Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Basic Electrical Engineering
Caricato da
netcity143Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Basic Electrical Engineering
Caricato da
netcity143Copyright:
Formati disponibili
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 3 1 0 4
COURSEOBJECTIVE:
1. To obtain basic knowledge on electrical quantities such as current, voltage, power and energy.
2. To provide adequate working knowledge on basic DC and AC circuits used in electrical and electronic
devices.
3. To understand the working principle, construction, applications of DC machines, AC machines & measuring
instruments.
4. To emphasize the importance of transformers in transmission and distribution of electric power.
UNIT I DC Circuits 12
Electrical circuit elements (R, L and C), voltage and current sources, Kirchoff current and voltage laws, Mesh and
Nodal analysis, Analysis of simple circuits with dc excitation, Wye↔Delta Transformation, Superposition, Thevenin
and Norton Theorems. Time-domain analysis of first-order RL and RC circuits.
UNIT II AC Circuits 12
Representation of sinusoidal waveforms, peak and rms values, phasor representation, real power, reactive power,
apparent power, power factor. Analysis of single-phase ac circuits consisting of R, L, C, RL, RC, RLC combinations
(series and parallel), resonance. Three phase balanced circuits, voltage and current relations in star and delta
connections.
UNIT III Transformers 12
Magnetic materials, BH characteristics, ideal and practical transformer, equivalent circuit, losses in transformers,
regulation and efficiency. Auto-transformer and three-phase transformer connections.
UNIT IV Electrical Machines & Power Converters 12
Generation of rotating magnetic fields, Construction and working of a three-phase induction motor, Significance of
torque-slip characteristic. Construction of Single phase induction motor. Construction, working, torque-speed
characteristic and speed control of separately excited dc motor. DC-DC buck and boost converters, duty ratio control.
Single phase Bridge Rectifier, Single Phase voltage source inverters.
UNIT V Electrical Installations 12
Components of LT Switchgear: Switch Fuse Unit (SFU), MCB, ELCB, MCCB, Types of
Wires and Cables, Earthing. Types of Batteries, Important Characteristics for Batteries. Elementary calculations for
energy consumption, power factor improvement and battery backup.
TOTAL:60h
COURSE OUTCOME:
At the end of this course the students will be able to,
CO1: Predict the behavior of any electrical and magnetic circuits. Formulate and solve complex AC, Dc circuits.
CO2: Identify the type of electrical machine used for that particular application.
CO3: Realize the requirement of transformers in transmission and distribution of electric power and other
applications.
CO4: Demonstrate wiring, earthing and to do power factor calculations.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Power Electronics and Energy Conversion Systems, Fundamentals and Hard-switching ConvertersDa EverandPower Electronics and Energy Conversion Systems, Fundamentals and Hard-switching ConvertersNessuna valutazione finora
- Bee SyllabusDocumento2 pagineBee SyllabusADARSH ANNADURAI 220801010Nessuna valutazione finora
- BEEE Mech SyllabusDocumento2 pagineBEEE Mech SyllabusSATHISH MOTHENessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus KEE101TDocumento1 paginaSyllabus KEE101TDr. Abhishek MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- DEMODocumento2 pagineDEMOShaik Abdul RaqeebNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Year Syllabus 2018 19Documento89 pagine1st Year Syllabus 2018 19Abhishek GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical SyllabusDocumento2 pagineElectrical Syllabusharsh dubeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Bee IliyasDocumento3 pagineBee Iliyassr2846877Nessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus - EE1100 (April - June 2021)Documento1 paginaSyllabus - EE1100 (April - June 2021)Phalgun Mukesh Vyas ch19b076Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocumento3 pagineBasic Electrical EngineeringAyush PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 0 - Introduction To The CourseDocumento4 pagineLecture 0 - Introduction To The CourseTushar SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Power El. SyllebusDocumento2 paginePower El. SyllebusVipul RamolaNessuna valutazione finora
- SEM1Documento26 pagineSEM1Soham JoitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Name of Department:-Electrical EngineeringDocumento2 pagineName of Department:-Electrical EngineeringAnonymous HyOfbJ6Nessuna valutazione finora
