Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Next Step After Pss & Sss Decoding Steps in RF
Caricato da
karunakar rajanTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Next Step After Pss & Sss Decoding Steps in RF
Caricato da
karunakar rajanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
AFTER PSS & SSS DECODING
Once, the UE has decoded both the PSS and SSS, it can derive the PCI which tells
the location of the RS and the PCFICH. This lets the UE get the RSRP and verify
that the cell is above the cell selection threshold. Then it goes for PBCH which is
after the PSS of the first subframe. PBCH tells about the system BW, System frame
number, PHICH config and number of Tx. Now that the UE knows PHICH, PCFICH and RS
location, all the other REs belong to PDCCH.
The UE looks for the DCI for SIB-1 by decoding the DCI masked with CRC of SI-RNTI.
The SIB-1 is sent after every 20 ms but the TTI is 80 ms (like PBCH – comes every
10 ms but the TTI is 40 ms). The copies of SIB-1 after 20 ms are different
redundacny versions of the same SIB-1. The SIB-1 tells about the other SIBs (SI
periodicity and SI Window length), including SIB-2 which tells about the RACH
information required for uplink synchronization.
The location of RACH is determined by the following parameters in SIB-2
PRACH CONFIGURATION INDEX ==> Tells the SFN (even/odd) and subframe number – thus
the location in time domain
PRACH FREQUENCY OFFSET ==> Tells the PRB offset and thus the location in frequency
domain
NCS VALUE ==> Tells the NCS value and the number of root sequences per cell needed
to generate 64 preambles
ROOT SEQUENCE INDEX ==> Tells the starting root sequence index for the cell
Based on these values, the UE generates a random preamble and sends a RACH request.
After the RACH request, the UE needs to start reading PDCCH for its RA-RNTI after 3
subframes (3 SF after the prach preamble transmission is finished). The RA RSP
WINDOW SIZE tells the maximum number of subframes within which the eNB needs to
send the RAR. Usually, it is set to 10 SF and therefore the eNB needs to respond to
a PRACH request within 12 SF. The RAR contains RA-RNTI or temporary C-RNTI and
RAPID (which contains the preamble ID that UE sent).
Once RAR is received, the UE sends msg3 which is RRC Conn Req message that contains
UE ID (TMSI or random value). eNB responds with a MCE Contention resolution message
before RRC Conn Setup and that contention resolution message contains the same UE
ID that is sent by UE in RRC Conn Req message. So, if there are two UEs using the
same preamble, then at this step the contention will be resolved. As the UE with
the same ID will send the HARQ ACK to Contention resolution message but the other
UE will consider RACH failure and re-initiate RACH. In response to RRC Connection
Request, eNB sends a RRC Connection Setup which carries SRB1 (Signalling Radio
Bearer) addition parameters. Before this, the UE uses SRB0 to send the RRC message.
Once the UE gets RRC Connection Setup message, the UE responds with the RRC Setup
Complete message. It is this message that carries NAS messages. At this moment, the
RRC setup is completed and SRB1 is also setup.
