Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Formula Pc1
Caricato da
Jose VasquezCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Formula Pc1
Caricato da
Jose VasquezCopyright:
Formati disponibili
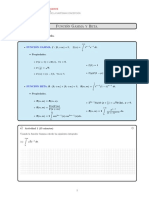
∞ b
Integrales impropia
1) ∫ f ( x ) dx → lim ∫ f ( x ) dx
b→∞ a
a
b b
2) ∫ f ( x ) dx → alim
→∞
∫ f ( x ) dx
−∞ a
∞ ∞ b
3) ∫ fxdx=∫ f ( x ) dx +¿ ∫ f ( x ) dx ¿
−∞ a −∞
∞
Funcion Gama
Γ ( x )=∫ e−t t x−1 dt , x> 0
0
Propiedades Γ ( x+ 1 )=x Γ ( x )
Γ ( 1 )=1
Γ ( n+1 ) =n !
1
Γ
2 ()
=√ π
∞
∫ e−u du= √2π
2
0
1
Funcion Beta Γ (x) Γ ( y)
Β ( x , y )=∫ t x−1 (1−t ) y−1 dt Β ( x , y )=
0 Γ(x+ y)
Propiendades
Β ( 12 , 12 )=π
Β (1,1 ) =1
Β ( m, n )=B( n , m)
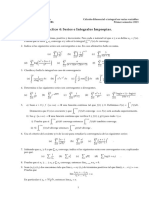
π /2
Modelo Polar o
Trigonometrico Sustitucion de t=2 senθ Β ( m, n )=2 ∫ (senθ )2m −1 ( cosθ)2 n−1 dθ
0
∞
m m p−1
Sustitucion de t= Β ( p , q )=∫ dm
1−m 0 (1+m)
p +q
Coordenadas a
r 2 ¿ a2 +b2 y tnθ=
polares b
( a , b )=(r . cosθ ,r . senθ)
( a , b )=(r , θ)
Grafica de a) Interseccion
coordenadas i) El eje polar θ=nπ , nϵZ
polares π π
ii) El eje :θ= + nπ ,nϵZ
2 2
iii) El polo r =0
b) Simetria
i) Eje polar: ( r , θ ) →( r ,−θ)
π
ii) Eje : ( r ,θ ) →(r , π−θ)
2
iii) Al Polo: ( r , θ ) →(−r ,θ)
c) Tabular
d) Graficar
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Funcion Gamma y BetaDocumento4 pagineFuncion Gamma y BetaNathalie Alejandra100% (1)
- AMASesion8 9Documento5 pagineAMASesion8 9Joan AirbagNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulario CalculoDocumento1 paginaFormulario CalculoAlejandro De La CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulario CuánticaDocumento10 pagineFormulario CuánticageneradorsuplenteNessuna valutazione finora
- Ayudanta 12Documento1 paginaAyudanta 12Martin CooperNessuna valutazione finora
- Señales y Sistemas 2da P.alvaradoDocumento463 pagineSeñales y Sistemas 2da P.alvaradoRandy ZamoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulario pc2Documento1 paginaFormulario pc2Cristopher Anthony Turpo GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Beta Function EsDocumento4 pagineBeta Function EsMaxi MaxiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cal2 Gu As I 2023 (5)Documento2 pagineCal2 Gu As I 2023 (5)cintia lizamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller 5Documento2 pagineTaller 5HarldValencia01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Problemas FísicaDocumento10 pagineProblemas FísicaJose MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas de Calculo 2Documento1 paginaFormulas de Calculo 2Juan David Caicedo TamayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cálculo II-Segundo 201815Documento5 pagineCálculo II-Segundo 201815Jikook KookminNessuna valutazione finora
- H2 Cal 2Documento6 pagineH2 Cal 2SHIGERU GONZALES CNessuna valutazione finora
- Practico 6 2022 SolDocumento6 paginePractico 6 2022 SolNat PanNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario Examen Parcial 2021-IiDocumento7 pagineSolucionario Examen Parcial 2021-IiNick S. Zegarra ChavezNessuna valutazione finora
- AMASesion10 11 1Documento6 pagineAMASesion10 11 1Joan AirbagNessuna valutazione finora
- EXAMEN SUSTITUTORIO-solucionario.Documento4 pagineEXAMEN SUSTITUTORIO-solucionario.Junior Ortega TurpoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hoja de Ejercicios 2Documento6 pagineHoja de Ejercicios 2César BocanegraNessuna valutazione finora
- Hoja 7 ResueltaDocumento10 pagineHoja 7 ResueltaGanso MansoNessuna valutazione finora
- PractA4 5Documento3 paginePractA4 5Jeremias SacchiNessuna valutazione finora
- Marco Teórico Act4, U2Documento3 pagineMarco Teórico Act4, U2Mariella LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Informe Calculo IIIDocumento4 pagineInforme Calculo IIILuis Fernando CárdenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Practico 8Documento3 paginePractico 8Mero1053Nessuna valutazione finora
- Calculo II Resumen Parcial 1-2Documento1 paginaCalculo II Resumen Parcial 1-2Estiven Garcia LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- PC1 2020.1Documento3 paginePC1 2020.1Neorgi O. GNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas Matematicas ExamenDocumento1 paginaFormulas Matematicas ExamenAnggie VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Facultad de Ingenier Ia Departamento de Matem Aticas, F Isica y Estad IsticaDocumento3 pagineFacultad de Ingenier Ia Departamento de Matem Aticas, F Isica y Estad IsticaMaria Alejandra Albornoz PovedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pauta Correccion Primera PruebaDocumento5 paginePauta Correccion Primera PruebaFelipe SantibáñezNessuna valutazione finora