- ES103Documento3 pagineES103Sualé SualéNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1: DC Circuits (8 Hours)Documento3 pagineModule 1: DC Circuits (8 Hours)Animesh KarmakarNessuna valutazione finora
- 5basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocumento2 pagine5basic Electrical and Electronics Engineeringpurushotham1982Nessuna valutazione finora
- BEEE SyllabusDocumento2 pagineBEEE Syllabushard.worker123hwNessuna valutazione finora
- Course 2. Basic Electrical Technology (Video Course) Faculty Coordinator(s) : 1Documento32 pagineCourse 2. Basic Electrical Technology (Video Course) Faculty Coordinator(s) : 1Ursap BuddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus of EECEDocumento33 pagineSyllabus of EECEshahzad pervezNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Electrical Engineering (ECE) : Unit 1 DC CircuitsDocumento2 paginePrinciples of Electrical Engineering (ECE) : Unit 1 DC CircuitsPavan KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus Sem4Documento5 pagineSyllabus Sem4Megha SaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee001 Power Generation Systems: L T P CDocumento32 pagineEe001 Power Generation Systems: L T P CPARTH DAVENessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus - Basic Electrical and Electronics Engg.Documento1 paginaSyllabus - Basic Electrical and Electronics Engg.JET JETNessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts of EEE (CS)Documento8 pagineConcepts of EEE (CS)Vikram RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ma205 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations: L T P CDocumento8 pagineMa205 Transforms and Partial Differential Equations: L T P CBharathwaj SreedharNessuna valutazione finora
- Text/Reference BooksDocumento5 pagineText/Reference BooksAnonymous DuNDBdNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus For ElectDocumento30 pagineSyllabus For Elects MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical EnggDocumento4 pagineBasic Electrical EnggRohit Parmar0% (1)
- Lesson Plan For BEEEDocumento18 pagineLesson Plan For BEEEdineshanand810100% (1)
- Beee SyllabusDocumento3 pagineBeee SyllabusHarshajit BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- T2F50C1 Type of Course: Core: Teaching Scheme (L-T-P: 3-0-2) Credits 04 Marks: 150 Theory: 100 Practical: 50Documento6 pagineT2F50C1 Type of Course: Core: Teaching Scheme (L-T-P: 3-0-2) Credits 04 Marks: 150 Theory: 100 Practical: 50sunilNessuna valutazione finora
- RevelectricalDocumento11 pagineRevelectricalapi-26789938Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ee100 Basics of Electrical EngineeringDocumento3 pagineEe100 Basics of Electrical EngineeringSh PNessuna valutazione finora
- BE 2nd SemDocumento2 pagineBE 2nd SemDorothy SaikiaNessuna valutazione finora
- 10133ee206 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering PDFDocumento1 pagina10133ee206 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering PDFMuruga Raj20% (5)
- To Impart Basic Knowledge About The Electrical EngineeringDocumento3 pagineTo Impart Basic Knowledge About The Electrical EngineeringSingam SridharNessuna valutazione finora
- UEE001 SyllabusDocumento2 pagineUEE001 SyllabusashNessuna valutazione finora
- 280 - BE8255 Basic Electrical and Electronics and Measurement Engineering - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusDocumento2 pagine280 - BE8255 Basic Electrical and Electronics and Measurement Engineering - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusIni IniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- FRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadDocumento1 paginaFRM Course Syllabus IPDownloadMovie ClipsNessuna valutazione finora
- 19EE211Documento3 pagine19EE211chaitanya200039Nessuna valutazione finora
- B.sc. I ElectronicsDocumento6 pagineB.sc. I ElectronicsitsquitenNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus UEE001 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGDocumento2 pagineSyllabus UEE001 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERINGWarden Hostel GNessuna valutazione finora
- Ece131 SyDocumento2 pagineEce131 SySmita Rani SatapathyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological University: Magnetic Fields and Magnetic CircuitsDocumento3 pagineGujarat Technological University: Magnetic Fields and Magnetic CircuitsDarshit KotadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3. Electrical Fundamentals 1Documento4 pagineModule 3. Electrical Fundamentals 1janhaviNessuna valutazione finora
