Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
PHY1 Specimen
Caricato da
Israfil TamimDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PHY1 Specimen
Caricato da
Israfil TamimCopyright:
Formati disponibili
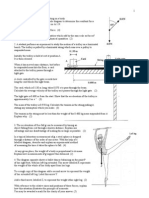
PHY1 SPECIMEN PAPER 1
1. The diagram shows a velocity-time graph for a ball bouncing vertically on a hard surface.
The ball was dropped at t = 0 s.
At what time does the graph show the ball in contact with the ground for the third time? (1 mark)
The downward sloping lines on the graph are straight and parallel with each other. Why? (2 marks)
Show that the height from which the ball was dropped is about 1.2 m. (2 marks)
Sketch a displacement-time
curve on the axes opposite for
the first second of the
motion. (3 marks)
What is the displacement of the ball when it finally
comes to rest? (1 mark)
(Total 9 marks)
2. An athlete of mass 55.0 kg runs up a flight of stairs
of vertical height 3.60 m in 1.80 s. Calculate the gain
in gravitational potential energy of the athlete in doing this.
Calculate the power that this athlete develops in
doing this. (4 marks)
One way of comparing athletes of different sizes is to compare their power-to-weight ratios. Find a unit for the power-
to-weight ratio in terms of SI base units. (2 marks)
Calculate the athlete’s power-to-weight ratio. (2 marks)
(Total 8 marks)
3. Palaeontologists are able to deduce much about the behaviour of dinosaurs
from the study of fossilised footprints.
The tracks below show the path of a Tyrannosaurus Rex as it
attacks a stationary Triceratops.
The time between footprints is 0.62 s.
Show that the maximum speed of the Tyrannosaurus Rex is about 10ms-1. (2 marks)
Tyrannosaurus Rex is believed to have attacked its prey by charging and locking its jaws on the prey. Tyrannosaurus
Rex would be at its maximum speed when it hit the stationary prey.
This Tyrannosaurus Rex has a mass of 7000 kg. Calculate its momentum just before it hits the Triceratops. (2 marks)
Triceratops has a mass of 5000 kg. Calculate their combined speed immediately after the collision. (3 marks)
The skull of Tyrannosaurus Rex is heavily reinforced to withstand the force produced in such a collision.
Calculate the force exerted on the Tyrannosaurus Rex if the time taken to reach their combined speed after the collision
is 0.30 s (3 marks)
(Total 10 marks)
PHY1 SPECIMEN PAPER 2
4. State in words how to calculate the work done by a varying force. (2 marks)
Under what circumstances is the work done by a force negative?
What happens to the kinetic energy of the body on which the force acts in such circumstances? (2 marks)
A runaway sledge slides down a slope at a constant speed. One force is shown on the free-body diagram of the sledge.
It is the normal contact push of the snow on the sledge.
Add to the free-body diagram
to show the other two forces
acting on the sledge.
Name each force and state
what is producing it. (3 marks)
The sledge slides 15 m down
the slope at a constant speed.
The force N = 40 N.
What is the resultant force
acting on the sledge? What is the work done by the force N? (2 marks)
(Total 9 marks)
5. State the principle of moments. (2 marks)
The diagram shows a lorry of weight 120 kN
on a bridge.
Calculate the additional upward force at each
of the bridge supports caused by the lorry
(that is; upward force at A and upward force
at B) (4 marks)
(Total 6 marks)
6. Name two sources of natural background
radiation. (2 marks)
Caesium-137 is a by-product of nuclear fission within a nuclear reactor. The nuclear equation below describes the
production of Caesium-137. Complete the two boxes.
(2 marks)
The half-life of caesium-137 is 30 years. When the fuel rods are removed from a nuclear reactor core, the total activity
of the caesium-137 is 6.4 x1015 Bq.
Explain the phrase the activity of caesium-137 is 6.4 x 1015 Bq. (2 marks)
After how many half-lives will this activity have fallen to 2.5 x 1013 Bq?
Explain your working. (2 marks)
Comment on the problems of storage of the fuel rods over this time period and beyond. (2 marks)
(Total 10 marks)
7. In 1909 Geiger and Marsden carried out an important experiment to investigate
alpha particle scattering. Alpha particles were directed towards a thin gold sheet
and detectors were used to observe the distribution of scattered alpha particles.
