Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
The Biology of the Southern Ocean
Caricato da
Ellie M.Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Biology of the Southern Ocean
Caricato da
Ellie M.Copyright:
Formati disponibili
30° 0° 30°
CONVER
IC— GE
R CT NC
E
TA
N
A
Prince Edward
Bouvetaya Marion
Island
Island
South South Sandwich
Georgia Islands
60° lies 60°
Crozet
Falkland South Orkney Sanae
Neumayer
SOUTH Islands Islands
AMERICA
Signy Syowa
South QUEEN MAUD
Shetland 75°S LAND lies
Islands Larsen Halley Kerguelen
ENDERBY McDonald Is
Ice Shelf LAND Mawson
AN Ronne Heard
T Island
Ice Prydz Bay
AR
Shelf GREATER
TIC
ANTARCTICA Davis
Siple
PE
NI
90° LESSER Amundsen Mirny 90°
NS
Scott
UL
Peter I Island ANTARCTICA
A
Oasis
WILKES
MARIE BYRD LAND
Ross Casey
LAND
Ice Shelf
VICTORIA
ROSS LAND
SEA
McMurdo Scott
75°W 70° 65° 60° 55°W
Bellingshausen Hallett
Frei Dumont
Balleny D'Urville
Arctowski
Deception I Islands
Scott Island
Palmer
65°S Faraday
60°S 120°
Rothera Almirante
Brown Macquarie
Island
Campbell
Island
Auckland Island
70°S Fossil 45°S
Bluff
NEW AUSTRALIA
80°W ZEALAND
50°W 180° 150°
Antarctica is both a continent and an ocean. The continent is inextricably linked to the vast extent of the Southern Ocean
surrounding it, an ocean that supports a teaming array of life, ranging from microscopic plants that form part of the
phytoplankton responsible for primary production to the mighty whales, our largest marine mammals. Whilst our knowledge
of the biology of these waters has been accumulating since the first voyages of discovery in the 18th century, there is yet
to be a comprehensive, single-author synthesis of the current state of that knowledge. This book sets out to correct that
deficiency.
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:48—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
Preface
Our knowledge of the biology of the seas surrounding the continent. The voluminous reports of these Discovery
Antarctic continent began with descriptions and specimens expeditions laid the indispensable foundation for subsequent
brought back by early naturalists on voyages of discovery in studies.
the Southern Ocean. Prominent among these were the early Southern Ocean marine research entered a new phase
French navigators such as Bouvet de Lozier, who discovered following the establishment, in 1957, of the Special (later the
Bouvet Island in 1739, and Yves Joseph de Kerguelen- Scientific) Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). This
Tremarez, who discovered the island that bears his name initiated the modern era of Southern Ocean research in which
some 30 years later. These were followed by the voyages of many countries played roles, notably the Soviet Antarctic
Captain Cook, who, in 1772, reached 718 10 0 S in the Expeditions in the Vitez and Ob and the United States Eltanin
Bellingshausen Sea. In 1819, the Russian explorer Admiral cruises. Other countries such as Great Britain, France, South
Bellingshausen was first to tow a net at the stern of his ship Africa, Chile, Argentina, Australia and Japan were also very
and he found that it collected more organisms during the active during this period. In 1972, a coordinated international
night than during the day. He was probably the first to collect research program was initiated with the establishment of the
the Antarctica krill, Euphausia superba. BIOMASS (Biological Investigations of Antarctic Systems
The first serious scientific marine research was carried and Stocks) Program (El-Sayed 1996).
out by James Eights who sailed in 1929 with the American My own involvement in Antarctic research began with
sealing Captains Palmer and Pendleton. Eights described the a visit to McMurdo Sound in 1960 where one of my staff
natural history of the South Shetland Islands. His best known in the Department of Zoology at the University of
discovery was of a ten-legged pycnogonid. Soon after, there Canterbury, Dr. Bernard Stonehouse, was initiating a
followed a series of national expeditions led by Dumont research program on Adelie penguins and McCormick
D’Urville of France (1837–1840), Charles Wilkie of the skuas. This led to the establishment of the University of
United States (1838–1842), and Sir James Clark Ross of Canterbury Antarctic Research Unit (Knox 1986, 1988)
Britain (1939–1943). Among the naturalists who accom- that carried out continuous summer research in the
panied these expeditions, the most notable were J.D. Dana, McMurdo Sound region over the period 1960–1983, the
on the Wilkie expedition, and J.D. Hooker, on the Ross last twelve years of which I was director of the unit.
expedition. These expeditions all made extensive collections During the summers of 1969 and 1970, I initiated an
of marine organisms. inshore marine research program that continued until the
There was a renewal of Antarctic exploration at the end 1982–1983 season. Throughout the operation of the unit,
of the nineteenth century. Major expeditions included the some sixty research students participated in its activities.
British (1899–1900), the Belgian (1898), the Swedish Interaction with these enthusiastic young minds had a
National Expedition (1902–1904), the Scottish National significant influence on many of the concepts developed in
Antarctic Expedition (1902–1904), the German expedition The Biology of the Southern Ocean. I also have had the
(1901–1903) in the Gauss, and the French Expedition in the good fortune to become involved in international Antarctic
Pourquoi Pas (1908–1910). All of these expeditions resulted science activities, first as a member and secretary of the
in taxonomic studies that laid the foundation for later studies SCAR Biology Working Group on Biology and as a
of the marine flora and fauna. member of SCAR since 1969. I was a member of the
Ecological studies in the Southern Ocean began with the Group of Specialists on the Living Resources of the
work of naturalists attached to land-based, over-wintering Southern Ocean from its inception and I attended the first
parties such as those of Sir Ernest Shackleton’s 1907–1909 two meetings of CCAMLR (Convention on the Conserva-
expedition and Captain Scott’s two polar expeditions. tion of Antarctic Marine Living Resources). These
Antarctic marine studies received a tremendous impetus activities brought me into contact with a wide range of
from the investigations that began in 1925 with the study of Antarctic scientists from all the SCAR countries.
whale carcasses at the whaling stations at Grytviken in South The suggestion for The Biology of the Southern Ocean
Georgia. The work of the scientists expanded to include, not was made by Dr. Bernard Stonehouse and, without his encour-
only studies on whale demography and ecology, but also of agement, it would not have been written. Discussions with
the physical, chemical and biological oceanography of the Antarctic colleagues throughout the SCAR community have
Southern Ocean in order to gain an understanding of the had a profound influence on its development. Amongst these I
factors influencing the distribution, reproduction, and growth particularly wish to thank Professor Sayed El-Sayed, the late
of whale stocks. These investigations contributed to the first Sir George Deacon, Professor A.L. DeVries, Professor M.
long-term studies of the Antarctic pelagic ecosystem, and Fukuchi, Sir Martin Holdgate, Professor T. Hoshiai. Dr. J.C.
they were the first that extended right around the Antarctic Hureau, Dr. K.B. Kerry, Dr. Y. Naito, the late Dr. T. Nemoto,
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
Dr. J. Oliver, Dr. J. Warham, and Professor E.C. Young. publication of the first edition of The Biology of the Southern
Access to literature was greatly facilitated by periods spent in Ocean. While some of the information in the first edition is
the libraries of the British Antarctic Survey and the National retained, it is essentially a new account. The task of
Institute of Polar Research, Tokyo. Dr. D.W.H. Walton summarizing the large volume of research has proved a
reviewed all chapters of the original edition in various drafts difficult task. Most of the figures in the text have been
and I am grateful for his assistance and encouragement. I redrawn from the originals.
would also like to thank Dr. Maria Murphy and the staff of The book commences with a description of the physico-
Cambridge University Press for their patience and support chemical environment of the Southern Ocean and then
during the preparation of the first edition and for seeing the follows a logical sequence covering phytoplankton and
project through to completion. primary production, the sea ice microbial communities, and
The first edition of The Biology of the Southern Ocean the secondary consumers, the zooplankton. There is an
was published in 1993 and was well received. The print run extended chapter on the biology and ecology of Antarctic
was sold out a number of years ago. Some 13 years have krill, in view of its central position in the Southern Ocean
passed since then and a considerable amount of research has food web. Additionally, krill has been the subject of intensive
been carried out during this period. The original SCAR research programs over the past decades, especially during
countries engaged in marine research in the Southern Ocean the BIOMASS Programmes and subsequently by CCAMLR.
have been joined by other countries including China, A series of chapters consider the higher consumers, nekton
Ukraine, Uruguay, Korea, Ecuador, India, Peru and Spain, (with an emphasis on cephalopods), fish, seals, whales and
resulting in a much increased research effort. seabirds. A series of chapters then follow on selected
The last decade in particular had seen the initiation of ecosystem components: the benthic communities, life
several scientific programs to study phenomena and beneath the fast ice and ice shelves, recent advances in
processes of global significance in which the Southern understanding decomposition processes, and the role of
Ocean plays a key role. Some of the major programs are bacteria and protozoa. These are followed by an attempt at a
listed below and brief descriptions of the objectives of these synthesis of ecosystem dynamics, with an emphasis of the
are given in El-Sayed (1991). pelagic ecosystem and then three chapters dealing with
- Antarctic Marine Living Resources (AMLR) program resource exploitation, the impact of such exploitation on the
(1986-present) marine ecosystem, and the problems involved in the
- Antarctic Marine Ecosystem Research at the Ice-Edge management of the living resources. Three new chapters
Zone (AMERIEZ) (1983–1988) have been added to the second edition exploring the impact
- Research on Antarctic Coastal Ecosystem Rates of increased UV radiation, human impact on the marine
Program (RACER) (1986–1993) environment, and the impact of global warming on Southern
- Long-Term Ecological Research (Palme LTER) Ocean marine ecosystems.
(1980-present) As can be seen by the reference list at the end of this
- Southern Ocean Joint-Global Ocean Ecosystem volume, there is a considerable body of recent literature on
Dynamics (SO-GLOBEC) (1991–2009) the biology of the Southern Ocean. Because of the growth of
- Coastal and Shelf Ecology of the Antarctic Sea-Ice published research, I have had to be selective in the material
Zone (CS-EASIZ) (1993–2004) that is included. Examples have been carefully chosen from
- Antarctic Pack-Ice Seals (APIS) (1995-present) the pool of published research to illustrate the concepts
- European Polarstern Study (EPOS) (1988–89) discussed. There are, doubtless, others that could have been
- Research on Ocean-Atmosphere Variability and used and I apologize to authors whose work has not been
Ecosystem Response in the Ross Sea (ROAVERRS) included.
(1996–1998) In the preparation of this volume I have been supplied
The multi-disciplinary, multi-national cruises of the R/V with advanced copies of papers prepared or accepted for
Polarstern have been of particular importance in recent publication and I am grateful to all who supplied them. I am
years, especially the ANDEP cruises (2002–2005) that also appreciative of the support and encouragement of John
investigated the benthic fauna of the deep Weddell Sea. Sulzycki and the staff of CRC Press, in particular Pat
Over the period 2000–2002, a series of iron fertilization Roberson, during the preparation of this edition and for
experiments (SOIRE, SOFex and EISENEX) investigated seeing the project through to the completion of a high quality
the potential role of iron in controlling algal production in the product.
Southern Ocean. Recently, the New Zealand National This book is an attempt to synthesize the available
Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA) information into a coherent account of one of the most
investigated the richness and diversity of the benthos in a fascinating systems on the globe. I hope that it will prove
latitudinal gradient in the western Ross Sea in relation to useful to advanced undergraduates and to professionals
broader-scale environmental factors and local-scale variation engaged in Antarctic marine research, as well as to all
in productivity sources. interested or involved in Antarctic marine conservation and
As the result of the research activities listed above, there management. It will have been worthwhile if it stimulates
has been a considerable volume of published research on the others to work on the fascinating aspects of Antarctic marine
biology of the Southern Ocean in the 13 years since the research that have been discussed in this book.
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
Acknowledgments
I would firstly express my indebtedness to the many international Antarctic scientists, some of whom have been listed in the
Preface, who I have interacted with over the years. Discussions with them have influenced the development of many of the
concepts dicussed in this book. I acknowledge the outstanding contribution of Cambridge University Press, in the preparation
of the first edition of this book. I owe a great debt to the staff members and students who participated in the research activities of
the University of Canterbury Antarctic Research Unit.
I owe a great deal to John Sulzycki and the staff of CRC Press, in particular Pat Roberson for their patience and support
during the preparation of this second edition. Together with the staff of Alden Press Services who typeset this book they have
produced a high quality product.
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
Author
George A. Knox, C.N.Z.M., M.B.E., F.R.S.N.Z., was head University of Canterbury Antarctic Research Unit. He
of the Department of Zoology, University of Canterbury, has participated in many field expeditions, including the
Christchurch, New Zealand, from 1959 to 1976. He is now Chatham Islands 1954 Expedition (leader); the Royal Society
professor emeritus of zoology. of London Darwin Centennial Expedition to southern Chile
Professor Knox was born in New Zealand and received (marine biologist and deputy leader); thirteen summer
his education at the University of Canterbury, where he was expeditions to McMurdo Sound, Antarctica; the establishment
appointed a staff member in 1948. He has been a visiting of the Snares Islands Research Program (he participated
fellow at the East-West Center, Honolulu, and a visiting in three field expeditions); and participation in field
professor at the Department of Oceanography, Texas A&M expeditions to Campbell and Auckland Islands. He has
University and the Department of Environmental Engin- published over 100 scientific papers and 28 environmental
eering, University of Florida, Gainesville. He has visited and reports, written five books, and edited and co-authored three
worked in laboratories in the U.S., Canada, Chile, Japan, other volumes.
Australia, Western Europe, the USSR, and China. Professor Knox has received a number of awards and
Professor Knox’s research has been wide ranging and fellowships for his contributions to science, including Fellow
includes: (1) the systematics and distribution of polychaeta of the Royal Society of New Zealand (FRSNZ), 1963; Hutton
with special reference to New Zealand and Antarctica; (2) Medal, Royal Society of New Zealand, 1978; Conservation
rocky shore intertidal ecology and biogeography; (3) the Trophy, New Zealand Antarctic Society; Honorary Member of
ecology and conservation of islands; (4) studies on the pelagic Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research, 1982; member of
and benthic ecosystems beneath the sea ice in McMurdo the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (MBE), 1985;
Sound, Antarctica; and (5) estuarine and coastal ecology and the New Zealand Association of Scientists’ Sir Ernest Marsden
management. He established and directed the Estuarine Medal for Service to Science, 1985; and Companion of the
Research Unit in the Department of Zoology and the New Zealand Order of Merit (CNZM), 2001.
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
Contents
Chapter 1 The Southern Ocean
1.1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................. 1
1.2 The Evolution of the Southern Ocean......................................................................................................... 3
1.3 Bathymetry................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.4 Climate......................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.5 Ice Cover...................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.6 Circulation Patterns and Water Masses ...................................................................................................... 7
1.7 Some Regional Hydrographic Features..................................................................................................... 13
1.8 Bottom Water Formation........................................................................................................................... 14
1.9 Nutrients..................................................................................................................................................... 15
Chapter 2 Phytoplankton and Primary Production
2.1 Introduction................................................................................................................................................ 18
2.2 Data Base ................................................................................................................................................... 19
2.3 Species Composition and Distribution...................................................................................................... 19
2.4 Latitudinal Zonation of the Planktonic Subsystems ................................................................................. 24
2.5 Phytoplankton Biomass ............................................................................................................................. 30
2.6 Primary Production.................................................................................................................................... 32
2.7 Seasonal and Geographic Variation of Phytoplankton Biomass and Primary Production ...................... 36
2.8 Factors Affecting Primary Production....................................................................................................... 38
2.9 Growth Rates ............................................................................................................................................. 53
2.10 Heterotrophic Nutrition ............................................................................................................................. 56
2.11 A Model of Phytoplankton Production ..................................................................................................... 56
Chapter 3 Sea-Ice Microbial Communities
3.1 Introduction................................................................................................................................................ 59
3.2 Sea Ice as a Habitat ................................................................................................................................... 60
3.3 Sea-Ice Micro- and Meiofauna.................................................................................................................. 94
3.4 Dynamics of Sea-Ice Microbial Communities.......................................................................................... 96
Chapter 4 Zooplankton
4.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 100
4.2 Species Composition and Distribution.................................................................................................... 101
4.3 Life History and Growth ......................................................................................................................... 111
4.4 Vertical Migration ................................................................................................................................... 114
4.5 Swarming ................................................................................................................................................. 115
4.6 Feeding..................................................................................................................................................... 116
4.7 Biomass and Production .......................................................................................................................... 121
4.8 Ecophysiology.......................................................................................................................................... 123
4.9 Strategies for Winter Survival................................................................................................................. 124
Chapter 5 Krill
5.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 128
5.2 Species of Euphausiids ............................................................................................................................ 129
5.3 Life History and Growth ......................................................................................................................... 129
5.4 Krill Aggregations ................................................................................................................................... 139
5.5 Distribution and Abundance.................................................................................................................... 147
5.6 General Distribution Patterns .................................................................................................................. 150
5.7 Factors Affecting Distribution................................................................................................................. 152
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
5.8 Overwintering Mechanisms..................................................................................................................... 158
5.9 Stock Seperation ...................................................................................................................................... 161
5.10 Feeding and Energy Expenditure ............................................................................................................ 162
5.11 Krill Production ....................................................................................................................................... 172
Chapter 6 Nekton
6.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 177
6.2 Species Composition and Distribution.................................................................................................... 177
6.3 Cephalopods............................................................................................................................................. 178
Chapter 7 Fish
7.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 185
7.2 Species Composition and Distribution.................................................................................................... 187
7.3 Morphological and Physiological Adaptations ....................................................................................... 191
7.4 Reproduction and Growth ....................................................................................................................... 193
7.5 Age, Growth, Mortality and Biomass Structure ..................................................................................... 196
7.6 Feeding Ecology ...................................................................................................................................... 198
7.7 Factors Controlling the Distribution, Abundance, and Trophic Ecology of Antarctic Fish.................. 207
Chapter 8 Seals
8.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 209
8.2 Species Composition and Distribution.................................................................................................... 210
8.3 Abundance ............................................................................................................................................... 215
8.4 Social Organization and Reproductive Behaviour.................................................................................. 216
8.5 Feeding Ecology ...................................................................................................................................... 220
8.6 Reproduction, Growth, and Development............................................................................................... 227
8.7 Population Dynamics............................................................................................................................... 228
Chapter 9 Whales
9.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 231
9.2 Species Composition ............................................................................................................................... 232
9.3 Distribution, General Life Histories, and Migrations ............................................................................. 235
9.4 Segregation .............................................................................................................................................. 238
9.5 Reproduction............................................................................................................................................ 239
9.6 Feeding Ecology ...................................................................................................................................... 241
9.7 Bioenergetics............................................................................................................................................ 243
9.8 Population Dynamics............................................................................................................................... 245
9.9 Role in the Ecosystem ............................................................................................................................. 247
Chapter 10 Birds
10.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 249
10.2 Species Composition and Distribution.................................................................................................... 250
10.3 Breeding Biology..................................................................................................................................... 256
10.4 Nonbreeding Biology............................................................................................................................... 259
10.5 Food and Feeding Ecology...................................................................................................................... 259
10.6 Energetics................................................................................................................................................. 270
10.7 Population Structure and Dynamics........................................................................................................ 271
10.8 Current Status and Population Trends in Antarctic Seabirds ................................................................. 272
10.9 Role in the Ecosystem ............................................................................................................................. 273
Chapter 11 Benthic Communities
11.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 275
11.2 The Antarctic Benthic Environment ....................................................................................................... 276
11.3 Littoral Communities............................................................................................................................... 277
11.4 Shallow Sublittoral Communities ........................................................................................................... 281
11.5 Epifaunal Communities ........................................................................................................................... 288
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
11.6 Infaunal Communities ........................................................................................................................... 294
11.7 Shelf and Upper Slope Communities.................................................................................................... 300
11.8 Deep Sea Communities ......................................................................................................................... 300
11.9 Microbial Communities ......................................................................................................................... 301
11.10 Meiofauna .............................................................................................................................................. 301
11.11 Biogeography and Origin of the Benthic Biota .................................................................................... 302
11.12 Factors Responsible for Shaping the Antarctic Benthos ...................................................................... 303
11.13 Biogeographical Schemes for the Antarctic Region............................................................................. 307
11.14 Diversity, Abundance, and Biomass ..................................................................................................... 307
11.15 Food and Feeding .................................................................................................................................. 309
11.16 Bentho-Pelagic Coupling....................................................................................................................... 311
11.17 Ecological Strategies ............................................................................................................................. 312
Chapter 12 The Fast Ice and Ice Shelves
12.1 Introduction............................................................................................................................................ 317
12.2 The Coastal Fast Ice Environment ........................................................................................................ 317
12.3 Primary Production................................................................................................................................ 319
12.4 Sedimentation and Resuspension .......................................................................................................... 324
12.5 Zooplankton ........................................................................................................................................... 324
12.6 The Sympagic Community.................................................................................................................... 327
12.7 The Platelet Ice Community.................................................................................................................. 330
12.8 The Cryopelagic Community ................................................................................................................ 330
12.9 The Ross and McMurdo Ice Shelves .................................................................................................... 332
Chapter 13 Ice-Edge Processes
13.1 Introduction............................................................................................................................................ 341
13.2 The Ice-Edge Habitat............................................................................................................................. 342
13.3 Ice-Edge Phytoplankton Biomass and Primary Production.................................................................. 343
13.4 Potential Causes of Phytoplankton Blooms .......................................................................................... 347
13.5 A Model of Ice Edge Bloom Dynamics ............................................................................................... 350
13.6 Bacterioplankton .................................................................................................................................... 351
13.7 Ice-Edge Microheterotrophs .................................................................................................................. 351
13.8 Ice-Edge Zooplankton and Nekton ....................................................................................................... 352
13.9 Ice-Edge Vertebrates ............................................................................................................................. 355
13.10 The Importance of the Ice Edge in the Ecology of the Southern Ocean............................................. 357
Chapter 14 Decomposition and the Roles of Bacteria and Protozoa
14.1 Introduction............................................................................................................................................ 361
14.2 Quantities and Sources of Organic Matter............................................................................................ 362
14.3 Sedimentation of POM .......................................................................................................................... 366
14.4 Biogenic Fluxes in the Water Column.................................................................................................. 368
14.5 Bacteria .................................................................................................................................................. 371
14.6 Viruses ................................................................................................................................................... 376
14.7 Protozoa ................................................................................................................................................. 376
14.8 Bacteria–Protozoa–POM Interactions ................................................................................................... 382
14.9 Interactions of Bactivorous Gazers and Heterotrophic Bacteria .......................................................... 385
14.10 The Microbial Loop............................................................................................................................... 386
14.11 Nutrient Cycling .................................................................................................................................... 392
Chapter 15 Ecosystem Dynamics
15.1 Introduction............................................................................................................................................ 398
15.2 Pelagic Zonation .................................................................................................................................... 399
15.3 Phytoplankton and Primary Production ................................................................................................ 401
15.4 Food Webs ............................................................................................................................................. 406
15.5 Ecosystem Models ................................................................................................................................. 420
15.6 Southern Ocean Environmental Variability and Its Impact on the Pelagic Ecosystem....................... 442
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
Chapter 16 Resource Exploitation
16.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 449
16.2 Krill .......................................................................................................................................................... 450
16.3 Fish........................................................................................................................................................... 454
16.4 Seals ......................................................................................................................................................... 458
16.5 Whales...................................................................................................................................................... 461
Chapter 17 Ecosystem Changes Resulting from Resource Exploitation
17.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 467
17.2 Ecosystem Changes Following the Decline in Whale and Fish Stocks................................................. 467
17.3 Changes in Seal Population Dynamics ................................................................................................... 470
17.4 Changes in Breeding Success in Birds.................................................................................................... 472
17.5 The “Whale Reduction–Krill Surplus” Hypothesis ................................................................................ 472
17.6 Potential Ecosystem Changes That Might Result from Future Resource Exploitation......................... 473
Chapter 18 Management of Living Resources
18.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 475
18.2 The Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR).................. 475
18.3 Ecosystem Approach to the Management of the Living Resources of the Southern Ocean................. 476
18.4 The Role of Modelling Studies ............................................................................................................... 480
18.5 Monitoring Indicators of Possible Ecological Changes in the Antarctic Marine Ecosystem................ 483
18.6 Experimental Fishing as a Management Tool ........................................................................................ 486
18.7 Alternative Management Strategies ........................................................................................................ 486
Chapter 19 Ultraviolet Radiation
19.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 489
19.2 Biological Hazards of Ultraviolet Radiation........................................................................................... 490
19.3 UV Tolerance Mechanisms ..................................................................................................................... 491
19.4 Impacts of Ultraviolet Radiation on Antarctic Marine Biota................................................................. 492
19.5 Conclusions.............................................................................................................................................. 498
Chapter 20 Global Warming and Antarctic Marine Ecosystems
20.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 499
20.2 The Physical Environment ...................................................................................................................... 500
20.3 Evidence of Global Warming in the Southern Ocean ............................................................................ 502
20.4 The Potential Impact of Global Warming on Antarctic Marine Ecosystems ........................................ 509
20.5 Potential Changes in Ecosystem Structure and Dynamics ..................................................................... 516
20.6 Some General Conclusions...................................................................................................................... 517
Chapter 21 Human Impact
21.1 Introduction.............................................................................................................................................. 519
21.2 Impact of Waste Disposal ....................................................................................................................... 519
21.3 Impact of Tourism ................................................................................................................................... 521
21.4 Disturbance of Nesting Seabirds ............................................................................................................. 521
21.5 Contamination of Marine Biota by Pollutants ........................................................................................ 523
21.6 Impact of Oil Spills ................................................................................................................................. 524
21.7 The Impact of Resource Exploitation ..................................................................................................... 525
Epilogue ................................................................................................................................................................................... 527
Appendix.................................................................................................................................................................................. 531
References................................................................................................................................................................................ 533
Index......................................................................................................................................................................................... 609
3394—Prelims—2/11/2006—18:49—RATHNAS—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–14
The Southern Ocean
1
CONTENTS
1.1 Introduction ..........................................................................................................................................................................1
1.2 The Evolution of the Southern Ocean .................................................................................................................................3
1.3 Bathymetry ...........................................................................................................................................................................4
1.4 Climate .................................................................................................................................................................................4
1.4.1 Wind .........................................................................................................................................................................4
1.4.2 Temperature..............................................................................................................................................................4
1.4.3 Solar Radiation .........................................................................................................................................................5
1.5 Ice Cover ..............................................................................................................................................................................6
1.5.1 Seasonal Variation....................................................................................................................................................6
1.5.2 Ice Shelves and Icebergs..........................................................................................................................................6
1.6 Circulation Patterns and Water Masses ...............................................................................................................................7
1.6.1 Introduction ..............................................................................................................................................................7
1.6.2 Driving Forces ..........................................................................................................................................................8
1.6.2.1 Wind ..........................................................................................................................................................8
1.6.2.2 Ocean-Atmosphere Heat and Fresh Water Flux.......................................................................................9
1.6.3 Oceanic Circulation................................................................................................................................................10
1.6.3.1 Antarctic Circumpolar Current (West Wind Drift) ................................................................................10
1.6.3.2 Antarctic Coastal Current (East Wind Drift)..........................................................................................10
1.6.3.3 Circumpolar Frontal Zones .....................................................................................................................10
1.6.3.4 Gyres, Eddies, and Rings ........................................................................................................................10
1.6.3.5 Polynas.....................................................................................................................................................10
1.6.4 Water Masses .........................................................................................................................................................12
1.7 Some Regional Hydrographic Features .............................................................................................................................13
1.7.1 Southwest Atlantic and the Antarctic Peninsula Region.......................................................................................13
1.7.2 The Ross Sea ..........................................................................................................................................................13
1.8 Bottom Water Formation ...................................................................................................................................................14
1.9 Nutrients .............................................................................................................................................................................15
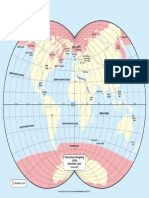
1.1 INTRODUCTION of the Southern Ocean (El-Sayed 1977, 1981, 1996;
Sahrhage 1988a), and they have also been the subject of
Over the past two decades in particular there has been an numerous reviews: Everson (1977b), Bengston (1978,
increasing emphasis on integrated studies of the Southern 1985a), Knox (1983, 1984), and Anonymous (USSR)
Ocean (Figure 1.1) aimed at understanding what has been (1984a, 1984b). The physical structure of the system has
termed “the Antarctic or Southern Ocean ecosystem.” While been described by Deacon (1937, 1982, 1984b), Brodie
the Southern Ocean can be considered a single ecosystem, it is (1965), Gordon (1967, 1983), Gordon and Goldberg (1970),
actually a series of interconnected ecosystems. These will be Gordon et al. (1978), Forster (1981, 1984), Gordon and
discussed in subsequent chapters. Descriptions of the Molinelli (1982), Amos (1984), Gordon and Owens (1987),
Southern Ocean system have been given by several workers Squire (1987), Foldvik and Gammelsrad (1988), and Smith
over the years (Hart 1942; Currie 1964; Holdgate 1967; Knox (1990b). Environmental data for the Southern Ocean is
1970, 1983; Everson 1977a, 1984c; Bengtson 1978, 1985a; available from a variety of sources. Some of the most
Baker 1979; Tranter 1982; Hempel 1985a, 1985b, 1987) valuable are the Discovery Reports, the Soviet Atlas of
The living resources of the Southern Ocean and their past Antarctica (Makismov 1966), the U.S. Navy Hydrographic
and future exploitation have been reviewed by the Office Oceanographic Atlas of the Polar Seas, the U.S.
SCAR/SCOR Group of Specialists on the Living Resources National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate of the
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
2 Biology of the Southern Ocean
90°W
Ice edge (March)
West wind drift South America
East wind drift
Weddell sea drift Falkland Is.
Drake passage
60°W
e
nc
e rg e
rctic c onv South Shetland Is.
Anta South Georgia
ce
g en
er
div South Orkney Is.
ic
rct
ta
An South Sandwich Is.
Weddell sea
Filchner
60° Ice Shelf 60°
Ross Sea Ross 0°
180°
Antipodes Is. Ice Shelf
Bouvet Is.
Campbell Is.
Auckland Is. Antarctic continent
Wilkes
Macquarie Is. Land
Tasman
Sea
Tasmania Prince Edward Is.
60° Marion Is.
Heard Is. Crozet Is.
Australia
Kerguelen Is.
90° E
FIGURE 1.1 Antarctica and the Southern Ocean showing the positions of oceanic fronts and surface currents. (From Knox, G.A., Antarctic
Resources Policy: Scientific Legal and Political Issues, Vicuna, F.O., Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 21, 1983. With
permission.)
Upper Air: Southern Hemisphere (Taljaard et al. 1971), and of whales and millions of penguins, and seals, and
the American Geophysical Union Antarctic Research Series abundant intermediate populations of fish and cephalopods,
(1964a). The interlinking of the biological and physical depending on the near surface productivity.” Among the
components of the system have been discussed by Knox important characteristics of the Southern Ocean system are
(1960, 1970, 1983, 1994), Holdgate (1967), Lubimova, the following:
Naumov, and Lagunov (1973), Lubimova et al. (1980),
Deacon (1982), Lubimova (1982, 1983), Tranter (1982), 1. It is a large system, indeed probably the largest
and Hempel (1985a, 1985b). marine ecosystem on the globe.
Hedgpeth (1977b) Points out that the Southern Ocean is 2. It is semi-enclosed, especially in the overlying
“a rich, apparently high productive plankton–pelagic water masses, and the Polar Front forms a distinct
system supporting (at least in the past) great populations northern boundary.
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
The Southern Ocean 3
3. It is an old system with a long evolutionary history understood within a palaeo-geographic framework of conti-
(Knox and Lowry 1977). The main circulation nental drift, plate tectonics and polar wandering (Knox 1979,
patterns and water mass distributions were estab- 1980; Norton and Slater 1979; Kennett 1983; Elliot 1985;
lished at least 20 million years ago (Knox 1980). Anderson 1999). Kennett (1977) has provided a detailed
4. Most of the major taxonomic groups are circum- synthesis of the information concerning the evolution and
polar in distribution. The principal variation is that palaeooceanography of the Southern Ocean, while Kemp
of productivity, which is greater in certain regions (1972) has discussed the broad trends in climate since
than in others. the Paleocene.
5. The quantitative and qualitative features of the A summary of the major events in this evolution
basic processes in the Southern Ocean system follows: during the Cretaceous period equatorial seas
differ obviously from those of other oceanic extended almost uninterrupted throughout the globe
systems, as demonstrated by the distribution of (Frakes and Kemp 1972). In the Southern Hemisphere,
the dominant herbivore and key species of the Antarctica (then part of Gondwanaland) was very close to
system, Euphausia superba. its present position near the rotational pole, but with
South America, New Zealand, and Australia attached
(Figure 1.2). New Zealand separated from Australia and
Antarctica in the Cretaceous, 60–80 million years before
1.2 THE EVOLUTION OF THE SOUTHERN
present (my BP). By the late Paleocene (50 my BP) the
OCEAN Tasman Sea had formed and Australia had begun to
The unique characteristics of the Southern Ocean are the separate from Antarctica. However, the South Tasman
result of a long evolutionary history that can only be Rise, which is of continental origin, was still part of
20°N Africa
South America
South America Africa
0°
0°
India
India
Antarctica Antarctica
lia
tra
Edge of continental shelf
a
ali
s
Mid-ocean ridge and associated faults
Au
South pole str
Au
(a) 20°S 40°S 60°S 80°S 40°S (b) 0° 20°S 40°S 60°S 60°S 40°S 20°S
Africa Africa
South
0° India South
America
America
Antarctica
Antarctica
a
ali
a
str
ali
Au
str
Au
(c) 0° 20°S 40°S 60°S 60°S 40°S 20°S (d) 0° 20°S 40°S 60°S 60°S 40°S 20°S
FIGURE 1.2 Stages in the dispersal of the Gondwana continents (after Norton and Sclater 1979). No account is taken of the possibility of
rearrangement of West Antarctica. Note that only a very limited separation of Australia and Antarctica had occurred by 53 my BP, and also
that South America and the Antarctic Peninsula were most likely still abutting each other at 39 my BP. The position of the South Pole is that
inferred for the time given in each diagram. (From Elliot, D.H., Antarctica, Key Environment Series, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 39, 1985.
With permission.)
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
4 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Victoria Land, and because of this no major current tend to restrict the flow of bottom water and in some areas
system could develop between Australia and Antarctica. they even deflect surface currents. The Drake Passage
Frakes and Kemp (1972) postulated that during the between South America and the Antarctic Peninsula restricts
Eocene large oceanic gyres extended from the equator the circulation of water masses and, as will be discussed
to high latitudes and brought warm water to the Antarctic later, has a profound effect on circulation in the
coastline. Their reconstructed palaeotemperatures at Southern Ocean.
608S latitude are 248S for Queen Maude Coast, 178C The continental shelf of the Southern Ocean differs
for the shallow sea between Australia and Antarctica, from that surrounding other continents in that it is
and 78C for the attached South American–Antarctic unusually deep, with the “shelf break” (the transition
Peninsula coastline. between the continental shelf and the continental slope)
In the Late Eocene-Early Oligocene (39 my BP), lying two to four times deeper than in other oceanic
major changes began to occur which transformed the regions. This is partly due to the isotactic equilibrium
global warm climate into the modern climatic regime of adjustment of the continent to the large mass of the
today. At that time there was a dramatic lowering Antarctic ice sheets. Both the Weddell Sea and the Ross
of austral temperatures. This resulted in near-freezing Sea are characterized by broad ice shelves: the Filchner
surface coastal waters along the Antarctic coastline, and Ronne Ice Shelves and the Ross Ice Shelf respect-
which probably caused sea level glaciation around the ively. These shelves, as we shall see, profoundly influence
continent, and the formation of cold Antarctic Bottom the near-shore circulation and water properties.
Water. Associated with the development of the thermo-
clinal circulation system was an increase in the calcium
carbonate compensation depth (CCD) (Heath 1969; Van
1.4 CLIMATE
Andel and Moore 1974). Evidence from sediment macro-
fossils (foraminiferans, diatoms, and radiolarians) 1.4.1 WIND
indicated a marked change to a cold water biota (Margolis
and Kennent 1970; Jenkins 1974). A ring of low pressure surrounds the Antarctic continental
In the Late Oligocene (25–28 BP) the South Tasman Rise plateau, while tropical anti-cyclones lie to the north.
finally separated from Victoria Land sufficient enough to Winds in the Southern Ocean blow towards the trough
allow the formation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current of low pressure, but are directed to the left by the earth’s
(West Wind Drift) (Figure 1.1). The Drake Passage had rotation (Coriolis effect). As a result, at about 508S of the
formed some time between the initial separation of Australia Southern Ocean, westerly winds occurs. The westerlies
from Antarctica and the final separation of the Tasman Rise. within this circumpolar belt are quite strong, with
In the Early Miocene (22 my BP) the Polar Front (Antarctic maximum intensity in the region of the Antarctic Circum-
Convergence) formed, producing a major biological barrier polar Current (ACC) (see Figure 1.6). It is this wind that
which is still operating today. Large ice sheets developed drives the Southern Ocean circulation. Superimposed upon
rapidly in East Antarctica during the Middle Miocene. Dell this westerly circulation are northwest–southeast
and Fleming (1975), using fossil molluscan evidence, moving depressions.
suggested that the sheltered rocky coastline of the Ross Sea Over the Antarctic continent itself, katabatic winds
was, at that time, probably ice-free and kelp-fringed, not dominate the weather system. These winds, driven by very
unlike Tierra del Fuego today. By the Late Miocene-Early cold and dense air flowing down the glaciers and ice streams
Pliocene, the West Antarctic ice sheet had formed and was of the ice cap, can often reach very high velocities, and they
much thicker than it is today (Shackleton and Kennett 1975). are also responsible for the strong southeast–northwest winds
During this time the production of siliceous phytoplankton extending many kilometers from the coast out to sea. Near
steadily increased. Hays (1969) observed two intervals of the peri-Antarctic trough of low pressure there is a belt of
distinct cooling at 2.5 and 0.7 my BP, and climatic oscil- easterly winds.
lations during the last 3.5 million years, with a steadily To summarize, the prevailing wind system of the
increasing coolness up to the present time. Southern Ocean comprises three main elements: a south-
easterly component near the coast, a zone of easterly flow
encircling the continent and extending north to about 658S,
1.3 BATHYMETRY and a wide zone of westerlies reaching as far north as about
408S (Squire 1987). This zonal circulation pattern is more
The bathymetry of the Southern Ocean is shown in
intense and constant here than in any other region of
Figure 1.3. Three deep-water basins (4,000–6,000 m deep)
the globe.
surround the Antarctic continent: the Atlantic–Indian Basin,
the Indian–Antarctic Basin, and the Pacific–Antarctic Basin.
These basins are partially bounded on the north by a series of 1.4.2 TEMPERATURE
ridges or rises; the Scotia Ridge and the Atlantic–Indian
Ridge, the Southeast Indian Ridge, and the Pacific Atlantic The Southern Ocean is cold. Across the Polar Frontal Zone
Ridge respectively. These ridges and the Kerguelen Plateau the temperature range in the summer is from 4 to 88C, and in
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
The Southern Ocean 5
Atlantic
Indian Basin
Argentine
Basin Atlantic Indian
Ridge
Indian Crozet
Weddell Antarctic Basin
Basin Basin
n
le
g ue au
r t e
Ke Pla
ian
Ind
Pacific
Antarctic
ge
st
ea
Basin
Rid
uth
So
Indian
Pacific Antarct Antarctic
ic R
id Basin
ge
Australian
Basin
Southwest
Pacific
Basin
FIGURE 1.3 Map of the sea bed surrounding Antarctica showing the principal deep water basins and submarine ridges. (From Squire, V.A.,
Primer Symposium Espanol de Estudiios Antarcticos Palma de Mallorca June–July, 201, 1987. With permission.)
the winter from 1 to 38C. Surface waters south of the Polar 1.4.3 SOLAR RADIATION
Front have an average temperature of about 1–28C in the
winter and 3–58C in the summer, while further south near the In the far south near the continent, the alternation between
continent temperatures range from only about K1.0 to total darkness for half of the year and continuous daylight for
K1.98C. Temperature differences between cold surface and the other half imposes a seasonal light regime in contrast to
bottom layers and intermediate warmer layers is less than the diurnal cycles of lower latitudes. In addition, the amount
58C; thus the total annual range throughout does not exceed of light penetrating the surface waters of the ocean is
4–58C and is considerably less for the greater part of the area determined not only by its intensity, angle of incidence,
(e.g. in McMurdo Sound temperatures range seasonally only surface reflection (up to 50% according to data given in 1967
from K1.7 to K1.98C). by El-Sayed for Marguerite Bay in February 1965), and
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
6 Biology of the Southern Ocean
absorption by suspended particles, but also by the presence of followed by increases over the next few years and
sea ice and snow cover (see Section 2.8.7). Light penetration leveling off for much of the 1980s, and (2) the area of
is also influenced by the transparency of the atmosphere. intra-annual variability in monthly average sea ice distri-
Anti-cyclonic conditions near the coast result in skies that are butions in summer far exceeded the summer-time area of
often lightly cloudy or clear. In the region of the ACC there is consistent ice coverage, this in sharp contrast to the
a continuous passage of low pressure systems and a predo- winter-time situation, when the area of consistent sea
minance of cloudy weather resulting in lower insolation in ice coverage is considerably larger. In winter, the sea
this region relative to areas close to the continent (Holm- ice distribution variability is largely confined to two
Hansen et al. 1977). regions: a relatively narrow band, generally 2–58 of
Oceanic waters surrounding Antarctica are typically blue latitude, surrounding the region of consistent ice coverage,
and highly transparent with a maximum Secchi depth (the and, for the mid-1970s, the region of an occasional large
depth at which a standard Secchi disc becomes invisible) of open water area within the pack ice in the Weddell Sea,
about 40 m (Slawyk 1979). The 1% light level is relatively termed the Weddell polyna. The length of the sea ice
deep at about 100 m. Tilzer et al. (1986) attribute the low season, calculated for the years 1979–1986, with satellite
concentrations of dissolved organic compounds and the low passive-microwave data coverage through all months of
abiotic turbidity to the very low terrestrial input of sediment the year, showed increases over the period in the Ross
and organic matter. Sea but decreases in the Weddell and Bellinghausen Seas.
In both cases it appears through comparisons with data
from 1973–1976, that the 1979–1986 changes more likely
1.5 ICE COVER reflect a fluctuating behavior of the ice cover than a
long-term trend.
1.5.1 SEASONAL VARIATION
At the minimum extent scattered areas along the
One of the salient characteristics of the Southern Ocean is the Antarctic coast retain some ice coverage. Most of this ice
dramatic changes that occur in sea ice cover, from about is found in the eastern Weddell Sea and the Bellinghausen–
20!106 km2 in late winter to about 4!106 km2 in late Amundsen Sea sector. No ice is found north of the Ross Ice
summer (Zwally et al. 1983a,1983b; Comiso and Zwally Shelf at this time. Around the margins of the continent areas
1984). The ways in which sea ice forms and decays and the of unbroken fast ice (ice attached to the shore) may persist for
characteristics of the different types of sea ice are considered two or more years, forming thick multi-year ice. This is in
in Section 3.2. While the general distribution of sea ice has contrast to the pack ice (drifting ice floes) zone of annual sea
been known for many years from scattered ship observations, ice, which is 1–2 m in thickness. The distribution of ice in the
it is only recently that continuous year-round observations pack ice zone is highly variable as the ice cover is frequently
have been available as a result of satellite imagery, thus broken up by storms, and the resulting floes, driven by
enabling the detailed changes over the year and year-to-year surface currents and wind, drift considerable distances.
variations to be documented. Leads of open water (open channels in the ice within the
Figure 1.4 illustrates the growth and decay of the sea ice pack) are highly variable.
in the Southern Ocean. The months of minimum extent
are February and March, while those of maximum extent
are September and October. The northern limit of the sea ice 1.5.2 ICE SHELVES AND ICEBERGS
changes by no more than a few degrees from year to year.
The most rapid advance of the ice edge occurs in May and The Antarctic continent is largely covered by ice, and
June, when it moves northward at a rate of 4.2 million km2 around the margins the extensive ice sheets extrude from
per month; November and December are the months of the the continent into the sea. In the Ross and Weddell Seas
most rapid retreat when the ice edge recedes at these ice sheets float on the ocean forming the extensive
6.9 million km2 per month (Squire 1987). The average Ross, Filchner, and Ronne Ice Shelves. The layer of water
rates of advance and retreat are respectively 2.4 and under the Ross Ice Shelf varies from a few meters to
3.3 million km2 per month. Figure 1.5 depicts the average several hundred meters thick. The ice layer varies from
seasonal cycle of the monthly Southern Ocean sea ice over 200 m thick at the seaward edge to over 800 m at the
the period 1978–1987, which was calculated from Nimbus 7 grounded edge. The ice shelves are continually moving
satellite imagery. seaward at about 1 m per day due to the accumulation of
Over time the sea ice records show considerable snow on the continent. As they extend into the open
variability from year to year in: (1) sea ice extent, (2) ocean, they are exposed to the action of long period
the spatial range experienced in the monthly average waves and eventually they crack and calve icebergs. The
Southern Ocean sea ice distribution, and (3) the length large tabular icebergs so produced can range from a few
of the sea ice season. Using the Nimbus 7 data, Parkinson hundred meters up to 100 km in horizontal extent and
(1992) has examined this variability. Regarding the three usually are about 200–300 m thick. It has been estimated
variables listed above, (1) maximum sea ice extent varied (Radok, Streten, and Weller 1975) that the total mass of
by approximately 12%, decreasing during the mid-1970s, icebergs is about one-third of the mass of sea ice at
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
The Southern Ocean 7
90°
60° 120°
30° 150°
0° 50° 60° 70° 80° 85° 180°
30° 150°
March September
60° 120°
1974
90°
FIGURE 1.4 The distribution of the pack-ice in winter (September) and summer (March). (From Knox, G.A., Ocean Management, 9, 113,
1984. With permission.)
maximum extent. The average life of icebergs is about becoming thermally isolated as the circumpolar current
four years, but large ones have been tracked for much developed (Robin 1988).
longer periods (Swithinbank, McClain, and Little 1977).
Figure 1.6. gives estimates of the variation of Antarctic
ice sheet parameters with time. It can be seen that a rapid 1.6 CIRCULATION PATTERNS AND WATER
change in the mass budget of the Antarctic ice sheet MASSES
occurred around 10 my BP when the total budget was two
1.6.1 INTRODUCTION
to three times its present level (Robin 1988). The curve
“total discharge to the sea” is ice lost by basal melting The basic feature of the circulation patterns and hydro-
beneath the ice shelf and ice tongues and by the calving of graphic processes in the Southern Ocean were first
icebergs. Both of these have decreased markedly since that described by Deacon (1937, 1963, 1964a, 1964b, 1977,
period. The extent of the pack ice (Figure 1.6c) shows the 1984b). Since then there have been a number of reviews
large increase in extent, especially during winter, since the including those of Gordon, George, and Taylor (1977a,
opening of the Drake Passage resulted in Antarctic waters 1977b), Forster (1981, 1984), Gordon and Molinelli
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
8 Biology of the Southern Ocean
2.0 below the main thermocline of the world’s oceans. Associ-
ated with this is significant heat flux across the ACC.
While the summary of circulation patterns given below
1.5 represents a generalized picture of the system dynamics, it
Ice extent (106 km2)
should be emphasized that, superimposed upon this, is a great
amount of temporal, seasonal, and year-to-year variability
1.0 (see Chapter 15). The Southern Ocean is not radically
symmetric, and many of the circulation and water mass
features vary markedly with longitude. The cryosphere
5 complicates water mass properties in two ways: (1) the
highly spatially and temporarily variable sea ice cover
strongly influences the coupling of ocean and atmosphere
0 in regard to momentum, heat, water and gas exchange, and
J F M A M J J A S O N D (2) ocean interaction with glacial ice has a marked influence
on the characteristics of water masses (Gordon 1988).
FIGURE 1.5 Average seasonal cycle of monthly average Southern
Ocean sea ice extents over the period with full-month coverage of
Nimbus 7 SMMR. November 1978 through July 1987. Ice extents 1.6.2 DRIVING FORCES
are calculated from passive-microwave SMMR data as the aerial
coverage of the Southern Ocean with ice concentrations exceeding 1.6.2.1 Wind
15%. (From Wadhams, P., Ice in the Oceans, Gordon & Breach
Science Publishers, London, 45, 1967. With permission.) In general, the principle driving force for the Southern
Ocean circulation is the wind field. The westerlies within
the circumpolar belt are quite strong with the maximum
(1982), Gordon (1983, 1988), Amos (1984), Gordon and westerlies situated in close proximity to the ACC. The
Owens (1987), Squire (1987), and Carmack (1992). wind field produces Ekman divergence (upwelling) south
The Southern Ocean-atmosphere-ice coupled system is of the ACC and convergence (sinking) to the north.
extremely complex. Processes within the Southern Ocean The upwelling poleward of the ACC carries about 45 Sv
are responsible for the production of water characteristics (1SvZ1!106 m2 s1) into the mixed layer, two-thirds of
Ice volume (km3 × 107) Glacier ice budget (km3 × 103) Pack ice (km2 × 106)
0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 0 10 20 30
0 0 0
Summer
20 20 20 Winter
Total discharge
to sea
Glacier berg discharge
40 40 40
Million years BP
Million years BP
Million years BP
Total mass budget
60 60 60
80 80 80
100 100 100
(a) (b) (c)
FIGURE 1.6 Estimated variation of the Antarctic ice sheet parameters with time. (a) Volume of ice sheet including the ice shelves; (b) Annual
(total) mass budget of the Antarctic ice sheet, together with annual ice discharge to sea across the flotation line, and the annual volume
discharged by glaciers directly to open water but not to ice shelves (glacier berg discharge); (c) Changes of the area extent of pack ice around
Antarctica. (From Robin, G. DeQ., Palaeogr. Palaeoclimat. Palaeoecol., 67, 45, 1988. With permission.)
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
The Southern Ocean 9
which is directed the north, with the rest towards the the surface circulation, although the former is more strongly
continent, where coastal sinking occurs (Gordon 1988). influenced by bottom topography.
Along the margins of the continent, south of about 608S,
the wind field results in westerly flowing water—the 1.6.2.2 Ocean-Atmosphere Heat and Fresh
Antarctic Coastal Current (East Wind Drift). Between the Water Flux
two well-defined current systems there is a series of eddies.
Figure 1.7 shows the general pattern of surface currents in the Within the region of the Southern Ocean there is a slight
Southern Ocean. Since the water column is weakly stratified excess of precipitation over evaporation (Gordon 1981). The
south of the Polar Front, the ocean currents extending to the annual freezing and thawing of the sea ice is a significant
bottom result in the deep circulation being similar to that of factor in the redistribution of freshwater. In addition,
°E
30°
30
W
Antarcti c circu
mpola
r cu
rre
nt °E
Antarctic 60
divergence
16
0°
W
Antarctic co
a s ta
lc
Weddell
ur
re
sea
nt
gyre
90° W 90° E
Ross
sea
gyre
12
W 0°
0° E
12
180°
Antarctic
convergence
Subtropical
convergence
15
0°
E
W 0°
15
Warm currents
Cold currents
FIGURE 1.7 Surface currents in the Southern Ocean and the mean positions of the principal frontal zones. Warm currents are shown dotted
and cold are shown solid. (From Knox, G.A., Antarctic Resources Policy: Scientific, Legal and Political Issues, Cambridge University Press,
Cambridge, 21, 1983. After Brodie [1975], adapted from Sverdrup, Johnson, and Fleming [1942]. With permission.)
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
10 Biology of the Southern Ocean
the waters of the Southern Ocean play a primary role in the 1.6.3.3 Circumpolar Frontal Zones
wastage of glacial ice, mainly by direct melting of the ice
along the underside of the shelf ice (Jacobs, Fairbanks, and There are number of fronts within the Southern Ocean
Horibe 1985; Schlosser 1986). (Deacon 1982). While some are circumpolar, such as the
As Gordon (1988) points out, estimates of ocean- Polar Front (Antarctic Convergence) they display much
atmosphere flux are subject to large errors due to the variability in characteristics with longitude. The most
lack of meteorological and sea ice (concentration, thick- significant of these fronts is the Polar Front which
ness) data, and especially the paucity of data from the divides the Southern Ocean into two distinct regions:
winter period. The strong seasonal variability of the sea ice SubAntarctic to the north and Antarctic to the south. It is
cover, coupled with approximately 10–20% inter-annual a zone of variable width characterized by steep gradients in
variability in maximum winter sea ice cover (Zwally et al. sea-surface temperature, abrupt changes in phytoplankton
1983a, 1983b), further complicates estimates of the mean abundance, zooplankton distribution, pelagic bird species,
ocean-atmosphere energy exchange. South of 608S, the weather conditions, and sometimes by a salinity maximum
northern limit of sea ice cover, heat loss is large an at the surface. A circumpolar subsurface salinity minimum
annual average of 30 W m2 (Gordon 1981) but it is closely follows the surface position of the front (Gordon,
highly dependent on ice cover. Heat flux across the ACC George, and Taylor 1977a, 1977b; Joyce, Zenk, and Toole
and Polar Front (average 558S) is 3.1!104 W, while that 1978; Sciermammano 1989).
across 608S is larger, amounting to 5.4!104 W (Gordon To the north of the Polar Front lies the SubAntarctic
and Owens 1987). In order to maintain a steady state Front, while to the south lies the Antarctic Divergence. This
condition, the net poleward heat flux must involve the divergence is caused partly by the northward component
poleward transport of a large volume of water. associated with the ACC and the southward component of
the Antarctic Coastal Current, and partly by circulatory and
thermohaline factors of the southern density gradient and the
1.6.3 OCEANIC CIRCULATION (FIGURE 1.7) distribution of pressure and winds. In the region of the
1.6.3.1 Antarctic Circumpolar Current (West divergence deep water upwells to reach the surface.
Wind Drift) The classical schematic diagram of the horizontal and
vertical movements of the Antarctic circumpolar water is
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is unique in that it presented in Figure 1.8.
is the only zonal current encircling the globe, and it is almost
unobstructed by land masses, being constricted only in the 1.6.3.4 Gyres, Eddies, and Rings
region of the Drake Passage. It displays significant variations
with longitude and is principally related to bottom topo- A characteristic of the zonation of circumpolar currents is the
graphy, being deflected where it passes over submarine development of eddies of variable size and duration. This
ridges with a strong northerly component after it passes eddy variability is due to a combination of factors (Gordon
through the Drake Passage. Its width varies from less than 1988). The current cores migrate laterally (Nowlin, Whit-
200 km south of Australia to over 1,000 km in the Atlantic. worth, and Pillsbury 1977) by as much as 100 km in 10 days.
Mean current speeds within the ACC are relatively low Meanders or waves form and propagate along the ACC fronts
(0.04–0.25 m sK1 , some 2–3% of the wind velocity). (Legechis 1977; Sciermammano 1989). These meanders
Although the predominant movement is to the east, there is sometimes develop into closed rings (Joyce and Patterson
a strong northerly component. There is also some evidence 1977). Cold and warm water core rings have both been
that there are meanders and even loops within the current observed. The eddies are generally 30–100 km wide with
(Tchernia 1974, 1980; Joyce and Patterson 1977). The ACC surface velocities typically 30 cm sK1 or more, and they are
joins the great current gyres of the South Atlantic, South vertically coherent from the surface to the bottom. Numerous
Indian, and South Pacific Oceans. current rings and meanders have been reported from the
Drake Passage.
1.6.3.2 Antarctic Coastal Current (East Wind In addition to eddies there are large permanent cyclonic
Drift) flowing gyres. The largest and best-defined of these is the
Weddell Gyre, extending east of the Antarctic Peninsula to
In the vicinity of the Antarctic continent south of about 658S, about 208W and from Antarctica near 70–608S (Deacon 1979;
where winds from the east and southeast blow off the ice Gordon, Martinson, and Taylor 1981; Comiso and Gordon
sheet, there is a surface current which flows westward. This 1987). Others are the Ross Sea Gyre, north and east in the Ross
Antarctic Coastal Current generally follows the coastline Sea (Tchernia and Jeannin 1984; Gouretski 1999). A review of
with two important indentations in the Ross and Weddell the Weddell Gyre system is found in Deacon (1977).
Seas. Its flow is estimated at 10 million m3 sK1, while its
speed is variable between 0.1 and 1 m sK1, with the largest 1.6.3.5 Polynas
values near the Ross Sea Shelf (Squire 1987). The current
may not be continuous but rather broken up by a series of As the sea ice cover expands in winter, areas of open water
gyres (Figure 1.7). occur polewards of the ice limit which do not freeze but
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
The Southern Ocean 11
70°W 60 50 40 30 20
35°S
00
00
30
10
00 SACW
50
STF
Brazil cu
40
r r ent
50
00
Falklan d current
p
Argentine Basin
ga
45
ge
5000
rid
d
an
lkl
SAF
Fa
SAZ
Falk
l and Ridge
50 escarpm
en te Falkland PF
Ewing
Falkland Bank Basin
Isl
Falkland
as
ia
(Malvinas) plateau Georg
orc
islands
ad
Scotia Ridge
r th
as
Burdwo
od No
ris
bank South
e
55 Georgia
Scotia sea
PFZ
SAF
AZ
Drake passage
60
FIGURE 1.8 The upper ocean water masses and fronts in the western South Atlantic, SACW, South Atlantic Central Water; PF, Polar Front;
SAZ, Subantarctic Zone; STF, Subtropical Front; PFZ, Polar Frontal Zone; SWAF, Subantarctic Front; AZ, Antarctic Zone; The broken line
around the Ewing Bank is the 2,000 m isobath. (From Stein, M., Heywood, R.B., Southern Ocean Ecology: The BIOMASS Perspective,
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 12, 1996. With permission.)
instead remain open to the atmosphere through all or part of Coastal polynas are a common feature of the continental
the winter. These regions of long-lived open water are called shelf round the Antarctic continent. They are primarily latent
polynas. Polynas tend to occur where high winds rapidly heat polynas where heat loss from the ocean surface is
disperse freshly-formed ice at times when air temperatures balanced by the latent heat of new ice formation and the
are well below the freezing point of sea water (Van Woert polyna is maintained by wind or current removal of the new
1999). Polynas play an important role in heat transfer from ice. The coastal polynas around Antarctic can be further
the oceans to the atmosphere, ice production, the formation subdivided into two categories: those off the front of major
of dense shelf water, spring disintegration of sea ice, bay ice shelves (the Ross, Filchner–Ronne, Amery etc.) and
phytoplankton and zooplankton production, and the distri- those in the lee of ice tongues or other coastal projections such
bution of higher trophic animals such as cephalopods, fish, as the Terra Nova Bay polyna in the Ross Sea (Bromwich, Liu,
birds, seals, and cetaceans. Within polynas, the oceanic heat and Rogers 1998) or along the Wilkes Land coast. Those off
loss may be 10–100 times above that of the ice- the front of the ice shelves involve processes of water
covered surface. circulation under the shelves and katabatic winds, whilst
A review has categorized two distinct types of polynas inhibition of ice drift into polyna areas is important for
(Smith et al. 1990b). A latent heat polyna is formed when sea those in the lee of ice tongues (Smith et al. 1990).
ice is continually removed from the region in which it is Processes inside latent heat polynas are significant for the
formed by winds or ocean currents, the heat needed to sea ice zone as a whole. Being regions of intense heat loss
balance the loss to the atmosphere being provided by the from the ocean to the atmosphere, these polynas can behave
latent heat of fusion of the ice which continually forms. as “ice factories,” contributing a significant fraction of the
A sensible heat polyna is formed when a continued source total annual sea ice production; it has been estimated, for
of heat from the ocean prevents ice formation. instance that the small polyna in Terra Nova Bay contributes
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
12 Biology of the Southern Ocean
(°C)
rat ure 0
mpe Anta
face te rctic Ice
Sur 2 An Dive shelf
6 4 surf tarctic rgen
ce
8 ace
Anta wate
10 rctic r Shelf
con water
verg
Sub en ce z
0 surf antarct one
ace ic
wat
er
(Upper)
1000
slo p e
c e
r c ti a t
2000 S u b a n t a i at e w
i nte r m e d
en t a l
Depth (m)
te r
nti n
wa
3000 e ep
Co
ar d
um p ol
C i rc
te r
tic
(Lower)
rc
4000
wa
ta
An
m
tt o
Bo
80°
5000
FIGURE 1.9 Schematic diagram of the meridional and zonal flow and water masses of the Southern Ocean. The diagram represents average
summer conditions and applies particularly to the Atlantic sector. (From Knox, G.A., Antarctic Resources Policy: Scientific, Legal, and
Political Issues, Vicuna, F.O., Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 113, 1983. After Brodie [1965], adapted from Sverdrup, Johnson,
and Fleming [1942]. With permission.)
