Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
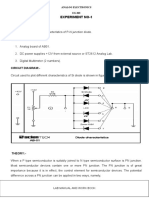
V-I Characteristics of Zener Diode and its Application as Zener Limiter
Caricato da
ShahZaib AnwarDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
V-I Characteristics of Zener Diode and its Application as Zener Limiter
Caricato da
ShahZaib AnwarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
_________________________________________________________________________
To plot V-I curve of Zener diode and
TITLE :
use it as Zener limiter.
DATE OF
: 07th Oct, 2019
EXPERIMENT
Lab Number : 04
NAME : ___________________
ROLL NO : ___________________
Mechanical Electronics Lab Page 1
_________________________________________________________________________
Objective:
• To observe and plot the V-I characteristics of Zener diode in forward and reverse
bias region.
• To build and analyze the Zener limiter circuit.
Equipment:
• Resistor (1K)
• Zener diode
• Multimeter
• Oscilloscope
• Function generator
• Connecting wires
Theory:
A Zener diode is a silicon semiconductor device that permits current to flow in either a
forward or reverse direction. The diode consists of a special, heavily doped p-n junction,
designed to conduct in the reverse direction when a certain specified voltage is reached.
The Zener diode has a well-defined reverse-breakdown voltage, at which it starts
conducting current, and continues operating continuously in the reverse-bias mode without
getting damaged. Additionally, the voltage drop across the diode remains constant over a
wide range of voltages, a feature that makes Zener diodes suitable for use in voltage
regulation, Zener limiter etc.
Forward biased Zener diode Reverse biased
Mechanical Electronics Lab Page 2
_________________________________________________________________________
Operation:
The Zener diode operates just like the normal diode when in the forward-bias mode, and
has a turn-on voltage of between 0.3 and 0.7 V. However, when connected in the reverse
mode, which is usual in most of its applications, a small leakage current may flow. As the
reverse voltage increases to the predetermined breakdown voltage (Vz), a current start
flowing through the diode. The current increases to a maximum, which is determined by
the series resistor, after which it stabilizes and remains constant over a wide range of
applied voltage.
There are two types of reverse breakdown regions in a Zener diode: avalanche breakdown
and Zener breakdown. The avalanche breakdown occurs in both normal diodes and Zener
diodes at high reverse voltage. While, Zener breakdown occur in Zener diodes at low
reverse voltage.
Task 1:(a)
1. Connect the circuit in forward biased direction.
2. Change the supply voltage from 0Vdc to 1.5 Vdc with a step of 0.1 V.
3. Observe the value of diode voltage drop and current passing through it using
multimeter in tabular form.
4. Make graph using these values to show the V-I characteristics curve of diode in
Forward bias region.
(b)
1. Connect the circuit in Reversed biased direction.
2. Change the supply voltage from 0Vdc to 30 Vdc with a step of 2 V.
3. Observe the value of diode voltage drop and current passing through it using
multimeter in tabular form.
4. Make graph using these values to show the V-I characteristics curve of Zener diode
in Reverse bias region.
(c)
• Combine both graphs to make V-I characteristics of Zener diode.
Mechanical Electronics Lab Page 3
_________________________________________________________________________
Task 2: (a) Zener limiter
1. Connect the circuit in forward biased direction.
2. Apply 5V peak sinusoidal signal with frequency of 50 Hz as input.
3. Observe the output waveform and take snap of it.
4. Measure the amplitude of signal in positive and negative half cycle using
oscilloscope.
(b)
1. Connect the circuit in reverse biased direction.
2. Apply 5V peak sinusoidal signal with frequency of 50 Hz as input.
3. Observe the output waveform and take snap of it.
4. Measure the amplitude of signal in positive and negative half cycle using
oscilloscope.
(c) Conclude Task 2 working principle in lab report briefly using circuit diagrams.
