Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Alternative Division of Scheduled Banks and Non Scheduled Banks (Without Non Scheduled Bank Structure)
Caricato da
Samuel HranlehDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Alternative Division of Scheduled Banks and Non Scheduled Banks (Without Non Scheduled Bank Structure)
Caricato da
Samuel HranlehCopyright:
Formati disponibili
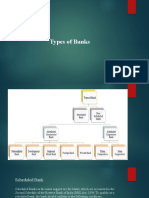
SCHEDULED BANKS:
Scheduled Commercial Banks in India are categorised in 2 broad different groups according to their ownership
/ nature of operation.
1. Scheduled commercial bank – Indian as well as foreign banks.
2. Schedule state cooperative bank’s
A. Scheduled Commercial Bank :
A commercial bank is a financial institution that grants loans, accepts deposits and offers basic financial
products like a savings account and certificate of deposits to individuals and businesses.
The commercial bank’s funds come from money deposited by the bank customers in saving account, checking
accounts, money market accounts and certificates of deposits.
Types of Schedule Commercial Bank:
1. Public sector banks
2. Private Sector banks
3. Foreign Banks
4. Regional Rural banks
Public Sector Banks:
Public sector banks are those banks in which the government has majority shareholding more than 51 percent.
Public sector banks are owned and controlled by the government either directly or indirectly through the
central banks. These banks are also known as the National Bank.
Private Sector Banks :
Private sector banks are those banks in which the government has majority shareholding less than 51 per cent.
Private sector banks are those banks which are owned by private individuals or business corporation.
Foreign Banks :
Foreign Banks are from out of the country it’s the origin. These banks are incorporated outside of the country
under the law of the home country but have a place of business in another country. Foreign Banks have their
presence from the British period in our country . Initially, they were allowed to operate only through branches
but now they are allowed to set up subsidiaries in India.
Some Example of Foreign Banks: Standard Chartered Banks, Hongkong Shanghai Banking Corporation,
American Express Banking Corporation, Bank of Tokyo, Citi Bank.
Regional Rural Banks :
In order to provide efficient banking services in rural areas, regional rural banks were set up in 1975 under the
sponsorship of the commercial bank’s. The regional rural banks are governed by the Regional Rural banks act
in 1976.
B. Scheduled State Cooperative Banks:
Cooperative banks are small-sized bank’s organised in the small cooperative sector which have the ability to
operate both urban and non-urban areas. Cooperative banks are registered under the cooperative societies
Act. The cooperative banks are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India. It is also governed by the Banking
regulation act 1949 and Banking laws act 1965.
Types of State Cooperative Banks:
1. State Cooperative bank’s
2. Primary credit society
3. Central cooperative bank’s
State Cooperative Bank’s:
These are the apex cooperative banks in all the states of the country. Cooperative banks mobilise funds and
help in the proper channelisation among various sectors. The money reaches the individual borrowers from
the state cooperative banks through the central cooperative banks and primary credit society. The cooperative
bank’s in India finance rural areas under Farming, Cattle, milk and personal finance including others.
Central Cooperative Bank’s:
These banks operate at the district level. It may have some of the primary credit societies belonging to the
same district as their members.
Primary Credit Society:
These societies are formed as the village level or town level with the borrower or non-borrower members
residing in one locality. The operation of each society is restricted to a small area so that the members know
each other and are able to watch over the activities of all members to prevent frauds.
NON-SCHEDULED BANKS:
Non-Scheduled Bank consists primarily of smaller banks in the Cooperative Sector which are not listed in the
Second Schedule of Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
In finer terms, the banks which do not comply with the provisions specified by the central bank, within the
meaning of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, or as per specific functions, etc. or as per the judgment of the
RBI, are not able to serve and protect the depositor’s interest, are known as non-scheduled banks.
Non- Scheduled Banks are also not eligible for having loans from the RBI for day to day activities but under the
emergency conditions RBI can grant loan to them.
Non-Scheduled Banks are also required to maintain the cash reserve requirement, not with the RBI, but with
themselves, as no compulsion has been made by the RBI to deposit it in the RBI. These are local area banks.
There is also no requirement of submission of periodic returns to the central bank, in case of non-scheduled
banks.
Further, no such facility as the right to become the member of the clearing house is available to the non-
scheduled banks.
When it comes to privileges, scheduled banks is ahead of non-scheduled banks. Scheduled banks get
remittances through the offices of the Reserve Bank of India and its agents, for free or at concessional rates.