- Curs 13 CTIDocumento7 pagineCurs 13 CTILucian RodjanNessuna valutazione finora
- MontecarloDocumento9 pagineMontecarloandyNessuna valutazione finora
- H2 Cal 2Documento7 pagineH2 Cal 2Walter SotoNessuna valutazione finora
- P. Dirigida 5Documento2 pagineP. Dirigida 5Daniela HinostrozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios de Teoría de La MedidaDocumento8 pagineEjercicios de Teoría de La MedidaCristian Adrian Cabrera PeñafielNessuna valutazione finora
- Pauta Certamen1 2016 DEF Mat 022 SPJEDocumento5 paginePauta Certamen1 2016 DEF Mat 022 SPJESiben de zastiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Guia 6Documento7 pagineGuia 6santanderb017Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formulario de Superficies PDFDocumento1 paginaFormulario de Superficies PDFGronexito Tolentino TarazonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario 1 PC 18 2 ModificasrDocumento7 pagineSolucionario 1 PC 18 2 Modificasrjair marinNessuna valutazione finora
- Apunte de Catedra - Integral de Linea en El Campo ComplejoDocumento17 pagineApunte de Catedra - Integral de Linea en El Campo ComplejoHenry Jose Cumana PolancoNessuna valutazione finora
- L Pez Ju Rez Emmanuel Tarea 4Documento4 pagineL Pez Ju Rez Emmanuel Tarea 4EMMANUEL LOPEZ JUAREZNessuna valutazione finora
- I3 SolucinDocumento3 pagineI3 SolucinMartin CooperNessuna valutazione finora
- Pract 8Documento5 paginePract 8Fer André WedderburnNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario Examen Parcial 2018-Ii PDFDocumento7 pagineSolucionario Examen Parcial 2018-Ii PDFAlex Cabrera LázaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework1 For STAT6202 2 PDFDocumento3 pagineHomework1 For STAT6202 2 PDFDiva's Hair StreNessuna valutazione finora
- Certamen Global - MAT022 (2008-2) PDFDocumento2 pagineCertamen Global - MAT022 (2008-2) PDFJohnny HuincahueNessuna valutazione finora
- Clase 5 2 1 EjerciciosDocumento3 pagineClase 5 2 1 EjerciciosAraceli PérezNessuna valutazione finora
- Mas 2020BDocumento8 pagineMas 2020BOSCO NEYRA LEIBNIZNessuna valutazione finora
- BMA02 SOL. Examen Sustitutorio 2023-IDocumento5 pagineBMA02 SOL. Examen Sustitutorio 2023-IFABRICIO ALEXANDER SARE VARGASNessuna valutazione finora
- Integracion Numerica PDFDocumento50 pagineIntegracion Numerica PDFMelisaBarraCasasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pauta de Pruebas Integrales DefinidasDocumento2 paginePauta de Pruebas Integrales DefinidasMAXIMILIANO ORTUZAR MARDONESNessuna valutazione finora
- Solucionario EPDocumento4 pagineSolucionario EPMaria RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Practico 4Documento2 paginePractico 4santiago iglesiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pauta Ayudantia 4 MAT024 2022-02Documento4 paginePauta Ayudantia 4 MAT024 2022-02Gabriel Retamal 4BNessuna valutazione finora
- Septiembre2013 IDocumento1 paginaSeptiembre2013 Ijosecarlos.camachoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios2 AFDocumento2 pagineEjercicios2 AFaldairslNessuna valutazione finora
- (Resuelto) AvE Junio 2020 PDFDocumento4 pagine(Resuelto) AvE Junio 2020 PDFImara Garcia JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Certamen 2 - MAT022 (2011-2) - StgoDocumento4 pagineCertamen 2 - MAT022 (2011-2) - StgoJeanDouglasCamposWachtendorffNessuna valutazione finora
- S09.s1-Clase 09Documento52 pagineS09.s1-Clase 09Jose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Gestión Cadena de ValorDocumento4 pagineGestión Cadena de ValorJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Tarea 03 - Análisis y Diseño de Sistemas de InformaciónDocumento6 pagineTarea 03 - Análisis y Diseño de Sistemas de InformaciónJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- GLOBALIZACIONDocumento8 pagineGLOBALIZACIONJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- S03 S1-MaterialDocumento17 pagineS03 S1-MaterialJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Análisis y Diseño de Sistemas de InformaciónDocumento2 pagineAnálisis y Diseño de Sistemas de InformaciónJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- S01 S2-MaterialDocumento27 pagineS01 S2-MaterialJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Sistemas DistribuidosDocumento45 pagineSistemas DistribuidosJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelo Programación Metas - Ejemplo 1Documento5 pagineModelo Programación Metas - Ejemplo 1Jose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- GEOPOLITICADocumento12 pagineGEOPOLITICAJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Gestion de La Cadena de ValoresDocumento4 pagineGestion de La Cadena de ValoresJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicio FCCSDocumento2 pagineEjercicio FCCSJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- S13.s1 Estado y Sociedad Material AlumnosDocumento12 pagineS13.s1 Estado y Sociedad Material AlumnosJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Desarrollo de SoftwareDocumento5 pagineDesarrollo de SoftwareJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- S03.s1 - MODELOS DE MADUREZ ORGANIZACIONALDocumento17 pagineS03.s1 - MODELOS DE MADUREZ ORGANIZACIONALJose Vasquez100% (1)
