Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Absorption English
Caricato da
حيدرالركابيDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Absorption English
Caricato da
حيدرالركابيCopyright:
Formati disponibili
THERMAL PROCESS ENGINEERING
BASIC KNOWLEDGE
ABSORPTION
Absorption is a separation process that involves Production of a liquid; one example would be
removing one or more gaseous components from a obtaining hydrochloric acid by absorption of HCl
gas flow using a washing fluid. Absorption can have gas in water.
different aims:
At least three substances are involved in the absorp-
The gaseous component to be removed is a product tion process: the gaseous component to be removed
that is wanted. (absorbate), the carrier gas and the washing fluid
(absorbent).
The gaseous component to be removed is
unwanted. This could be the case when removing
contaminantes from an exhaust gas flow.
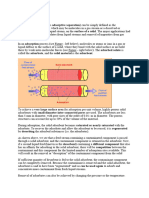
Absorption Regeneration
(pressure , temperature ) (pressure , temperature )
Absorption system: 1 gas flow with component to be removed and carrier gas, 2 compressor, 3 washing fluid,
charged with component to be removed, 4 regenerated washing fluid, 5 heating, 6 desorption column, 7 removed gaseous
component, 8 expansion valve, 9 cooler, 10 pressure pump, 11 carrier gas, 12 cooling, 13 absorption column
An appropriate washing fluid is used, either absorbed by physical dissolv- solubility of the gases in the washing
depending on the gaseous compo- ing (physical absorption) or chemical fluid, thus expelling them. The wash-
nent to be removed. The washing bonding (chemical absorption). ing fluid can therefore be recycled for
fluid selectively dissolves the gase- further use.
ous component i.e. the washing fluid To remove the gaseous components
primarily absorbs the component(s) from the solvent, an absorption stage
to be removed and not the carrier gas. is normally followed by a desorption
High pressures and low temperatures stage for regeneration of the wash-
enhance absorption. Depending on ing fluid. Here, high temperatures or
the type of washing fluid, the gas is low pressures are used to reduce the
19
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Oil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesDa EverandOil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Dictionary of Textile Finishing: Deutsch/Englisch, English/GermanDa EverandDictionary of Textile Finishing: Deutsch/Englisch, English/GermanValutazione: 1.5 su 5 stelle1.5/5 (3)
- Absorption EnglishDocumento1 paginaAbsorption English菖蒲素敵Nessuna valutazione finora
- Absorption and Stripping Equipment Manual FDocumento17 pagineAbsorption and Stripping Equipment Manual FShoaib PathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Drying EquipmentDocumento6 pagineGas Drying EquipmentJustin Paul CongeNessuna valutazione finora
- Tema 5Documento8 pagineTema 5Andrés JiménezNessuna valutazione finora
- Reflux in A Gas Dehydration PlantDocumento5 pagineReflux in A Gas Dehydration Plantghasem_726990287Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-3 Absorption2-DilanDocumento29 pagineUnit-3 Absorption2-Dilanchinna erannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-3 Absorption2Documento43 pagineUnit-3 Absorption2chinna erannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas AbsorptionDocumento10 pagineGas AbsorptionReggie DueñasNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Absorptio1Documento3 pagineGas Absorptio1마비 니제시카Nessuna valutazione finora
- Absorption Lecture Note - DR Akinsiku PDFDocumento7 pagineAbsorption Lecture Note - DR Akinsiku PDFGlory UsoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Dehydration of Natural Gas by Solid DesiccantDocumento20 pagineDehydration of Natural Gas by Solid DesiccantMadhankumar LakshmipathyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas AbsorptionDocumento12 pagineGas Absorptionaya mahmoudNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Solid BedDocumento27 pagineChapter 4 Solid BedTaha Azab MouridNessuna valutazione finora
