Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Metric Handbook - Planning and Design Data - 5th Edition - Copy 18
Caricato da
yit0rrentDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Metric Handbook - Planning and Design Data - 5th Edition - Copy 18
Caricato da
yit0rrentCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Design information and dimensional coordination 1-7
Low detail representation Medium detail representation
Scale 1:100/1:200 Scale 1:50
High detail representation
Scale 1:20
4.6 Graded components Component Grade 2 – Defined
With 3D modelling systems it is possible to replace an object with
another showing more detail as the design progresses. To facilitate x Contains all relevant meta-data and technical information, and
this, the AEC BIM Standards recommend that all components cre- is sufficiently modelled to identify type of chair and component
ated, or otherwise obtained should be graded, named and stored materials.
accordingly in the project structure as follows. x Typically contains level of 2D detail suitable for the ‘Preferred’
scale.
x Sufficient for most projects.
Component Grade 3 – Rendered
x Identical to the Grade 2 version if scheduled or interrogated by
annotation. Differs only in 3D representation.
x Used only when a 3D view at a sufficient scale deems the detail
Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 necessary due to the object’s proximity to the camera.
In addition to the grading, a component may make use of Low,
Medium and High levels of detail to control its graphical representa-
tion in relation to the chosen scale as indicated in Section 4.3.
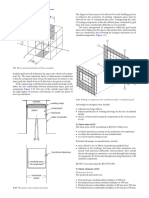
5 DIMENSIONAL COORDINATION
5.1 General
Current building practice involves the assembly of many facto-
ry-made components: in some cases the whole project consists of
such components slotted together like a child’s construction kit.
Dimensional coordination (DC) is essential to ensure the success
of the system, and consists of a range of dimensions relating to the
sizing of building components and assemblies, and to the build-
ings incorporating them. DC enables the coordination of the many
Component Grade 1 – Concept parts that go to make up the total construction which are supplied
from widely separated sources. At an international level, 100 mm
x Simple place-holder with absolute minimum level detail to be is accepted as the basic module (often referred to by the letter ‘M’).
identifiable, e.g. as any type of chair. Dimensional coordination relies on establishment of rectangular
x Superficial dimensional representation. three-dimensional grids of basic modules into which components
x Generic in terms of manufacturer information and technical data. can be introduced in an interrelated pattern of sizes, Figure 1.9. The
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Project Charter v3Documento6 pagineProject Charter v3stephenNessuna valutazione finora
- Software DesignDocumento38 pagineSoftware DesignRishabh ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Design Specification Template PDFDocumento6 pagineSoftware Design Specification Template PDFjames kilonzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Unreal Engine Pro: Advanced Development Secrets: Mastering Unreal Engine: From Novice to ProDa EverandUnreal Engine Pro: Advanced Development Secrets: Mastering Unreal Engine: From Novice to ProNessuna valutazione finora
- Tuma Research ManualDocumento57 pagineTuma Research ManualKashinde Learner Centered Mandari100% (1)
- SE-LEC-UOG-12 - Design Concepts and PrincipleDocumento59 pagineSE-LEC-UOG-12 - Design Concepts and PrincipleshavzzNessuna valutazione finora
- Highlights ASME Guides Preheat PWHT IDocumento4 pagineHighlights ASME Guides Preheat PWHT IArul Edwin Vijay VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Mushroom Project - Part 1Documento53 pagineMushroom Project - Part 1Seshadev PandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual Reality BIM Execution PlansDocumento12 pagineVirtual Reality BIM Execution PlansCharmaine100% (1)
- BIM Execution Plan: Phase II - ConstructionDocumento26 pagineBIM Execution Plan: Phase II - ConstructionFayyazAhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- BIM Level2 ExplainedDocumento1 paginaBIM Level2 Explainednicehornet100% (1)