Moreover, borrowing facilities by Central Bank on the submission of the documents. Such facilities are not
provided to the non-scheduled banks.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Comparative Analysis of Commercial Bank (Icici and Idbi Bank)Documento27 pagineComparative Analysis of Commercial Bank (Icici and Idbi Bank)GUDDUNessuna valutazione finora
- Banking Structure in IndiaDocumento5 pagineBanking Structure in IndiaCharu Saxena16Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Analysis of Commercial Bank (Icici and Idbi Bank)Documento31 pagineComparative Analysis of Commercial Bank (Icici and Idbi Bank)GUDDUNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Banking IndustryDocumento12 pagineOverview of Banking Industrybeena antuNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Banks IndiaDocumento3 pagineTypes of Banks India17-075 Upgna PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Indian Banking SystemDocumento11 pagine01 Indian Banking SystemAmir AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Banking Practice Unit 1Documento13 pagineBanking Practice Unit 1Nandhini VirgoNessuna valutazione finora
- Banking Management Additional NotesDocumento118 pagineBanking Management Additional NotesLokesh ChNessuna valutazione finora
- RTL - BOB - LU1 - SLU1.4 - Indian Banking System-1 PDFDocumento9 pagineRTL - BOB - LU1 - SLU1.4 - Indian Banking System-1 PDFUtkarshMalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Devast IncDocumento19 pagineDevast IncPiyush SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- L15 Scheduled BANKS PDFDocumento14 pagineL15 Scheduled BANKS PDFakshita raoNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract - Role of Commercial Banks in IndiaDocumento8 pagineAbstract - Role of Commercial Banks in Indiasalman.wajidNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank and Types of BanksDocumento9 pagineBank and Types of BanksreshNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank and Types of BanksDocumento9 pagineBank and Types of BanksreshNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank and Types of BanksDocumento9 pagineBank and Types of BanksreshNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank and Types of BanksDocumento9 pagineBank and Types of BanksreshNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank and Types of BanksDocumento9 pagineBank and Types of Banksanju skariaNessuna valutazione finora
- A.2 AssignmentDocumento5 pagineA.2 AssignmentNijiraNessuna valutazione finora
- 0 Ashay% PDFDocumento55 pagine0 Ashay% PDFAshay AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Banks: BankingDocumento11 pagineTypes of Banks: BankingKaviya KaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Cooperative BankingDocumento8 pagineCooperative BankingvmktptNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 - Chapter 1Documento27 pagine04 - Chapter 1shantishree04Nessuna valutazione finora
- Banking Sector in IndiaDocumento5 pagineBanking Sector in IndiajaamssNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report)Documento38 pagineProject Report)Swathi JNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank & Its ClassificationDocumento20 pagineBank & Its ClassificationMansha KakkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Commercial Banks in IndiaDocumento11 pagineStructure of Commercial Banks in IndiaVijayalakshmi100% (2)
- 18.04 - COMMERCIAL BANKS, NBFCS, COOPERATIVE BANKSDocumento12 pagine18.04 - COMMERCIAL BANKS, NBFCS, COOPERATIVE BANKSramixudinNessuna valutazione finora
- BankingDocumento8 pagineBankingkarthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Banking Structure in IndiaDocumento31 pagineBanking Structure in IndiaRishabhShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Banking System - Structure and Other Details (With Diagrams)Documento14 pagineIndian Banking System - Structure and Other Details (With Diagrams)krunaldedehiya100% (1)
- BankingDocumento74 pagineBankingAbhishek DubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Banking StructureDocumento5 pagineIndian Banking StructurevivekNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of The Indian Banking System Sem IDocumento2 pagineStructure of The Indian Banking System Sem IAshitosh ChavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Banking & Financial Institutions in India: Historical BackgroundDocumento6 pagineBanking & Financial Institutions in India: Historical BackgroundRUPA GOELNessuna valutazione finora
- Banking Practical 1 InformationDocumento4 pagineBanking Practical 1 InformationMadhur AbhyankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Banking System in India: 12 Types of BanksDocumento7 pagineBanking System in India: 12 Types of Banksप्रॉजेक्टपैराडायसNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Banking in IndiaDocumento14 pagineStructure of Banking in IndiaHimani DhingraNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept of BankingDocumento36 pagineConcept of BankingDhaval B MasalawalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Scheduled BanksDocumento21 pagineScheduled BanksShreyansh JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Cooperative Banks: School of Law, Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies, BangaloreDocumento13 pagineCooperative Banks: School of Law, Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies, BangaloreHIMANSHU GOYALNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Banks: Central BankDocumento2 pagineTypes of Banks: Central BankMunna MunnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bankinng PPT - PPTMDocumento19 pagineBankinng PPT - PPTMKeshav ThadaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Banking System in IndiaDocumento3 pagineBanking System in Indiahello707Nessuna valutazione finora