- S09.s1 - Implementación de Un Sistema deGCDocumento21 pagineS09.s1 - Implementación de Un Sistema deGCJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- HITD Examen FinalDocumento11 pagineHITD Examen FinalJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Matrices en C++Documento4 pagineMatrices en C++Jose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- GLOBALIZACIONDocumento8 pagineGLOBALIZACIONJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- PC03 Redes1 2020-1Documento2 paginePC03 Redes1 2020-1Jose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicio de VLSMDocumento9 pagineEjercicio de VLSMJose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Práctica Calificada N°01Documento1 paginaPráctica Calificada N°01Jose VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cap 5 - Valor PresenteDocumento12 pagineCap 5 - Valor PresenteLaura Alejandra GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Resumen Formulas Ingenieria EconomicaDocumento5 pagineResumen Formulas Ingenieria Economicasheila0517Nessuna valutazione finora
- UDocumento2 pagineURandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Generalidades Del SilogismoDocumento11 pagineGeneralidades Del SilogismoMariangel JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemas de VectoresDocumento1 paginaProblemas de VectoresLuis Angel Mandujano AllpoccNessuna valutazione finora
- Normalizacion Pau PDFDocumento25 pagineNormalizacion Pau PDFLeticiaCastilloSanzNessuna valutazione finora
- Saberes Matemáticas 6 - Unidad 5Documento53 pagineSaberes Matemáticas 6 - Unidad 5Eva Elisa Vásquez ErazoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sesión 01Documento40 pagineSesión 01Abel Alfio Martinez CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Actividad 3 GRAFICACIÓNDocumento11 pagineActividad 3 GRAFICACIÓNMiguel Antonio Alfaro100% (4)
- Lectura Logica MatematicaDocumento8 pagineLectura Logica MatematicaDIDIER FERNANDO GUERRERO SUMALAVENessuna valutazione finora
- Metodo de Interpolacion - ScribpDocumento20 pagineMetodo de Interpolacion - ScribpFaby GüemezNessuna valutazione finora
- Problemas de Estadistica DescriptivaDocumento184 pagineProblemas de Estadistica DescriptivaRaul Eros100% (1)
- Cartilla de Tecnologia Octubre 19Documento7 pagineCartilla de Tecnologia Octubre 19Jimena BeltranNessuna valutazione finora
- Tipos-Diseños de InvestigaciónDocumento14 pagineTipos-Diseños de InvestigaciónLidio Omar Villena CorahuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual de Uso de Fotografía Aérea y Cartografía Topográfica Agropecuaria Revisó - Líder Marcos Agropecuarios. ContenidoDocumento68 pagineManual de Uso de Fotografía Aérea y Cartografía Topográfica Agropecuaria Revisó - Líder Marcos Agropecuarios. ContenidoVera MauricioNessuna valutazione finora
- Guía de TP-Energia-Prof. Carlos Cruz - 2023Documento2 pagineGuía de TP-Energia-Prof. Carlos Cruz - 2023Tupac 2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- La Investigación Científica, InFORMEDocumento6 pagineLa Investigación Científica, InFORMEJose RengifoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cap - 7 Momentos InerciaDocumento26 pagineCap - 7 Momentos Inerciacamilo andres lazaro julioNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 5-6 COMPLETODocumento12 pagineTest 5-6 COMPLETOJacquelinne Cristina Rivera Ochoa100% (4)
- ANHÍDRIDOSDocumento3 pagineANHÍDRIDOSJhunior QuispeNessuna valutazione finora
- Planos y Posiciones AnatomicasDocumento3 paginePlanos y Posiciones AnatomicasAdela Nataly Tiul cuculNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 5Documento3 paginePaper 5christian rodasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios de Tamaño de MuestraDocumento5 pagineEjercicios de Tamaño de MuestraMaicol Ramos100% (1)
- Preguntas Semiabiertas TomaÌ S de AquinoDocumento2 paginePreguntas Semiabiertas TomaÌ S de AquinoSonia Nieto ConesaNessuna valutazione finora
