Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
3 3.102P
Caricato da
YogeshThakurDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
3 3.102P
Caricato da
YogeshThakurCopyright:
Formati disponibili
<!
--<TO-DETERMINE>-->
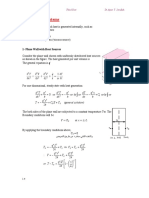
The steady state radial temperature distribution in the solid.
<!--</TO-DETERMINE>-->
<!--<ANSWER>-->
The steady state radial temperature distribution in the solid is:
qr q
ro 2 r 2 T
T r o
3h 6k
<!--</ANSWER>-->
<!--<EXPLANATION>-->
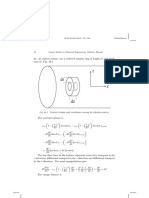
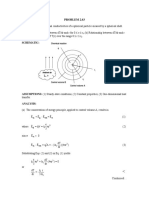
Given:
The radius of the solid sphere is ro
The volumetric heat generation rate is q
The thermal conductivity of the radioactive material is k
The temperature of the liquid bath is T
The convection coefficient of the liquid bath is h
Formula used:
The heat equation for uniform heat generation in the sphere is given as,
1 d 2 dT q
r 0
r 2 dr dr k
Here, r is the radius inside the sphere and T is the temperature at the required r .
The Boundary conditions are given as,
dT
0
dr r 0 Q Qconv r ro
and cond
Here, Qcond is the conduction heat transfer, Qconv is the convection heat transfer and ro is
the radius of the solid sphere.
The conduction heat transfer is given as,
dT
Qcond k
dr
The convection heat transfer is given as,
Qconv h T r T
T r
Here, is the temperature at a radius r in the sphere.
Calculation:
The temperate distribution inside the solid sphere can be calculates as,
1 d 2 dT q
r 0
r 2 dr dr k
d 2 dT 2
qr
r
dr dr k
Integrate the above equation with respect to r ,
d 2 dT 2
qr
dr dr k
r
2 dT 3
qr
r C1
dr 3k
dT qr
C
21
dr 3k r
Here, C1 is the integration constant.
Integrate the above equation again with respect to r ,
dT qr C
dr 3k r 21
2 C1
qr
T r C2
6k r ......(1)
Here, C 2 is the integration constant.
The integration constants C1 and C 2 can be calculated as,
Apply the boundary condition,
dT
0
dr r 0
q 0 C1
0 2
3k r
C1 0
Apply the boundary condition,
Qcond Qconv r r o
dT
k h T ro T
dr r ro
qr
o qr
o2
k 0 h 0 C 2 T
3k 6k
qr o2
o qr
C2 T
3h 6k
Substitute all the values in equation (1),
2 0 qr
qr 2
qr
T r o o T
6k r 3h 6k
qr q
ro 2 r 2 T
o
3h 6k
Conclusion:
Therefore, the steady state radial temperature distribution in the solid is:
qr q
ro 2 r 2 T
T r o
3h 6 k
<!--</EXPLANATION>-->
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsDa EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.103PDocumento2 pagine3 3.103PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiDa EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.96PDocumento2 pagine3 3.96PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.105PDocumento2 pagine3 3.105PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.98PDocumento3 pagine3 3.98PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.104PDocumento3 pagine3 3.104PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Source Systems: 1-Plane Wall With Heat SourcesDocumento5 pagineHeat Source Systems: 1-Plane Wall With Heat SourcesAnonymous 2BJgxbxJNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Boundary Layer - 1-2Documento3 pagineThermal Boundary Layer - 1-2Ajay BansalNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 5129 - Principles of Thermal Energy Conversion: Review of Thermodynamics, Fluid Flow and Heat TransferDocumento28 pagineME 5129 - Principles of Thermal Energy Conversion: Review of Thermodynamics, Fluid Flow and Heat TransferAnandNessuna valutazione finora
- HEAT CONDUCTION IN A STEAM PIPE Introductory Transport Phenomena-Wiley (2014) - R. Byron Bird Et AlDocumento5 pagineHEAT CONDUCTION IN A STEAM PIPE Introductory Transport Phenomena-Wiley (2014) - R. Byron Bird Et AlGael MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 049 PDFDocumento3 paginesm2 049 PDFNilton MafraNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Chap02 126Documento11 pagineHeat Chap02 126Kerem GönceNessuna valutazione finora
- Radial Systems: CommentsDocumento12 pagineRadial Systems: CommentsJHON JAIRO ORTEGA ORTEGANessuna valutazione finora
- L11 - Heat Transfer - 2016Documento11 pagineL11 - Heat Transfer - 2016shamiul himelNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.95PDocumento1 pagina3 3.95PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento37 pagineUntitledLê Phạm HoàngNessuna valutazione finora
