeial
standards where a monograph exists, and other requirements (ICH)
Proposed tests and limits should be fully justified
Residual solvents: requirements of ICH Q3C
Impurities: Requirements of ICH Q3A/ICH Q3B
Dissolution: biolot profile
Limits proposed should also take into account biobatch/primary
batch results, manufacturing capability and stability results.
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Tests
ICH Q6A recommends tests (universal & specific) that may be
considered when setting specifications for APIs and FPPs
Some of the common tests for the API include:
Description
Identification
Assay
Impurities (Organic/Inorganic)
Particle size
Polymorph
Microbial limits/Sterility
Bacterial endotoxins
Water content
Chirality
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Tests…
Some of the common tests for the FPP include:
Description
Identification
Assay
Impurities
Dissolution
Disintegration
Uniformity of dosage units
Water content
Bacterial endotoxins
Microbial limits/Sterility
Hardness
Friability
Test methods should be validated, as appropriate (as per ICH Q2).
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Model dossier - API specifications
Levonorgestrel:
Structure
No polymorphs
Brief narrative description of manufacturing process:
Monographs exist in the PhInt, USP, BP, PhEur
To be used to manufacture a tablet formulation
What likely tests would you propose for control of the API?
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Considerations
Levonorgestrel is poorly soluble in water i.e. DSV > 250 mL
Has chiral centres but supplier claims to manufacture as single
enantiomer
Residual solvents used in the last step of synthesis: methanol
and ethyl acetate
No polymorphs
To be used for manufacture of a tablet formulation
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Tests for Levonorgestrel API (Model dossier)
Description: Appearance
Identification – IR
Assay
Specific optical rotation and enantiomeric purity
Related substances: Process and degradation impurities, limit for unknowns
Residual solvents incl. methanol and ethyl acetate (refer to ICH Q3C)
Loss on drying
Particle size
Inorganic impurities: Heavy metals, sulphated ash
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Other considerations
Applicant claims BP/Ph.Eur. & In House standard
Check whether BP/Ph.Eur. tests and limits adopted
Confirm whether BP/Ph.Eur. test methods have been adopted and
verified
If In House test methods used, these methods must be validated and
equivalency to BP/Ph.Eur. methods demonstrated
API fully dissolved in solvent during FPP manufacture: particle
size no longer a critical parameter
Refer to section 2.3.S.4.1 on page 16/96 of the QOS of Model
dossier for summary of actual specifications
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Identification test
Identification test should be specific to the API i.e. should be able to
discriminate between compounds of closely related structure e.g. IR
spectroscopy for the API, whenever possible.
A single HPLC retention time is not regarded as being specific.
Two chromatographic procedures, where the separation is based on
different principles (HPLC + TLC) or combination of tests into a
single procedure is generally acceptable, such as HPLC/MS, or
GC/MS.
Identification test for the salt, where applicable e.g. test for sulfate
A test for optical rotation for chiral APIs
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Related substances
Process related or degradation products
Appropriate test and limits should be included for
Specified (identified / unidentified)
Unspecified (individual unknowns)
Total related substances
Should be monitored during stability
Take cognizance of ICH Q3A and ICH Q3B reporting,
identification and qualification thresholds when setting limits
Consult ICH Q6A, Decision trees #1 & #2 on setting limits
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
API impurity thresholds
Based on maximum daily dose
Must be aware of the Total daily intake thresholds in addition to the
% thresholds (the lower of the two)
Identification threshold for Levonorgestrel is 0.10% (MDD <
2g/day)
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
FPP impurity thresholds
Also based on maximum daily dose
Note: Total daily intake thresholds in addition to the % thresholds
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
What this means
Any impurity:
> reporting threshold should be reported and added to the total
impurities
> Identification Threshold (IT) should be specified
> Qualification Threshold (QT) should be qualified
Unspecified (individual unknowns) ≤ Identification threshold
Critical to correctly establish thresholds
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Assay Test
Specific, stability-indicating assay test in the specifications
Non-specific assay methods (when justified) should be used with
suitable test for impurities to achieve overall specificity e.g. titration
for assay, HPLC for related substances.
Tighter limits set at release of the FPP e.g. 95.0-105.0%.