- 3D Model Development Manual Acc101422Documento50 pagine3D Model Development Manual Acc101422Maria Clara AlvesNessuna valutazione finora
- BIM E-Submission - General GuidelinesDocumento13 pagineBIM E-Submission - General GuidelinesTamouh ZakrtNessuna valutazione finora
- Cohesion and CouplingDocumento5 pagineCohesion and CouplingasdfNessuna valutazione finora
- BIM StandardDocumento102 pagineBIM StandardMC Min NaingNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1.2 MC and SDDocumento30 pagineUnit 1.2 MC and SDsubita manoharanNessuna valutazione finora
- Axisvm V8.0 Features and Benefits: Integrated Building ModelDocumento8 pagineAxisvm V8.0 Features and Benefits: Integrated Building ModelGeorge StefNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1.2 MC and SDDocumento30 pagineUnit 1.2 MC and SDSUBITA DEENESHWARI CIVILNessuna valutazione finora
- 08-08-20 MPS PDFDocumento4 pagine08-08-20 MPS PDFSona NingNessuna valutazione finora
- Design ModelDocumento5 pagineDesign Modelpolelor663Nessuna valutazione finora
- Building Information Modelling (BIM) User Guide For Development and Construction Division of Hong Kong Housing AuthorityDocumento53 pagineBuilding Information Modelling (BIM) User Guide For Development and Construction Division of Hong Kong Housing AuthoritySyl Vain RissNessuna valutazione finora
- 2023x ENOVIA SEM HandoutDocumento4 pagine2023x ENOVIA SEM Handoutkiran babuNessuna valutazione finora
- Cim 2Documento10 pagineCim 2Arun KolurNessuna valutazione finora
- The Book - Revit Ar 2011 PDFDocumento171 pagineThe Book - Revit Ar 2011 PDFgladdice taduranNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluating Physical and Spatial Requirements of Apartment Unit Floor PlansDocumento8 pagineEvaluating Physical and Spatial Requirements of Apartment Unit Floor PlansAnthony SabinorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Aecosin BentleyDocumento2 pagineAecosin BentleyLuiz Amilton SalesNessuna valutazione finora
- NBS LODGuide Ss - 25 30Documento169 pagineNBS LODGuide Ss - 25 30Diego PluchinoNessuna valutazione finora
- NBS LODGuide Ss - 32 40Documento69 pagineNBS LODGuide Ss - 32 40Diego PluchinoNessuna valutazione finora
- General Purpose Building Description SystemsDocumento10 pagineGeneral Purpose Building Description SystemsBruno HenriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3. Design Qualities: 3.1 ConceptDocumento13 pagineChapter 3. Design Qualities: 3.1 ConceptSamiksha SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Effective Loss ReconsDocumento21 pagineEffective Loss ReconsCaithyralNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy and Air Filter Fact HandbookDocumento3 pagineEnergy and Air Filter Fact HandbookpNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Driven Framework For Networked Application Software GenerationDocumento10 pagineModel Driven Framework For Networked Application Software GenerationJournal of ComputingNessuna valutazione finora
- Bim and Cost EstimatingDocumento9 pagineBim and Cost Estimatingle_canh65Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-3 Notes SE Part-IDocumento5 pagineUnit-3 Notes SE Part-Isunnyvemulavadatrynow6506Nessuna valutazione finora
- Group 3 TLE: Identify Different Kind of Technical DrawingsDocumento19 pagineGroup 3 TLE: Identify Different Kind of Technical Drawingsduncan lincalloNessuna valutazione finora
- X3D: Expanding Architectures For Efficient Video RecognitionDocumento11 pagineX3D: Expanding Architectures For Efficient Video RecognitionPAARTH BIRNessuna valutazione finora
- NBS LODGuide Ss - 45 50Documento61 pagineNBS LODGuide Ss - 45 50Diego PluchinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Semantic Segmentation Architecture: A Key Part of Scene Understanding ApplicationsDocumento9 pagineSemantic Segmentation Architecture: A Key Part of Scene Understanding ApplicationsSunilmahek MahekNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling Componnet Level Design (2) - STUDENTDocumento25 pagineModeling Componnet Level Design (2) - STUDENTBuncy MaddalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Metric Handbook - Planning and Design Data - 5th Edition - Copy 19Documento1 paginaMetric Handbook - Planning and Design Data - 5th Edition - Copy 19yit0rrentNessuna valutazione finora