The black dots in the diagram represent the nuclei of gold atoms. Copy out, and add
to the diagram to illustrate what happened in this experiment. (3 marks)
Explain why this experiment led to the conclusion that an atom was composed
mainly of space, with a very small positive nucleus. (3 marks)
Below are some order of magnitude values for lengths:
10-21 m, 10-18 m, 10-15 m, 10-12 m, 10-9 m, 10-6 m, 10-3m.
Choose from these an approximate value for
(i) the diameter of a gold atom
(ii) the diameter of a gold nucleus (2 marks)
(Total 8 marks)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Da EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- A Complete Course in Physics (Graphs) - First EditionDa EverandA Complete Course in Physics (Graphs) - First EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy Spec-1Documento2 paginePhy Spec-1phliewNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys 699Documento25 paginePhys 699joseftrihandokoNessuna valutazione finora
- CAPE Physics Unit I MarathonDocumento26 pagineCAPE Physics Unit I MarathonLeighton ThompsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys 698Documento21 paginePhys 698joseftrihandokoNessuna valutazione finora
- Annual Examination Physics (Theory) Code - B: Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70Documento4 pagineAnnual Examination Physics (Theory) Code - B: Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70Sumathi SrinivasNessuna valutazione finora
- XI Question BankDocumento5 pagineXI Question BankRaviVarshneyNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-07 (Solved)Documento21 pagineCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-07 (Solved)cbsesamplepaper100% (2)
- (05!12!2021) II Puc Neet Question Paper - 11Documento18 pagine(05!12!2021) II Puc Neet Question Paper - 11Kavitha SaravanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chanakya Vidyalaya STD 11: Physics Unit TestDocumento51 pagineChanakya Vidyalaya STD 11: Physics Unit TestANUBHAV ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics - 11Documento11 paginePhysics - 11Ishika GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Allen Kota Test Papers (Medical)Documento47 pagineAllen Kota Test Papers (Medical)Dr AwesomeNessuna valutazione finora
- SQP Hy 11 2022 23Documento13 pagineSQP Hy 11 2022 23It's all About fitnessNessuna valutazione finora
- Fisdas1 Tugas 3 FixDocumento9 pagineFisdas1 Tugas 3 FixNopran KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Std. PHYSICS Pre Model Exam (31 10 2021)Documento9 pagine11 Std. PHYSICS Pre Model Exam (31 10 2021)FtssyNessuna valutazione finora
- Class-Xi Half Yearly ExaminationDocumento3 pagineClass-Xi Half Yearly Examinationapi-328778920Nessuna valutazione finora
- C 2Documento11 pagineC 2RushmoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Half Yearly Examination 2018-19Documento3 pagineHalf Yearly Examination 2018-19Kavya RajpootNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Std. PHYSICS Pre Model Exam (31 10 2021)Documento9 pagine11 Std. PHYSICS Pre Model Exam (31 10 2021)FtssyNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 2 Study Guide PhysicsDocumento11 pagineTest 2 Study Guide PhysicsKerry Roberts Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment2 Anuradhaanand 18508491 FinalDocumento21 pagineAssignment2 Anuradhaanand 18508491 Finalapi-333711903Nessuna valutazione finora
- Section A Physics Paper 1 Mechanics Revision Questions For A Level With AnswersDocumento120 pagineSection A Physics Paper 1 Mechanics Revision Questions For A Level With Answersakramkaweesi7Nessuna valutazione finora
- olympic 2023 النسخة الانجليزيةDocumento3 pagineolympic 2023 النسخة الانجليزيةphysicsolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neet Mm21 m1Documento43 pagineNeet Mm21 m1.aju12.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ex3mech 2019Documento8 pagineEx3mech 2019Nasim RazaviNessuna valutazione finora
- AssignmentDocumento6 pagineAssignmentAishley MatharooNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen.-Physics-1 Ch-46 Plus Week 6 Complete 10 Pages.v.1.0Documento10 pagineGen.