Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CHM12-3L Final Report 5
Caricato da
Paul Javen0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
11 visualizzazioni3 pagineExperiment 5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoExperiment 5
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
11 visualizzazioni3 pagineCHM12-3L Final Report 5
Caricato da
Paul JavenExperiment 5
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
Objectives:
1. To assemble a voltaic cell.
2. To illustrate the electrochemical nature of corrosion of iron.
3. To demonstrate cathodic protection.
Interpretation of Results
Our data showed that the zinc sulfate is the anode and the copper sulfate was the cathode.
Anode and cathode are defined by the flow of current. Cathodes are negatively charged
electrodes the source of electrons or an electron donor. It accepts or attracts cations (positive
charges). Anodes are positively charged electrodes that attracts electrons or anions. Anodes are
source of positive charges or an electron acceptor.
Apparently, the zinc electrode became oxidized. Oxidation occurs when a reactant loses
electrons during the reaction. The copper electrode is reduced. Reduction occurs when a
reactant gains electrons during the reaction. Visually, the zinc electrode became thinner and
the copper electrode became thicker.
Upon testing the products of corrosion of iron, we observed that the Fe 2+ ion reacted with
potassium ferricyanide was deep blue/navy blue. Adding phenolphtalein was added to the
solution that contained OH- gave a pinkish-purple hue to it. This is caused by corrosion.
Corrosion is a process where it converts a refined metal to a more stable form with the
environment such as oxides, hydroxides, or sulfides. Oxidation happens and it subjects the
metal to gradual destruction. When the solution is combined with potassium ferricyanide,
reduction happens because it gains electrons. And when the other solution is combined with
phenolphtalein, oxidation happened because it losed electrons. This was observed through the
color change, indicating the respective reactions.
Redox sites and cathodic protection was shown as an experiment on nails layed with cotton on
two seprate petri-dishes; and nails were straight and bent. We observed that oxidation took
place at the tip and middle of the bent nail, while it took place at the tip and end part of
unbent nail. Reduction took place at the tip of the unbent iron, while it also took place in the
middle part of the bent iron. Upon generalizing the effect of metal straight to corrosion of iron,
metal strain causes more chances of corrosion in iron.
Cathodic protection is for protection of iron against corrosion. We are asked which of the two
metals, magnesium or copper, can be used to protect the iron. We found out that magnesium
protects the iron because upon referring to the activity series of metals, magnesium more
active than copper. Therefore, it acts as a sacrificial anode. Sacrificial anodes are metals that are
oxidized more quickly. Hence, saving the refined metal.
Conclusion:
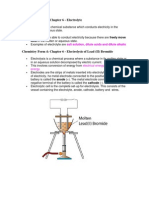
On the first part of this experiment, we observed that the RedOx reaction (Zinc-Copper Voltaic
Cell), generates electricity made up of two half-cells. This acts pretty much like a battery. It is
joined by a salt bridge (the U-shaped tube) that gives way to the flow of electrons upon the
half-cells, zinc and copper. Voltaic cells are consist of two half-cells, such that the electrode of
one half-cell is composed of a some metal, x. And the other electrode of the half-cell is metal y.
Metal x is the anode that oxidizes or losses and electron where in y is the cathode that reduces
or gains an electron.
Second part of the experiment pertains to demonstrating the electrochemical nature of the
corrosion of iron. We define corrosion as the natural process in metals that decreases their
energy states by losing electrons due to natural oxidizers in the environment. Therefore, this
makes them more chemically stable: decreasing activity. On the bad side of corrosion, this
weakens the metal physically.
