Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Science
Caricato da
Er Purushottam PalTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Science
Caricato da
Er Purushottam PalCopyright:
Formati disponibili
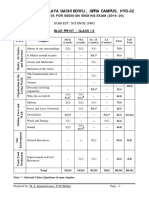
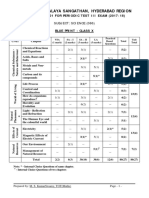
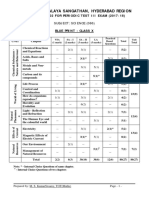
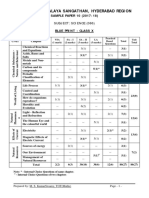
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, GPRA CAMPUS, HYD–32
SAMPLE PAPER 08 (2019-20)
SUBJECT: SCIENCE (086)
BLUE PRINT : CLASS X
MCQ VSA SA LA Unit
UNIT Chapter (1 mark) (1 mark) (3 marks) (5 marks)
Total
Total
Chemical Reactions and
1(1) -- 3(1) -- 4(2)
Chemical Substances -
Nature and Behaviour
Equations
Acids, Bases and Salts 1(1) -- 3(1)* -- 4(2)
Metals and Non-metals -- -- -- 5(1)* 5(1) 25(11)
1(1)
Carbon and its compounds -- -- 5(1) 7(3)
1(1)AR
Periodic Classification of
1(1)* 1(1) 3(1) -- 5(3)
Elements
Life Process -- -- 3(1) 5(1) 8(2)
World of Living
Control and Coordination 2(2) 2(2) 3(1) -- 7(5)
23(9)
How do organisms
-- -- -- 5(1)* 5(1)
reproduce?
Heredity and Evolution -- -- 3(1) -- 3(1)
Light - Reflection and
Phenomena
-- -- 3(1) 3(1)
Natural
Refraction
5(1)* 12(4)
The Human Eye and the
1(1)* -- 3(1)* 9(3)
colourful world
Effects of
Electricity 2(2) -- -- 5(1) 7(3)
Current
13(7)
Magnetic Effects of Electric 2(2)
-- 3(1) -- 6(4)
Current 1(1)AR
Sources of energy 1(1) 2(2) -- -- 3(3)
Resources
Natural
Our Environment -- -- 3(1)* -- 3(1) 7(5)
Management of Natural
1(1)* -- -- -- 1(1)
Resources
Total 10(10) 10(10) 30(10) 30(6) 80(36) 80(36)
Note: * - Internal Choice Questions of same chapter.
AR
– Assertion, Reason based question
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 1 -
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI, GPRA CAMPUS, HYD–32
SAMPLE PAPER 08 (2019-20)
SUBJECT: SCIENCE MAX. MARKS : 80
CLASS : X DURATION : 3 HRS
General Instructions:
1. The question paper comprises three sections – A, B and C. Attempt all the sections.
2. All questions are compulsory.
3. Internal choice is given in each section.
4. All questions in Section A are one-mark questions comprising MCQ, VSA type and assertion-reason
type questions. They are to be answered in one word or in one sentence.
5. All questions in Section B are three-marks, short-answer type questions. These are to be answered in
about 50 - 60 words each.
6. All questions in Section C are five-marks, long-answer type questions. These are to be answered in about
80 – 90 words each.
7. This question paper consists of a total of 30 questions.
SECTION – A
1. A dilute ferrous sulphate solution was gradually added to the beaker containing acidified
permanganate solution. The light purple colour of the solution fades and finally disappears.
Which of the following is the correct explanation for the observation?
(a) KMnO4 is an oxidising agent, it oxidises FeSO4
(b) FeSO4 acts as an oxidising agent and oxidises KMnO4
(c) The colour disappears due to dilution; no reaction is involved
(d) KMnO4 is an unstable compound and decomposes in presence of FeSO4 to a colourless
compound.