-Physics-1 Ch-46 Plus Week 6 Complete 10 Pages.v.1.0John Bernard Abella GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wheat Fields Public School Ghudda, Bathinda S.A 1, Xi - PhysicsDocumento2 pagineWheat Fields Public School Ghudda, Bathinda S.A 1, Xi - PhysicsGurvinder SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch15 ReviewDocumento3 pagineCh15 ReviewHeimer SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Sem 2015-16Documento5 pagineSem 2015-16Samya QureshiNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY1 June 2003Documento2 paginePHY1 June 2003api-3726022Nessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 11 Physics Exam Preparation BookletDocumento64 pagineGrade 11 Physics Exam Preparation Bookletjass krishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mark Scheme Practice Mechanics 1110Documento26 pagineMark Scheme Practice Mechanics 1110XhanAfaqNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-08 (Solved)Documento22 pagineCBSE Class 11 Physics Sample Paper-08 (Solved)cbsesamplepaperNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 10 PHY1321 - Fall2018 Solutions PDFDocumento3 pagineAssignment 10 PHY1321 - Fall2018 Solutions PDFBrian LeNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement 1Documento20 pagineMeasurement 1Gaurav ShekharNessuna valutazione finora
- Psphystestju 02Documento20 paginePsphystestju 02STNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level PhysicsDocumento6 pagineA Level PhysicsPratibha BaluniNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Test-1 Class: Xi Subject: Physics Physical World (Chapter-1) Units & Measurement (Chapter-2)Documento21 paginePractice Test-1 Class: Xi Subject: Physics Physical World (Chapter-1) Units & Measurement (Chapter-2)Sunil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Paper Tallentex Class 9th 2023 24Documento16 pagineSample Paper Tallentex Class 9th 2023 24Rudresh kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- +1 Model 2011Documento4 pagine+1 Model 2011Xavier KattukulamNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics (Theory) Class - Xi Course Code-042Documento10 paginePhysics (Theory) Class - Xi Course Code-042Puneet KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- End of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CDocumento4 pagineEnd of Year AP Problems - 4 - Momentum CChristina ZhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice 11 23-24Documento4 paginePractice 11 23-24Gamer RocksyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbse Mixed Test Paper-01Documento12 pagineCbse Mixed Test Paper-01kamalkantmbbsNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys 697Documento19 paginePhys 697joseftrihandokoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento19 pagineChapter 4Shashank ShekharNessuna valutazione finora
- Mini PhyDocumento22 pagineMini PhyMichael LeungNessuna valutazione finora
- Jr. Inter Physics IMP QuestionsDocumento12 pagineJr. Inter Physics IMP Questionsnarasimharaov840Nessuna valutazione finora
- Class Xi Physics Sample PaperDocumento7 pagineClass Xi Physics Sample PaperHarekrishna DasNessuna valutazione finora
- National Tsing Hua University Physics Pre-TestDocumento4 pagineNational Tsing Hua University Physics Pre-TestPhyo ThetNessuna valutazione finora
- Newtons Laws of Motion MCQDocumento17 pagineNewtons Laws of Motion MCQApex Institute92% (12)
- Cbse Xi Physics Test PapersDocumento14 pagineCbse Xi Physics Test PapersBhavesh DesaiNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Physics Sample Papers Solved 05Documento24 pagine11 Physics Sample Papers Solved 05Shivam GargNessuna valutazione finora
- STPM 2015 Term 1 Trial SMK Sultan Abdul Hamid QuestionsDocumento9 pagineSTPM 2015 Term 1 Trial SMK Sultan Abdul Hamid QuestionsSouseiseki ChromeNessuna valutazione finora
- EM ModelDocumento4 pagineEM ModelArunGopal PonnusamyNessuna valutazione finora
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Da EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Valutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Murad Hosssain CVDocumento2 pagineMurad Hosssain CVIsrafil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- Further Pure Mathematics: Paper 1Documento36 pagineFurther Pure Mathematics: Paper 1Israfil Tamim100% (1)
- Section A Answer All The QuestionsDocumento17 pagineSection A Answer All The QuestionsIsrafil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- FrenxitDocumento2 pagineFrenxitIsrafil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2015 (IAL) QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelDocumento28 pagineJune 2015 (IAL) QP - Unit 1 Edexcel Physics A-LevelIsrafil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel GCE: 9801 Mathematics Advanced Extension AwardDocumento6 pagineEdexcel GCE: 9801 Mathematics Advanced Extension AwardIsrafil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics HW 27 - 4 - 20Documento2 paginePhysics HW 27 - 4 - 20Israfil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- 4PH1 1P Que 20200305 PDFDocumento32 pagine4PH1 1P Que 20200305 PDFIsrafil Tamim100% (8)