Wider FPP limits may be accepted during shelf life e.g. 90.0-110.0%
Monitored during stability
Limit narrow for APIs, 98.0-102.0% for most APIs using HPLC
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Uniformity of dosage units
Critical especially for low dose FPP formulations.
PQP requirements aligned with those of the Ph. Int.
Content uniformity(CU): a test and limit for CU is required for each API
present in the FPP at < 5 mg or < 5% of the weight of the dosage unit.
Mass uniformity: a test and limit for weight variation for API(s) present at ≥
5 mg and ≥ 5% of the weight of the dosage unit
Pharmacopoeial tests/limits would be accepted e.g. USP <905>
Scored tablets: CU must also be demonstrated for half-tablets (one-
time study) if CU is required for whole tablets and also if half-tablet
contains < 5mg of the API. CU may be required for half-tablets for
paediatric use even if ≥ 5 mg.
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Dissolution
Dissolution is considered product-specific: method and limits
should be appropriate for the proposed product.
Dissolution limits at release and shelf-life should be identical -
provide confidence about release properties of the FPP
Expressed in terms of 'Q' – allows for 3 stage testing S1, S2 & S3
Limits proposed should be meaningful – reflect dissolution
profile results observed for biolot; must be in line with basis of
biowaiver acceptance; & not too wide as to be irrelevant
May have limits at > 1 time points e.g. Artemether dissolution
limits NLT 40%(Q) in 1 hour and NLT 60% (Q) in 3 hours
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Example specifications - FPP
You have been provided with Exercise 1 - Specifications in
your folder.
Please review the specifications. What proposals for
improvement would you make on these specifications?
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Example specifications – Possible answers
Description should include colour of tablets (full description of appearance)
Related substances test and limits missing
Dissolution limits should be expressed in terms of 'Q' – allows for 3 stage
testing S1, S2 & S3 i.e. NLT 70% (Q) in 60 minutes
Assay limits at release should be revised to 95.0-105.0%, unless justified
Uniformity of weight should be amended to be in line with harmonized
pharmacopoeial texts e.g. Uniformity of dosage units USP chapter <905>
Disintegration limits should be revised to at least NMT 3 minutes
Include an identification test for the API
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Model dossier FPP specifications
Please turn to section 2.3.P.5.1(a) on page 50/96 of the QOS of
Model dossier for summary of specifications of Levonorgestrel
0.75 mg tablets.
Please identify the positive aspects of these specifications.
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Positive aspects
Clear tablet appearance description
More than one identification tests based on different principles
Uniformity of dosage units by content uniformity in line USP <905> (API
content 0.75 mg)
Degradation products test with limit for unspecified impurities NMT 0.5%
in line with ICH Q3B
Assay limit at release 95.0-105.0%
Dissolution limits expressed in terms of 'Q'
Standard of the specifications declared
Release and shelf life specifications separate & version-controlled
Tests, reference to analytical procedures and appropriate acceptance criteria
provided
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Common deficiencies
• Specification not version-controlled, not dated, not signed and no standard
claimed/declared
• Critical test parameters not included e.g. missing PSD limits for low solubility
API, no identification test etc.
• Proposed limits not considered appropriate e.g. assay limits at release being too
wide
• Officially recognized pharmacopoeial monograph exists and the proposed In
House tests/limits do not meet minimum pharmacopoeial requirements
• Pharmacopoeial standard claimed not met by proposed tests/limits or
equivalence of proposed In House test methods is not demonstrated
• References to test methods missing from the specifications
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
Thank you
Questions?