Based on this, the eNB initiates S1 Initial UE message to the MME and MME can
respond to this message in different ways but the most common response is S1
Initial Context Setup Request. This message is considered as the ERAB Setup Request
and it usually contains the ERAB-ID and QCI that has to be setup for the UE along
with MBR configuration of the bearer.Consequently, the eNB reconfigures UE using
RRC Connection Reconfiguration message which contains the addition for SRB2 and DRB
(data radio bearer) based on the QCI requirement. eNB also sends Security Mode
Command to UE to configure the security context at this stage. Once this is done,
the eNB responds to MME with S1 Initial Setup Response and at this point the ERAB
Setup is considered successful.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Jbase Locking MecanismeDocumento33 pagineJbase Locking MecanismeMamat AdoumaNessuna valutazione finora
- GPS and GSM Based Vehicle Tracking SystemDocumento16 pagineGPS and GSM Based Vehicle Tracking SystemShreyas Sridhar0% (2)
- Ameer Hamza (iOS Developer)Documento4 pagineAmeer Hamza (iOS Developer)Ali ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation - Sécheron - Stray Current Monitoring - English - 24082011Documento24 paginePresentation - Sécheron - Stray Current Monitoring - English - 24082011曾乙申100% (2)
- Cartilla de Actividades de Inglés: Escuela N°127 DR Mariano MorenoDocumento6 pagineCartilla de Actividades de Inglés: Escuela N°127 DR Mariano MorenoJosé Sisalli SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Schneider Electric Price List Feb 2020 V2Documento478 pagineSchneider Electric Price List Feb 2020 V2Amr SohilNessuna valutazione finora
- Hive Main InstallationDocumento2 pagineHive Main InstallationpareekNessuna valutazione finora
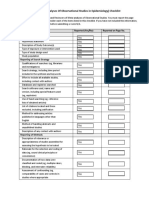
- MOOSE (Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies in Epidemiology) ChecklistDocumento2 pagineMOOSE (Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies in Epidemiology) ChecklistNesru Ahmed AkkichuNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual de Servicios Simplex 4010Documento72 pagineManual de Servicios Simplex 4010Eduardo MegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Udl Classroom-Ryan CrumDocumento5 pagineUdl Classroom-Ryan Crumapi-663455706Nessuna valutazione finora
- Price List Ymh B.indonesia 20-02-2020Documento928 paginePrice List Ymh B.indonesia 20-02-2020LighterNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Basket AnalysisDocumento15 pagineMarket Basket AnalysisAkanksha KadamNessuna valutazione finora
- ReactivepowerComp usingSTATCOMDocumento126 pagineReactivepowerComp usingSTATCOMsreddy4svuNessuna valutazione finora
- TeSys LT3 - LT3SA00EDDocumento2 pagineTeSys LT3 - LT3SA00EDVincent Ferrer NironNessuna valutazione finora
- Handle Inventory Management BW - Easy StepsDocumento13 pagineHandle Inventory Management BW - Easy StepsJohn Barrero100% (1)
- Mini Pak HoneywellDocumento78 pagineMini Pak Honeywellliviu_dovaNessuna valutazione finora
- DESI GIShomework 4 ExcDocumento7 pagineDESI GIShomework 4 ExcAndrea HuertaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5713 How Microsoft Moves Their SAP Landscape Into AzureDocumento41 pagine5713 How Microsoft Moves Their SAP Landscape Into AzureHaitham DesokiNessuna valutazione finora
- MC Line: Multifunction Three Phase Overvoltage / Undervoltage RelayDocumento3 pagineMC Line: Multifunction Three Phase Overvoltage / Undervoltage RelayCerduardo Chanchisco Roga RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- B.Sc. Chemistry Honours-2022: 1 ListDocumento4 pagineB.Sc. Chemistry Honours-2022: 1 ListSrijaNessuna valutazione finora
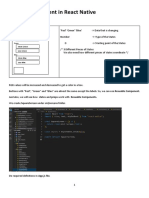
- State Management in React NativeDocumento25 pagineState Management in React NativeRüstem EleçNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Item Bank Utilizaton PDFDocumento6 pagineTest Item Bank Utilizaton PDFElaine Gladys Vicente Magaling60% (5)
- Nebula - 150 User ManualDocumento94 pagineNebula - 150 User ManualSamuel MongeNessuna valutazione finora
- Compiler Lab VivaDocumento6 pagineCompiler Lab VivaGaurav SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lic Unit 1 (1) eDocumento114 pagineLic Unit 1 (1) eganeshNessuna valutazione finora
- JNTU Old Question Papers 2007Documento8 pagineJNTU Old Question Papers 2007Srinivasa Rao GNessuna valutazione finora
- Proposal Project PrintingDocumento13 pagineProposal Project PrintinglodewNessuna valutazione finora
- Desain Layout Mobil Toko Laundry SepatuDocumento7 pagineDesain Layout Mobil Toko Laundry SepatuKlinikrifdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On Personal SellingDocumento11 pagineReport On Personal SellingGirish Harsha100% (5)
- Internsship - Project - Arjun Singh FinalDocumento78 pagineInternsship - Project - Arjun Singh FinalAnmol DubeyNessuna valutazione finora