- Physics HW 27 - 4 - 20Documento2 paginePhysics HW 27 - 4 - 20Israfil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- Classwork and Homework FormatDocumento3 pagineClasswork and Homework FormatIsrafil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions PDFDocumento27 pagineFunctions PDFIsrafil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- General Certificate of Education: Pure Mathematics Syllabus BDocumento9 pagineGeneral Certificate of Education: Pure Mathematics Syllabus BIsrafil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- Web Based Result Publication System For Education Boards PDFDocumento2 pagineWeb Based Result Publication System For Education Boards PDFIsrafil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- AS Physics - Revision Notes Unit 3 - Medical PhysicsDocumento3 pagineAS Physics - Revision Notes Unit 3 - Medical PhysicsIsrafil TamimNessuna valutazione finora
- თინათინ ზურაბიშვილი, თვისებრივი მეთოდებიDocumento111 pagineთინათინ ზურაბიშვილი, თვისებრივი მეთოდებიNino LomaiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Faculty of AyurvedaDocumento9 pagineFaculty of AyurvedaKirankumar MutnaliNessuna valutazione finora
- My LH Cover LetterDocumento3 pagineMy LH Cover LetterAkinde FisayoNessuna valutazione finora
- TRUMPF Marking Laser BrochureDocumento48 pagineTRUMPF Marking Laser BrochureKKM SBNessuna valutazione finora
- Śāntarak ItaDocumento8 pagineŚāntarak ItaÁtilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solow 5e Web SolutionsDocumento58 pagineSolow 5e Web SolutionsOscar VelezNessuna valutazione finora
- HLA HART Concept of LawDocumento19 pagineHLA HART Concept of LawHarneet KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. N. Kumarappan IE (I) Council Candidate - Electrical DivisionDocumento1 paginaDr. N. Kumarappan IE (I) Council Candidate - Electrical Divisionshanmugasundaram32Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Software Architecture For The Control of Biomaterials MaintenanceDocumento4 pagineA Software Architecture For The Control of Biomaterials MaintenanceCristian ȘtefanNessuna valutazione finora
- Orange County Sheriff's Office SeaWorld Death Investigative ReportDocumento43 pagineOrange County Sheriff's Office SeaWorld Death Investigative ReportWESH2News100% (1)
- Federal Public Service CommissionDocumento2 pagineFederal Public Service CommissionNasir LatifNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulletin - February 12, 2012Documento14 pagineBulletin - February 12, 2012ppranckeNessuna valutazione finora
- 陳v Endometrial Cancer 2Documento48 pagine陳v Endometrial Cancer 201范芷紜Nessuna valutazione finora
- Roles of Community Health NursingDocumento2 pagineRoles of Community Health Nursingdy kimNessuna valutazione finora
- AromatherapyDocumento15 pagineAromatherapymurrmurreNessuna valutazione finora
- EUROJAM Diary3Documento4 pagineEUROJAM Diary3Susan BakerNessuna valutazione finora
- The Senior High School in The Phillipines: The Way To The WorldDocumento5 pagineThe Senior High School in The Phillipines: The Way To The WorldRodel Ramos DaquioagNessuna valutazione finora
- M14 PManualDocumento382 pagineM14 PManualnz104100% (2)
- CrumpleZonesSE (Edit)Documento12 pagineCrumpleZonesSE (Edit)Dah Unknown MarksmenNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental and Chemical Policy Module3Documento47 pagineEnvironmental and Chemical Policy Module3jahazi1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ip TunnelingDocumento15 pagineIp TunnelingBon Tran HongNessuna valutazione finora
- Self-Actualization in Robert Luketic'S: Legally Blonde: A HumanisticDocumento10 pagineSelf-Actualization in Robert Luketic'S: Legally Blonde: A HumanisticAyeshia FréyNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of Woman Role in SocietyDocumento12 pagineIntroduction of Woman Role in SocietyApple DogNessuna valutazione finora
- Wapda CSR 2013 Zone 3Documento245 pagineWapda CSR 2013 Zone 3Naveed Shaheen91% (11)
- FacebookDocumento2 pagineFacebookAbhijeet SingareNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Research 2Documento16 paginePractical Research 2Benedict Coloma BandongNessuna valutazione finora
- Service Marketing - Term End Examination 2021 School of Business Management Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies, HyderabadDocumento2 pagineService Marketing - Term End Examination 2021 School of Business Management Narsee Monjee Institute of Management Studies, Hyderabadnatasha bennyNessuna valutazione finora
- THE PERFECT DAY Compressed 1 PDFDocumento218 pagineTHE PERFECT DAY Compressed 1 PDFMariaNessuna valutazione finora
- The English We SpeakDocumento2 pagineThe English We Speakcaeronmustai100% (1)