10% of the ice production in the Ross Sea (Kurtz and recurring annually and persisting throughout the winter,
Bromwich 1985). Brine rejected during the ice growth is although it appears to vary in extent from less than a
concentrated in the polyna areas and can cause intense kilometer to 5,000 km2. Van Woert (1999) suggests that
localized water mass modification as well as significantly the extent of the polyna is due to both local and katabatic
increasing the salinity of the Antarctic shelf water. The ice- winds at Terra Nova Bay and regional katabatic winds
free polynas also play an important role for Antarctic marine blowing off the Ross Ice Shelf.
ecosystems and in the control of biogeochemical fluxes.
A summary of recurrent polynas that have been detected 1.6.4 WATER MASSES
and studied using passive microwave data has been given by
Zwally, Comiso, and Gordon (1985). These include the Figure 1.9 presents an idealized schematic diagram of the
coastal polyna in the Cosmonaut Sea (Comiso and Gordon meridional and zonal flow in the Southern Ocean. There are
1987, 1996) and in Terra Nova Bay in the Ross Sea (Kurtz three principal hydrographic regimes: the area north of the
and Browich 1983; Bromwich, Liu, and Rogers 1998). Polar Front, the area south of the Polar Front, and the area on
Zwally, Comiso, and Gordon (1985) and Bromwich, Liu, the continental shelf round Antarctica. Excluding the surface
and Rogers (1998) have reviewed the occurrence, extent, and waters, three water masses dominate the deep ocean: the
variability of the Ross Sea polyna, which covers an area of Subantarctic Intermediate Water north of the Polar Front
about 27,000 km2. This polyna owes its existence to a near the 1,000 m level, the Antarctic Bottom Water near the
persistent cyclone near Roosevelt Island, which induces a bottom, and the Antarctic Circumpolar Deep Water in
sea level pressure distribution over the Ross Ice Shelf. This between at various depths.
phenomenon results in an intensification and northward Warm Deep Water upwells at the Antarctic Divergence.
propagation of katabatic winds across the ice shelf and out Here the oxygen minimum and the temperature maximum
to the sea. The immediate effect of such katabatic surge coincide and rise together with the underlying salinity
events is the development of the Ross Sea Polyna. maximum. The cold, low-salinity, high-oxygen Antarctic
Other polynas which also occur in the Ross Sea include surface waters move north to the Polar Front where they
small polynas off Cape Royds, Ross Island, and a larger one sink and contribute to the formation of the low salinity
in Terra Nova Bay (Kurtz and Bromwich 1985; Van Woert Intermediate Water. North of the Polar Front is the warmer
1999). The Terra Nova Bay polyna is a stable feature, SubAntarctic Surface Water.
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
The Southern Ocean 13
Near the bottom of the ocean, very cold Antarctic Bottom separate water masses of different temperature and salinity,
Water moves north from its primary site of generation around and they exhibit marked biological and physical changes.
the continental margin, especially in the Weddell Sea. The interchange of these water masses, especially at the
Sandwiched between the two Antarctic water masses is the Antarctic Divergence, provides the minerals and nutrients
broad compensatory flow of high-salinity Warm Deep Water. fundamental to marine biological production.
The south-flowing Deep Water mixes with the Antarctic The Polar Frontal Zone lies between about 558S and 608S
waters above and contributes to the Circumpolar Deep Water and separates Subantarctic Water to the north from Antarctic
which, in terms of volume, is the dominating water mass of Water to the south. This is a zone of variable width,
the Southern Ocean. Mixing takes place across the characterized by steep gradients in sea surface temperature
boundaries between the water masses. and abrupt changes in phytoplankton composition,
zooplankton distribution, pelagic bird species, and weather
conditions. The Polar Front lies within the Antarctic Circum-
polar Current (West Wind Drift). It is a complex system
1.7 SOME REGIONAL HYDROGRAPHIC where wave-like disturbances frequently close on themselves
FEATURES to form rings and eddies with lifetimes that vary from days to
1.7.1 SOUTHWEST ATLANTIC AND THE ANTARCTIC years (Forster 1984).
South of about 658S, where winds blow from the east
PENINSULA REGION
and southeast off the ice sheet, the Antarctic Coastal
Stein and Haywood (1994) have reviewed the physical Current (East Wind Drift) flows in the opposite direc-
oceanography of the Southwest Atlantic region and the tion—from east to west. The boundary between the East
Antarctic Peninsula area (Figure 1.8). On leaving the
confines of the Drake Passage and entering the Scotia
Sea the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is deflected
180° 170°W
north and west by the submerged ridge of the Scotia Arc,
Antarctic convergence 60°S
before it turns east again to flow round South Georgia and
across the Atlantic Ocean sector of the Southern Ocean
(Deacon 1937; Gordon and Goldberg 1970). It consists of
Subantarctic and Antarctic Surface waters from the Pacific
Ocean sector of the Southern Ocean and from the Bellin-
ghausen Sea (Nowlin and Clifford 1977). Some mixing West wind drift
with Weddell Sea Surface Water occurs in the Scotia Sea.
However, the southern arm of the Scotia Arc effectively 65°S
restricts the flow of water out of the Weddell Sea (Carmack
and Foster 1975) and most enters the Scotia Sea across the Antarctic divergence
Weddell–Scotia Confluence east of the South Orkney
Islands (Gordon 1967). Consequently there is a marked
East wind drift
gradient of mixing across the Scotia Sea with the influence
of the Weddell Sea Surface Water being greatest to the
south and east of South Georgia (Anonymous 1983;
Heywood, Everson, and Priddle 1985). 70°S
From north to south a number of fronts separate distinct
water masses. The most northerly front, the Subtropical Anta
rctic
Front, marks the northern boundary of the sub-Antarctic
Zone, while the Subantarctic Front marks its southern
boundary. South of this front is the Polar Frontal Zone
Sl
with its southern boundary marked by the Polar Front. To op
ef
the south lies the Antarctic Zone. This complex of fronts and ro
nt 75°S
water masses (Zones) is the result of the passage of water
through the Drake Passage being influenced by the various
banks and ridges: the Burwood Bank, the North Scotia
Ridge, the Ewing Bank, and the Falkland Ridge. Ross
Ross ice shelf
FIGURE 1.10 Oceanic fronts and surface water circulation in the
1.7.2 THE ROSS SEA (FIGURE 1.10) Ross Sea region. Three main oceanic fronts occur: the Polar Front
(Antarctic Convergence), the Antarctic Divergence, and the
Three main oceanic fronts occur within the Ross Sea region: Antarctic Slope Front. (From Knox, G.A., Ross Sea Region: State
the Polar Front (Antarctic Convergence), the Antarctic of the Environment Report for the Ross Sea Region of Antarctica,
Divergence, and the Antarctic Slope Front. These fronts Antarctic Institute, Christchurch, 54, 2001. With permission.)
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
14 Biology of the Southern Ocean
and West Wind Drifts forms the second frontal zone, the during the summer, with surface temperatures generally
Antarctic Divergence, where deeper water rich in nutrients higher in the south where the pack ice opens up earlier in
upwells to the surface, resulting in enhanced the summer and a wide range of salinities occur. Below this
phytoplankton production. layer are dense shelf waters. High Salinity Shelf Water is the
A third frontal zone, the Antarctic Slope Front, lies over densest water found in the Southern Ocean and these high
the edge of the continental shelf in the southern Ross Sea salinities are explained by the intensive processes of ice
(Ainley and Jacobs 1981; Jacobs 1991) and it is centered formation in polynas along the coast (Jacobs, Fairbanks, and
10–45 km seaward of the shelf break, placing it just south of Horibe 1985). Low Salinity Shelf Water is found in the
the 1,000 m depth contour. This topographically controlled eastern Ross Sea and it is marked by slightly warmer sea
front is marked by strong subsurface gradients in ocean surface freezing temperatures, and low salinities. Ice Shelf
currents and temperature, and by along-shore currents that Water exhibits temperatures below the sea surface freezing
are stronger than those occurring in most surface waters of point, an indication of interaction with the Ross Ice Shelf at
the adjacent continental shelf. The slope front lies at the depth. This water is concentrated in the west of the Ross Sea
northern margin of the massive phytoplankton bloom that where it emerges from under the ice shelf (Jacobs and Giuvili
occurs over the Ross Sea continental shelf in summer.
1999). Modified Circumpolar Deep Water represents deep
Warm deep water approaches the continental slope of the
oceanic waters that have penetrated the continental shelf.
Ross Sea from the northeast in the west and from the east-
This water is warmer and occupies depths between 100
northeast in the east. These waters are seasonally cooled and
and 300 m.
warmed, Stalinized by the formation of sea ice, and fresh-
ened by water from melting ice. Ice and water is then moved
west and north by surface circulation, which is mainly due to
the extensive cyclonic gyre on the western side of the Ross
Sea. Surface waters move to the southeast along the eastern 1.8 BOTTOM WATER FORMATION
periphery of this cyclonic system. As the southeast flowing
water approaches the Ross Ice Shelf, the current is deflected Antarctic Bottom Water is an important component of the
to the west, with part joining the cyclonic circulation and part Southern Ocean system, responsible for about 34 Sv of the
passing beneath the shelf. Along the Victoria Land coast, a northward flow, and providing cold water at depth to all
northward flowing coastal current forms a well defined and the oceans of the southern hemisphere. Its formation involves
comparatively narrow stream (Tressler and Ommundsen a mixing of water types, helped by surface interaction.
1962). Some of this water returns to the cyclonic circulation, Observations from the Discovery Expeditions (Deacon
while the rest turns round Cape Adare and eventually joins 1937) confirmed the Weddell Sea as the main source of
the Antarctic Coastal Current. Bottom water. It accounts for more than 50% of the total
Subsurface circulation is formed by two different anti- volume produced. Second to this is the Ross Sea Shelf
cyclonic gyres at each end of the Ross Sea, which are (Jacobs, Amos, and Buckhausen 1970; Jacobs, Fairbanks,
connected by a U-shaped cyclonic feature in the vicinity of and Horibe 1985) with some other sites in the sector from
the Ross Ice Shelf. 308E to 1708E also being possible sources (Baines and
In the Ross Sea region, several distinct water masses can Condie 1998).
be distinguished and are generally defined by the particular According to Gordon (1988), postulated processes
relationships between temperature and salinity (Jacobs and and sources contributing to Weddell Sea Bottom Water
Comiso 1989, 1992; Jacobs and Giulivi 1989; Carmack formation include haline convection by evaporation or
1992). Three water masses can be distinguished in the
freezing in open leads and polynas, cooling under the
deeper oceanic waters of the Ross Sea and five over the
Filchner Ice Shelf, Ekman-layer effects, sinking along
continental shelf and slope (Gouretski 1999).
frontal zones, derivation form deeper oceanic areas,
Antarctic Surface Water, Circumpolar Deep Water,
overflow of dense water from the Bransfield Strait, and
and Antarctic Bottom Water occupy the oceanic parts of
soluble diffusive convection. Estimates of the circumpolar
the region. Of these, Circumpolar Deep Water constitutes
production rates of Bottom Water are in excess of 13 Sv
the greatest volume of water in the Southern Ocean and is
characterized by high nutrient levels, generated from (Jacobs, Fairbanks, and Horibe 1985). The principal
phytoplankton as it sinks through the water column. mechanism was believed to involve frontal zone mixing
Antarctic Bottom Water occupies the deepest region of between water masses at the continental shelf break, with
the water column and plays a major role in the global the dense water sinking down the slope (Gill 1973;
oceanic system. Foster and Carmack 1976). Recent observations by
Antarctic Surface Water, High Salinity Shelf Water, Low Norwegian scientists (Foldvik and Gammelsrad 1988)
Salinity Shelf Water, Ice Shelf Water, and modified Circum- have shown that large volumes of Weddell Sea Bottom
polar Deep Water can be identified over the continental shelf Water originate from Ice Shelf Water formed under
and slope of the Ross Sea, although in contrast to other water floating ice shelves by flowing down the continental
masses, those of the continental shelf are highly variable. slope as organized plumes and mixing with the overlying
Antarctic Surface Water is found throughout the Ross Sea Weddell Sea Deep Water.
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
The Southern Ocean 15
1.9 NUTRIENTS transit), and postulated that one would expect to find
almost complete stripping of the nutrients in aged waters
In the Southern Ocean the concentration of nutrients is close to the Polar Front. However, data from studies by
lowest in the surface waters and greatest in the Warm Kuramoto and Koyama (1982), and Watanabe and Nakajima
Deep Water for nitrate and phosphate, and usually near the (1982) from a transect along 458 longitude reveals a
bottom for silicate. In general, the concentration of nutrients
completely different picture. Nitrate was 27 mM at 628S,
in surface waters south of the Polar Front is much higher than
22 mM at the Polar Front (528S) and 20 mM a few degrees
that found in other oceanic waters (Knox 1970; El-Sayed
south of the Subtropical Convergence (418S). Silica, on the
1978). Nutrient rich water upwells at the Antarctic Diver-
other hand, was high (57 mM) at 678S and it decreased
gence spreading out to ultimately downwell at the Polar
sharply to 15 mM at 608S, and dropped to low values
Front. On the basis of data from other upwelling regions,
(approximately 1 mM) just north of the Polar Front, reflecting
with time one would expect to find almost complete stripping
of plant nutrients in the upper 50–100 m due to the growth of its assimilation and polymerization by diatoms and silico-
phytoplankton (Barlow 1982). Holm-Hansen (1985) esti- flagellates. The significance of these data and the degree to
mated that between 25 and 30 mM of nitrate per liter would which nutrient depletion can occur in the waters of the
have been consumed by the time the upwelled water reached Southern Ocean will be considered in detail in Chapter 2
the zone of the Polar Front (approximately 200 days in (Figure 1.10).
3394—CHAPTER 1—25/10/2006—14:52—KADAMBADI—14440—XML MODEL C – pp. 1–15
References
Abrams, R.W., Energy and food requirements of pelagic aerial seabirds Adams, N.J., Klages, N.T., Temporal variation in the diet of gentoo
in different regions of the African sector of the Indian Ocean, in penguins (Pygoscelis papua) at Marion Island, Colonial Water-
Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, birds, 12, 30–36, 1989.
P.R., Laws, R.M. Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985a, 466–472. Adelung, D., Buchholz, F., Calik, B., Keck, A., Fluoride in the tissues of
Abrams, R.W., Environmental determinants of pelagic seabird distri- krill (Euphausia superba Dana and Meganyctiphanes norvegica
bution in the African sector of the Southern Ocean, J. Biogeogr., M.Sars) in relation to the moult cycle, Polar Biol., 7, 43–50, 1987.
12, 473–492, 1985b. Adie, R.J., Geological history, in Antarctic Research: A Review of
Accornero, A., Marino, C., Arrigo, K.P., Martion, A., Tucci, S., Vertical British Scientific Achievement in Antarctica, Priestley, R., Adie,
flux of particulate matter in the polyna of Terra Nova Bay, Part I: R.J., de Q Robin, G., Eds., Butterworths, London, 1964, 118–162.
Chemical constituents, Antarc. Sci., 15, 119–132, 2003. Admiral, W., Venekamp, A.H., Significance of tintinnid grazing during
Accornero, A., Marino, C., Esposito, F., Gambi, M.C., Vertical flux of blooms of Phaeocystis pouchetii (Heptophyceae) in Dutch coastal
particulate matter in the polyna of Terra Nova Bay, Part II: waters, Neth. J. Sea Res., 20, 61–66, 1986.
Biological components, Antarc. Sci., 15, 175–188, 2003. Agnew, D., Review of the CCAMLR Ecosystem Monitoring Program,
Ackley, S.F., Ice-scavenging and nucleation: Two mechanisms for Antarc. Sci., 9(3), 235–242, 1997.
incorporation of algae into newly-forming sea ice, EOS Trans., Aguaya, A., The present status of the Antarctic fur seal, Arctocephalus
Am. Geophy. Union, 63, 54–55, 1982. gazella, at the South Shetland Islands, Polar Rec., 19, 167–176,
Ackley, S.P., Sullivan, C.W., Physical controls on the development and 1978.
characteristics of Antarctic sea ice biological communities—a Ahlgren, J.A., DeVries, A.L., Comparison of antifreeze glycoproteins
review and synthesis, Deep-Sea Res., 41, 1583–1604, 1994. from several Antarctic fishes, Polar Biol., 3, 93–97, 1984.
Ackley, S.F., Taguchi, S., Buck, K.R., Sea ice algal relationships in the Ahlgren, J.A., Cheng, C.C., Schrag, J.D., DeVries, A.L., Freezing
Weddell Sea, Antarc. J. U.S., 13, 7–10, 1978a. avoidance and the distribution of antifreeze glycopeptides in
Ackley, S.F., Taguchi, S., Buck, K.R., Primary productivity in sea ice of
body fluid and tissues of Antarctic fish, J. Exp. Biol., 137,
the Weddell Region, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Cold Regions
549–563, 1988.
Research and Engineering Report, 78, 191–217, 1978b.
Ahn, L.V., Kang.Y.-C., Preliminary study on the macrobenthic commu-
Ackley, S.F., Buck, K.R., Taguchi, S., Standing crop of algae in the sea
nity of Maxwell Bay, South Shetland Islands, Korean J. Polar Res.,
ice of the Weddell Sea region, Deep-Sea Res., 26A, 269–381,
2, 61–71, 1991.
1979.
Ainley, D.G., Biomass of birds and mammals in the Ross Sea, in
Ackley, S.F., Dieckmann, G.S., Shen, H., Algal and foram incorporation
Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R.,
into new sea ice, EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union, 68, 1736, 1987.
Condy, W.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 498–515.
Ackley, S.F., Bengston, J.L., Boveng, P., Castellini, M., Daly, K.L.,
Ainley, D.G., Boekelheide, R.J., An ecological comparison of oceanic
Jacobs, S., Kooyman, G.L., Laake, J., Quetin, L., Ross, R., Siniff,
seabird communities in the South Pacific Ocean, Stud. Avian Biol.,
D.B., Stewart, B.S., Stirling, I., Torres, J., Yochem, P.K., The top-
8, 2–23, 1983.
down multidisciplinary study of the structure and function of the
Ainley, D.G., DeMaster, D.P., Survival and mortality in a population of
pack ice ecosystem in the eastern Ross Sea, Antarctica, Polar Rec.,
penguins, Ecology, 61, 522–530, 1980.
39, 219–230, 2003.
Ainley, D.G., DeMaster, D.P., Upper trophic levels in polar marine
ACMRR (FAO), Report on the Scientific Consultation on the Conserva-
ecosystems, in Polar Oceanography, Part B: Chemistry, Biology
tion and Management of Marine Mammals and their Environment
and Geology, Smith, W.O., Jr., Ed., Academic Press, San Diego,
and ACMRR Working Party on Marine Mammals, Bergen,
CA, 1990, 599–630.
Norway, 31 August–9 September 1976, 1976.
Acosta Pomer, M.-L.C., Bruni, V., Maugeri, T.L., Picoplankton biomass Ainley, D.G., Jacobs, S.S., Seabird affinities for ocean and ice
in the Ross Sea, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 13, 1–6, 1993. boundaries in the Antarctic, Deep-Sea Res., 28A, 1173–1185,
Adams, N.J., Brown, C.R., Dietary differentiation and trophic relation- 1981.
ships in the sub-Antarctic penguin community at Marion Island, Ainley, D.G., LeResche, R.E., The effects of weather and ice conditions
Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 57, 249–258, 1989. on breeding Adélie Penguins, Condor, 75, 235–239, 1973.
Adams, N.J., Klages, N.T., Seasonal variation in the diet of king Ainley, D.G., Sullivan, C.W., AMERIEZ 1983: A summary of activities
penguins (Aptenodytes patagonicus) at subAntarctic Marion on board RV Melville and USGS Westwind, Antarc. J. U.S., 19,
Island, J. Zool. (Lond.), 212, 303–324, 1987. 100–102, 1984.
533
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:47—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
534 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Ainley, D.G., LeResche, R.E., Sladen, W.J.L., Breeding Biology of Alvarifio, A., Bathymetric distribution of chaetognaths, Pac. Sci., 18,
Adélie Penguins, University of California Press, Berkeley, CA, 64–82, 1964.
1983. Amaratunga, T., Population Biology, in Cephalopod Life Cycles, Vol. 2,
Ainley, D.G., O’Connor, E.F., Borkelheide, R.J., The marine ecology Boyle, P.R., Ed., Academic Press, London, 1987, 239–252.
of the birds in the Ross Sea, Ornithol. Monogr., 32, 1–97, AMERIEZ A Research Plan for Antarctic Marine Ecosystem Research
1984. at the Ice Edge Zone (AMERIEZ). (1983), AMERIEZ Steering
Ainley, D.G., Fraser, W.R., Sullivan, C.W., Torres, J.J., Hopkins, T.L., Committee, Washington, DC, 1983.
Smith, W.O., Jr., Antarctic mesopelagic micronekton: evidence Amos, A.F., Distribution of krill (Euphausia superba) and the hydro-
from seabirds that pack ice affects community structure, Science, graphy of the Southern Ocean: Large-scale processes,
232, 847–849, 1985. J. Crustacean Biol., 4(Special Issue No.1), 306–329, 1984.
Ainley, D.G., Fraser, W.R., Daley, K.L., Effects of pack ice on the Amsler, C.D., Rowley, R.J., Laur, D.R., Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M.,
composition of micronekton communities in the Weddell Sea, in Vertical distribution of Antarctic peninsular macroalgal cover:
Antarctic Ocean and Resources Variability, Sahrhage, D., Ed., Biomass and species composition, Phycologia, 34, 424–430, 1995.
Springer, Berlin, 1988, 140–146. Anderson, H.T., The Biology of Marine Mammals, Academic Press, New
Ainley, D.G., Fraser, W.R., Smith, W.O., Jr., Hopkins, T.L., Torres, J.J., York, 1969.
The structure of upper-level pelagic food webs in the Antarctic: Anderson, V., Filtration and ingestion rates of Salpa fusiformis Cuvier
effect of phytoplankton distribution, J. Mar. Syst., 2, 111–122, (Tunicata: Thaliacea): effects of size, individual weight and algal
1991. concentration, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 87, 13–27, 1985.
Ainley, D.G., Ribec, C.A., Fraser, W.R., Does prey preference affect Anderson, H.T. Ed., The Biology of Marine Mammals, Academic Press,
habitat choice in Antarctic seabirds?, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 90, New York, 1999.
Anderson, B., Chague-Goff, C., Benthic Foraminifera and Trace Metals
207–221, 1992.
in Sediments off the Scott Base Sewer Outfall, Antarctica, Antarctic
Ainley, D.G., Ribic, C.A., Fraser, W.R., Ecological structure among
Data Series No. 18, Antarctic Research Centre, Research School of
migrant and resident seabirds of the Scotia–Weddell confluence
Earth Sciences, Victoria University, Wellington, 1996, 1–12.
region, J. Anim. Ecol., 63, 347–364, 1994.
Anderson, P., Fenchel, T., Bactivory by microheterotrophic flagellates in
Alberti, G., Kils, U., The filtering basket of Euphausia superba, ICES
sea water samples, Limnol. Oceanogr., 30, 198–202, 1985.
CM 1980/L, 54–63, 1990.
Anderson, V., Nival, P., A pelagic ecosystem model simulating
Alder, V.A., Boltavoskay, D., The ecology and biogeography of tintinnid
production and sedimentation of biogenic particles: role of salps
ciliates in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean, Mar. Chem.,
and copepods, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 44, 37–50, 1988.
35(1–4), 337–346, 1991.
Andersson, A., Azam, F., Hagstrom, A., Release of aminoacids and
Alexander, V., Interrelationships between seasonal sea ice zone
inorganic nutrients by heterotrophic marine microflagellates, Mar.
and biological regimes, Cold Reg. Sci. Technol., 2, 157–178,
Ecol. Prog. Ser., 23, 99–106, 1995.
1980.
Andreae, M.O., Ocean–atmosphere interactions in the global biogeo-
Alexander, V., Niebauer, J.H., Oceanography of the eastern Bering
chemical sulfur cycle, Mar. Chem., 30, 1–29, 1990.
Sea ice-edge zone in spring, Limnol. Oceanogr., 26, 1111–1125,
Andreev, M.P., Bykov, V.P., Smirov, V.M., Investigation of the
1981.
influence of post-modem in krill on the quality of processed
Aleyev, Y., Nekton, Dr. W. Junk Publishers, The Hague, 1977.
flesh, in Krill Processing Technology, Bykov, V.P., Ed., VNIRO,
Allanson, B.R., Hart, R.C., Lutjeharms, J.R., Observations on the
Moscow, 1981, 68–72.
nutrients, chlorophyll, and primary production of the Southern Andrew, D., Review of the CCAMLR Ecosystem Monitoring Program,
Ocean south of Africa, S. Afr. J. Antarc. Res., 10/11, 3–14, Aust. Sci., 9, 235–242, 1997.
1981. Andrews, K.J.H., The distribution and life-history of Calanoides acutus
Allanson, B.R., Boden, B., Parker, L., Duncombe, R., A contribution to (Giesbrecht), Discov. Rep., 34, 117–162, 1966.
the oceanology of the Prince Edward Islands, in Antarctic Nutrient Andriashev, A.P., A general review of the Antarctic fish fauna, in
Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Biogeography and Ecology of Antarctica, van Oye, P., van
Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 38–43. Meigham, J., Eds., Dr. W. Junk, The Hague, 1965, 491–550.
Alldredge, A.L., Madin, L.P., Pelagic tunicates: unique herbivores in Andriashev, A.P., The problem of the life community associated with the
marine plankton, BioScience, 32, 655, 1982. lower layer of the Antarctic fast ice, SCAR/SCOR/IABO/IUBS
Alldredge, A.L., Silver, M.W., Characteristics, dynamics, and signi- Symposium on Antarctic Oceanography, Santiago, Chile, 13–16
ficance of marine snow, Prog. Oceanogr., 20, 41–82, 1988. September, 1966, Currie, R.I., Ed., 1968, 147–155.
Allen, K.R., Some methods for estimating exploited populations, J. Fish. Andriashev, A.P., Butskaya, N.A., Faleeva, T.I., Polovye tsikly antark-
Res. Board Canada, 23(10), 1553–1574, 1966. ticheskih ryb Trematomus bernachii i Pagothenia borchgrevinki
Allen, K.R., Simplification of a method for estimating exploited (Notheniidae) v sviazis adaptatsiei k usloviian obitaniia, Dolklady
populations, J. Fish. Res. Board Canada, 25, 270–1143, 1968. Akademii Nauk SSSR, 248, 400–502, 1979.
Allen, K.R., Relation between production and biomass, J. Fish. Res. Angel, M.V., Detrital organic fluxes through pelagic ecosystems, in
Board Canada, 28, 1573–1581, 1971. Flows of Energy and Materials in Marine Ecosystems: Theory and
Allen, K.R. Conservation and Management of Whales, University of Practice, Fasham, M.J., Ed., Plenum Press, New York, 1984,
Washington Press, Seattle,WA, 1980. 475–516.
Almeida Prado-Par, M.S., Diel vertical migration of zooplankton at a Angel, M.V., Fasham, M.J.R., Eddies and biological processes, in Eddies
fixed station in the Bransfield Strait, summer 1985, Pesquisa in Marine Science, Robinson, A.R., Ed., Springer, Berlin, 1983,
Antártica Brasileira, 1, 89, 1989. 492–524.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 535
Anonymous, FIBEX acoustic survey design, Biomass Rep. Ser., 20, Archer, S.D., Leakey, R.J.G., Burkill, P.H., Sleigh, M.A., Appleby, C.J.,
1–14, 1980. Microbial ecology of sea ice at a coastal Antarctic site: Community
Anonymous, Post-FIBEX data interpretation workshop, Biomass Rep. composition, biomass, and temporal change, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.,
Ser., 20–27, 1981a. 135, 179–195, 1996.
Anonymous, Convention on the conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Aristegui, J., Montero, M.F., Batesteros, S., Basterretx, G., van Lenning,
Resources, SCAR Bull., 67, 383–395, 1981b. K., Plankton primary production and microbial respiration
Anonymous, Technical group on programme implementation and measured by 14C assimilation and dissolved oxygen changes in
coordination, Third Meeting, Biomass Rep. Ser., 29, 1–28, 1982. coastal waters of the Antarctic Peninsula during austral summer:
Anonymous, Second Post-FIBEX Hydrograhic Data Interpretation Implications of carbon flux studies, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 132,
Workshop, Hamburg, F.R. Germany, 16–20 May 1983, Biomass 191–201, 1996.
Rep. Ser., 31, 1–26, 1983. Armstrong, A.J., Siegfried, W.R., Consumption of Antarctic krill by
Anonymous, Results of research into distribution and status of stocks of Minke whales, Antarc. Sci., 3(1), 13–18, 1991.
target species in the Convention area—Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Arnaud, P.M., Nature de l’entagement du benthos algal et animal dans
Ocean Sectors of Antarctica, in Selected Papers Presented to the l’Antarctique, Compt. Rendu. Acad. Sci., Paris, 262, 16–26, 1965.
Scientific Committee of CCAMLR 1982–84, Part I, Commission Arnaud, P.M., Frequency and ecological significance of necrophagy
for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, among benthic species in Antarctic coastal waters, in Antarctic
Hobart, 1984a, 227–325. Ecology.Vol. I, Holdgate, W.M., Ed., Academic Press, London,
Anonymous, General circulation of the Southern Ocean: Status and 1970, 259–267.
recommendations for research: a report by SCOR Working Group Arnaud, P.M., Contribution a la bionomie marine benthique des regions
74, World Climate Programme Series No. 108, 1–50, 1984b. antarctiques et subantarctiques, Tethys, 6, 467–653, 1974.
Anonymous, An approach to a management strategy for the Antarctic Arnaud, P.M., Adaptations within the Antarctic marine benthic eco-
marine ecosystem, in Selected Papers Presented to the Scientific system, in Adaptations within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A.,
Committee of CCAMLR, Part II, Convention on the Conservation Ed., Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC, 1977, 135–157.
of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 1985a, 1–14. Arnaud, P.M., Jazdzewski, K., Presler, P., Sicinski, J., Preliminary
Anonymous, Ecosystem management: Proposal for undertaking a survey of benthic invertebrates collected by Polish Antarctic
coordinated fishing and research experiment at selected sites expeditions in Admiralty Bay (King George Island, South Shetland
around Antarctica, in Selected Papers Presented to the Scientific Island), Pol. Polar Res., 7(1–2), 7–24, 1986.
Committee of CCAMLR, Part II, Commission on the Conservation Arnould, J.P.V., Whitehead, M.D., Diet of Antarctic petrels, cape
of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 1985b, 285–294. pigeons, and southern fulmars rearing chicks at Prydz Bay,
Anonymous, Post-FIBEX acoustic workshop, Frankfurt, Federal Antarc. Sci., 3, 19–27, 1991.
Republic of Germany, September 1984. Biomass Rep. Ser. No. Arrigo, K.R., Impact of ozone depletion on phytoplankton growth in the
40, 1–106, 1986. Southern Ocean: Large-scale spatial and temporal variability, Mar.
Anonymous, Report of the Workshop on Southern Elephant Seals, Ecol. Prog. Ser., 114, 1–12, 1994.
CCAMLR Wg-GEMP-91/92, 8 pp, 1991. Arrigo, K.R., McClain, C.R., Spring phytoplankton production in the
Antezana, T., Ray, K., Aggregation of Euphausia superba as an adaptive western Ross Sea, Science, 226, 261–263, 1994.
group strategy to the Antarctic ecosystem, Berichte zur Polar- Arrigo, K.R., Sullivan, C.W., The influence of salinity and temperate
forschung, 4, 199–215, 1983. covariation on the photophysical characteristics of Antarctic sea
Antezana, T., Ray, K., Active feeding of Euphausia superba in a swarm ice microalgae, J. Phycol., 28, 746–756, 1992.
north of Elephant Island, J. Crustacean Biol., 4(Special Issue Arrigo, K.R., Thomas, D.N., Large-scale importance of sea ice biology
No.1), 142–155, 1984. in the Southern Ocean, Antarc. Sci., 16, 471–486, 2004.
Antezana, T., Ray, K., Melo, C., Trophic behaviour of Euphausia Arrigo, K.R., Robinson, D.H., Sullivan, C.W., A high resolution study of
superba in laboratory conditions, Polar Biol., 1, 77–82, 1982. the platelet ice ecosystem in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica: Photo-
Antz, W.E., T. Brey, Eds. The expedition of ANTARKTIS XVII/3 (EASIZ) synthetic and bio-optical characteristics of a dense algal bloom,
of the RV Polarstern in 1998, Ber. Polarforsch., 1–229, 402. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 98, 173–185, 1993.
Antz, W.E., Gutt, J., Eds., The expedition of the ANTARKTIS XIII/3 Arrigo, K.R., Dieckmann, G., Gosselin, M., Robinson, D.H., Fritzen,
(EASIZ) of the RV Polarstern to the eastern Weddell Sea in 1996, C.H., Sullivan, C.W., High-resolution study of the platelet ice
Ber. Polarforsch., 249, 1–239, 1997. ecosystem in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica: Biomass, nutrient, and
Antz, W.E., Gutt, J., Eds., The expedition of ANTARKTIS XV/3 (EASIZ production profiles within a dense microalgal bloom, Mar. Ecol.
II) of the RV Polarstern in 1998, Berichte zur Polarforschung, Prog. Ser., 127, 255–268, 1995.
301, 1–148, 1999. Arrigo, K.A., Worthen, D.L., Lizotte, M.P., Primary production of near-
Antz, W.E., Brey, T., Gerdes, D., Gorny, M., Gutt, J., Hosin, S., Klages, surface communities within Antarctic pack ice, Antarc. Res. Ser.,
M., Pattern of life history and population dynamics of benthic 73, 23–43, 1998.
invertebrates under the high conditions of the Weddell Sea, Arrigo, K.R., Ditullio, G.R., Dunbar, R.B., Robinson, D.H., van Woert,
Antarctica, Polar Biol., 11, 169–177, 1992. M., Worthen, D.L., Lizotte, M.P., Bio-optical properties of the
Antz, W.E., Brey, T., Gallardo, V.A., Antarctic zoobenthos, Oceanogr. southwestern Ross Sea, J. Geophys. Res., 103, 21683–21695, 2000.
Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev., 32, 241–304, 1994. Aseev, Y.P., Size structure and longevity of krill populations from the
Antz, W.E., Gutt, J., Klages, M., Antarctic marine biodiversity: an Indian Ocean sector of Antarctica, in Antarctic Krill: Distribution
overview, in Antarctic Communities: Species, Structure, and Pattern and Environment, Lubimov, T.G., Ed., Trudy VNIRO,
Survival, Antz, W.E., Gutt, J., Klages, M., Eds., Cambridge Moscow, Sbornik Nauk Trudy Vses Nauchno-issled Rybnogoz
University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1997, 3–13. Khoziaistra Okeanografii, 1983, 103–110.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
536 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Asencio, G., Moreno, C.A., Dieta y selectividad alimentaria de Proto- Azam, F., Hodson, R.E., Multiphasic kinetics for D-glucose uptake by
myctophum bolini Fraser-Brunner (Pisces: Myctophidae) en el assemblages of natural marine bacteria, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 6,
paso Drake (Antarctica), Serie Cientı́fico del Instituto Antártico 213–222, 1981.
Chileno, 31, 85–96, 1984. Azam, F., Ammerman, J.W., Cooper, N., Bacterioplankton distributional
Asheimer, H., Krause, H., Rakusa-Suszcewski, S., Modelling individual patterns and metabolic activities in the Scotia Sea, Antarc. J. U.S.,
growth of the Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Polar Biol., 4, 16, 164–165, 1981.
65–73, 1985. Azam, F., Ammerman, J.W., Fenchel, T., Field, J.G., Gray, J.S., Meyer-
Ashmole, N.P., Seabird ecology and the marine environment, in Avian Reil, L.A., Thingstad, F., The ecological role of water-column
Biology, Vol. I, Farner, D.S.F., King, K., Eds., Academic Press, microbes in the sea, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 10, 257–263, 1983.
New York, 1971, 192–304. Azam, F., Smith, D.C., Hollibaugh, J.T., The role of the microbial
Ashmole, N.P., Ashmole, M.J., Comparative feeding ecology of sea loop in Antarctic pelagic ecosystems, Polar Res., 102, 239–243,
birds of a tropical oceanic island, Bull. Peabody Mus. Nat. Hist., 1991.
24, 1–131, 1967. Azam, F., Beers, R.J., Campbell, L., Carlucci, A.F., Holm-Hansen, O.,
Atkinson, A., Distribution of six major copepod species around South Reid, F.M.H., Occurrence and metabolic activity of organisms
Georgia during an austral summer, Polar Biol., 9, 3–11, 1989. under the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarctica, at Station J9, Science, 203,
Atkinson, A., Peck, J.M., A summer-winter comparison of the 451–453, 1998.
zooplankton in the oceanic area around South Georgia, Polar Azzali, M., Kalinowski, J., Spatial and temporal distribution of krill
Biol., 8, 463–473, 1988. (Euphausia superba) biomass in the Ross Sea (1989–1990 and
Atkinson, A., Peck, J.M., The distribution of zooplankton in relation to 1994), in Ross Sea Ecology, Farando, F.M., Guglielmo, L.,
the South Georgia shelf in summer and winter, in Antarctic Ianova, A., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1998, 433–455.
Ecosystems: Ecological Change and Conservation, Kerry, K.R., Azzali, M., Kalinowski, J., Castagnani, R., How much krill is there?
Hempel, G., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1990, 159–165. Results of the 5th Italian Expedition to the Ross Sea, 1989/90,
BIOMASS Newsletter, Biomass/Scar/IABO/ACMRR, Vol. 13,
Atkinson, A., Sinclair, T.D., Zonal distribution and seasonal vertical
Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, 1991, 6–7.
migration of copepod assemblages in the Scotia Sea, Polar Biol.,
Azzali, M., J. Kalinowski, N. Saino, Estimation of biomass of krill
23, 46–58, 2000.
(Euphausia superba) and birds and mammal census during Xth
Atkinson, A., Snyder, R., Krill-copepod interactions at South Georgia,
Italian Expedition to the Ross Sea, November–December 1994,
Antarctica, I: Omnivory by Euphausia superba, Mar. Ecol. Prog.
DOC WB-EMM 96/63 Agenda Item No. 3, Commission for the
Ser., 160, 63–76, 1997.
Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, CCAMLR
Atkinson, A., Whitehouse, M.J., Ammonium excretion by Antarctic krill
Hobart, 1996, 21–26.
Euphausia superba at South Georgia, Limnol. Oceanogr., 45,
Baarud, T., Klem, A., Hydrological and chemical investigations in the
55–63, 2000.
coastal waters off More in the Romsdatfjord, Hvalradets Skrifter,
Atkinson, A., Whitehouse, M.J., Ammonium regeneration by Antarctic
1, 1–88, 1931.
mesoplankton: an allometric approach, Mar. Biol., 139, 301–311,
Bada, J.L., Lee, C., Decomposition and alteration of organic compounds
2001.
dissolved in seawater, Mar. Chem., 5, 523–534, 1977.
Atkinson, A., Ward, P., Williams, R., Poulet, S.A., Diel vertical
Baines, P.G., Condie, S., Observations and modelling of Antarctic
migration and feeding of copepods at an oceanic site near South
downslope flows: A review, in Interactions at the Antarctic
Georgia, Mar. Biol., 113, 583–593, 1992.
Continental Margin, Jacobs, S.S., Weiss, R., Eds., Antarct. Res.
Atkinson, A., Shreene, R.S., Pakhomov, E.A., Priddle, J., Blight, S.P.,
Ser., 75, 20–49, 1998.
Ward, P., Zooplankton response to a phytoplankton bloom near
Baker, A.deC., The circumpolar continuity of Antarctic plankton species,
South Georgia, Antarctica, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 144, 195–210, Discov. Rep., 29, 201–218, 1954.
1996. Baker, A.deC., The distribution and life history of Euphausia tricantha
Atkinson, A., Ward, P., Hill, A., Brierley, A.S., Cripps, G.C., Krill- Holt and Tattersall, Discov. Rep., 29, 309–340, 1959.
copepod interactions at South Georgia, II: Euphausia superba as a Baker, A.deC., The problem of keeping animals alive in the laboratory,
major control on copepod abundance, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 176, J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K., 43, 291–294, 1963.
63–79, 1999. Baker, D.J., Polar oceanography II: South Ocean, Rev. Geophys. Space.
Atkinson, A., Whitehouse, M.J., Priddle, J., Cripps, G.C., Ward, P., Phys., 17, 1578–1585, 1979.
Brandon, M.A., South Georgia Antarctica: a productive cold-water Balbontin, F., Garreton, M., Newling, J., Composicion del alimento y
pelagic system, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 216, 279–308, 2001. tarnano de las presas en larvas de peces del estrecho Bransfield
Atkinson, A., Siegel, V., Pakhomov, E., Rothery, P., Long-term decline (SIBEX Fase II-Chile), Serie Cientı́fica del Instituto Antártico
in krill stocks and increase in salps within the Southern Ocean, Chileno, 35, 25–144, 1986.
Nature (Lond.), 432, 100–103, 2004. Balech, E., Clave ilustrada de dinoflagelados Antarcticos, Buenos Aires:
Ayala, F.J., Valentine, J.W., Zumwalt, G.S., An electrophoretic study of Instituto Antártico Argentino Direccion Nacional del Antartico,
the zooplankter Euphausia superba, Limnol. Oceanogr., 20, Publ. IAA No. 11, 99 pp, 1975.
635–640, 1975. Bannister, J.L., The biology and status of the sperm whale off Western
Azam, F., Ammerman, J.W., Cycling of organic material by bacter- Australia—an extended summary of results of recent work, Int.
ioplankton in pelagic marine ecosystems: Environmental Whaling Committee Rep., 19, 70–76, 1969.
considerations, in Flows of Energy and Materials in Marine Bannister, J.L., Baker, A.deC., Observations on food and feeding of
Ecosystems, Fasham, M.J.R., Ed., Plenum Press, New York, baleen whales off Durban, Norwegian Whaling Gazette, 56, 78–82,
1984, 345–360. 1967.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 537
Banse, K., Determining the carbon-to-chlorophyll ratios of natural Basson, M., Beddington, J.R., Preliminary analysis of growth and
phytoplankton, Mar. Biol., 41, 199–212, 1977. mortality rates of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) from
Banse, K., Does iron really limit phytoplankton production in offshore length frequency analysis, Ant. Spec. Top, 51–55, 1989.
subarctic Pacific?, Limnol. Oceanogr., 35, 772–775, 1990. Bates, T.S., Charlson, R.J., Gammon, R.H., Evidence for the climatic
Barber, R.T., Smith, R.L., Coastal upwelling systems, in Analysis of role of marine biogenic sulphur, Nature (Lond.), 329(6137),
Marine Ecosystems, Longhurst, A.R., Ed., Academic Press, New 319–321, 1987.
York, 1981, 32–68. Bathmann, U.V., Fischer, G., Müller, P.J., Gerdes, D., Short-term
Bargagli, R., Monachi, F., Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C., Cateni, D., variations in particulate matter sedimentation off Kapp Norvegia,
Biomagnification of mercury in an Antarctic food web, Mar. Weddell Sea, Antarctica: Relation to water mass advection, ice
Ecol. Prog. Ser., 169, 65–76, 1998. cover, plankton biomass, and feeding activity, Polar Biol., 11,
Bargmann, H.E., The development and life history of adolescent and 185–195, 1991.
adult krill (Euphausia superba), Discov. Rep., 23, 103–176, Bathmann, U.V., Schanek, R., Klass, C., Dubischer, C.P., Smetacek, V.,
1945. Spring development of phytoplankton biomass and composition in
Barkley, E., Nahrung und Filterapparat des Walkrebschens Euphausia major water masses of the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean,
superba Dana, Zeitschrift für Fischerei und deren Hilfswis- Deep-Sea Res. II, 44, 51–67, 1997.
senschaften, 1, 65–156, 1940. Battershill, C.N., Distribution and abundance of benthic marine species
Barlow, R.G., Phytoplankton ecology in the Southern Benguela Current at Cape Armitage, Ross Island, Antarctica—initial results, NZ
III: Dynamics of a bloom, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 63, 239–248, Antarc. Rec., 9, 35–52, 1989.
1998. Beardall, J., Beer, S., Raven, J.A., Biodiversity of marine plants in an era
Barnes, D.K.A., Sublittoral epifaunal commuities at Signy Island, of climate change: some predictions based on physiological
Antarctica, I: The ice-foot zone, Mar. Biol., 121, 553–564, 1995a. performance, Botanica Marina, 41(1), 113–123, 1998.
Barnes, D.K.A., Sublittoral epifaunal communities at Signy Island, Beck, J.R., Food, moult, and age of first breeding in the cape pigeon,
Daption capensis Linneaus, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 21, 33–44,
Antarctica, II: Below the ice-foot zone, Mar. Biol., 121, 565–572,
1969.
1995b.
Beck, J.R., Breeding seasons and moult in some smaller Antarctic
Barnes, D.K.A., The influence of ice on polar nearshore benthos, J. Mar.
petrels, in Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 1, Holdgate, M.W., Ed.,
Biol. Assoc. UK, 79, 401–407, 1999.
Academic Press, London, 1970, 542–550.
Barnes, D.K.A., Invasions by marine life in plastic debris, Nature
Becquevort, S., Mathot, S., Lancelot, C., Interactions in the microbial
(Lond.), 416, 808–821, 2002a.
community of the marginal ice zone in the northwestern Weddell
Barnes, D.K.A., Human rubbish assists alien invasions of sea, Directions
Sea through size distribution analysis, Polar Biol., 12, 211–218,
Sci., 1, 107–112, 2002b.
1992.
Barnes, D.K.A., Brockington, S., Zooplankton diversity, biomass and
Beddington, J.R., Cooke, J.G., Development of an assessment technique
abundance at Adélie Island, Antarctica, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 249,
for male sperm whales based on length data in catches, with special
145–255, 2003.
reference to the Northwest Pacific stock, Int. Whaling Committee
Barrat, A., Note sur le petrel gris, Procellaria cinerea, Comité National
Rep., 31, 747–760, 1981.
Français des Recherches Antarctiques, 33, 19–24, 1974.
Beddington, J.R., Cooke, J.G., The potential yield of fish stocks, FAO
Barrat, A., Quelques aspects de la biologie et de l’ecologie du manchant
Fish. Tech. Papers, 242, 1–47, 1983.
royal (Aptenodytes patagonicus) de ı̂les Crozet, Comité National
Beddington, J.R., de la Mare, W.K., Marine mammal fishery
Français des Recherches Antarctiques, 40, 9–52, 1976.
interactions, in Selected Papers Presented to the Scientific
Barrat, A., Mougin, J.L., Donnes numeriques sur le zoogeographie de
Committee of CCAMLR 1982–1984, Part II, Commission for the
l’avifauna antarctique et subantarctique, Comité National Français Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 1984,
des Recherches Antarctiques, 33, 1–10, 1974. 155–178.
Barrera-Oro, E., Casaux, R., Ecology of demersal fish species from Beddington, J.R., de la Mare, W.K., Marine mammal-fishery
Potter Cove, Berichte zur Polarforschung, 299, 156–167, 1998. interactions: Modelling and the Southern Ocean, in Marine
Barrett-Hamilton, G.E.K., Seals, Expedition Antarctiques Belgique. Mammals and Fisheries, Beddington, J.R., Beverton, R.J.,
Results Voyage “Belgica” 1897–1899, Rap. Scient. Zool., 1–19, Lavigne, D.M., Eds., George Allen & Unwin, London, 1985,
1901. 94–105.
Barry, J.P., Hydrographic patterns in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica and Beddington, J.R., Grenfell. B., The Status of Major Zoological Groups in
their relationship to local benthic communities, Polar Biol., 8, the Southern Ocean, International Union for the Conservation of
367–376, 1998. Nature, Gland, Switzerland, 1980, 1–237.
Barry, J.P., Dayton, P.K., Current patterns in McMurdo Sound, Antarc- Beddington, J.R., May, R.M., Maximum sustainable yields in ecosys-
tica, and their relationships to local biotic communities, Polar tems subject to harvesting at more than one trophic level, Math.
Biol., 8, 367–376, 1988. Biosci., 51, 261–281, 1980.
Bartsch, A., Die Eislagenflora des Weddellmeeres (Antarktis): Anten- Beddington, J.R., May, R.M., The harvesting of interacting species in a
zusammensetzung und Biomasse soeie Okophysologie augeuahlter natural ecosystem, Sci. Am., 247, 62–69, 1982.
Arten, Berichte zur Polarforschung, 63–70, 1989. In German with Beddington, J.R., Beverton, R.J.H., Lavigne, D.M. Marine Mammals
English abstract. and Fisheries, George Allen & Unwin, London, 1985.
Basalaev, V.M., Petuchov, A.G., Experimental poutassou fishing in the Beers, J.R., Trent, J.D., Reid, F.M.H., Shanks, A.L., Macroaggregates
Scotia Sea from the research factory ship Academik Kripovich, and their phytoplankton components in the Southern California
Trudy VNIRO, 66, 307–310, 1969. In Russian. Bight, J. Plankton Res., 8, 475–487, 1986.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
538 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Bell, W., Mitchell, R., Chemotactic and growth responses of marine Berkmann, P.A., Waller, T.R., Alexander, S.P., Unprotected larval
bacteria to algal extracellular products, Biol. Bull., Mar. Biol. Lab., development in the Antarctic scallop Adamussium colbecki
Woods Hole, 143, 265–277, 1972. (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Pectinidae), Antarc. Sci., 3, 151–157, 1991.
Bellido, A., Les biocenoses du littoral rocheux aux Îles Kerguelen, Berman, T., Holm-Hansen, O., Release of photoassimilated carbon as
Colloque sur les Ecosystemes Subantarctiques, 1981, CNFRA, 51, dissolved organic matter by marine phytoplankton, Mar. Biol., 28,
81–93, 1982. 305–310, 1974.
Bengtson, J.L., Review of Information Regarding the Conservation of Berman, M.S., McVey, A.L., Ettertshank, G., Age determination of
Living Resources of the Antarctic Marine Ecosystem, Report Antarctic krill using fluorescence and image analysis of size, Polar
prepared for the U.S. Mammal Marine Commission, Washington, Biol., 9, 267–271, 1989.
DC, 1978. Bernard, K., Froneman, P.W., Mesozooplankton community structure in
Bengtson, J.L., Reproductive ecology of crabeater and leopard seals the Southern Ocean upstream of Prince Edward Islands, Polar
along the Antarctic Peninsula, Antarc. J. U.S., 17(5), 185, 1982. Biol., 25, 597–604, 2002.
Bengtson, J. L.,Review of Antarctic marine fauna, in Selected Papers Bernard, K., Froneman, P.W., Mesozooplankton community structure
Presented to the Scientific Committee of CCAMLR 1982–1984, and grazing impact in the Polar Frontal Zone during the austral
Part I, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine autumn 2003, Polar Biol., 26, 268–275, 2003.
Living Resources, Hobart, 1 pp, 1985a. Bernard, K., Froneman, P.W., Trophodynamics of selected mesozoo-
Bengtson, J. L.,Monitoring indicators of possible ecological changes in plankton in the west Indian sector of the Polar Frontal Zone,
the Antarctic marine ecosystem. in Selected Papers Presented to Southern Ocean, Polar Biol., 28, 594–606, 2005.
the Scientific Committee of CCAMLR 1982–1984, Part II, Berruti, A., The breeding biologies of the sooty albatross, Phoebetria
Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living fusca and P. palpebrata, at Marion Island, S. A. J. Antarc. Res., 8,
Resources, Hobart, 1985b, 43–154. 99, 1979.
Bengtson, J.L., Long-term trends in the foraging patterns of female Berry, A.J., The occurrence of a leopard seal (Hydrurga leptonyx) in the
Antarctic fur seals at South Georgia, in Antarctic Ocean and tropics, Annual Magazine of Natural History, 13th series 1960
Resources Variability, Sahrhage, D., Ed., Springer, Berlin, 1988, (1961), 587–591, 1961.
286–291. Bertram, G.C.L., The biology of the Weddell and crabeater seals, with
Bengtson, J.L., Laws, R.M., Trends in crabeater seal age at maturity: an a study of the comparative behaviour of the Pinnipedia, British
insight into Antarctic marine interactions, in Selected Papers Grahamland Expedition 1934–37 Scientific Reports 1, 1940.
Presented to the Scientific Committee of CCAMLR 1982–1984. Berzin, A.A. The Sperm Whale, Israel Program for Scientific Trans-
Part II, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine lations, Jerusalem, 1972.
Living Resources, Hobart, 1984, 341–368. Best, P.B., Distribution and feeding habits of baleen whales off the Cape
Bengtson, J.L., Laws, R.M., Trends in crabeater seal age at maturity: an Province, Div. Sea Fish. Invest. Rep., S. Afr., 57, 1–44, 1967.
insight into Antarctic marine ecosystem interactions, in Antarctic Best, P.B., The sperm whale (Physeter catadon) off the west coast of
Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., South Africa. 2. Reproduction in the female, Div. Sea Fish Invest.
Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 667–675. Rep. S. Afr., 66, 1–32, 1968.
Bengtson, J.L., Siniff, D.B., Reproductive aspects of female crabeater Best, P.B., The sperm whale (Physeter catadon) off the west coast of
seals (Lobodon carcinophagus) along the Antarctic Peninsula, South Africa, 3: Reproduction in the male, Div. Sea Fish. Invest.
Can. J. Zool., 59, 92–102, 1981. Rep., S. Afr., 72, 1–20, 1969.
Bengston, J.L., Boven, W.D., Jansen., S.K., Foraging areas of krill- Best, P.B., The sperm whale (Physeter catadon) off the west coast of
consuming penguins and fur seals near Seal Island, Antarctica, South Africa, 5: Age, growth and maturity, Div. Sea Fish. Invest.
Antarc. J. U.S., 26(5), 217–218, 1991. Rep., S. Afr., 79, 1–27, 1970a.
Berger, W.H., Herger, J.C., Reading the sedimentary record of the Best, P.B., Exploitation and recovery of right whale (Eubalaena
ocean’s productivity, in Primary Productivity and Biogeochemical australis) off the Cape Province, Div. Sea Fish. Invest. Rep.,
Cycles in the Sea, Falkowski, P.G., Woodhead, A.O., Eds., Plenum S. Afr., 80, 1–20, 1970b.
Press, Oxford, 1992, 455–486. Best, P.B., Status of the whale population off the west coast of South
Bergstrom, B.I., Hempel, G., Marschall, H.P., North, A., Siegel, V.G., Africa and current research, in The Whale Problem: A Status
Stromberg, J.O., Spring distribution, size composition, and Report, Schevill, W.E., Ed., Harvard University Press, Cambridge,
behaviour of krill (Euphausia superba) in the western Weddell MA, 1974a, 53–81.
Sea, Polar Res., 26, 85–89, 1990. Best, P.B., The biology of the sperm whale as it relates to stock manage-
Berkes, F., Some aspects of the feeding mechanisms of euphausiid ment, in The Whale Problem: A Status Report, Schevill, W.E., Ed.,
crustaceans, Crustaceana, 29, 266–270, 1975. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA, 1974b, 257–293.
Berkman, P.A., Ecological variability in Antarctic coastal environments: Best, P.B., Social organization in sperm whales, Physeter macroce-
past and present, in Antarctic Communities. Species, Structure phalus, in Behavior of Marine Mammals, Vol. 3, Winn, H.E., Olla,
and Survival, Battaglia, B., Valencia, J., Walton, D.W.H., Eds., B.L., Eds., Plenum Press, New York, 1979, 227–289.
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1997, 349–357. Best, P.B., Seasonal abundance, feeding, reproduction and growth in
Berkman, P.A., Nigro, M., Trace metal concentrations in scallops around minke whales off Durban (with incidental observations from
Antarctica: Extending the Mussel Watch Programme to the Antarctica), Rep. Int. Whal. Commun., 32, 755–786, 1982.
Southern Ocean, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 24, 322–323, 1992. Bester, M.N., Laycock, P.A., Cephalopod prey of the sub-Antarctic fur
Berkman, P.A., Marks, D.S., Shreve, G.P., Winter sediment resuspen- seal Arctocephalus tropicalis at Gough Island, in Antarctic
sion in McMurdo Sound and its ecological implications, Polar Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R.,
Biol., 6, 1–3, 1986. Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 551–554.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 539
Bester, M.N., Erickson, A.W., Ferguson, J.W.H., Seasonal changes in Bienfang, P.K., Phytoplankton sinking rates in oligotrophic water off
the distribution and density of seals in the pack ice of the Princess Hawaii, Mar. Biol., 61, 69–77, 1980.
Martha Coast, Antarctica, Antarc. Sci., 7(4), 357–364, 1995. Bienfang, P.K., Sinking rates of heterogeneous temperate phyto-
Beverton, R.J.H., Holt, S.J., A review of methods estimating mortality plankton populations, J. Plankton Res., 3, 235–253, 1981.
rates in exploited fish populations, with special reference to sources Bienfang, P.K., Size, structure, and sedimentation of biogenic micro-
of bias in catch sampling, Rapports et Proces Verbeux de particulates in a subarctic ecosystem, J. Plankton Res., 6, 983–994,
Reunions, Council International pour l’Exploration de la Mer, 1984.
140, 67–83, 1956. Bienfang, P.K., Size, structure, and sinking rates of various microparti-
Beverton, R.J.H., Lee, A.J., Hydrographic fluctuations in the North culate constituents in oligotrophic Hawaiian waters, Mar. Ecol.
Atlantic Ocean and some biological consequences, in The Eco- Prog. Ser., 23, 143–151, 1985.
logical Significance of Biological Change in Britain, Johnson, Bienfang, P.K., Harrison, P.J., Sinking rate response of natural assem-
C.G., Smith, L.P., Eds., Institute of Biology Symposia, London, blages of temperate and subtropical phytoplankton to nutrient
1965, 79–107. depletion, Mar. Biol., 83, 293–300, 1994.