| Prequalification Quality assessment training | CPH May 2016
31
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideDa EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Validation of Analytical ProceduresDocumento15 pagineValidation of Analytical ProceduresildamonalisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationDa EverandPractical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationNessuna valutazione finora
- Diss Method DevDocumento17 pagineDiss Method DevAnnisaIndahPNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Investigation and Effective CAPA SystemsDa EverandHandbook of Investigation and Effective CAPA SystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- ANDA Impurities GuidanceDocumento11 pagineANDA Impurities GuidanceFDA Lawyers BlogNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmaceutical Quality Management System (QMS) Questions and AnswersDa EverandPharmaceutical Quality Management System (QMS) Questions and AnswersNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.11. Nitrosamine Impurities IPCDocumento18 pagine5.11. Nitrosamine Impurities IPCDarshan PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Risk Management in the FDA-Regulated IndustryDa EverandQuality Risk Management in the FDA-Regulated IndustryNessuna valutazione finora
- QBD in Dissolution Method Development - KshirsagarDocumento63 pagineQBD in Dissolution Method Development - KshirsagarAnonymous GL66NMKJ100% (1)
- Steps For Analytical Method Development - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesDocumento1 paginaSteps For Analytical Method Development - Pharmaceutical GuidelinesAnju NarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Workshop - Specifications in Early Development (Regulatory Perspective-Stephen Miller, FDA)Documento30 pagineWorkshop - Specifications in Early Development (Regulatory Perspective-Stephen Miller, FDA)lhthang1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- GMPs Workshop - Analytical Method Validation (Regulatory Perspective - Linda NG, FDA)Documento31 pagineGMPs Workshop - Analytical Method Validation (Regulatory Perspective - Linda NG, FDA)Helena DordioNessuna valutazione finora
- USP 1086 Impurities in Drug Substances and Drug ProductsDocumento3 pagineUSP 1086 Impurities in Drug Substances and Drug ProductsMuhammad JamilNessuna valutazione finora
- Fda'S Question-Based Review (QBR) : A Risk-Based Pharmaceutical Quality Assessment ToolDocumento50 pagineFda'S Question-Based Review (QBR) : A Risk-Based Pharmaceutical Quality Assessment Toollalooprasad15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Drugs PDFDocumento24 pagineControl of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Drugs PDFSrinivasNessuna valutazione finora
- HPLCDocumento46 pagineHPLCJunaidi HidayatNessuna valutazione finora
- 01-How-to-identify-CQA-CPP-CMA-Final Imp PDFDocumento40 pagine01-How-to-identify-CQA-CPP-CMA-Final Imp PDFmarwa100% (1)
- The New Quality Paradigm in Ich q8 q9 q10 q11Documento30 pagineThe New Quality Paradigm in Ich q8 q9 q10 q11ishtidu34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sir William Henry Bragg: Noble Prize 1915!Documento53 pagineSir William Henry Bragg: Noble Prize 1915!Harneysia JaneNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Identify Critical Quality Attributes and Critical Process ParametersDocumento40 pagineHow To Identify Critical Quality Attributes and Critical Process ParametersNicolas Mateo Gonzalez LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Q8 9 10 TogetherDocumento21 pagine02 Q8 9 10 TogethermlaorrcNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Controls Microbiology Testing - CGMP Regulations GuidanceDocumento51 pagineLaboratory Controls Microbiology Testing - CGMP Regulations GuidanceTarikNessuna valutazione finora
- 41 1.13 Stability Workshop ICH M4, ICH M4Q CDocumento11 pagine41 1.13 Stability Workshop ICH M4, ICH M4Q CDrHaresh MulaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 USP Impurities - 0501Documento74 pagineModule 2 USP Impurities - 0501sreekanthsharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- D1S02 Kopcha PDFDocumento39 pagineD1S02 Kopcha PDFHemant SankhalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitrosamine Contamination in Pharmaceuticals - Threat, Impact, and ControlDocumento11 pagineNitrosamine Contamination in Pharmaceuticals - Threat, Impact, and ControlliêmNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Principles of GMP: Qualification and ValidationDocumento28 pagineBasic Principles of GMP: Qualification and Validationhyde2520015754100% (1)