- ScrubberDocumento3 pagineScrubbervijay kumar honnaliNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.0 Introduction To AbsorptionDocumento25 pagine6.0 Introduction To AbsorptionJassimMohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Transfer Operations - IDocumento26 pagineMass Transfer Operations - IKondeti Venkata AbhinavaNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT Proses IN Chemical EngineeringDocumento21 pagineUNIT Proses IN Chemical EngineeringZakiyah Kamto IrfinNessuna valutazione finora
- Adsorption DryingDocumento11 pagineAdsorption DryingReza JabbarzadehNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Absorption Operation NoteDocumento14 pagineGas Absorption Operation NoteBasseyNessuna valutazione finora
- NG Engineering by Engr DR CIC AnyadiegwuDocumento31 pagineNG Engineering by Engr DR CIC Anyadiegwudavidchinedu008Nessuna valutazione finora
- ScrubberDocumento3 pagineScrubberriz2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Distillation Absorption StrippingDocumento6 pagineDistillation Absorption StrippingLulav BarwaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Absorption SumaDocumento6 pagineAbsorption SumaLulav BarwaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Adsorption Group 7-1Documento16 pagineAdsorption Group 7-1Junior J DliwayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Linde PSAsDocumento8 pagineLinde PSAsSiji AntonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Aqm Module 6 Lec 3Documento18 pagineAqm Module 6 Lec 3fromashokNessuna valutazione finora
- Displacement Purge AdsorptionDocumento2 pagineDisplacement Purge AdsorptionNithya RamNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect 16 Natural Gas Pet EngDocumento15 pagineLect 16 Natural Gas Pet EngKurdish DriverNessuna valutazione finora
- AdsorptionDocumento6 pagineAdsorptionBekithembaNessuna valutazione finora
- MASS TRANSFER - 11.weekDocumento27 pagineMASS TRANSFER - 11.weekesra göçenNessuna valutazione finora
- Wet Scrubbing: Dry Sorbent Injection Involves The Addition of AnDocumento2 pagineWet Scrubbing: Dry Sorbent Injection Involves The Addition of AnJordan MosesNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Dehydration and Molecular Sieves FPSO SaquaremaDocumento28 pagineGas Dehydration and Molecular Sieves FPSO SaquaremamohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Ion Exchange: Application of Ion Exchanger Water SofteningDocumento7 pagineIon Exchange: Application of Ion Exchanger Water SofteningListo A4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Absorption: Separation Process Report Instructor: DR - Bilal NiaziDocumento19 pagineAbsorption: Separation Process Report Instructor: DR - Bilal Niazi2k17che 26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Introduction: 1.1 Stripping MethodDocumento5 pagineChapter 1 Introduction: 1.1 Stripping MethodBishal LamichhaneNessuna valutazione finora
- April 11 - Gas Sweetening ProcessDocumento95 pagineApril 11 - Gas Sweetening Processhoangduy7696Nessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid - Gas: Absorption of Gases ( (Separation) )Documento7 pagineLiquid - Gas: Absorption of Gases ( (Separation) )ايمن العراقيNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Absorption: This Chapter Deals With The Mass-Transfer Operations Known As GasDocumento9 pagineGas Absorption: This Chapter Deals With The Mass-Transfer Operations Known As GasChristian NwekeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Absorption Group ReportDocumento18 pagineGas Absorption Group ReportSimesihle ZamisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Title of Experiment: Gas Absorption Objective of Experiment: To Calculate The Mass Transfer Coefficient of Oxygen Through TheDocumento2 pagineTitle of Experiment: Gas Absorption Objective of Experiment: To Calculate The Mass Transfer Coefficient of Oxygen Through TheJoson ChaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation SystemsDocumento24 pagineSeparation SystemsLeencie SandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas RPDocumento46 pagineGas RPdhruvNessuna valutazione finora