Beylev, G.M., Uschakov, P.V., Certain regularities in the quantitative Biggs, D.C., Zooplankton excretion and NH4 cycling in near-surface
distribution of the benthic fauna in Antarctic waters, Dolklady waters of the Southern Ocean, I: Ross Sea, austral summer
Akademii Nauk SSSR, 112, 137–140, 1957. 1977–1978, Polar Biol., 1, 55–67, 1982.
Bianchi, F., Brine investigations, Ber. Polarforsch., 62, 95–97, 1989. Biggs, D.C., Johnson, M.A., Bigidare, R.R., Guffy, J.D., Holm-Hansen, O.,
Bianchi, F., Boldrin, A., Coice, F., Nöthig, E.-M., Sehlstedt, P.L., Socal, Shipboard autoanalyzer studies of nutrient chemistry, 0–200 m, in
G.T., Syverten, E.E., Phytoplankton distribution in relation to sea the eastern Scotia Sea during FIBEX, Technical Report 82-11-T,
ice, hydrography, and nutrients in the northwestern Weddell Sea in Department of Oceanography, Texas A&M University, College
early spring during EPOS, Polar Biol., 12, 225–235, 1992. Station, TX, 1983.
Bianchi, M., Feliatra, F., Treguer, P., Vincendeau, M.A., Morvan, J., Billen, G., Heterotrophic utilization and regeneration of nitrogen, in
Nitrifiction rates, ammonium and nitrate distribution in upper
Heterotrophic Activity in the Sea, Hobbie, J.E., Williams, P.L.leB.,
layers of the water column and sediments of the Indian sector of
Eds., Plenum Press, New York, 1984, 313–356.
the Southern Ocean, Deep-Sea Res., 44, 1017–1032, 1997.
Billen, G., Becquevort, S., Phytoplankton-bacterial relationship in the
Bibik, V.A., Maslennikov, V.V., Delevin, A.S., Polonsky, V.E.,
Antarctic marine ecosystem, Polar Biol., 10, 245, 1991.
Solyankin, E.N., The current system and distribution of waters of
Billen, G., Fontigny, A., Dynamics of a Phaeocystis spring bloom in
different modifications in the Cooperation and Cosmonaut Seas, in
Belgian coastal waters. II. Bacterioplankton dynamics, Mar. Ecol.
Interdisciplinary Investigations of the Pelagic Ecosystem in the
Prog. Ser., 37, 249–257, 1987.
Cooperation and Cosmonaut Seas, Makarov, R.R., Ed., NIRO
Billen, G., Joiris, C., Wijnant, J., Gillain, G., Concentration and
Publishing, Moscow, 1988, 16–43.
microbial utilization of small organic molecules in the Scheldt
Biddanda, B.A., Microbial synthesis of macroparticulate matter, Mar.
Estuary, the Belgian coastal zone of the North Sea, and the English
Ecol. Prog. Ser., 20, 241–251, 1985.
Channel, Estuar. Coast. Mar. Sci., 11, 279–294, 1980.
Biddanda, B.A., Structure and function of microbial aggregates, Ocea-
Binnerup, S.J., Jensen, K., Revsheck, N.P., Jensen, M.H., Sorenson, J.,
nologica Acta, 9, 209–211, 1986.
Denitrification, dissimilatory reduction in nitrate to ammonium,
Biddanda, B.A., Pomeroy, L.R., Microbial aggregation and degradation
and nitrification in a bioturbated sediment as measured with 15N
of phytoplankton-derived detritus in sea water, I: Microbial
and microsensor techniques, Appl. Environ. Microbio., 58,
succession, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 42, 79–88, 1988.
303–313, 1992.
Bidenko, M.S., Rasulova, T.A., Odintsor, A.B., On the activity of
proteolytic ferments in Antarctic krill, in Research in technological Bird, D.F., Maranger, R., Karl, D.M., Palmer LTER: Aquatic virus
characterization and processing of krill, Bidenko, M.S., Ed., abundance near the Antarctic Peninsula, Antarc. J. U.S., 28,
Atlant-VNIRO, Kalingrad, 1981, 15–18. In Russian with English 234–235, 1993.
summary. Bird, D.F., Juniper, S.K., Riccardi-Rigault, M., Martine, P., Prarie, Y.T.,
Bidigare, R.R., Potential effects of UV-B radiation in marine Calvert, S.E., Subsurface viruses and bacteria in Holocene/Late
organisms of the Southern Ocean: Distribution of phytoplankton Pleistocene sediments of Saanich Inlet, B.C.: ODP Holes 1033B
and krill during austral spring, Photochem. Photobiol., 50, and 1034B, leg 1695, Mar. Geol., 174, 227–239, 2001.
469–477, 1989. Bischof, K., Hanelt, D., Wiencke, C., UV-radiation can affect depth
Bidigare, R.R., Johnson, M.A., Duffy, J.D., Biggs, D.C., Nutrient zonation of Antarctic macroalgae, Mar. Biol., 131, 597–601, 1998.
chemistry of ammonium in Antarctic surface waters, Antarc. Bjørnsen, P.K., Kuparinen, J., Growth and herbivory by heterotrophic
J. U.S., 16, 168–170, 1981. dinoflagellates in the Southern Ocean, studied by microcosm
Bidigare, R.R., Itiarte, J.L., Kang, S.H., Ondrusek, M.E., Karentz, D., experiments, Mar. Biol., 109, 397–405, 1991.
Fryxall, G.A., Phytoplankton quantitative and qualitative assess- Blome, D., Riemann, F., Antarctic sea ice nematodes, with description of
ments, in Foundations for Ecosystem Research in the Western Geomonhystera glaciei sp. nov. (Monhysteridae). Mitteilungen
Antarctic Peninsula Region. Antarctic Research Series 70, Ross, Hamb. Zool. Mus. Inst., 96, 15–20, 1999.
A., Hofmann, E.H., Quetin, L.B., Eds., American Geophysical Boak, A.C., Goulder, R., Bacterioplankton in the diet of the calanoid
Union, Washington, DC, 1995, 173–178. copepod Eurytemora sp. in the Humber Estuary, Mar. Biol., 73,
Bienati, N.L., Gomes, R.A., Spiedo, H., Primary production in Antarctic 139–149, 1994.
waters: seasonal variation and production in fertilized samples Bo Chen, Distribution and abundance of choanoflagellates in Great Wall
during the summer cycle, in Polar Oceans, Dunbar, M.T., Ed., Bay, King George Island, Antarctica, in austral summer, NIPR
Arctic Institute of North Amarica, Calgary, 1977, 377–390. Symp. Polar Biol., 7, 32–42, 1994.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
540 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Bocher, P., Cherel, Y., Hobson, K.A., Complete trophic segregation Boucher, N.P., Prezelin, B.B., An in situ biological weighting function
between South Georgian and common diving petrels during for UV inhibition of phytoplankton carbon fixation in the Southern
breeding at Isles Kerguelen, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 208, Ocean, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 146, 223–236, 1996.
249–264, 2000. Bouvey, M., Soyer, J., Benthic seasonality in an intertidal mud flat at
Boesch, D.F., Species diversity in the macrobenthos of the Virginia area, Kerguelen Islands (Austral Ocean). The relationship between
Chesapeake Sci., 13, 206–211, 1972. meiofaunal abundance and their potential microbial food, Polar
Boesch, I., Beauchamp, K.A., Steele, M.E., Pearse, J.S., Development, Biol., 10, 19–27, 1989.
metomorphosis, and seasonal abundance of embryos and larvae of Bowen, S.H., Evidence of a detritus food chain based on the consump-
the Antarctic sea urchin Sterechinus neumayeri, Biol. Bull., 1763, tion of organic precipitates, Bull. Mar. Sci., 35, 440–448, 1984.
126–135, 1987. Bowman, J.P., Brown, M.V., Nichols, D.S., Biodiversity and ecophy-
Bogdanov, M.A., Solyankin, E.V., Radionev, S.N., The distribution of siology of bacteria associated with Antarctic sea ice, Antarc. Sci.,
mingled water and secondary frontal zone in the Sea of Scotia and 9, 134–142, 1997.
the distribution of krill swarms, in Biological Resources of Boyd, I.L., Pup production and distribution of breeding Antarctic fur
Antarctic Krill, Lubimova, T. G., Ed., VNIRO, Moscow, 1980, seals (Arctocephalus gazella) at South Georgia, Antarc. Sci., 5,
218–231. In Russian. 17–25, 1993.
Bolter, M., Dawson, R., Heterotrophic utilization of biochemical Boyd, I.L., Croxall, J.P., Preliminary estimates of krill consumption by
compounds in Antarctic waters, Neth. J. Sea Res., 16, 315–332, 1982. Antarctic fur seals and macaroni penguins at South Georgia,
Boltovosk, D., Alder, V.A., Spinelli, F., Summer Weddell Sea micro- Document WG-Emm-96/96, Commission for the Conservation of
plankton: Assemblage structure, distribution, and abundance, Antarctic Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 1996.
with special emphasis on the tintinnina, Polar Biol., 9, 447–456, Boyd, P.W., Law, C.S., The Southern Ocean Iron Release Experiment
1980. (SOIREE)—Introduction and summary, Deep-Sea Res. II, 48,
Bonner, W.N., Notes on the southern fur seal in South Georgia, Proc.
2425–2438, 2001.
Zool. Soc. London, 130, 241–252, 1958.
Boyd, J.C., Sladen, J.L., Telemetry studies of the internal body
Bonner, W.N., Population increase in the fur seal, Arctocephalus tropicalis
temperatures of Adélie and emperor penguins at Cape Crozier,
gazella, at South Georgia, in Biologie Antarctique, Carrick, R.,
Ross Island, Antarctica, The Auk, 88, 366–391, 1971.
Holdgate, W.M., Prevost, J., Eds., Herman, Paris, 1964, 438–443.
Boyd, C.M., Heyraud, M., Boyd, C.N., Feeding of Antarctic krill,
Bonner, W.N., The fur seal of South Georgia, Sci. Rep. Br. Antarc. Surv.,
Euphausia superba, J. Crustacean Biol., 4 (Special Issue No.1),
56, 1–81, 1968.
123–141, 1984.
Bonner, W.N., The status of the Antarctic fur seal, Arctocephalus
Boyd, P.W., Watson, A.J., Law, C.S., Abraham, E.R., Trull, T.,
gazella. FAO Advisory Committee on Marine Resources Research,
Murdoch, R., Bakker, D.C.E., Bowie, A.R., Buesseler, K.O.,
Scientific Consultation on Marine Mammals, ACMRR/MM/SC/50,
Chang, H. et al., A mesoscale phytoplankton bloom in the polar
18, 1976.
Southern Ocean stimulated by iron fertilization, Nature (Lond.),
Bonner, W.N., Southern fur seals: Arctocephalus (Geoffrey SaintHilaire
407, 695–702, 2000.
and Cuvier, 1926), in Handbook of Marine Mammals, Vol. 1,
Boyle, P.R., Ed, Cephalopod Life Cycles, Vol. 1, Academic Press,
Ridgway, S.R.H., Harrison, R.J., Eds., Academic Press, London,
London, 1983.
1981, 161–208.
Boyle, P.W., Pumping iron makes thinner diatoms, Nature (Lond.), 393,
Bonner, W.N., Conservation and the Antarctic, in Antarctic Ecology,
733–734, 1998.
Vol. 2, Laws, R.M., Ed., Academic Press, London, 1984, 821.
Boysen-Ennen, E., Piatkowski, U., Meso- and nanozooplankton commu-
Bonner, W.N., Birds and mammals—Antarctic seals, in Key Environ-
ments—Antarctica, Bonner, W.N., Walton, D.W.H., Eds., nities in the Weddell Sea, Polar Biol., 9, 17–35, 1988.
Pergamon Press, London, 1985a, 202–222. Boysen-Ennen, E., Hagen, W., Hubold, G., Piatkowski, U., Zooplankton
Bonner, W.N., Impact of fur seals on the terrestrial environment at South biomass in the ice-covered Weddell Sea, Antarctica, Mar. Biol.,
Georgia, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, 111, 227–235, 1991.
W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985b, Bracher, A., Photoacclimation of phytoplankton in different biogeo-
640–641. chemical provinces of the Southern Ocean and its significance for
Bonner, W.N., Laws, R.M., Seals and sealing, in Antarctic Research, estimating primary production, Berichte zur Polarforscherung,
Priestly, R., Adie, R.J., deQ. Robin, G., Eds., Butterworth, London, 341, 1–88, 1999.
1964, 163–190. Bracher, A.W., Wiencke, C., Simulation of the effects of naturally-
Bonner, W.N., Watson, D.W.H., Marine habitats—introduction, in Key enhanced UV radiation on photosynthesis of Antarctic phyto-
Environments—Antarctica, Bonner, W.N., Ed., Pergamon Press, plankton, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 196, 127–141, 2000.
Oxford, 1985, 133–142. Bracher, A., Kroon, B.M.A., Lucas, M.I., Primary production and
Bonner, W.N., Everson, I., Prince, P.A., A shortage of krill, Euphausia physiological state of the phytoplankton in the Atlantic sector of
superba, around South Georgia, International Council for the the Southern Ocean, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 190, 1–16, 1999.
Exploration of the Sea, Series C, CM, 1978, L/22. Bradfield, P., The ecology of Trematomus borchgrevinki in McMurdo
Boone, R.J., Manthey, M., The anatomical distribution of fluoride within Sound, Antarctica. BSc. (Hons) Project in Zoology, University of
various body segments and organs of Antarctic krill, Archiv für Canterbury, Christchurch, 1980.
Fischereiwissenschaft, 34, 81–85, 1983. Bradford, J.M., The fauna of the Ross Sea, 8: Pelagic Copepoda, Bull.—
Boronin, A.V., Frolkina, Zh.A., Age determination in green notothenia NZ Depart. Sci. Ind. Res., 206, 9–31, 1971.
(Notothenia gibberifrons) from the Southwest Atlantic, Trudy Bradford, J.M., Sea-ice organisms and their importance in the Antarctic
Atlantic NIRO, 70, 29–37, 1976. In Russian. ecosystem, NZ Antarc. Rec., 1, 43–50, 1978.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 541
Bragg, J.R., Prince, R.C., Harner, E.J., Atlas, R.M., Effectiveness of Brinton, E., The oceanographic structure of the eastern Scotia Sea,
bioremediation for the Exxon-Valdez oil spill, Nature, 308, III: Distribution of euphausiid species and their development
413–418, 1994. stages in in relation to hydrography, Deep-Sea Res., 32,
Brandini, F.P., Phytoplankton biomass in an Antarctic coastal environ- 1153–1180, 1985.
ment during stable water conditions—implications for the iron Brinton, E., Antezana, T., Structure of swarming and dispersed popu-
limitation theory, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 93, 267–275, 1993. lations of krill (Euphausia superba) in Scotia Sea and South
Brandini, F.P., Kutner, M.B.B., Phytoplankton and nutrient distri- Shetland waters during January–March, determined by bongo
bution off the northern South Shetland Islands (summer 1984 nets, J. Crustacean Biol., 4(Special Issue No.1), 45–60, 1984.
BIOMASS/SIBEX), La Mer, 25, 93–99, 1997. Brinton, E., Townsend, A.W., Regional relationships between develop-
Brandt, A., The deep-sea isopod genus Echinozone Sars and its ment and growth in larvae of Antarctic krill Euphausia superba,
occurrence on the continental shelf of Antarctica, Antarc. Sci., 2, from field samples, J. Crustacean Biol., 4(Special Issue No.1),
215–219, 1990. 224–246, 1984.
Brandt, A., Evolution of Antarctic biodiversity in the context of the past: Brock, V.E., Riffenberg, R.H, Fish schooling: a possible factor in
the importance of the Southern Ocean deep sea. Abstracts Scar reducing predation, Journal du Conseil Council International
Open Science Conference, Bremen, 2004, 83, 2004. pour l’Exploration de la Mer, 25, 307–317, 1960.
Bratbak, G., Thingstad, T.F., Phytoplankton-bacteria interactions: an Brodie, J., Oceanography, in Antarctica, Hatherton, T., Ed.,
apparent paradox? Analysis from a model system with Methuen&Co. Ltd, London, 1965, 101–127.
both competition and commensalism, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., Brodie, P.F., Cetacean energetics: an overview of intraspecific size
25, 23–30, 1985. variation, Ecology, 56, 152–161, 1975.
Bregazzi, P.K., Life cycles and seasonal movements of Cheriimedon Broecker, W.S., Comment on “Iron deficiency limits phytoplankton
femoratus (Pfeffer) and Tryphosella kergueleni (Miers) (Crusta- growth in Antarctic waters” by John H. Martin, et al., Global
cea:Amphipoda), Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 30, 1–34, 1972. Biogeochem. Cycles 4, 5–12, 1990.
Brenner, M., Buck, B.H., Cordes, S., Dietrich, L., Jacob, U., Mintenbeck, Bromwich, D., Liu, Z., Rogers, A.N., Winter atmosphere forcing of the
K., Schroder, A., Brey, T., Knust, R., Antz, W., The role of iceberg Ross Sea polyna. in Ocean, Ice, and Atmosphere Interactions of the
scours in niche separation within the Antarctic fish genus Trema- Antarctic Continental Margin, Jacobs, S.S., Weller, R.F., Eds.,
tomus, Polar Biol., 24, 502–507, 2001. Antarctic Research Series 75, 1998, 103–133.
Brey, T., Temperature and reproductive metabolism in macrobenthic Brooke, M.deL., Prince, P.A., Nocturnality in seabirds, Acta XX
populations, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 125, 87–93, 1995. Congressus Internationalis Ornithologici, 1113–1121, 1991.
Brey, T., Clarke, A., Population dynamics of marine benthic invert- Brown, K.G., The leopard seal at Heard Island, 1951–54, Aust. Natl
ebrates in Antarctic and sub-Antarctic environments: are there Antarc. Res. Exped. Interim Rep., 16, 1–34, 1957.
unique adaptations?, Antarc. Sci., 5, 253–266, 1993. Brown, S.G., The movements of fin and blue whales within the Antarctic
Brey, T., Gerdes, D., Is Antarctic benthos really higher than elsewhere?,
zone, Discov. Rep., 33, 1–54, 1962a.
Antarc. Sci., 1, 266–267, 1997.
Brown, S.G., A note on the migration of fin whales, Norsk Hvalfangsttid,
Brey, T., Gerdes, D., High Antarctic macrobenthic production, J. Exp.
50, 13–16, 1962b.
Mar. Biol. Ecol., 231, 191–200, 1998.
Brown, S.G., Whale marking—progress report, 1970, Int. Whaling
Brieley, A.S., Watkins, J.L., Effects of sea ice cover on the swarming
Committee Rep., 21, 31–55, 1971.
behaviour of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Canadian J. Fish.
Brown, S.G., Some results of sei marking in the Southern Hemisphere,
Aquatic Sci., 51(S3), 24–30, 2000.
Int. Whaling Committee Rep. Spec. Issue, 1, 39–43, 1977.
Brierley, A.S., Goss, C., Acoustic estimates of krill density at South
Brown, R.G.B., Seabirds as marine animals, in Behaviour of Marine
Georgia, December-January 1989/90. CCAMLR Scientific
Animals, Vol. 4: Marine Birds, Berger, J., Olla, B.L., Winn, H.E.,
Abstracts WG-EMM, 1999.
Eds., Plenum Press, New York, 1980, 80.
Brierley, A.S., Thomas, D.N., Ecology of Southern Ocean pack ice, Adv.
Brown, S.G., Lockyer, G.H., Whales, in Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 2,
Mar. Biol., 43, 171–276, 2002.
Laws, R.M., Ed., Academic Press, London, 1984, 717–782.
Brieley, A.S., Watkins, J.L., Goss, C., Wilkinson, M.T., Everson, I.,
Brown, R.G.B., Nettleship, D.N., The biological significance of polynas
Acoustic estimates of krill density at South Georgia, 1981–1998,
to Arctic colonial seabirds, Can. Wildlife Ser. Occas. Papers, 45,
CCAMLR Sci., 6, 47–57, 1999.
59–63, 1981.
Brierley, A.S., Fernandes, P.G., Brandon, M.A., Armstrong, F., Millard,
Brown, R.G.B., Cooke, F., Kinner, P.K., Mills, E.L., Summer seabird
N.W., McPhail, S.D., Stevenson, P., Pebody, M., Perrett, J.,
distributions in the Drake Passage, Chilean fjords, and off Southern
Squires, M., Bone, D.G., Griffiths, G., Antarctic krill under sea
South America, Ibis, 117, 339–356, 1975.
ice: elevated abundance in a narrow band just south of the ice edge,
Brown, K.M., Keiron, P.P.F., Barnes, D.K.A., Peck, L.S., Links between
Science, 295, 1890–1892, 2002.
the structure of an Antarctic shallow-water community and ice
Briggs, K.T., Tyler, W.B., Lewis, D.B., Carlson, D.P., Bird communities
scour frequency, Oecologia, 146, 121–129, 2004.
at sea off California, Stud. Avian Biol., 16, 1–74, 1987.
Brownell, R.L., Jr., Small odontocetes in the Antarctic, Antarctic Map
Brightman, R.I., Smith, W.O., Jr., Photosynthesis-irradiance relation-
Folio Series, Vol. 18, American Geographical Society,
ships of Antarctic phytoplankton during the austral winter, Mar.
Washington, DC, 1974, PP. 13–19.
Ecol. Prog. Ser., 53, 143–151, 1989.
Broyer, C., Jazdzewski, K., Contribution to the marine biodiversity
Brinton, E., Observations of plankton organisms obtained by bongo nets
during the November–December iceedge investigations, Antarc. inventory: a checklist of the Amphipoda (Crustacea) of the
J. U.S., 19, 113–115, 1984. Southern Ocean, Bet. Inst. Naturwiss, Brussels, 73, 1–114, 1993.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
542 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Bruckhausen, P.M., Raymond, J.A., Jacobs, S.S., DeVries, A.L., Bunt, J.S., Introductory studies: Hydrology and plankton at Mawson,
Thorndike, E.M., Dewitt, H.H., Fish, crustaceans, and the sea June to February 1957, ANARE Rep., 56, 1–135, 1960.
floor under the Ross Ice Shelf, Science, 203(4379), 449–451, Bunt, J.S., Diatoms in Antarctic sea ice as agents of primary production,
1979. Nature (Lond.), 199, 1255–1257, 1963.
Bryden, M.M., Kirkwood, G.P., Slade, R.W., Humpback whales, Area Bunt, J.S., Primary productivity under sea ice in Antarctic waters,
V: An increase in numbers off Australia’s east coast, in Antarctic 1: Concentrations and photosynthetic activities of Antarctic
Ecosystems: Ecological Change and Conservation, Kerry, K.R., marine microalgae, Antarc. Res. Ser., 1, 13–26, 1964a.
Hempel, G., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1990, 271–277. Bunt, J.S., Primary productivity under the sea ice in Antarctic waters.
Buchholz, F., Drach’s moult staging system, adapted for euphausiids, Influence of light and other factors on photosynthetic activities of
Mar. Biol., 66, 301–305, 1982. Antarctic marine microalgae, Antarc. Res. Ser., 1, 27–31, 1964b.
Buchholz, F., Moulting and moult physiology in krill, Berichte zur Bunt, J.S., Some characteristics of microalgae isolated from Antarctic
Polarforschung, 4, 81–88, 1983. sea ice, Antarc. Res. Ser., 11, 1–14, 1967.
Buchholz, F., Moult and growth in euphausiids, in Antarctic Nutrient Bunt, J.S., Microalgae of the Antarctic pack ice zone, in Symposium on
Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, W.R., Antarctic Oceanography, Currie, R.I., Ed., Scott Polar Research
Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 339–345. Institute, Cambridge, UK, 1968a, 198–218.
Buck, K.R., A study of choanoflagellates (Acanthoecidae) from the Bunt, J.S., Influence of light and other factors on the photosynthetic
Weddell Sea, including a description of Diaphanoeca multiannu- activities of Antarctic marine microalgae, Antarc. Res. Ser., 11,
lata n.sp, J. Protozool., 28, 47–54, 1981. 27–31, 1968b.
Buck, K.R., Garrison, D.L., Protists from the ice-edge region of the Bunt, J.S., Microbiology of sea ice, Antarc. J. U.S., 4, 193–197, 1969.
Weddell Sea, Deep-Sea Res., 30, 1261–1278, 1983. Bunt, J.S., Lee, C.C., Seasonal primary production in Antarctic sea ice at
Buck, K.R., Garrison, D.L, Distribution and abundance of choanofla- McMurdo Sound in 1967, J. Mar. Res., 28, 304–320, 1970.
gellates (Acanthoecidae) across the ice-edge zone in the Weddell Bunt, J.S., Wood, E.J.F., Microalgae and Antarctic sea ice, Nature
Sea, Antarctica, Mar. Biol., 98, 263–269, 1988. (Lond.), 199, 1254–1255, 1963.
Buck, K.R., Garrison, D.L., Hopkins, T.L., Abundance and distribution Bunt, J.S., Lee, C.C., Boggs, W.J., Jr., Microalgae and Protozoa of
of tintinnids in an ice-edge zone: An AMERIEZ study, EOS, 68, Antarctic pack ice, Antarc. J. U.S., 3, 87–90, 1968.
1773, 1987. Burchett, M.S., The ecology of some coastal fish populations at South
Buck, K.R., Bolt, P.A., Garrison, D.L., Phagotrophy and fecal pellet Georgia, Prog. Underwater Sci., 7, 15–20, 1982.
production by an athecate dinoflagellate in Antarctic sea ice, Mar. Burchett, M.S., Food, feeding, and behaviour of Notothenia rossii
Ecol. Prog. Ser., 60, 75–84, 1990. nearshore at South Georgia, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 61, 45–51,
Buck, K.R., Garrison, D.L., Hopkins, T.L., Abundance and distribution 1983a.
of tintinnid ciliates in an ice-edge zone during the austral summer, Burchett, M.S., Age and growth of the Antarctic fish Notothenia rossii
Antarc. Sci., 4, 3–8, 1992. Fisher (1885) from South Georgia, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 60,
Buckley, R.G., Trodahl, H.J., Scattering and absorption of visible light 45–61, 1983b.
by sea ice, Nature (Lond.), 326, 867–869, 1987. Burchett, M.S., Life cycle of Notothenia rossii from South Georgia, Br.
Buckley, R.G., Trodahl, H.J., Radiation risk, Nature (Lond.), 346,
Antarc. Surv. Bull., 61, 71, 1983c.
24–31, 1990.
Burchett, M.S., Sayers, P.J., North, A.W., White, G.M., Some biological
Buckley, J.R., Gammelsrod, T., Johannesson, J.A., Johannesson, O.M.,
aspects of the nearshore fish populations at South Georgia, Br.
Roed, L.P., Upwelling: Oceanic structure at the edge of the Arctic
Antarc. Surv. Bull., 59, 63–74, 1983.
ice pack in winter, Science, 203, 165–167, 1979.
Burchett, M.S., DeVries, A., Briggs, A.J., Age determination and growth
Budd, W.F., Antarctic glaciation and global change, Climate Change,
of Dissothicus mawsoni (Norman, 1937) (Pisces, Nototheniidae)
18, 271, 1991.
from McMurdo Sound (Antarctica), Cybium, 8, 27–31, 1984.
Budkoviskiy, T.V., Yaragov, B.A., Studying the Antarctic krill for the
Burger, A.E., Breeding biology, moult, and survival of lesser sheathbills
purpose of organizing krill fisheries, in Soviet Fishery on Antarctic
(Chionis minor) at Marion Island, Ardea, 67, 1–14, 1979.
Krill, Burukovsky, R.N., Ed., U.S. Department of Commerce (TT-
Burger, A.E., Lindeboom, H.J., Williams, A.J., Mineral and energy
67-32683), Washington, DC.
contribution of guano of selected species of seabirds in the
Budylenko, G.A., Distribution and migration of sei whales in the
Marion Island terrestrial ecosystem, S. Afr. J. Antarc. Res., 8,
Southern Hemisphere, Int. Whaling Committee Rep., 28,
59–65, 1978.
373–377, 1978.
Burkholder, P.R., Mandelli, E.F., Productivity of microalgae in
Budzinski, E., Bykowski, P., Dutkiewicz, D. Possibilities of processing
Antarctic sea ice, Science, 149, 972–974, 1965.
and marketing of products made from Antarctic krill, FAO Fish-
Burkholder, P.R., Mandelli, E.F., Productivity of microalgae in
eries Technical Paper 268, Rome, 1985.
Antarctic sea ice, Nature (Lond.), 199, 972–984, 1965.
Buma, A.G.J., De Baar, H.J.W., Nöthig, R.F., van Bennekom, A.J.,
Burkill, P.H., Ciliates and other microplankton components of a nearshore
Metal enrichment experiment in the Weddell-Scotia Seas: effects
food web: Standing stocks and production processes, Annu. Rep.
of iron and magnesium in various plankton communities, Limnol.
Natl Inst. Oceanogr., 58(Suppl.), 335–350, 1982.
Oceanogr., 36(8), 1865–1878, 1991.
Burkill, P.H., Edwards, E.S., Sleigh, M.A., Microzooplankton and
Buma, A.G.J., Gieskes, W.W.C., Thomson, H.A., Abundance of
their role in controlling phytoplankton growth in a marginal ice
Cryptophyceae and chlorophyll b-containing organisms in the
zone of the Bellinghausen Sea, Deep-Sea Res. II, 42, 1277–1290,
Weddell-Scotia Confluence in the spring of 1988, Polar Biol.,
1995.
12, 43–52, 1992.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 543
Burns, J.M., Trumble, S.J., Castellini, M.A., Testa, J.W., The diet of Carmack, E.C., Large-scale physical oceanography of polar oceans, in
Weddell seals in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, as determined from Polar Oceanography, Part A: Physical Sciences, Smith, W.O., Jr.,
scat collections and stable isotope analysis, Polar Biol., 19, Ed., 1992, 171–222.
272–282, 1998. Carmack, E.C., Forster, T.D., On the flow of water out of the Weddell
Butterworth, D.S., Antarctic ecosystem management, in Selected Papers Sea, Deep-Sea Res., 22, 711–724, 1975.
Presented to the Scientific Committee of CCAMLR 1982–1984, Caron, D.A., Grazing of attached bacteria by heterotrophic microflagel-
Part II, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine lates, Microb. Ecol., 13, 203–218, 1987.
Living Resources, Hobart, 15–42, 1985. Caron, D.A., Heterotrophic flagellates associated with sedimentary
Butterworth, D.S., Antarctic marine ecosystem management, Polar Rec., detritus, in The Biology of Free-living Heterotrophic Flagellates,
23, 37–47, 1986. Patterson, D.J., Larsen, J., Eds., Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1996,
Butterworth, D.S., Punt, A.E., Basson, M., A simple approach to 77–92.
calculating the potential yield of krill from biomass survey Caron, J.McN., Davis, P.G., Madin, L.P., Siebruth, J.McN., Hetero-
trophic bacteria and bacterivorous Protozoa in oceanic
results, in Selected Scientific Papers, 1991 (SC-CAMLR,-
macroaggregates, Science, 218, 795–797, 1982.
SSR/8), Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine
Caron, D.A., Madin, I.D., Cole, J.J., Composition and degradation of
Living Resources, Hobart, 207–217, 1991.
salp fecal pellets: Implications for vertical flux in oceanic systems,
Butterworth, D.S., Gluckman, G.R., Thompson, R.B., Chalis, S.,
J. Mar. Res., 47, 829–856, 1989.
Hiramatsu, K., Agnew, D., Further computations of the conse-
Carpenter, E.J., Capone, D.G., Eds., Nitrogen in the Marine Environ-
quences of settling the annual catch limit to a fixed fraction of the
ment, Academic Press, New York, 1983.
estimate of krill biomass from a survey, CCAMLR Sci., 1, 81–106,
Carrada, G.C., Mangoni, O., Russo, G.F., Saggioma, V., Phytoplankton
1994.
size fractionated biomass in the Ross Sea: Spatial and temporal
Bykova, V.P., Radakova, T.N., Changes in the properties of precooked
variations during the austral spring, in Ross Sea Ecology, Farando,
frozen krill flesh during storage, in Krill Processing Technology, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Ianora, A., Eds., Springer-Verlag, New York,
Bykov, V.P. Ed., VNIRO, Moscow, 1981, 7–16. In Russian with 1999, 205–216.
English summary. Carrick, R., Southern seals as subjects of ecological research, in Biologie
Cadee, G.C., Gonzales, H., Schnack-Schiel, S.B., Krill diet affects faecal Antarctique, Carrick, R., Holdgate, W.M., Prévost, J., Eds.,
string settling, Polar Biol., 12, 75–80, 1992. Herman, Paris, 1964, 421–432.
Calhaem, I., Christoffel, D.A., Some observations of the feeding habits Carrick, R., Population ecology of the Australian black-backed magpie,
of a Weddell seal and measurements of its prey, NZ J. Mar. royal penguin, and silver gull, in Population Ecology of Migratory
Freshwater Res., 3, 181–190, 1969. Birds: A Symposium, U.S. Department of the Interior Wildlife
Capriulo, G.M., Feeding-related ecology of marine protozoa, in Ecology Research Report No. 2, U.S. Department of the Interior,
of Marine Protozoa, Carpenter, G.M., Ed., Oxford University Washington, DC, 41–49, 1972.
Press, New York, 1992, 186–259. Carrick, R., Ingham, S.E., Studies on the southern elephant seal,
Capriulo, G.M., Sherr, E.B., Sherr, B. F., Trophic behaviour and related Mirounga leonina (L.), IV: Breeding and development, CSIRO
community feeding activities of heterotrophic marine protists, in Wildlife Res., 7, 161–197, 1962.
Protozoa and Their Role in Marine Processes, Nato ASI Series G Casaux, R., Baroni, A., Corlini, A., The diet of the Weddell Seal
Ecological Sciences, Vol. 25, Springer, Heidelberg, 219–265, Leptonychotes weddelli at Harmony Point, South Shetland
1991. Islands, Polar Biol., 18, 371–375, 1997.
Car, M., Codspoti, L.A., Oceanographic cruise summary, Ross Sea, Cassie, I., The distribution of surface phytoplankton between New
Antarctica, February 1968. Informal Report No. 68–64, Naval Zealand and Antarctica December, 1957, Transa-Atarc. Exped.—
Oceanographic Office, Washington, DC, 1968. Sci. Rep., 7, 1–11, 1963.
Carey, A.G., Jr., Marine ice fauna: Arctic, in Sea Ice Biota, Horner, R.A., Castellanos, Z.J.A., Perez, J.C.L., Algunos aspectos bioecologicos de la
Ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1985, 173–190. zona intercotidal de Carbo Primavera (Costa de Danco, Peninsula
Carlson, C.A., Hansell, P.A., The contribution of DOM to the biogeo- Antártica), Contribución Instituto Antártico Argentino, 50, 1–29,
chemistry of the Ross Sea, in Biogeochemical Cycles in the Ross 1963.
Sea, DiTullio, G.R., Dunbar, R.B., Eds., American Geophysical Castellini, M.A., Davis, R.W., Davis, M., Horning, M., Antarctic marine
Union, Washington, DC, 2002. life under the McMurdo Ice Shelf at White Island: A link between
nutrient flux and seal population, Polar Biol., 2, 229–231, 1984.
Carlson, C.A., Ducklow, H.W., Hansell, D.A., Smith, W.O., Jr., Organic
Castilla, J.C., Rozbaczylo, N., Rocky intertidal assemblages and preda-
carbon partitioning during spring phytoplankton blooms in the
tion on the gastropod Nacella (Patinigera) concinna at Robert
Ross Sea polyna and the Sargasso Sea, Limnol. Oceanogr., 43,
Island, South Shetlands, Antarctica, Serie Cientı́fica Instituto
375–386, 1998.
Antártico Chileno, 32, 65–74, 1985.
Carlucci, A.F., Cuhel, R.L., Vitamins in the South Polar Seas: Distri-
Catalano, G., Povero, P., Fabiano, M., Benedetti, F., Goffart, A., Nutrient
bution and significance of dissolved and particulate Vitamin B12,
utilization and particulate organic mater changes during summer in
thymine, and biotin in the Southern Indian Ocean, in Adaptations
the upper mixed layer (Ross Sea, Antarctica), Deep-Sea Res., 44,
Within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smithsonian
97–112, 1997.
Institution, Washington, DC, 1977, 115–123.
Catry, P., Phillips, R.A., Phalan, B., Silk, J.R.D., Croxall, J.P. et al.,
Carmack, E.C., Circulation and mixing in ice-covered waters, in The Foraging strategies of grey-headed albatross, Thalassarche chry-
Geophysics of Sea Ice, Untershiner, N., Ed., Plenum Press, New sotomaInteraction of movements, activity, and feeding events,
York, 1986, 646–712. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 280, 261–273, 2004.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
544 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Cattaneo-Viette, R., Bavestrello, G., Cerrano, C., Gano, E., Manzella, L., Chen, Bo, Distribution and abundance of choanoflagellates in Great Wall
Pansivi, M., Sara, M., The role of sponges in the Terra Nova Bay Bay, King George Island, Antarctica, in austral summer, NIPR
ecosystem, in Ross Sea Ecology, Farmando, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Symp. Polar Biol., 7, 32–44, 1994.
Ianora, A., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1998, 539–549. Cheng, C.C., DeVries, A.L., The role of antifreeze glycopeptides and
Cauwet, G., Non-living particulate matter, in Marine Organic Chemistry, peptides in the freezing avoidance of cold-water fish, in Life Under
Dursma, E.K., Dawson, R., Eds., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1981, Extreme Conditions: Biochemical Adaptation, di Prisco, G., Ed.,
71–89. Springer, Berlin and Heidelberg, 1991, 1–14.
Cavender-Bares, K.K., Karl, D.M., Chisholm, S.W., Nutrient gradients Cherel, Y., Duhamel, G., Diet of the squid Moroteuthis ingens
in the western North Atlantic Ocean: Relationships to microbial (Teuthoidea: Onychoteuthidae) in the upper slope waters of the
community structure and to patterns in the Pacific Ocean, Deep- Kerguelen Islands, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 250, 197–203, 2003.
Sea Res. I., 48, 2373–2395, 2001. Cherel, Y., Klages, N., A review of the food of albatrosses, in Albatross
Cawthron, M.W., Whale research in New Zealand, Int. Whaling Biology and Conservation, Robertson, G., Gales, R., Eds., Beaty
Committee Rep., 28, 109–113, 1978. and Sons, Chipping Norton, Surrey, 1998, 113–136.
Cherel, Y., Kooyman, G.L., Food of emperor penguins (Aptenodytes
CCAMLR Standard Methods for Monitoring Parameters of Predatory
forsteri) in the western Ross Sea, Antarctica, Mar. Biol., 130,
Species, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine
335–344, 1998.
Living Resources, Hobart, 1988.
Cherel, Y., Wiemerskirch, H., Seabirds as indicators of marine
CCAMLR Ecosystem Monitoring Program: Standard Methods for
resources: Black-browed albatrosses feeding on ommastrephid
Monitoring Studies, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic
squids in Kerguelen waters, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 129,
Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 2003.
295–300, 1995.
Cerri, R.D., Fraser, D.F., Predation and risk in foraging minnows:
Cherel, Y., Weimerskirch, H., Duhamel, G., Interactions between long-
Balancing conflicting demands, Am. Nat., 121, 552–561, 1983.
line vessels and seabirds in Kerguelen waters and a method to
Chang, F.H., The ultrastructure of Phaeocystis pouchetii (Prymnesio-
reduce seabird mortality, Conservation Biology, 75, 63–70, 1996.
phyceae) vegetative colonies, with special reference to the Chiba, S., Ishimani, T., Hosie, G.W., Fukuchi, M., Spatio-temporal
production of new gelatinous envelope, NZ J. Mar. Freshwater variability of zooplankton community structure off east Antarctica
Res., 18, 303–308, 1984. (908 to 1608 E), Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 216, 95–108, 2001.
Chaolum, L., Zhang, S.G., Peng, J.I., Summer feeding activities of Chisholm, S.W., Morel, F.M.M., What controls phytoplankton pro-
zooplankton in Prydz Bay, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 24, 892–900, duction in nutrient-rich areas of the open sea?, Papers from the
2001. Symposium of the American Society of Limnology and Ocean-
Chapman, D.G., Re-analysis of Antarctic fin whale population data, Rep. ography, 36(8), 1507–1565, 1991.
Int. Whal. Commun., 20, 510–559, 1970. Chittleborough, R.G., Determination of the age in humpback whale,
Chapman, D.G., Management of international whaling and North Pacific Megaptera nodosa (Bonnaterre), Australian Journal of Marine and
fur seals: implications for fisheries management, J. Fish Res. Freshwater Research, 9, 1–10, 1959.
Board Can., 30, 24198–24260, 1972. Chittleborough, R.G., Marked humpback whale of known age, Nature
Chapman, D.G., Whales, Oceanus, 31, 64–70, 1988. (Lond.), 187, 164, 1960.
Charnov, E.L., Orians, G.H., Hyatt, K., The ecological implications of Chittleborough, R.G., Australian catches of humpback whales, 1961,
resources depression, Am. Nat., 110, 247–259, 1970. Reports of the Division of Fisheries and Oceanography, CSIRO,
Charrassin, J.-B., Bost, C.-A., Putz, K., Zora, T., Le Maho, Y., Foraging Australia, 34, 1–13, 1962.
strategy of incubating and brooding king penguins, Aptenodytes Chittleborough, R.G., Dynamics of two populations of humpback
Patagonicus, Oecologia, 114, 194–201, 1998. whales, Megaptera novaeangliae (Borowski), Australian Journal
Charrassin, J-B., Kato, A., Handrich, Y., Sato, K., Naito, Y., Ancel, A., of Marine and Freshwater Research, 16, 33–128, 1965.
Bost, C.-A., Gauthier-Clerc, M., Ropert-Coudert, Y., Le Maho, Y., Choi, C., Primary production and release of dissolved organic carbon
Feeding behaviour of free-ranging penguins determined by oeso- from phytoplankton in the Western North Atlantic, Deep-Sea Res.,
phageal temperatures, Proc. R. Soc. Lond., Ser. B: Biol. Sci., 2, 19, 731–735, 1972.
151–157, 2001. Chojancki, J., Wegelenska, T., Periodicity of composition, abundance,
Charassin, J.-B., Le Maho, Y., Bost, C.-A., Seasonal changes in the and vertical distribution of summer zooplankton (1977/1978) in
diving parameters of king penguins (Aptenodytes Patagonicus), Ezcurra Inlet, Admiralty Bay (King George Island, South Shet-
Mar. Biol., 141, 581, 2002. land), J. Plankton Res., 6, 997, 1984.
Chown, S.L., Kelp degradation by Paractora trichosterma (Thompson)
Chavez, F.P., Barker, R.T., An estimate of new production in the
(Diptera: Helcomyzidae) at subantarctic South Georgia, Polar
equatorial Pacific, Deep-Sea Res., 34, 1229–1243, 1987.
Biol., 16, 171–178, 1996.
Chechun, I.S., Feeding and food interrelationships of some subantarctic
Christaki, U., Dolan, J.R., Pelegri, S., Rassoulzadegan, F., Consumption
fishes of the Indian Ocean. Proceedings of the Zoological Institute
of picoplankton-size particles by marine ciliates: Effects of
of Leningrad, 127, 38–68, 1984. In Russian.
physiological state of the ciliate and particle quality, Limnol.
Chekunova, V.I., Naumov, A.G., Energy metabolism and food require-
Oceanogr., 43, 458–464, 1998.
ments of the marbled Notothenia, Notothenia rossii mammorata
Christians, O., Leinemann, M., Untersuchungen über Fluor im Krill,
(Nototheniidae), Journal of Ichthyology, 22, Translated from
Informationer für Fischwirtschaft, 27, 254–260, 1980.
Vorosy Ikhtiologii, 112–121, 1972
Christians, O., Leinemann, M., Mahanty, M., Neue Ertentnisse uber den
Chekunova, V.I., Rynkova, T.I., Energy requirements of the Antarctic
Flouridgehalt im krill, Informationer fur Fischwirtschaft, 28,
crustacean, Euphausia superba, Oceanology, 14, 434–440, 1974. 70–72, 1981.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 545
Clarke, G.L., Dynamics of production in a marine area, Ecological Clarke, D.B., Ackley, S.F., Sea ice structure and biological activity in the
Monographs, 16(4), 321–337, 1946. marginal ice zone, J. Geophys. Res., 89, 2087–2095, 1981.
Clarke, M.R., Sperm whales of the Azores, Discovery Reports, 28, Clarke, A., Crame, J.A., The origins of the Southern Ocean marine
237–298, 1956. fauna, in Macroecology: Reconciling Divergent Views, Ormons,
Clarke, M.R., New technique for the study of sperm whale migrations, R.F.C., Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1997a,
Nature (Lond.), 238, 405–406, 1972. 253–268.
Clarke, A., Some observations on krill (Euphausia superba Dana) Clarke, A., Crame, J.A., Diversity, latitude, and time patterns in the
maintained in the laboratory, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 43, shallow sea, in Macroecology: Reconciling Divergent Views,
111–118, 1976. Ormons, R.F.C., Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge,
Clarke, M.R., Beaks, nets, and numbers, Symp. Zool. Soc. Lond., 38, UK, 1997b, 122–147.
89–126, 1977. Clarke, A., Johnston, N.M., Antarctic marine benthic diversity, Ocean-
Clarke, A., On living in cold water: Kstrategies in AntarcticAntarctic ography and Marine Biology: Annual Reviews, 41, 47–114, 2003.
benthos, Mar. Biol., 7, 111–119, 1979. Clarke, A., Lakhami, K.H., Measures of biomass, moulting behaviour
Clarke, A., The biochemical composition of krill, Euphausia superba and the pattern of early growth in Chorismus antarcticus (Pfeffer),
Dana, from South Georgia, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 43, 221–236, Br. Antarct. Surv. Bull., 47, 61–88, 1979.
1980. Clarke, A., Lakani, K.H., Measures of biomass, moulting behaviour, and
Clarke, M.R., Squids and whales, NERC News J., 9, 4–6, 1980a. the pattern of early growth in Chorismus antarcticus (Pfeffer),
Clarke, M.R., Cephalopoda in the diet of sperm whales of the Southern British Antarctic Survey Bulletin, 47, 61–68, 1996.
Hemisphere and their bearing on sperm whale biology, Discov. Clarke, A., Leakey, R.J., Seasonal cycle of phytoplankton, macronu-
Rep., 37, 1–324, 1980b. trients, and the microbial community in nearshore Antarctic marine
Clarke, M.R., Cephalopod biomass estimation from predation, Memoirs sediments, Limnol. Oceanogr., 41, 1281–1294, 1996.
of the National Museum of Victoria, 44, 95–107, 1983. Clarke, M.R., MacLeod, N., Cephalopods in the diet of elephant seals at
Clarke, W.G., Antarctic fin whale, Balaenoptera physalus, recruitment Signy Island, South Orkney Islands, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 57,
rates inferred from cohort analysis, Int. Whaling Committee Rep. 22–31, 1982a.
Spec. Issue, 198–203, 1983. Clarke, M.R., MacLeod, N., Cephalopod remains in the stomachs of
Clarke, A., Life in cold water: The physiological ecology of polar marine eight Weddell seals, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 57, 33–40, 1982b.
ectotherms, Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Clarke, A., Morris, D.J., Development of an energy budget for
Review, 21, 341–453, 1983. Euphausia superba, Berichte zur Polarforschung, 4, 102–110,
Clarke, A., Lipid content and composition of Antarctic krill, Euphausia 1983a.
superba Dana, J. Crustacean Biol., 4(Special Issue No.1), Clarke, A., Morris, D.J., Towards an energy budget for krill: The
285–294, 1984. physiology and biochemistry of Euphausia superba Dana, Polar
Clarke, A., Energy flow in the Southern Ocean food web, in Antarctic Biol., 2, 69–86, 1983b.
Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Clarke, A., Peck, L.S., The physiology of polar marine zooplankton,
Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 571–580. Proc. Pro Mare Symp. Polar Mar. Ecol., 355–369, 1991.
Clarke, M.R., Marine habitats—Antarctic cephalopods, in Key Environ- Clarke, A., Prince, P.A., Chemical composition and calorific value of
ments—Antarctica, Bonner, W.N., Walton, D.W.H., Eds., food fed to Mollymawk chicks (Diomedea melanophris and
Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1985, 191–200. D. crysostoma) at Bird Island, South Georgia, Ibis, 122,
Clarke, A., The adaptation of aquatic animals to low temperatures, in 488–494, 1980.
The Effects of Low Temperatures on Biological Systems, Grout, Clarke, M.R., Croxall, J.P., Prince, P.A., Cephalopod remains in
B.W.W., Morris, G.J., Eds., Edward Arnold, London, 1987, regurgitations of the wandering albatross at South Georgia, Br.
313–348. Antarc. Surv. Sci. Rep., 75, 1, 1981.
Clarke, A., Seasonality in the Antarctic marine environment, Comp. Clarke, A., Holmes, L.J., White, M.G., The annual cycle of temperature,
Biochem. Physiol., 90B, 461–473, 1988. chlorophyll, and minor nutrients at Signy Island, South Orkney
Clarke, A., A reappraisal of the concept of metabolic cold adaptation in Islands, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 80, 65–90, 1988a.
polar marine invertebrates, Biol. J. Linnean Soc., 14, 77–92, 1989. Clarke, A., Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Laboratory and field estimates of
Clarke, A., Is there a latitudinal diversity gradient in the sea?, Trends faecal pellet production by Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba,
Ecol. Evol., 7, 286–287, 1990a. Mar. Biol., 98, 557–563, 1988b.
Clarke, A., Temperature and evolution: Southern Ocean cooling and the Clarke, J., Manly, B., Kerry, K., Gardner, H., Franchi, E., Corsolini, S.,
Antarctic marine fauna, in Antarctic Ecosystems: Ecological Focardi, S., Sex differences in Adélie Penguins (Eudyptes), in
Change and Conservation, Kerry, K.R., Hempel, G., Eds., Penguin biology, Davis, L.S., Darby, J.T., Eds., Academic Press,
Springer, Berlin, 1990b, 9–22. San Diego, CA, 1998, 131–196.
Clarke, A., What is cold adaptation and how should we measure it?, Am. Claustre, H., Poulet, S.A., Williams, R., Marley, J.-C., Coombs, S., Ben
Zoologist, 3, 81–92, 1991. Mlih, F., Hapette, A.M., Martin-Jezequel, V., A biochemical
Clarke, A., Temperature and extinction in the sea—a physiologist’s investigation of a Phaeocystis sp. bloom in the Irish Sea, J. Mar.
view, Palaeobiology, 19, 499–518, 1993. Biol. Assoc. UK, 70, 197–207, 1990.
Clarke, A., The distribution of Antartic benthic marine communities, Clementson, L.A., Parsluo, J.S., Griffiths, F.B., Lyne, V.D., Mackey,
Antarc. Res. Ser., 70, 219, 1996. D.J., Harris, G.P., McKenzie, D.C., Bomham, P.L., Rathbone,
Clarke, D.B., Ackley, S.F., Physical, chemical and biological properties C.A., Rintoul, S., Controls on phytoplankton production in the
of winter sea ice in the Weddell Sea, Antarct. J. U.S., 17, 107–109, Australian sector of the Subtropical Convergence, Deep-Sea Res.,
1981. 45, 1627–1661, 1998.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
546 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Clowes, A.J., Phosphate and silicate in the Southern Ocean, Discov. Conroy, J.W.H., White, M.G., The breeding status of the King Penguin
Rep., 19, 1–170, 1938. (Aptenodytes patagonica), Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 32, 31–40,
Cobley, N.D., Shears, J.R., Breeding performance of gentoo penguins 1973.
(Pygoscelis papua) at a colony exposed to high levels of human Conroy, J.W.H., Darling, O.W.H., Smith, H.G., The annual cycle of the
disturbance, Polar Biol., 21, 335–360, 1999. chinstrap penguin (Pygoscelis antarctica) on Signy Island, South
Cole, Y., Findlay, S., Pace, M.L., Bacterial production in fresh and Orkney Islands, in The Biology of Penguins, Stonehouse, B., Ed.,
saltwater systems: a cross-system overview, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., Macmillan, London, 1975, 353–363.
43, 1–10, 1988. Constable, A.J., CCAMLR ecosystem monitoring and management:
Colos, Y., Slawyk, G., C13 and N14 uptake by marine phytoplankton, Future work, CCAMLR, 9, 233–253, 2002.
4: Uptake ratios and the contribution of nitrate to the productivity Constable, A.J., CCAMLR ecosystem monitoring and management
of Antarctic waters (Indian Ocean sector), Deep-Sea Res., 33(8A), framework. WG-EMM-01 Presentation Paper, CCAMLR Science,
1039–1051, 1986. 9, 235, 2004.
Comiso, J.C., Gordon, A.L., Recurring polynas over the Cosmonaut Sea Constable, A.J., de la Mare, W.Y., Agnew, D.J., Everson, I., Miller,
and Maud Rise, J. Geophys. Res., 92, 2819–2833, 1987.
D.G.M., Managing fisheries to conserve the Antarctic marine
Comiso, J.C., Gordon, A.L., Cosmonaut polyna in the Southern
ecosystem: practical implementation of the Convention on the
Ocean: Structure and variability, J. Geophys. Res., 101,
Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR)
19297–19313, 1996.
ICES, Mar. Sci., 57, 778–791, 2000.
Comiso, J.C., Sullivan, C.W., Satellite microwave and in situ obser-
Cooke, J.C., Beddington, J.R., Further development of an assessment
vations of Weddell Sea ice cover and its marginal ice zone,
technique for male sperm whales based on length data from the
J. Geophys. Res., 91, 9663–9681, 1986.
catches, Rep. Int. Whal. Commun., 32, 239–241, 1982.
Comiso, J.C., Zwally, H.T., Concentration gradients and growth and
Cooke, J.G., de la Mare, W.K., The effects of variability in age data on
decay characteristics of seasonal sea ice cover, J. Geophys. Res.,
the estimation of biological parameters in minke whales (Balae-
89(C5), 8081–8103, 1984.
Comiso, J.C., Maynard, N.G., Smith, W.O., Jr., Sullivan, C.W., Satellite noptera acutorostratus), Int. Whaling Committee Rep., 33,
ocean colour studies of Antarctic ice edges in summer and autumn, 333–338, 1983.
J. Geophys. Res., 95(C6), 9481–9496, 1990. Cooper, J., Berruti, A., The conservation status of South Africa’s
Condy, P.R., Results of the third seal survey in the Haakon VII Sea, continental and oceanic islands, in Biotic Diversity in South
Antarctica, S. Afr. J. Antarc. Res., 6, 2–8, 1976. Africa: Concepts and Conservation, Huntley, B.J., Ed., Oxford
Condy, P.R., Annual cycle of the elephant seal, Mirounga leonina University Press, Cape Town, 1989, 239–253.
(Linn.), at Marion Island, S. Afr. J. Antarc. Res., 14, 95–102, Cooper, J., Woehler, E.J., Consumption of Antarctic krill (Euphausia
1977a. superba) by seabirds during the summer in the Prydz Bay region,
Condy, P.R., Results of the fourth seal survey in the KingHaakonVII Antarctica, in Southern Ocean Ecology: The BIOMASS Perspec-
Sea, Antarctica, S. Afr. J. Antarc. Res., 6, 2–8, 1977b. tive, El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge,
Condy, P.R., Annual food consumption and seasonal fluctuations in UK, 1994, 247–260.
biomass of seals at Marion Island, Mammalia, 45, 21–30, Cooper, J., Brown, C.R., Gales, R.P., Hindell, M.A. et al., Diets and
1981. dietary segregation of crested penguins (Eudyptes), in Penguin
Condy, P.R., van Aarde, R.J., Bester, M.V., The seasonal occurrence and Biology, Davis, L.S., Darby, J.T., Eds., Academic Press, London,
behaviour of killer whales (Orcinus orca) at Marion Island, J. Zool. 1990, 131–156.
(Lond.), 184, 449–464, 1978. Copping, A.E., Lorenzen, C.J., Carbon budget of a marine phyto-
Conlon, K.E., Rau, G., McFeters, G.A., Kvitek, R., Influence of the plankton-herbivore system with carbon-14 as a tracer, Limnology
McMurdo Station sewage outfall on coastal marine fauna, in and Oceanography, 25, 873–882, 1980.
Antarctic Ecosystems: Models for Wider Understanding, Corless, J.O., Snyder, R.A., A preliminary description of several new
Davidson, W., Howard-Williams, C., Broady, P., Eds., New ciliates from the Antarctica, including Cohnilembus grassei n. sp.,
Zealand Natural Sciences, Christchurch, 2000, 315–318. Protistologica, 22, 39–46, 1986.
Conlon, K.E., Kim, S.I., Hunter, S., Lenihan, S., Oliver, J.S., Benthic Cormaci, M., Funari, G., Scammacca, B., The benthic algal flora of Terra
community changes at McMurdo Station: A response to sewage Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica), Botanica Marina, 35(6),
abatement?, in Antarctic Biology in a Global Context, Huiskes, 541–552, 1992.
A.H.L., Gieskes, W.W.C., Rozema, J., Schorno, R.M.L., van der
Cormaci, M., Funari, G., Scammacca, B., The macrophytobenthos of
Vies, S.M., Wolff, W.J., Eds., Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, The
Terra Nova Bay, in Ross Sea Ecology, Farando, F.M., Guglielmo,
Netherlands, 2003, 264–270.
L., Ianora, A., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1998, 493–502.
Conover, R.J., Huntley, M., Copepods in an ice-covered sea—Distri-
Corner, R.W.M., Observations on a small crabeater seal breeding group,
bution, adaptations to seasonally-limited food, metabolism, growth
Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 30, 104–106, 1972.
pattern, and life cycle, J. Mar. Syst., 2, 1–41, 1991.
Corsolini, S., Focardi, S., Bioconcentration of polychlorinated biphenyls
Conroy, J.W.H., Recent increases in penguin populations in the
in the pelagic food chain of the Ross Sea, in Ross Sea Ecology,
Antarctic and sub-Antarctic, in The Biology of Penguins,
Farando, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Ianora, A., Eds., Springer, Berlin,
Stonehouse, B., Ed., MacMillan, London, 1975, 321–370.
1998, 575–584.
Conroy, J.W.H., Twelves, E.L., Diving depths of the Gentoo Penguin
Costa, D.P., Reproductive and foraging energetics of pinnipeds:
(Pygoscelis papua) and Blue-eyed Shag (Phalacorocorax atriceps)
from the South Orkney Islands, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 30, Implications for life history patterns, Am. Zoologist, 31,
106–108, 1972. 111–130, 1991.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 547
Costa, D.P., Reproductive and foraging energetics of pinnipeds: Impli- Croxall, J.P., Use of indices of predation status and performance in
cations for life history patterns, in Pinniped Behaviour, Renouf, D., CCAMLR fishery management, CCAMLR Selected Scientific
Ed., Chapman Hall, London, 1991, 300–344. Papers SC-CCAMLR SSP16, 333–336, 1989.
Costa, D.P., The relationship between reproductive and foraging ener- Croxall, J.P., Southern Ocean environmental changes: Effects on
getics and the evolution of the Pinnipedia, in Recent Advances in seabird, seal, and whale populations, in Antarctic and Environ-
Marine Mammal Science, Boyd, I., Ed., Oxford University Press, mental Change, Drewry, D.J., Laws, R.M., Pyle, J.A., Eds., Oxford
Oxford, 1993, 293–314. University Press, Oxford, 1992, 319–328.