- Type of Banks: Different Types of Banks in India & Their FunctionsDocumento15 pagineType of Banks: Different Types of Banks in India & Their FunctionscecilNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Banking System Final 52Documento7 pagineClassification of Banking System Final 52sonam1991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Banking Theory Law and PracticesDocumento67 pagineBanking Theory Law and PracticesJESUINE J BBAENessuna valutazione finora
- Banking Industry 1Documento11 pagineBanking Industry 1Sohini KarNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Commercial BanksDocumento3 pagineStructure of Commercial BanksKŕiśhñą ŚińghNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Banking System in IndiaDocumento34 pagineStructure of Banking System in IndiaAyushi SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of BankDocumento2 pagineTypes of Bankashisghadai02Nessuna valutazione finora
- CBS NewDocumento92 pagineCBS NewBen MathewsNessuna valutazione finora
- DRA TrainingDocumento3 pagineDRA Trainingbhaskar mandadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Commercial BanksDocumento9 pagineCommercial BanksPrathyusha ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-4 Commercial Bank: Types of Banks They Are Given Below: 1. Commercial BanksDocumento13 pagineChapter-4 Commercial Bank: Types of Banks They Are Given Below: 1. Commercial BanksRuthvik RevanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6Documento107 pagineUnit 6Avinaash PraveenNessuna valutazione finora
- Study MaterialDocumento42 pagineStudy MaterialLion Naresh PradhanNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT-1 Overview of Banking System in India 1-History of Banking in IndiaDocumento14 pagineUNIT-1 Overview of Banking System in India 1-History of Banking in Indiaaanya meenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of BanksDocumento15 pagineStructure of BanksAmogh AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- BankingDocumento85 pagineBankingZeel kachhiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingDa EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingNessuna valutazione finora
- SDG - Themes, Sub-Themes and Core IndicatorsDocumento3 pagineSDG - Themes, Sub-Themes and Core IndicatorsSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Development Role of The RBIDocumento3 pagineDevelopment Role of The RBISamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Regulated and Unregulated Credit Market in IndiaDocumento1 paginaTypes of Regulated and Unregulated Credit Market in IndiaSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Scheduled VS Non ScheduledDocumento1 paginaScheduled VS Non ScheduledSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimal Level of PollutionDocumento1 paginaOptimal Level of PollutionSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Pawimawh TakinDocumento1 paginaPawimawh TakinSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- ROLE OF DEVELOPMENT BANKS (Summary of Three Views)Documento2 pagineROLE OF DEVELOPMENT BANKS (Summary of Three Views)Samuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Exchange MarketDocumento11 pagineForeign Exchange MarketSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Informal Credit Markets in India: Thomas TimbergDocumento24 pagineInformal Credit Markets in India: Thomas TimbergSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Eurodollar PDFDocumento6 pagineEurodollar PDFSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions of Foex MarketDocumento2 pagineFunctions of Foex MarketSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Components of Balance of Payments I: NtroductionDocumento3 pagineComponents of Balance of Payments I: NtroductionSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Meaning and Objectives of Development BanksDocumento1 paginaMeaning and Objectives of Development BanksSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Development BanksDocumento4 pagineStructure of Development BanksSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- ROLE OF COOPERATIVE INSTITUTIONS IN INDIA (4 Points)Documento1 paginaROLE OF COOPERATIVE INSTITUTIONS IN INDIA (4 Points)Samuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Development BanksDocumento4 pagineStructure of Development BanksSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ - Importance and History of Development BanksDocumento1 paginaMCQ - Importance and History of Development BanksSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- ROLE OF DEVELOPMENT BANKS (Summary of Three Views)Documento2 pagineROLE OF DEVELOPMENT BANKS (Summary of Three Views)Samuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ - Importance and History of Development BanksDocumento1 