Cathodic protection is a way of shielding the metal against corrosion. This is done by directing
the oxidation reaction at the anodes, therefore blocking (or minimizing) corrosion of the
cathodes. There are a few ways of protecting the cathodes against corrosion. A few tips will be
using sacrificial anodes: an alloy with a more active metal (galvanizing or some alloys
combination such as zinc and magnesium) or applying paint as protective coating.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 0007190-Fundamentals of Corrosion and Corrosion Control ForDocumento25 pagine0007190-Fundamentals of Corrosion and Corrosion Control ForPDHLibraryNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion (Study Material)Documento8 pagineCorrosion (Study Material)SANDEEP NAYAKNessuna valutazione finora
- Shipwrecks Corrosion and Conservation SummaryDocumento11 pagineShipwrecks Corrosion and Conservation SummaryChris Johnson100% (1)
- Lecture8-Environmental Degradation and Material SelectionDocumento29 pagineLecture8-Environmental Degradation and Material SelectionRUGERO KeslyneNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Informatory ProjectDocumento7 pagineChemistry Informatory ProjectGaming WorldNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemical Industries' ImpactsDocumento4 pagineElectrochemical Industries' ImpactsSally ChewNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 AWT Corrosion ControlDocumento72 pagine04 AWT Corrosion ControlTony NietoNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion Process & TypesDocumento38 pagineCorrosion Process & TypesArchit MadaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Effects of Electric CurrentDocumento4 pagineChemical Effects of Electric CurrentTanishq SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lyle James BanoDocumento3 pagineLyle James BanoMichael BalindanNessuna valutazione finora
- Metals and Non Metals NotesDocumento3 pagineMetals and Non Metals NotesVUDATHU SHASHIK MEHERNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 1 CorrosionDocumento6 pagineSection 1 CorrosionOmar DhiebNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolysis PDFDocumento13 pagineElectrolysis PDFShaikh Irad100% (1)
- Galvanic Corrosion Cells: Understanding Potential Differences Between MetalsDocumento5 pagineGalvanic Corrosion Cells: Understanding Potential Differences Between MetalsAdnan Choirul ANessuna valutazione finora
- محاضرة تاكل الأولىDocumento8 pagineمحاضرة تاكل الأولىHmid AljbreNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry corrosion engineeringDocumento2 pagineChemistry corrosion engineeringRheymarkbutron RamadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tarnish Corrosion Mouth MetalsDocumento3 pagineTarnish Corrosion Mouth MetalsangelrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Chemistry-II 2 MARKSDocumento11 pagineEngineering Chemistry-II 2 MARKSViswa NathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 Eng - ChemistryDocumento32 pagineModule 3 Eng - Chemistrypythondef2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity and ChemistryDocumento10 pagineElectricity and ChemistrybiancaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolysis Grade 9 Science LessonDocumento6 pagineElectrolysis Grade 9 Science LessonSwarnapaliliyanageNessuna valutazione finora
- Metal Coupling On Rusting of IronDocumento16 pagineMetal Coupling On Rusting of IronDakshya ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- ASDFDocumento8 pagineASDFrajesh2ndNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion Lab ConclusionDocumento5 pagineCorrosion Lab ConclusionDiane Iloveyou LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - Iii: Electrochemical Cells and CorrosionDocumento25 pagineUnit - Iii: Electrochemical Cells and Corrosion320126512165 VSAICHARANGUPTANessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion PDFDocumento92 pagineCorrosion PDFヤシール マドリードNessuna valutazione finora
- Cover Page With Pages RemovedDocumento24 pagineCover Page With Pages RemovedNikitha MPNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 AWT Corrosion Control PDFDocumento72 pagine04 AWT Corrosion Control PDFCarlos NeiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosionscienceroshni 180423175407Documento26 pagineCorrosionscienceroshni 180423175407MohankumarNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectroplatingDocumento5 pagineElectroplatingPraneet PokhriyalNessuna valutazione finora