- RGPV Syllabus Btech Ee 5 Sem All SubjectsDocumento17 pagineRGPV Syllabus Btech Ee 5 Sem All SubjectsSandeep TaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec2151 Syllab Electric Circuits and Electron DevicesDocumento2 pagineEc2151 Syllab Electric Circuits and Electron DevicesJahith HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- 0133EE206 BASIC Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocumento8 pagine0133EE206 BASIC Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDeena DhayalanNessuna valutazione finora
- III Sem SyllbusDocumento11 pagineIII Sem SyllbusS B RajNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Module EASADocumento4 pagine3 Module EASARzVaan ArfiNessuna valutazione finora
- ENGG 112 Elements of Engineering II 3 CreditsDocumento1 paginaENGG 112 Elements of Engineering II 3 CreditsRojan PradhanNessuna valutazione finora
- BEEE SyllabusDocumento2 pagineBEEE SyllabusVivek GaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Under Civil, Mechanical and Technology Faculties) : L T P C 4 0 0 4 Unit I: Electrical Circuits and Measurments 12Documento7 pagineUnder Civil, Mechanical and Technology Faculties) : L T P C 4 0 0 4 Unit I: Electrical Circuits and Measurments 12Deena DhayalanNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Semester Electrical SyllabusDocumento4 pagine3rd Semester Electrical SyllabusHimanshu MalviyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus FeeDocumento2 pagineSyllabus Feedarsh.dave999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Fundamentals: LevelDocumento6 pagineElectrical Fundamentals: LevelSajjad ShamimNessuna valutazione finora
- Generation and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseDa EverandGeneration and Transmission of Electric Power: Lecture Notes of the Generation and Transmission of Electric Power CourseNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseDa EverandPower Electronics: Lecture Notes of Power Electronics CourseNessuna valutazione finora
- CCTV QuotationDocumento1 paginaCCTV Quotationnetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pan Update FormDocumento1 paginaPan Update FormAbhilash AbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- MC Format PDFDocumento1 paginaMC Format PDFnetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Website Redesign ProposalDocumento2 pagineWebsite Redesign ProposalDarshan100% (1)
- Hospital PDFDocumento31 pagineHospital PDFPon KrithikhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mahathma Gandhi International School CuddaloreDocumento1 paginaMahathma Gandhi International School Cuddalorenetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- FromDocumento1 paginaFromnetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical ChangesDocumento3 pagineChemical Changesnetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anna Univ - 2018Documento1 paginaAnna Univ - 2018netcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Salary CertificateDocumento1 paginaSalary Certificatenetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Age Declaration Form PDFDocumento1 paginaAge Declaration Form PDFdhokalerajNessuna valutazione finora
- PCCDocumento1 paginaPCCnetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bhabha Atomic Research CentreDocumento2 pagineBhabha Atomic Research Centrenetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bank Verfication Letter FormatDocumento1 paginaBank Verfication Letter Formatnetcity143100% (1)
- APP FormDocumento2 pagineAPP Formnetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Age Declaration Form PDFDocumento1 paginaAge Declaration Form PDFdhokalerajNessuna valutazione finora
- Salary CertificateDocumento1 paginaSalary Certificatenetcity143100% (2)
- Salary CertificateDocumento1 paginaSalary Certificatenetcity1430% (1)
- M Com Strategic Management Project Topics PDFDocumento4 pagineM Com Strategic Management Project Topics PDFnetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Company ProfileDocumento13 pagineCompany Profilenetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Satisfaction Project ReportDocumento75 pagineCustomer Satisfaction Project ReportSiddareddy Siddu84% (108)
- Age Declaration Form PDFDocumento1 paginaAge Declaration Form PDFdhokalerajNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Satisfaction Project ReportDocumento75 pagineCustomer Satisfaction Project ReportSiddareddy Siddu84% (108)