2. What happens when a solution of an acid is mixed with a solution of a base in a test tube?
(i) The temperature of the solution increases
(ii) The temperature of the solution decreases
(iii) The temperature of the solution remains the same
(iv) Salt formation takes place
(a) (i) only (b) (i) and (iii) (c) (ii) and (iii) (d) (i) and (iv)
3. Opposition to the constrution of large dams is due to
(a) social reasons (b) economic reasons
(c) enviromental reasons (d) all the above
OR
Khadins, Bundhis, Ahars and Kattas are ancient structures that are examples for
(a) grain storage (b) wood storage
(c) water harvesting (d) soil conservation
4. In an electrical circuit three incandescent bulbs A, B and C of rating 40 , 60 and 100
respectively are connected in parallel to an electric source. Which of the following is likely to
happen regarding their brightness?
(a) Brightness of all the bulbs will be the same
(b) Brightness of bulb A will be the maximum
(c) Brightness of bulb B will be more than that of A
(d) Brightness of bulb C will be less than that of B
5. An electric kettle consumes 1 kW of electric power when operated at 220 V. A fuse wire of what
rating must be used for it?
(a) 1 A (b) 2 A (c) 4 A (d) 5 A
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 2 -
6. The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles
(a) are relaxed and lens becomes thinner
(b) contract and lens becomes thicker
(c) are relaxed and lens becomes thicker
(d) contract and lens becomes thinner
OR
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) A person with myopia can see distant objects clearly
(b) A person with hypermetropia can see nearby objects clearly
(c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly
(d) A person with hypermetropia cannot see distant objects clearly
7. Which of the following statements about the Modern Periodic Table is correct:
(a) It has 18 horizontal rows known as Periods (b) It has 7 vertical columns known as Periods
(c) It has 18 vertical columns known as Groups (d) It has 7 horizontal rows known as Groups
OR
The elements A, B, C, D and E have atomic number 9, 11, 17, 12 and 13 respectively. Which
pair of elements belong to the same group?
(a) A and B (b) B and D (c) A and C (d) D and E
8. Choose the incorrect statement
(a) We are encouraged to plant more trees so as to ensure clean environment and also provide
bio-mass fuel
(b) Gobar-gas is produced when crops, vegetable wastes etc., decompose in the absence of
oxygen
(c) The main ingredient of bio-gas is ethane and it gives a lot of smoke and also produces a lot of
residual ash
(d) Bio-mass is a renewable source of energy
9. On moving from left to right in the second period what happens to the number of valence
electrons?
10. Draw the structure of butanone molecule, CH3COC2H5.
11. Question number 11(i)-11(iv) are based on context and table given below. Study the context
and answer the following questions.
(a) Aditya is a student of 10th standard. He went to a remote area of Rajasthan for trekking with
his friends. Aditya found that it was a sparsely inhabited area. He was surprised to know that
there was still no electricity in this area. The people used kerosene oil lamps to light up their
homes at night and there were no street lights. The children also had to study with kerosene
lamps at night. The village farmers used diesel to run irrigation pumps. Actually, there were no
power transmission lines which could bring electricity to this remote area. Aditya was really
disturbed by the living conditions of the people in this part of Rajasthan. One day Aditya
gathered all the people of village in the village school. He told them that if they put pressure on
their area MLAs and MP for making available the required funds, then he could tell them about
the devices to light up their homes and streets at night, play radio and television and also run
irrigation pumps with electricity without there being power transmission lines. All the people
agreed and Aditya described them the devices to get electricity in their area in detail. The village
people were very happy to know this and soon they got electricity in their area.
11(i) What was the device described by Aditya to the village people to obtain electricity locally?
11(ii) What source of energy is made use of in this device to obtain electricity?
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 3 -
(b) A DC generator also called a DC dynamo converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
(DC). It works on the principle that when a coil rotates in a uniform magnetic field, a current is
induced in the coil. The direction of induced current is determined by Fleming's right hand rule.