Costa, D.P., Crocker, D.E., Marine mammals in the Southern Ocean, Croxall, J.P., Southern Ocean environmental changes: Effects on
Antarc. Res. Ser., 70, 287–301, 1996. seabird, seal, and whale populations, Philosophical Transactions
Costa, D.P., Croxall, J., Duck, C., Foraging energetics of Antarctic fur of the Royal Society of London, Series B: Biological Sciences, 338,
seals in relation to changes in prey availability, Ecology, 70, 319–328, 1992.
596–606, 1989. Croxall, J.P., Davis, R.W., Metabolic rate and foraging behaviour of
Cota, G.F., Photoadaptation in high Arctic ice algae, Nature (Lond.), Pygoscelis and Eudyptes penguins at sea, in Penguin Biology,
315, 219–222, 1985. Davis, L.S., Darby, J.T., Eds., Academic Press, San Diego, CA,
Cota, G.F., Kottmeier, S.T., Robinson, D.H., Smith, W.O., Jr., Sullivan, 1990, 207–228.
W.C., Bacterioplankton in the marginal ice zone of the Weddell Croxall, J.P., Furse, J.R., Food of the chinstrap penguin, Pygoscelis
Sea: Biomass, production and metabolic activities during the antarctica, and macaroni penguin, Eudyptes chrysolophus, at the
austral autumn, Deep-Sea Res., 37, 1145–1167, 1990. Elephant Island group, South Shetland Islands, Ibis, 122, 237–245,
Cota, G.F., Smith, W.O., Jr., Nelson, D.M., Nutrient and biogenic 1980.
particulate distributions, primary production, and nitrogen uptake Croxall, J.P., Hiby, L., Fecundity, survival, and site fidelity in Weddell
in the Weddell-Scotia Sea marginal ice zone during winter, J. Mar. seals, Leptonychotes weddelli, J. Appl. Ecol., 20, 19–32, 1983.
Res., 50, 155–181, 1992. Croxall, J.P., Kirkwood, E.D., The breeding distribution of penguins on
the Antarctic peninsula and the islands of the Scotia Sea, British
Court, G.S., Dacis, L.S., Focardi, S., Bargargli, R., Fossi, C., Leonizu,
Antarctic Survey, Cambridge, UK, 1979.
C., Marili, L., Chlorinated hydrocarbons in the tissues of South
Croxall, J.P., North, A.W., Fish prey of Wilson’s storm petrel (Oceanites
Polar skuas (Catharacta maccormicki) and Adélie Penguins
oceanicus) at South Georgia, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 78, 37–42,
(Pygoscelis adeliae) from Ross Sea, Antarctica, Environ. Pollut.,
1988.
97, 295–301, 1997.
Croxall, J.P., Prince, P.A., Antarctic seabird and seal monitoring studies,
Cox, G.F.N., Weeks, W.F., Equations for determining the gas and
Polar Rec., 19, 573–595, 1979.
brine volumes in sea ice samples, J. Glaciol., 29(102), 306–316,
Croxall, J.P., Prince, P.A., Food feeding, and ecological segregation of
1983.
seabirds at South Georgia, Biol. J. Linnean Soc., 14, 103–131,
Crafford, J.E., Life cycle and kelp consumption of Paractora dreuxi
1980a.
mirabilis (Diptera: Helcomzidae) a primary decomposer of
Croxall, J.P., Prince, P.A., The food of gentoo penguins (Pygoscelis
stranded kelp on Marion Island, S. Afr. J. Antarc. Res., 14(1),
papua) and macaroni penguins (Eudyptes chrysolophus) at South
18–22, 1984.
Georgia, Ibis, 122, 245–253, 1980b.
Crafford, J.E., Scholtz, C.H., Phenology of stranded kelp degradation by
Croxall, J.P., Prince, P.A., Calorific value of squid (Mollusca: Cephalo-
the kelp fly Paractora dreuxi mirabilis (Helcomyzidae) at Marion
poda), Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull. , 55, 27–31, 1982.
Island, Polar Biol., 7(2), 289–294, 1987.
Croxall, J.P., Prince, P.A., Seabirds as predators in marine resources,
Cram, D.L., Agenbag, J.J., Hampton, I., Robertson, A.A., SAS Protea
especially krill, at South Georgia, in Seabirds: Feeding Ecology
Cruise, The general results of the acoustics and remote sensing and Role in Marine Ecosystems, Croxall, J.P., Ed., Cambridge
study, with recommendations for estimating the abundance of krill University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1987, 345–368.
(Euphausia superba Dana), S. Afr. J. Antarc. Res., 9, 3, 1979. Croxall, J.P., Rothery, P., Population regulation of seabirds: Implications
Crawford, R.M., The role of sea ice in the sedimentation of a diatom of their demography for conservation, in Bird Population Studies:
bloom, Limnol. Oceanogr., 40, 200–204, 1995. Relevance to Conservation and Management, Perrins, C.M.,
Crawford, C.C., Hobbie, J.E., Webb, K.L., The utilization of dissolved LeBreton, J.D., Hirons, G.M., Eds., Oxford University Press,
free amino acids by estuarine microorganisms, Ecology, 55, Oxford, 1991, 272–296.
331–363, 1974. Croxall, J.P., Prince, P.A., Hunter, I., McInnes, S.J., Copestake, P.G.,
Crisafi, E., Assaro, F., La Ferla, R., Monticelli, S., Microbial The seabirds of the Antarctic Peninsula, islands of the Scotia Sea,
biomass and respiratory activity related to the ice-melting and Antarctic Continent between 808 W and 208 W: their status and
upper layers in the Ross Sea (Antarctica), in Ross Sea Ecology, conservation, in The Status and Conservation of the World’s
Faranda, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Ianora, A., Eds., Springer, Berlin, Seabirds, Technical Publication No. 2, 637–666, 1984.
1998, 171–180. Croxall, J.P., Ricketts, C., Prince, P.A., Impact of seabirds on marine
Crocker, K.M., Ondrusek, M.E., Petty, R.L., Smith, R.C., Dimethyl- resources, especially krill, of South Georgia waters, in Seabird
sulphide, algal pigments, and light in an Antarctic Phaeocystis sp. Energetics, Waters, G.C., Rahn, H., Eds., Plenum Press, New
bloom, Mar. Biol., 124, 335–340, 1995. York, 1984, 285–318.
Croll, D.A., Tersky, B.R., Penguins, fur seals, and fishing: Prey Croxall, J.P., Prince, P.A., Ricketts, C., Relationships between prey life-
requirements and potential competition in the South Shetland cycles and the extent, nature, and timing of seal and seabird
Islands, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 19, 365–374, 1998. predation in the Scotia Sea, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and
Croxall, J.P., Seabirds, in Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 2, Laws, R.M., Ed., Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds.,
Academic Press, London, 1984, 533–619. Springer, Berlin, 1985, 516–533.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
548 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Croxall, J.P., Davis, R.W., O’Connell, M.J., Diving patterns in relation Daly, K.L., Overwintering development, growth, and feeding of larval
to diet of gentoo and macaroni penguins at South Georgia, Condor, Euphausia superba in the Antarctic marginal zone, Limnol.
90, 157–167, 1988a. Oceanogra., 35, 1564–1576, 1990.
Croxall, J.P., Davis, R.W., O’Connell, M.J., Diving patterns in relation Daly, K.L., Macaulay, M.C., Influence of physical and biological
to diet of gentoo and macaroni penguins at South Georgia, Condor, mesoscale dynamics on the seasonal distribution and behaviour
96, 157–167, 1988b. of Euphausia superba in the marginal ice zone, Mar. Ecol. Prog.
Croxall, J.P., McCann, T.S., Prince, P.A., Rothery, P., Reproductive Ser., 79, 37–66, 1991.
performance of seabirds and seals at Georgia Signy Island, South Daly, K.L., Macaulay, M.C., Abundance and distribution of krill in the
Orkney Islands, 1976–1987: Some implications for Southern ice edge zone of the Weddell Sea, austral spring1983, Deep-Sea
Ocean monitoring studies, in Antarctic Ocean and Resources Res., 35, 21–41, 1998.
Variability, Sahrhage, D., Ed., Springer, Berlin, 1988, 261–285. Daniels, R.A., Nesting behaviour of Harpagifer bispinis in Arthur
Croxall, J.P., Ricketts, C., Wood, A.G., Food consumption by Harbour, Antarctic Peninsula, J. Fish Biol., 12, 465–474, 1979.
predators in a CCAMLR Integrated Study Region, in Selected Daniels, R.A., Feeding ecology of some fishes of the Antarctic
Scientific Papers 1990 (SC-CAMLR-SSD/7), Commission for the Peninsula, Fish. Bull. US Natl Mar. Fish. Serv., 80, 575–588, 1979.
Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, Hobart, Daniels, R.A., Feeding ecology of some fishes of the Antarctic
1990, 489–579. Peninsula, Fish. Bull. US Natl Mar. Fish. Serv., 12, 575–588, 1982.
Croxall, J.P., Rothery, P., Pickering, S.P.C., Prince, P.A., Reproductive Danovaro, R., Puseddy, S., Mirto, S., Fabio, M., Meiofaunal assem-
performance, recruitment, and survival of wandering albatrosses blages associated with scallop beds (Adamussium colbecki) in the
(Diomedea exulans) at Bird Island, South Georgia, J. Anim. Ecol., coastal sediments of Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica),
59, 775–796, 1990. Antarc. Sci., 11, 415–418, 1999.
Croxall, J.P., Reid, K., Prince, P.A., Diet, provisioning and productivity Darnell, R.M., The organic detritus problem, in Estuaries, Publication
responses of marine predators to differences in availability of No. 83 of the American Association for the Advancement of
Antarctic krill, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 177, 115–131, 1999.
Science, Lauff, G.H., Ed., American Association for the Advance-
Culik, B., Flouride turnover in Adélie Penguin (Pygoscelkis adeliae) and
ment of Science, Washington, DC, 1967a, 374–375.
other bird species, Polar Biol., 7, 179–187, 1987.
Darnell, R.M., Organic detritus in relation to the estuarine system, in
Culik, B.M., Wilson, P.R., Penguins crowded out?, Nature (Lond.), 351,
Estuaries, Publication No. 83 of the American Association for the
331–340, 1991.
Advancement of Science, Lauff, G.H., Ed., American Association
Culik, B.M., Woakes, A.J., Adelung, D., Wilson, R.P., Coria, N.R.,
for the Advancement of Science, Washington, DC, 1967b,
Spairani, H.J., Energy requirements of Adélie Penguins (Pygoscelis
376–382.
adeliae) chicks, J. Compar. Physiol. B: Biochem., 160, 61–70,
David, P.M., The distribution of Sagitta gazellae Ritter-Zahoney,
1990.
Discov. Rep., 27, 235–278, 1955.
Cullen, J.J., Hypothesis to explain high-nutrient conditions in the open
David, P.M., The distribution of chaetognaths in the Southern Ocean,
sea, Limnol. Oceanogr., 36, 1578–1599, 1991.
Discov. Rep., 29, 199–228, 1958.
Cullen, J.J., Lesser, M.P., Inhibition of photosynthesis by ultraviolet
David, P.M., The chaetognatha of the Southern Ocean, in Biogeography
radiation as a function of dose and dosage rates: Results for a
and Ecology of Antarctica, van Meighem, J., van Oye, P., Eds., Dr.
marine diatom, Mar. Biol., 111, 183–190, 1991.
W. Junk., The Hague, 1965, 296–303.
Currie, R., Environmental features in the ecology of Antarctic sea, in
Davidson, K., Modelling microbial food webs, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.,
Biologie Antarctique, Holdgate, M.W., Prévost, J., Eds., Herman,
145, 279–296, 1996.
Paris, 1964, 87–94.
Cushing, D.H., Temporal variation in production system, in Analysis of Davidson, W., Lowe, C.L., How stenothermal are Antarctic marine
Marine Ecosystems, Longhurst, A.R., Ed., Academic Press, animals, Abstracts, Final Symposium on Ecology of the Antarctic
London, 1981, 443–471. Sea Ice Zone, Korcula, Croatia, 05, 2002.
Cuzin-Roudy, J., Gonad history of the Antarctic krill Euphausia superba Davidson, A.T., Marchant, H.J., Binding of manganese by Antarctic
Dana during its breeding season, Polar Biol., 7, 237–244, 1987. Phaeocystis pouchetii and the role of bacteria in its release, Mar.
Cuzin-Roudy, J., Schalk, P.H., Macrozooplankton—biomass, develop- Biol., 95, 481–487, 1987.
ment and activity, Berichte zur Polarforschung, 66, 146–159, 1989. Davidson, A.T., Marchant, H.J., Protist abundance and carbon concen-
Cziko, P., Cheng, C.-H., DeVries, A.L., Ice active protein in Antarctic tration during a Phaeocystis-dominated bloom at an Antarctic
echinoderms: Do isosmotic marine organisms risk freezing in coastal site, Polar Biol., 12, 387–395, 1992.
freezing seawater? IX SCAR Biology Symposium Abstracts, Davidson, A.T., Marchant, H.J., Comparative impact of in situ UV
p. 67, 2005. exposure on productivity, growth, and survival of Antarctic
Dahlback, A., Recent changes in the surface UV radiation and atmos- Phaeocystis and diatoms, Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Biol., 4,
pheric ozone in a high Arctic site, in Radiation and the Arctic 53–69, 1994.
System, Hesson, D.O., Ed., Springer, Berlin, 2002, 3–22. Davidson, A.T., Bramich, D., Marchant, H.J., McMinn, A., Effects of
Dahms, H.U., Bergmans, S.M., Schminke, H.R., Distribution and UV-B irradiation on growth and survival of Antarctic marine
adaptations of sea ice-inhabiting Harpacticoida (Crustacea: Cope- diatoms, Mar. Biol., 119, 507–515, 1994.
poda) of the Weddell Sea, Antarctica, PSNZI, Mar. Ecol., 11, Davies, J.L., The southern form of the pilot whale, J. Mammal., 41,
207–226, 1990a. 29–34, 1960.
Dahms, H.U., Bergmans, S.M., Schminke, H.R., Distribution adap- Davis, R.W., Kooyman, G.L., Free-ranging energetics of penguins, in
tations of sea ice-inhabiting Harpacticoida (Crustacea: Seabird Energetics, Whitlow, G.C., Rahn, H., Eds., Plenum Press,
Copepoda), Limnol. Oceanogr., 35, 1569–1576, 1990b. New York, 1984, 245–253.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 549
Davis, P.G., Siebruth, J.McN., Estuarine and microflagellate preda- Deacon, G.E.R., Antarctic oceanography: The physical environment, in
tion of actively-growing bacteria: Estimates by frequency of Biologie Antarctique, Carrick, R., Holdgate, M.W., Prévost, J.,
dividing-divided bacteria, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 19, 237–246, Eds., Herman, Paris, 1964b, 81–86.
1984. Deacon, G.E.R., Antarctic Ocean, Interdisciplinary Science Review, 2,
Davis, R.W., Castellini, M., Horning, M., Davis, M.P., Kooyman, G.L., 109–123, 1977.
Maue, R., Winter ecology of Weddell seals at White Island, Deacon, G.E.R., Physical and biological zonation in the Southern Ocean,
Antarc. J. U.S., 17, 183–184, 1982. Deep-Sea Res., 29, 1–15, 1982.
Davis, R.W., Kooyman, G.L., Croxall, J.P., Water flux and estimated Deacon, G.E.R. The Antarctic Circumpolar Ocean, Cambridge
metabolism of free-ranging gentoo and macaroni penguins at South University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1984.
Georgia, Polar Biol., 2, 41–46, 1983. Dearborn, J.H., Reproduction in the Nototheniid fish Trematomus
Davis, L.S., Boersma, P.D., Court, G.S., Satellite telemetry of the winter bernacchii Boulenger at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Copeia,
migration of Adélie Penguin (Pygoscelis adeliae), Polar Biol., 16, 3, 302–308, 1965a.
221–225, 1996. Dearborn, J.H., Food of Weddell seals at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica,
Davis, L.S., Harcourt, R.G., Bradshaw, C.J.A., The winter migration of J. Mammal., 106, 37–43, 1965b.
Adélie Penguins breeding in the Ross Sea sector of Antarctica, Dearborn, J.H., Food and reproduction of Glyptonotus antarcticus
Polar Biol., 24, 593–597, 2002. (Crustacea: Isopoda) at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Transactions
Dawbin, W.H., The seasonal migratory cycle of humpback whales, in of the Royal Society of New Zealand, 8, 163–168, 1967.
Whales, Dolphins, and Porpoises, Norris, K.S., Ed., University of Dearborn, J.H., Benthic invertebrates, Aust. Nat. Hist., 16, 134–139,
California Press, Berkeley, CA, 1966, 145–170. 1968.
Dayton, P.K., Observations on the growth, dispersal and population De Broyer, C., Analysis of gigantism and dwarfness of Antarctic and
dynamics of some sponges in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, in Sub-Antarctic Gammaridean Amphipoda, in Adaptations Within
Biologie des Spongaires, Vol. 391, Levi, C., Bouvy-Esnant, N., Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G., Ed., Smithsonian Institution,
Eds., 1979, 271–282. Washington, DC, 1977, 327–334.
Dayton, P.K., Polar benthos, in Polar Oceanography Part B: Chemistry, De Broyer, C., Jazdzewski, K., Dauby, P., Biodiversity pattern in the
Biology and Geology, Smith, W.O., Jr., Ed., Academic Press, San Southern Ocean: Lessons from Crustacea, in Antarctic Biology in a
Diego, CA, 1990, 631–685. Global Context, Huiskes, A.H.L., Gieskes, W.W.C., Rozema, J.,
Dayton, P.K., Hessler, R.R., Role of biological disturbance in main- Schorno, R.M.L., van der Vies, S.M., Wolff, W.J., Eds., Backhuys
taining diversity in the deep sea, Deep-Sea Res., 19, 199–208, Publishing, Leiden, The Netherlands, 2003, 201–204.
1972. Decho, A.W., Microbial exopolymer secretions in ocean environments:
Dayton, P.K., Martin, S., Observations on ice stalactites in McMurdo their role(s) in food webs and marine processes, Oceanography and
Sound, Antarctica, J. Geophys. Res., 76, 1595–1599, 1971. Marine Biology: Annual Reviews, 28, 73–153, 1990.
Dayton, P.K., Oliver, S., Antarctic soft-bottom benthos in oligotrophic Deflandre, G., Sur la presence de Pavicorbicula n.g. socialis dans le
and eutrophic environments, Science, 197, 55–58, 1977. plankton de l’Antarctique (Terre Adélie), Reviews in Algology,
Dayton, P.K., Robilliard, G.A., Notes on the biology of the Chae- 5, 183–188, 1960.
nichthyid fish Pagetopsis macropterus from McMurdo Sound, Deflandre, G., Deflandre-Rigand, M., Nanofossils siliceux, I: Archae-
Antarctica, Antarc. J. U.S., 4(6), 304–305, 1969. omonadacae, Fichier Micropaleontologique, 19, 4173–4400, 1970.
Dayton, P.K., Robilliard, G.A., DeVries, A.L., Anchor ice formation in Dehairs, F., Goeyens, L., Stroobants, N., Mathot, S., Elemental compo-
McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, and its biological significance, sition of suspended matter in the Scotia–Weddell Confluence area
Science, 163, 273–274, 1969. during spring and summer (EPOS Leg 2), in Weddell Sea Ecology,
Dayton, P.K., Robilliard, G.A., Paine, R.T., Benthic faunal zonation as a Hempel, G. Ed., Springer, Berlin, 1995, 25–34.
result of anchor ice formation at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, in de la Mare, W.K., Some principles for fisheries regulation from an
Antarctic Ecology, Vol. I, Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Academic Press, ecosystem perspective. in Selected Scientific Papers, 1986 (SC-
London, 1970, 244–258. CAMLR-SSP/3), Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic
Dayton, P.K., Robilliard, G.A., Paine, R.T., Dayton, L.B., Biological Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 1986, 323–339.
accommodation in the benthic community at McMurdo Sound, de la Mare, W.K., Preliminary consideration of performance criteria
Antarctica, Ecol. Monogr., 44, 105–128, 1974. for the evaluation of conservation strategies, Document WG-CSD
Dayton, P.K., Watson, D., Palmisano, A.C., Barry, J.P., Oliver, J.S., 88/9, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living
Rivera, D., Distribution patterns of benthic microalgal standing Resources, Hobart, 1988.
stock at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 6, 207–213, de la Mare, W.K., Some recent developments in the management of
1986. marine living resources, in Frontiers of Ecology, Floyd, R.R.,
Deacon, G.E.R., A general account of the hydrology of the Southern Sheppard, A.W., Barro, P.J.D., Eds., CSIRO Publishing,
Ocean, Discov. Rep., 15, 177–238, 1937. Melbourne, 1996, 559–616.
Deacon, G.E.R., The Southern Ocean, in The Sea, Volume 2: The de la Mare, K.W., Tidier fisheries management requires a new MOP
Composition of Sea-Water, Comparative and Descriptive Ocean- (management-orientated paradigm, Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish, 8,
ography, Hill, M.N., Ed., Interscience Publishers, New York, 1963, 349–356, 1998.
281–296. de la Mare, W.K., Abrupt mid-twentieth century decline in Antarctic
Deacon, G.E.R., The Southern Ocean, in Antarctic Research, Priestley, sea ice extent from whaling records, Nature (Lond.), 389, 87–90,
R., Ed., Herman, Paris, 1964a, 292–307. 1997.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
550 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Delepine, R., La vegetation marine dans l’Antarctique de l’Ouest Desbruyeres, D., Guile, A., La faune benthic de l’archipel de Kerguelen:
comparée a cell des Îles Australes Françaises: Consequences Premiéres données quantitatives, Comptes-rendus de l’Académie
biogeographiques, Compte rendu sommaire des séances. Société des Sciences Paris, 276, 633–636, 1973.
Biogéographique de Paris, 374, 52–68, 1966. Desperin, B., Note preliminaire sur la manchot papou (Pygoscelis
Delepine, R., Hureau, J.C., Comparative study of the vertical distribution papua) de l’ı̂le de la Possession (archipel Crozet), L’Oiseau et la
of marine vegetation of Archipel de Kerguelen and Isles Crozet, in RFO, 42, 69–83, 1972.
Symposium on Antarctic Oceanography, Scott Polar Research De Villiers, A.F., Littoral ecology of Marion and Prince Edward Islands
Institute, Cambridge, UK, 1968, 164–165. (Southern Ocean), S. Afr. J. Antarc. Res. (Suppl. 1), 1–40, 1976.
Delepine, R., Loamb, I.M., Zimmerman, M.H., Preliminary report on the DeVries, A.L., Survival at freezing temperatures, in Biochemical and
marine vegetation of Archipel de Kerguelen and Isles Crozet, in Biophysical Perspectives in Marine Biology, Vol. 1, Mallins,
Proceedings of the 5th International Seaweed Symposium, Halifax, D.W., Sargent, J.R., Eds., Academic Press, London, 1974,
Vol. 107, Plenum Press, London, 1965, 116. 289–330.
Delille, D., Seasonal changes in the abundance and composition of the DeVries, A.L., The physiology of cold adaptations in polar marine
marine heterotrophic bacterial community in an Antarctic coastal poikilotherms, in Polar Oceans, Dunbar, J.M., Ed., Arctic Institute
area, Polar Biol., 13, 463–470, 1993. of North America, Calgary, 1977, 409–420.
Delille, D., Marine bacterioplankton at the Weddell Sea ice edge: Distri- DeVries, A.L., The physiology and biochemistry of low temperature
bution of psychrophilic and psychrotrophic populations, in adaptations in polar marine ecosystems, in Polar Research: To
Weddell Sea Ecology, Hempel, G., Ed., Springer, Berlin, 1995, the Present and the Future, AAAS Selected Symposium No.
205–210. 7, McWhinnie, M.A., Ed., Westview Press, Boulder, 1978,
Delille, D., Rosiers, C., Seasonal changes of Antarctic marine bacter- 175–202.
ioplankton and sea ice bacterial assemblages, Polar Biol., 16, DeVries, A.L., Biological antifreezes and survival in freezing environ-
27–34, 1995a. ments, in Animals and environmental fitness, Gilles, R., Ed.,
Delille, D., Fiala, M., Rosiers, C., Seasonal changes in phytoplankton Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1980, 583–607.
and bacterioplankton in an ice-water interface in the Antarctic DeVries, A.L., Antifreeze peptides and glycopeptides in cold—water
neritic ice, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 123, 225–233, 1995b. fishes, Annu. Rev. Physiol., 45, 245–260, 1983.
Dell, R.K., Marine biology, in Antarctica, Hatherton, T., Ed., A.W. DeVries, A.L., The role of antifreeze glycoproteins and peptides in the
Reed, Wellington, 1965, 129–157. freezing avoidance of Antarctic fishes, Comp. Biochem. Physiol.,
Dell, R.K., Antarctic benthos, Adv. Mar. Biol., 10, 1–126, 1972. 90B, 611–621, 1988.
Dell, R.K., Fleming, C.A., Oligocene-Miocene bivalve Mollusca and DeVries, A.L., The role of antifreeze proteins in survival of Antarctic
fishes in freezing environments, in Antarctic Communities:
other macrofossils from sites 270 and 272 (Ross Sea), DSDP, Leg
Species, Structure and Survival, Valencia, J., Walton, D.W.H.,
8, Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, 28, 693–703,
Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1997,
1975.
202–208.
Delord, K., Gasco, N., Weimerskirch, H., Barbraud, C., Nicol, T.,
DeVries, A.L., Lin, Y., The role of glycoprotein antifreezes in the
Seabird mortality in the Patagonian toothfish longline fishery at
survival of Antarctic fishes, in Adaptations Within Antarctic
Crozet and Kerguelen Islands, CCAMLR Science, 12, 53–60, 2005.
Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Gulf Publishing Company,
DeMaster, D.P., The supply and accumulation of silica in the marine
Houston, TX, 1977, 439–457.
environment, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 45, 1715–1732,
DeWitt, H.H., The character of the midwater fish fauna of the Ross Sea,
1981.
Antarctica, in Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 1, Holdgate, M.W., Ed.,
Demers, S., Legendre, L.J., Therriault, C., Ingram, R.G., Biological
Academic Press, London, 1970, 305–314.
production at the ice-water ergocline, in Marine Interfaces Ecohy-
DeWitt, H.H., Coastal and deep-water benthic fishes of the Antarctic,
drodynamics, Elsevier Oceanography Series, Nihoul, J.C.J., Ed.,
Antarctic Map Folio Series, Vol. 15, American Geographical
Vol. 42, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1985, 31–44.
Society, Washington, DC, 1971.
Deming, J.W., Psychophiles and polar regions, Curr. Opin. Microbiol.,
DeWitt, H.H., Hopkins, T.L., Aspects of the diet of the Antarctic
5, 301–309, 2000.
silverfish, Pleurogramma antarcticum, in Adaptations Within
Denham, K.L., Powell, T.M., Effects of physical processes on planktonic
Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smithsonian Institution,
ecosystems in the coastal oceans, Oceanogr. Mar. Biol.: Annu.
Washington, DC, 1977, 557–567.
Rev., 22, 125–168, 1984.
DeWitt, H.H., Tyler, J.C., Fishes of the Stanford Antarctic Biological
Denys, C.J., McWhinnie, M.A., Fecundity and ovarian and preliminary
Research Programme, 1958–1959, Stanford Ichthyol. Bull., 7,
assessment of contaminated sites at Casey Station, Wilkes Land,
162–199, 1960.
Antarctica, Polar Biol., 35, 299–306, 1999.
Dichie, L.M., Perspective on fisheries biology and implications for
Deprez, P.P., Arens, M., Locher, H., Identification and preliminary
management, J. Fish Res. Board Can., 36, 838–844, 1979.
assessment of contaminated sites at Casey Station, Wilkes Land,
Dickie, L.M., Problems in predation, Oceanus, 18, 30–35, 1975.
Antarctica, Polar Rec., 35, 299–316, 1999.
Dickinson, A.B., Tagging elephant seals for life-history studies, Polar
Desbruyeres, D., Benthic bionomy of the continental shelf of the
Rec., 13, 443–446, 1967.
Kerguelen Archipelago, Macrofauna, 2: Diversity of benthic Dieckmann, G.S., Arrigo, K., Sullivan, C.W., A high-resolution sampler
annelid population in a Fjord close to the Morbihan Gulf, in for nutrient and chlorophyll a profiles of the sea ice platelet layer
Adaptations Within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G., Ed., Smith- and underlying water column below the fist ice in polar oceans:
sonian Institution, Washington, DC, 1977, 227–238. Preliminary results, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 80, 291, 1992.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 551
Dieckmann, G., Reicharalt, W., Zielinski, K., Growth and production of Domach, E.W., McClennen, C.E., Accumulation of glacial marine
the seaweed Himanothalia grandifolius at King George Island, in sediments in fjords of the Antarctic Peninsula and their use as
Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, Holocene palaeoenviromental indicators, Antarct. Res. Ser., 70,
P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 105–108. 735–754, 1996.
Dieckmann, G.S., Rohart, G., Hellmer, H., Kipfskuhi, J., The occurrence Domach, E.W., McDenney, C.E., Accumulation of glacial marine
of ice platelets at 150m depth near the Filchner Ice Shelf and its sediments of the Antarctic Peninsula and their use as Holocene
significance for sea ice biology, Deep-Sea Res., 33, 141–148, 1986. paleoenvironmental indicators, Antarc. Res. Ser., 70, 135–154,
Dieckmann, G.S., Lange, M., Spindler, M., Ackley, S.F., The forami- 1996.
nifer Neogloboquadrina pachyderma in sea ice of the Weddell Sea, Domanov, M.M., Lipiski, M., Annual cycle of chlorophyll a and primary
Eos, 69, 1267–1270, 1988. production of phytoplankton in Admiralty Bay (Antarctica),
Dieckmann, C.S., Lange, M.A., Ackley, S.F., Jennings, J.C., The Polskie Archiwum Hydrobiologii, 37, 471–478, 1990.
nutrient status of sea ice of the Weddell Sea during winter: Donnelly, B.G., Further observations on the southern right whale,
Effects of sea ice texture and algae, Polar Biol., 11, 449–456, 1991. Eubalena australis, in South African waters, J. Reprod. Fertil.
Dieckmann, G.S., Eicken, H., Haas, C. et al., A compilation of data on (Suppl.), 6, 347–352, 1969.
sea ice algal standing crop from the Bellinghausen, Amundsen, and Dore, J.E., Tien, G., Letelier, R., Parrish, G., Szyper, J., Burgett, J., Karl,
Weddell Seas from 1983 to 1994, Antarc. Res. Ser., 73, 85–92, D., RACER: Distribution of nitrogenous nutrients near receding
1998. pack ice in Marguerite Bay, Antarc. J. U.S., 27, 177–179, 1992.
di Prisco, G.D., Physiological and biochemical adaptation in fish to a Doroshenko, N.V., Populations of minke whales in the Southern Hemi-
cold marine environment, in Antarctic Communities: Species, sphere, Int. Whaling Committee Rep., 29, 361–364, 1979.
Structure and Survival, Battaglia, B., Valencia, J., Walton, Douglas, D.P., Novitzky, J.A., Fournier, R.O., Microaudiography-based
D.W.H., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, enumeration of bacteria with estimates of thymidine-specific
1997, 251–260. growth and reproduction rates, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 26, 91–99,
1987.
di Prisco, G.D., Arino, R., Molecular adaptation of the blood of Antarctic
Dower, K.M., Lucas, M.I., Photosynthesis-irradiance relationships and
teleosts to environmental conditions, Antarc. Sci., 1, 119–124, 1989.
production associated with a warm-core ring shed from the
Di Tuillo, G.R., Geesey, M.E., Jones, D.R., Daly, K.L., Campbell, L.,
Agulhas Retrofection, South Africa, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 95,
Smith, W.O., Jr., Phytoplankton assemblage structure and primary
141–154, 1993.
productivity along 1708 W in the South Pacific Ocean, Mar. Ecol.
Dower, K.M., Lucas, M.I., Phillips, R., Diechmann, G., Robinson, D.H.,
Prog. Ser., 255, 55–80, 2003.
Phytoplankton biomass, P-I relationships and primary production
Divorky, G.J., Sea ice as a factor in seabird distribution and ecology
in the Weddell Sea, Antarctica, during the austral summer, Polar
in the Beaufort, Chukchi, and Bering Seas, in Conservation of
Biol., 16, 41–52, 1996.
Marine Birds of Northern North America, U.S. Fish and Wildlife
Drew, E.A., Hastings, R.M., A year-round ecophysiological study of
Service, Wildlife Research Report No. 11, Bartonek, J.C., Nettle-
Himentothallus grandifolius (Desmarestiales: Phaeophyta) at
ship, D.N., Eds., U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington, DC,
Signy Island, Antarctica, Phycologia, 31, 262–277, 1992.
9–17, 1977.
Drewery, D.J., Morris, E.M., The response of large ice sheets to
Doake, C.S.M., Vaughan, D.G, Rapid disintegration of the Wordie Ice
climate change, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., Ser. B, 338,
Shelf in response to atmospheric warming, Nature (Lond.), 350,
235–342, 1992.
328–330, 1991.
Dring, M.J., Jewson, D.H., What does 14C-uptake by phytoplankton
Dohler, G., Effect of ultraviolet radiation on pigmentation and nitrogen
really measure? A fresh approach using a theoretical model, Br.
metabolism of Antarctic phytoplankton and ice algae, J. Plant Phycol. J., 14, 122–123, 1979.
Physiol., 153, 603–609, 1998. Drits, A.N., Pasternak, A.F., Feeding of mass species of Antarctic
Doi, T., Ohsumi, S., Nemoto, T., Population assessment of sei whales in zooplankton in summer, in Pelagic Ecosystems of the Southern
the Antarctic, Norsk Hvafangsttd, 56, 25–41, 1967. Ocean, Voronina, N.M., Ed., Nauka, Heyka, 1993, 250–259.
Doidge, D.W., McCann, T.S., Croxall, J.P., Attendance behaviour of Droop, M.R., Heterotrophy of carbon, in Physiology and Biochemistry of
Antarctic fur seals, Arctocephalus gazella, in Fur Seals: Maternal Algae, Stewart, W.D.P., Ed., University of California Press,
Strategies at Land and at Sea, Gentry, R.L., Kooyman, G.L., Eds., Berkeley, CA, 1974, 530–559.
Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, 1986, 102–114. Dubischer, C.D., Bathmann, U.V., Grazing impact of copepods and salps
Doige, D.W., Croxall, J.P., Breeding density, pup mortality, and mother- on phytoplankton in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean,
pup behaviour in Antarctic fur seals at South Georgia, in Proceed- Deep-Sea Res. II, 44, 415–433, 1997.
ings of the Fourth Biennial Conference on the Biology of Marine Dubreuil, C., Denis, M., Conan, P., Ray, S., Spatial-temporal variability
Mammals, San Francisco, December 14–18, 1981, 1983. of ultraplankton vertical distribution in Atlantic frontal zones
Doige, D.W., Croxall, J.P., Diet and energy budget of the Antarctic fur 60–668 E, 43–468 S, Polar Biol., 26(11), 734–745, 2003.
seal (Arctocephalus gazella) at South Georgia, in Antarctic Ducklow, H., Production and fate of bacteria in oceans, BioScience, 33,
Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., 494–501, 1983.
Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 460–465. Dugdale, R.C., Goering, J.J., Uptake of new and regenerated forms of
Dolzhenkov, V.N., Peculiarities of the distribution of Euphausia superba nitrogen in primary productivity, Limnol. Oceanogr., 12, 196–206,
Dana in the Western part of the Pacific sector of Antarctica. 1967.
Abstracts of papers, AllUnion Conference on Macroplankton, Dugdale, R.C., Wilkerson, F.P., Iron addition experiments in the
AllUnion Research Institute of Marine Fisheries and Ocean- Antarctic: a reanalysis, Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 4, 13–19,
ography, Moscow, 10–12, 1973. In Russian. 1990.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
552 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Duhamel, G., Biology and population dynamics of Notothenia rossii Eberhart, L.L., Siniff, D.B., Population dynamics and marine manage-
rossii from the Kerguelen Islands (Indian Sector of the Southern ment policies, J. Fish. Res. Board Canada, 34, 183, 1977.
Ocean), Polar Biol., 1, 141–151, 1982. Eberlein, K., Leal, M.T., Hammer, K.D., Hickel, W., Dissolved organic
Duhamel, G., Reproduction des Nototheniidae et Channichthyidae des substances during Phaeocystis blooms in the German Bight (North
Isles Kerguelen. In Antes du colloquer sur l’ecologie marine ı̂les Sea), Mar. Biol., 89, 311–316, 1985.
subantartiques, Comité Nacional Français des Recherches Antarc- Eddie, G.C., The harvesting of krill, FAO, GLO/SO/77/2, Southern
tiques, 57, 91–108, 1987. Ocean Fisheries Survey Programme, Rome, 1977.
Duhamel, G., Hureau, J.C., La situation de la peche aux ı̂les Kerguelen Edwards, D.M., Heap, J.A., Convention on the conservation of Antarctic
en 1981, La Peche Maritime, 5, 1–8, 1981. Marine Living Resources: A commentary, Polar Rec., 20 (127),
Duhamel, G., Hureau, J.-C., The role of zooplankton in the diet of certain 353–362, 1981.
sub-Antarctic marine fishes, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Edwards, R., Hennemuth, R., Maximum yield: Assessment and attain-
Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, ment, Oceanus, 18(2), 3–9, 1975.
Berlin, 1985, 422–429. Edwards, D.D., McFeters, G.A., Venkatsan, M.I., Distribution of
Duhamel, G., Hureau, J.-C., Changes in fish populations and fisheries Clostridium perfringens and fecal sterols in a benthic coastal
around the Kerguelen Islands during the last decade, in Antarctic marine environment influenced by the sewage outfall from
Ecosystems: Ecological Change and Conservation, Kerry, K.R., McMurdo Station, Antarctica, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 64,
Hempel, G., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1990, 323–333. 2596–2600, 1998.
Duhamel, G., Pletikowsic, M., Données biologiques sur les Notothe- Efremenko, V.N., Atlas of the fish larvae of the Southern Ocean,
niidae de Îles Crozets, Cybium, 7, 43–57, 1983. Cybium, 7, 1–74, 1983.
Dunbar, M.J., Physical causes and biological significance of polynas and Efremenko, V.N., Distribution of eggs and larvae of Myctophidae in the
other open water, in Polynas and the Canadian Arctic, Canadian southern Atlantic. Voporsykittiologii 20:620. In Russian; repro-
Wildlife Service Occasional Paper, Ottawa, 1981, 29–41. duced in English in J. Ichthyol., 26, 141–147, 1986.
Dunbar, R.B., Sediment trap experiments on the Antarctic continental Ehrenberg, C.G., Einige vorlanffge Desultale der Untersuchungen der
margin, Antarct. J. U.S., 19, 71–74, 1983. von der Südpoleise des Capitain Ross, so wie von den Herren
Dunbar, R.B., Anderson, J.B., Domack, E.W., Oceanographic influences Schayer und Darwin zugehommenen Materialen, Meber Preus-
on sedimentation along the Antarctic continental shelf, in Ocea- siche Academie der Wissenschaften, 182–187, 1844.
nology of the Antarctic Continental Shelf, Antarctic Research Ehrenberg, C.G., Uber neue Anschauungen des Kleinsten nordlicher
Series 43, Jacobs, S.S., Ed., 1985, 291–312. Polarlebens, Monaistker der Berlin Akademie, 522–529, 1853.
Dungan, M.L., Miller, T.E., Thompson, D.A., Catastrophic decline of a Eicken, H., The role of sea ice in structuring Antarctic ecosystems, Polar
top carnivore in the Gulf of California rocky intertidal zone, Biol., 12, 3–13, 1992.
Science, 215, 989–991, 1982. Eicken, H., Lange, M., Development and properties of sea ice in the
Eastman, J.T., Evolutionary divergence in McMurdo Sound fishes, coastal region of the southeastern Weddell Sea, J. Geophys. Res.,
Antarc. J. U.S., 15, 151–153, 1980. 98, 8193–8206, 1989.
Eastman, J.T., The evolution of neutrally-buoyant notothenoid fishes: Eicken, H. et al., The underice water layer. In “The winter expedition of
their specializations and potential interactions in the Antarctic the RV Polarstern to the Antarctic” (SNT V/13), Berichte zur
food web, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, Polarforschung 39, 102–183, 1987.
W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985a, Ekau, W., Okmorphologie natotheniidae Fische aus dem Weddellmeer,
430–436. Antarktis, Berichte zur Polarforscherung, 51, 1–140, 1988.
Eastman, J.T., Pleurogramma antarcticum (Pisces: Nototheniidae) as Ekau, W., Demersal fish fauna of the Weddell Sea, Antarc. Sci., 2,
food for other fishes in McMurdo Sound, Polar Biol., 4, 155–160, 129–137, 1990.
1985b. Ekman, V.K., A survey of some theoretical investigations in ocean
Eastman, J.T., Evolution and diversification of Antarctic notothenioid current, Journal du Conseil, Conseil Permanent International pour
fishes, Am. Zoologist, 31, 93–109, 1991. l’Exploration de la Mer, 3, 295–297, 1928.
Eastman, J.T. Antarctic Fish Biology: Evolution in a Unique Environ- Ekman, V.K., Zoogeography of the Sea, Sidgwick and Jackson, London,
ment, Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 1993. 1953.
Eastman, J.T., DeVries, A.L., Lipid sacs as a buoyancy adaptation in Eldred, G.E., Miller, G.V., Stark, W.S., Feeney-Burns, L., Lipofuscin:
Antarctic fish, Nature (Lond.), 271, 352–353, 1978. Resolution of discrepant fluorescence data, Science, 216, 757–759,
Eastman, J.T., DeVries, A.L., Buoyancy adaptations in a swim-bladder- 1982.
less Antarctic fish, J. Morphol., 167, 91–102, 1981. Elizarov, A.A., Peculiarities of water dynamics in places of krill
Eastman, J.T., DeVries, A.L., Buoyancy studies of notothenioid fishes in concentrations (Euphausia superba Dana), Trudy Vsesoiuznogo
McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Copeia, 2, 385–393, 1982. Naucho-issledovatel’skii Morskogo Rybnogo Khoziaistva i
Eastman, J.T., DeVries, A.L., Adaptations for cryopelagic life in the Okeanographii, 79, 31–40, 1971. In Russian with English
Antarctic notothenioid fish Pagothenia borchgrevinki, Polar Biol., summary.
4, 45–52, 1985. Elliot, D.H., Physical geography–geological evolution, in Antarctica
Eastman, J.T., DeVries, A.L., Antarctic fishes, Sci. Am., 254, 106–114, (IUCN Key Environment Series), Bonner, W.N., Walton, D.W.H.,
1986. Eds., Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1985, 39–61.
Eastman, J.T., Hubold, G., The fish fauna of the Ross Sea, Antarctica, El-Sayed, S.Z., Primary productivity of the Antarctic and suban-
Antart. Sci., 11, 293–304, 1999. tarctic, in Biology of the Antarctic Seas II, Schmidt, W.,
Eberhart, L.L., Optimal policies for conservation of large mammals, Llano, G., Eds., American Geophysical Union, Washington,
Environ. Conserv., 4, 205–212, 1977. DC, 1967, 15–47.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 553
El-Sayed, S.Z., Prospects of primary productivity studies in Antarctic El-Sayed, S.Z. Southern Ocean ecology: The BIOMASS perspective,
waters, in Symposium on Antarctic oceanography, Santiago, Chile, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1996.
1966, Currie, R.I., Ed., Scott Polar Research Institute/SCAR, El-Sayed, S.Z., Jitts, H.R., Phytoplankton production in the southeastern
Cambridge, UK, 1968a, 227–239. Indian Ocean, in Biology of the Indian Ocean, Zeitzschel, B., Ed.,
El-Sayed, S.Z., On the productivity of the southwest Atlantic Ocean and Chapman and Hall, London, 1973, 131–134.
the waters west of the Antarctic Peninsula, in Biology of the El-Sayed, S.Z., Mandelli, E.F., Primary production and standing crop of
Antarctic Seas III, Schmidt, W., Llano, G., Eds., American phytoplankton in the Weddell Sea and Drake Passage, in Biology of
Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, 1968b, 15–47. the Antarctic Seas II, Llano, G.A., Ed., American Geophysical
El-Sayed, S.Z., Primary productivity of the Antarctic and subAntarctic, Society, Washington, DC, 1965, 87–106.
in Antarctic Map Folio Series 10, Bushnell, V., Ed., American El-Sayed, S.Z., McWhinnie, M.A., Protein of the last frontier, Oceanus,
Geographical Society, New York, 1968c, 1–6. 22(1), 13–20, 1979.
El-Sayed, S.Z., On the productivity of the Southern Ocean, in Antarctic El-Sayed, S.Z., Taguchi, S., Primary production and standing crop of
Ecology, Vol. 1, Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Academic Press, London, phytoplankton along the iceedge in the Weddell Sea, Deep-Sea
1970a, 119–135. Res., 28(A), 1017–1032, 1981.
El-Sayed, S.Z., Phytoplankton production in the South Pacific sector of El-Sayed, S.Z., Turner, J.T., Productivity of the Antarctic and tropical-
Antarctica, in Scientific Exploration of the South Pacific, Worster, subtropical regions: a comparative study, in Polar Oceans, Dunbar,
W.S., Ed., National Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC, M.J., Ed., Arctic Institute of North America, Calgary, 1977,
1970a, 193–210. 463–504.
El-Sayed, S.Z., Biological aspects of the pack ice ecosystem, in El-Sayed, S.Z., Weber, L.H., Spatial and temporal variation in phyto-
Symposium on Antarctic Water Masses, Tokyo, Japan, Sept. 19, plankton biomass and primary productivity in the southwest
1970, Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research, Cambridge, Atlantic and Scotia Sea, Polar Biol., 1, 83–90, 1982.
UK, 35–54 pp, 1971a. El-Sayed, S.Z., Weber, L.H., Size fractionation of Atlantic phyto-
El-Sayed, S.Z., Observations on a phytoplankton bloom in the Weddell
plankton, Antarc. J. U.S., 19, 141–143, 1986.
Sea, in Biology of the Antarctic Seas 17, Llano, G., Wallen, I.E.,
El-Sayed, S.Z., Stockwell, P.A., Reheim, H.A., Taguchi, S., Meyer,
Eds., American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, 1971b,
M.A., On the productivity of the southwestern Indian Ocean,
301–312.
CNFRA, 44, 1–43, 1979.
El-Sayed, S.Z., Dynamics of trophic relationships in the Southern
El-Sayed, S.Z., HolmHansen, O., Biggs, D.C., Phytoplankton standing
Ocean, in Research in the Antarctic, Quam, L.O., Ed., American
crop, primary productivity, and nearsurface nitrogenous nutrient
Association for the Advancement of Science, Washington, DC,
fields of the Ross Sea, Antarctica, Deep-Sea Res., 30(8), 871–886,
1971c, 73–91.
1983.
El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., Biological investigations of marine Antarctic
El-Sayed, S.Z., Stephens, F.C., Bidigare, R.R., Ondrusek, M.E.,
systems and stocks, Vol. 1: Research proposals, Scientific
Effects of ultraviolet radiation on Antarctic marine phyto-
Committee on Antarctic Research, Cambridge, UK, 1977.
plankton, in Antarctic Ecosystems: Ecological Change and
El-Sayed, S.Z., Primary productivity and estimates of potential yields on
Conservation, Kerry, K.R., Hempel, G., Eds., Springer, Berlin,
the Southern Ocean, in Polar Research: To the Present and the
1990a, 379–385.
Future, AAAS Selected Symposia 7, Whinnie, M.A., Ed., Amer-
El-Sayed, S.Z., Stephens, F.C., Bidigare, R.R., Ondrusek, M.E.,
ican Association for the Advancement of Science, Washington,
Potential effects of solar ultraviolet radiation on Antarctic phyto-
DC, 1978, 141–160.
plankton in Effects of Solar Ultraviolet Radiation on Biochemical
El-Sayed, S.Z., Biological Investigations of Antarctic Systems and
Stocks (BIOMASS), II: Selected Contributions to the Dynamics in Aquatic Environments, Woods Hole Oceanographic
Woods Hole Conference on Living Resources of the Southern Institution Technical Report WHOI-90-09, Blough, N.V., Zepp,
Ocean, Scott Polar Research Institute/SCAR, Cambridge, UK, R.G., Eds., Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole,
1981. MA, 141–142, 1990b.
El-Sayed, S.Z., Productivity of Antarctic waters—a reappraisal, in Emerson, W.B., Feeding preferences of the Adélie Penguin at Cape
Marine Phytoplankton and Productivity, HolmHansen, O., Bolis, Crozier, Ross Island, in Antarctic Bird studies, Antarctic Research
L., Gilles, R., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1984, 19–34. Series 12, Austin, O.L., Ed., American Geophysical Society,
El-Sayed, S.Z., Plankton of the Antarctic seas, in Key Environments— Washington, DC, 1968, 191–212.
Antarctica, Bonner, W.N., Walton, D.W.H., Eds., Pergamon Press, Emslie, S.D., McDonald, J.D., Adélie Penguin diet and climate change
Oxford, 1985, 135–154. during the middle to late Holocene in northern Marguerite Bay,
El-Sayed, S.Z., Biological productivity of Antarctic waters: Present Antarctic Peninsula, Polar Biol., 25, 222–229, 2002.
paradoxes and emerging paradigms, in Antarctic Aquatic Emslie, S.D., Fraser, W., Smith, R.C., Walker, W., Abandoned penguin
Biology, BIOMASS Scientific Series 7, El-Sayed, S.Z., Tomo, rookeries and environmental change in the Palmer Station area,
A.P., Eds., SCAR Scott Polar Research Institute, Cambridge, Anvers Island, Antarctic Peninsula, Antarc. Sci., 10, 257–268,
UK, 1987, 1–21. 1998.
El-Sayed, S.Z., Seasonal and interannual variabilities in Antarctic Endo, Y., Asari, H., Watanuki, Y., Biological characteristics of
phytoplankton, with reference to krill distribution, in Antarctic euphausiids preyed upon by Adélie Penguins, Pygoscelis adeliae,
Ocean and Resources Variability, Sahrhage, D., Ed., Springer, breeding at Hukuro Cove, Lützow-Holm Bay, in 1995/96, Polar
Berlin, 1988a, 101–119. Biosci., 13, 66–73, 2000.
El-Sayed, S.Z., Productivity of the Southern Ocean: a closer look, Comp. Enzenbacher, D., Antarctic tourism and environmental concerns, Mar.
Biochem. Physiol., 90B, 489–498, 1988b. Poll. Bull., 25, 258–265, 1992.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
554 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Eppley, R.W., Temperature and phytoplankton growth in the sea, Fish. Everson, I., Reproduction in Notothenia neglecta Nybelin, Br. Antarc.
Bull. Natl Ocean. Atmos. Adm., 70, 1063, 1972. Surv. Bull., 23, 81–92, 1970b.
Eppley, R.W., Estimating phytoplankton growth rates in oligotrophic Everson, I., Antarctic krill: A reappraisal of its distribution, Polar Rec.,
oceans, in Primary Productivity in the Sea, Falkowski, P.K., Ed., 112, 15–23, 1976.
Plenum Press, New York, 1980, 231–242. Everson, I., Antarctic marine secondary production and the phenomenon
Eppley, Z.A., Assessing indirect effects of oil in the presence of natural of cold adaptation, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., Ser. B, 279, 55–66,
variation: The problem of reproductive failure of South Polar skuas 1977a.
during Bahia Paraiso oil spill, Marine Pollution Bulletin, 25, Everson, I. The Living Resources of the Southern Ocean FAO, Southern
307–312, 1992. Ocean Fisheries Survey Programme, Rome, GLO/SO/77/1, 1–156,
Eppley, Z.A., Rubega, M.A., Indirect effects of an oil spill: Reproductive 1977.
failure of a population of South Polar skuas following the Bahia Everson, I., Antarctic fisheries, Polar Rec., 19, 233–251, 1978.
Paraiso oil spill in Antarctica, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 67, 1–6, Everson, I., Antarctic krill, in Biological Investigations of Marine
1990. Antarctic Systems and Stocks. Vol. II: Selected Contributions to
Eppley, R.W., Horrigan, S.G., Fuhrman, J.A., Brooks, E.R., Price, C., the Woods Hole Conference on the Living Resources of the
Sellner, K., Origins of dissolved organic matter in Southern Southern Ocean, El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., Scott Polar Research Insti-
California coastal waters: Experiments on the role of zooplankton, tute/SCAR, Cambridge, UK, 1981, 31–46.
Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 6, 149–159, 1981. Everson, I., Diurnal variations in mean volume backscattering strength
Erickson, A.W., Aerial census of seals, whales, and penguins in the pack of an Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) patch, J. Plankton Res.,
ice of the northwestern Weddell Sea, November 1983, Antarc. 4, 155–162, 1982.
J. U.S., 19, 121–124, 1984. Everson, I., Estimation of krill abundance, Berichte zur Polarforschung,
Erickson, A.W., Hofman, R.J., Antarctic seals, Antarctic Map Folio 4, 156–158, 1983.
Everson, I., Zooplankton, in Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 2, Laws, R.M., Ed.,
Series, Vol. 18, American Geographical Society, Washington, DC,
Academic Press, London, 1984a, 463–490.
4–12, 1974.
Everson, I., Fish biology, in Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 2, Laws, R.M., Ed.,
Erickson, A.W., Siniff, D.B., Cline, D.R., Hofman, R.J., Distributional
Academic Press, London, 1984b, 491–492.
ecology of Antarctic seals, in Symposium on Antarctic Ice and
Everson, I., Marine interactions, in Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 2, Laws,
Water Masses, Deacon, G., Ed., Scientific Committee on Antarctic
R.M., Ed., Academic Press, London, 1984c, 783–819.
Research, Cambridge, UK, 1971, 55–76.
Everson, I., Can we satisfactorily estimate krill abundance?, in Antarctic
Estep, K.W., Davis, P.G., Keller, M.D., Siebruth, J.McN., How import-
Ocean and Resources Variability, Sahrhage, D., Ed., Springer,
ant are oceanic algal nanoflagellates in bacterivory?, Limnology
Berlin, 1988, 199–208.
and Oceanography, 31, 646–650, 1986.
Everson, I., Managing Southern Ocean krill and fish stocks in a changing
Estep, K.W., Nejstgaard, J.C., Skjoldal, R.H., Rey, F., Predation by
environment, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., Ser. B, 338, 311–317,
copepods upon natural populations of Phaeocystis pouchettii as a
1992.
function of the physiological state of the prey, Mar. Ecol. Prog.
Everson, I., Consideration of the major issues in ecosystem monitoring
Ser., 67, 235–249, 1990.
and management, CCAMLR Sci., 9, 213–232, 2002.
Estrada, M., Delgado, M., Summer phytoplankton distribution in the
Everson, I., Goss, C., Krill fishing activity in the southwest Atlantic,
Weddell Sea, Polar Biol., 10, 413–422, 1990.
Antarct. Sci., 3, 351–358, 1991.
Estrup, K.W., Nejsgaard, J.C., Skjoldal, R.H., Rey, I., Predation by
Everson, I., Miller, D.G.M., Krill mesoscale distribution and abundance:
copepods on natural populations of Phaeocystis pouchetti as a
Results and implications of research during the BIOMASS
function of the physiological state of the prey, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Program, in Southern Ocean Ecology: The BIOMASS Perspective,
Ser., 67, 235–249, 1986. El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK,
Ettershank, G., A new look at the age structure of the Antarctic krill, 1996, 129–144.
Euphausia superba, BIOMASS Newsletter, 4, 5–9, 1982. Everson, I., Ralph, R., Respiratory metabolism of Chaenocephalus
Ettershank, G., Age structure and cyclical annual size changes in aceratus, in Antarctic Ecology Vol. I, Holdgate, M.W., Ed.,
Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba), Polar Biol., 2, 189–193, 1983. Academic Press, London, 1970, 315–319.
Ettershank, G., A new approach to the assessment of longevity in the Everson, I., Ward, P., Aspects of Scotia Sea zooplankton, Biol.
Antarctic krill Euphausia superba, J. Crustacean Biol., 4(Special J. Linnean Soc., 14, 93–101, 1980.
issue No.1), 295–305, 1984. Fabiano, M., Danovaro, R., Meiofauna distribution and mesoscale
Ettershank, G., MacDonald, I., Croft, R., The estimation of age in the variability in two sites of the Ross Sea (Antarctica) with
flesh fly (Sarcophaga bullata) using the age pigment lipofuscin, contrasting food supply, Polar Biol., 22, 115–123, 1999.
Aust. J. Z., 31, 131–138, 1982. Falkowski, P.G., Raven, J.A. Aquatic Photosynthesis, Blackwell Scien-
Evans, R.H. Unpublished manuscript. Current observations and lead line tific Publishers, Oxford, MA, 1997.
soundings McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, U.S. Naval Oceano- Falkowski, P.G., Rosenthal, Y., Biological diversity and resource
graphic Office. IMR No. 0-18-65. plunder in the geological record: Causal correlations or causal
Everitt, D.A., Thomas, D.P., Observations on the seasonal change in relationships?, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 98, 4290–4292, 2002.
diatoms at inshore localities near Davis Station, East Antarctica, Falkowski, P.G., Winick, C.D., A simulation model of the effects of
Hydrobiologica, 139, 3–12, 1986. vertical mixing on primary production, Mar. Biol., 65, 69–75, 1981.
Everson, I., The population dynamics and energy budget of Notothenia Falkowski, P.G., Scholes, R.J., Boyle, E., Canadell, J., Canfield, D.,
neglecta Nybelin at Signy Island, South Orkney Islands, Br. Elser, J., Gruber, N., Hibbard, K., Högberg, P., Linder, S.,
Antarc. Surv. Bull., 23, 25–50, 1970a. Mackenzie, F.T., Moore, B. III, Pedersen, T., Rosenthal, Y.,
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 555
Seitzinger, S., Smetacek, V., Steffen, W., The global carbon cycle: Mesoscale surface distribution of biogeochemical characteristics
A test for our knowledge of the earth as a system, Science, associated with a frontal system in the Crozet Basin (southern
290(5490), 291–296, 2000. Indian Ocean) during austral summer, 1999, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.,
FAO, Mammals of the Sea, Vol. 3. FAO Fisheries Series No. 5. (1981), 249, 1–14, 2003.
Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Figuerias, F.G., Estrada, M., Lopez, O., Arbores, B., Photosynthetic
1981. parameters and primary production in the Bransfield Strait: Relation-
FAO, Southern Ocean CCAMLR Convention Area. Fishing Areas 48, 58 ships with mesoscale hydrographic structures, J. Mar. Syst., 17,
and 88. FAO Species Identification Sheets for Fishery Purposes 129–141, 1998.
Volume II, Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Filin, A.A., Gorchusky, K.V., Kischeva, V.M., Biomass of myctophids
Nations/Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean estimated by
Living Resources, Rome, 233–471, 1985. acoustic surveys, SC-CCAMLR Selected Scientific Papers 1990,
Fay, R.R., Significance of nanoplankton in primary production of the 417–429, 1990.
Ross Sea, Antarctica, during the 1972 austral summer. Ph.D. Filipova, J.A., New data on the squids (Cephalopoda, Oegosida) from
Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX., 1973. the Scotia Sea, Malacologia, 11, 391–406, 1972.