Mechanical Electronics Lab Page 4
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lab 2 - Diode CharacteristicsDocumento7 pagineLab 2 - Diode CharacteristicsFasil EndalamawNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 2 Wave Shaping CircuitsDocumento9 pagineExperiment 2 Wave Shaping CircuitsMaria Abia Lapena50% (2)
- Nonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsDa EverandNonlinear Electronics 1: Nonlinear Dipoles, Harmonic Oscillators and Switching CircuitsNessuna valutazione finora
- 16FF TSMCDocumento17 pagine16FF TSMCPraful GaikwadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4 (To Plot V-I Curve of Zener Diode and Use It As Zener Limiter)Documento5 pagineLab 4 (To Plot V-I Curve of Zener Diode and Use It As Zener Limiter)afaq ahmad khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2 (To Measure The V-I Characteristics Curve of Silicon Diode in Forward and Reverse Bias Mode)Documento4 pagineLab 2 (To Measure The V-I Characteristics Curve of Silicon Diode in Forward and Reverse Bias Mode)afaq ahmad khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Build and Analyze Diode RectificationDocumento6 pagineBuild and Analyze Diode Rectificationafaq ahmad khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of diode in half and full wave rectificationDocumento7 pagineAnalysis of diode in half and full wave rectificationShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Diode As RectifiersDocumento13 pagineDiode As RectifiersShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- EEB501 - Lab 8Documento3 pagineEEB501 - Lab 8Rahul Deo100% (1)
- Lab 3 and 4Documento10 pagineLab 3 and 4SARANG ABBASINessuna valutazione finora
- Zener Diode Characteristics Lab ReportDocumento4 pagineZener Diode Characteristics Lab ReportKashif Mujeeb Abdul MujeebNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Wave RectifierDocumento6 pagineFull Wave RectifierXavier0% (1)
- EL - 124 Electronic Devices & Circuits: Experiment # 06Documento10 pagineEL - 124 Electronic Devices & Circuits: Experiment # 06Jawwad IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Zener Diode CharacteristicsDocumento1 paginaZener Diode CharacteristicsPercivalEgauNessuna valutazione finora
- #1 The Diode Characteristic CurveDocumento4 pagine#1 The Diode Characteristic CurveNizamaddin İsrafilliNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronics Half Wave Rectification LabDocumento13 pagineBasic Electronics Half Wave Rectification LabPaa Kwesi ArhinfulNessuna valutazione finora
- PElabmanual (Fall 2022)Documento32 paginePElabmanual (Fall 2022)Qurat Ul AinNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE 1 Experiment 7 ZENER DIODESDocumento6 pagineECE 1 Experiment 7 ZENER DIODESNicole Soriano CalisinNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate 3Documento21 paginePlate 3James EricNessuna valutazione finora
- Theejaswini PhyDocumento22 pagineTheejaswini Phyindianaashika72Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ex 305Documento51 pagineEx 305DineshKumarCholkarNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB LEDs and ZenerDocumento12 pagineLAB LEDs and ZenerjosembosemNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics 1Documento42 pagineElectronics 1Shanti Emmanuelle EscabarteNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 5 Introduction To Diodes, Rectifiers, and Construction of A DC Power SupplyDocumento15 pagineExperiment 5 Introduction To Diodes, Rectifiers, and Construction of A DC Power SupplyJessica Laine TumbagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab ExperimentsDocumento45 pagineBasic Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab ExperimentsChirag Sachdeva100% (2)
- Electronic Circuits and Devices Laboratory - ELCE-221 Experiment No. 2 Diode Applications (Part A) Rectifiers, ClippersDocumento6 pagineElectronic Circuits and Devices Laboratory - ELCE-221 Experiment No. 2 Diode Applications (Part A) Rectifiers, ClippersLittle VoiceNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY547 - Lab Manual-Exp2 - SimulationDocumento3 paginePHY547 - Lab Manual-Exp2 - SimulationNurul Naafizah SulaimanNessuna valutazione finora
- Clamp and Clipper CircuitsDocumento19 pagineClamp and Clipper CircuitsAhmed Sobhy KhattabNessuna valutazione finora
- EMI Laboratory 2Documento2 pagineEMI Laboratory 2DEO SALVACIONNessuna valutazione finora
- KEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEDocumento34 pagineKEC151P - Lab - Experiments - UPDATED ONEAkshat GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- 15e282 18 Lab1Documento10 pagine15e282 18 Lab1shahid aliNessuna valutazione finora
- DEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Documento4 pagineDEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Pablo ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- KAlam LabManual EEE102 EWU Summer 2012Documento18 pagineKAlam LabManual EEE102 EWU Summer 2012Max TanNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE20L 2 ACTIVITY 2 Semiconductor DiodesDocumento10 pagineECE20L 2 ACTIVITY 2 Semiconductor DiodesDuque Raza - BlexelereyNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 3Documento12 pagineActivity 3Kurt Vendane VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- 15E282 18lab1Documento10 pagine15E282 18lab1Yadhuvanth kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Voltage Divider Bias Stability for BJTsDocumento13 pagineVoltage Divider Bias Stability for BJTsroden fabregasNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE Lab ManualDocumento81 pagineECE Lab Manualumaranitg2188Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - 07 14ME - Sec ADocumento4 pagineLab - 07 14ME - Sec AKhanSaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Clippers and Clampers LabDocumento21 pagineClippers and Clampers LabballDISCOVERIES PHballDISCOVERIESNessuna valutazione finora