- CircuferenciaDocumento2 pagineCircuferenciapalomaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nivel Avanzado - Nivel SecundariaDocumento128 pagineNivel Avanzado - Nivel Secundariamiguel angeito arcibia mendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Orffe Fasol - Canto y Flauta 24 JunioDocumento90 pagineOrffe Fasol - Canto y Flauta 24 JunioMiguel RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- RespuestasDocumento4 pagineRespuestasFrancisco CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambio de Correas Sistemas Auxiliares BMW E46 136 CVDocumento9 pagineCambio de Correas Sistemas Auxiliares BMW E46 136 CVleoper100% (7)
- Prueba3 Fisica 3 C PautaDocumento8 paginePrueba3 Fisica 3 C PautaAndres Rehbein MNessuna valutazione finora
- Había una vez el átomo: O cómo los científicos imaginan lo invisibleDa EverandHabía una vez el átomo: O cómo los científicos imaginan lo invisibleValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Guía práctica para la refracción ocularDa EverandGuía práctica para la refracción ocularValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- La teoría de casi todo: El modelo estándar, triunfo no reconocido de la física modernaDa EverandLa teoría de casi todo: El modelo estándar, triunfo no reconocido de la física modernaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (32)
- Armónicas en Sistemas Eléctricos IndustrialesDa EverandArmónicas en Sistemas Eléctricos IndustrialesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (12)
- El Tao de la física: Una exploración de los paralelismos entre la física moderna y el misticismo orientalDa EverandEl Tao de la física: Una exploración de los paralelismos entre la física moderna y el misticismo orientalValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Mentalidades matemáticas: Cómo liberar el potencial de los estudiantes mediante las matemáticas creativas, mensajes inspiradores y una enseñanza innovadoraDa EverandMentalidades matemáticas: Cómo liberar el potencial de los estudiantes mediante las matemáticas creativas, mensajes inspiradores y una enseñanza innovadoraValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (5)
- Didáctica de la matemática en la escuela primariaDa EverandDidáctica de la matemática en la escuela primariaValutazione: 2.5 su 5 stelle2.5/5 (3)
- Electricidad: Fundamentos y problemas de electrostática, corriente continua, electromagnetiDa EverandElectricidad: Fundamentos y problemas de electrostática, corriente continua, electromagnetiValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (5)
- Mi proyecto escolar Matemáticas Lúdicas: Adaptaciones curriculares para preescolar, primaria y secundariaDa EverandMi proyecto escolar Matemáticas Lúdicas: Adaptaciones curriculares para preescolar, primaria y secundariaValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- El principio de posibilidad: Cómo la física cuántica puede mejorar tu forma de pensar, vivir y amarDa EverandEl principio de posibilidad: Cómo la física cuántica puede mejorar tu forma de pensar, vivir y amarValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- Razonamiento Lógico Matemático para la toma de decisionesDa EverandRazonamiento Lógico Matemático para la toma de decisionesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (8)
- La Teoría de Conjuntos y los Fundamentos de las MatemáticasDa EverandLa Teoría de Conjuntos y los Fundamentos de las MatemáticasValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Modelamiento y simulación de sistemas con Simulink: Aplicaciones en ingeniería estructuralDa EverandModelamiento y simulación de sistemas con Simulink: Aplicaciones en ingeniería estructuralValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Fundamentos de matemática: Introducción al nivel universitarioDa EverandFundamentos de matemática: Introducción al nivel universitarioValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (9)
- Física cuántica para principiantes: Descubra los fundamentos de la mecánica cuántica y cómo afecta al mundo en que vivimos a través de todas sus teorías más famosasDa EverandFísica cuántica para principiantes: Descubra los fundamentos de la mecánica cuántica y cómo afecta al mundo en que vivimos a través de todas sus teorías más famosasValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- Fundamentos de mecánica de fluidos.: Con ejercicios parcialmente resueltosDa EverandFundamentos de mecánica de fluidos.: Con ejercicios parcialmente resueltosNessuna valutazione finora
























































































































![Diseño de Experimentos [Métodos y Aplicaciones]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/436271314/149x198/596c96deb2/1654336147?v=1)