Fell, H.B., Dawsey, S., Asteroidea, Antarctic Map Folio Series, Vol. 11, Fischer, G., Fütterer, D., Gersonde, R., Honjo, S., Ostertman, D., Wefer,
American Geographical Society, Washington, DC, 41, 1969. G., Seasonal variability of particle flux in the Weddell Sea and its
Fell, H.B., Holzinger, T., Sherraden, M., Ophiuroidea, Antarctic Map relation to ice cover, Nature (Lond.), 335, 426–428, 1988.
Folio Series, Vol. 11, American Geographical Society, Washington, Floodgate, G.D., Some environmental aspects of marine hydrocarbon
DC, 42–43, 1969. bacteriology, Aqua. Microbial Ecol., 9, 3–11, 1995.
Fenchel, T., The ecology of heterotrophic microflagellates, I: Some Focardi, S., Bargagli, R., Cotsolini, S., Isomer-specific analysis and toxic
important forms and their functional morphology, Mar. Ecol. Prog. potential evaluation of the polychlorinated biphenyls in Antarctic
Ser., 8, 211–223, 1982a.
fish, seabirds, and Weddell seals from Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea),
Fenchel, T., The ecology of heterotrophic flagellates, II: Quantitative
Antarc. Sci., 7, 31–35, 1995.
occurrence and importance as consumers of bacteria, Mar. Ecol.
Fogg, G.E., The extracellular products of algae, Oceanogr. Mar. Biol.:
Prog. Ser., 9, 35–42, 1982b.
Annu. Rev., 4, 195–212, 1966.
Fenchel, T., Marine plankton food chains, Annual Review of Ecology
Fogg, G.E., Aquatic primary production in Antarctica, Philosophical
and Systematics, 19, 19–38, 1988.
Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B, 279, 27–38,
Fenchel, T., Harrison, D., The significance of bacterial grazing and
1977.
mineral cycling for the decomposition of particulate detritus, in
Fogg, G.E., Nitrogen cycling in sea waters, Philosophical Transactions
The Role of Terrestrial and Aquatic Organisms in Decomposition
of the Royal Society of London, Series B, 296, 511–520, 1982.
Processes, Anderson, J.M., Macfadyen, A., Eds., Blackwell,
Fogg, G.E., Nalewajko, C., Watt, W.D., Extracellular products of
Oxford, 1976, 285–299.
phytoplankton phorosynthesis, Proceedings of the Royal Society
Fenchel, T., Lee, C.C., Studies on ciliates associated with sea ice from
of London, Series B, 162, 517–534, 1965.
Antarctica, I: The nature of the fauna, Archiv für Protistenkunde,
Foldvik, A., Gammelsrad, T., Notes on Southern Ocean sea-ice and
114, 231–236, 1972.
bottom water formation, Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology,
Ferguson, R.L., Rublee, P., Contributions of bacteria to the standing crop
Palaeoecology, 67, 3–17, 1988.
of phytoplankton, Limnology and Oceanography, 21, 141–145,
Forster, T.D., The temperature and salinity fields under the Ross Ice
1976.
Shelf, Antarctica, Antarc. J. U.S., 13, 81–82, 1978.
Fevolden, S.E., Investigations of krill (Euphausiacea) sampled during
the Norwegian Antarctic Research Expedition, Sarsia, 64, Forster, T.D., The physical oceanography of the Southern Ocean,
189–198, 1979. BIOMASS Scientific Series, 2, 9–22, 1981.
Fevolden, S.E., Genetic variation of Euphausia superba in the Antarctic Forster, T.D., The marine environment, in Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 2,
Peninsula waters, Sarsia, 66, 169–175, 1986. Laws, R.M., Ed., Academic Press, London, 1984, 345–371.
Fevolden, S.E., Ayala, F.J., Enzyme polymorphism in Antarctic krill Forster, B.A., Composition and abundance of zooplankton under the
(Euphausiacea); genetic variation between populations and spring sea-ice of McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 8,
species, Sarsia, 66, 167–181, 1987. 41–48, 1989.
Fevolden, S.E., Schneppenheim, R., Genetic structure of Euphausia Forster, B.A., Time and depth comparison of sub-ice zooplankton in
superba Dana in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean as McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 9, 431–435, 1989.
demonstrated by different electrophoretic techniques, Polar Biol., Forster, T.D., Carmack, E.C., Frontal zone mixing and Antarctic bottom
9, 15–298, 1988. water formation in the southern Weddell Sea, Deep-Sea Res., 23,
Fiala, M., Delille, D., Annual changes of microalgae biomass in 301–317, 1976.
Antarctic sea ice contaminated by crude oil and diesel fuel, Forster, M.E., Franklin, C.E., Taylor, H.H., Davidson, W., The aerobic
Polar Biol., 21, 391–396, 1999. scope of an Antarctic fish, Pagothenia borchgrevinki, and its
Fiala, M., Semerich, M., Oriol, L., Size-fractionated phytoplankton significance for cold adaptation, Polar Biol., 8, 155–159, 1987.
biomass and species composition in the Indian sector of the Forster, B.A., Cargill, J.M., Montgomery, J.C., Planktivory in
Southern Ocean during austral summer, J. Mar. Syst., 17, Pagothenia borchgrevinki (Pisces: Nototheniidae) in McMurdo
179–197, 1998. Sound, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 8, 49–54, 1989.
Fiala, M., Delille, B., Debreuil, C., Kopczynska, E., Leblanc, K., Fortier, L., Le Fevre, S., Legendre, L., Export of biogenic carbon to fish
Morvan, J., Quéguiner, B., Blain, S., Cailliau, C., Conan, P., and to the deep ocean: The role of large planktonic microphages,
Corvaisier, R., Denis, M., Frankignoulle, M., Oriol, L., Roy, S., J. Plankton Res., 7, 809–839, 1994.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
556 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Fowler, C.W., Indices of population status, in A Search for Management Fritzen, C.H., Sullivan, C.W., Distribution and dynamics of microbial
Criteria, Fowler, C.W., Bunderson, M.B., Cherry, M.B., Ryel, R.J., communities in the pack ice of the western Weddell Sea, Antarc-
Steele, B.B., Eds., United States Marine Mammal Commission, tica, in Antarctic Communities: Species, Structure and Survival,
Washington, DC, 1980, 283–295. Battaglia, B., Valencia, J., Walton, D.W.H., Eds., Cambridge
Fowler, G.S., Field studies, tourism, and stress responses in Magellanic University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1999, 101–108.
penguins, in Report: Workshop on Researcher-Seabird Fritzen, C.H., Lythe, V.I., Ackley, S.F., Sullivan, C.W., American
Interactions, Fraser, W.R., Trivelpiece, W.Z., Eds., Montana, Zoologist, 32, 17–33, 1994.
MN, 1993, 44–55. Froneman, P.W., Balarin, M.S., Structure and grazing impact of the
Fowler, S.W., Knauer, G.A., Role of large particles in the transport of protozooplankton community in the waters surrounding the sub-
elements and organic compounds through the oceanic water Antarctic Prince Edward Islands, Polar Biol., 20, 198–205, 1998.
column, Prog. Oceanogr., 16, 147–194, 1986. Froneman, P.W., Bernard, K.S., Trophic cascading in the Polar Frontal
Fowler, C.W., Smith, T.D., Dynamics of Large Mammal Populations, Zone of the Southern Ocean during austral autumn 2002, Polar
Wiley, New York, 1981. Biol., 26, 268–275, 2004.
Foxton, P., The distribution of the standing crop of zooplankton in the Froneman, P.W., Pakhomov, E.A., Perissinotto, R., Meaton, V., Feeding
Southern Ocean, Discovery Reports, 28, 191–236, 1956. and predation impact of two chaetognath species, Euchronia
Foxton, P., Seasonal variation in the plankton of Antarctic waters, in hamata and Sagitta gazellae, in the vicinity of Marion Island
Biologie Antarctique, Carrick, R., Holdgate, W.M., Prevost, J., (Southern Ocean), Mar. Biol., 131, 95–101, 1992.
Eds., Herman, Paris, 1964, 311–318. Froneman, P.W., Perissinotto, R., Pakhomov, E.A., Biogeographical
Foxton, P., The distribution and life history of Salpa thompsoni Foxton structure of the micro-phytoplankton assemblage in the region of
with observations on a related species, Salpa gerlachii Foxton, the Subtropical Convergence and across the warm core eddy during
Discov. Rep., 34, 1–116, 1966. the austral winter, J. Plankton Res., 19, 519–531, 1997.
Foxton, P., Roe, R.S.J., Observations on the nocturnal feeding of some Froneman, P.W., Pakhomov, E.A., Perissinotto, R., McQuaid, C.D.,
Zooplankton structure and grazing in the Atlantic sector of the
mesopelagic crustaceans, Mar. Biol., 28, 37–49, 1974.
Southern Ocean in the late austral summer 1973, Part 2: Bio-
Fradet, G., Evaluation of chitosan as a thermostatic agent, in Proceed-
chemical zonation, Deep-Sea Res., 147, 1687–1692, 2000.
ings of the Third International Conference on Chitan/Chitosan,
Frost, G.W., McCrone, L.E., Vertical distribution and abundance of
Seregallia, Italy, 1985.
some mesopelagic fishes in the eastern subarctic Pacific Ocean in
Frakes, L., Kemp, E.M., Influence of continental positions on early
summer, Fish. Bull., 76, 751–770, 1979.
tertiary climates, Nature (Lond.), 240, 97–100, 1972.
Fry, B., Sherr, E.B., 13C measurements as indicators of carbon flow in
Franks, P.J.S., Sink or swim: Accumulation of biomass at fronts, Mar.
marine and freshwater ecosystems, in Stable Isotopes in Ecological
Ecol. Prog. Ser., 82, 1–12, 1992.
Research, Rundell, P.W., Ehleringer, J.R., Nagy, K.A., Eds.,
Franz, G., Hagen, W., Hempel, I., Marshall, H.-P., Marshall, S., Mizdal
Springer, New York, 1988, 169–229.
Shi, E., Die Winter-Expedition mit FS Polarstern in die Antarktkis
Fryxell, G.A., Marine phytoplankton at the Weddell Sea ice edge:
(ANT VII-3), Berichte zur Polarforschung, 39, 197–204, 1987.
Seasonal changes at the specific level, Polar Biol., 10, 1–18, 1989.
Fraser, F.C., On the development and distribution of the young stages of
Fryxell, G.A., Hasle, G.R., The genus Thalassiosira: T.trifuta sp. nov.,
krill (Euphausia superba), Discov. Rep., 14, 1–192, 1936.
and other species with tricolumnar support on strutted processes,
Fraser, W.R., Ainley, D.G., Ice edges and seabird occurrence in
Beihefte zur Nova Hedwiga, 64, 13–31, 1979.
Antarctica, BioScience, 36, 258–263, 1986.
Fryxell, G.A., Kendrick, G.A., Austral spring microalgae across the
Fraser, W.R., Patterson, D.L., Human disturbance and long-term
Weddell Sea ice edge: Spatial relationships found along a north-
changes in Adélie Penguin populations: A natural experiment at
ernward transect during AMERIEZ 83, Deep-Sea Res., 35, 1–20,
Palmer Station, Antarctic Peninsula, in Antarctic Communities: 1988.
Species, Structure and Survival, Battaglia, B., Valencia, J., Walton, Fryxell, G.A., Theriot, E.C., Buck, K.B., Phytoplankton, ice algae and
D.W.H., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1997, choanoflagellates from AMERIEZ, the Southern Atlantic, and
445–452. Indian Ocean, Antarc. J. U.S., 19, 107–109, 1984.
Fraser, W.R., Trivelpiece, W.Z., Ainley, D.G., Trivelpiecer, S.G., Fuhrman, J.A., Close coupling between release and uptake of dissolved
Increases in Antarctic penguin populations: Reduced competition free amino acids in seawater studied by isotope dilution approach,
with whales or a loss of sea ice due to environmental warming, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 37, 45–55, 1987.
Polar Biol., 11, 525–531, 1992. Fuhrman, J.A., Marine viruses and their biogeochemical and ecological
Fraser, T.H., Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Energetic demands of larval krill, effects, Nature (Lond.), 399, 541–548, 1999.
Euphausia superba, in winter, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 277, Fuhrman, J.A., Azam, F., Bacterioplankton secondary production
157–171, 2002a. estimates for coastal waters of British Columbia, Antarctica, and
Fraser, T.H., Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Abundance, sizes and develop- California, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 39, 1085–1095, 1980.
ment stages of larval krill, Euphausia superba, during winter in Fuhrman, J.A., Azam, F., Thymidine incorporation as a measure of
ice-covered seas west of the Antarctic Peninsula, J. Plankton Res., heterotrophic bacterioplankton in marine surface waters: Evalu-
24, 1067–1077, 2002b. ation and field results, Mar. Biol., 73, 79–89, 1982.
Friedberg, E.C., DNA Repair, W.H., Freeman, New York, 1985, 614. Fuhrman, J.A., McManus, G.B., Do bacteria-sized eucaryotes consume
Freyer, G., The food of some fresh-water cyclopoid copepods and its significant bacterial production?, Science, 224, 1257–1260, 1984.
ecological significance, J. Anim. Ecol., 26, 263–286, 1957. Fukami, K., Simidu, O., Taga, N., Microbial decomposition of phyto-
Freytag, C.E., Betrage zur Biologie von Notothenia rossii mamorata and zooplankton in seawater, 1: Changes in organic matter, Mar.
Fischer. MS thesis, University of Keil, 1977. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 21, 1–5, 1985a.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 557
Fukami, K., Simidu, O., Taga, N., Microbial decomposition of phyto- Gallardo, V.A., Castilla, J.G., Quantitative observations on the benthic
and zooplankton, 2: Changes in the bacterial community, Mar. macrofauna of Port Foster (Deception Island) and Chile Bay
Ecol. Prog. Ser., 21, 7–23, 1985b. (Greenwich Island), in Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 1, Holdgate,
Fukuchi, M., Chlorophyll a content in surface waters along the course of M.W., Ed., Academic Press, London, 1970, 242–243.
the Fuji to and from Antarctica in 1976–77, Antarc. Rec., 60, Gallardo, V.A., Castilla, J.G., Retamel, M., Yanez, A., Moyana, H.I.,
57–69, 1977. Hermosilla, H.G., Quantitative studies on the soft-bottom macro-
Fukuchi, M., Phytoplankton chlorophyll stocks in the Antarctic Ocean, benthic communities of shallow Antarctic bays, in Adaptations
J. Oceanogr. Soc. Jpn, 36, 73–84, 1980. within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G., Ed., Smithsonian Insti-
Fukuchi, M., Sasaki, H., Phytoplankton and zooplankton stocks and tution, Washington, DC, 1977, 361–387.
downward flux of particulate matter around the fast ice edge of Gambell, R., Seasonal cycles and reproduction in sei whales of the
Lützow-Holm Bay, Antarctica, Memoirs Natl Inst. Polar Res., 34, southern hemisphere, Discov. Rep., 35, 31–134, 1968.
52–59, 1981. Gambell, R., Seasonal cycles and reproduction in sei whales of the
Fukuchi, M., Tanimura, S., A preliminary note on the occurrence of southern hemisphere, Discov. Rep., 35, 35–133, 1972.
copepods under the sea ice near Syowa Station, Antarctica, Gambell, R., Some effects of exploitation on reproduction in whales,
Memoirs Nat. Inst. Polar Res., Special Issue, 52, 51–59, 1981. Journal of Reproduction and Fertility (Supplement), 19, 531–551,
Fukuchi, M., Tanimura, S., Chlorophyll a distribution in the Indian 1973.
sector of the Southern Ocean in 1978–1979, Antarc. Rec., 74, Gambell, R., Variations in reproductive parameters associated with
143–162, 1982. whale stock size, Intl. Whaling Committee Rep., 25, 182–189,
Fukuchi, M., Tanimura, S., Ohtsuka, H., Seasonal change of chlorophyll 1975.
a under fast ice in Lützow-Holm Bay, Antarctica, Memoirs Natl Gambell, R. in Population Biology and the Management of Whales,
Inst. Polar Res., Spec. Issue, 32, 51–59, 1984. Croker, T.H., Ed., Applied Biology, Vol. 1, Academic Press,
Fukuchi, M., Tanimura, S., Ohtsuka, H., Marine biological and oceano- London, 1976, 247–343.
graphical investigations in Lützow-Holm Bay, Antarctica, in Gambell, R., Dentinal layer formation in sperm whale teeth, in A Voyage
Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., of Discovery, Angel, M., Ed., Pergamon Press, London, 1977,
Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985a, 52–59. 583–590.
Fukuchi, M., Tanimura, S., Ohtsuka, H., Zooplankton community Gambell, J.C., Copepod grazing during a declining spring phytoplankton
conditions under the sea ice near Syowa Station, Antarctica, bloom in the North Sea, Mar. Biol., 49, 303–315, 1978.
Bulletin of Marine Science, 37, 518–528, 1985b. Gambell, R., Birds and mammals: Antarctic whales, in Key Environ-
Fukuchi, M., Fukuda, Y., Ohno, M., Hattori, H., Surface phytoplankton ments, Bonner, W.N., Walton, D.W.H., Eds., Pergamon Press,
chlorophyll distributions continuously observed in the JARE-26 Oxford, 1985, 223–241.
cruise (1984/85) to Syowa Station, Antarctica (SIBEX II), Gambell, R., How many great whales in Antarctica?, BIOMASS News-
Memoirs Natl Inst. Polar Res., 44, 15–23, 1986. letter, 10, 4, 1989.
Fukuchi, M., Hattori, H., Sasaki, H., Hoshiai, T., A phytoplankton bloom Gambi, M.C., Bussott, S., Composition, abundance and stratification of
and associated processes observed with a long-term moored system soft-bottom macrobenthos for selected areas of the Ross Sea
in Antarctic waters, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 45, 279–288, 1988. (Antarctica), Polar Biol., 21, 347–354, 1999.
Fukuda, Y., Ohno, M., Fukuchi, M., Surface chlorophyll a distribution in Gambi, M.C., Lorenzi, M., Russo, G.F., Scipione, M.B., Benthic
the marginal ice zone in Antarctica in 1984/85, Memoirs Natl Inst. associations of the shallow hard bottoms off Terra Nova Bay,
Polar Res., 44, 15–23, 1985. Ross Sea: Zonation, biomass, and population structure, Antarc.
Fukui, F., Otomo, K., Okabe, S., Nutrient depression in a blooming area Sci., 5, 449–462, 1994.
in Prydz Bay, Antarctica, Memoirs Natl Inst. for Polar Res., 44, Gammie, F., Breakaway ‘iceberg’ due to warming, Nature (Lond.),
43–54, 1986. 374(6518), 108, 1995.
Furness, R.W., Estimating the food requirements of seabird and seal Garrison, D.L., Marine planktonic diatoms, in Significance of Planktonic
populations and interactions with commercial fisheries and fish Life Cycles in Population Survival, Steidinger, K.A., Walker, L.M.,
stocks, in Proceedings of the Symposium on Sea and Shore Birds, Eds., CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1984, 1–17.
African Seabird Group, Capetown, Cooper, J., Ed., 1982, 1–14. Garrison, D.L., Antarctic sea ice biota, Am. Zoologist, 31, 17–34, 1991a.
Gain, L, La flore algaloique et subantarcticques, Seconde Expedition Garrison, D.L., An overview of the abundance and role of protozoo-
Antarctiques Francaise, Science naturalle Documentation Scien- plankton in Antarctic waters, J. Mar. Syst., 2, 317–331, 1991b.
tifique, Paris, 1912. Garrison, D.L., Buck, K.R., Microheterotrophs in the ice edge zone: An
Galeron, J., Herman, R.L., Arnaud, P.M., Antz, W.E., Hain, S., Klages, AMERIEZ study, Antarc. J. U.S., 21, 169–171, 1985a.
M., Macrofaunal communities on the continental shelf and slope of Garrison, D.L., Buck, K.R., Sea-ice algal communities in the Weddell
the southeastern Weddell Sea, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 12(2), Sea: Species composition in ice and plankton assemblage, in
283–290, 1992. Marine Biology of Polar Regions and Effects of Stress on Marine
Gales, N.J., Klages, N.T.W., Williams, R., Woehler, E.J., The diet of Organisms, Grey, J.S., Christiansen, M.E., Eds., Wiley, New York,
emperor penguins, Aptenodytes forsteri, in Admiralty Bay, Prin- 1985b, 103–122.
cess Elizabeth Land, Antarctica, Antarc. Sci., 2, 185–186, 1990. Garrison, D.L., Buck, K.R., Organism losses during ice melting: A
Gallardo, V.A., The sublittoral benthos of the Antarctic shelf, Environ. serious loss in sea ice community studies, Polar Biol., 6, 237–239,
Intl., 13, 71–81, 1988. 1986.
Gallardo, V.A., Castilla, J.G., Quantitative observations on the benthic Garrison, D.L., Buck, K.R., The biota of the Antarctic pack ice in the
infauna of Chile Bay (Greenwich Island, South Shetland Islands), Weddell Sea and Antarctic Peninsula region, Polar Biol., 10,
Gayana (Zoologı́a), 16, 3–18, 1969. 211–219, 1989a.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
558 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Garrison, D.L., Buck, K.R., Protozooplankton in the Weddell Sea, Gerdes, D., Klages, M., Antz, W.E., Herman, R.L., Galeron, J., Hain, S.,
Antarctica: Abundance and distribution in the ice edge zone, Quantitative investigations on macrobenthos communities of the
Polar Biol., 8, 341–351, 1989b. southeastern Weddell Sea based on multibox corer samples, Polar
Garrison, D.L., Buck, K.R., Surface layer assemblages in Antarctic pack Biol., 12, 291–301, 1992.
ice during austral spring: Environmental conditions, primary Gerdes, D., Hilbeg, B., Montiel, A., Impact of iceberg scouring on
production and community structure, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 75, macrobenthic communities in the high-Antarctic Weddell Sea,
161–172, 1991. Polar Biol., 26, 295–301, 2003.
Garrison, D.L., Close, A.I., Winter ecology of the sea ice biota in the Gersonde, R., Wefer, G., Sedimentation of biogenic siliceous particles in
Weddell Sea pack ice, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 96, 17–31, 1993. Antarctic waters (Atlantic Sector), Mar. Micropaleontol., 11,
Garrison, D.L., Gowing, M.M., Protozooplankton, in Antarctic Micro- 311–332, 1987.
biology, Friedman, E.I.F., Ed., Wiley-Liss, New York, 1992, Gibson, J.A.E., Garrick, R.C., Burton, H.R., McTaggert, A.R.,
123–165. Dimethylsulphide and the alga Phaeocystis pouchetti in Antarc-
Garrison, D.L., Mathot, S., Pelagic and sea ice microbial communities, ticAntarctic coastal waters, Mar. Biol., 104, 339–346, 1989.
Antarc. Res. Ser., 70, 155–172, 1996. Gibson, J.A.E., Garrick, R.C., Burton, H.R., Seasonal fluctuation of
Garrison, D.L., van Scoy, K., Wilkes Land Expedition 1985: Biological bacterial numbers near the Antarctic continent, Proc. NIPR Symp.
observations in the ice-edge zone, Antarc. J. U.S., 19, 123–124, Polar Biol., 3, 16–22, 1990.
1985. Giese, M., Effects of human activity on Adélie Penguins Pygoscelis
Garrison, D.L., Ackley, S.F., Buck, H.R., A physical mechanism for adeliae breeding success, Biological Conservation, 75, 157–164,
establishing ice algal populations in frazil ice, Nature (Lond.), 306, 1996.
363–365, 1983. Gieskes, W.W.C., Elbracher, M., Abundance of nanoplankton-size
Garrison, D.L., Buck, K.R., Silver, M.W., Microheterotrophs in the ice chlorophyll-containing particles caused by diatom disruption in
edge zone, Antarc. J. U.S., 19, 109–111, 1984. surface waters of the Southern Ocean (Antarctic Peninsula region),
Garrison, D.L., Sullivan, C.W., Ackley, S.F., Sea ice microbial commu- Neth. J. Sea Res., 20, 291–303, 1986.
nities in the ice-edge zone, Antarc. J. U.S., 19, 10–13, 1986a. Gieskes, W.W.C., Kray, G.W., Baars, M.A., Current 14C method for
Garrison, D.L., Sullivan, C.W., Ackley, S.F., Sea ice microbial commu- measuring primary production: Gross underestimates in oceanic
nities in Antarctica, BioScience, 36, 243–250, 1986b. waters, Neth. J. Sea Res., 13, 58–78, 1979.
Garrison, D.L., Buck, K.R., Fryxell, G.A., Algal assemblages in Gilbert, N.S., Microphytobenthic seasonality in near-shore marine
Antarctic pack ice and ice edge plankton, J. Phycol., 23, sediments at Signy Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica,
564–572, 1987. Estuarine, Coast. Shelf Sci., 33, 89–104, 1991a.
Garrison, D.L., Close, A.I., Gordon, L.I., in Sea Ice Processes and Gilbert, N.S., Primary production by benthic microalgae in nearshore
Properties, Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Labora- marine sediments of Signy Island, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 11,
tory (CRREL) Monograph 90-1, Ackley, S.F., Weeks, W.F., Eds., 339–346, 1991b.
35–59, 1989. Gilbert, J.R., Ericksen, A.W., Status of seals in pack ice of the pacific
Garrison, D.L., Buck, K.R., Gowing, M.M., Plankton assemblage in the sector of the Southern Ocean, in Adaptations within Antarctic
ice edge zone in the Weddell Sea during the austral winter, J. Mar. Ecosystems, Llano, G., Ed., Smithsonian Institution, Washington,
Syst., 2, 123–130, 1991. DC, 1977, 703–735.
Garrison, D.L., Buck, K.R., Gowing, M.M., Winter plankton assemblage Gilbert, P.M., Biggs, D.C., McCarthy, J.J., Utilization of ammonium and
in the ice edge zone of the Weddell and Scotia Seas: Composition, nitrate during austral summer in the Scotia Sea, Deep-Sea Res., 29,
biomass and spatial distributions, Deep-Sea Res., 40, 311–338, 837–850, 1982.
1993. Gill, A.E., Circulation and bottom water formation in the Weddell Sea,
Garside, C., Garside, J.C., The ‘f-ratio’ on 208 W during the North Deep-Sea Res., 20, 111–140, 1973.
Atlantic Bloom Experiment, Deep-Sea Res., 40, 75–90, 1993. Gille, S.T., Warming of the Southern Ocean since the 1950s, Science,
Gartshore, N.A., Steele, W.K., Klages, N.T.W., Summer diet of the 295, 1275–1277, 2002.
Salvin’s prion at sub-Antarctic Marion Island, S. Afr. J. Zool., 23, Gille, S.T., Kelly, K.A., Scales of spatial and temporal variability in the
309–313, 1988. Southern Ocean, J. Geophys. Res., 101, 8759–8773, 1996.
Gaskin, D.E., The evolution, zoogeography, and ecology of Cetacea, Gillespie, P.A., Morita, R.Y., Jones, L.P., The heterotrophic actvity for
Oceanogr. Mar. Biol: Annu. Rev., 14, 247–346, 1976. amino acids, glucose and acetate in Antarctic waters, Journal of the
Gaskin, D.E., The Ecology of Whales and Dolphins, Heinman, London, Oceanographical Society of Japan, 32, 4, 1976.
1982. Gilmour, A.E., McMurdo Sound hydrological observations 1972–73,
Geesey, G.G., Microbial exopolymers: Ecological and economic NZ. J. Mar. Freshwater Res., 9, 75–95, 1975.
considerations, Am. Soc. Microbiol. News, 48, 9–14, 1982. Gilmour, A.E., Ross Ice Shelf sea temperatures, Science, 203, 438–439,
George, R.W., Biology of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, 1979.
J. Crustacean Biol., 4(Special Issue No.1), 1984a, 537pp. Gilmour, A.E., MacDonald, W.J.P., van der Hoeven, F.G., Ocean
George, R.W., Ontogenetic adaptations in growth and respiration of currents in McMurdo Sound, Nature (Lond.), 474, 867–870, 1960.
Euphausia superba in relation to temperature and pressure, Gilmour, A.E., MacDonald, W.J.P., van der Hoeven, F.G., Winter
J. Crustacean Biol., 4(Special Issue No.1), 252–262, 1984b. measurements of sea currents in McMurdo Sound, NZ J. Geol.
Geraci, J.R., Pinniped nutrition, Rapports et Proces-Verbaux des Geophys., 5, 778–789, 1962.
Reunion Conseil Interntional Pour l’Exploration de la Mer, 169, Gilstard, M., Effects of photoperiod and irradiance on phytoplankton
312, 1975. growth. M.S. thesis, University of Trondheim, Norway, 1987.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 559
Gleitz, M., Kirst, G.O., Photosynthesis irradiance relationships and Goodall, R.N.P., Report on the small crustaceans stranded on the coast of
carbon metabolism of different ice algal assemblages collected Tierra del Fuego, Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 30, 197–223,
from the Weddell Sea pack ice during austral spring, Polar Biol., 1978.
11, 385–392, 1991. Goodall, R.N.P., Galeazzi, A.R., A review of the food habits of the small
Gleitz, M., Thomas, D.N., Variation in phytoplankton standing stock, cetaceans from the Atlantic and Sub-Antarctic, in Antarctic
chemical composition and physiology during sea ice formation in Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R.,
the southeastern Weddell Sea, Antarctica, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 566–572.
173, 211–230, 1993. Gordon, A.L., Structure of Antarctic waters between 208 W and 1708 W,
Gleitz, M., Kurtert, H., Riebsell, U., Dieckman, G.S., Carbon acquisition Antarctic Map Folio Series 6, American Geographical Society,
and growth of Antarctic sea ice diatoms in closed-bottle incu- 1967.
bations, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 135, 169–177, 1996. Gordon, A.L., Seasonality of the Southern Ocean sea ice, J. Geophys.
Glover, H.E., Smith, A.E., Shapiro, L., Diurnal variations in photosyn- Res., 86, 4193–4197, 1981.
thetic rates: Comparison of ultraphytoplankton with larger Gordon, A.L., Polar oceanography, Rev. Geophys. Space Phys., 21,
phytoplankton size fractions, J. Plankton Res., 7, 519–535, 1985. 1124–1131, 1983.
Godlewska, M., Vertical migration of krill (Euphausia superba Dana), Gordon, A.L., Spatial and temporal variability within the Southern
Polskie Archiwum Hydrobiologii, 43(1), 9–63, 1996. Ocean, in Antarctic Ocean and Resources Variability, Sahrhage,
Godlewska, M., Klusek, Z., Vertical distribution and diurnal migrations D., Ed., Springer, Berlin, 1988, 41–56.
of krill (Euphausia superba Dana) from hydroacoustical obser- Gordon, A.L., Goldberg, R.D., Circumpolar characteristics of Antarctic
vations, SIBEX, December 1983/January 1984, Polar Biol., 8, waters, Antarctic Map Folio Series 13, American Geographical
17–22, 1987. Society, Washington, DC, 1970.
Goeyens, L., Treguer, P., Lancelot, J., Mathot, S., Becquevort, S., Gordon, A.L., Huber, B.A., Physical oceanography program in the
Morvan, J., Dehairs, F., Baeyens, W., Ammonium regeneration US-USSR Weddell Sea Polyna Expedition—1981, Antarc. J. US,
17, 150–152, 1982.
in the Scotia-Weddell confluence area during spring 1978, Mar.
Gordon, A.L., Molinelli, E.M., The Southern Ocean Atlas: Thermoha-
Ecol. Prog. Ser., 78, 241–252, 1991.
line and Chemical Distribution and the Atlas Data Set, Columbia
Goeyens, L., Treguer, P., Baumann, M.E.M., Breyens, W., Dehairs, F.,
University Press, New York, 1982.
The leading role of ammonium in the nitrogen uptake regime of
Gordon, A.L., Owens, W.B., Polar oceans, Rev. Geophys., 25, 227–233,
Southern Ocean marginal ice zones, J. Mar. Syst., 6, 345–361,
1987.
1995.
Gordon, A.L., George, D.T., Taylor, H.W., Antarctic Polar Front Zone in
Goldman, J.C., Ocean nutrient cycles, in Flow of Energy and Materials
the western Scotia Sea: Summer 1975, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 7,
in Marine Ecosystems: Theory and Practice, Fasham, M.J.R., Ed.,
309–328, 1977a.
Plenum Press, New York, 1984a, 103, 130–176.
Gordon, A.L., George, D.T., Taylor, H.W., Antarctic oceanographic
Goldman, J.C., Conceptual role for microaggregates in pelagic waters,
zonation, in Polar Oceans, Dunbar, M.J., Ed., Arctic Institute of
Bull. Mar. Sci., 35, 462–476, 1984b.
North America, Calgary, 1977a, 45–76.
Goldman, J.C., Caron, D.A., Experimental studies on the omnivorous
Gordon, A.L., Molinelli, E.M., Baker, T., Large-scale relative dynamic
microflagellate: Implications for grazing and nutrient regeneration
topography of the Southern Ocean, J. Geophys. Res., 83,
in the marine microbial food chain, Deep-Sea Res., 32, 899–915,
3023–3032, 1978.
1985.
Gordon, A.L., Martinson, D.G., Taylor, H.W., The wind-driven circulation
Gomez, I., Wiencke, C., Weykam, C., Seasonal photosynthetic charac-
in the Weddell-Enderby Basin, Deep-Sea Res., 28A, 151–163, 1981.
teristics of Ascoseira mirabilis (Ascoscirales: Phaeophyta) from Gorelova, M., Gerasimchuk, V.V., Data on nutrition and daily consump-
King George Island, Antarctica, Mar. Biol., 123, 167–172, 1997. tion of juvenile Pleurogramma antarcticum Boulenger, in Fishes
Gon, O., Bovichtidae (thornfish), in Fishes of the Southern Ocean, Gon, of the Ocean, Parvin, N.V., Ed., Academy of Sciences, USSR,
O., Heemstra, P.C.H., Eds., J.L.B. Smith Institute of Ichthyology, Moscow, 1981, 103–109.
Grahamstown, South Africa, 1990, 277–278. Gorney, M., Untersuchungen zur Okologie antarktischer Garnelen
Gon, O., Heemstra, P.C. Fishes of the Southern Ocean, J.L.B. Smith (Decapoda: Natantia). Ph.D. thesis, University of Bremen,
Institute of Ichthyology, Grahamstown, South Africa, 1990. Germany, 1992.
Gonzales, H.E., Distribution and abundance of minipellets around the Goss, C., Everson, I., An acoustic survey of Antarctic krill on the South
Antarctic Peninsula: Implications for protistan feeding behaviour, Georgia shelf, CCAMLR Subarea 48.3, in January 1992,
Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 90, 223–236, 1992a. WG-Emm-96/42, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic
Gonzales, H.E., The distribution and abundance of krill fecal material Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 1996.
and oval pellets in the Scotia and Weddell Seas (Antarctica) and Goss, C., Bone, D.G., Peck, J.M., Everson, I., Hunt, G.L., Murray,
their role in particle flux, Polar Biol., 12, 81–89, 1992b. A.W.A., Small-scale interactions between prions (Pachyptila spp.)
Gonzales, H.E., The distribution and abundance of krill faecal material and their zooplankton prey at an inshore site near Bird Island,
and oval pellets in the Scotia and Weddell Seas (Antarctica) and South Georgia, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 154, 41–51, 1997.
their role in particle flux, in Weddell Sea Ecology, Hempel, G., Ed., Gouretski, V., The large-scale thermohaline structure of the Ross Sea
Springer, Berlin, 1995, 81–91. Gyre, in Oceanography of the Ross Sea, Spezie, G., Mabzella,
Gonzales, H.E., Kurbjeweit, F., Bathman, U.V., Occurrence of cyclo- G.M.R., Eds., Springer, Milan, 1999, 77–100.
poid copepods’ faecal material in the Halley Bay region, Gow, A.J., Ackley, S.F., Weeks, W.F., Gowing, J.W., Physical and
Antarctica, during January-February 1991, Polar Biol., 14, structural characteristics of Antarctic sea ice, Ann. Glaciol., 3,
331–342, 1994. 118–124, 1982.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
560 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Gow, A.J., Ackley, S.F., Buck, K.R., Golden, K.M., Physical and Grossi, S. McG., Response of a sea ice microalgal community to a
structural characteristics of Weddell Sea pack ice. Cold Reg. gradient in under ice irradiance, Ph.D Dissertation, University of
Res. Eng. Lab. Rep., 87-14-R, 1987. Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, 1985.
Gowing, M.M., Abundance and feeding ecology of Antarctic phaeo- Grossi, S.McG., Sullivan, C.W., Sea ice microbial communities, 5: The
darian radiolarians, Mar. Biol., 103, 107–118, 1989. vertical zonation of diatoms in an Antarctic fast ice community,
Gowing, M.M., Silver, M.W., Minipellets: A new and abundant size J. Phycol., 21, 401–409, 1985.
class of marine faecal pellets, J. Mar. Res., 43, 395–418, 1985. Grossi, S.McG., Kottmeier, S.T., Sullivan, C.W., Sea ice microbial
Gradinger, R., Integrated abundance and biomass of sympagic meio- communities, III: Seasonal abundance of microalgae and associ-
fauna in Arctic and Antarctic pack ice, Polar Biol., 22, 169–177, ated bacteria, McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Microb. Ecol., 10,
1999. 231–242, 1984.
Gran, H.H., Phytoplankton: Methods and problems, Journal du Conseil, Grossi, S.McG., Kottmeier, S.T., Moe, R.L., Taylor, G.T., Sullivan,
Conseil Permanent pour l’Exploration de la Mer, 8, 343–358, 1932. C.W., Sea microbial communities, VI: Growth and primary
Granata, A., Guglielmo, L., Greco, S., Vacchi, M., Sidali, O., Zagami, production in bottom ice under graded snow cover, Mar. Ecol.
G., Lathesa, M., Spatial distribution and feeding habitats of larval Prog. Ser., 35, 153–164, 1987.
and juvenile Pleurogramma antarcticum in the western Ross Sea, Grossman, S., Lochte, K., Scharek, R., Algal and bacterial processes in
in Ross Sea Ecology, Farando, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Ianora, A., platelet ice during late austral summer, Polar Biol., 16, 623–633,
Eds., Springer, New York, 1998, 369–393. 1996.
Graneli, E., Rabbani, M.M., Fransz, G., Granéli, W., Daugbjerg, N., Grua, P., Introduction ecologique invertebres de l’infralittoral rocheux
Cuzin-Roudy, J., Alder, V.A., The influence of copepod and krill dans Archipel de Kerguelen, CNFRA, 30, 1–66, 1971.
grazing on the species composition of phytoplankton communities Gruzov, E.N., Seasonal alterations in coastal communities in the Davis
from the Scotia-Weddell Sea: An experimental approach, Polar Sea, in Adaptations within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G., Ed.,
Biol., 13, 201–213, 1993. Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC, 1977, 263–278.
Grant, W.S., Horner, R.A., Growth responses to salinity variations in Gubsch, G., Investigation of krill (Euphausia superba Dana) off South
four Arctic ice diatoms, J. Phycol., 12, 180–185, 1976. Shetland Islands, ICES C.M.1979/L, 34–41, 1979.
Grantham, G.J., The Utilization of Krill, Southern Ocean Fisheries Gubsch, G., Zur Verbreitung und Biologie der Eisfische (Chaenichthyidae)
programme, FAO GLO/So/77/3, FAO, Rome, 1977. im atlantischen Sektor der Antarktis, Fischereiforschung, 20, 39–47,
Grassle, J.F., Sanders, H.L., Life histories and the role of disturbance, 1982.
Deep-Sea Res. 20, 643, 1973. Guglielmo, L., Granata, A., Greco, S., Distribution and abundance of
Gray, J.S., Antarctic marine benthic biodiversity in a worldwide postlarval and juvenile Pleurogramma antarcticum (Pisces:
latitudinal context, Polar Biol., 24, 633–641, 2001. Nototheniidae) off Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica), Polar
Green, K.A., Role of krill in the Antarctic marine ecosystem. Final Biol., 19, 37–51, 1998.
Report to the Department of State, Division of Ocean Affairs, Guillard, R.R.L., Kilham, P., The ecology of marine planktonic diatoms,
Contract, 1722-720248, 1977. in The Biology of Diatoms, Werner, D., Ed., University of
Green, K., Williams, R., Burton, H.R., The diet of Antarctic fur seals California Press, Berkeley, CA, 1977, 372–469.
during the late autumn and early winter around Heard Island, Guinet, C., Cherel, Y., Ridoux, V., Jouventin, P., Consumption of marine
Antarc. Sci., 3, 359–361, 1991. resources by seabirds and seals in Crozet and Kerguelen waters:
Green-Hammond, K.A., Modelling Antarctic ecosystems, in Biological Changes in relation to consumer biomass, Antarc. Sci., 8, 23–30,
Investigations of Antarctic Systems and Stiocks, the BIOMASS 1996.
Perspective, El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., SCAR SCOR, Cambridge, 1981, Gulland, J.A., The development of the resources of the Antarctic seas, in
22–45. Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 1, Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Academic Press,
Green-Hammond, K.A., Ainley, D.G., Diniff, D.B., Urquart, N.S., London, 1970, 217–223.
Selection criteria and monitoring requirements for indirect Gulland, J.A., Antarctic baleen whales: History and prospects, Polar
indicators of changes in the availability of Antarctic krill applied Rec., 18, 5–13, 1976.
to some pinniped and seabird information, Rep. US. Mar. Mammal Gulland, J.A., The development of fisheries and stock assessment of
Comm., 1983. resources in the Southern Ocean, Mem. Nat. Inst. Polar Res. Spec.
Grinley, J.R., David, P., Nutrient upwelling and its effect in the lee of Issue, 27, 233–246, 1983a.
Marion Island, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Gulland, J.A., Fish stock assessment: A manual of basic methods,
Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, FAO/Wiley Series on Food and Agriculture, Vol. 1, Wiley ,
Berlin, 1995, 46–51. Chichester, 1983b.
Grinley, J.R., Lane, S.B., Zooplankton around Marion and Prince Gulland, J.A., Comments and questions on ecosystem management,
Edward Islands, CNFRA, 44, 111–125, 1979. Selected Papers Presented to the Sci. Comm. CCAMLR, Part II,
Groscholas, R., Study of the moult fasting followed by an experimental Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living
forced fasting in the Emperor penguin Aptenodytes forsteri: Resources, Hobart, 179–201, 1985.
Relationship between feather growth, body weight loss, body Gulland, J.A., Antarctic treaty system as a resource management
temperature, and plasma fluid level, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., mechanism—living resources, in Antarctic Treaty System, National
61A, 287–295, 1978. Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC, 221–234 pp, 1986.
Groscolas, R., Clement, C., Utilization des reserves energetiques au Gunther, E.R., The habits of whales, Discov. Rep., 25, 113–142, 1949.
cours jeline de la reproduction cnez le manchot emperor Apteno- Günther, S., Dieckmann, G.S., Vertical zonation and community
dytes forsteri, Comptes-Rendus de l’Académie des Sciences transition of sea-ice diatoms in fast ice and platelet layers in the
(Paris), Série D, 282, 297–303, 1976. Weddell Sea, Antarctica, Antarc. Sci., 11, 305–315, 2001.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 561
Günther, S., George, K.H., Gleitz, M., High sympagic metazoan Hamada, E., Numanami, H., Naito, Y., Taniguchi, A., Observation of the
abundance in platelet layers at Drescher Inlet, Weddell Sea, marine benthic organisms at Syowa Station in Antarctica using a
Antarctica, Polar Biol., 22, 82–89, 1999. remotely-operated vehicle, Mem. Nat. Inst. Polar Res. Special
Günther, S., Gleitz, M., Dieckmann, G.S., Biogeochemistry of Antarctic Issue, 40, 289–298, 1986.
sea ice: A case study on platelet ice layers at Drescher Inlet, Hamilton, J.E., The leopard seal, Hydrurga leptonyx (de Blainville),
Weddell Sea, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 177, 1–13, 1999. Discovery Rep., 18, 239–264, 1939.
Gustafsen, D.E., Jr., Anderson, M.R., Rivkin, R.B., Bacterioplankton Hamner, W.M., Aspects of schooling in Euphausia superba, J. Crust.
abundance and productivity at the ice-edge zone of McMurdo Biol., 4(Special Issue No.1), 67–74, 1984.
Sound, Antarctica, Antarc. J. US, 25, 191–193, 1990. Hamner, W.M., Hamner, P.R., Stroud, S.W., Gilmer, R.W., Behaviour of
Gutt, J., Zur Verbreitung und Okdeg und Okelegie der Seegarken Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba: Chemoreception, feeding,
(Holothuroidea: Echinodermata) im Weddellmeer (Antarcktis), schooling, and molting, Science, 220, 433–435, 1983.
Ber. Polarforsch., 41, 1–87, 1988. Hamner, W.M., Hamner, P.R., Obst, B.S., Carleton, J.H., Field obser-
Gutt, J., Some ‘driving forces’ structuring communities of the subtidal vations on the ontogeny of schooling of Euphausia superba
Antarctic macrobenthos, Antarc. Sci., 12(3), 297–313, 2000. furciliae and its relationship to ice in Antarctic waters, Limnol.
Gutt, J., On the distribution and ecology of holothurians in the Weddell Oceanogr., 34, 451–456, 1989.
Sea (Antarctica), Polar Biol., 11, 312–329, 1991a. Hampton, I., Preliminary report of the FIBEX acoustic work to estimate
Gutt, J., Investigations on brood protection in Psolus dubiosus (Echino- the abundance of Euphausia superba, Mem. Nat. Inst. Polar Res.
dermata: Holothuroidea) from Antarctica in spring and autumn, Special Issue, 27, 165–175, 1983.
Mar. Biol., 11, 533–544, 1991b. Hampton, I., Abundance, distribution, and behaviour of Euphausia
Gutt, J., On direct impact of ice on marine benthic communities: A superba in the Southern Ocean between 158 and 308 during
review, Polar Biol., 24, 553–564, 2001. FIBEX, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried,
Gutt, J., Piepenburg, D., Scale-dependent impact on diversity of W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985,
Antarctic benthos caused by grounding of icebergs, Mar. Ecol. 294–303.
Prog. Ser., 253, 77–83, 2003. Hanelt, D., Melchersmann, B., Wiencke, C., Nultscher, W., Effects of
Gutt, J., Starmans, A., Quantification of iceberg impact and benthic high light stress on photosynthesis of polar macroalgae in relation
recolonization patterns in the Weddell Sea (Antarctica), Polar to depth distribution, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 149, 255–266, 1997.
Biol., 24, 615–619, 2001. Haney, T.F., Diel patterns of zooplankton behaviour, Bull. Mar. Sci., 43,
Gutt, J., Starmans, A., Dieckmann, G., Impact of iceberg scouring on 583–603, 1988.
polar benthic habitats, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 137, 311–316, 1996. Hanks, J., Characteristics of population conditions, in Dynamics of
Gutt, J., Sirenko, B.I., Smirov, I.S., Arntz, W.E., How many macro- Large Mammal Populations, Fowler, C.W., Smith, T.D., Eds.,
benthic species might inhabit the Antarctic shelf? Antarc. Sci., 16, Wiley, New York, 1981, 47–73.
Hannah, F.J., Boney, A.D., Nanoplankton in the Firth of Clyde, Scot-
11–16, 2004.
land: Seasonal abundance, carbon fixation and species
Guzman, D., Distribution and abundance of Antarctic krill (Euphausia
composition, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 67, 105–147, 1983.
superba) in the Bransfield Strait, Ber. Polarforsch., 4, 169–190,
Hanson, R.B., Lowery, H.K., Spatial distribution, structure, biomass, and
1983.
physiology of microbial assemblages across the Southern Ocean
Gutzmann, E., Martinez, A.P., Rose, A., Viet-Kohler, G., Meiofauna
frontal zones during the late austral winter, Appl. Environ.
communities along an abyssal gradient in the Drake Passage,
Microbiol., 49(5), 1029–1035, 1985.
SCAROpen Science Conference, Abstracts, 172 pp, 2004.
Hanson, R.B., Lowery, H.K., Shafer, D., Sorocco, R., Pope, D.H.,
Guzman, O., Marin, B., Hydroacoustic and photographic techniques
Microbes in Antarctic waters of the Drake Passage: Vertical
applied to study the behaviour of krill (Euphausia superba), Mem.
patterns of substrate uptake, productivity, and biomass in January
Nat. Inst. Polar Res. Special Issue, 17, 129–152, 1983.
1980, Polar Biol., 2, 179–188, 1983.
Hader, P., Worrest, R.C., Effects of enhanced solar ultraviolet radiation
Hanson, R.B., Shafer, D., Pole, D.H., Lowery, H.K., Bacterioplankton in
on aquatic ecosystems, Phytochem. Phytobiol., 53, 717–725, 1991.
Antarctic Ocean waters during the late austral winter: Abundance,
Hagen, W., On the significance of lipids in Antarctic zooplankton, Ber.
frequency of dividing cells, and estimates of production, Appl.
Polarforsch., 49, 103–120, 1988.
Environ. Microbiol., 45(5), 1622–1632, 1983.
Hagen, W., Kattner, G., Tergruggen, A., van Vleet, E.S., Lipid
Hara, S., Tanoue, E., Zenimata, M., Komaki, Y., Takashi, E., Hepero-
metabolism of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) and its eco-
trophic processes along a transect of 708E in the Southern Ocean,
logical implications, Mar. Biol., 139, 95–104, 2001.
Mem. Nat. Inst. Polar Res. (Special Issue), 40, 69–80, 1986.
Hain, S., Die beschalten benthischen Mollusken (Gastropoda and
Hardy, A.C., Great Waters, Collins, London, 1967.
Bivalvia) des Weddellmeeres, Antarktis, Ber. Polarforsch., 70,
Hardy, P., Biomass estimates for some shallow-water infaunal commu-
1–181, 1990.
nities at Signy Island, South Orkney Islands, Br. Antarc. Surv.
Hall, J.A., Barre, H., Jaines, M.B., The importance of phytoflagellate,
Bull., 31, 93–106, 1972.
heteroflagellate and ciliate grazing on bacteria and phytoplankton
Hardy, A.C., Günther, E.R., The plankton of the South Georgia whaling
sized prey in a coastal marine environment, J. Plankton Res., 15,
grounds and adjacent waters, 1926–1927, Discov. Rep., 11, 1–456,
1075–1086, 1993.
1936.
Hallegraeff, G.M., Seasonal study of phytoplankton pigments and
Hargraves, B.T., The importance of total and mixed-layer depth in the
species composition at a coastal station off Sydney: Importance supply of organic material to bottom consumers, Symp. Biol.
of diatoms and nanoplankton, Mar. Biol., 61, 107–118, 1984. Hung., 15, 157–165, 1975.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
562 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Harper, P.C., Knox, G.A., Spurr, E.B., Taylor, R.H., Wilson, G.J., Heath, G.R., Mineralogy of Cenozoic deep-sea sediments from
Young, E.C., The status and conservation of birds in the Ross the equatorial Pacific Ocean, Geol. Soc. Am. Bull., 80(10),
Sea sector of Antarctica, in The Status and Conservation of the 1997–2018, 1969.
World’s Seabirds, International Council for Bird Preservation Heath, R.A., Circulation and hydrology under the seasonal ice in
Technical Publication No. 2, 593–608, 1984. McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, N.Z. J. Mar. Freshwat. Res., 5,
Harris, G.P., The measurement of photosynthesis in natural populations 497–515, 1971.
of phytoplankton, in The Physiological Ecology of Phytoplankton, Heath, G.R., Dissolved silica and deep-sea sediments, in Studies in
Morris, J., Ed., University of California Press, Berkeley, CA, 1980, Paleooceanography, Hay, W.W., Ed., Society of Economic
129–187. Paleontologists and Mineralogists Special Publication 20, 1974,
Harris, G.P., Comparison of the feeding behaviour of Calanus and 77–93.
Pseudocalanus in experimentally-manipulated enclosed systems, Heath, R.A., Circulation across the ice shelf edge in McMurdo Sound,
J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK, 62, 71–91, 1982. Antarctica, in Polar Oceans, Dunbar, M.J., Ed., Arctic Institute of
Harrison, R.J., Reproduction and reproductive organs, in Biology of North America, Calgary, 1977, 129–149.
Marine Mammals, Anderson, T.H., Ed., Academic Press, New Hebling, E.W., Marguet, E.R., Villafane, V.E., Holm-Hansen, O.,
York, 1969, 253–348. Bacterioplankton viability in Antarctic waters as affected by
Harrison, W.G., Respiration and its size-dependence in microplankton solar ultraviolet radiation, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 123, 296–298,
populations from the surface waters of the Canadian Arctic, Polar 1995.
Biol., 6, 145–152, 1986. Hecq, J.H., Brasseur, P., Goffart, A., Lacroix, G., Guglielmo, I.,
Harrison, G.R., Observations on the epipelagic gelatinous fauna of Modelling approach of the planktonic vertical structure in deep
McMurdo Sound, Antarc. J. U.S., 23, 135–136, 1988. Austral Ocean: The example of the Ross Sea ecosystem, in Belgian
Harrison, W.G., Platt, T., Photosynthesis-irradiance relationships in Oceanographic Research, Proceedings of the Annual Workshop on
polar and temperate phytoplankton populations, Polar Biol., 5, Belgian Oceanographic Research, Academy of Sciences, Brussels,
153–164, 1986. 235–249, 1993.
Harrison, W.G., Platt, T., Irwin, B., Primary production and nutrient Hecq, J.H., Guglielmo, L., Goffart, A., Catalano, G., Goosse, H., A
assimilation by natural phytoplankton populations of the eastern modelling approach to the Ross Sea plankton ecosystem, in Ross
Canadian Arctic, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 39, 335–345, 1982. Sea Ecology, Farando, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Ianora, A., Eds.,
Hart, T.J., On the phytoplankton of the southwest Atlantic and the Springer, Berlin, 1998, 395–411.
Bellinghausen Sea, Discovery Rep., 8, 1–268, 1934. Hedgpeth, J.W., Introduction to Antarctic zoogeography, Antarctic Map
Hart, T.J., Phytoplankton periodicity in Antarctic surface waters, Folio Series Vol. 2, American Geographical Society, Washington,
Discovery Rep., 21, 261–356, 1942. DC, 1–9 pp, 1969.
Hartman, O., Larval development of benthic invertebrates in Antarctic Hedgpeth, J.W., Marine biogeography of the Antarctic regions, in
Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 1, Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Academic
seas: Early development of Nothria notialis (Monro) and Paronu-
Press, London, 1970, 97–104.
phis antarctica (Monro) in Bransfield Strait, Antarctica Peninsula,
Hedgpeth, J.W., Perspectives of benthic ecology in Antarctica, in
JARE Sci. Rep. Spec. Issue, 1, 205–208, 1967.
Research in Antarctica, American Association for the Advance-
Hasle, G.R., Nitzschia and Fragilariopsis species studied in the light and
ment of Science Publication No. 9, Quasim, L.O., Ed., American
electron microscopes, I: Some marine species of the groups
Association for the Advancement of Science, Washington, DC,
Nitzschiella and Lanceolata, Skr. Norske Videnskaps-Akademi,
1977a, 667–684.
16, 1–48, 1964.
Hedgpeth, J.W., The Antarctic marine ecosystem, in Adaptations within
Hasle, G.R., Nitzschia and Fragilariopsis species studied in the light and
Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smithsonian Institution,
electron microscopes, III: The genus Fragilariopsis, Skr. Norske
Washington, DC, 1977b, 3–10.
Videnskaps-Akademi, 21, 1–49, 1965.
Heinbokel, J.F., Beeres, J.R., Studies on the functional role of tintinnids
Hasle, G.R., An analysis of the phytoplankton of the Pacific Southern
in the Southern California Bight III: Grazing impact on natural
Ocean: Abundance, composition, and distribution during the
assemblages, Mar. Biol., 52, 23–32, 1979.
Brategg Expedition, 1947–48, Hvalradets Skr., 52, 1–168, 1969.
Heinbokel, J.F., Coats, D.W., Reproductive dynamics of ciliates in the
Hay, M.E., Fenical, W., Chemical mediation of seaweed-herbivore
ice-edge zone, Antarc. J. U.S., 19, 111–113, 1984.
interactions, in Plant-Animal Interactions in the Marine Benthos,
Heinbokel, J.F., Coats, D.W., Ciliates and nanoplankton in Arthur
John, D.M., Hawkins, S.J., Price, J.H., Eds., Clarendon press,
Harbor, December 1984 and January 1985, Antarc. J. U.S., 19,
Oxford, 1992, 319–337.
135–136, 1985.
Hay, C.H., Adams, N., Parsons, N.M., Marine algae of the subantarctic
Heinbokel, J.F., Coats, D.W., Patterns of tintinnine abundance and
islands of New Zealand, National Museum of New Zealand
reproduction near the edge of the seasonal pack ice in the
Miscellaneous Series No. 11, 1985.
Weddell Sea, November 1983, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 33, 71–80,
Hayes, P.K., Whitaker, T.M., Fogg, G.E., Distribution and nutrient status
1986.
of phytoplankton in the Southern Ocean between 208 and 708 W,
Heine, A.J., Seals at White Island, Antarctic, 2, 272–273, 1960.
Polar Biol., 3, 153–165, 1984. Heinle, D.R., Flemer, D.A., Carbon requirements of a population of the
Hays, J.D., Climatic record of Late Cenozoic Antarctic Ocean sediments estuarine copepod Eurytemora affinis, Mar. Biol., 31, 235–247,
related to the record of world climate, in Paleoecology of Africa 1975.
and the Surrounding Islands and Antarctica, van Zinderen Bakker, Heinle, D.R., Harris, R.P., Ustach, J.F., Flemer, D.A., Detritus as a food
E.M., Ed., A.A. Balkkema, Capetown, 1969, 139–164. for estuarine copepods, Mar. Biol., 40, 341–353, 1977.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 563
Heip, C., Vinex, M., Vranken, G., The ecology of marine nematodes, Hempel, I., Hempel, G., Field observations on the developmental ascent
Oceanogr. Mar. Biol., Annu. Rev., 23, 399–484, 1985. of larval Euphausia superba (Crustacea), Polar Biol., 6, 121–126,
Helbling, E.W., Villafane, V., Holm-Hansen, O., Effect of iron on 1986.
productivity and size distribution of Antarctic phytoplankton, Hempel, G., Manthey, M., On the fluoride content of larval krill,
Limnol. Oceanogr., 36, 1879–1885, 1991. Meeresforschung/Rep. Mar. Res., 29, 60–63, 1981.
Helbling, E.W., Villafane, V., Ferrario, M., Holm-Hansen, O., Impact of Hempel, I., Hempel, G., Baker, A.deC., Early life history stages of krill
natural ultraviolet radiation on rate of photosynthesis and on (Euphausia superba) in Bransfield Strait and Weddell Sea, Meer-
specific marine phytoplankton species, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 80, esforschung, 27, 267–268, 1979.
89–100, 1992. Hense, I., Bathmann, U.K., Timmermann, R., Plankton dynamics in frontal
Helbling, E.W., Villafane, V., Holm-Hansen, O., Effects of ultraviolet systems of the Southern Ocean, J. Mar. Syst., 27, 235–252, 2000.
radiation on Antarctic marine phytoplankton photosynthesis, with Herberg, L.-M., Thomas, P.N., Kennedy, H.H., Dieckmann, G.S.,
particular attention to the influence of mixing, Antarc. Res. Ser., Dissolved carbohydrates in Antarctic sea ice, Antarc. Sci., 13(2),
62, 207–227, 1994. 119–125, 2001.