- 3Dmfv: 3D Point Cloud Classification in Real-Time Using Convolutional Neural NetworksDocumento8 pagine3Dmfv: 3D Point Cloud Classification in Real-Time Using Convolutional Neural NetworksNina MouhoubNessuna valutazione finora
- 008-BIM Guideline MalaysiaDocumento207 pagine008-BIM Guideline MalaysiaengsonikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hanm123 - f2 G FinalDocumento7 pagineHanm123 - f2 G FinalseirphenyoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3d Modeling For The Architectural Engineering andDocumento7 pagine3d Modeling For The Architectural Engineering andicNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3Documento31 pagineUnit 3Pulkit JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Presman 8th SE-283-315Documento33 paginePresman 8th SE-283-315Andreas NababanNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Develop A BIM-Workflow For Landscape Architecture: A Practical ApproachDocumento9 pagineHow To Develop A BIM-Workflow For Landscape Architecture: A Practical ApproachRajat MaheshwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Exam - BLDGDESIGN-PRELIM-SY-2022-2023-1ST-SEMDocumento2 pagineMidterm Exam - BLDGDESIGN-PRELIM-SY-2022-2023-1ST-SEMSean Kenneth Anthony PamintuanNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1.1 Working Environment & Graphical User Interface - Digital Factory Planning and Simulation With TecnomatixDocumento3 pagine2.1.1 Working Environment & Graphical User Interface - Digital Factory Planning and Simulation With TecnomatixanupNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Abstract: Dev Barbhaya, Ankit Yadav, Lochan Gupta, Utkarsh Agrawal, and Vinamra ShrivastavaDocumento1 pagina1 Abstract: Dev Barbhaya, Ankit Yadav, Lochan Gupta, Utkarsh Agrawal, and Vinamra ShrivastavaAryann kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The Value of GD&T ImplementationDocumento6 pagineWhat Is The Value of GD&T Implementationgpb76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Revit Structure and AutoCAD Feb07Documento19 pagineRevit Structure and AutoCAD Feb07welwelNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Goal-Use Analysis Worksheet-V2.0 (Excel)Documento5 pagine03 Goal-Use Analysis Worksheet-V2.0 (Excel)ale10201Nessuna valutazione finora
- Briefly: Embodiment Actually JustifiedDocumento5 pagineBriefly: Embodiment Actually JustifiedDivanshu InsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Btewst1 N02222118KDocumento3 pagineBtewst1 N02222118KAaron MushunjeNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial No.7Documento7 pagineTutorial No.7Pallavi BhartiNessuna valutazione finora
- Enabling Efficient Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Based Sensor Fusion For Autonomous DrivingDocumento6 pagineEnabling Efficient Deep Convolutional Neural Network-Based Sensor Fusion For Autonomous DrivingcthfmzNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Design Towards 5-Dimensions: Meik Kabath, Iez GMBH, 64625 Bensheim, GermanyDocumento10 pagineBuilding Design Towards 5-Dimensions: Meik Kabath, Iez GMBH, 64625 Bensheim, GermanyGuilherme PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Vero Software - DEVELOP3D Reviews VISI 17Documento7 pagineVero Software - DEVELOP3D Reviews VISI 17marc5135Nessuna valutazione finora
- CS504 McqsDocumento555 pagineCS504 Mcqssabiha kamranNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 6 Miie - Mcs NewDocumento103 pagineTopic 6 Miie - Mcs NewFaruk AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Dimitrov - Vision Based Recognition and Unordered Site ImageDocumento13 pagineDimitrov - Vision Based Recognition and Unordered Site Imagesamir.amanNessuna valutazione finora
- Metric Handbook - Planning and Design Data - 5th Edition - Copy 20Documento1 paginaMetric Handbook - Planning and Design Data - 5th Edition - Copy 20yit0rrentNessuna valutazione finora
- Metric Handbook - Planning and Design Data - 5th Edition - Copy 21Documento1 paginaMetric Handbook - Planning and Design Data - 5th Edition - Copy 21yit0rrentNessuna valutazione finora