The schematic diagram of a DC generator is as shown in figure.
11(iii) What type of dynamo is used in a bicycle?
11(iv) A DC motor is rotating in clockwise direction. How can the direction of rotation be
reversed?
12. Answer question numbers 12(i)-11(iv) on the basis of your understanding of the following
paragraph and the related studied concepts.
Different plant hormones help to coordinate growth, development and responses to the
environment. They are synthesized at places away from where they act and simply diffuse to the
area of action. When growing plants detect light, a hormone called auxin, synthesized at the
shoot tip, helps the cells to grow longer. When light is coming from one side of the plant, auxin
diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to
grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light. Thus, the plant appears to bend
towards light.
Another example of a plant hormone is gibberellins which, like auxins, help in the growth of the
stem. Cytokinins promote cell division, and it is natural then that they are present in greater
concentration in areas of rapid cell division, such as in fruits and seeds. These are examples of
plant hormones that help in promoting growth. But plants also need signals to stop growing.
Abscisic acid is one example of a hormone which inhibits growth. Its effects include wilting of
leaves.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 4 -
12(i) What do plant hormones do?
12(ii) What hormone inhibits the growth of a plant?
12(iii) Which hormone is synthesized at the at the shoot tip?
(a) auxin (b) gibberellins (c) Cytokinins (d) Abscisic acid
12(iv) Which hormone stimulates the growth of the stem?
(a) auxin (b) gibberellins (c) Cytokinins (d) Abscisic acid
For question numbers 13 and 14, two statements are given- one labeled Assertion (A) and
the other labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) as given below
i) Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
ii) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
iii) A is true but R is false.
iv) A is false but R is true.
13. Assertion (A): Acetic acid is less acidic than alcohol.
Reason (R): The ion formed after the removal of proton from acetic acid is less stable.
14. Assertion (A): Lenz’s law violates the principle of conservation of energy.
Reason (R): Induced e.m.f. always opposes the change in magnetic flux responsible for its
production.
SECTION – B
15. When you have mixed the solutions of lead(II) nitrate and potassium iodide.
(a) What was the colour of the precipitate formed and can you name the precipitate ?
(b) Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction.
(c) Is this also a double displacement reaction?
16. Why is atomic number considered to be a more appropriate parameter than atomic mass for the
classification of elements in a periodic table? How does the metallic character of elements vary
as we move (i) from left to right in a period, and (ii) top to bottom in a group in the modern
periodic table? Give reasons to justify your answers.
17. Draw a diagram of human alimentary canal and label on it: Oesophagus, Gallbladder, Liver and
Pancreas.
18. (a) The pH of soil A is 7.5 while that of soil B is 4.5. Which of the two soils A or B should be
treated with powdered chalk to adjust its pH and why?
(b) Explain how the pH change in the river water can endanger the lives of aquatic animals like
fish?
OR
(a) State the chemical properties on which the following uses of baking soda are based:
(i) as an antacid
(ii) as soda-acid fire extinguisher
(iii) to make bread and cake soft and spongy.
(b) How washing soda is obtained from baking soda? Write balanced chemical equation.
19. List any three factors and mention how they could lead to the rise of a new species.
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 5 -
20. (a) If the image formed by a mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always
diminished, erect and virtual, state the type of the mirror and also draw a ray diagram to justify
your answer.
(b) Define the radius of curvature of spherical mirrors. Find the nature and focal length of a
spherical mirror whose radius of curvature is +24 cm.
21. Define ‘hormones’. Name the hormone secreted by thyroid. Write its function. Why is the use of
iodised salt advised to us?
22. Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances with the help of one
example for each. List two changes in habit that people must adopt to dispose non-biodegradable
waste, for saving the environment.
OR
(a)What is meant by food chain?
(b) Give reason to justify the following:
(i) The existence of decomposers is essential in a biosphere.
(ii) The number of trophic levels in a food chain is limited.
23. Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning? Will this phenomenon be observed by an
observer on the moon? Justify your answer with a reason.
OR
When we place a glass prism in the path of a narrow beam of white light, a spectrum is obtained.
What happens when a second identical prism is placed in an inverted position with respect to the
first prism? Draw a labelled ray diagram to illustrate it.
24. Why is pure iron not used for making permanent magnets? Name one material used for making
permanent magnets. Describe how permanent magnets are made electrically.
SECTION – C
25. (a) What are hydrocarbons? Write the general formula of (i) saturated hydrocarbons, and (ii)
unsaturated hydrocarbons and draw the structure of one hydrocarbon of each type.
(b) Explain, giving reason, why carbon neither forms C4+ cations nor C4− anions, but forms
covalent compounds which are bad conductors of electricity and have low melting point and low
boiling point.
26. (a) Why is the magnification produced by a concave lens always less than 1?
(b) You are provided with two lenses of focal lengths 10 cm and 20 cm. Which of the two lenses
would you suggest to obtain greater convergence of refracted light? Justify your choice.
(c) An image 2/3rd the size of object is formed by a convex lens at a distance of 12 cm from it.
Find the focal length of the lens.
OR
(a) Write the functions of each of the following parts of the human eye:
(i) Cornea (ii) Iris (iii) Crystalline (Eye) lens (iv) Ciliary muscles (v) Retina
(b) A person is unable to see distinctly the objects closer than 1 m. Name the defect of vision he
is suffering from. Draw ray diagrams to illustrate the cause of the defect and its correction by
suitable lens.
27. (a) Explain how does the exchange of gases occur in plants across the surface of stems, roots and
leaves.
(b) How are water and minerals transported in plants ?
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 6 -
28. (a) What are sexually transmitted diseases? Name four such diseases. Which one of them
damages the immune system of human body?
(b) State one mode of transmission of this disease. Explain in brief one measure for the
prevention of this disease.
OR
State in brief the changes that take place in a fertilised egg (zygote) till birth of the child in the
human female reproductive system. What happens to the egg when it is not fertilised?
29. (a) Give two methods to prevent the rusting of iron.
(b) Name the ores of the following metals:
(i) mercury, and (ii) zinc
(c) Explain with the help of a diagram, how copper metal can be refined? Label the important
arrangements in the experimental set up.
OR
(a) Distinguish between ‘roasting’ and ‘calcination’. Which of these two is used for sulphide ores
and why?
(b) Write a chemical equation to illustrate the use of aluminium for joining cracked railway lines.
(c) Name the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte used in the electrolytic refining of impure
copper.
30. (a) What does the electric circuit mean?
(b) Distinguish between an open and a closed circuit.
(c) Find out the reading of ammeter and voltmeter in the circuit given below :
Prepared by: M. S. KumarSwamy, TGT(Maths) Page - 7 -
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocumento7 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: Sciencehweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocumento8 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020Documento7 pagineScience Class X Sample Paper 04 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Documento6 pagineScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020CharuNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2020Documento7 pagineScience Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Documento6 pagineScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2020Gowtham LNessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocumento7 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020Documento7 pagineScience Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020SubhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocumento7 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper 08: Science Class XDocumento5 pagineSample Paper 08: Science Class XKamal0% (1)
- Science Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Documento5 pagineScience Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03Documento6 pagineScience Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam 2020 Sample Paper 03darshan8422Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01Documento5 pagineScience Class X Periodic Test III Sample Paper 01hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2019Documento5 pagineScience Class X Sample Paper 01 For Board Exam 2019KamalNessuna valutazione finora