Helbling, E.W., Marguet, E.R., Villafane, V., Holm-Hamsen, O., Bacter- Herman, R.L., Dahms, H.U., Meiofauna communities along a depth
ioplankton viability in Antarctic waters as affected by solar transect off Halley Bay (Weddell Sea, Antarctica), Polar Biol., 12,
ultraviolet radiation, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 127, 293–298, 1995. 313–320, 1992.
Hellebust, J.A., Extracellular products, in Algal Physiology and Hernandez-Leon, S., Portillo-Hahnefeld, A., Almaida, G., Becongee, R.,
Biochemistry, Stewart, W.D.P., Ed., University of California Moreno, I., Diel feeding behaviour of krill in Gerlache Strait,
Press, Berkeley, CA, 1974, 838–893. Antarctica, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 223, 235–242, 2001.
Hellebust, J.A., Lewin, J., Heterotrophic nutrition, in The Biology of Herndl, G.J., Peduzzi, P., The ecology of amorphous aggregations
Diatoms, Werner, D., Ed., University of California Press, Los (marine snow) in the Northern Adriatic Sea, 1: General consider-
Angeles, CA, 1977, 169–178. ations, Mar. Ecol., 9, 79i–99, 1988.
Hellmer, H.H., Bersch, M., Augstein, E., Grabmann, I., The Southern Hewes, C.D., Holm-Hansen, O., Sakshaug, E., Nanoplankton and
Ocean: A survey of oceanographic and marine meterological microplankton studies during the Circumnavigation Cruise,
research work, Ber. Polarforsch., 26, 1–115, 1985. Antarc. J. U.S., 18, 169–173, 1983.
Hemmingsen, E.A., Douglas, E.L., Respiratory characteristics of the Hewes, C.D., Holm-Hansen, O., Sakshaug, E., Alternate carbon
haemoglobin-free fish Chaenocephalus aceratus, Comp. Biochem. pathways at the lower trophic levels in the Antarctic food web,
Physiol., 33, 733–744, 1970. in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R.,
Hemmingsen, E.A., Douglas, E.L., Respiratory and circulatory adap- Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 277–283.
tations to the absence of haemoglobin in Chaenichthyid fishes, in Hewes, C.D., Sakshaug, E., Reid, F.M.H., Holm-Hansen, O., Microbial
Adaptations within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G., Ed., Gulf autotrophic and heterotrophic eucaryotes in Antarctic waters:
Publishing Company, Houston, TX, 1977, 479–487. Relationships between biomass and chlorophyll, adenosine tripho-
Hempel, G., Antarctica, in Fish Resources of the Ocean, Gulland, J.A., sphate and particulate organic carbon, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 63,
Ed., FAO, Rome, 1970. 27–35, 1990.
Hempel, I., Vertical distribution of eggs and nauplii of krill (Euphausia Hewitt, R.P., Demer, D.A., Dispersion and abundance of Antarctic krill
superba) south of Elephant Island, Meeresforschung, 29, 53, 1978. in the vicinity of Elephant Island in the 1992 austral summer, Mar.
Hempel, I., Studies on eggs and larvae of Euphausia superba and Ecol. Prog. Ser., 99, 29–39, 1993.
Euphausia crystallorophias in the Atlantic Sector of the Southern Heyerdahl, E.F., Hvalindustrien Kommander Chr. Christensens Hval-
Ocean, Ber. Polarforsch., 4, 30–46, 1983. fangstrumuseum, Sandjeford. Publication No. 7, 1932.
Hempel, G., On the biology of polar seas, particularly the Southern Heywood, R.B., Light, J.J., First direct evidence of life under the
Ocean, in Marine Biology of Polar Regions and Effects of Stress on Antarctic Ice Shelf, Nature (Lond.), 254, 591–593, 1978.
Marine Organisms, Gray, J.S., Christiansen, M.E., Eds., Wiley, Heywood, R.B., Priddle, J., Retention of phytoplankton in an eddy, Cont.
Chichester, 1985a, 3–33. Shelf Res., 7, 937–955, 1987.
Hempel, G., Antarctic marine food webs, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles Heywood, R.B., Whitaker, T.M., The Antarctic marine flora, in
and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 2, Laws, R.M., Ed., Academic Press,
Springer, Berlin, 1985b, 266–270. London, 1984, 373–419.
Hempel, I., Vertical distribution of larvae of Antarctic krill, Euphausia Heywood, R.B., Everson, I., Priddle, J., The absence of krill from the
superba, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, South Georgia zone, winter 1983, Deep-Sea Res., 32, 369–378,
W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 1985.
308–310. Hicks, G.R.F., Variation in zooplankton biomass with hydrological
Hempel, I., Variation in geographical distribution and abundance of regime beneath the seasonal ice, McMurdo Sound, Antarctica,
larvae of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, in the Southern N.Z. J. Mar. Freshwat. Res., 8, 67–77, 1974.
Atlantic Ocean, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Higgenbottom, R., Hosie, G.W., Biomass and population structure of a
Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, large aggregation of krill near Prydz Bay, Antarctica, Mar. Ecol.
Berlin, 1985, 304–307. Prog. Ser., 58, 197–203, 1989.
Hempel, G., The krill-dominated pelagic system of the Southern Ocean, Hill, K.T., Radthe, R.L., Gerontological studies on the damsel fish
Environ. Int., 13, 33–36, 1987. Dascyllus albisella, Bull. Mar. Sci., 42, 424–434, 1988.
Hempel, I., Hempel, G., Larval krill (Euphausia superba) in the plankton Hill, K.T., Womersley, C., Critical aspects of fluorescent age-pigment
and neuston samples of the German Antarctic Expedition 1975/76, methodologies: Modification for accurate analysis and age assess-
Meeresforschung, 26, 206–216, 1978. ments in aquatic organisms, Mar. Biol., 109, 1–11, 1991.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
564 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Hinton, M.A.C., Report of papers left by the late Major Barrett- Holm-Hansen, O., Mitchell, B.G., Spatial and temporal distribution of
Hamilton, relating to the whales of South Georgia, Crown phytoplankton and primary production in the western Bransfield
Agents for the Colonies, London, 1925, 57–209. Strait, Deep-Sea Res., 38, 961–980, 1991.
Hobbie, J.E., Holm-Hansen, O., Packard, T.T., Pomeroy, L.R., Sheldon, Holm-Hansen, O., El-Sayed, S.Z., Franceschini, G.A., Cuhel, G.A.,
R.W., Thomas, J.P., Wiebe, W.J., A study of the distribution of Cuhel, R.L., Primary production and the factors controlling
activity of microorganisms in ocean water, Limnol. Oceanogr., 17, phytoplankton growth in the Southern Ocean, in Adaptations
554–555, 1972. within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smithsonian Insti-
Hobson, K.A., Stable isotope determinations of the trophic relationships tution, Washington, DC, 1977, 11–73.
of seabirds: Preliminary investigations of alcids from coastal Holm-Hansen, O., Azam, F., Cambell, L., Carlucci, A.F., Karl, D.M.,
British Columbia, in Studies of High-Latitude Seabirds, 1: Beha- Microbial life beneath the Ross Ice Shelf, Antarc. J. U.S., 13,
vioral, Energetic and Oceanographic Aspects of Seabird Feeding 129–130, 1978.
Ecology, Occasional Paper No. 88, Canadian Wildlife Service, Holm-Hansen, O., Neori, A., Koike, I., Phytoplankton distribution,
Ottawa, 16–20 pp, 1991. biomass, and activity in the southwest Ross Sea, Antarc. J. U.S.,
Hobson, L.A., Menzel, D.W., Barber, R.T., Primary productivity and 17, 150–152, 1982.
sizes of parts of organic carbon in the mixed layers of the ocean, Holm-Hansen, O., Mitchell, B.G., Hewes, C.P., Karl, D.M., Phyto-
Mar. Biol., 19, 298–306, 1973. plankton blooms in the vicinity of Palmer Station, Polar Biol.,
Hodgson, R.E., Azam, F., Carlucci, A.F., Fuhrman, J.A., Karl, D.M., 10, 49–57, 1989.
Holm-Hansen, O., Microbial uptake of dissolved organic matter in Holm-Hansen, O., Helbling, E.W., Lubin, D., Ultraviolet radiation in
McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Mar. Biol., 71, 89–94, 1981. Antarctica: Inhibition of primary production, Photochem. Photo-
Hoepffner, N., Strategies d’adaption photosynthetiques chez les diato- biol., 58, 567–570, 1993.
mees de l’Ocean Antarctique: Variations du nombre et de la tailles Holm-Hansen, O., Villefane, V.E., De Vries, E.W., Effects of solar
des unites photosynthetiques, J. Plankton Res., 6, 881–895, 1984. ultraviolet radiation on primary production in Antarctic waters, in
Hofmann, E.E., Huntly, M.E., GLOBEC: Southern Ocean Program: Antarctic Communities: Species, Structure and Survival,
GLOBEC Workshop on Southern Ocean on Marine Mammal Baggatalia, B., Valencia, J., Walton, D.W.H., Eds., Cambridge
Animal Populations and Global Change, U.S. GLOBEC Reports University Press, Cambridge,UK, 1997, 375–380.
No. 5, 1991. Holt, S., Marine fisheries, in Oceans Yearbook, Vol. 1, Beregse, E.M.,
Hofmann, E.E., Murphy, E.J., Advection, krill and the Antarctic marine Ginsberg, N., Eds., Chicago University Press, Chicago, IL, 1978,
ecosystem, Antarc. Sci., 16, 487–499, 2004. 38–83.
Hofman, R., Erickson, A., Siniff, D., The Ross Seal (Ommatophoca Honjo, S., Roman, M.R., Marine copepod fecal pellets: Production,
rossii), International Union for the Conservation of Nature and preservation and sedimentation, J. Mar. Res., 36, 45–57, 1978.
Natural Resources Publication New Series Supplementary Paper Hooker, J.D., Diatomaceae, in The Botany of the Antarctic Voyage of
No. 39, 1973, 129–139. H.M. Discovery Ships Erebus and Terror, Years 1839–1843, Vol.
Hofman, R., Reichle, R., Siniff, D.B., Muller-Schwarze, D., The leopard LVI, London, 1847, 503–521.
seal (Hydrurga leptonyx) at Palmer Station, Antarctica, in Adap- Hopkins, T.L., Zooplankton standing crop in the Pacific sector of the
tations within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smithsonian Antarctic, in Biology of the Antarctic Sea VI, Antarctic Research
Institution, Washington, DC, 1977, 769–782. Series, Vol. 17, Llano, G.A., Wallen, I.E., Eds., American
Hofmann, E.E., Klinck, J.M., Lascara, C.M., Smith, D.A., Water mass Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, 1971, 347–362.
distribution and circulation west of the Antarctic Peninsula, Hopkins, T.L., The zooplankton community of Croker Passage,
Antarc. Res. Ser., 70, 61–80, 1996. Antarctic Peninsula, Polar Biol., 4, 161–170, 1985a.
Holden, M.J., Long-term changes in landings of fish from the North Sea, Hopkins, T.L., Food webs of an Antarctic midwater ecosystem, Mar.
Rapp. P.-V. de la Reun. Conseil Permanent International de la Biol., 89, 197–212, 1985b.
Mer, 172, 11–26, 1978. Hopkins, T.L., Midwater food web in McMurdo Sound, Ross Sea,
Holdgate, M.W., The Antarctic ecosystem, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., Antarctica, Mar. Biol., 96, 93–106, 1987.
Ser. B, 152, 363–383, 1967. Hopkins, T.L., Lancraft, T.M., The composition and standing stock of
Holeton, G.F., Oxygen uptake and circulation by a haemoglobinless mesopelagic micronekton at 278 N 868 W in the eastern Gulf of
Antarctic fish (Chaenocephalus aceratus Lönnberg) compared Mexico, Contrib. Mar. Sci., Univ. Tex., 27, 143–158, 1984.
with three red-blooded Antarctic fish, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., Hopkins, T.L., Torres, J.J., Midwater food web in the vicinity of a
34, 447–471, 1970. marginal ice zone in the western Weddell Sea, Deep-Sea Res., 36,
Holeton, G.F., Metabolic cold adaptation of polar fish: Fact or artefact?, 543–561, 1989.
Physiol. Zool., 47, 137–152, 1974. Hopkins, T.L., Ainley, D.G., Torres, J.J., Lancraft, L.M., Trophic
Holm-Hansen, O., Microbial uptake of dissolved organic matter in structure in open waters of the marginal ice zone in the Scotia-
McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Mar. Biol., 61, 89–94, 1981. Weddell Confluence region during spring (1983), Polar Biol., 13,
Holm-Hansen, O., Nutrient cycles in Antarctic marine ecosystems, in 389–397, 1983.
Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, Hopkins, T.L., Lancraft, T.M., Torres, J.J., Donnelly, J., Community
P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 6–10. structure and trophic ecology of zooplankton in the Scotia Sea
Holm-Hansen, O., Forster, T.D., A multidisciplinary study of the eastern marginal ice zone in winter (1978), Deep-Sea Res., 40, 81–105,
Scotia Sea, Antarc. J. U.S., 16, 159–160, 1981. 1993.
Holm-Hansen, O., Huntley, M., Feeding requirements of krill in relation Hoppe, H.G., Blue-green algae agglomeration in surface waters: A
to food sources, J. Crust. Biol., 4(Special Issue No.1), 156–173, microbiotope of high bacterial activity, Kiel. Meeresforsch., 5,
1984. 291–303, 1981.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 565
Hoppe, H.G., Attachment of bacteria -advantage or disadvantage for Hoshiai, T., Tanimura, A., Watanabe, K., Ice algae as food of an ice-
survival in the aquatic environment, in Microbial Adhesion and associated copepod, Paralabidocera antarctica (I. C. Thompson),
Aggregation, Marshall, K.C., Ed., Springer, Berlin, 1984, 383–401. Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Biol., 1, 105–111, 1987b.
Horne, A.J., Fogg, E.G., Eagle, D.J., Studies in situ of primary Hoshiai, T., Tanimura, A., Fukuchi, M., Watanabe, K., Feeding by the
production of an area of inshore Antarctic sea, J. Mar. Biol. nototheniid fish Pagothenia borchgrevinki on the ice-associated
Assoc. U.K., 49, 393–405, 1969. copepod Paralabidocera antarctica, in Proceedings of the NIPR
Horner, R.A., Taxonomy of sea ice microalgae, in Sea Ice Biota, Horner, Symposium on Polar Biology, Vol. 2, 1989, 61–64.
R.A., Ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1985, 147–157. Hosie, G.W., Distribution and abundance of euphausiid larvae in the the
Horner, R.A., Ecology of sea ice microalgae, in Sea Ice Biota, Horner, Prydz Bay region, Antarctica, Antarc. Sci., 3, 167–180, 1991.
R.A., Ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1986, 83–103. Hosie, G.W., The macrozooplankton communities in the Prydz Bay
Horner, R.A., Ice-associated diatoms, in Polar Marine Diatoms, Medlin, region, Antarctica, in Southern Ocean Ecology: A BIOMASS
L.K., Priddle, J., Eds., British Antarctic Survey, Natural Environ- Perspective, El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., Cambridge University Press,
ment Research, Cambridge, UK, 1990, 9–14. Cambridge, UK, 1994, 93–123.
Horner, R.A., Schrader, G.C., Relative contributions of ice algae, Hosie, G.W., Cochran, T.G., Mesoscale distribution patterns of macro-
phytoplankton, and benthic microalgae to primary production in zooplankton communities in Prydz Bay, Antarctica—January to
nearshore regions of the Beaufort Sea, Arctic, 35, 485–503, 1982. February 1991, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 196, 21–39, 1994.
Horner, R.A., Syversten, E.E., Thomas, D.P., Lange, C., Proposed Hosie, G.W., Stolp, M., Krill and zooplankton in the western Prydz Bay
terminology and reporting units for sea ice algal assemblages, region, September–November 1985, Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar
Polar Biol., 8, 249–253, 1988. Biol., 2, 33–45, 1989.
Horner, R.A., Ackley, S.F., Dieckmann, G.S., Gulliksen, B., Hoshiai, T., Hosie, G.W., Cochran, T.G., Pauly, T., Beaumont, K.L., Wright, S.W.,
Legendre, L., Melnikov, I.A., Reeburch, W.S., Spindler, M., Kitchener, J.A., Zooplankton community structure of Prydz Bay,
Sullivan, C.W., Ecology of sea ice biota: Habitat, terminology Antarctica, January–February 1993, Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Biol.,
and methodology, Polar Biol., 12, 417–427, 1992. 10, 90–133, 1997.
Horwood, J.W., On the joint exploitation of krill and whales, in Houghton, J.T., Jenkins, G.J., Ephrauyms, J.J., Climate Change: The
Mammals in the Seas, Volume III, FAO Fisheries Series, Rome, IPPC Scientific Assessment, Cambridge University Press,
1981, 355–383. Cambridge, 1990a, 1–364.
Hosaka, N., Nemoto, T., Size structure of phytoplankton carbon and Houghton, J.T., Jenkins, G.-J., Ephraum, J.J., Climate Change. The
primary production in the Southern Ocean south of Australia IPPC Scientific Assessment, World Meterological Organization/-
during the summer of 1983–1984, Mem. Nat. Inst. Polar Res. United Nations Environment Programme, Cambridge University
Special Issue, 40, 15–24, 1986. Press, Cambridge, 1990b, 1–365.
Hoshiai, T., Seasonal variation of chlorophyll a and hydrological Houghton, J.T., Callander, B.A., Varney, S.K. Climate Change 1992:
conditions under sea ice at Syowa Station, Antarctica, Antarc. The Supplementary Report to the IPCC Scientific Assessment,
Rec., 35, 52–67, 1969. In Japanese with English abstract. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, NY, 1992.
Hoshiai, T., Diatom distribution in sea ice near McMurdo Station and Houghton, J.T., Callander, B.A., Varney, S.K., Climate Change.
Syowa Station, Antarc. J. U.S., 7, 85–87, 1972. Supplementary Report to the IPPC Scientific Assessment, World
Hoshiai, T., Seasonal change of ice communities in the sea ice near Meterological Organization/United Nations Environment
Syowa Station, Antarctica, in Polar Oceans, Dunbar, M.J., Ed., Programme, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2002,
Arctic Institute of North America, Calgary, 1977, 307–317. 1–200, Ser., 107, 23–40, 1994.
Hoshiai, T., Feeding behaviour of Notothenia rossii marmorata Fischer Houghton, J.T., Filho, L.G.M., Callander, B.A., Harris, N., Kattenburg,
at South Georgia, Antarc. Rec., 66, 25–36, 1979. A., Maskell, K., Climate Change 1995: The Science of Climate
Hoshiai, T., Proliferation of ice algae in the Syowa Station area, Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, NY, 1996.
Antarctica, Mem. Nat. Inst. Polar Res., 34, 1–12, 1981a. Houghton, J.T., Ding, Y., Griggs, D.J., Noguer, M., van der Linden, P.J.,
Hoshiai, T., Solar radiations and stability of the undersurface of sea ice Dai, X., Maskell, K., Johnson, C.A., Climate change 2001: The
governing ice algal proliferation, Antarc. Rec., 73, 23–29, 1981b. Scientific Basis, Contribution of Working Group 1 to the third
Hoshiai, T., Autumn proliferation of ice algae in Antarctic sea ice, in assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate
Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, NY, 2001.
P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 89–92. Houghton, J.T., Filho, L.G.M., Bruce, J.P., Lee, H., Callander, B.A.,
Hoshiai, T., Kato, M., Ecological notes on the diatom community of the Haites, E.F., Climatic Change 1994: Radioactive Forcing of
sea ice in Antarctica, Bull. Mar. Biol. Station of Asamushi, Tohoku Climate Change and an Evaluation of the IPCC 1992 Emission
University, 10, 221–230, 1961. Scenario, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, NY.
Hoshiai, T., Tanimura, A., Copepods in the stomach of a Nototheniid Howington, J.P., McFeters, G.A., Barry, J.D., Smith, J.J., Distribution of
fish, Trematomous borchgrevinki, at Syowa Station, Antarctica, the McMurdo Station sewage plume, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 25,
Mem. Nat. Inst. Polar Res., 34, 44–88, 1981. 324–327, 1992.
Hoshiai, T., Tanimura, A., Sea ice meiofauna at Syowa Station, Mem. Howington, J.P., McPeters, G.A., Smith, J.J., The effect of low
Nat. Inst. Polar Res. Special Issue, 44, 118–124, 1986. temperature on BOD in Antarctic seawater, Water Res., 28,
Hoshiai, T., Tanimura, A., Fukuchi, M., Watanabe, K., Feeding by the 2585–2587, 1994.
nototheniid fish Pagothenia borchgrevinki on the ice-associated Hoyer, V., Occurrence, induction and physiological importance of
copepod Paralabidocera antarctica, Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar UV-absorbing substances in polar microalgae, Ber. Polarforsch.,
Biol., 2, 61–64, 1987a. 440, 112–155, 2003.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
566 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Hoyer, V., Karsten, U., Sewell, T., Wiencke, C., Photoprotective Hunt, B.P., Pakhomov, E.A., McQuaid, C.P., Short-term variation and
substances in Antarctic macroalgae and their variation with long-term changes in the oceanographic environment and
respect to depth distribution, different tissues and development zooplankton community in the vicinity of a sub-Antarctic archi-
stages, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 211, 117–120, 2001. pelago, Mar. Biol., 138, 369–381, 2001.
Hoyer, K., Karsten, U., Wiencke, C., Induction of sunscreen compounds Hunter, S., The food and feeding ecology of the giant petrels Macro-
in Antarctic microalgae by different radiation conditions, Mar. nectes halli and M. giganteus at South Georgia, Aust. J. Zool., 200,
Biol., 141, 619–627, 2002. 521–538, 1983.
Hoyer, K., Karsten, U., Wiencke, C., Inventory of UV-absorbing Hunter, S., Breeding biology and population dynamics of giant petrels
microsporine-like amino acids in polar macroalgae and factors Macronectes halli and M. giganteus at South Georgia, Aust.
controlling their content, in Antarctic Biology in a Global Context, J. Zool., 203, 441–460, 1985.
Huiskes, H.H., Gieskes, W., Eds., Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, Huntley, M.E., Brinton, E., Mesoscale variation in growth and early
The Netherlands, 2003, 56. development of Euphausia superba Dana in the western Bransfield
Hoyer, K., Schafer, S., Karsten, U., Wiencke, C., Interactive effects of Strait region, Deep-Sea Res., 38, 1213–1240, 1991.
Huntley, M.E., Escritor, F., Dynamics of Calanoides acutus (Copepoda:
temperature and radiation on polar macroalgae, Ber. Polarforsch.,
Calanoida) in Antarctic coastal waters, Deep-Sea Res., 38,
440, 69–89, 2003.
1145–1167, 1991.
Hubold, G., The early life-history of the high-Antarctic silverfish,
Huntley, M., Tandy, K.S., Eilertsen, H.C., On the trophic fate of
Pleurogramma antarcticum, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and
Phaeocystis pouchetii, II: Grazing rates of Calanus hyperboreus
Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds.,
feeding on diatoms and different size categories of P. pouchetii,
Springer, Berlin, 1985, 445–451.
J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 110, 197–212, 1987.
Hubold, G., Stomach contents of the Antarctic silverfish Pleurogramma
Huntley, M.E., Sykes, P.F., Marin, V., Biometry and trophodynamics of
antarcticum from the southern and eastern Weddell Sea, Polar
Salpa thompsoni (Tunicata: Thaliacea) near the Antarctic Penin-
Biol., 5(1), 43–48, 1985.
sula in austral summer 1983–1984, Polar Biol., 10, 59–70, 1989.
Hubold, K.G., Seasonal pattern of ichthyoplankton in the southern Huntley, M.E., Karl, D.M., Miller, P.P., Holm-Hansen, O., Research in
Weddell Sea, in Ecological Change and Conservation, Springer, Antarctic Coastal Ecosystem Roles (RACER) on interdisciplinary
Berlin, 149 pp, 1990. field experiments, Deep-Sea Res., 58, 911–941, 1991.
Hubold, G., Ecology of notothenioid fish in the Weddell Sea, in Biology Huntley, M.E., Nordhausen, W., Lopez, M.D.G., Elemental compo-
of Antarctic Fish, Di Prisco, G., Maresco, B., Tota, B., Eds., sition, metabolic activity and growth of Antarctic krill (Euphausia
Springer, Berlin, 1991, 3–22. superba) during winter, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 107, 23–40, 1994.
Hubold, G., Ekau, W., Midwater fish fauna of the Weddell Sea, Hureau, J.-C., Biologie comparée de quelques poissons antarctiques
Antarctica, in Proceedings of the 5th European Ichthyological (Nototheniidae), Bull. Inst. Oceanogr. Fish., 68, 1–44, 1966.
Congress, Kullander, S.O., Fernholm, B., Eds., Swedish Museum Hureau, J.-C., La faune ichthyologique du secteur indien de l’ocean
of Natural History, Stockholm, 1987, 391–396. antarctique et estimation du stock de poissons autour de ı̂les
Hubold, K.G., Tomo, A.P., Age and growth of Antarctic silverfish Kerguelen, Mem. Mus. Nat. Hist. Natur., 43, 235–247, 1979.
Pleurogramma antarcticum Boulenger, 1902, from the southern Hureau, J.-C., The significance of fish in the marine Antarctic ecosystem,
Weddell Sea and Antarctic Peninsula, Polar Biol., 9, 205–212, Polar Biol., 14, 307–315, 1994.
1989. Hureau, J.-C., Petit, D., Fine, I.M., Marneux, M., New cytological,
Hubold, G., Hempel, I., Meyer, M., Zooplankton communities in the biochemical and physiological data on the colourless blood of the
southern Weddell Sea, Meeresforschung, 31, 185–192, 1985. Channichthyidae (Pisces, Teleostei, Perciformes), in Adaptations
Hudson, R., Adult survival estimates for two Antarctic petrels, Br. within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G., Ed., Gulf Publishing
Antarc. Surv. Bull., 8, 63–73, 1966. Company, Houston, TX, 1977, 459–477.
Huey, L.M., Capture of an elephant seal off San Diego, California, with Hustedt, F., Diatomeen aus der Antarktis und dem Südatlanktik
notes on stomach contents, J. Mammal., 11, 229–231, 1990. Deutsche Antarktische Expedition 1938–39, Wissenschaft Ergeb-
Hughes, L., Biological consequences of global warming: Is the signal nisse, 2, 103–191, 1958.
already apparent?, Trends Ecol. Evol., 15(2), 41–81, 2000. Hutchins, P.A., Bruland, K.W., Iron-limited diatom growth and Si–N
Hulley, P.A., Myctophidae (lanternfish), in Fishes in the Southern uptake ratios in a coastal upwelling regime, Nature (Lond.), 393,
Ocean, Gon, O., Heenstra, P.C., Eds., Grahamstown Institute of 561–564, 1998.
Ichthyology, Grahamstown, South Africa, 1990, 146. Hyland, J., Laur, D., Jones, J., Shrake, J., Cadian, D., Harris, L., Effects
of an oil spill on the soft-bottom macrofauna of Arthur Harbour,
Hulley, P.A., Camus, P., Duhamel, G., Ichthyological results of cruise
Antarctica, compared with long-term natural change, Antarct. Sci.,
MD-42/SIBEX II. Part 1. Fishes from RMT-8stations with
6, 37–44, 1994.
additional records from lanternfishes (Myctophidae: Osteichthyes)
Ichihara, T., The pigmy blue whale, Balaenoptera musculus brevicauda,
from Indian and Atlantic Seas of the Southern Ocean, Cybium, 13,
a new subspecies from the Antarctic, in Whales, Dolphins and
83–99, 1991.
Porpoises, Norris, K.S., Ed., University of California Press,
Hunt, F., Observations on the seals of Elephant Island, South Shetland
Berkeley, 1966, 79–111.
Islands, 1970–71, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 36, 99–104, 1973.
Ichihara, T., Criteria for determining age of the fin whale with reference
Hunt, G.L., Heinemann, D., Veit, R.R., Heywood, R.B., Everson, I., The
to ear plug and baleen plate, Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 20,
distribution, abundance and community structure of marine birds
17–82, 1966.
in Southern Drake Passage and Bransfield Strait, Antarctica, Cont. Ichii, T., Kato, H., Food and daily food consumption of southern minke
Shelf Res., 16, 243–257, 1990. whales in the Antarctic, Polar Biol., 11, 479–487, 1991.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 567
Idyll, P., The anchovy crisis, Sci. Am., 288, 22–29, 1973. International Whaling Commission (IWC), Report of the Scientific
Iganake, D., Matsura, E., Kunta, Y., Stock and quantitative distribution Committee, International Whaling Committee Reports, 40 pp, 1990.
of the Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba Dana) in the Antarctic IPPC, Climate Change: The IPPC Scientific Assessment, Intergovern-
Ocean south of Australia, January and February 1984, Trans. ment Panel on Climate Change, World Meterological
J. Tokyo Univ. Fish., 6, 139–147, 1984. Organization/United Nations Environment Programme,
Iizuka, H., Tanabe, I., Meguro, H., Microorganisms in plankton-ice of Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1990.
the Antarctic Ocean, J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol., 12, 101–102, 1966. IPPC, IPPC First Assessment Overview and Policy Maker Summaries,
Ikeda, T., Relationship between respiration rate and body size in marine Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Geneva, 168 pp.
plankton animals as a function of the temperature of the habitat, 1992.
Bull. Hokkaido Univ. Fac. Fish., 21, 91–112, 1970. IPPC, Second IPPC Assessment—Climate Change 1996, Intergovern-
Ikeda, T., Development of the Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) mental Panel on Climate Change, Geneva, 64 pp, 1995a.
observed in the laboratory, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 75, IPPC, Climate Change 1995: The Science of Climate Change, Contri-
107–117, 1984. bution of the Working Group I to the Second Assessment of the
Ikeda, T., Sequences in metabolic rates and elemental composition (C, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Haughton, J.T., Ed.,
N, P) during the development of Euphausia superba Dana and Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1995b.
estimated food requirements during its life span, J. Crust. Biol. Irwin, B.D., Primary production of ice algae on a seasonally-ice-covered
Spec. Issues, 4, 273–284, 1984. continental shelf, Polar Biol., 10, 247–254, 1990.
Ikeda, T., Life history of Antarctic krill Euphausia superba: a new look Iturriaga, R., Mitchell, B.G., Chromococcoid cyanobacteria: a signi-
from an experimental approach, Bull. Mar. Sci., 37, 599–608, 1985. ficant component in the food web dynamics of the open ocean,
Ikeda, T., Bruce, B., Metabolic activity and elemental composition of Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 28, 291–297, 1986.
krill and other zooplankton from Prydz Bay, Antarctica during Ivanov, A.I., Characteristics of the phytoplankton in Antarctic waters at
early summer (November–December), Mar. Biol., 92, 545–555, the whaling grounds of the flotilla Slava in 1957–58, Soviet
Antarct. Expedition Info. Bull., 1, 314–321, 1964.
1986.
Ivanov, B.G., On the biology of the Antarctic krill Euphausia superba,
Ikeda, T., Dixon, P., Observations on the moulting in Antarctic krill
Mar. Biol., 7, 340–351, 1970.
(Euphausia superba Dana), Aust. J. Mar. Freshwat. Res., 33,
Iwanami, K., Futatsumachi, S., Taniguchi, A., Short-term variation of
71–76, 1982.
chemical property of water and microplankton community in the
Ikeda, T., Dixon, P., Body shrinkage as a possible overwintering
coastal area near Syowa Station, Antarctica, in midsummer of
mechanism of the Antarctic krill Euphausia superba Dana,
1984, 1. Chemical property including chlorophyll a, Mem. Nat.
J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 62, 143–151, 1982.
Inst. Polar Res. Special Issue, 40, 1–14, 1986.
Ikeda, T., Kirkwood, R., Metabolism and body composition of two
Jacka, J.T., Budd, W.P., Detection of temperature and sea ice extent
Euphausiids (Euphausia superba and E. crystallorophias)
changes in the Antarctic and Southern Ocean, Ann. Glaciol., 27,
collected from under the pack ice off Enderby Island, Mar. Biol.,
553–559, 1998.
101, 339–343, 1989.
Jackson, L.T., Linick, T.W., Michel, R.L., Williams, P.M., Tritium and
Ikeda, T., Dixon, P., Kirkwood, J., Laboratory observations of moulting,
carbon-14 distributions in McMurdo Sound, 1977, Antarct. J. U.S.,
growth and maturation in Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba
13, 71–73, 1978.
Dana), Polar Biol., 4, 1–8, 1985.
Jacob, A., Kirst, G., Wiencke, C., Lehmann, H., Physiological responses
Iken, K., Feeding ecology of the Antarctic gastropod Laevilacunaria
of the Antarctic green alga, Prasiola crispa spp. antarctica, to
antarctica Martens, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 236(1), 133–148,
salinity stress, J. Plant Physiol., 139, 57–62, 1991.
1999. Jacobs, S.S., Ross ice shelf project: physical oceanography, Antarct.
Iken, K., Quartino, M.L., Barrera-Oro, E., Palermo, J., Wiencke, C., J. U.S., 12(4), 43–46, 1977.
Brey, T., Trophic relations between macroalgae and herbivores, in Jacobs, S.S., On the nature and significance of the Antarctic slope front,
The Potter Cove Coastal Ecosystem Synopsis 1998, 1998, Mar. Chem., 35(1–4), 9–24, 1991.
258–262. Jacobs, S.S., Comiso, K., Sea and oceanic processes on the Ross Sea
Imber, M.J., Breeding biology of the grey-faced petrel, Pterodroma continental shelf, J. Geophys. Res., 94, 18195–18211, 1989.
macroptera gouldi, Ibis, 118, 51–64, 1976. Jacobs, S.S., Giulivi, C.F., Thermohaline data and ocean circulation on
Ingham, S.E., Branding elephant seals for life history studies, Polar Rec., the Ross Sea continental shelf, in Oceanography of the Ross Sea,
13, 447–449, 1967. Antarctica, Spezie, G., Manzella, G.M.R., Eds., Springer, Milan,
Inglis, G., The colonization and degradation of stranded Macrocystis 1999, 3–16.
pyrifera (L.) C. Ag. by the macrofauna of a New Zealand sandy Jacobs, S.S., Amos, A.F., Buckhausen, P.M., Ross Sea oceanography
beach, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 125, 203–217, 1989. and Antarctic bottom water formation, Deep-Sea Res., 17,
Innamotati, M., Mori, G., Mazzi, L., Lazzari, L., Naccio, L., Phyto- 935–962, 1970.
plankton biomass related to environmental factors, in Ross Sea Jacobs, S.S., Bruckhausen, P.M., Ardai, J.L., Physical oceanography of
Ecology, Faranda, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Ianora, A., Eds., Springer, the Ross Sea, Antarct. J. U.S., 13, 83–85, 1978.
New York, 2000, 217–245. Jacobs, S.S., Gordon, A.L., Ardai, J.L., Circulation and melting beneath
International Whaling Commission (IWC), International Whaling the Ross Ice Shelf, Science, 203, 439–443, 1979.
Committee Reports, 28 pp, 1978. Jacobs, S.S., Fairbanks, R., Horibe, Y., Origin and evolution of
International Whaling Commission (IWC), Report of a special meeting water masses near the Antarctic continental margin: Evidence
on Southern Hemisphere minke whales, Seattle,WA, May 1978, from H18 O=H16 2 O ratios in seawater, in Oceanology of the Antarctic
International Whaling Committee Reports, 29 pp, 1979. Shelf, Antarct. Res. Ser., Vol. 43, 1985, 59–85.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
568 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Jacobsen, D.J., Anderson, D.M., Thecate heterotrophic dinoflagellates: Johanssen, O.O., Johanssen, J.A., Morison, J., Farrelly, B.A., Svendsen,
Feeding behaviour and mechanisms, J. Phycol., 22, 249–258, E.A.S., Oceanographic conditions in the marginal ice zone north of
1986. Svalbard in early fall 1979, with an emphasis on mesoscale
Jacobsen, T.R., Azam, F., Role of bacteria in copepod faecal pellet processes, J. Geophys. Res., 88, 2755–2769, 1983.
decomposition and colonization, growth rates and mineralization, John, D.D., The southern species of the genus Euphausia, Discovery
Bull. Mar. Sci., 35, 495–502, 1984. Rep., 14, 195–323, 1936.
Jacques, G., Some ecophysiological aspects of the Antarctic phyto- John, D.D., Crinoidea, Discovery Rep., 18, 121–122, 1938.
plankton, Polar Biol., 2, 27–33, 1983. John, D.D., Crinoidea, Br., Aust. N.Z. Antarct. Res. Expedition 1901–
Jacques, G., Primary production in the open Antarctic ocean during the 1904, Rep. B, 4, 189–212, 1939.
austral summer: A review, Vie et Milieu, 39, 1–17, 1989. John, D.M., Tinley, I., Lawson, G.W., Pugh, P.J.A., Distribution of
Jacques, G., Hoepffner, N., Sinking rates of subantarctic phytoplankton, seaweed flora in the Southern Ocean, Bot. Mar., 37, 235–239,
Comptes rendus de l’Académie des Sciences Paris 299 (Serie III), 1994.
14, 581–585, 1984. Johnson, T.O., Smith, W.O., Jr.,, Sinking rates of phytoplankton
assemblages in the Weddell Sea marginal ice zone, Mar. Ecol.
Jacques, G., Minas, M., Production primaire dans le secteur indien de
Prog. Ser., 33, 131–137, 1986.
l’Océan Antarctique en fin d’été, Oceanol. Acta, 4, 33–41, 1981.
Johnston, I.A., Walesby, N.J., Molecular mechanisms of temperature
Jacques, G., Panouse, M., Biomass and composition of size-fractionated
adaptation in fish myofibrillar adenosine triphosphate, J. Comp.
phytoplankton in the Weddell Sea Confluence area, Polar Biol., 11,
Physiol., 119, 195–206, 1977.
315–325, 1991.
Johnston, I.A., Johnson, T.P., Battram, J.C., Low temperature limit burst
Jacques, G., Treguer, P., Les Ecosystems Pelagiques Marins, Collections
swimming performance in Antarctic fish, in Biology of Antarctic
Ecologiques 19, Masson, Paris, 1986.
Fishes, di Prisco, G., Maresca, B., Tolton, B., Eds., Springer,
Jakubowski, M., Byczkowski-Smyk, W., Respiratory surfaces of white-
Heidelberg, 1991, 179–190.
blooded fish Chaenichthys rugosus Regan (Perciformes), Pol.
Johnstone, G.W., Comparative feeding ecology of the giant petrels
Arch. Hydrobiol., 17, 273–281, 1970.
Macronectes giganteus (Gmelin) and M. halli (Mathews), in
Jaragov, A., On the physico-geographical conditions of the krill habitat, Adaptations within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smith-
Trudy Vsesoiuznogo Naucho-issledovatel’skii Instituta Morskogo sonian Institution, Washington, DC, 1977, 647–668.
Rybnogo Khoziaistva i Okeanographii, 61, 85–102, 1969. In Johnstone, G.W., Agonistic behaviour of the giant petrels Macronectes
Russian. giganteus and M. halli feeding at seal carcasses, Emu, 79, 129–132,
Jarman, S., Elliot, N., Nicol, S., McMinn, A., Newman, S., The base 1979.
composition of the krill genome: Its potential susceptibility to Joint, I.R., Morris, R.J., The role of bacteria in the turnover of organic
damage by UV-B, Antarct. Sci., 11, 23–26, 1999. matter in the sea, Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev., 20, 65–118,
Jazdzewski, K., Porebski, J., Rakusa-Suszczewski, S., Witek, Z., 1982.
Wolnomeijski, N., Biological studies on krill near South Shetland Jones, P.D., Antarctic temperatures over the present century—a study of
Islands, Scotia Sea and South Georgia in the summer 1978, Pol. the early expedition record, J. Clim., 3, 1193–1203, 1990.
Arch. Hydrobiol., 25, 607–631, 1978. Jones, E.P.J., Nelson, D.M., Treguer, P., Chemical oceanography, in
Jazdzewski, K., Kittel, W., Lotaki, K., Krill monitoring in Admiralty bay Polar Oceanography, Smith, W.O., Jr., Ed., Academic Press, San
(King George Island, South Shetland Islands) in summer 1979/80, Diego, CA, 1990, 407–476.
Polar Biol., 1, 117–125, 1982. Jonker, F.C., Bester, M.V., Seasonal movements and foraging areas of
Jazdzewski, K., Jurasz, W., Kittel, W., Presler, E., Presler, P., Sicinski, adult southern female elephant seals, Mirounga leonina, from
J., Abundance and biomass estimates of the benthic fauna in Marion Island, Antarct. Sci., 10, 21–30, 1998.
Admiralty Bay, King George Island, South Shetland Islands, Joris, C.R., Spring distributions and ecological role of seabirds and
Polar Biol., 6, 5–16, 1986. marine mammals in the Weddell Sea, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 11,
Jenkins, D.G., Initiation of the protocircum-Antarctic current, Nature 415–424, 1991.
(Lond.), 252, 371–373, 1974. Jorgensen, B.B., Processes at the sediment-water interface, in SCOPE
Jennings, J.C., Jr, Gordon, L.I., Nelson, D.M., Nutrient depletion 21, The Major Biogeochemical Cycles and Their Interactions,
indicates high primary productivity in the Weddell Sea, Nature Bolin, B., Cook, R., Eds., Wiley, Chichester, 1983, 477–515.
(Lond.), 309, 51–54, 1984. Jouventain, P., Mortality parameters in emperor penguins, in The
Jerome, T.H., Bukata, R.P., Tracking the propogation of solar ultraviolet Biology of Penguins, Stonehouse, B., Ed., MacMillan, London,
1975, 435–440.
radiation: dispersal of ultraviolet photons in inland waters, J. Great
Jouventein, P., Mougin, J.-L., Les strategies adaptatives des oiseau de
Lakes Res., 24, 666–690, 1998.
mer, Terre et la Vie, Revue d’Ecologie, 35, 217–273, 1981.
Jewell, P.A., Holt, S., Eds., Problems of Management of Locally-
Jouventin, P., Weimerskirch, H., Long-term change in seabird and seal
Abundant Wild Animals, Academic Press, London, 1982.
populations in the Southern Ocean, in Antarctic Ecosystems.
Jitts, H.R., Morel, A., Saijo, Y., The relationship of oceanic primary
Ecological Change and Conservation, Kerry, K.R., Hempel, G.,
production to available photosynthetic radiation, Aust. J. Mar.
Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1990, 208–213.
Freshwat. Res., 27, 441–454, 1976.
Jouventin, P., Weimerskirch, H., Changes in the population size and
Jobling, M., Towards an explanation of specific dynamic action, J. Fish
demography of southern seabirds: the management implications, in
Biol., 23, 549–555, 1983.
Bird Population Studies: Their Reference to Conservation and
Johannes, R.E., Influence of marine protozoa on nutrient regeneration,
Management, Perrina, C.M., Lebreton, J.D., Hirons, C.J.M., Eds.,
Limnol. Oceanogr., 10, 433–442, 1965. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1991, 297–316.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 569
Jouventin, P., Stahl, J.C., Weimerskirch, H., Mougin, J.L., The seabirds Karentz, D., Ultraviolet tolerance mechanisms in Antarctic marine organ-
of the French Subantarctic islands and Adélie land: their status and isms, in Radiation in Antarctica: Measurements and Biological
conservation, in The Status and Conservation of the World’s Effects, Weller, C.S., Penhale, P.A., Eds., American Geophysical
Seabirds, International Council for Bird Preservation Technical Union, Washington, DC, 1994, 93–110.
Publication, Vol. 2, 609–625 pp, 1984. Karentz, D., Environmental change in Antarctica: Ecological impacts
Joyce, T.M., Patterson, S.L., Cyclonic ring formation at the Antarctic and responses, in Antarctic Biology in a Global Context, Huiskes,
Polar Front in the Drake Passage, Nature (Lond.), 256, 131–133, A.H.L., Gieskes, W.W.C., Rozema, J., Schorno, R.M.L., van der
1977. Vies, S.M., Wolff, W.J., Eds., Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, The
Joyce, T.M., Zenk, W., Toole, J.M., The anatomy of the Antarctic Front Netherlands, 2003, 45–55.
in the Drake Passage, J. Geophys. Res., 83, 6093–6113, 1978. Karentz, D., Lutz, L.H., Evaluation of biologically-harmful ultraviolet
Joyner, T., Mahnken, C.V.W., Clark, A.R., Salmon future harvest from radiation in Antarctica with a biological dosimeter designed for
the Antarctic Ocean, Mar. Fish. Rev., 35, 20–28, 1974. aquatic environments, Limnol. Oceanogr., 35, 549, 1990.
Kalinowski, J., Vertical migration of krill in the region of South Georgia, Karentz, D., McEuen, F.S., Lord, K.M., Dunlap, A., A survey of
February–March 1976, Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol., 25, 573–583, 1978. mycosporine-like amino acids in Antarctic marine organisms:
Kalinowski, J., Witek, Z., Forms of Antarctic krill aggregations, ICES Potential protection from ultraviolet radiation, Mar. Biol., 188,
Biological and Oceanographic Committee C.M., 1982/L 60, 1982. 151–166, 1991.
Kalinowski, J., Witek, Z., Elementy biologii formy grupowego wgste- Karentz, D., Bosch, I., Dunlop, W.C., Distribution of UV-absorbing
powania i Zasoby Antarktycznego kryla Euphausia superba Dana compounds in the Antarctic limpet Nacella concinna, Antarct.
(some aspects of biology, forms of aggregation and stocks of J. U.S., 27, 121–122, 1992.
Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba Dana), Joint Ph.D. thesis, Sea Karentz, D., Bosch, I., Mitchell, D.M., Limited effect of Antarctic ozone
Fisheries Institute, Godynia, Poland, 1983, In Polish. depletion on sea urchin development, Mar. Biol., 145, 277–292,
Kalinowski, J., Witek, Z., Scheme for classifying aggregations of
2004.
Antarctic krill. BIOMASS Handbook No. 27, 1985.
Karl, D.M., The grounding of the Bahia Paraiso: Microbial ecology of
Kampa, E.M., Boden, B.P., Submarine illumination and twilight move-
the 1989 Antarctic spill, Microb. Ecol., 24, 77–89, 1992.
ments of a sonic scattering layer, Nature (Lond.), 174, 869–873,
Karl, D.M., Microbial processes in the Southern Ocean, in Antarctic
1954.
Microbiology, Friedman, E.I., Ed., Wiley-Liss, New York, 1993,
Kanda, K., Takagi, K., Seki, Y., Movement of the larger swarms of
1–63.
Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, populations off Enderby Land
Karl, D.M., Novitsky, J.A., Dynamics of microbial growth in surface
during the 1976–77 season, J. Tokyo Univ. Fish., 68, 24–42, 1982.
layers of a coastal marine sediment ecosystem, Mar. Ecol. Prog.
Kane, J.E., The distribution of Parathemisto gaudichaudii (Guer) with
Ser., 50, 169–176, 1988.
observations on its life history on the 08 to 208 E Sector of the
Karl, D.M., Tilbrook, D., Tein, G., Seasonal coupling of organic matter
Southern Ocean, Discovery Rep., 34, 163–198, 1966.
and particle flux in the western Bransfield Strait, Antarctica, Deep-
Kang, S.-H., Fryxell, G.A., Phytoplankton in the Weddell Sea, Antarc-
Sea Res., 38, 1097–1126, 1991.
tica: Composition, abundance and distribution in water-column
Karpov, K.A., Cailliet, G.M., Feeding dynamics of Loligo opalescens,
assemblages of the marginal ice edge zone during austral summer,
Fish. Bull. (California Depart. Fish Game), 169, 45–65, 1978.
Mar. Biol., 116, 335–348, 1993.
Karsten, U., Wiencke, C., Kirst, G.D., The effect of salinity changes
Kang, S-H., Kang, J.S., Seasonal variation of environmental factors and
upon the physiology of green microalgae from Antarctica and
nearshore microalgae in Marion Cove, King George Island,
southern Chile, 1: Cell viability, growth, photosynthesis, and dark
Antarctica, during 1996: Preliminary study for long-term moni-
toring, in Environmental Monitoring on Human Impacts at King respiration, J. Plant Physiol., 138, 667–673, 1991.
Sejong Station, KORDI, 1997, 57–112. Karsten, U., Sewell, T., Hanelt, D., Bischof, K., Figuera, F., Moya, A.,
Kang, S.-H., Lee, S.-H., Antarctic phytoplankton assemblage in the Wiencke, C., An inventory of UV-absorbing mycrosporine-like
western Bransfield Strait region, February 1992: Composition, amino acids in macroalgae for polar and warm temperate regions,
biomass and mesoscale distribution, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 129, Biol. Mar., 41, 443, 1998.
253–267, 1995. Kasamatsu, F., Joyce, G.G., Current status of odontocetes in Antarctica,
Kang, J.S., Kang, S.-H., Lee, J.H., Lee, S.H., Seasonal variation of in Antarctic Biology in a Global Context, Huiskes, A.H.L.,
microalgal assemblages at a fixed station on King George Island, Gieskes, W.W.C., Rozema, J., Schorno, R.M.L., van der Vies,
Antarctica, 1996, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 229, 19–32, 2002. S.M., Wolff, W.J., Eds., Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, The Nether-
Kappen, L., Redon, J., Microclimate influencing the lichen vegetation on lands, 2003, 26.
different aspects of a coastal rock in maritime Antarctica, Serie Kasamatsu, F., Ohsumi, S., Distribution pattern of minke whales in the
Cientı́fica Instituto Antártico Chileno, 31, 53–65, 1984. Antarctic with special reference to the sex ratios of the catch, Rep.
Karantz, D., McEuen, F.S., Land, M.C., Dulop, A., Survey of mycos- Int. Whal. Commun. Rep., 34, 345–348, 1987.
porine-like amino acid compounds in Antarctic marine organisms: Kasamatsu, F., Ensor, P., Joyce, G.G., Clustering and aggregation of
potential protection from ultraviolet exposure, Mar. Biol., 108, minke whales in Antarctic feeding grounds, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.,
157–166, 1991. 168, 1–11, 1998.
Karentz, D., Report on studies related to the ecological implications of Kato, H., Some considerations of the age at sexual maturity of Antarctic
ozone depletion on the Antarctic environment, Antarct. J. U.S., 24, minke whales, Int. Whaling Comm. Rep., 33, 393–399, 1983.
175, 1989. Kato, H., Diversity-dependent changes in growth parameters of the
Karentz, D., Ecological considerations of Antarctic ozone depletion, Southern minke whale, Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst., Tokyo, 38,
Antarct. Sci., 3, 3–11, 1991. 47–73, 1997.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
570 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Kato, M., Murano, M., Segawa, S., Estimates of the filtration rate of Kennett, J.P., The fauna of the Ross Sea, Part 6: Ecology and distribution
Antarctic krill under laboratory conditions, Trans. J. Tokyo Univ. of the Foraminifera, N.Z. Oceanogr. Inst. Mem., 46, 1–46, 1968.
Fish., 3, 107–112, 1979. Kennett, J.P., Cenozoic evolution of Antarctic glaciation, the circum-
Kato, M., Mujrano, M., Segawa, S., Estimates of the filtration rate of Antarctic Ocean, and their impact on global paleo-oceanography,
Antarctic krill, Euyphausia superba Dana, Trans. Tokyo Univ. J. Geophys. Res., 82, 3843–3860, 1977.
Fish., 5, 167–175, 1982. Kennett, J.P., Paleooceanography: Global ocean evolution, Rev.
Kato, M., Sehawa, S., Tanoue, E., Murano, M., Filtering and ingestion Geophys. Space Res., 21, 1258–1274, 1983.
rates of Antarctic krill, Euphausis superba Dana, Trans. Tokyo Kennett, J.P., Houtz, R.E., Andrews, P.B., Edwards, A.R., Gostin, V.A.,
Univ. Fish., 5, 167–175, 1982. Hajas, M., Hampton, M. et al., Cenozoic paleo-oceanography in
Kaufman, G.W., Siniff, D.B., Reichle, R., Colony behaviour of Weddell the southwest Pacific ocean, Antarctic glaciation, and the develop-
seals (Leptonychotes weddelli) at Hutton Cliffs, Antarctica, ment of the circum-Antarctic current, Initial Rep. Deep Sea
Rapports et Proces-Verbaux des Renunions Conseil International Drilling Proj., 29, 1155, 1976.
Pour l’Exploration de la Mer, 169, 228–246, 1975. Kennicutt, H.M.C., Oil spillage in Antarctica: Initial report of the
Kawaguchi, K., Ishikawa, S., Matsuda, O., Overwintering strategy of National Science Foundation—sponsored quick-response team
Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba Dana) under the coastal fast ice on the grounding of the Bahia Paraiso, Environ. Sci. Technol.,
off Ongul Islands in Lützow-Holm Bay, Antarctica, Mem. Nat. 24, 620–624, 1990.
Inst. Polar Res. Special Issue, 44, 67–85, 1986. Kennicutt, H.M.C., Sweet, S.T., Fraser, W.R., Stockton, W.I., Culver,
Kawakami, T., Doi, T., Natural mortality of krill and density of swarms, M., Grounding of the Bahia Paraiso at Arthur Harbor, Antarctica:
in Comprehensive Report on the Population of Krill (Euphausia Distribution and fate of oil spill-related hydrocarbons, Environ.
superba) in the Antarctic, Doi, T., Ed., Tokai Regional Fisheries Sci. Technol., 25(3), 509–518, 1991.
Research Laboratory, Japan, 1979, 19–21. Kennicutt, H.M.C., McDonald, T.J., Denoux, G.J., McDonald, S.J.,
Kawamura, A., Food and feeding ecology in the southern sei whale, Sci. Hydrocarbon contamination in the Antarctic Peninsula, I: Arthur
Harbor—subtidal sediments, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 24(10), 499–506,
Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 22, 127–152, 1974.
1992.
Kawamura, A., A consideration of an available source of energy and its
Kennicutt, H.M.C., McDonald, T.J., Denoux, G.J., McDonald, S.J.,
cost for locomotion in fin whales, with special reference to
Hydrocarbon contamination on the Antarctic Peninsula, II:
seasonal migrations, Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 27,
Arthur Harbor—inter- and subtidal limpets (Nacella concinna),
61–79, 1975.
Mar. Pollut. Bull., 24(10), 506–511, 1992.
Kawamura, A., An interim consideration on a possible interspecific
Kenny, R., Hayson, N., Ecology of the rocky shores organisms at
relation in the southern baleen whales from the viewpoint of their
Macquarie Island, Pac. Sci., 16, 245–263, 1962.
food habits, Int. Whaling Comm. Rep., 28, 411, 1978.
Keyes, M.C., The nutrition of pinnipeds, in The Behaviour and
Kawamura, A., Food habitats of Euphausia superba Dana and the
Physiology of Pinnipeds, Harrison, R.J., Hubbard, R.C., Petersen,
diatom community, in Selected Contributions to the Woods Hole
C.E., Schusterman, R.J., Eds., Appleton-Centuary-Crofts, New
Conference on the Living Resources of the Southern Ocean,
York, 1968, 359–395.
El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., BIOMASS Scientific Series 2, 1981, 65–68.
Keys, J.R., Antarctic Marine Environments and Offshore Oil, Commis-
Kellerman, A., Zur Biologie der Jugendstadien der Notothenioidei
sion for the Environment, New Zealand Government, Wellington,
(Pisces) an der Antarktischen Halbinsel, Ber. Polarforsch., 31,
1984.
1–155, 1986.
Keysner, E.E., Tot, V.S., Shilov, V.N., Characteristics of the behaviour
Kellerman, A., Food and feeding ecology of postlarval and juvenile
and biological cycles of the marbled notothenia (Notothenia rossii)
Pleurogramma antarcticum (Pisces: Notothenioidei) in the in relation to bottom topography, bottom materials and currents,
seasonal pack ice zone off the Antarctic Peninsula, Polar Biol., J. Ichthyol., 14, 610–613, 1974.
7, 307–315, 1987. Khailov, K.M., Burkalova, Z.D., Release of dissolved organic matter
Kellerman, A., The larval food community in the zone of the seasonal by marine seaweeds and distribution of their total organic
pack ice cover and its seasonal and interannual variability, Arch. production to inshore communities, Limnol. Oceanogr., 14,
Fischereiwiss., 39, 89–109, 1989. 521–527, 1976.
Kellerman, A., Catalogue of early life stages of Antarctic notothenioid Kikuno, T., Spawning behaviour and early development of the Antarctic
fishes, Ber. Polarforsch., 67, 44–136, 1990a. krill, Euphausia superba Dana, observed on board R.V. Kaiyo
Kellerman, A., Food and feeding dynamics of the larval Antarctic fish Maru in 1979/80, Antarct. Rec., Tokyo, 73, 97–102, 1981.
Nototheniops larseni, Mar. Biol., 106, 159–167, 1990. Kils, U., Schwimmverhalten, Schwimmleistung, und Energiebilanz des
Kellerman, A., Kock, K.-H., The distribution of postlarval and juvenile Antarktischen Krills Euphausia superba, Ber. Inst. Meereskd.
notothenoids (Pisces: Perciformes) in the southern Scotia Sea (57– Christian-Albrechts-Univ. Kiel, 65, 1–79, 1979.
648 S/48–568 W) during FIBEX 1981, Meeresforschung, 30, Kils, U., Swimming speed and escape response of Antarctic krill,
82–93, 1984. Euphausia superba, Meeresforschung, 27, 264–266, 1979.
Kellerman, A., North, A.W., The contribution of the BIOMASS Kils, U., Swimming behaviour, swimming performance, and energy
Programme to Antarctic fish biology, in Southern Ocean Ecology: balance of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Biomass Scientific
The BIOMASS Perspective, El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., Cambridge Series 3, SCAR and SCOR, Scott Polar Research Institute,
University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1996, 191–210. Cambridge, UK, 1981.
Kellogg, D.E., Kellogg, T.B., Dearborn, J.H., Edwards, E.C., Fratt, D.B., Kils, U., Swimming and feeding of Antarctic krill Euphausia superba—
Diatoms from brittle star stomachs: Implications for sediment some outstanding energetics and dynamics—some unique morpho-
reworking, Antarct. J. U.S., 17, 167–169, 1983. logical details, Ber. Polarforsch., 4, 130–155, 1983.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 571
Kim, D., Seasonality of marine algae and grazers of an Antarctic rocky Knox, G.A., Antarctic marine ecosystems, in Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 1,
intertidal, with emphasis on the role of the limpet Nacella concinna Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Academic Press, London, 1970, 69–96.
Strebel (Gastropoda: Patellidae), Ber. Polarforsch., 397, 1, 2001. Knox, G.A., The marine benthic ecology and biogeography, in Biogeo-
Kinder, T.H., Hunt, G.L., Jr., Schneider, D., Schumacker, J.D., Corre- graphy and Ecology of New Zealand Shores, Kuschel, G., Ed., Dr.
lations between seabirds and oceanic fronts around the Pribolof W. Junk Publishers, The Hague, 1975, 353–405.