- 191.patel PratikDocumento13 pagine191.patel PratikPratik PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Analogy of Heat Transfer: Simple Ideas To Eliminate Discontinuities in Solution DomainDocumento29 pagineElectrical Analogy of Heat Transfer: Simple Ideas To Eliminate Discontinuities in Solution DomainThomyNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment-2 With AnswersDocumento3 pagineAssignment-2 With AnswersMarinhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Nama: Nadiya Damara NPM: 1415041038 Hari, Tanggal Ujian: Selasa, 31 Maret 2020 Uts Transfer Massa Dan PanasDocumento5 pagineNama: Nadiya Damara NPM: 1415041038 Hari, Tanggal Ujian: Selasa, 31 Maret 2020 Uts Transfer Massa Dan PanasNadiya DamaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Models of Physical SystemsDocumento5 pagineMathematical Models of Physical SystemsAmitava BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cilindros - IncroperaDocumento6 pagineCilindros - IncroperaJoseCarlosCastroRodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- ps2 SolutionsDocumento8 pagineps2 SolutionsJulcris JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.97PDocumento1 pagina3 3.97PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Math24 SolDocumento2 pagineMath24 SolSharif M Mizanur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Resistance: Asst. Prof. Krongkaew Laohalidanond (Dr.-Ing.)Documento27 pagineThermal Resistance: Asst. Prof. Krongkaew Laohalidanond (Dr.-Ing.)oloNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Simulation of 1D Heat Conduction in Spherical and Cylindrical Coordinates by Fourth-Order Finite Difference MethodDocumento5 pagineNumerical Simulation of 1D Heat Conduction in Spherical and Cylindrical Coordinates by Fourth-Order Finite Difference MethodGokma Sahat Tua SinagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Conduction in Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesDocumento21 pagineHeat Conduction in Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesskarnaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Ie8b00601 Si 001Documento7 pagineIe8b00601 Si 001Adhan AkbarNessuna valutazione finora
- L5-8 - Heat Transfer - 2023Documento32 pagineL5-8 - Heat Transfer - 2023TurzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Chap02 068Documento24 pagineHeat Chap02 068Kerem GönceNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - 4,5 HDE - Cylinderical & Spherical Co-OrdinatesDocumento24 pagineLecture - 4,5 HDE - Cylinderical & Spherical Co-OrdinatesHew LetNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Conduction in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates IDocumento14 pagineHeat Conduction in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates IMohammed Siddique25% (4)
- Compressible Flow1Documento28 pagineCompressible Flow1hs sNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Heat Transfer: Conduction Convection RadiationDocumento11 pagineIntroduction To Heat Transfer: Conduction Convection RadiationWilmer AsuncionNessuna valutazione finora
- CN2106 Part 1 Additional Questions (L1-L3) Solutions (4849)Documento10 pagineCN2106 Part 1 Additional Questions (L1-L3) Solutions (4849)Kek Yi QingNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 063 PDFDocumento2 paginesm2 063 PDFNilton MafraNessuna valutazione finora
- E Q Q E T E E E MCT T Cart TDocumento2 pagineE Q Q E T E E E MCT T Cart TAnonymous ncBe0B9bNessuna valutazione finora
- Please Refer To: Fluid Mechanics & Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery, 5 Edition S.L. DixonDocumento11 paginePlease Refer To: Fluid Mechanics & Thermodynamics of Turbomachinery, 5 Edition S.L. DixonNor Amziela Bt AniNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 052 PDFDocumento4 paginesm2 052 PDFNilton MafraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019-ME-127 Exp.4 HMT LabDocumento11 pagine2019-ME-127 Exp.4 HMT LabZeeshan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY - IIT ENTHUSE - PAPER-1 - RT-3 - Mrinal Sir - 18-06-23Documento17 paginePHY - IIT ENTHUSE - PAPER-1 - RT-3 - Mrinal Sir - 18-06-23Rajanikanta PriyadarshiNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 047 PDFDocumento1 paginasm2 047 PDFNilton MafraNessuna valutazione finora