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER FOR PERIODIC TEST IIIDocumento5 pagineKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER FOR PERIODIC TEST IIIhweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocumento5 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SCIENCE SAMPLE PAPERDocumento5 pagineKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SCIENCE SAMPLE PAPERrajman1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Documento5 pagineScience Class Ix Periodic Test III Sample Paper 03Trust In godNessuna valutazione finora
- 1095549296science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Documento5 pagine1095549296science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 01Abhishek JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 09 (2017-18Documento5 pagineKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 09 (2017-18hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocumento5 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173100% (1)
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocumento5 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02Documento5 pagineScience Class Ix Sessing Ending Final Exam Sample Paper 02darshan8422Nessuna valutazione finora
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 02 (2017-18Documento5 pagineKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 02 (2017-18hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: ScienceDocumento5 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Sangathan, Hyderabad Region: Subject: Sciencehweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 08 (2017-18Documento5 pagineKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 08 (2017-18BHARAT kommanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2018Documento5 pagineScience Class X Sample Paper 05 For Board Exam 2018Maruti AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Blue PrintDocumento1 paginaBiology Blue Printaniketyadav122311Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Class Xii Blue Prints For Board Exam 2023Documento1 paginaChemistry Class Xii Blue Prints For Board Exam 2023aniketyadav122311Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science BP PB1Documento1 paginaScience BP PB1ashly BTS (sushi)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01Documento3 pagineScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 01garNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 ScienceDocumento1 pagina8 ScienceMegha TalukdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Chem EngDocumento3 paginePhy Chem Engnrupesh.kumar.mohanty28031Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blue Print CHEMISTRY SEE 2023-24 AGRA REGIONDocumento2 pagineBlue Print CHEMISTRY SEE 2023-24 AGRA REGIONVanshNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Documento3 pagineScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Documento3 pagineScience Class Ix Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Anonymous TvppppNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Documento4 pagineScience Class Viii Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03Kajal GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Class XII Sample PapersDocumento111 pagineClass XII Sample PapersDhruv VigNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03Documento3 pagineScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 03hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Merge 01Documento7 pagineMerge 01nrupesh.kumar.mohanty28031Nessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class VII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01Documento4 pagineScience Class VII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01soni.satindraNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02Documento4 pagineScience Class VIII Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02sparsh bagalNessuna valutazione finora
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGTHAN JAMMU REGION PRE BOARD -1( 2022-23) CLASS – XII CHEMISTRY (043) SET-1 BLUE PRINTDocumento1 paginaKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGTHAN JAMMU REGION PRE BOARD -1( 2022-23) CLASS – XII CHEMISTRY (043) SET-1 BLUE PRINTshivanandNessuna valutazione finora
- BP Maths Ix See 2022 23Documento1 paginaBP Maths Ix See 2022 23Chirag PadhiyarNessuna valutazione finora
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER 01 FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAM SCIENCE CLASS XDocumento5 pagineKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER 01 FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAM SCIENCE CLASS Xhweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9th CBSE Blue PrintDocumento2 pagineClass 9th CBSE Blue PrintYash BawiskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Something From My FilesDocumento1 paginaSomething From My Filesankitajamatia06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class Xii - Chemistry - BPDocumento1 paginaClass Xii - Chemistry - BPsarodeabhishek21Nessuna valutazione finora