- Half wave rectifier experimentDocumento5 pagineHalf wave rectifier experimentsaba rasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices & Circuits Lab ManualDocumento73 pagineElectronic Devices & Circuits Lab ManualVijayalakshmi PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Device Circuit Lab SheetDocumento27 pagineElectronics Device Circuit Lab Sheetjimfinch512Nessuna valutazione finora
- Diode Clipping Circuit ExperimentDocumento4 pagineDiode Clipping Circuit ExperimentMohsin TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 6 - Semiconductor DiodesDocumento8 pagineActivity 6 - Semiconductor DiodesskskskskNessuna valutazione finora
- Device Exp 2 Student ManualDocumento4 pagineDevice Exp 2 Student Manualgg ezNessuna valutazione finora
- A3 Relleta JamesDocumento9 pagineA3 Relleta JamesLorenzo AbolarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Engineering LaboratoryDocumento29 pagineElectrical Engineering Laboratorybrhanu degeneNessuna valutazione finora
- EC2700 LAB: Experiments Iii-VDocumento12 pagineEC2700 LAB: Experiments Iii-VS GNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Device Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsDocumento9 pagineElectronic Device Lab 1 Diode CharacteristicsVy NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- EDC Lab I ManualsDocumento101 pagineEDC Lab I ManualskattaswamyNessuna valutazione finora
- BVM Engineering College Certificate of Completion for Basic Electronics LabDocumento34 pagineBVM Engineering College Certificate of Completion for Basic Electronics LabKASHYAP BLOGNessuna valutazione finora
- BJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseDocumento29 pagineBJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseKrista JacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- Diode Lab CharacteristicsDocumento7 pagineDiode Lab CharacteristicsshahidNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Zener Voltage Regulator Diode Clippers ClampersDocumento7 pagine4 Zener Voltage Regulator Diode Clippers ClampersmakreloadedNessuna valutazione finora
- عملي دوائر اليوم2Documento24 pagineعملي دوائر اليوم2معاً إلى الجنةNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics & Microprocessor Lab ManualDocumento80 pagineElectronics & Microprocessor Lab ManualCyril Robinson Azariah John100% (5)
- Lab 5Documento5 pagineLab 5ShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Valutazione: 2.5 su 5 stelle2.5/5 (3)
- Hydrokinetic Turbine ProjectDocumento9 pagineHydrokinetic Turbine ProjectShahZaib Anwar0% (1)
- Water Level Indicator AlarmDocumento7 pagineWater Level Indicator AlarmShahZaib Anwar100% (1)
- Dynamics Project-Evaluation Criteria (2019)Documento1 paginaDynamics Project-Evaluation Criteria (2019)ShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 6Documento4 pagineLab 6ShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan: Institute of Space TechnologyDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan: Institute of Space TechnologyShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 9Documento3 pagineLab 9ShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan: Institute of Space TechnologyDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan: Institute of Space TechnologyShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- YaenDocumento2 pagineYaenShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics II Lesson PlanDocumento4 pagineThermodynamics II Lesson PlanShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 1Documento1 paginaQuiz 1ShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan: Institute of Space TechnologyDocumento3 pagineLesson Plan: Institute of Space TechnologyShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan: Institute of Space TechnologyDocumento3 pagineLesson Plan: Institute of Space TechnologyShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan: Institute of Space TechnologyDocumento3 pagineLesson Plan: Institute of Space TechnologyShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 5Documento5 pagineLab 5ShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- ProposalDocumento1 paginaProposalShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- ProposalDocumento2 pagineProposalShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermo ProjectDocumento5 pagineThermo ProjectShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Design and Development of Single Slider Crank MechanismDocumento1 paginaDesign and Development of Single Slider Crank MechanismShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics-1 Semester AssignmentDocumento9 pagineThermodynamics-1 Semester AssignmentShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- MS&E 11 Raja Muhammad Usama Muhammad Asim