- M3 pdf (2)Documento19 pagineM3 pdf (2)Veda BalajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee DraftDocumento10 pagineEe DraftHarshavarthini AnanthasayananNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion: Six Group: Hanif Ardianto Yelsi Sasmita Fara Gita Afifah Putri (121180170)Documento11 pagineCorrosion: Six Group: Hanif Ardianto Yelsi Sasmita Fara Gita Afifah Putri (121180170)Gita AfifahNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolysis NotesDocumento11 pagineElectrolysis NotesMichaela PowellNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - ElectrochemicalDocumento29 pagineChapter 2 - ElectrochemicalEDU Academic Programs CoordinatorNessuna valutazione finora
- Rusting Is A Chemical Process ThatDocumento5 pagineRusting Is A Chemical Process ThatGopal GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module-3 ProbabilityDocumento37 pagineModule-3 Probabilitythu broNessuna valutazione finora
- Galvanic CorrosionDocumento9 pagineGalvanic Corrosionesakkibabu19870% (1)
- Electrochemistry and Redox ReactionsDocumento2 pagineElectrochemistry and Redox ReactionsJeremy De CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Unit 3 Corrosion and Its PassivationDocumento6 pagineNotes Unit 3 Corrosion and Its PassivationAditya SalunkheNessuna valutazione finora
- Anodes and Cathodes in Corrosion ReactionsDocumento10 pagineAnodes and Cathodes in Corrosion ReactionsSyed50% (4)
- Chemistry Investigatory Project 1Documento16 pagineChemistry Investigatory Project 1Shubhankar Oad100% (1)
- Index: Session: 2022-23Documento18 pagineIndex: Session: 2022-23Prime BeymasterNessuna valutazione finora
- CORROSION PREVENTION AND CONTROL GUIDEDocumento8 pagineCORROSION PREVENTION AND CONTROL GUIDECsir RimlaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Reactivity Series of MetalsDocumento27 pagineThe Reactivity Series of Metals118latelyNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.corrosion TheoryDocumento77 pagine1.corrosion Theoryamitvaze316100% (1)
- Corrosion Engineering: Presented by M.LogeshDocumento19 pagineCorrosion Engineering: Presented by M.Logeshlogeshboy007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 Notes Chem Mescenotes - inDocumento31 pagineModule 2 Notes Chem Mescenotes - inHafizNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistryprojec On CorrosionDocumento23 pagineChemistryprojec On CorrosionSandeep Kumar Yadav100% (1)
- Corrosion Prevention and ControlDocumento8 pagineCorrosion Prevention and ControlBonay BalotNessuna valutazione finora
- Investigatory Project ChemistryDocumento17 pagineInvestigatory Project ChemistryRishav PatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolysis in Metal ExtractionDocumento12 pagineElectrolysis in Metal Extractionnor ainNessuna valutazione finora
- Class-8 ElectricityDocumento4 pagineClass-8 ElectricityMamta JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IIIDocumento17 pagineUnit IIIAthirath VeldandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxidation Reduction and Metal-04Documento4 pagineOxidation Reduction and Metal-04SimantoPreeomNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemical SeriesDocumento9 pagineElectrochemical Seriesasim zeeshanNessuna valutazione finora
- How Galvani, Volta, Davy and Faraday Advanced Understanding of Electron TransferDocumento17 pagineHow Galvani, Volta, Davy and Faraday Advanced Understanding of Electron TransferJananee SundarakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrochemistry Laboratory ReportDocumento6 pagineElectrochemistry Laboratory ReportSteven LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Form 4: Chapter 6 - Electrolyte: Ions in The Molten or Aqueous StateDocumento16 pagineChemistry Form 4: Chapter 6 - Electrolyte: Ions in The Molten or Aqueous StateVinayNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksDa EverandWhy Do Metals Rust? An Easy Read Chemistry Book for Kids | Children's Chemistry BooksNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM12-3L Final Report 2Documento7 pagineCHM12-3L Final Report 2Paul JavenNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM12-3L Final Report 4Documento4 pagineCHM12-3L Final Report 4Paul JavenNessuna valutazione finora
- Objectives: 1. To Compute The Percent by Weight of Acetic Acid in A Vinegar Sample. 2. To Compute The Dissolved Oxygen Content of A Water SampleDocumento5 pagineObjectives: 1. To Compute The Percent by Weight of Acetic Acid in A Vinegar Sample. 2. To Compute The Dissolved Oxygen Content of A Water SamplePaul JavenNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY11L Experiment 6 (E206)Documento7 paginePHY11L Experiment 6 (E206)Paul JavenNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM12-3L Final Report 6Documento3 pagineCHM12-3L Final Report 6Paul JavenNessuna valutazione finora