- ScrubberDocumento28 pagineScrubberMuhammad Jajar Pambudi0% (1)
- Advance Separation Techniques: Pressure Swing AdsorptionDocumento26 pagineAdvance Separation Techniques: Pressure Swing AdsorptionJaykumar Bhupendrabhai PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Psa RecoveryDocumento8 paginePsa RecoverypalluraviNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 AdsorbersDocumento6 pagine3 AdsorbersOr ReshefNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen Recovery: by Pressure Swing AdsorptionDocumento8 pagineHydrogen Recovery: by Pressure Swing AdsorptionBamrung SungnoenNessuna valutazione finora
- State of Libya University Al-Mergib Faculty Engineering Department Engineering Chemical & PetroleumDocumento12 pagineState of Libya University Al-Mergib Faculty Engineering Department Engineering Chemical & PetroleumSiraj AL sharif100% (1)
- Unit II AbsorptionDocumento16 pagineUnit II AbsorptionAnkita SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- ScrubbersDocumento5 pagineScrubbersleoboyaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Absorption & Stripping: Senior Design CHE 396Documento44 pagineAbsorption & Stripping: Senior Design CHE 396PIratȅ IlıNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid Desiccant DehydrationDocumento5 pagineSolid Desiccant Dehydrationca_minoNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Gas DehydrationDocumento12 pagineNatural Gas DehydrationSagar DadhichNessuna valutazione finora
- Aqm Assignment 2Documento44 pagineAqm Assignment 2nithin M SNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Transfer: Unit OperationDocumento4 pagineMass Transfer: Unit OperationazibanjumNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Pollution ControlDocumento35 pagineAir Pollution ControlPraveen YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Distillation ProcessDocumento6 pagineBasic Distillation ProcessAmeerRashidNessuna valutazione finora
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingDa EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- 21 CN Requirements For NDT Suppliers - Final - 2Documento8 pagine21 CN Requirements For NDT Suppliers - Final - 2حيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- Superalloys 1992 257 265Documento9 pagineSuperalloys 1992 257 265حيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- Coating Thickness Gage: 6000 SERIESDocumento7 pagineCoating Thickness Gage: 6000 SERIESحيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- For Duplex Coatings: Positector 6000 Fnds ProbeDocumento4 pagineFor Duplex Coatings: Positector 6000 Fnds ProbeحيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- Rotating EquipmentDocumento5 pagineRotating EquipmentحيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab-Sheets: ET 792 Two-Shaft Gas Turbine / Jet EngineDocumento13 pagineLab-Sheets: ET 792 Two-Shaft Gas Turbine / Jet EngineحيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 301 Understanding The Principles and Practices of AssessmentDocumento32 pagineUnit 301 Understanding The Principles and Practices of AssessmentحيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding The Principles and Practices of Assessment: D/601/5313 VRQ UV30563Documento20 pagineUnderstanding The Principles and Practices of Assessment: D/601/5313 VRQ UV30563حيدرالركابي100% (1)
- Lab-Sheets: ET 792 Two-Shaft Gas Turbine / Jet EngineDocumento13 pagineLab-Sheets: ET 792 Two-Shaft Gas Turbine / Jet EngineحيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- Poster 500x700 m500 Cutaway enDocumento1 paginaPoster 500x700 m500 Cutaway enحيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- MCT Centrifugal Compressor O MDocumento3 pagineMCT Centrifugal Compressor O MحيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- Enrollment Form 3Documento1 paginaEnrollment Form 3حيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- GAPS Guidelines: Steam Turbine Loss Prevention InspectionDocumento5 pagineGAPS Guidelines: Steam Turbine Loss Prevention InspectionحيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- Centrifugal Pumps & Positive Displacement Pumps CoursesDocumento2 pagineCentrifugal Pumps & Positive Displacement Pumps CoursesحيدرالركابيNessuna valutazione finora