Islands, Alaska, Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci., 16, 309–319, 1983. Knox, G.A., Distribution patterns of the Southern Hemisphere marine
King, J.E., On a pup of the crabeater seal, Lobodon carcinophagus, Ann. biota: some comments on their origin and evolution, in Proceed-
Mag. Nat. Hist. Ser., 12, 619–624, 1957. ings of the International Symposium on Marine Biogeography and
King, J.E., The feeding mechanism and jaws of the crabeater seal Evolution in the Southern Hemisphere, Auckland, July 1978, 1979,
(Lobodon carcinophagus), Mammalia, 25, 462–466, 1961. 43–52.
King, J.E., Seals of the World, British Museum (Natural History), Knox, G.A., Plate tectonics and the evolution of intertidal and shallow-
London, 1964. water benthic biotic distribution patterns of the Southwest Pacific,
King, J.E., Some aspects of the anatomy of the Ross seal, Ommatophoca Palaeogeogr., Palaeoclimateol., Palaeoecol., 31, 267–297, 1980.
rossi (Pinnipedia: Phocidae), Br. Antarct. Surv. Sci. Rep., 63, 1–54, Knox, G.A., The living resources of the Southern Ocean: a scientific
1969. overview, in Antarctic Resources Policy: Scientific, Legal and
Kirkwood, G.P., Estimating population sizes from relative abundance Political Issues, Vicuna, F.O., Ed., Cambridge University Press,
data: A simulation study, Rep. Int. Whal. Commun., 36, 721–735, Cambridge, UK, 1983, 21–60.
1981. Knox, G.A., The key role of krill in the ecosystem of the Southern
Kirkwood, R., Robertson, G., The foraging ecology of female emperor Ocean, with special reference to the convention on the conserva-
penguins in winter, Ecol. Monogr., 67, 155–176, 1997. tion of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, Ocean Manage., 9,
Kirst, G.O., Wiencke, C., Ecophysiology of polar algae, J. Phycol., 31, 113–156, 1984.
181–199, 1995. Knox, G.A., Recent New Zealand marine research in the Ross Sea Sector
Kittel, W., Stepnik, R., Distribution of Euphausia crystallorophias,
of Antarctica, Mem. Nat. Inst. Polar Res. Special Issue, 40,
E. frigida, and Thysanoessa macrura in the southern part of the
245–363, 1986.
Drake Passage and in the Bransfield Strait during 1983–1984
Knox, G.A., Primary production and consumption in McMurdo Sound,
austral summer (BIOMASS-SIBEX), Polar Res., 6, 133–149,
Antarctica, in Antarctic Ecosystems: Ecological Change and
1983.
Conservation, Kerry, K.R., Hempel, G., Eds., Springer, Berlin
Klaas, C., Distribution and role of microprotozoa in the Southern Ocean,
Heidelberg, 1990, 115–128.
Ber. Polarforsch., 253, 1–119, 1997.
Knox, G.A., The Biology of the Southern Ocean, Cambridge University
Klages, M., Food and feeding ecology of emperor penguins in the eastern
Press, Cambridge, UK, 1994.
Weddell Sea, Polar Biol., 9, 385–390, 1989.
Knox, G.A., State of the Ross Sea region marine environment, in Ross Sea
Klages, M., Biology of the Antarctic gammaridean amphipod Eusirus
Region: State of the Environment Report for the Ross Sea Region of
perdentatus Gevreux (Crustacea: Amphipoda): Distribution, repro-
Antarctica, Antarctic Institute, Christchurch, 2001, 5.1–5.53.
duction and population dynamics, Antarct. Sci., 5, 349–359, 1993.
Knox, G.A., Ensor, P.H., (in preparation), The shallow water benthic
Klages, N.T.W., Bester, M.V., Fish as prey for fur seals, Arctocephalus
community beneath the McMurdo Ice Shelf at White Island,
spp., at subantarctic Marion Island, Mar. Biol., 131(3), 559–566,
McMurdo Sound, Antarctica.
1998.
Knox, G.A., Lowry, J.K., A comparison between the benthos of the
Klages, N.T.W., Gales, R., Pemberton, D., The stomach contents of
Southern Ocean and the North Polar Ocean, with special reference
Antarctic petrels Thalassoica antarctica feeding young chicks at
Scuta Manotik, Marion Coast, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 10, to the Amphipoda and Polychaeta, in Polar Oceans, Dunbar, M.J.,
545–547, 1990. Ed., Arctic Institute of North America, Calgary, 1977, 423–462.
Klinck, J.M., Hofmann, E.E., Deep-flow variability in the Drake Knox, G.A., Pierce, L., Bassett, J., (in preparation), The summer pelagic
Passage, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 16, 1281–1292, 1986. ecosystem beneath the sea ice at the edge of the McMurdo Ice
Kloser, H., Description basica de cateta pottery y costas abertas Shelf, McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Polar Biol.
adjacennes. Direccion Nacional del Antarcticos: Reporte de Knox, G.A., Waghorn, E.H., Ensor, P.H., (in press), The summer
datos Estuctura y dinamica de unecosystema costera Antártico, plankton beneath the McMurdo Ice Shelf at White Island,
Estacion cientifica “Terniente Jubany” en la Isla 25 de mayo (King McMurdo Sound, Antarctica.
George Island), Islas Shetland del Sur, Contribucion No. 419B, Knust, R., Arntz, W.E., Boche, M., Brey, T., Gerdes, D., Mintenbeck, K.,
1994. Schröder, A., Starmans, A., Teixidó, N., Iceberg scouring on the
Kloser, H., Habitats and distribution patterns of benthic diatoms in Potter Eastern Weddell Sea shelf (Antarctica): a benthic system shaped
Cove (King George Island) and its vicinity, Ber. Polarforsch., 299, by physical disturbances, in Antarctic Biology in a Global Context,
95–105, 1998. Huiskes, A.H.L., Gieskes, W.W.C., Rozema, J., Schorno, R.M.L.,
Kloser, H., Ferreyra, G., Schloss, I., Mercuri, G., Laturnus, F., Curtosi, van der Vies, S.M., Wolff, W.J., Eds., 2003, 96–107.
A., Seasonal variation of algal growth and conditions in sheltered Kock, K.-H., Verbreitung und biologie der Wichtigsten nutzfischarten
Antarctic bays: the example of Potter Cove (King George Island, der Antarktis, Mitt. Institut für Seefischerei, Hamburg, 16, 1–75,
South Shetlands), Polar Biol., 14, 11–16, 1993. 1975.
Knox, G.A., Littoral ecology and biogeography of the Southern Ocean, Kock, K.-H., On the fecundity of Chamsocephalus gunnari Lönnberg
Proc. R. Soc. Lond. ,Ser. B Biol. Sci., 162, 577–624, 1960. 1906 and Chaenocephalus aceratus Lönnberg 1906 (Pisces,
Knox, G.A., The biogeography and intertidal ecology of Australian Channichthyidae) off South Georgia Island, Meeresforschung,
coasts, Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev., 1, 341–404, 1963. 27, 177–185, 1979.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:48—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
572 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Kock, K.-H., Fischereibiologische Untersuchungen an drei antarktischen Kompowski, A., Studies on juvenile Chaenocephalus aceratus Lönn-
Fischarten: Chamsocephalus gunnari Lönnberg 1905, Chaenoce- berg, 1906 (Pisces: Chaenichthyidae) off South Georgia, Acta
phalus aceratus Lönnberg 1906, and Pseudochaenichthys Ichtyol. Pisc., 10(1), 45–53, 1980.
georgianus Norman 1937 (Notothenioidei: Channichthyidae), Kompowski, A., Biological characteristics of Scotia Sea icefish Chae-
Mitt. Institut für Seefischerei, Hamburg 32, 1981, 1–127. nocephalus aceratus (Lönnberg, 1906) from the South Georgia
Kock, K.-H., Fischerbiologische Unterschungen bei Elephant Island im area, Rep. Sea Fish. Inst., Grodyna, 22, 49–71, 1990.
Marz, 1981, Archiv für Fischereiwissenschaft, 33, 127–142, 1982. Kooyman, G.L., Erythrocyte analysis of some Antarctic fishes, Copeia,
Kock, K.-H., Marine habitats—fish, in Key Environments—Antarctica, 2, 457–458, 1963.
Bonner, W.N., Walton, D.W.H., Eds., Pergamon Press, Oxford, Kooyman, G.L., The physiology of diving in penguins, in The Biology
1984, 17–192. of Penguins, Stonehouse, B., Ed., Macmillan, London, 1975,
Kock, K.-H., Krill consumption by Antarctic notothenioid fish, in 115–137.
Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Kooyman, G.L., Crabeater seal—Lobodon carcinophagus (Hombron &
Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 437–444. Jacquinot, 1842), in Handbook of Marine Mammals, Vol. 2: Seals,
Kock, K.-H., Marine consumers: fish and squid, Environ. Int., 13, 37–45, Ridgeway, S.H., Harrison, R.J., Eds., Academic Press, London,
1987. 1981, 221–235.
Kock, K.-H., Reproduction in fish around Elephant Island, Archiv für Kooyman, G.L., Leopard seal—Hydrurga leptonyx (Blainville, 1820), in
Fischerewissenschaft, 39(1), 171–210, 1989. Handbook of Marine Mammals, Vol. 2: Seals, Ridgeway, S.H.,
Kock, K.-H., The status of exploited fish stocks in the Southern Ocean, Harrison, R.J., Eds., Academic Press, London/New York, 1981,
Archiv für Fischereiwissenschaft, 41, 1–65, 1991. 261–274.
Kock, K.-H., Antarctic Fish and Fisheries, Cambridge University Press, Kooyman, G.L., Weddell seal—Leptonychotes weddelli Lesson, 1826,
Cambridge, UK, 1992. in Handbook of Marine Mammals, Vol. 2: Seals, Ridgeway, S.H.,
Kock, K.-H., Kellerman, A., Reproduction in Antarctic notothenioid
Harrison, R.J., Eds., Academic Press, London/New York, 1981,
fish, Antarct. Sci., 3, 125–130, 1991.
275–296.
Kock, K.-H., Koster, F.-W., The state of exploited fish stocks in the
Kooyman, G.L., Weddell Seal: Consummate Diver, Cambridge Univer-
Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean, in Antarctic Ecosystems:
sity Press, New York, 1981.
Ecological Change and Conservation, Kerry, K.R., Hempel, G.,
Kooyman, G.L., Davis, R.W., Feeding behaviour of female Antarctic fur
Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1990, 308–322.
seals, Arctocephalus gazella, Antarct. J. U.S., 15, 159–160, 1980.
Kock, K.-H., Shimadzu, Y., Trophic relationships and trends in popu-
Kooyman, G.L., Davis, R.W., Croxall, J.P., Costa, D.P., Diving depths
lation size and reproductive parameters in Antarctic high-level
and energy requirements of King Penguins, Science, 217, 726–727,
predators, in Southern Ocean Ecology: The BIOMASS Perspective,
1971.
El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK,
Kooyman, G.L., Keren, D.H., Campbell, W.B., Wright, J.J., Pulmonary
1996, 287–312.
gas exchange in freely diving Weddell seals, Leptonychotes
Kock, K.-H., Stein, M., Krill and hydrographic conditions off the
weddelli, Respir. Physiol., 17, 283–290, 1973.
Antarctic Peninsula, Meeresforschung, 26, 79–95, 1978.
Kooyman, G.L., Davis, R.W., Croxall, J.P., Diving behaviour of
Kock, K.-H., Schneppenheim, R., Siegel, V., A contribution to the fish
Antarctic fur seals, in Fur Seals: Maternal Strategies on Land
fauna of the Weddell Sea, Archiv für Fischereiwissenschaft, 34,
and at Sea, Gentry, R.L., Kooyman, G.L., Eds., Princetown
103–120, 1984.
University Press, Princetown, 1986, 115–125.
Kock, K.-H., Duhamel, G., Hureau, J.-C., Review of the biology and present
Kooyman, G.L., Cherel, Y., Le Maho, Y., Croxall, J.P., Thorson, P.H.,
status of exploited Antarctic fish stock, Biomass Scientific Series No.
7, SCAR, Scott Polar Research Institute, Cambridge, UK, 1985. Ridoux, V., Kooyman, C.A., Diving behaviour and energetics
Kock, K.-H., Belcher, M., Joines, C.D., Is the attempt to estimate the during foraging cycles in king penguins, Ecol. Monogr., 62,
biomass of Antarctic fish from multi-species surveys appropriate 143–163, 1992.
for the targeted species? Noththenia rossii in the Atlantic Ocean Kopczynska, E.E., Spatial structure of phytoplankton in the Scotia Front
sector revisited, CCAMLR Sci., 13, 141–153, 2004. west of Elephant Island (BIOMASS II), October–November 1986,
Kogure, K., Fukami, K., Simidu, U., Taga, N., Abundance and production Polar Biol., 9, 231–242, 1988.
of bacterioplankton in the Antarctic, Mem. Natl. Inst. Polar Res., Kopczynska, E.E., Fiala, M., Surface phytoplankton composition and
Spec. Issue, 40, 414–422, 1986. carbon distribution in the Crozet Basin during austral summer of
Koike, I., Ronner, U., Holm-Hansen, O., Microbial nitrogen metabolism 1999: Variability across frontal zones, Polar Biol., 27, 17–28,
in the Scotia Sea, Antarct. J. U.S., 16, 165–166, 1981. 2003.
Koike, I., Holm-Hansen, O., Biggs, D.C., Inorganic nitrogen metabolism Kopczynska, E.E., Weber, L.H., El-Sayed, S.Z., Phytoplankton species
by Antarctic phytoplankton, with special reference to ammonia composition in the Indian sector of the Antarctic Ocean, Polar
cycling, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 30, 105–116, 1986. Biol., 6, 161–169, 1986.
Koltun, V.M., Porifera, Antarctic Map Folio Series, Vol. 11, American Kosahi, S., Takahashi, M., Yamaguchi, Y., Aruya, Y., Some charac-
Geographical Society, Washington, DC, 13–14 pp, 1969. teristics of chlorophyll particles in the Southern Ocean, Trans.
Komaki, Y., Technical notes on keeping euphausiids alive in the Tokyo Univ. Fish., 6, 85–97, 1985.
laboratory, with a review of experimental studies on euphausiids, Kosaka, S., Takahashi, M., Yamaguchi, Y., Aruya, Y., Size charac-
Bull. Plankton Soc. Japan, 13, 95–106, 1966. teristics of chlorophyll particles in the southern Ocean, Trans.
Kompowski, A., On feeding of Champocephalus gunnari Lönnberg, Tokyo Univ. Fish., 6, 85–97, 1985.
1905 (Pisces: Chaenichthyidae) off South Georgia and Kerguelen Kott, P., Antarctic Ascidacea, Antarct. Res. Ser., 13, 1–239, 1969.
Island, Acta Ichtyol. Pisc., 10, 25–42, 1980. Kott, P., Antarctic Ascidacea II, Antarct. Res. Ser., 17, 18–82, 1971.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 573
Kottmeier, S.T., Sullivan, C.W., Late winter primary production and Kristiansen, S., Syvertsen, E.E., Farbrot, T., Nitrogen uptake in the
bacterial production in sea ice and seawater west of the Antarctic Weddell Sea during late winter and spring, Polar Biol., 12,
Peninsula, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 36, 287–298, 1987. 245–251, 1992.
Kottmeier, S.T., Sullivan, C.W., Sea ice microbial communities Kristiansen, S., Farbrot, T., Kosa, H., Myklestad, S., Quillfeldt, C.H.,
(SIMCO) 9: Effects of temperature and salinity on rates of Nitrogen uptake in the infiltration community: An ice algal
metabolism and growth of autotrophs and heterotrophs, Polar community in Antarctic pack ice, Polar Biol., 19, 307–315, 1998.
Biol., 8, 293–304, 1988. Krzysztof, W., Opalinski-Maciejewska, M., Georgiera, L.V., Notes on
Kottmeier, S.T., Sullivan, C.W., Bacterial biomass and production in food selection in Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Polar Biol.,
pack ice of Antarctic marginal ice zones, Deep-Sea Res., 37, 17, 350–357, 1997.
1311–1330, 1990. Kuhl, S., Schneppenheim, R., Electrophoretic investigation of genetic
Kottmeier, S.T., Musat, A.M., Craft, L.L., Kastendiek, J.E., Sullivan, variation in two krill species, Euphausia superba and E. crystal-
C.W., Ecology of sea ice microbial communities in McMurdo lorophias (Euphaudiidae), Polar Biol., 6, 17–23, 1986.
Sound, Antarct. J. U.S., 19, 129–131, 1984. Kundo, K., Fukuchi, M., Vertical distribution of chlorophyll a in the
Kottmeier, S.T., Miller, M.A., Lizotte, M.P., Craft, L.L., Sullivan, C.W., Indian sector of the Antarctic Ocean in 1972–1973, Antarct. Rec.,
Ecology of sea ice microbial communities during the 1984 winter– 74, 127–142, 1982.
summer transition in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Antarct. J. U.S., Kunzmann, A., Blood physiology and ecological consequences in
20, 128–130, 1986. Weddell Sea fishes, Ber. Polarforsch., 91, 1–79, 1996.
Kottmeier, S.T., Grossi, S.McG., Sullivan, C.W., Sea ice microbial Kuosa, H., Norman, B., Kivi, K., Brandini, F., Effects of Antarctic sea
communities, VIII: Bacterial production in annual sea ice of ice biota on seeding as studied in aquarium experiments, Polar
McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 35, Biol., 12, 333–339, 1992.
175–186, 1987. Kuparinen, J., Bjornsen, P.K., Spatial distribution of bacterioplankton
across the Weddell-Scotia Confluence during early austral summer
Kowalke, J., Abele, D., A first record of the sift bottom infauna
1988–1989, Polar Biol., 12, 197–204, 1992.
community of Potter Cove, Ber. Polarforsch., 299, 106–112, 1998.
Kuramoto, S., Koyama, K., Preliminary report of the oceanographic
Kozlov, A.N., Ecologophysiological peculiarities of Notothenia rossii
observations on the 22nd Japanese Antarctic Research Expedition
mamorata Fischer and Notothenia gibberifrons Lönnberg at certain
(1980–1981), Mem. Natl. Inst. Polar Res., Spec. Issue, 23, 5–12,
periods of the annual life cycle, in An Ecological and Biological
1982.
Description of Some Species of Antarctic Fishes, All-Union
Kurtz, P.P., Bromwich, D.H., Satellite-observed behaviour of the Terra
Research Institute of Marine Fisheries and Oceanography,
Nova Bay polyna, J. Geophys. Res., 88, 9717–9722, 1983.
Moscow, 1980. In Russian.
Kurtz, P.P., Bromwich, P.H., A recurring, atmospherically-formed
Kozlov, A.N., Seasonal changes of morphophysiological characteristics
polyna in Terra Nova Bay, in Oceanology of the Antarctic Shelf,
of the marbled notothenia, Notothenia rossii mamorata Fischer
Antarctic Research Series 45, Jacobs, S.S., Ed., American Geophy-
(Nototheniidae). Voprosy Ikhtiologii 22, 782. In Russian published
sical Union, Washington, DC, 1985, 177–201.
in English in Journal of Ichthyology, 22, 52–58, 1982.
Kussakin, O.G., Fauna of Isopoda and Tanaidacea in the coastal zones of
Kozlov, A.N., A review of the trophic role of mesopelagic fish of the
Antarctic and sub-Antarctic waters: biological zones of the
family Myctophidae in the Southern Ocean ecosystem, CCAMLR
Antarctic and subantarctic waters, Biological Reports of the
Sci., 2, 71–77, 1995.
Soviet Antarctic Expeditions (1955–1958), Akademiya nauk
Kozlov, A.N., Tarverdiera, M.I., Feeding of different species of Mycto-
SSSR Zoologoscheskii Institut Issledovaniya a Fauny morei,
phidae in different parts of the Southern Ocean, J. Ichthyol., 29,
220–389 pp, 1967.
160–167, 1989. Translated from Voprosy Ikhtiologii. Laevastu, T., Favourite, F., Holistic simulation models of shelf-seas
Kramp, P.L., Hydromedusae from Discovery collections, Discov. Rep., ecosystems, in Analysis of Marine Ecosystems, Longhurst, A.R.,
29, 1–128, 1957. Ed., Academic Press, London, 1981, 701–727.
Krause, G.H., Weis, E., Chlorophyll fluorescence and photosynthesis: Laevastu, T., Larkin, H.H., Marine Fisheries Ecosystem—Its Quan-
the basics, Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 42, titative Evaluation and Management, Fishing News Books,
313–349, 1991. Farnham, Surrey, 1981.
Krebs, W.M., Ecology of neretic diatoms, Arthur Harbor, Antarctica, Lake, S., Burton, H., van den Hoff, J., Regional, temporal, and fine-scale
Micropalaeontology, 29, 267–297, 1983. spatial variation in Weddell seal diet at four coastal locations in
Krebs, W.M., Lipps, J.H., Burckle, L.H., Ice diatom floras, Arthur east Antarctica, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 254, 293–305, 2003.
Harbour, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 7, 163–171, 1987. La Mesa, M., Eastman, J.T., Vacchi, M., The role of notothenioid fishes
Krembs, C., Eiken, H., Juinge, K., Deming, J.W., High concentrations of in the food web of the Ross Sea shelf waters, Polar Biol., 27,
exopolymeric substances in Arctic winter sea ice: Implications for 321–338, 2004.
the polar ocean carbon cycle and cryoprotection of diatoms, Deep- Lampitt, R.S., Noji, T., von Bodungen, B., What happens to zooplankton
Sea Res., 49, 2163–2181, 2002. faecal pellets? Implication for material flux, Mar. Biol., 104,
Krempin, D.M., The role of bacterioplankton as producers in two high- 15–23, 1990.
productivity marine ecosystems, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Lancelot, C., Mathot, S., Biochemical fractionation of primary pro-
Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, 1985. duction by phytoplankton in Belgium coastal waters during short-
Kriss, A.Ye., Quantitative distribution of saprophytic bacteria between and long-term incubations with 14C-bicarbonate. II. Phaeocysts
New Zealand and Antarctica, Microbiology, 42, 913–917, 1973. pouchetii colonial population, Mar. Biol., 65, 13, 1985.
Kristensen, T.K., Periodical growth rings in cephalopod statoliths, Dana, Lancelot, C., Keller, M.D., Rousseau, V., Smith, W.O., Jr., Mathot, S.,
1, 39–51, 1980. Auto-ecology of the haptophyte Phaeocystis sp, in The
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
574 Biology of the Southern Ocean
physiological ecology of harmful algal blooms, NATO ASI Series Laws, R.M., Reproduction, growth, and age of Southern Hemisphere fin
Vol. G41, Anderson, D., Hallrgraeff, G., Cambella, A., Eds., whales, Discov. Rep., 31, 327–486, 1961.
Springer, Heidelberg, 1998, 211–224. Laws, R.M., Comparative biology of Antarctic seals, in Biologie Antarc-
Lancraft, T.M., Torres, J.J., Hopkins, T.L., Micronekton and macro- tique, Carrick, R., Holdgate, M.W., Prevost, J., Eds., Hermann,
zooplankton in the open waters near Antarctic ice edge zones Paris, 1964, 445–457.
(AMERIEZ 1983 and 1986), Polar Biol., 9, 225–233, 1989. Laws, R.M., Population increase of fur seals at South Georgia, Polar
Lancraft, T.M., Hopkins, T.L., Torres, J.J., Donnelly, J., Oceanic Biol., 16, 856–858, 1973.
micronekton/macrozooplankton community structure and feeding Laws, R.M., Seals and whales of the Southern Ocean, Philos. Trans. R.
in ice-covered Antarctic waters (AMERIEZ 1986), Polar Biol., 11, Soc. Lond., Ser. B, 279, 81–96, 1977a.
157–167, 1991. Laws, R.M., The significance of vertebrates in the Antarctic marine
Lange, M.A., Basic properties of Antarctic sea ice as revealed by textural ecosystem, in Adaptations within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano,
analysis of ice cores, Ann. Glaciol., 10, 95–101, 1988. G.A., Ed., Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC, 1977b,
Lange, M.A., Ackley, S.F., Wadhams, P., Dieckman, G.S., Eicken, H., 411–438.
Development of sea ice in the Weddell Sea, Ann. Glaciol., 12, Laws, R.M., Monitoring whale and seal populations, in Monitoring the
97–103, 1989. Marine Environment, Symposium of the Institute of Biology No. 7,
Lange, M.A., Schlosser, P., Ackley, S.F., Wahdhams, P., Dieckmann, Nichols, D., Ed., 1979, 114–115.
G.S., 18O concentrations in sea ice of the Weddell Sea, Antarctica, Laws, R.M., Seal surveys, South Orkney Islands, 1971 and 1974, Br.
Ann. Glaciol., 36(124), 315–323, 1990. Antarct. Surv. Bull., 54, 136–139, 1981.
Larrian, E., Consecuencia en la biota bentónica de las erupciones Laws, R.M., Seals, in Antarctic Ecology, Laws, R.M., Ed., Vol. 2,
volcánicas en Isla Decepción (628 57 0 S, 608 29 0 S, 598 04 0 W) y Academic Press, London, 1984, 621–715.
su comparación con Bahı́a Chile (628 29 0 S, 598 04 0 W), Antarc. Laws, R.M., Decade of research on Antarctic and subantarctic seals,
S. Afr. J. Sci., 80, 25–35, 1984.
Mem. Biol. Mar. Universidad de Concepción, 1–150, 1986.
Laws, R.M., The ecology of the Southern Ocean, Am. Sci., 73, 26–38,
Larson, R.J., Pelagic Scyphomedusae (Scyphozoa: Coronatae and
1985.
Semaeostomeae) of the Southern Ocean, Antarct. Res. Ser., 41,
Laws, R.M., Purves, P.E., The ear plug of Mysticeti as an indicator of
59–165, 1986.
age, with special reference to the North Atlantic fin whale, Norsk
Larsson, P., Jarnmnark, C., Sodergren, A., PCBs and chlorinated
Hvalgangsttid, 45, 414–425, 1956.
pesticides in the atmosphere and aquatic organisms of Ross
Leakey, R.J., Archer, S.D., Grey, J., Microbial dynamics in coastal
Island, Antarctica, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 25, 281–287, 1992.
waters of East Antarctica: Bacterial production and nanoflagellate
Lasker, R., Feeding, growth, respiration, and carbon utilization of a
bactivory, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 142, 3–17, 1996.
euphausiid crustacean, J. Fish. Res. Board Can., 23, 1291–1317,
LeBlond, P.H., Satellite observations of the Labrador Current undula-
1966.
tions, Atmosphere-Ocean, 20, 129–142, 1982.
Lasker, R., Field criteria for survival of anchovy larvae: the relation
LeBoeuf, R.J., Croker, D.E., Blackwell, S.B., Morris, P.A., Thorson,
between the inshore chlorophyll layers and successful first feeding,
D.H., Sex differences in diving and foraging behaviour of northern
U.S. Fish. Bull., 71, 453–462, 1975.
elephant seals, Symp. Zool. Soc. Lond., 66, 149–178, 1993.
Lasker, R., Field criteria for survival of anchovy larvae: The relation
Lee, H.J., Gerdes, D., Vanhove, S., Vinex, M., Meiofauna response to
between the inshore chlorophyll layers and successful first feeding,
iceberg disturbance on the Antarctic continental shelf at Kapp
U.S. Fish. Bull., 71, 847–855, 1980a.
Norvegia (Weddell Sea), Polar Biol., 24(12), 926–933, 2001.
Lasker, R., Factors contributing to variable recruitment of the northern
Lee, H.J., Vanhove, S., Peck, L.S., Vinex, M., Recolonization of
anchovy (Eugraulis mordax) in the Californian current, contrasting meiofauna after catastrophic iceberg scouring in shallow Antarctic
years 1975 through 1978, in Proceedings of the 2nd Symposium on sediments, Polar Biol., 24, 918–925, 2001.
the Early Life History of Fish, ICES/EHL Symposium/PE, 1980b, Leford-Hoffman, P.A., DeMaster, D.J., Nittrouer, C.A., Biogenic-silica
1–11. accumulation in the Ross Sea and the importance of the Antarctic
Latogurskij, V.L., Euphausia superba Dana as a food item of Notothenia continental shelf deposits in the marine silica budget, Geochim.
rossii marmorata, Trudy Atl. NIRO, 42, 167–169, 1972. In Russian. Cosmochim. Acta, 50, 2099–2110, 1986.
Laubscher, R.K., Perrisinotto, R., McQuaid, C.D., Phytoplankton pro- Legechis, R., Oceanic polar front in the Drake Passage: Satellite
duction and biomass at frontal zones in the Atlantic sector of the observations during 1976, Deep-Sea Res., 24, 701–704, 1977.
Southern Ocean, Polar Biol., 13, 471–481, 1993. Legendre, L., Hydrodynamic control of marine phytoplankton pro-
Lavigne, D.M., Barchard, W., Innes, S., Oritzland, N.A., Pinniped duction: the paradox of stability, in Marine Interface
energetics, FAO Fish. Ser., 4(5), 191–235, 1982. Ecohydrodynamics, Nihoul, J.C.J., Ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam,
Lavigne, D.M., Innes, S., Worthy, G.A.J., Kovacs, K.M., Schmitz, O.J., 1985, 191–207.
Hickie, J.P., Metabolic rates of seals and whales, Can. J. Zool., 64, Legendre, L., The biological CO2 pump in seasonally ice-covered
279–284, 1986. waters, Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Biol., 9, 61–74, 1996.
Laws, R.M., The elephant seal (Mirounga leonina Linn.), II: General, Legendre, L., Le Fevre, J., Hydrodynamic singularities as controls of
social and reproductive behaviour, Falkl. Isl. Depend. Surv. Sci. recycled versus export production in oceans, in Productivity in the
Rep., 13, 1–88, 1956. Oceans: Present and Past, Berger, W.H. et al., Eds., Wiley,
Laws, R.M., Problems of whale conservation, Trans. N. Am. Wildl. Chichester, 1989, 49–63.
Conf., 25, 304–309, 1960a. Legendre, L., Le Fevre, J., Interactions between hydrodynamic and
Laws, R.M., The southern elephant seal (Mirounga leonina Linn.) at pelagic ecosystems: Relevance to resource exploitation and
South Georgia, Norsk Hvalfangst-Tidende, 49, 466–476, 1960b. climate change, S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci., 12, 477–486, 1992.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 575
Legendre, L., Michaud, J., Flux of biogenic carbon in oceans: Size- Lewis, E.L., Weeks, W.F., Sea ice: Some polar contrasts, in Symposium
dependent regulation by pelagic food webs, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., on Antarctic Ice and Water Masses, Deacon, G., Ed., Scientific
164, 1–11, 1998. Committee on Antarctic Research, Tokyo, 1971, 23–34.
Legendre, L., Rassoulzadegan, F., Food-web mediated export of Lewis, M.R., Horne, E.P.W., Cullen, J.J., Oakey, N.S., Platt, T.,
biogenic carbon in oceans: Environmental control, Mar. Ecol. Turbulent motions may control phytoplankton photosynthesis in
Prog. Ser., 145, 179–193, 1996. the upper ocean, Nature (Lond.), 311, 49–50, 1984.
Legendre, M.L., Ingram, R.G., Poulin, M., Physical control of phyto- Leynaert, A., Nelson, D.M., Queguirer, R., Treguer, P., The silica cycle
plankton under sea ice (Monitounuk Sound, Hudson Bay), Can. in the Antarctic Ocean: Is the Weddell Sea atypical?, Mar. Ecol.
J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 38, 1385–1392, 1981. Prog. Ser., 96, 1–15, 1993.
Legendre, L., Ackley, S.F., Dieckmann, G.S., Guillksen, B., Horner, R., Li, W.K.W., Experimental approaches to field measurements: Methods
Hoshiai, T., Melnikov, I.A., Reeburgh, W.S., Ecology of sea ice and interpretations, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 214, 251–286, 1986.
biota: Global significance, Polar Biol., 12, 429–444, 1992. Li, W.K.W., Subba Rao, D.V., Harrison, W.G., Smith, J.C., Cullen, J.J.,
Le Jehan, S., Treguer, P., The distribution of inorganic nitrogen, Irwin, B., Platt, T., Autotrophic picoplankton in the tropical ocean,
phosphorus, silicon, and dissolved organic matter in surface and Science, 219, 292–295, 1983.
deep waters of the Southern Ocean, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles Liebezeit, G., Residual amino acid fluxes in the upper water column of
and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., the Bransfield Strait, Oceanol. Acta, 8, 59–65, 1985.
Springer, Berlin, 1985, 22–29. Liebezeit, G., Bolter, M., Distribution of particulate amino acids in the
Le Maho, Y., Delclitte, P., Chatonnet, J., Thermoregulation in fasting Bransfield Strait, Polar Biol., 2, 225–228, 1986.
emperor penguins, Am. J. Physiol., 231, 913–922, 1976. Liebezeit, G., von Bodungen, B., Biogenic fluxes in the Bransfield Strait:
Le Maho, Y., Karmann, H., Briot, D., Handrich, Y., Robin, J.P., Planktonic versus microalgal sources, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 36,
Mioskowski, E., Cherel, Y., Farni, J., Stress on birds due to 23–32, 1987.
Lien, R., Solheim, A., Elverhoi, A., Rokoengen, K., Iceberg scouring and
routine handling and a technique to avoid it, Am. J. Physiol.,
sea bed morphology on the eastern Weddell Sea shelf, Polar Res.,
263, 775–781, 1992.
7, 43–57, 1989.
Lenihan, H.S., Benthic marine pollution around McMurdo Station,
Ligowski, R., Phytogenic food of Euphausia superba Dana caught in the
Antarctica: A summary of findings, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 25(9–12),
drake passageand bransfield strait, February–March 1981
318–323, 1992.
(BIOMASS-FIBEX), Polish Polar Biol., 3, 281–288, 1982.
Lenihan, H.S., Oliver, J.S., Oakden, J.M., Slattery, M.D., Intense and
Ligowski, R., Glony lodu morskiego Zatoka Admiralicji Pol redakeja
localized benthic marine pollution around McMurdo Sound, Mar.
prof. dr S. Rakusa-Susczwakego, Oficyna Wyd IE PAN Dziekanaw
Pollut. Bull., 21, 422–450, 1990.
Lesny 85, 1992. In Polish.
Lenihan, H.S., Keist, K.A., Conlan, K.E., Slattery, P.N., Konar, B.H.,
Ligowski, R., Benthic feeding by krill, Euphausia superba Dana, in
Oliver, J.S., Patterns of survival and behaviour in Antarctic
coastal waters off West Antarctica and in Admiralty Bay, South
invertebrates exposed to contaminated sediments: Field and labora-
Shetland Islands, Polar Biol., 23, 619–625, 2000.
tory experiments, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 192, 233–255, 1995.
Lillo, S., Guzman, O., Study of the abundance, distribution, and
Lessard, E.J., Swift, E., Species-specific grazing rates of heterotrophic
behaviour of krill at the Bransfield Strait and Drake Passage by
dinoflagellates in oceanic waters measured with dual-labelled
means of hydroacoustic techniques, Instituto Antártico Chileno
radioisotope technique, Mar. Biol., 87, 289–296, 1985.
(INACH) Scientific Series, 28, 17–45, 1982.
Lessard, E.J., Voytek, M., Rivkin, R., The heterotrophic-based nutrition
Lin, Y., Raymond, J.A., DeVries, A.L., Compartmentalization of NaCl
of microzooplankton and macrozooplankton in McMurdo Sound,
in frozen solutions of antifreeze glycoproteins, Cryobiology, 13(3),
Antarctica, EOS, 68, 1773–1778, 1987. 334–340, 1976.
Leventer, A., Sediment trap diatom assemblages from the northern Lindeman, R.I., The trophic-dynamic aspect of ecology, Ecology, 23,
Antarctic Peninsula, Deep-Sea Res., 38(8/9), 1127–1143, 1991. 399–418, 1942.
Leventer, A., Particulate flux from sea ice in polar waters, in Sea Ice: An Lindsay, A.A., Weddell seals in the Bay of Whales, Antarctica,
Introduction to its Physics, Chemistry, Biology and Geology, J. Mammal., 18, 127–144, 1937.
Thomas, D.N., Dieckmann, G.S., Eds., Blackwell Science, Linkowski, T.B., Population biology of the myctophid fish Gymnosco-
Oxford, 2003, 303–332. pelus nicholsi (Gilbert 1911) from the western South Atlantic,
Leventer, A., Dunbar, R.B., Diatom flux in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, J. Fish Biol., 27, 683–698, 1985.
Mar. Micropaleontol., 12, 49–64, 1987. Linkowski, T.B., Rembiszewski, J.M., Ichthyological observations off the
Leventer, A., Domack, E.W., Ishman, S.E., Brachfeld, S., McClennen, South Georgia coasts, Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol., 25, 697–704, 1978.
C.E., Manley, P., Productivity cycles of 200–300 years in the Linkowski, T.E., Presler, P., Zubowski, C., Food habits of Nototheniid
Antarctic Peninsula region: Understanding linkages among the fishes (Nototheniidae) in Admiralty Bay (King George Island,
sun, atmosphere, oceans, sea-ice and biota, Bull. Geol. Soc. Am., South Shetland Islands), Pol. Polar Res., 4, 75–79, 1983.
108(12), 1626–1644, 1996. Linley, E.A.S., Newell, R.C., Estimates of bacterial growth yields based
Levin, S.A., Marin, A., Powell, T.M., Patterns and processes in the on plant detritus, Bull. Mar. Sci., 35, 409–425, 1984.
distribution and dynamics of Antarctic krill, in Selected Scientific Lipps, J.H., Hickman, C.S., Origin, age, and evaluation of Antarctic
Papers, Part I. SC-CCAMLR-SS P/5, Commission on the Conser- deep-sea fauna, in The Environment of the Deep Sea, Errista, W.G.,
vation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 281–299 pp, Morin, J.G., Eds., Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1982,
1988. 325–356.
Lewis, E.L., Perkins, R.G., Oceanographic investigations in McMurdo Lipps, J.H., Krebs, W.N., Planktonic foraminifera associated with
Sound, Antarct. Res. Ser., 5, 1–37, 1985. Antarctic sea ice, J. Foram. Res., 4, 80–85, 1974.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
576 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Lipps, J.H., DeLaca, T.E., Krebs, W., Stockton, W., Shallow-water Lockyer, C., Observations on the diving behaviour of the sperm whale,
Foraminifera studies, Antarctic Peninsula, Antarct. J. U.S., 7, Physeter catadon, in A Voyage of Discovery, Angel, M., Ed.,
82–83, 1972. Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1977, 591–609.
Lipps, J.H., Krebs, W.N., Temnikow, N., Microbes under Antarctic ice Lockyer, C., A theoretical approach to the balance between growth and
shelves, Nature (Lond.), 265, 232–233, 1977. food consumption in fin and sei whales, with special reference to
Lipps, J.H., DeLaca, J.F., Showeres, W. et al., Benthic marine biology: the female reproductive cycle, Int. Whaling Comm. Rep., 28,
Ross Ice Shelf project, Antarct. J. U.S., 13, 134–141, 1978. 243–249, 1978.
Lipps, J.H., Roman, T.E., DeLaca, T.E., Life below the Ross Ice Shelf, Lockyer, C., Growth and energy budgets of large baleen whales from the
Antarctica, Science, 203, 447–449, 1979. Southern Hemisphere, in Mammals of the Sea, FAO Fisheries
Lipski, M., Chlorophyll a in the Bransfield Strait and the southern part of Series No. 5, Vol. 3, Food and Agriculture Association of the
the Drake Passage during BIOMASS-SIBEX (December 1983– United Nations, Rome, 379–487 pp, 1981a.
January 1984), Pol. Polar Res., 6, 21–30, 1985. Lockyer, C., Estimates of the growth and energy budget for the sperm
Lishman, G.S., The food and feeding ecology of Adélie Penguins
whale, Physeter catadon, in Mammals of the Sea, FAO Fisheries
(Pygoscelis adeliae) and chinstrap penguins (P. antarctica) at
Series No. 5, Vol. 3, Food and Agriculture Organization of the
Signy Island, South Orkney Islands, J. Zool., Lond., 205,
United Nations, Rome, 489–504 pp, 1981b.
245–263, 1985.
Lockyer, C., Brown, S.G., The migration of whales, in Animal
Lishman, G.S., Croxall, J.P., Diving depths of the chinstrap penguin, Br.
Migration, Cambridge Society for Experimental Biology,
Antarct. Surv. Bull., 61, 21–25, 1983.
Seminar Series 13, Ainley, D.G., Ed., Cambridge University
Lisitzin, A.P., Sedimentation in the World Ocean, Society for Economic
Press, Cambridge, UK, 1981, 105–132.
Paleontology and Mineralogy, Special Publication 17, 1972.
Loeb, V., Siegel, V., Holm-Hansen, O., Hewitt, R., Fraser, W.,
Lisovenko, L.A., Svetlov, M.F., Some data on the biology of Paraliparis
Trivelpiece, W., Trivelpiece, S., Effects of sea ice extent on krill
(Family Liparidae) for the South Shetlands, J. Ichthyol., 20,
131–135, 1980. salp dominance in the Antarctic food web, Nature (Lond.), 307,
Littlepage, J.R., Seasonal variation in lipid content of two Antarctic 897–900, 1997.
marine crustacea, in Biologie Antarctique, Carrrick, R., Holdgate, Lomakina, N.B., The euphausiid fauna of the Antarctic and notal regions,
M.W., Prevost, J., Eds., Herman, Paris, 1964, 163–176. in Biological results of the Soviet Antarctic Expedition (1955–
Littlepage, J.R., Oceanographic investigations in McMurdo Sound, 1958), Nauka, Moscow/Leningrad, 260–342 pp, 1964. In Russian.
Antarct. Res. Ser., 5, 1–37, 1965. Longhurst, A.R., Vertical migration, in The Ecology of the Seas,
Littlepage, J.L., Pearse, J.C., Biological and oceanographic observations Cushing, D.H., Walsh, J. Eds., Blackwell Scientific Publications,
under an Antarctic ice shelf, Science, 137, 679–680, 1962. Oxford, 1976, 116–137.
Lizotte, M.P., Microbiology of sea ice, in Sea Ice: An Introduction to its Longhurst, A.R., Significance of spatial variability, in Analysis of
Physics, Chemistry, Biology and Geology, Thomas, D.N., Marine Systems, Longhurst, A.R., Ed., Academic Press, New
Dieckmann, G.S., Eds., Blackwell Science, Oxford, 2003, York, 1981, 415–441.
184–210. Lopez, M.D.G., Huntley, M.E., Lorette, J.T., Calanoides acutus in
Lizotte, M.P., Sullivan, C.W., Photosynthesis-irradiance relationships in Gerlache Strait, Antarctica, I: Distribution of late copepodite
microalgae associated with Antarctic pack ice: Evidence for in situ stages and reproduction during spring, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.,
activity, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 71, 175–184, 1991. 100, 153–168, 1993.
Lizotte, M.P., Sullivan, C.W., Rates of photoadaptation in sea ice Lorenzo, L.M., Arbones, B., Figueiras, F.G., Tiltstone, G.H., Figueroa,
diatoms from McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, J. Phycol., 27, F.L., Photosynthesis, primary production, and phytoplankton
367–373, 1991. growth rates in Gerlache and Bransfield Straits during Austral
Lizotte, M.P., Sullivan, C.W., Photosynthetic capacity in microalgae summer cruise FRUEIA 95, Deep-Sea Res., 11, 707–721, 2002.
associated with Antarctic pack ice, Polar Biol., 12, 497–502, 1992. Lowry, J.K., The soft bottom macrobenthic community of Arthur
Lockyer, C., The age of sexual maturity of the southern fin whale Harbor, Antarctica, Master’s Thesis, College of William and
(Balaenoptera physalus) using annual layer counts in the ear plug, Mary, Williamsburg, Virginia, 1969.
Journal du Conseil, Counseil Permanent International pour Lowry, J.K., Soft bottom macrobenthic community of Arthur Harbor,
l’Exploration de la Mer, 34, 276–294, 1972. Antarctica, Antarct. Res. Ser., 23(1), 1–19, 1975.
Lockyer, C., Wet weight, volume, and length correlation in Antarctic Lowry, J.K., Studies on the macrobenthos of the Southern Ocean, Ph.D.
krill, Euphausia superba, Discov. Rep., 36, 152–155, 1973.
Thesis in Zoology, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, 1976.
Lockyer, C., Investigation of the ear plug of the southern sei whale,
Lubimova, T.G., Zonation of the oceanographic structure and biological
Balaenoptera borealis, as a valid means of determining age,
resources of the Southern Ocean, in Tesisy Vesesoyaz konf po teorii
Journal du Conseil, Conseil Permanent International pour
formiarovaniya chiselnnosti i ratsionalonogo ispolzovaniya stad
l’Exploration de la Mer, 36, 71–81, 1974.
promyslovykh ryb, VNIRO, Moscow, 1982, 205–207. In Russian.
Lockyer, C., Estimates of growth and energy budget for the sperm whale,
Lubimova, T.G., Ecological basis of exploitation of the resources of
Physeter catadon, United Nations Scientific Consultation on
Antarctic krill, Mem. Natl. Inst. Polar Res., Spec. Issue, 27,
Marine Mammals, Bergen, Norway, 31 August–9 September,
211–219, 1983.
1976, FAO of the UN ACMRR/MM/SC/38, Rome, 1975.
Lubimova, T.G., Shust, K.V., Quantitative study of Antarctic krill
Lockyer, C., Growth and energy budgets of large baleen whales from the
consumed by principal groups of species, in Biological Resources
Southern Hemisphere, United Nations Scientific Consultation on
Marine Mammals, Bergen, Norway, 31 August–9 September, of Antarctic Krill, Lubimova, T.G., Ed., VNIRO, Moscow, 1980,
1976, FAO of the UN ACMRR/MM/SC/41, Rome, 1976. 203–224.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 577
Lubimova, T.G., Naumov, A.G., Lagunov, L.L., Prospects of the Maciejewaka, K., Opalinski, K.W., Spatial and temporal differentiation
utilization of krill and other unconvential resources of the world of food in Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Pol. Arch. Hydro-
ocean, J. Fish. Res. Board Can., 30, 2196–2201, 1973. biol., 40, 291–311, 1993.
Lubimova, T.G., Makarov, R.R., Maselenikov, V.V., Shevtsov, W., Mackintosh, N.A., Distribution of the macroplankton of the Atlantic
Shust, K.V., The ecological pecularities, stocks, and the role of sector of the Antarctic, Discov. Rep., 9, 65–160, 1934.
E. superba in the trophic structure of the Antarctic ecosystem, in Mackintosh, N.A., The seasonal circulation of the Antarctic macro-
Selected Papers Presented to the Scientific Committee of plankton, Discov. Rep., 16, 365–412, 1937.
CCAMLR, 1981–1984, Part II, Commission for the Conservation Mackintosh, N.A., The southern stocks of whalebone whales, Discov.
of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 1980, 391–505. Rep., 22, 197–300, 1942.
Lubimova, T.G., Makarov, R.R., Maselenikov, V.V. et al., The ecologi- Mackintosh, N.A., The Stocks of Whales, Fishing News Books, London,
cal pecularities, stocks and role of E. superba in the trophic 1965.
structure of the Antarctic ecosystem, in Selected Papers Presented Mackintosh, N.A., Whales and krill in the twentieth century, in Antarctic
to the Scientific Committee of CCAMLR 1981–1984, Part II, Ecology, Vol. 1., Holdgate, M., Ed., Academic Press, London,
Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living 1970, 185–212.
Resources, Hobart, 391–505, 1984. Mackintosh, N.A., Life cycle of krill in relation to ice and water
Lubimova, T.G., Shust, K.V., Paphov, W., Ecology of mesopelagic conditions, Discov. Rep., 36, 1–94, 1972.
fishes, family Myctophidae, Southern Ocean, in Biological Mackintosh, N.A., Distribution of post-larval krill in the Antarctic,
Resources of the Arctic and Antarctic, Nauka, Moscow, 1987, Discov. Rep., 36, 95–156, 1973.
330–377. Mackintosh, N.A., Brown, S.G., Preliminary estimates of the southern
Lubin, D., Mitchell, B.G., Frederick, J.E., Alberts, A.D., Booth, C.R., populations of the larger baleen whale, Norsk Hvalfangstti, 45,
Lucas, T., Neuschuler, D., A contribution towards understanding 469–480, 1953.
the biospheric significance of Antarctic ozone depletion, Mackintosh, N.A., Wheeler, J.F., Southern blue and fin whales, Discov.
J. Geophys. Res., 97(D8), 7817–7827, 1992. Rep., 1, 257–540, 1929.
Lucchitta, R.K., Rosanova, C.E., Retreat of the northern margins of Madin, L.P., Production, composition and sedimentation of salp faecal
George VI and Wilkins Ice Shelves, Antarctic Peninsula, Ann. pellets in oceanic waters, Mar. Biol., 67, 39–45, 1982.
Glaciol., 27, 41–46, 1998. Mague, T.H., Friberg, E., Hughes, D.H., Morris, I., Extracellular release
Lüning, K., Dieckman, I.T., Environmental triggers in algal seasonality, of carbon by marine phytoplankton: A physiological approach,
Bot. Mar., 32, 389–397, 1989. Limnol. Oceanogr., 25, 262–279, 1979.
Lutjeharms, J.R.E., Walter, N.M., Allanson, B.R., Oceanic frontal Maher, W.J., Breeding biology of the snow petrel near Cape Hallett,
systems and biological enhancement, in Antarctic Nutrient Antarctica, Condor, 64, 488–499, 1962.
Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, Makarov, R.R., Life cycle and dispersion of Euphausia superba Dana,
R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 11–21. Trudy VNIRO, 77, 85–92, 1972. In Russian.
Luxmore, R.A., Moulting and growth in serolid isopods, J. Exp. Mar. Makarov, R.R., Some peculiarities of the reproduction of Euphausia
Biol. Ecol., 56, 63–85, 1982. superba (Crustacea: Euphausiacea). Abstracts of papers from All-
Lynnes, A.S., Reid, K., Croxall, J.P., Tratham, P.N., Foraging distri-
Union Conference on Macroplankton, All-Union Research Insti-
bution and competition for prey between Adélie and chinstrap
tute of Marine Fisheries and Oceanography, Moscow, 1973, 34–35.
penguins, Mar. Biol., 14, 1165–1175, 2002.
In Russian.
Lythgoe, J.M., Dartnall, H.J.A., A deep sea rhodopsin in a mammal,
Makarov, R.R., A study of the repeated maturation of females in
Nature (Lond.), 227, 955–956, 1990.
euphausiids (Eucarida: Euphausiacea), J. Zool., 54, 670–681, 1975.
Macaulay, M.C., Madriolas, A., Paly, K., Morrison, P., Hydroacoustic
Makarov, R.R., Vertical distribution of euphausiid eggs and larvae of the
survey for prey organisms, in AMLR 1989/90 Field Session Report:
northeastern coast of South Georgia Island, Oceanology, 15,
Objectives, Accomplishments and Tentative Conclusions. Admin-
1101–1106, 1978.
istrative Report LH-90-11, AERG staff, Ed., 1990, 34–36.
Makarov, R.R., Spawning times of Antarctic euphausiids, Biologii
Macauley, M.C., English, T.S., Mathisen, O.A., Acoustic character-
Morya, Vladivostok, 3, 30, 1979a. In Russian.
ization of swarms of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) from
Makarov, R.R., Larval distribution and reproductive ecology of Thysa-
Elephant Island and Bransfield Strait, J. Crust. Biol., 4(Special
noessa macrura (Crustacea: Euphausiacea), Mar. Biol., 52,
Issue 3), 16–44, 1984.
377–386, 1979b.
MacDonald, J.A., Montgomery, J.C., Animal adaptations to the
Makarov, R.R., Size composition and conditions of existance of
Antarctic environment, in Antarctica: The Ross Sea Region,
Euphausia superba Dana (Crustacea: Euphausiacea) in the
Hatherton, T., Ed., DSIR Publishing, Wellington, 1990, 220–239.
eastern part of the Pacific sector of the Southern Ocean, Ocea-
MacDonald, C.M., Schneppenheim, R., Breeding structure and stock
nology, 19, 582–585, 1979.
identity n the Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Ber. Polar-
Makarov, R.R., Some problems in the investigation of larval Euphau-
forsch., 4, 240–251, 1983.
siids in Antarctica, Ber. Polarforsch., 4, 58–69, 1983.
MacDonald, C.M., Williams, R., Adams, M., Genetic variation and
Makarov, R.R., Solyankin, E.V., Living conditions and structure of the
population structure of krill (Euphausia superba Dana) from the
population of Euphausia superba in the Lasarev Sea area. Tez
Prydz Bay region of Antarctic waters, Polar Biol., 6, 233–236,
dolkl III Veses Korf “Prolemy natsional” nogo ispol ’zovaniya
1986.
promyslovykh bespozvonochnykh, Atlant NIRO, Karlingrad,
MacDonald, J.A., Montgomery, J.C., Wells, R.M.G., Comparative
physiology of Antarctic fishes, Adv. Mar. Biol., 24, 321–388, 1987. 61–66, 1982. In Russian.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
578 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Makarov, R.R., Spiridonov, V.V., Life cycle and distribution of the Marchant, H.J., Davidson, A.T., Wright, S.W., Glasebrook, J., The
Antarctic krill: Some results of the studies and problems, in distribution and abundance of viruses in the Southern Ocean
Pelagic Ecosytems of the Southern Ocean, Veronina, N., Ed., during spring, Antarct. Sci., 12, 414–417, 2000.
Nauka Press, Moscow, 1993, 158–168. In Russian. Margolis, S., Kennett, J.P., Antarctic glaciation during the Tertiary
Makarov, R.R., Sysoera, N.V., Biological conditions and distribution of recorded in sub-Antarctic deep-sea cores, Science, 170,
Euphausia superba Dana in the Lazarev Sea and adjacent waters, 1085–1087, 1970.
in Antarctic Krill: The Distribution Pattern and Environment, Marin, V., The oceanographic structure of the eastern Scotia Sea, IV:
Makarov, R.R., Ed., Legkajaiopishevaja Promyshlennost Press, Distribution of copepod species in relation to hydrography in 1981,
Moscow, 1983, 110–117. In Russian. Deep-Sea Res., 34, 105–121, 1987.
Makarov, R.R., Naumov, A.G., Shevstov, V.V., The biology and Marin, V., Independent life cycles: An alternative to the asynchronism
distribution of Antarctic krill, in Antarctic Ecology Vol. 1, hypothesis for Antarctic calanoid copepods, Hydrobiol., 167/168,
Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Academic Press, London, 1970, 173–176. 161–168, 1988a.
Makinrtosh, N.A., Maintenance of living Euphausia superba and Marin, V., Qualitative models of the life cycles of Calanoides acutus,
frequency of moults, Nortsk Hvalfangst-Tidinde, 5, 97–102, 1967.
Calanus propinquus, and Rhincalanus gigas, Polar Biol., 8,
Maksimov, I.V., Atlas of Antarctica, Vol. 1, VNIRO, Moscow, 1966.
439–446, 1988b.
Malakoff, D., Antarctic ice sheet collapses, Science, 295, 2359–2365,
Marin, V.H., Schnack-Schiel, S.B., The occurrence of Rhincalanus
2002.
gigas, Calanoides acutus, and Calanus propinquus (Copepoda:
Malone, T.C., Algal size, in The Physiological Ecology of Phyto-
Calanoida) in late May in the area of the Antarctic Peninsula, Polar
plankton, Morris, I., Ed., Blackwell Scientific Publications,
Biol., 13, 35–40, 1993.
London, 1980, 433–463.
Marin, V., Brinton, E., Huntley, M., Depth relationships of Euphausia
Mandelli, E.F., Burkholder, P.R., Primary productivity in the Gerlache
superba eggs and adults near the Antarctic Peninsula 1986–1987,
and Bransfield Straits of Antarctica, J. Mar. Res., 24, 15–27, 1966.
Deep-Sea Res., 38, 1241–1249, 1991.
Mangel, M., Switzer, P.V., A model of the level of foraging trip for the
indirect effects of krill (Euphausis superba) on krill predators, Marlow, R.J., Mating behaviour of the leopard seal, Hydrurga leptonyx,
Ecol. Model., 105, 235–256, 1998. in captivity, Aust. J. Zool., 15, 1–5, 1967.
Mann, K.H., Ecology of Coastal Waters: A Systems Approach, Marr, J.S., The natural history and geography of the Antarctic krill
University of California Press, Berkeley, CA, 1982. Euphausia superba, Discov. Rep., 32, 33–464, 1962.
Mansfield, A.W., The breeding behaviour and reproductive cycle of the Marra, J., Vertical mixing and primary production, in Primary Pro-
Weddell seal (Leptonychotes weddelli Lesson), Falkland Islands ductivity in the Sea, Falkowski, P.G., Ed., Plenum Press, New
Dependencies Survey, Scientific Reports, 18, 1–41, 1958. York, 1980, 121–137.
Marchant, H.J., Choanoflagellates in the Antarctic marine food chain, in Marschall, H.-P., Sinking speed of krill eggs and timing of early life
Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, history stages, Ber. Polarforsch., 4, 70–73, 1983.
P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 271–276. Marschall, H.-P., Overwintering strategy of the Antarctic krill under the
Marchant, H.J., Possible impacts of climate change on the organisms of pack-ice of the Weddell Sea, Polar Biol., 9, 129–135, 1988.
the Antarctic marine ecosystem, in Impact of Climate Change on Marshall, N.B., Egg size in Arctic, Antarctic and deep-sea fishes,
Antarctica–Australia, Australian Government Publication Service, Evolution, 7, 328–341, 1953.
Canberra, 26–33 pp, 1992. Marshall, N.B., Fish, in Antarctic Research, Priestly, R., Adie, R.J.,
Marchant, H.J., Impacts of ozone depletion on Antarctic organisms, Robin, G.de Q., Eds., Butterworth, London, 1964, 206–217.
in Antarctic Communities: Species, Structure and Survival, Marshall, S.M., Orr, A.P., On the biology of Calanus finmarchicus, VIII:
Baggatalia, B., Valencia, J., Walton, D.W.H., Eds., Cambridge Food uptake, assimilation, and excretion in adult stage V, J. Mar.
University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1997, 367–374. Biol. Assoc. U.K., 34, 495–529, 1955.
Marchant, H.J., Davidson, A.T., Possible impacts of ozone depletion on Martin, D., Kauffman, P., Parkinson, C., The movement and decay of ice
trophic interactions and biogenic vertical carbon flow, in Proceed- bands in the Bering Sea, J. Geophys. Res., 88, 2803–2812, 1983.
ings of the International Conference on the Role of Polar Regions Martin, J.H., Knauer, G.A., Karl, P.M., Broenkow, W.W., VERTEX:
in Global Climate Change, Weller, G., Wilson, C.L., Severin, Carbon cycling in the northeast Pacific, Deep-Sea Res., 34,
B.A.B., Eds., Geophysical Institute, Fairbanks, 1991, 397–400. 267–285, 1987.
Marchant, H.J., McEldowney, A., Nanoplankton siliceous cysts from Martin, J.H., Fitzwater, S.E., Gordon, R.M., Iron deficiency limits
Antarctica are algae, Mar. Biol., 92, 53–57, 1986. phytoplankton growth in Antarctic waters, Global Biogeochem.
Marchant, H.J., Murphy, E.J., Interactions at the base of the Antarctic Cycles, 4, 5–12, 1990a.
food web, in Antarctic Ecology: The BIOMASS Perspective,
Martin, J.H., Fitzwater, S.E., Gordon, R.M., Iron in Antarctic waters,
El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge,
Nature (Lond.), 345, 156–158, 1990b.