- Report 3Documento8 pagineReport 3Paul Adrian JavénNessuna valutazione finora
- CHM12-3L Final Report 1Documento3 pagineCHM12-3L Final Report 1Paul JavenNessuna valutazione finora
- Report 5Documento6 pagineReport 5Paul Adrian JavénNessuna valutazione finora
- Report 2Documento6 pagineReport 2Paul Adrian JavénNessuna valutazione finora
- Report 1Documento11 pagineReport 1Paul Adrian JavénNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY12 Report 3Documento4 paginePHY12 Report 3Paul JavenNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY12 Report 4Documento8 paginePHY12 Report 4Paul JavenNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY12 Report 1Documento7 paginePHY12 Report 1Paul JavenNessuna valutazione finora
- TWI Tuition Notes for 3.1U Course (DIS 1Documento382 pagineTWI Tuition Notes for 3.1U Course (DIS 1Brandon Erickson100% (2)
- Good Practice Guide No. 121: Corrosion Control For Buried PipelinesDocumento22 pagineGood Practice Guide No. 121: Corrosion Control For Buried PipelinesMochamad Irvan MaulanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tesi Lorenzo VeronelliDocumento136 pagineTesi Lorenzo VeronelliJorge LunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chloride-Induced Corrosion of Steel PDFDocumento11 pagineChloride-Induced Corrosion of Steel PDFeid elsayedNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion Protection of Ships: RecommendedDocumento38 pagineCorrosion Protection of Ships: RecommendedMuhammad adi100% (1)
- Rrs Cracks in Concrete & Their PreventionDocumento22 pagineRrs Cracks in Concrete & Their PreventionJaswant SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analyse de La Performance Financière de La SAR PDFDocumento80 pagineAnalyse de La Performance Financière de La SAR PDFattiori fabriceNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry ISA 4Documento24 pagineChemistry ISA 4Aryan AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Ti Condenser TubingDocumento8 pagineTi Condenser Tubingaman131Nessuna valutazione finora
- Is 12560Documento10 pagineIs 12560Srikanth VoletiNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion (Piles)Documento8 pagineCorrosion (Piles)JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- BOQ - Gurgaon - 25.06.23Documento3 pagineBOQ - Gurgaon - 25.06.23Anurag ZullurwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion and Rusting On IronDocumento17 pagineCorrosion and Rusting On IronRajashwi MaharjanNessuna valutazione finora
- CP Brochure YuxiDocumento41 pagineCP Brochure YuxibertaNessuna valutazione finora
- Galvanic Corrosion WikipediaDocumento7 pagineGalvanic Corrosion WikipediaCharles HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Cathodic PresentDocumento51 pagineCathodic Presentravi chandra mavuri100% (1)
- Ce2071 - Repair and Rehablitation of Structures (For Viii - Semester)Documento15 pagineCe2071 - Repair and Rehablitation of Structures (For Viii - Semester)Abera MamoNessuna valutazione finora
- RE-286330 - MS Installation & Commissioning Rev ADocumento12 pagineRE-286330 - MS Installation & Commissioning Rev AJohn Philip Buntales100% (1)
- Nace Index PDFDocumento8 pagineNace Index PDFluisantoniocoy100% (1)
- 6 Cathodic Protection Final RedactedDocumento175 pagine6 Cathodic Protection Final Redactedzaheer ahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Cathodic Protection Corrosion Control and PreventionDocumento67 pagineCathodic Protection Corrosion Control and PreventionRully KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- GalvalumDocumento9 pagineGalvalumAdrian M FahriNessuna valutazione finora
- Tuition Notes For 3.3U CourseDocumento417 pagineTuition Notes For 3.3U Coursepoetazzo80Nessuna valutazione finora
- C52 PDFDocumento26 pagineC52 PDFAbdulsalam MaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cathodic Protection - Wikipedia PDFDocumento31 pagineCathodic Protection - Wikipedia PDFAnonymous SAxdsfVN9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sacrificial AnodesDocumento32 pagineSacrificial AnodesluisNessuna valutazione finora
- IR R55i ManualDocumento32 pagineIR R55i ManualBrian KomivesNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathcad Marine TechnologyDocumento22 pagineMathcad Marine TechnologyOkolo ObinnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion Protection Strategies For High Speed CraftDocumento8 pagineCorrosion Protection Strategies For High Speed CraftMahdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Corrosion in Oil&gasDocumento108 pagineCorrosion in Oil&gas55595% (20)