Harris Hassan Usman Ahmed SiddiquiDocumento28 pagineMS&E 11 Raja Muhammad Usama Muhammad Asim Harris Hassan Usman Ahmed SiddiquiShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Materials ProjectDocumento12 pagineEngineering Materials ProjectShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Materials Semester AssignmentDocumento16 pagineEngineering Materials Semester AssignmentShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Function of Crank Slider:: Calculation MethodologyDocumento2 pagineFunction of Crank Slider:: Calculation MethodologyShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties Advantages:: High Strength To Weight RatioDocumento7 pagineProperties Advantages:: High Strength To Weight RatioShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- TINDocumento16 pagineTINShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Axially Loaded MembersDocumento13 pagineAxially Loaded MembersUnknownNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Materials Semester AssignmentDocumento16 pagineEngineering Materials Semester AssignmentShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Page SummaryDocumento3 pagine2 Page SummaryShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Axially Loaded MembersDocumento13 pagineAxially Loaded MembersUnknownNessuna valutazione finora
- GSA Chipset Report November 2018Documento14 pagineGSA Chipset Report November 2018Muhammad Jamil AwanNessuna valutazione finora
- 300+ Top Microprocessors Questions and Answers PDF: Prisma™ Cloud SecurityDocumento14 pagine300+ Top Microprocessors Questions and Answers PDF: Prisma™ Cloud SecurityAawez AkhterNessuna valutazione finora
- Broadband Microstrip AntennasDocumento6 pagineBroadband Microstrip AntennasthgnguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Electronics July 2017 (2015 Scheme)Documento3 pagineAnalog Electronics July 2017 (2015 Scheme)Movies and tv showsNessuna valutazione finora
- Leader lsg-17 0.1..150mhz Signal GeneratorDocumento13 pagineLeader lsg-17 0.1..150mhz Signal GeneratorTheodor EikeNessuna valutazione finora
- Fast Audio Peak Limiter CircuitDocumento4 pagineFast Audio Peak Limiter CircuitLuiz Clemente PimentaNessuna valutazione finora
- CAMPVS2580Documento3 pagineCAMPVS2580xdsmNessuna valutazione finora
- ViewSonic VPW500 PlasmaDocumento82 pagineViewSonic VPW500 PlasmaMikhailNessuna valutazione finora
- THEVA12LVDR820 Manual Rev.1.00 E PDFDocumento4 pagineTHEVA12LVDR820 Manual Rev.1.00 E PDFAnarsinh SolankiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pinout at Haval M4 PDFDocumento4 paginePinout at Haval M4 PDFErasmo Israel Garcia OchoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Intelligent Power MOSFETDocumento6 pagineIntelligent Power MOSFETfreddys merchanNessuna valutazione finora
- REN R20ut0757ej3500-Pgfp5-List MAN 20201006Documento35 pagineREN R20ut0757ej3500-Pgfp5-List MAN 20201006KingNessuna valutazione finora
- LAN TopologiesDocumento31 pagineLAN TopologiesDinku Minda100% (1)
- 05 - List of SymbolsDocumento6 pagine05 - List of Symbolsrajath RaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Microphone Order # 406.910: Eatures Echnical PecificationsDocumento2 pagineDynamic Microphone Order # 406.910: Eatures Echnical PecificationsgbNessuna valutazione finora
- 3RK12071BQ400AA3 Datasheet enDocumento5 pagine3RK12071BQ400AA3 Datasheet enNhân LêNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Training Report From Bharti Airtel Limited, ON Bts Installation and MaintenanceDocumento43 pagineIndustrial Training Report From Bharti Airtel Limited, ON Bts Installation and MaintenanceGagleen KourNessuna valutazione finora
- Sony kdl-22cx520 kdl-32cx520 cx523 kdl-40cx520 523 Chassis Az2g SM PDFDocumento98 pagineSony kdl-22cx520 kdl-32cx520 cx523 kdl-40cx520 523 Chassis Az2g SM PDFBoKi PoKiNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro GalDocumento15 pagineIntro GalFilozófus ÖnjelöltNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet - HK 1ss357 2716684Documento2 pagineDatasheet - HK 1ss357 2716684Jairo Antonio Carreño RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- © J Wagner March 20, 2000Documento31 pagine© J Wagner March 20, 2000S.S. MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 FET Amplifier PDFDocumento21 pagine9 FET Amplifier PDFabdullah mohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical Properties of Mos and Cmos CircuitsDocumento3 pagineBasic Electrical Properties of Mos and Cmos Circuitsmayamohan72550% (2)
- Programmable Interval Timer Initialization and Operation ModesDocumento34 pagineProgrammable Interval Timer Initialization and Operation ModesSayan GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- MN 012479 R02 HV40.000 Chipeo SiteDocumento20 pagineMN 012479 R02 HV40.000 Chipeo SiteSecun lasogaNessuna valutazione finora
- Prog Controller Wiring SystemsDocumento208 pagineProg Controller Wiring SystemsKyle StackNessuna valutazione finora
- Millman's Theorem: Chapter 10 - DC Network AnalysisDocumento17 pagineMillman's Theorem: Chapter 10 - DC Network AnalysisAce Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Programador AVR PDFDocumento7 pagineProgramador AVR PDFGustavoFloresNessuna valutazione finora
- DC aDCghskjskksks FjsDocumento4 pagineDC aDCghskjskksks FjsSaiteja GundapuNessuna valutazione finora