- SCIDocumento2 pagineSCIDeepika KarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Blue Print Final Paper Class 11TH ChemistryDocumento1 paginaBlue Print Final Paper Class 11TH ChemistryDevansh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 11Documento2 paginePhysics 11RishabhNessuna valutazione finora
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAMDocumento4 pagineKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN SAMPLE PAPER FOR PERIODIC TEST II EXAMhweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 6 SA1 Science Model Question PaperDocumento8 pagineCBSE Class 6 SA1 Science Model Question PaperDhrutiNessuna valutazione finora
- LFSC 2020 Gr10 Memo Nov Decmopani East DistrictDocumento6 pagineLFSC 2020 Gr10 Memo Nov Decmopani East Districtdeveloping habit and lifestyle of praise and worshNessuna valutazione finora
- Maths Basic Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020Documento6 pagineMaths Basic Class X Sample Paper 06 For Board Exam 2020Dharmendra SankhlaNessuna valutazione finora
- G.C.E. (O.L.) Support Seminar - 2016: Science IDocumento14 pagineG.C.E. (O.L.) Support Seminar - 2016: Science ISandamali PereraNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02Documento4 pagineScience Class X Periodic Test II Sample Paper 02hweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blueprint, See, XiDocumento1 paginaBlueprint, See, XikavisanjurohillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Xi PhysicsDocumento1 paginaXi PhysicsjollygalileoNessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocumento7 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution: Career InstituteDocumento2 pagineEvolution: Career InstituteEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution: Career InstituteDocumento1 paginaEvolution: Career InstituteEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution: Career InstituteDocumento2 pagineEvolution: Career InstituteEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution: Career InstituteDocumento2 pagineEvolution: Career InstituteEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceDocumento7 pagineKendriya Vidyalaya Gachibowli, Gpra Campus, Hyd-32: Subject: ScienceEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus Changes for Biology, Chemistry and Computer Science (2020-21Documento9 pagineSyllabus Changes for Biology, Chemistry and Computer Science (2020-21AnantNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOLOGY (Code No. 044) 2020-21Documento13 pagineBIOLOGY (Code No. 044) 2020-21innovative studiesNessuna valutazione finora
- G A L S: MetallurgyDocumento24 pagineG A L S: MetallurgyEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Brochure PDFDocumento2 pagineBrochure PDFEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Aieea 2020 PDFDocumento1 paginaAieea 2020 PDFSreenivasa PaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of a Student Project on Visiting a Handicraft UnitDocumento31 pagineAnalysis of a Student Project on Visiting a Handicraft UnitEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Alumni 2019Documento4 pagineAlumni 2019Er Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Date Subject English Hindi Science Mathematics Social Science Feb. 26, 2020 Feb. 29, 2020 Arch 04, 2 M 020 Arch 12, 2 M 020 C Mar H 18, 2020Documento2 pagineDate Subject English Hindi Science Mathematics Social Science Feb. 26, 2020 Feb. 29, 2020 Arch 04, 2 M 020 Arch 12, 2 M 020 C Mar H 18, 2020Er Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Haloalkane Haloarenes by KetanDocumento32 pagineHaloalkane Haloarenes by KetanEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- By: - Er. Purushottam Pal Formula BookletDocumento12 pagineBy: - Er. Purushottam Pal Formula BookletEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- NEET UG Biology Transport in PlantsDocumento17 pagineNEET UG Biology Transport in PlantsEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Google Scholar - WikipediaDocumento8 pagineGoogle Scholar - WikipediaEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- 2D MotionDocumento33 pagine2D MotionEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento12 pagineMultiple Choice Questionsdevli falduNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 English Sample Paper 2020 Set 1 Solved PDFDocumento6 pagine9 English Sample Paper 2020 Set 1 Solved PDFEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Gaseous State Theory Final EDocumento10 pagine01 Gaseous State Theory Final EEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 MathsDocumento2 pagine12 MathsEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-VIII Chapter-8. Animal Husbandary and Plant BreedingDocumento6 pagineUnit-VIII Chapter-8. Animal Husbandary and Plant BreedingEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Alumni 2019Documento4 pagineAlumni 2019Er Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - Plant Diversity PDFDocumento160 pagineModule 1 - Plant Diversity PDFDasari krishna chanduNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic Counselling: Chaitanya.P Ii Mds Dept of Public Health DentistryDocumento72 pagineGenetic Counselling: Chaitanya.P Ii Mds Dept of Public Health DentistryEr Purushottam PalNessuna valutazione finora