- M Com Strategic Management Project TopicsDocumento1 paginaM Com Strategic Management Project Topicsnetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Railway Reservation Form Date:: Train No./ NameDocumento1 paginaRailway Reservation Form Date:: Train No./ Namenetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Short Essay On ApjDocumento2 pagineShort Essay On Apjnetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tia 568 C.2 PDFDocumento230 pagineTia 568 C.2 PDFMarco Cruz100% (1)
- Sign:: Passport Application Form DateDocumento1 paginaSign:: Passport Application Form Datenetcity143Nessuna valutazione finora
- Identification CertificateDocumento1 paginaIdentification Certificatenetcity14367% (6)
- كتاب التوزيع الكهربى الجزء الثانىDocumento218 pagineكتاب التوزيع الكهربى الجزء الثانىMohammed SalahNessuna valutazione finora
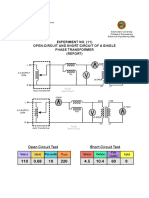
- Experiment No.11 - Machines LabDocumento3 pagineExperiment No.11 - Machines LabSBNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical June 2012 NewDocumento4 pagineBasic Electrical June 2012 NewPrasad C MNessuna valutazione finora
- Transmission Monitor PDFDocumento31 pagineTransmission Monitor PDFKyle WatsonNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hubbard Energy Transformer by Gaston Burridge, Fate Magazine 1956Documento24 pagineThe Hubbard Energy Transformer by Gaston Burridge, Fate Magazine 1956pplowe2305tedNessuna valutazione finora
- Instructions Tower T1-T3-T5-T2-T4-T6 Controller Gm.2.001050.en.01 PDFDocumento33 pagineInstructions Tower T1-T3-T5-T2-T4-T6 Controller Gm.2.001050.en.01 PDFazizanNessuna valutazione finora
- Smps 1Documento23 pagineSmps 1Tewodros ShegawNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Arc Furnace1Documento8 pagineElectric Arc Furnace1havejsnjNessuna valutazione finora
- TPRO - 87T - 3 Winding 3 Phase - Trip TestDocumento40 pagineTPRO - 87T - 3 Winding 3 Phase - Trip Testsykimk8921Nessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing Electrode CorporateDocumento53 pagineEarthing Electrode CorporateRAVI KUMAR0% (1)
- Sumesh.S: Sumeshsudhakarr@yahoo - Co.inDocumento4 pagineSumesh.S: Sumeshsudhakarr@yahoo - Co.inAbhilash P PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Shubham DVC NewDocumento39 pagineShubham DVC NewRohan Kumar SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculam Vitae: Position Desire: Career ObjectiveDocumento6 pagineCurriculam Vitae: Position Desire: Career ObjectiveTreesa ArchnanaNessuna valutazione finora
- A2-112 CIGRE 2012: 21, Rue D'artois, F-75008 PARISDocumento10 pagineA2-112 CIGRE 2012: 21, Rue D'artois, F-75008 PARISMohd Ghazali Mohd NorNessuna valutazione finora
- 500W Mos-Fet Power Inverter..Documento4 pagine500W Mos-Fet Power Inverter..slam12125Nessuna valutazione finora
- Proddocspdf 2 248 PDFDocumento20 pagineProddocspdf 2 248 PDFRaj KrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Easy Understanding of 3-Phase Transformer Connections (Delta-Delta, Wye-Wye, Delta-Wye and Wye-Delta) - EEPDocumento14 pagineEasy Understanding of 3-Phase Transformer Connections (Delta-Delta, Wye-Wye, Delta-Wye and Wye-Delta) - EEProbert_rjc100% (1)
- Fault - Current XR Relation React-ResistDocumento6 pagineFault - Current XR Relation React-ResistRiAlNessuna valutazione finora
- 36kV GISDocumento19 pagine36kV GISNiket GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Training ReportDocumento70 pagineFinal Training ReportkushalchandelNessuna valutazione finora
- Elctric Supply ManualDocumento834 pagineElctric Supply ManualThirunavukkarasu VaratharajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Arcing FaultDocumento86 pagineArcing FaultMehdi_Mashayekhi_172100% (1)
- Alter TTB Drive For DC Motors With Field ControlDocumento48 pagineAlter TTB Drive For DC Motors With Field ControlJorge SánchezNessuna valutazione finora
- FusesDocumento34 pagineFusesOrlando RomaniNessuna valutazione finora
- SECTION 16055 General Provision of Low Voltage Electrical WDocumento35 pagineSECTION 16055 General Provision of Low Voltage Electrical Wefmartin21100% (1)
- Case 1: Equal Impedance, Ratios and Same kVA: ExampleDocumento2 pagineCase 1: Equal Impedance, Ratios and Same kVA: ExampleSohail ANessuna valutazione finora
- 1MDB02006-En en COMBIFLEX Generator Protection RelaysDocumento16 pagine1MDB02006-En en COMBIFLEX Generator Protection Relaysshaik abdulaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- Voltage ProfileDocumento443 pagineVoltage Profileexecutive design2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Item Wise Details of Vendor Registration With Registration No. and DateDocumento20 pagineItem Wise Details of Vendor Registration With Registration No. and DatesunilgvoraNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Sep-603b Thol Ret 670Documento9 pagine08 Sep-603b Thol Ret 670m khNessuna valutazione finora