- Oos GuidanceDocumento48 pagineOos GuidancefelipemolinajNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Principles of Analytical Method ValidationDocumento34 pagineBasic Principles of Analytical Method ValidationClarkStewartFaylogaErmilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analy Meth DevDocumento51 pagineAnaly Meth DevkandasaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Excipact StandardsDocumento96 pagineExcipact Standardselighi100% (1)
- 09-Q9 HaccpDocumento8 pagine09-Q9 HaccpKristof MCNessuna valutazione finora
- USFDA Regulatory Toxicology OverviewDocumento100 pagineUSFDA Regulatory Toxicology OverviewHarsh KoshtiNessuna valutazione finora
- ECA CrossContaminationDocumento4 pagineECA CrossContaminationshivanagiriNessuna valutazione finora
- Stability Studies: Gabriel K. Kaddu Head, Drug Assessment and Registration National Drug Authority UgandaDocumento38 pagineStability Studies: Gabriel K. Kaddu Head, Drug Assessment and Registration National Drug Authority Ugandanajiha0% (1)
- Patel Riddhiben M., Patel Piyushbhai M., Patel Natubhai MDocumento9 paginePatel Riddhiben M., Patel Piyushbhai M., Patel Natubhai Msandriss-2Nessuna valutazione finora
- DA NUT2013 B4 Rune Frederiksen PDFDocumento56 pagineDA NUT2013 B4 Rune Frederiksen PDFMaheshNessuna valutazione finora
- HPLC Column Cleaning and RegenerationDocumento2 pagineHPLC Column Cleaning and RegenerationOrc PharNessuna valutazione finora
- Protocol Validation Residual of BetalactamDocumento14 pagineProtocol Validation Residual of BetalactamDoan Chi ThienNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Shelf LifeDocumento27 pagineDrug Shelf LifeAurora SavageNessuna valutazione finora
- Taticek-Product Monitoring & Post-Approval Lifecycle Management of Biotech ProductsDocumento36 pagineTaticek-Product Monitoring & Post-Approval Lifecycle Management of Biotech Products刘朝阳Nessuna valutazione finora
- The APIC Audit Programme Version 6Documento18 pagineThe APIC Audit Programme Version 6Ngoc Sang HuynhNessuna valutazione finora
- Analytical Control Strategies of VaccineDocumento20 pagineAnalytical Control Strategies of VaccineDimitris PapamatthaiakisNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry, Manufacturing and Controls (CMC) Regulation of PharmaceuticalsDocumento66 pagineChemistry, Manufacturing and Controls (CMC) Regulation of PharmaceuticalsDiti ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Good Manufacturing Practice & Drug Manufacturing QualityDocumento54 pagineCurrent Good Manufacturing Practice & Drug Manufacturing QualityGopinath GopiNessuna valutazione finora
- Inspecciones - CasosDocumento25 pagineInspecciones - CasoszombiecorpNessuna valutazione finora
- Handling of Out of Specification Results: International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance April 2015Documento8 pagineHandling of Out of Specification Results: International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance April 2015Pavana KharwalNessuna valutazione finora
- ICH GuidelinesDocumento4 pagineICH Guidelinesaakash sahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lean Stability: Global Regulatory Reception - Successes and Challenges of Recent Case StudiesDocumento19 pagineLean Stability: Global Regulatory Reception - Successes and Challenges of Recent Case StudiesMartin CelestinoNessuna valutazione finora
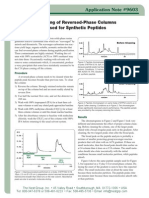
- Cleaning Reverse Phase ColumnDocumento2 pagineCleaning Reverse Phase ColumnhbordasmNessuna valutazione finora
- Impurity ProfileDocumento17 pagineImpurity ProfileNishit SuvaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2006 09 FDA - Ind Statistics SlidesDocumento36 pagine2006 09 FDA - Ind Statistics SlidesSudhagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Huber 1 Method ValidationDocumento38 pagineHuber 1 Method ValidationhasnanursNessuna valutazione finora
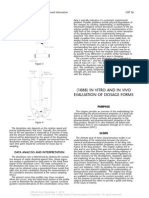
- 1088 in Vitro & in Vivo Evaluation of Dosage Forms - USP 36 PDFDocumento10 pagine1088 in Vitro & in Vivo Evaluation of Dosage Forms - USP 36 PDFKarlaBadongNessuna valutazione finora
- Dosage Form: Pre-Formulation StudiesDocumento7 pagineDosage Form: Pre-Formulation StudiesNimra AmeenNessuna valutazione finora