- XL T PDFDocumento5 pagineXL T PDFSheelendra Mangal BhattNessuna valutazione finora
- Asuudaltai - MYP by Concept 4 5 - Physics by Paul MorrisDocumento679 pagineAsuudaltai - MYP by Concept 4 5 - Physics by Paul Morrisxcvd xcvd0% (1)
- UNN Past Questions (MED)Documento250 pagineUNN Past Questions (MED)Black arab GaladimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan GuideDocumento8 pagineLesson Plan GuideKharyl GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Reading Ni Putu Anastasia Diana Yanti 112019249Documento8 pagineJournal Reading Ni Putu Anastasia Diana Yanti 112019249andi siregarNessuna valutazione finora
- 0625 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocumento7 pagine0625 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersHira MajidNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Still Photography 106Documento35 pagineNotes Still Photography 106Diya KapoorNessuna valutazione finora
- This Study Resource Was: Ch.1: Film As Art: Creativity, Technology, and BusinessDocumento7 pagineThis Study Resource Was: Ch.1: Film As Art: Creativity, Technology, and BusinessMax SinrichNessuna valutazione finora
- Certificate: Study of Eye DiseasesDocumento20 pagineCertificate: Study of Eye DiseasesDhruvNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of Microscope: Eyepiece Lens: TubeDocumento4 pagineParts of Microscope: Eyepiece Lens: TubeRegienald PuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Honeywell Uvex Clear - BrochureDocumento4 pagineHoneywell Uvex Clear - BrochureLuis Angel Sierra BeltranNessuna valutazione finora
- Math 350 Study Guide 5Documento5 pagineMath 350 Study Guide 5Krizia Jenuel G. BacalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Test Bank For Hdev 6th Edition Rathus PDF Full ChapterDocumento36 pagineFull Download Test Bank For Hdev 6th Edition Rathus PDF Full Chapterconvolve.trunkedh95op100% (12)
- Articles For Magazine - MAPAGKAWANGGAWADocumento9 pagineArticles For Magazine - MAPAGKAWANGGAWANikclausse MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- White Paper General 4th 2015Documento48 pagineWhite Paper General 4th 2015john BronsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Science XDocumento12 pagineScience Xartika.ashuNessuna valutazione finora
- SSTDocumento2 pagineSSTkWaNgyANessuna valutazione finora
- Telescopes TontarraDocumento20 pagineTelescopes Tontarrag5quadNessuna valutazione finora
- JEE Main Online Question Papers & Answer Keys (2014-2017) Export PDFDocumento46 pagineJEE Main Online Question Papers & Answer Keys (2014-2017) Export PDFashish reddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometrical Optics NotesDocumento17 pagineGeometrical Optics NotesOzzy Calibo100% (3)
- LAB EXERCISE 2 Microscope AssDocumento5 pagineLAB EXERCISE 2 Microscope AssArianne Jans MunarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers To Review ScienceDocumento2 paginePointers To Review Sciencederapite.ceeNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics P2 March 23 QPDocumento16 paginePhysics P2 March 23 QPMuhammad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Form 4 SPM P2Documento22 paginePhysics Form 4 SPM P2Rui Shan LiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex LensDocumento18 paginePhysics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex Lenscarl pintoNessuna valutazione finora
- eALOM PysicsPracBookDocumento113 pagineeALOM PysicsPracBookRochana SasmithaNessuna valutazione finora
- NTSE Stage 1 Jharkhand Solved Paper 2014 PDFDocumento34 pagineNTSE Stage 1 Jharkhand Solved Paper 2014 PDFAbhinav PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Wind energy production in Tamil NaduDocumento10 pagineWind energy production in Tamil NaduSayandip RoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental Examination of Light Pressure - Annalen Der Physik - Pyotr Lebedev - 1901 - EnglishDocumento26 pagineExperimental Examination of Light Pressure - Annalen Der Physik - Pyotr Lebedev - 1901 - EnglishadnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sira Engineers Training Study MaterialDocumento14 pagineSira Engineers Training Study MaterialSujith KunjumonNessuna valutazione finora
- Photographer's Companion - User GuideDocumento96 paginePhotographer's Companion - User GuideAntonio Jorge ValerioNessuna valutazione finora