paginaMCQ - Importance and History of Development BanksSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Meaning and Objectives of Development BanksDocumento1 paginaMeaning and Objectives of Development BanksSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- The Process of Environmental Impact AssessmentDocumento3 pagineThe Process of Environmental Impact AssessmentSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)Documento4 pagineCentral Pollution Control Board (CPCB)Samuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Components of Balance of Payments I: NtroductionDocumento3 pagineComponents of Balance of Payments I: NtroductionSamuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- ROLE OF COOPERATIVE INSTITUTIONS IN INDIA (4 Points)Documento1 paginaROLE OF COOPERATIVE INSTITUTIONS IN INDIA (4 Points)Samuel HranlehNessuna valutazione finora
- Direct Insite SecretCaps Research ReportDocumento16 pagineDirect Insite SecretCaps Research ReportAnonymous Ht0MIJNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Quality of Public Sector Banks - A Study: ManagementDocumento7 pagineService Quality of Public Sector Banks - A Study: ManagementgherijaNessuna valutazione finora
- KTT - CONTRACT - CDB - AMROCK PETROLEUM LTD - 500m-AaaDocumento24 pagineKTT - CONTRACT - CDB - AMROCK PETROLEUM LTD - 500m-AaaRakibul Islam67% (3)
- Business Finance Week 1 and 2Documento56 pagineBusiness Finance Week 1 and 2Jonathan De villaNessuna valutazione finora
- Groupwork 3: Team GorgeousDocumento4 pagineGroupwork 3: Team GorgeousAdliana ColinNessuna valutazione finora
- Programme On: Enhancing Branch PerformanceDocumento6 pagineProgramme On: Enhancing Branch Performanceadelani_oniNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Eco O99 NotesDocumento20 pagineFull Eco O99 NotesWafaa AzreenNessuna valutazione finora
- Ugb 322.viet Ha NguyenDocumento53 pagineUgb 322.viet Ha NguyenPhạm Huyền100% (1)
- Adtp Fee 2022 IntiDocumento1 paginaAdtp Fee 2022 IntiAsma AkterNessuna valutazione finora
- Treasury Manager Back-Office Management: Main Purposes of The FunctionDocumento2 pagineTreasury Manager Back-Office Management: Main Purposes of The FunctionDuma DumaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Joe Owen: Contact MeDocumento2 pagineJoe Owen: Contact MeRia LedNessuna valutazione finora
- The Importance of Good Office Layout in Business OrganizationDocumento11 pagineThe Importance of Good Office Layout in Business OrganizationOmotere TopeNessuna valutazione finora
- Live CAMS PrepDocumento187 pagineLive CAMS Prepvinttt13409Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercito V. Sandiganbayan G.R. No. 157294-95Documento4 pagineEjercito V. Sandiganbayan G.R. No. 157294-95Sabel FordNessuna valutazione finora
- (Defined Hereinafter) (Defined Hereinafter)Documento15 pagine(Defined Hereinafter) (Defined Hereinafter)TharshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fake L&T Interview Call LetterDocumento4 pagineFake L&T Interview Call LetterjramesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Terms-of-Use-21 01 21-26 02 21Documento14 pagineTerms-of-Use-21 01 21-26 02 21AbdulHafeezNessuna valutazione finora
- 303 - Banking, Insurance & Financial ServicesDocumento3 pagine303 - Banking, Insurance & Financial ServicesDixa PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Vietnam Deals Review 2011: High Capital Inflows From Japanese CorporationsDocumento53 pagineVietnam Deals Review 2011: High Capital Inflows From Japanese CorporationsManh Cuong Nguyen TuNessuna valutazione finora
- Form A Fund ManagementDocumento88 pagineForm A Fund ManagementAh MhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Product - Retail CASA - Privacy Policy v2 - 08jun2021Documento6 pagineProduct - Retail CASA - Privacy Policy v2 - 08jun2021SorryNessuna valutazione finora
- A-Level Macroeconomics PLC (AQA)Documento11 pagineA-Level Macroeconomics PLC (AQA)Karim El-GawlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Post Dated Cheque PDC Process in SAPDocumento47 paginePost Dated Cheque PDC Process in SAPmannoj2001100% (1)
- SBN-859: Comprehensive Revision of The Charter of The Bangko Sentral NG Pilipinas (BSP)Documento42 pagineSBN-859: Comprehensive Revision of The Charter of The Bangko Sentral NG Pilipinas (BSP)Ralph RectoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cash and Cash Equivalents Mock TestDocumento3 pagineCash and Cash Equivalents Mock Testwednesday addamsNessuna valutazione finora
- 27th Standing Committee On Finance PDFDocumento74 pagine27th Standing Committee On Finance PDFJustinaMatthewNessuna valutazione finora
- Tybms ProjectDocumento5 pagineTybms Projectpanzu50% (2)
- Job Description Job Title Level Division Company No of Positions Location Reporting ToDocumento2 pagineJob Description Job Title Level Division Company No of Positions Location Reporting Tosuganth samuelNessuna valutazione finora
- Abridged - TRANSITIONAL STABILISATION PROGRAMMEDocumento74 pagineAbridged - TRANSITIONAL STABILISATION PROGRAMMEAaron KuudzeremaNessuna valutazione finora
- Proposal Form: Commercial Vehicle Insurance Policy - Package WWW - Sbigeneral.in/downloadDocumento5 pagineProposal Form: Commercial Vehicle Insurance Policy - Package WWW - Sbigeneral.in/downloadPanchanan MuniNessuna valutazione finora