- (Perpan) Heat Conduction Through A Cylindrical and Spherical WallDocumento12 pagine(Perpan) Heat Conduction Through A Cylindrical and Spherical WallNi LamNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions: Solutions Manual For Introduction To The Thermodynamics of Materials 6Th Edition GaskellDocumento228 pagineSolutions: Solutions Manual For Introduction To The Thermodynamics of Materials 6Th Edition Gaskellhamed pirboneh75% (4)
- 3 HomogeneouseDocumento26 pagine3 HomogeneouseSayd KamalNessuna valutazione finora
- EntropyDocumento10 pagineEntropyShyam DevNessuna valutazione finora
- AITS-2021-OPEN TEST-II-JEEA-PAPER-2-SolDocumento16 pagineAITS-2021-OPEN TEST-II-JEEA-PAPER-2-Solfunny videoNessuna valutazione finora
- Simplified Models For Complex Heat Transfer Due To Micro-Molecular Movements!!!Documento27 pagineSimplified Models For Complex Heat Transfer Due To Micro-Molecular Movements!!!Muket AgmasNessuna valutazione finora
- Q QV QR W MDocumento4 pagineQ QV QR W Mjrobs314Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4.2 4.3 Part 2Documento25 pagineChapter 4.2 4.3 Part 2splint6969Nessuna valutazione finora
- Facts and Formulae SheetDocumento7 pagineFacts and Formulae SheethenryNessuna valutazione finora
- AITS-1920-OPEN TEST-JEEA-PAPER-2-SolDocumento16 pagineAITS-1920-OPEN TEST-JEEA-PAPER-2-SolShaikh AffanNessuna valutazione finora
- Conduction and Convection Heat Transfer Assignment-Week 3Documento12 pagineConduction and Convection Heat Transfer Assignment-Week 3SAWAN KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat TransferDocumento16 pagineHeat Transferprasanna0% (1)
- Problem Set 2 (Prof. Chen)Documento7 pagineProblem Set 2 (Prof. Chen)Hagere EthiopiaNessuna valutazione finora
- HazopDocumento34 pagineHazopSyuhadah NoordinNessuna valutazione finora
- General Heat Conduction Equations: Rectangular/cartesian CoordinatesDocumento29 pagineGeneral Heat Conduction Equations: Rectangular/cartesian CoordinatesSyarifah Anis AqilaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.101PDocumento3 pagine3 3.101PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.99PDocumento3 pagine3 3.99PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.100PDocumento2 pagine3 3.100PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.95PDocumento1 pagina3 3.95PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3.97PDocumento1 pagina3 3.97PYogeshThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- A4 Heat Press Manual PDFDocumento13 pagineA4 Heat Press Manual PDFmapache66Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics of Mechanisms and Machines Assignment-0Documento5 pagineKinematics of Mechanisms and Machines Assignment-0Appam NiharNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Braced Non-SwayDocumento23 pagineSimple Braced Non-SwaydineshNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Programming Assignment - 3Documento3 pagineComputer Programming Assignment - 3Waqas MehmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- MIT5 067F09 Lec1 DataDocumento28 pagineMIT5 067F09 Lec1 DataAlexandra BarthNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Class 6 Final ExamDocumento4 pagineGeometry Class 6 Final ExamTanzimNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Question Paper - 1: Class - XDocumento12 pagineSample Question Paper - 1: Class - XABHISHEK VERMANessuna valutazione finora
- Prediction of Fatigue Failure in A Camshaft Using The Crack MethodDocumento9 paginePrediction of Fatigue Failure in A Camshaft Using The Crack MethodDiego PovedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Steel: Statistical Analysis of Steel FormabilityDocumento12 pagineSteel: Statistical Analysis of Steel FormabilitynadhabindhuNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL StatesDocumento53 pagineSQL StatesSuriya PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemguide Atom, MoleculeDocumento28 pagineChemguide Atom, MoleculeSabina SabaNessuna valutazione finora
- REF615 Standard ConfigurationDocumento11 pagineREF615 Standard Configurationmaruf048Nessuna valutazione finora
- S4 MathematicsDocumento4 pagineS4 MathematicsDaniel MarkNessuna valutazione finora