- Metric Handbook - Planning and Design Data - 5th Edition - Copy 19Documento1 paginaMetric Handbook - Planning and Design Data - 5th Edition - Copy 19yit0rrentNessuna valutazione finora
- Perkins Eastman Job OpeningsDocumento50 paginePerkins Eastman Job Openingsyit0rrentNessuna valutazione finora
- SP-Chapter 14 PresentationDocumento83 pagineSP-Chapter 14 PresentationLoiDa FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- FHWA Guidance For Load Rating Evaluation of Gusset Plates in Truss BridgesDocumento6 pagineFHWA Guidance For Load Rating Evaluation of Gusset Plates in Truss BridgesPatrick Saint-LouisNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Reinforced Cement Concrete ElementsDocumento14 pagineDesign of Reinforced Cement Concrete ElementsSudeesh M SNessuna valutazione finora
- Applying For A Job: Pre-ReadingDocumento5 pagineApplying For A Job: Pre-ReadingDianitta MaciasNessuna valutazione finora
- Create A Visual DopplerDocumento1 paginaCreate A Visual DopplerRahul GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Perdarahan Uterus AbnormalDocumento15 paginePerdarahan Uterus Abnormalarfiah100% (1)
- Pubb-0589-L-Rock-mass Hydrojacking Risk Related To Pressurized Water TunnelsDocumento10 paginePubb-0589-L-Rock-mass Hydrojacking Risk Related To Pressurized Water Tunnelsinge ocNessuna valutazione finora
- European Asphalt Standards DatasheetDocumento1 paginaEuropean Asphalt Standards DatasheetmandraktreceNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample CVFormat 1Documento2 pagineSample CVFormat 1subham.sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cobol v1Documento334 pagineCobol v1Nagaraju BNessuna valutazione finora
- Jul - Dec 09Documento8 pagineJul - Dec 09dmaizulNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Term Project 4º Eso Beauty Canons 2015-16 DefinitivoDocumento2 pagine2nd Term Project 4º Eso Beauty Canons 2015-16 DefinitivopasferacosNessuna valutazione finora
- USER MANUAL ABRITES Commander For Nissan PDFDocumento20 pagineUSER MANUAL ABRITES Commander For Nissan PDFBosi GashiNessuna valutazione finora
- A Literature Review of Retailing Sector and BusineDocumento21 pagineA Literature Review of Retailing Sector and BusineSid MichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To EthicsDocumento18 pagineIntroduction To EthicsMarielle Guerra04Nessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Trigonometry Using Empirical Modelling: 2.1 Visual Over Verbal LearningDocumento5 pagineTeaching Trigonometry Using Empirical Modelling: 2.1 Visual Over Verbal LearningJeffrey Cariaga Reclamado IINessuna valutazione finora
- SPC FD 00 G00 Part 03 of 12 Division 06 07Documento236 pagineSPC FD 00 G00 Part 03 of 12 Division 06 07marco.w.orascomNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 3 Transes in Reading in Philippine HistoryDocumento17 pagineLesson 1 3 Transes in Reading in Philippine HistoryNAPHTALI WILLIAMS GONessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Data Sheet SDS For CB-G PG Precision Grout and CB-G MG Multipurpose Grout Documentation ASSET DOC APPROVAL 0536Documento4 pagineSafety Data Sheet SDS For CB-G PG Precision Grout and CB-G MG Multipurpose Grout Documentation ASSET DOC APPROVAL 0536BanyuNessuna valutazione finora
- GGG Sri MDocumento2 pagineGGG Sri MGiovanni LuigiNessuna valutazione finora
- D25KS Sanvick PDFDocumento4 pagineD25KS Sanvick PDFJiménez Manuel100% (1)
- Csir Life Sciences Fresh Instant NotesDocumento4 pagineCsir Life Sciences Fresh Instant NotesAlps Ana33% (3)
- DCS800ServiceManual RevADocumento96 pagineDCS800ServiceManual RevAElinplastNessuna valutazione finora
- Generation III Sonic Feeder Control System Manual 20576Documento32 pagineGeneration III Sonic Feeder Control System Manual 20576julianmataNessuna valutazione finora
- RARE Manual For Training Local Nature GuidesDocumento91 pagineRARE Manual For Training Local Nature GuidesenoshaugustineNessuna valutazione finora
- 40 Sink and FloatDocumento38 pagine40 Sink and Floatleandro hualverdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Shri Naina Devi Aarti English 167Documento5 pagineShri Naina Devi Aarti English 167ratt182Nessuna valutazione finora