- CDER's Quality Management Maturity Program: Fda/Cder/Opq/OqsDocumento26 pagineCDER's Quality Management Maturity Program: Fda/Cder/Opq/OqsAmbadas RautNessuna valutazione finora
- ICH Guidelines IndexDocumento5 pagineICH Guidelines Indexyashpandya01Nessuna valutazione finora
- EDQM PAT Proceedings, 2004Documento141 pagineEDQM PAT Proceedings, 2004huynhhaichauchauNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Metrics Poster PDA March 2016Documento1 paginaQuality Metrics Poster PDA March 2016Anthony CollierNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 213: Experiment 7 Determining Water Hardness by EDTA TitrationDocumento6 pagineChemistry 213: Experiment 7 Determining Water Hardness by EDTA TitrationAvinashNessuna valutazione finora
- ITP-3041 For PipeDocumento8 pagineITP-3041 For PipeSkinhead TvNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical EnergerticsDocumento24 pagineChemical EnergerticsAnotidaishe ChakanetsaNessuna valutazione finora
- BOSS Hydraulic Valve O-Ring Sizing Chart: InchesDocumento1 paginaBOSS Hydraulic Valve O-Ring Sizing Chart: InchesssinokrotNessuna valutazione finora
- Moles Lab ReportDocumento2 pagineMoles Lab ReportShiloh FrederickNessuna valutazione finora
- Equiseti HerbaDocumento3 pagineEquiseti HerbaArtem KulikovNessuna valutazione finora
- PHARM 122 7 CycloalkanesDocumento19 paginePHARM 122 7 CycloalkanesTrixie Anne FelicitasNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation On Effluent Treatment PlantDocumento17 paginePresentation On Effluent Treatment Plantarun dubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- IMFA Real Life ApplicationsDocumento2 pagineIMFA Real Life ApplicationsJoana Jean SuymanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bansal R.K. (Ed.) - Phosphorous Heterocycles 1 PDFDocumento323 pagineBansal R.K. (Ed.) - Phosphorous Heterocycles 1 PDFKashilal Indra100% (1)
- Manual de Diseño Andritz Bauer CleanersDocumento145 pagineManual de Diseño Andritz Bauer CleanersLUCERO VILLAMIL FRANCO100% (1)
- BLA FTP I DS 00 001 Rev.1ADocumento14 pagineBLA FTP I DS 00 001 Rev.1Asugeng wahyudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure Mark Scheme: Science Exams SortedDocumento8 pagineAtomic Structure Mark Scheme: Science Exams SortedSaima Usman - 41700/TCHR/MGBNessuna valutazione finora
- Why A Polarimeter - Different Polarimeter ApplicationsDocumento4 pagineWhy A Polarimeter - Different Polarimeter ApplicationsSuresh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- BLAGDON B06 - Non-Metallic - DatasheetDocumento2 pagineBLAGDON B06 - Non-Metallic - DatasheetJose Miguel MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- HPTLCDocumento28 pagineHPTLCVshn VardhnNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/33Documento16 pagineCambridge International AS & A Level: BIOLOGY 9700/33Sumaya TraoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Gaseous State - QuizDocumento4 pagineGaseous State - QuizMuffadal AlaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentDocumento10 pagineChemical Effects of Electric Currentpragunjain2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base Webquest Friday 10 27 17Documento4 pagineAcid Base Webquest Friday 10 27 17api-262586446Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - Electrochemistry (Part 2)Documento13 pagineModule 1 - Electrochemistry (Part 2)Steven LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 The MoleDocumento48 pagine5 The MoleCas AndersNessuna valutazione finora
- Ped Unit 4Documento45 paginePed Unit 4bala saiNessuna valutazione finora
- Niello Manning - ChrisDocumento12 pagineNiello Manning - ChrisSinisa VuckovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry of CarbonDocumento33 pagineChemistry of CarbonDavyieNessuna valutazione finora
- Heng Yin, Yuguang Du (Eds.) - Research Progress - CopieDocumento100 pagineHeng Yin, Yuguang Du (Eds.) - Research Progress - Copievincent cordeilleNessuna valutazione finora
- Igcse Past PaperDocumento12 pagineIgcse Past PaperSalwa A.haiNessuna valutazione finora
- Halfen Natural Stone Support SystemsDocumento32 pagineHalfen Natural Stone Support SystemsHoang Duc LocNessuna valutazione finora
- CHROMATOGRAPHYDocumento4 pagineCHROMATOGRAPHYMansi SingalNessuna valutazione finora
- Matlab Patch Clamp TechniqueDocumento3 pagineMatlab Patch Clamp TechniqueRafael Hernández MendezNessuna valutazione finora