- Plaxis 3DDocumento41 paginePlaxis 3DafvilavilanoriegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Math - 7th Grade Teaching NotesDocumento16 pagineMath - 7th Grade Teaching NotesPara ParadiseNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Axial Load Mode Shapes A N D Frequencies BeamsDocumento33 pagineEffect of Axial Load Mode Shapes A N D Frequencies BeamsYoyok SetyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sea Defences Dutch Guidelines On Dike ProtectionDocumento125 pagineSea Defences Dutch Guidelines On Dike ProtectionChimhuee ChuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 11 Homework 5.3Documento4 pagineLesson 11 Homework 5.3afodcauhdhbfbo100% (1)
- Interpreting and Using Statistics in Psychological Research 1St Edition Christopher Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento41 pagineInterpreting and Using Statistics in Psychological Research 1St Edition Christopher Test Bank Full Chapter PDFhungden8pne100% (12)
- Symmetry in The Music of Thelonious Monk PDFDocumento97 pagineSymmetry in The Music of Thelonious Monk PDFMicheleRusso100% (1)
- 0606 s14 QP 22Documento16 pagine0606 s14 QP 22AKRAMNessuna valutazione finora
- S Cet Prospectus 2013Documento99 pagineS Cet Prospectus 2013Muhammad Tariq SadiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanics: Topic 2 AS-Level English Language School DubaiDocumento28 pagineMechanics: Topic 2 AS-Level English Language School DubaiHamza ShabbirNessuna valutazione finora
- Tu 5 Mechanics PDFDocumento4 pagineTu 5 Mechanics PDFJyotish VudikavalasaNessuna valutazione finora
- FMEA Minus The Pain FiguresDocumento3 pagineFMEA Minus The Pain FiguresMUNISNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Logic PDFDocumento74 pagineDigital Logic PDFWyky Un-NaunNessuna valutazione finora
- Aljabar Linier Elementer: Howard Anton Chris RorresDocumento78 pagineAljabar Linier Elementer: Howard Anton Chris RorresLukmanulhakim AlmamalikNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Relation 1Documento17 pagineTypes of Relation 1Justin Adrian BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Erc111 DKRCC - Es.rl0.e3.02 520H8596Documento24 pagineErc111 DKRCC - Es.rl0.e3.02 520H8596Miguel BascunanNessuna valutazione finora
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDa EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNessuna valutazione finora
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDa EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDa EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2193)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDa EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDa EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (69)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceDa EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDa EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (49)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDa EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeDa EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDa EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDa EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (125)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDa EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (410)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDa EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1396)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Da EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (157)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeDa EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDa EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (60)
- Vibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeDa EverandVibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (13)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDa EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (6)
- What If?: Serious Scientific Answers to Absurd Hypothetical QuestionsDa EverandWhat If?: Serious Scientific Answers to Absurd Hypothetical QuestionsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itDa EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (13)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDa EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (54)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessDa EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (57)