- Benzene and Phenol (25-05-2023)Documento55 pagineBenzene and Phenol (25-05-2023)hibajama72Nessuna valutazione finora
- ABB Photovoltaic DisconnectorsDocumento6 pagineABB Photovoltaic DisconnectorsBog PenNessuna valutazione finora
- Compound Wall Toilet Revised (4) - ModelDocumento1 paginaCompound Wall Toilet Revised (4) - ModelInfra SupportNessuna valutazione finora
- Board of Technical Education Uttar Pradesh Lucknow: CODE 2298Documento2 pagineBoard of Technical Education Uttar Pradesh Lucknow: CODE 2298Md Shaaz100% (1)
- Lesson Plan 1 - Agriculture in Your LifeDocumento6 pagineLesson Plan 1 - Agriculture in Your Lifeapi-235918896Nessuna valutazione finora
- F115a'12 Fl115a'12: (68VB) (68WB)Documento96 pagineF115a'12 Fl115a'12: (68VB) (68WB)AlexDiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Zeolites and Ordered Porous Solids - Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocumento376 pagineZeolites and Ordered Porous Solids - Fundamentals and ApplicationsHenrique Souza100% (1)
- Astm A479Documento7 pagineAstm A479Martin RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- LightsDocumento33 pagineLightsEduardo Almeida SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S0092867422011734 MainDocumento29 pagine1 s2.0 S0092867422011734 MainIoanna NikdimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Think Before Buying: ReadingDocumento1 paginaThink Before Buying: ReadingadrianmaiarotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manuel D'utilisation Maison AnglaisDocumento17 pagineManuel D'utilisation Maison AnglaisVanesssNessuna valutazione finora
- Rolling Fig Q A AnalysisDocumento11 pagineRolling Fig Q A AnalysisRavinder Antil100% (9)
- Text For Number 1-3: How To Make Passion Fruit Juice IngredientsDocumento4 pagineText For Number 1-3: How To Make Passion Fruit Juice Ingredientsakmal maulanaNessuna valutazione finora
- PEPSIDocumento99 paginePEPSIkingloiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ford6000cd Rear ConnectorDocumento2 pagineFord6000cd Rear ConnectorAnonymous WcYW9AeNessuna valutazione finora
- TNB Ar2011Documento334 pagineTNB Ar2011Duncan LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-Theory of Metal Cutting PDFDocumento144 pagine1-Theory of Metal Cutting PDFNithinArvindNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Whisperer PDFDocumento4 pagineAnimal Whisperer PDFKevinPriestmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental and Technical Analysis of Iron and Steel SIP PROJECTDocumento34 pagineFundamental and Technical Analysis of Iron and Steel SIP PROJECThaveuever910Nessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Topography of PakistanDocumento25 pagineNatural Topography of Pakistansatayish100% (1)
- Nukote Aegis SubmittalDocumento112 pagineNukote Aegis SubmittalMarco Dos Santos NevesNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper 1Documento4 paginePaper 1asa.henfield2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Morality Speaks of A System of Behavior in Regards To Standards of Right or Wrong Behavior. The WordDocumento3 pagineMorality Speaks of A System of Behavior in Regards To Standards of Right or Wrong Behavior. The WordTHEO DOMINIC REQUERME SILVOSANessuna valutazione finora
- GPT Protocol - Trypcase Soy AgarDocumento8 pagineGPT Protocol - Trypcase Soy AgarmailboxofmurliNessuna valutazione finora
- Preventive Pump SetDocumento67 paginePreventive Pump Setwtpstp sardNessuna valutazione finora
- 447.010 Screen Operating Manual v001Documento67 pagine447.010 Screen Operating Manual v001José CarlosNessuna valutazione finora
- Bugreport Dandelion - Eea QP1A.190711.020 2022 02 15 07 45 54Documento9.715 pagineBugreport Dandelion - Eea QP1A.190711.020 2022 02 15 07 45 54João Carlos Pereira ChoinasNessuna valutazione finora
- TNM Sites May 2023Documento24 pagineTNM Sites May 2023Joseph ChikuseNessuna valutazione finora
- P&S U V PracticeDocumento4 pagineP&S U V PracticeHari KrushnaNessuna valutazione finora