UK, 1996, 267–286.
Martinez, R., Pycnocline and psychotrophic respiratory metabolism in
Marchant, H.J., Davidson, A.T., Wright, S.W., The distribution and
Antarctic microplankton, Polar Biol., 16, 483–489, 1996.
abundance of chroococcoid cyanobacteria in the Southern Ocean,
Martinson, D.G., The role of Southern Ocean/sea ice interaction in
Proc. Natl Inst. Polar Res. Symp. Polar Biol., 1, 1–9, 1987.
global climate change, in International Conference on the Role of
Marchant, H.J., Davidson, A.T., Kelly, G.J., UV-B protecting
Polar Regions in Global Change, University of Alaska, June
compounds in the marine alga Phaeocystis pouchetii from
11–15, 1990, 1990, 269–274.
Antarctica, Mar. Biol., 109, 391–395, 1991.
Martinson, D.G., Killworth, P.D., Gordon, A.L., A convective model for
Marchant, H.J., Watanabe, ?., Kawacke, M., Marine snow in Antarctic
the Weddell Polynya, J. Geophys. Res., 11, 466–488, 1981.
coastal waters, Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Biol., 9, 75–83, 1996.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 579
Maruyama, T., Toyodo, H., Suzuki, S., Preliminary report on the Mauchline, J., The biology of mysids and euphausiids, Adv. Mar. Biol.,
biomass of macroplankton and micronekton collected with a 18, 1–681, 1980a.
bongo net during the Umituka Moni FIBEX Cruise, Trans. Mauchline, J., Studies of patches of krill, Euphausia superba Dana.
Tokyo Univ. Fish., 5, 145–153, 1982. BIOMASS Handbook No. 6, 1980b.
Masaka, Y., Yearly changes of the biological parameters for the Mauchline, J., Fisher, L.R., The biology of euphausiids, Adv. Mar. Biol.,
Antarctic sei whale, Rep. Int. Whal. Commun., 29, 175–195, 1979. 7, 1–454, 1969.
Masaki, Y., Yearly changes in of the biological parameters for the Maxwell, J.G.H., The breeding biology of Chorismus antarcticus
Antarctic sei whale, Int. Whaling Comm. Rep., 27, 421–429, 1977. (Pieffer) and Notocragnon antarcticus (Pieffer) (Crustacea: Deca-
Masaki, Y., Yearly changes in the biological parameters of the minke poda) and its bearing on the problem of the impoverished Antarctic
whale, Rep. Int. Whal. Commun., 29, 375–395, 1979. decapod fauna, in Adaptations within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano,
Maslennikov, V.V., On the effect of water dynamics on the distribution G.A., Ed., Gulf Publications, Houston,TX, 1977, 335–342.
of Euphausia superba Dana in the area of South Georgia, Trudy Maxwell, J.G.H., Ralph, R., Non-cold-adapted metabolism in the
Vesesoiuznogo Naucho-issledovatel’skii institita Morskogo decapod Chlorismus antarcticus and other sub-Antarctic marine
Rybngo Khoziaiska i Okeanographii, 75, 107–117, 1972. crustaceans, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs,
Maslennikov, V.V., Long-term variability in hydrometeorological Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer,
characteristics of the Southwest Antarctic Atlantic Ocean, Trudy Berlin, 1985, 397–406.
VNIRO, 136, 50–56, 1979. May, R.M., Beddington, J.R., Clark, C.W., Holt, S.J., Laws, R.M.,
Maslennikov, V.V., Modern concepts of large-scale circulation of Management of multispecies fisheries, Science, 205, 267–277,
Atlantic water and results of mass drift of Euphausia superba, in 1979.
Biological Resources of Antarctic Krill, Lubimova, T.G., Ed., Maykut, G.A., The ice environment, in Sea Ice Biota, Horner, R.A., Ed.,
VIRNO, Moscow, 1980, 8–27. In Russian. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1985, 21–82.
Maslennikov, V.V., Solyankin, E.V., Patterns of fluctuations in the Maykut, G.A., Grenfell, T.C., The spectral distribution of light beneath
hydrological conditions of the Antarctic and their effect on the first-year sea ice in the Arctic Ocean, Limnol. Oceanogr., 20,
distribution of krill, in Antarctic Ocean and Resources Variability, 554–563, 1975.
Sahrhage, D., Ed., Springer, Berlin, 1988, 209–213. Maynard, S.D., Riggs, F.V., Walters, J.F., Mesopelagic micronekton in
Massalaski, A., Leppard, G.G., Morphological examination of fibrillar Hawaiian waters: Faunal composition, standing stock and diel
colloids associated with algae and bacteria in lakes, J. Fish. Res. vertical migration, Fish. Bull., 73, 726–736, 1973.
Board Can., 36, 922–938, 1979. Mayzand, P., Faber-Lorda, J., Corre, M.C., Aspects of nutritional
Mathisen, O.A., Macaulay, M.C., The morphological features of a super metabolism of two Antarctic euphausiids: Euphausia superba
swarm of krill, Mem. Natl Inst. Polar Res., Spec. Issue, 27, and Thysanoessa macrura, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and
153–164, 1983. Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds.,
Mathot, S., Dundois, T.-M., Lancelot, C., Gross and net primary Springer, Berlin, 1985, 330.
production in the Scotia-Weddell Sea sector of the Southern McAlister, W.B., Sayer, G.A., Perez, M.S., Preliminary estimates of
Ocean during spring 1988, Polar Biol., 12, 321–332, 1992. pinnipoed-finfish relationship in the Bering Sea. Background
Mathot, S., Dundois, T.-M., Lancelot, C., Gross and net primary Paper 19thMeeting Fur Seal Commission, Moscow, 1976, U.S.
production in the Scotia-Weddell Sea sector of the Southern Department of Commerce, NOAA, NMFS, Seattle, WA, 1976,
Ocean during spring 1988, in Weddell Sea Ecology, Hempel, G., 1–10.
Ed., Springer, Berlin, 1995, 321–332. McCann, T.S., Population structure and social organization of southern
Mathewa, L.H., The humpback whale, Megaptera nodosa, Discov. Rep., elephant seals, Mirounga leonina (L.), Biol. J. Linn. Soc., 14,
17, 70–92, 1937. 133–150, 1980a.
Matsuda, O., Ishikawa, S., Kawaguchi, K., Seasonal variation of down- McCann, T.S., Territoriality and breeding behaviour of adult male
ward flux of particulate organic matter under the Antarctic fast ice, Antarctic fur seals, Arctocephalus gazella, J. Zool. (Lond.), 192,
Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Biol., 1, 23–34, 1987. 295–310, 1980b.
Matsuda, O., Ishikawa, S., Kawaguchi, K., Fine-scale observation on McCann, T.S., Aggression and sexual activity of male southern elephant
salinity stratification in an ice hole during the melting season, seals, Mirounga leonina, J. Zool. (Lond.), 195, 295–310, 1981a.
Antarct. Rec., 34, 357–362, 1990. McCann, T.S., The social organization and behaviour of the southern
Matsuoka, K., Watanabe, T., Ichii, T., Kishimata, H., Nishiwaki, S., elephant seal, Mirounga leonina (L.), Ph.D. thesis, University of
Large-scale distribution (south of 608 S, 358 E–1308 E) in relation London, 1981b.
to the southern boundary of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, in McCann, T.S., Population size and demography of the southern elephant
Antarctic Biology in a Global Context, Huiskes, A.H.L., Gieskes, seal, in Sea Mammals of Southern Latitudes, Bryden, M.M., Ling,
W.W.C., Rozema, J., Schorno, R.M.L., van der Vies, S.M., Wolff, J., Eds., South Australia Museum, Adelaide, 1983, 1–19.
W.J., Eds., Backuys Publishers, Leiden, The Netherlands, 2003, McCarthy, J.J., Canziani, O.F., Leung, N.A., Dokken, D.J., White, J.S.,
26–30. Climate change 2001: Impacts, adaptations and vulnerability,
Matthews, L.H., The natural history of the elephant seal, Discov. Rep., 1, Contribution of the Working Group II to the Third Assessment
233–250, 1929. Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change,
Matthews, L.H., South Georgia: The British Empire’s Subantarctic Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2001.
Outpost, Simpkin Marshall, London, 1931. McClatchie, S., Food-limited growth of Euphausia superba in Admiralty
Mauchline, J., Antarctic krill biology, BIOMASS Rep. Ser., 10, 1–52, Bay, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica, Cont. Shelf Res., 8,
1979. 329–345, 1988.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
580 Biology of the Southern Ocean
McClatchie, S., Boyd, C.M., A morphological study of sieve efficiencies Meguro, H., Plankton ice in the Antarctic Ocean, Antarc. Rec., 14,
and mandibular surfaces in the Antarctic krill Euphausia superba, 1192–1199, 1962.
Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 40(7), 955–967, 1983. Meguro, H., Ito, K., Fukushima, H., Ice flora (bottom type): A
McClintock, J.B., Karentz, K., Mycosporine-like amino acids in 38 mechanism of primary production in polar seas and the growth
species of subtidal marine organisms from McMurdo Sound, of diatoms in sea ice, Arctic, 20, 114–133, 1967.
Aquat. Sci., 9, 392–398, 1997. Meissner, E.E., Tom, V.S., Silon, V.N., Characteristics of the behaviour
McConville, M.J., Wetherbee, R., The bottom-ice microalgal commu- and biological cycles of the marbled Notothenia, Notothenia rossii,
nity from the annual ice in the inshore waters of East Antarctica, in relation to bottom topography, bottom materials, and currents,
J. Phycol., 19, 431–439, 1983. J. Ichthyol., 14, 706–708, 1974.
McConville, M.J., Mitchell, C., Wetherbee, R., Productivity and patterns Mengesha, S., Dehairs, F., Fiala, M., Elskens, M., Goryens, L., Seasonal
of carbon assimilation in a microalgal community from annual sea variation of phytoplankton community structure and nitrogen
ice, East Antarctica, Polar Biol., 4, 135–141, 1985. uptake regime in the Indian Sector of the Southern Ocean, Polar
McDonald, S.J., Kennicutt, M.C. III, Sericano, J., Wade, T.L., Liu, H., Biol., 20, 259–272, 1998.
Safe, S.H., Correlation between bioassay-derived P4501 A1 Menshenina, L.L., Mrlnihov, I.A., Under-ice zooplankton of the western
induction activity and chemical analysis of clam (Laternula Weddell Sea, Proc. NIPR Symp. Polar Biol., 8, 126–138, 1995.
elliptica) extracts from McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Chemo- Mercer, J.H., West Antarctic ice sheets and greenhouse effect: A threat
sphere, 28, 2237–2248, 1994. of disaster, Nature (Lond.), 271, 321–325, 1978.
McElroy, J.K., The economics of harvesting krill, in The Management of Meredith, M.P., Renfrew, A., Claeke, A., King, J.C., Brandon, M.A.,
the Southern Ocean, Mitchell, B., Sandbrook, R., Eds., Inter- Impact of the 1997; 98 ENSO on upper waters in Marguerite Bay,
national Institute for Environment and Development, London, western Antarctic Peninsula, J. Geophys. Res., 109, 2240–2257,
1980a, 81–103. 2004.
McElroy, J.K., Economic evaluation of krill fishing systems, in Meridith, M.P., Vassie, J.M., Hayward, K.J., Spencer, R., On temporal
Advances in Fish Science and Technology, Connell, J.J., Ed.,
variability in the transport through Drake passage, J. Geophys.
Fishing News Books Ltd, Farnham, 1980b, 314–321.
Res., 101, 22485–22494, 1996.
McFeters, G.A., Barry, J.P., Howington, J.P., Distribution of enteric
Metz, C., Feeding of Oncaea curvata (Poecilostomatoida: Copepoda),
bacteria in Antarctic seawater surrounding a sewage outfall, Water
Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 229, 229–235, 1998.
Res., 27(4), 645–650, 1993.
Metz, C., Schnack-Schiel, S.B., Observations on carnivorous feeding in
McHugh, J.L., The role and history of the International Whaling
Antarctic calanoid copepods, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 129, 71–75,
Commission, in The Whale Problem: A Status Report, Schevil,
1995.
W.E., Ed., Harvard University Press, Harvard, NJ, 1974, 359–368.
Metz, B., Davidson, O., Swaet, R., Pari, J., Eds., Climate Change 2001:
McMinn, A., Preliminary investigation of the contribution of fast-ice
Mitigation Contribution of Working Group III to the Third
algae to the spring phytoplankton bloom in Ellis Fjord, Antarctica,
Assessment of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change,
Polar Biol., 16, 301–307, 1996.
Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2001.
McMinn, A., Heijnis, H., Hodgson, D., Preliminary sediment core
Meyer, M.A., El-Sayed, S.Z., Grazing of Euphausia superba on natural
evidence against short-term UV-B induced changes in Antarctica
populations, Polar Biol., 1, 193–197, 1983.
coastal diatom communities, in Antarctic Communities: Species,
Meyer, B., Atkinson, A., Blume, B., Bathmann, U.V., Feeding and
Structure and Survival, Baggatalia, B., Valencia, H., Walton,
energy budgets of larval Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) in
D.W., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1997,
summer, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 257, 167–178, 2003.
381–387.
McMinn, A., Skerratt, J., Trull, T., Ashworth, C., Lizotte, M., Nutrient Mezykowski, T., Rakusa-Suszczewski, S., The circadian rhythms in
stress gradient in the bottom 5 cm of fast ice, McMurdo Sound, Euphausia superba Dana and its carbohydrate metabolism, Meer-
Antarctica, Polar Biol., 21, 220–227, 1999. esforschung, 27, 124–129, 1979.
McRoy, C.P., Goering, J.J., The influence of ice on the primary Michel, R.L., Linck, T.W., Williams, P.M., Tritium and carbon-14
productivity of the Bering Sea, in Oceanography of the Bering distributions in sea water from under the Ross Ice Shelf Project
Sea, Hand, D.W., Ed., Institute of Marine Science, University of Hole, Science, 203, 445–446, 1989.
Alaska, Fairbanks, AK, 1974, 403–421. Mileikovsky, S.A., Types of larval development in marine bottom
McSweeny, E.S., Systematics and morphology of the Antarctic cranchiid invertebrates, their distribution, and ecological significance: A
squid Galiteuthis glacialis (Chun.), Antarct. Res. Ser., 27, 1–39, re-evaluation, Mar. Biol., 10, 193–213, 1971.
1978. Miller, D.G.M., Cannibalism in Euphausia superba Dana, S. Afr.
McWhinnie, M.A., Denys, C., Biological studies of Antarctic krill, J. Antarc. Res., 12, 50–57, 1982.
austral summer, Antarct. J. U.S., 13, 133–137, 1978a. Miller, D.G.M., The South African SIBEX I Cruise to the Prydz Bay
McWhinnie, M.A., Denys, C., Antarctic Marine Living Resources With region, 1984. IX: Krill (Euphausia superba Dana), S. Afr. J. Antarc.
Special References to Krill Euphausia superba: Assessment of Res., 15, 33–41, 1985.
Adequacy of Present Knowledge, Antarctic Science Foundation, Miller, D.G.M., Results from biological investigations of krill (Euphausia
Washington, DC, Report No. NSF/RA 768/4889, 1978b. superba Dana) in the Southern Ocean during SIBEX I, Mem. Natl
McWhinnie, M.A., Denys, C., Parkin, R., Parkin, K., Biological Inst. Polar Res., Spec. Issue, 40, 117–139, 1986a.
investigations of Euphausia superba Dana, Antarct. J. U.S., 14, Miller, D.G.M., Modelling and decision-making as part of the CCAMLR
163–164, 1979. management regime. SC-CAMLR-V/BG/17 in Selected scientific
Medlin, K., Priddle, J., Eds., Polar Marine Diatoms, British Antarctic papers 1986, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic
Survey, Natural Research Council, Cambridge, UK, 1990. Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 1986b, 295–322.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 581
Miller, D.G.M., Antarctic krill and ecosystem management, WG-Emm- Mizroch, S.A., Analysis of some biological parameters of the Antarctic
01 Presentation Paper, CCAMLR Science, 9, 174–212, 2003. fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus), Int. Whaling Comm. Rep., 31,
Miller, D.G.M., Hampton, I., Biology and Ecology of the Antarctic Krill 425–434, 1981b.
(Euphausia superba Dana): A Review, BIOMASS Scientific Series Mizroch, S.A., Reproductive rates in southern hemisphere baleen
No. 9, 1–166 pp, 1985. whales, M.A. Thesis, University of Washington, 1983.
Miller, D.G.M., Hampton, I., Biology and Ecology of Antarctic Krill Mizroch, S.A., York, A.E., Have pregnancy rates of southern hemisphere
(Euphausia superba Dana), 9, 1–166, 1989. fin whales, Balaenoptera physalis, increased, in Whales, Dolphins
Miller, K.A., Pearse, J.S., Ecological studies of seaweeds in McMurdo and Porpoises, International Whaling Commission Special Issue,
Sound, Antarctica, Am. Zool., 31, 35–48, 1991. 6, 401–410, 1984.
Miller, M.A., Krempin, D.W., Manahan, D.T., Sullivan, C.W., Growth Mizroch, S.A., Rice, D.W., Bengtson, J.L., Prodomus of an Atlas of
rates, distribution, and abundance of bacteria in the ice-edge zone Balaenopterid Whale Distribution in the Southern Ocean Based on
of the Weddell and Scotia Seas, Antarctica, Antarct. J. U.S., 19, Pelagic Catch Data, U.S. National Marine Fisheries Service,
103–105, 1984. National Marine Laboratory, Seattle, WA, 1986.
Miller, D.G.M., Hampton, I., Henry, J., Abrams, R.W., Cooper, J., The Mizutani, H., Wada, E., Nitrogen and carbon isotope ratios in seabird
relationship between krill food requirements and phytoplankton rookeries and their ecological implications, Ecology, 69, 340–349,
production in a sector of the Southern Indian Ocean, in Antarctic 1988.
Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Moe, R.L., DeLaca, T.E., Occurrence of macroscopic algae along the
Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 362–371. Antarctic Peninsula, Antarc. J. U.S., 11, 20–24, 1976.
Minagawa, M., Wada, E., Stepwise enrichment of 15N along food chains: Moebus, K., Johnson, K.M., Exudation of dissolved organic carbon by
Further evidence and the relationship between 15N and annual age, brown algae, Mar. Biol., 26, 117–125, 1974.
Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 48, 1135–1140, 1984. Moiseev, P.A., Some aspects of commercial use of krill resources of the
Minelli, A., Ecology and Systematics. The State of the Art, Chapman and Antarctic seas, in Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 1, Holdgate, M.W., Ed.,
Hall, London, 1993. Academic Press, London, 1970, 213–216.
Minks, S., Smith, C.M., DeMaster, D., Persistance of labile organic Moline, M.A., Prezelin, B.B., Longterm monitoring and analysis of
matter and microbial biomass in Antarctic shelf sediments: physical factors regulating variability in coastal Antarctic phyto-
Evidence of a sediment “food bank”, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 300, plankton biomass, in situ productivity and taxonomic composition
3–19, 2005. over subseasonal, seasonal and interannual time scales, Mar. Ecol.
Mitchell, B.G., Predictive bio-optical relationship for polar oceans and Prog. Ser., 145, 143–160, 1996.
marginal ice zones, J. Mar. Syst., 3, 91–105, 1992. Moline, M.A., Preslen, B.B., High resolution time series data for
Mitchell, E., Trophic relationships and competition for food in northwest 1991/1992 primary production and related parameters at a
Antarctic waters, in Proceedings of the Canadian Zoologists Palmer LTER coastal site: Implications for modelling carbon
Annual Meeting, Burt, O., Ed., 1975, 123–133. fixation in the Southern Ocean, Polar Biol., 97, 39–53, 1997.
Mitchell, E., Trophic relationships and competition for food in northwest Moline, M.A., Prézelin, B.B., Schofield, O., Smith, R.C., Temporal
Antarctic whales, in Proceedings of the Canadian Zoologists dynamics of coastal Antarctic phytoplankton: Environmental
Annual Meeting, Burt, M.D.B., Ed., 1994, 123–125. driving forces and impact of a 1991/92 summer diatom bloom
Mitchell, B.G., Holm-Hansen, O., Observations and modelling of the on the nutrient regimes, in Antarctic Communities: Species,
Antarctic phytoplankton standing crop in relation to mixing depth, Structure and Survival, Battaglia, B., Valencia, H., Walton,
Deep-Sea Res., 38, 981–1007, 1991. D.W.H., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK,
Mitchell, B.G., Karentz, D., The induction and repair of DNA photo- 1997, 67.
damage in the environment, in Environmental UV Photobiology, Molloy, K.D., Holman, M.A., Mitchell, D., Dietrich, H.W., Solar
Young, A.R., Ed., Plenum Press, New York, 1993, 345–377. UVB-induced DNA damage and photosynthetic DNA repair in
Mitchell, B., Sandbrook, R. The Management of the Southern Ocean, Antarctic zooplankton, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 1258–1263,
Institute for Environment and Development, London, 1980. 1997.
Mitchell, J.G., Silver, M.W., Modern archaeomonads indicate sea-ice Monmin, E., Indermühle, A., Dällenbach, A., Flückiger, J., Stauffer, B.,
environments, Nature (Lond.), 196, 437–439, 1982. Stocker, T.F., Raynaud, D., Barnola, J.-M., Atmospheric CO2
Mitchell, B.G., Brody, E.A., Holm-Hansen, O., McCain, C., Bishop, J., concentrations over the last glacial termination, Science, 291,
Light limitation of phytoplankton biomass and macronutrient 112–114, 2001.
utilization in the Southern Ocean, Limnol. Oceanogr., 36, Montague, T.L., Food of Antarctic petrels (Thalassoica antarctica),
1662–1677, 1991. Emu, 84, 144–245, 1984.
Mitskevich, I.N., Kriss, A.Ye., Total numbers and production of Montu, M., de Olivera, I.R., Zooplankton associations, trophic relation-
microorganisms in the waters of the Southern Ocean, Microbio- ships, standing stock of krill, and other groups of the community
logia, 44, 135–140, 1973. near Elephant Island (February–March 84/85), Neritica, 1,
Mitskevitch, L.G., Mosolov, V.V., A study of proteolytic enzymes of 111–130, 1986.
krill, in Krill Processing Technology, Bykov, V.P., Ed., VNIRO, Moors, P.J., Spier, T.W., Lyon, G.L., Soil analyses and 13C/12C ratios
Moscow, 1981, 21–24. In Russian with English summary. identify sites of deserted Rockhopper Penguin colonies, The Auk,
Mizroch, S.A., Some notes on southern hemisphere baleen whale 106, 796–799, 1985.
pregnancy trend rates, Int. Whaling Comm. Rep., 30, 361–374, 1980. Mopper, K., Zhou, V., Hydroxyl radical photoreproduction in the sea and
Mizroch, S.A., Further notes on southern hemisphere baleen whale its potential impact on marine processes, Science, 250, 661–664,
pregnancy rates, Int. Whaling Comm. Rep., 31, 629–633, 1981a. 1990.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
582 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Morales, C.E., Harris, R.D., Head, R.V., Tranter, P.R.G., Copepod Mougin, J.-L., Prévost, J., Evolution annuelle des effectifs de des
grazing in the oceanic northeast Atlantic during a 6-week drifting biomasses des oiseaux antarctiques, Rev. Ecol. (Terre Vie), 34,
station: The contribution of size classes and vertical migration, 101–133, 1980.
J. Plankton Res., 15, 185–211, 1993. Muench, R.D., Mesoscale oceanographic features associated with the
Moran, X.A.G., Gasol, J.M., Pedros-Alio, C., Estrada, M., Dissolved and central Bering Sea ice edge: February–March 1981, J. Geophys.
particulate primary production and bacterial production on Res., 88, 2715–2722, 1983.
offshore Antarctic waters during austral summer: Coupled or Muench, R.D., Charnell, R.L., Observations on medium-scale features
uncoupled?, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 222, 25–39, 2001. along the seasonal ice edge in the Bering Sea, J. Phys. Oceanogr.,
Mordy, C.W., Penny, D.M., Sullivan, C.W., Spatial distribution of 7, 602–606, 1977.
bacterioplankton biomass and production in the marginal ice- Muench, R.D., LeBond, P.H., Hachmeister, L.E., On some possible
edge zone of the Weddell-Scotia Sea during austral winter, Mar. interactions between internal waves and sea ice in the marginal ice
Ecol. Prog. Ser., 122, 9–19, 1995. zone, J. Geophys. Res., 88, 2819–2826, 1983.
Moreno, C.A., Somatometria y alimentación natural de Hapagifer Mujica, A.R., Asencio, V., Distribution and abundance of krill
georgians antarctica Nyblin, en Bahia Fildes, Isla Rey Jorge, larvae (Euphausia superba Dana), Ber. Polarforsch., 4, 21–29,
Antártica, Bol. Inst. Antárt. Chil., 6, 9–14, 1971. 1983.
Moreno, C.A., Observations on food and reproduction in Trematomus Mujica, A.R., Torres, A.G., Quantitative and qualitative analysis of
bernacchii (Pisces: Nototheniidae) from Palmer Archipelago, Antarctic zooplankton, Ser. Cient. INACH, 28, 165–174, 1982.
Antarctica, Copeia, 1, 171–173, 1980. Müller-Karger, F., Alexander, V., Nitrogen dynamics in a marginal sea-
Moreno, C.A., Bahamonde, N., Nichos alimentarios y competercia por ice zone, Cont. Shelf Res., 7, 805–823, 1987.
alimento entre Notothenia coreiiceps neglecta Nybelin y Müller-Schwarze, D., Müller-Schwarze, C., Relations between leopard
Notothenia rossii marmmorata Fischeren Shetland del Sur seals and Adélie Penguins, Rapp. P.-V. Reun. CIESM Mediterr.
Antarctica, Instituto Antárctico Chileno, Serie Cientı́fico, 3, Monaco, 169, 394–404, 1975.
45–62, 1975. Müller-Schwarze, D., Müller-Schwarze, C., Interactions between South
Moreno, C.A., Osorio, H.H., Bathymetric food habits in the Antarctic Polar skuas and Adélie Penguins, in Adaptations within Antarctic
fish Notothenia gibberifrons Lönnberg (Pisces: Nototheniidae), Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smithsonian Institution, Washington,
Hydrobiologica, 55, 139–144, 1977. DC, 1977, 619–646.
Morita, R.Y., Psychrophilic bacteria, Bacteriol. Rev., 39, 144–167, 1975. Mullin, M.M., In situ measurement of filtering rates of the salp, Thalia
Morita, R.Y., Griffith, R.P., Hayasaka, S.S., Heterotrophic activity of democratica, on phytoplankton and bacteria, J. Plankton Res., 5,
microorganisms in Antarctic waters, in Adaptations within 279–288, 1983.
Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smithsonian Institution, Mullin, M.M., Brooks, R.E., Extractable lipofuscin in larval Euphausia
Washington, DC, 1977, 99–113. superba, Fisheries Bulletin of the United States, 86, 407–415,
Morris, D.J., Filtration rates of Euphausia superba Dana: Under- or 1989.
overestimates?, J. Crust. Biol., 4(Special Issue No. 1), 185–197, Mullins, B.W., Priddle, J., Relationships between bacteria and phyto-
1984. plankton in the Bransfield Strait and Southern Drake Passage, Br.
Morris, D.J., Integrated model of moulting and feeding of Antarctic krill Antarc. Surv. Bull., 76, 51–64, 1987.
Euphausia superba off South Georgia, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 22, Mumm, N., Zur Ernahrungsphyiologies des Krill (Euphausia superba)
207–217, 1985. im Winter Untersuchungen anhand der Verdauungstenzyme
Morris, D.J., Keck, A., The time course of the moult cycle and growth of Amylase und Trypsin. Diplomarbeit, Universität Keil, 1987.
Euphausia superba in the laboratory, A Preliminary Study. Meer- Murano, M., Segawa, S., Kato, M., Moulting and growth of the Antarctic
esforschung, 30, 94–100, 1984. krill in the laboratory, Transactions of the Tokyo University of
Morris, D.J., Priddle, J., Observations on feeding and moulting of the Fishery, 3, 99–106, 1979.
Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba Dana, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., Murphy, R.C., Notes on the sea elephant, Mirounga leonina Linne, Bull.
65, 57–63, 1984. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist., 33, 63–79, 1914.
Morris, D.J., Ricketts, C., Feeding of krill around South Georgia, I: A Murphy, G.I., Clupeoids, in Fish Population Dynamics, Gulland, J.A.,
model of feeding activity in relation to depth and time of day, Mar. Ed., Wiley, London, 1977, 283–308.
Ecol. Prog. Ser., 16(1), 1–7, 1984. Murphy, E.J., Reid, K., Modelling Southern Ocean krill population
Morris, D.J., Ward, P., Clarke, A., Aspects of the feeding in Antarctic dynamics: Biological processes generating fluctuations in the
krill, Euphausia superba, Polar Biol., 2, 21–26, 1983. South Georgia ecosystem, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 217, 175–189,
Morris, D.J., Watkins, J., Ricketts, C., Buchholz, F., Priddle, J., An 2001.
assessment of the merits of length and weight measurements of Murphy, E.J., Morris, D.J., Watkins, J.L., Priddle, J., Scales of
Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 79, interaction between Antarctic krill and the environment, in
27–50, 1988. Antarctic Ocean and Resources Variability, Sahrhage, D., Ed.,
Mortensen, T., Echinoidea and Ophiuroidea, Discov. Rep., 12, 199–348, Springer, Berlin, 1988, 120–130.
1936. Murphy, E.J., Everson, I., Murray, A., Analysis of acoustic line-transect
Motoi, T., Ono, N.O., Wakatsuchi, M., A mechanism for the formation of data from the waters around South Georgia: Estimation of krill
the Weddell Polyna in 1974, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 17, 2241–2247, (Euphausia superba Dana) biomass, in Selected scientific papers,
1987. 1991, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine
Mougin, J.-L., Ecologie comparée des Procelariidae antarctique et sub- Living Resources, Hobart, 1991, 225–243.
antarctique, Comité National Français des Recherches Antar- Murphy, E.J., Watkins, J.L., Reid, K., Trathan, P.N., Everson, I., Croxall,
tiques, 36, 1–195, 1975. J.P.., Priddle, J., Brandon, M.A., Brierley, A.S., Hofmann, E.,
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 583
Interannual variability of the South Georgia marine ecosystem: Nelson, D.M., Gordon, L.I., Production and dissolution of biogenic
Biological and physical sources of variation in the abundance of silica in the Southern Ocean, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta., 46,
krill, Fish. Oceanogr., 7, 381–390, 1998. 491–501, 1982.
Murray, A.G., Jackson, G.A., Viral dynamics, 2: a model of the Nelson, D.M., Smith, W.O., Jr., Phytoplankton bloom dynamics of the
interaction of ultraviolet light and mixing processes on viral western Ross Sea ice edge, II: Mesoscale cycling of nitrogen and
survival in seawater, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 102, 105–114, 1993. silica, Deep-Sea Res., 33, 1389–1412, 1986.
Muzzarelli, R.A.A., Chitin, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1977. Nelson, D.M., Smith, W.O., Jr., Sverdrup revisited: Critical depths,
Nagata, Y., Michada, Y., Umimura, Y., Variation in the positions and maximum chlorophyll levels, and the control of Southern Ocean
structures of oceanic fronts in the Indian ocean for the period from productivity by the irradiance-mixing regime, Limnol. Oceanogr.,
1965 to 1987, in Antarctic Ocean and Resources Variability, 36, 1650–1661, 1991.
Sahrhage, D., Ed., Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 1988, 92–98. Nelson, D.M., Goering, J.J., Boisseau, D., Consumption and regen-
Naito, Y., Iwami, T., Fish fauna in the northeastern parts of Lützow- eration of silicic acid in three coastal upwelling systems, in Coastal
Holm Bay, with some notes on stomach contents, Memoirs Natl Upwelling, Richards, F.A., Ed., American Geophysical Union,
Inst. Polar Res., Spec. Issue, 32, 64–72, 1982. Washington, DC, 1981, 242–256.
Naito, Y., Taniguchi, A., Hamada, E., Some observations on swarms and Nelson, D.M., Smith, W.O., Jr., Gordon, L.I., Huber, B.A., Spring
mating behaviour of Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba Dana), distributions of density, nutrients and phytoplankton biomass in
Memoirs Natl Inst. Polar Res., Spec. Issue, 40, 153–161, 1986. the ice edge zone of the Weddell Sea, J. Geophys. Res., 92,
Nakamura, S., Development of Euphausia as a valuable protein for 7181–7190, 1987.
humans. Unpublished note, FAO Internal Consultation on Krill, Nelson, D.M., Smith, W.O., Jr., Muench, R.D., Gordon, L.I., Sullivan,
Rome, 1974. C.W., Husby, D.M., Particulate matter and nutrient distributions in
Nast, F., The vertical distribution of larval and adult krill (Euphausia the ice-edge zone of the Weddell Sea: Relationship to hydrography
superba Dana) on a time station south of Elephant Island, South during the late summer, Deep-Sea Res., 36, 191–209, 1989.
Shetlands, Meeresforschung, 27, 103–118, 1978. Nemoto, T., Food of baleen whales with reference to whale movements,
Nast, F., The assessment of krill (Euphausia superba Dana) biomass from Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 14, 149–290, 1959.
a net sampling programme, Meeresforsch, 24, 154–159, 1982. Nemoto, T., Feeding of bakeen whales and the value of krill as a marine
Nast, F., Gieskes, W.W.C., Phytoplankton observations relative to krill resource, in Symposium on Antarctic Oceanography, Santiago,
abundance around Elephant Island in November 1983, Arch. Chile, 1966, Currie, R.I., Ed., Scott Polar Research Institute,
Fischereiwiss., 37, 95–106, 1986. Cambridge, 1966, 340–353.
Nasu, K., Hydrography in relation to the distribution of euphausiids in Nemoto, T., Feeding patterns of baleen whales in the ocean, in Marine
the Antarctic Ocean, Bull. Jap. Soc. Fish. Oceanogr., 24, 35–38, Food Chains, Steele, J.H., Ed., University of California Press,
1974. Berkeley, CA, 1970, 241–252.
Nasu, K., On the geographic boundary of Antarctic krill distribution, Nemoto, T., History of research into food and feeding of euphausiids,
Ber. Polarforsch., 4, 216–222, 1983. Proc. Rl. Soc. Edinb., Ser. B (Biol.), 73, 259–265, 1972.
National Academy of Sciences, An Evaluation of Antarctic Marine Nemoto, T., Harrison, G., High-latitude ecosystems, in Analysis of
Ecosystem Research. (1981), National Academy of Sciences Marine Ecosystems, Longhurst, A.R., Ed., Academic Press,
Press, Washington, DC, 1981. London/New York, 1981, 95–126.
Naumov, A.G., Some features of the distribution and biology of Nemoto, T., Nasu, K., Present status of exploitation of krill in the
Euphausia superba Dana, Informational Bulletin of the Soviet Antarctic, in Oceanology International 75, BPS Exhibitions Ltd,
Antarctic Expedition, 39, 191–193, 1962. London, 1975, 353–360.
Naumov, A.G., Chekunova, V.I., Energy requirements of pinnipeds Nemoto, T., Doi, T., Nasu, K., Biological characteristics of krill caught
(Pinnipedia), Oceanology (Mosc.), 20, 348–350, 1980. in the Southern Ocean, in Biological Investigations of Marine
Naumov, A.G., Permitin, Y.Y., Trophic relationships of Euphausia Antarctic Systems and Stocks, Volume II, El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed.,
superba Dana and fish of the Southern Ocean (Scotia Sea), SCAR and SCOR, Scott Polar Research Institute, Cambridge,
Trudy VNIRO, 93, 216–229, 1973. In Russian. UK, 1981, 46–63.
Neale, P.J., Lesser, M.P., Cullen, J.J., Effects of ultraviolet radiation on the Nemoto, T., Okiyama, M., Takahashi, M., Aspects of the roles of squid
photosynthesis of phytoplankton in the vicinity of McMurdo in food chains of marine Antarctic ecosystems, in Antarctic
Station, Antarctica, in Ultraviolet Radiation in Antarctica: Measu- Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R.,
rements and Biological Effects, Sweiler, C., Penhale, P.A., Eds., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 415–420.
American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, 1994, 125–142. Neori, A., Holm-Hansen, O., Effect of temperature on rate of photo-
Neale, P.J., Davis, R.F., Cullen, J.J., Interactive effects of ozone synthesis in Antarctic phytoplankton, Polar Biol., 1, 33–38, 1982.
depletion and vertical mixing on photosynthesis of Antarctic Nettleship, D.N., Sanger, G.A., Springer, P.F., Marine birds: Their
phytoplankton, Nature (Lond.), 392, 585–589, 1998. feeding ecology and commercial fisheries relationships,
Nedwell, D.B., Walker, T.R., Sediment-water fluxes of nutrients in an Canadian Fisheries and Wildlife Service, Ottawa, Special Publi-
Antarctic coastal environment: Influence of bioturbation, Polar cation, 1984.
Biol., 15, 57–64, 1995. Neushul, M., Benthic marine algae, Antarctic Map Folio Series, Vol. 10,
Nelson, D.M., Particulate matter and nutrient distributions in the ice- American Geographical Society, Washington, DC, 9–10 pp, 1968.
edge zone of the Weddell Sea: Relationship to hydrography during Newell, R.C., The Biology of Intertidal Animals, 3rd Ed., Marine
the late summer, Deep-Sea Res., 36, 191–209, 1989. Ecological Surveys, Faversham, Kent, 1979, 781.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
584 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Newell, R.C., Linley, E.A.S., Significance of microheterotrophs in the Noble, R.T., Fuhrman, J.A., Virus decay and its causes in coastal waters,
decomposition of phytoplankton: Estimates of carbon and nitrogen Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 33, 77–83, 1997.
flow based on the biomass of plankton communities, Mar. Ecol. Noji, T.T., Estep, K.W., MacIntyre, F., Norrbin, F., Image analysis of
Prog. Ser., 16, 105–119, 1984. faecal material grazed upon by three species of copepods:
Newell, R.C., Lucas, M.I., Linley, E.A.S., Rate of degradation and Evidence for coprohexy, coprophagy and coprochaly, J. Mar.
efficiency of conversion of phytoplankton debris by marine Biol. Ass. U.K., 71, 465–486, 1991.
microorganisms, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 6, 123–136, 1981. Norhko, A., Thrush, S.F., Cummings, V.J., Funnell, G.A., Schwarz,
Newman, S.J., Nicol, S., Ritz, D., Marchant, H., Susceptibility of A.-M., Andrew, N.L., Hawes, I., Ecological role of Phyllophora
Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) to ultraviolet radiation, antarctica drift accumulations in coastal soft-sediment commu-
Polar Biol., 22(1), 50–55, 1999. nities of McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 27(8), 482–494,
Newman, S.I., Dunlap, W.C., Nicol, S., Ritz, D., Antarctic krill 2004.
(Euphausia superba) acquire a UV-absorbing mycosporine-like Norman, J.R., B.A.N.Z. Antarctic Research Expedition 1929–1931
amino acid from dietary algae, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 255, under the command of Douglas Mawson, Kt OBE, BE, D.Sc.,
93–110, 2000. FRS. Fishes, Reports of the B.A.N.Z. Antarc. Res. Exped., Ser. B, 1,
New Zealand Antarctic Institute, Ross Sea Region: A State of the 49, 1937.
Environment Report for the Ross Sea Region of Antarctica Norris, K.S., Mohl, B., Do odontocetes debilitate their prey acoustically,
(2001), New Zealand Antarctic Institute, Wellington, 2001. in Fourth Biennial Conference on the Biology of Marine Animals,
Nicol, D., Some characteristics of cold-water marine pelecypods, San Francisco, California 14–18 December 1981, 1981, 12–18.
J. Paleontol., 41, 1330–1340, 1967. North, A.W., Distribution of fish larvae at South Georgia: Horizontal,
Nicol, S., Some limitations on the use of lipofuscin aging technique, vertical and temporal distribution and early life history relative to
Mar. Biol., 93, 609–614, 1987. monitoring year-class strength and recruitment, CCAMLR Selected
Nicol, D., Lack of shell-attached pelecypods in Arctic and Antarctic Scientific Reports (WG-FSA-87-19), 105–142, 1987.
North, A.W., Kellerman, A., Key to the early stage of Antarctic fish, Ber.
waters, Nautilus, 77, 92–93, 1964; B53, 1–119, 1988.
Polarforsch., 67, 1–44, 1990.
Nicol, S., Age-old problem of krill longevity, BioScience, 40(11),
North, A.W., Ward, D., Initial feeding of fish larvae during winter at
833–836, 1990.
South Georgia, Cybium, 15, 357–364, 1989.
Nicol, S., CCAMLR and its approach to management of the krill fishery,
North, A.W., White, M.G., Key to fish postlarvae from the Scotia Sea,
Polar Biol., 27, 220–236, 1991.
Cybium, 6, 13–32, 1982.
Nicol, S., Stolf, M., Sinking rates of cast exoskeletons of Antarctic krill
North, A.W., White, M.G., Reproductive strategies of Antarctic fish, in
(Euphausia superba) and their role in the vertical flux of particulate
Proceedings of the Vth Congress of the European Ichthyological
matter and fluoride in the Southern Ocean, Deep-Sea Res., 36,
Society 1985, Stockholm 1987, 381–390 pp, 1987.
1753–1762, 1989.
North, A.W., Croxall, J.D., Doidge, D.W., Fish prey of the Antarctic fur
Nicol, S., de la Mare, W.K., Stolf, M., The energetic cost of egg
seal Arctocephalus gazella at South Georgia, Br. Antarct. Surv.
production in Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba Dana), Antarct.
Bull., 61, 27–37, 1983.
Sci., 7, 25–30, 1995.
Norton, O.I., Slater, J.G., A model for the evolution of the Indian Ocean
Nicol, S., Constable, A.J., Pauly, T., Estimates of circumpolar abun-
and the breakup of Gondwanaland, J. Geophys. Res., 84,
dance of Antarctic krill based on recent acoustic measurements,
6803–6830, 1979.
CCAMLR Sci., 7, 87–99, 2000.
Nöthig, E.-M., Untersuchungen zur Okologie des Photoplanktons in
Niebauer, H.J., Sea ice and temperature variability in the eastern Bering
südöstlichen Weddellmeer im Januar/Februar 1985 (Antarktis
Sea and relation to atmospheric fluctuations, J. Geophys. Res., 85, III/3), Ber. Polarforsch., 53, 1–119, 1988.
7507–7575, 1980. Nöthig, E.-M., Occurrence and vertical flux of faecal pellets of probably
Nimon, A.J., Schroter, R.C., Stonehouse, B., Heart rate of disturbed protozoan origin in the Weddell Sea (Antarctica), Mar. Ecol. Prog.
penguins, Nature (Lond.), 374, 415, 1995. Ser., 56, 281–289, 1989.
Nishida, S., Nanoplankton flora in the Southern Ocean, with special Nöthig, E.-M., Gowing, M.M., Late winter abundance and distribution
reference to siliceous varieties, Memoirs of the National Institute of phaeodarian radiolarians, other large protozooplankton and
for Polar Research, Special Issue, 40, 56–68, 1986. copepod nauplii in the Weddell Sea, Antarctica, Mar. Biol., 111,
Nishikawa, J., Tsuda, A., Diel vertical migration of the tunicate Salpa 473–484, 1991.
thompsoni in the Southern Ocean during summer, Polar Biol., 24, Nöthig, E.-M., von Bodungen, B., Occurrence and vertical flux of faecal
299–302, 2001. pellets of probably protozoan origin in the southeastern Weddell
Nishino, Y., Kawamura, A., Food habits of the Antarctic krill Sea (Antarctica), Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 56, 281–289, 1989.
(Euphausia superba Dana) collected in the South Shetland Nöthig, E.-M., von Bodungen, B., Sui, Q., Phyto- and protozooplankton
waters, Bull. Plankton Soc. Japan, 43, 9–19, 1996. biomass during austral summer in surface waters of the Weddell
Nishiwaki, M., Age characteristics of ear plugs in whales, Sci. Rep. Sea and vicinity, Polar Biol., 11, 293–304, 1991.
Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 12, 23–32, 1957. Novitsky, J.A., Microbial growth rates and biomass production in a
Nishiwaki, M., Distribution of toothed whales in the Antarctic Ocean, in marine sediment: Evidence for a very active but mostly nongrowing
Adaptations within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smith- community, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 53, 2368–2372, 1987.
sonian Institution, Washington, DC, 1977, 783–789. Nowlin, W.D., Jr., Clifford, M., The kinematic and thermohaline
Nishiwaki, M., Ichihara, T., Ohsumi, S., Age studies of the fin whale zonation of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current at Drake
based on the ear plug, Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 13, Passage from short-term measurements, J. Mar. Res., 40,
155–169, 1958. 481–507, 1977.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 585
Nowlin, W.D., Jr., Whitworth, T. III, Pillsbury, R.D., Structure and Ohsumi, S., Masaki, Y., Kawamura, A., Stock of Antarctic minke whale,
transport of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current at Drake Passage Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 20, 1–16, 1970.
from short-term measurements, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 7, 788–802, Okutani, T., Clarke, M.R., Identification key and species description for
1977. Antarctic squids, BIOMASS Handbook No. 21, 1985.
Nybelin, O., Antarctic fishes, Sci. Res. Norweg. Ant. Exped., 1927–1928, Oliver, J.S., Slattery, P.N., Effects of crustacean predators on species
26, 1–76, 1947. composition and population structure of soft-bodied infauna from
Nyssen, F., Brey, T., Lepoint, G., Bouquegneau, J.-M., De Broyer, C., McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Ophelia, 24(3), 155–175, 1985.
Dauby, P., A stable isotope approach to the eastern Weddell Sea Oliver, J.S., Oakden, J.M., Slattery, P.S., Phoxocephalid amphipod
trophic web: Focus on benthic amphipods, Polar Biol., 25, crustaceans as predators on larvae and juveniles in marine soft
280–287, 2002. bottom communities, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 7, 179–184, 1982.
Obermüller, B., Karsten, U., Portner, H.O., Abele, D., Effects of Oliver, J.S., Slattery, P.N., O’Connor, E.F., Lowry, L.F., Walrus
UV-radiation on oxidative stress parameters in polar marine Odobenus rosmarus feeding in the Bering Sea: A benthic perspec-
amphipods, and the role of UV-absorbing mycosporine-like tive, Fish. Bull., 81(3), 501–512, 1983.
amino acids (AAAS) in their diet, in Antarctic Biology in a Olsen, S., South Georgia cod, Notothenia rossii marmorata Fischer,
Global Context, Huiskes, A.H.L., Gieskes, W.W.C., Rozema, J., Norsk Hvalfangstid, 43, 373–382, 1954.
Schorno, R.M.L., van der Vies, S.M., Wolff, W.J., Eds., Backhuys Olsen, S., A contribution to the systematics and biology of Chae-
Publishers, Leiden, The Netherlands, 2003, 63–68. nichthyid fishes from South Georgia, Nytt Magasin fur Zoologi,
O’Brien, D.P., Description of escape responses of krill (Crustacea: Oslo, 3, 79–93, 1955.
Euphausiacea), with particular reference to swarming behaviour Olson, R.J., Nitrate and ammonium uptake on Antarctic waters, Limnol.
and the size and proximity of the predator, J. Crust. Biol., 7, Oceanogr., 25, 1064–1074, 1980.
449–457, 1987. Ommaney, F.D., Rhincalanus gigas (Brady), a copepod of the southern
Obst, B.S., Densities of Antarctica seabirds at sea and the presence of macrozooplankton, Discov. Rep., 13, 279–362, 1936.
krill Euphausia superba, The Auk, 102, 540–549, 1985. Omori, M., Zooplankton fisheries of the world: A review, Mar. Biol.,
Odate, T., Fukuchi, M., Distribution and community structure of 48(3), 199–205, 1978.
picophytoplankton in the Southern Ocean during the late austral Omori, M., Ikeda, T., Methods in Zooplankton Ecology, Wiley,
summer of 1992, NIPR Symp. Polar Biol., 8, 86–100, 1995. New York, 1984.
Oelenschlager, J., Manthy, M., Fluoride content of Antarctic marine Omura, H., A review of pelagic whaling operations in the Antarctic
animals caught off Elephant Island, Polar Biol., 1, 125–137, 1982. based on the effort and catch data in 10 squares of latitude and
Oelke, H., Breeding behaviour and success in a colony of Adélie longitude, Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 25, 105–203, 1973.
Penguins, Pygoscelis adeliae, at Cape Crosier, Antarctica, in The Omura, H., Ohsumi, S., Nemoto, T., Nasu, K., Kasuya, T., Black right
Biology of Penguins, Stonehouse, B., Ed., Macmillan, London, whales in the North Pacific, Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 21,
1975, 363. 1–78, 1969.
Offredo, C., Ridoux, V., The diet of emperor penguins, Aptenodytes Øresland, V., Feeding and predation impact of the chaetognath
forsteri, in Adélie Land, Antarctica, Ibis, 128, 409–413, 1986.
Eukrohnia hamata in Gerlache Strait, Antarctica, Mar. Ecol.
Offredo, C., Ridoux, V., Clarke, M.R., Cephalopods in the diets of
Prog. Ser., 63, 201–209, 1990a.
emperor penguins and Adélie Penguins in Adélie Land, Antarctica,
Øresland, V., Feeding of the carnivorous copepod Euchaeta antarctica
Mar. Biol., 86, 199–202, 1985.
in Antarctic coastal and oceanic waters, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 78,
Ohno, M., Fukada, Y., Fukuchi, M., Vertical distribution and standing
41–47, 1990b.
stocks of chlorophyll a in the coastal waters of the Antarctic Ocean,
Øresland, V., Winter population structure and feeding of the chaetognath
Antarct. Rec., 31, 93–106, 1987.
Eukrohnia antarctica in the Gerlache Strait, Antarctic Peninsula,
Ohsumi, S., Examination on age determination of the fin whale, Sci. Rep.
Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 119, 77–84, 1995.
Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 18, 49–88, 1964.
Øresland, V., Ward, P., Summer and winter diet of four carnivorous
Ohsumi, S., Some investigations of the school structure of the sperm
copepod species around South Georgia, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 98,
whale, Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst. Tokyo, 23, 1–25, 1971.
73–78, 1993.
Ohsumi, S., Examination of the recruitment rate of Antarctic fin whale
Ørheim, O., Iceberg discharge and mass balance of Antarctica, in
stock by use of mathematical models, Int. Whaling Committee
Glaciers, Ice Sheets, and Sea Level Effect of CO2-induced
Rep., 22, 69–90, 1972.
Climate Change, U.S. Department of Energy, Washington, DC,
Ohsumi, S., An attempt to standardize fishing efforts as applied to stock
13 pp, 1985.
assessment of the minke whale in Antarctic Area IV, Int. Whaling
Øritzland, T., Biology and population dynamics of Antarctic seals, in
Committee Rep., 26, 404–408, 1976.
Antarctic Ecology, Volume 1, Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Academic
Ohsumi, S., Feeding habits of the minke whale in the Antarctic, Int.
Press, London/New York, 1970a, 361–372.
Whaling Committee Rep., 29, 473–476, 1979.
Øritzland, T., Sealing and seal research in the Southwest Atlantic pack
Ohsumi, S., Masaki, Y., Biological parameters of the Antarctic minke
ice, September–October, 1964, in Antarctic Ecology, Volume 1,
whale at the virginal population level, J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada, 32,
Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Academic Press, London/New York, 1970b,
995–1004, 1975.
367–376.
Ohsumi, S., Nasu, K., Range and habitat of the female sperm whale, with
Øritzland, T., Food consumption of seals in the Antarctic pack ice, in
reference to the oceanographic structure. International Whaling
Commission Paper Sp/7 to Special Meeting on Sperm Whale Adaptations within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smith-
Biology and Stock Assessments, 1970 (Honolulu), 1970. sonian Institution, Washington, DC, 1977, 749–768.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
586 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Orsi, A.H., Whitworth, T. III, Nowlin, W.D., Jr., On the meridional Palmisano, A.C., Sullivan, C.W., Physiology of sea ice diatoms, I:
extent and fronts of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, Deep-Sea Response of three diatoms to a simulated summer–winter tran-
Res., 42, 641–673, 1995. sition, J. Phycol., 18, 489–498, 1982.
Ostapoff, F., Antarctic oceanography, in Biogeography and Ecology in Palmisano, A.C., Sullivan, C.W., Sea ice microbial communities
Antarctica, Van Meigham, J., van Oye, P., Eds., Dr. W. Junk, The (SIMCO) I: Distribution, abundance and primary production of
Hague, 1965, 97–126. ice microalgae in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, in 1980, Polar
Ottestad, P., On the biology of some southern Copepoda, Hvalradets Biol., 2, 171–177, 1983a.
Skr., 5, 1–61, 1932. Palmisano, A.C., Sullivan, C.W., Physiology of sea ice diatoms, II: Dark
Overland, J.E., Reynolds, R.M., Pearse, C.H., A model of the atmos- survival of three ice diatoms, Can. J. Microbiol., 29, 157–160,
pheric boundary layer over the marginal ice zone, J. Geophys. Res., 1983b.
88, 2836–2840, 1983. Palmisano, A.C., Sullivan, C.W., Pathways of photosynthetic carbon
Owens, N.J.P., Priddle, J., Whitehouse, M.J., Variations in phyto- assimilation in sea-ice microalgae from McMurdo Sound,
plankton nitrogen assimilation around South Georgia and in the Antarctica, Limnol. Oceanogr., 30, 674–678, 1985.
Palmisano, A.C., Sullivan, C.W., Growth, metabolism, and dark survival
Bransfield Strait (Southern Ocean), Mar. Chem., 35, 287–304,
in sea ice algae, in Sea Ice Algae, Horner, R.A., Ed., CRC Press,
1991.
Boca Raton, FL, 1985b, 131–146.
Pace, M.L., Glasser, J.E., Pomeroy, L.R., A simulation analysis of
Palmisano, A.C., Sullivan, C.W., Physiological response of micro-algae
continental shelf food webs, Mar. Biol., 82, 47–63, 1984.
in the ice-platelet layer to low-light conditions, in Antarctic
Paerl, H.W., Bacterial uptake of dissolved organic matter in relation to
Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R.,
detrital aggregation in marine and freshwater systems, Limnol.
Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985c, 84–88.
Oceanogr., 19, 966–972, 1974.
Palmisano, A.C., SooHoo, J.B., Sullivan, C.W., Photoadaptation in sea-
Pages, F., Lurbjewtt, F., Vertical distribution and abundance of meso-
ice microalgae in McMurdo Sound, Antarct. J. U.S., 19, 131–132,
planktonic medusae and siphonophores from the Weddell Sea,
1984.
Antarctica, Polar Biol., 14, 243–251, 1994. Palmisano, A.C., SooHoo, J.B., Sullivan, C.W., Photosynthesis-irradi-
Paine, R.T., Food web complexity and species diversity, Am. Nat., 100, ance relationship in sea ice microalgae from McMurdo Sound,
65–75, 1966. Antarctica, J. Phycol., 21, 341–346, 1985a.
Painting, S.J., Lucas, M.I., Stenton-Dosey, J.M.E., South African SIBEX Palmisano, A.C., Kottmeier, S.T., Moe, R.L., Sullivan, C.W., Sea ice
I criuse to the Prydz Bay region, 1984, 10: Biomass and production microbial communities, VI: The effect of light perturbation on
of bacterioplankton, detritus and bacterial relationships, S. Afr. microalgae at the ice-seawater interface in McMurdo Sound,
J. Antarct. Res., 15, 42–52, 1985. Antarctica, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 21, 37–45, 1985b.
Pakhomov, E.A., Demographic studies of Antarctic krill Euphausia Palmisano, A.C., SooHoo, J.B., White, D.C., Smith, G.A., Stanton, G.R.,
superba in the Cooperation and Cosmonaut Seas (Indian Sector Shade-adapted benthic diatoms beneath Antarctic sea ice,
of the Southern Ocean), Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 119, 45–61, 1995. J. Phycol., 21, 664–667, 1985c.
Pakhomov, E.A., Froneman, P.W., Macroplankton/microplankton Palmisano, A.C., SooHoo, J.B., SooHoo, S.L., Craft, L.L., Sullivan,
dynamics in the vicinity of Prince Edward Islands (Southern C.W., Photoadaptation in Phaeocystis pouchetii advected beneath
Ocean), Mar. Biol., 134, 501–516, 1999. the annual sea ice in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, J. Plankton
Pakhomov, E.A., Froneman, P.W., Zooplankton dynamics in the eastern Res., 8, 891–906, 1986.
Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean during austral summer Palmisano, A.C., SooHoo, J.B., Sullivan, C.W., Effects of four environ-
1997/1998, Part I: Community structure, Deep-Sea Res. II, 51, mental variables on photosynthesis-irradiance relationships in
2599–2616, 2004. Antarctic sea-ice microalgae, Mar. Biol., 94, 299–306, 1987a.
Pakhomov, E.A., McQuaid, C.D., Distribution of surface zooplankton Palmisano, A.C., SooHoo, J.B., Moe, R.L., Sullivan, C.W., Sea ice
and seabirds across the Southern Ocean, Polar Biol., 15, 271–286, microbial communities, VII: Changes in under-ice spectral irra-
1996. diance during the development of Antarctic sea ice microalgal
Pakhomov, E.A., Perissinotto, R., Trophodynamics of the hyperiid communities, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 35, 165–173, 1987b.
amphipod Themisto gaudichaudii in the South Georgia region Palmisano, A.C., Lizotte, M.P., Smith, G.A. et al. Changes in photo-
during the late summer, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 134, 91–100, 1996. synthetic carbon assimilation in Antarctic sea-ice diatoms during a
Pakhomov, E.A., Perissinotto, R., McQuaid, C.P., Comparative structure spring bloom: Variation in the synthesis of lipid classes, J. Exp.
of the macrozooplankton communities of the Subtropical and Mar. Biol. Ecol., 116, 1–13, 1988.
Papenfuss, G.F., Problems in taxonomy and geographical distribution of
Antarctic Polar Fronts, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 111, 655–669, 1994.
Antarctic marine algae, in Biiologie Antarctique, Prevost, J., Ed.,
Pakhomov, E.A., Verheye, H.M., Atkinson, A., Laubscher, R.K.,
Herman, Paris, 1964, 155–160.
Tainton-Clark, J., Structure and grazing impact of the mesozoo-
Paranjape, M.A., Moulting and respiration of euphausids, J. Fish. Res.
plankton community during late summer 1994 near South Georgia,
Board Can., 24, 1229–1240, 1967.
Antarctica, Polar Biol., 18, 180–192, 1997.
Park, Y.H., Gamberoni, L., Charriaud, E., Frontal structure and transport
Palmisano, A.C., Changes in photosynthetic metabolism of sea-ice
of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current in the South Indian Ocean
microalgae during a spring bloom in McMurdo Sound, Antarct.
sector, 40–808 E, Mar. Chem., 35, 45–62, 1991.
J. U.S., 21, 176–177, 1986.
Park, M.-G., Yang, S.-H., Chung, K.H., Shim, J.H., Phytoplankton
Palmisano, A.C., Garrison, D.L., Microorganisms in Antarctic sea ice,
biomass and primary production in the marginal ice zone of the
in Antarctic Microbiology, Friedman, E.I., Ed., Wiley Liss,
northwestern Weddell Sea during the austral summer, Polar Biol.,
New York, 1993, 167–218. 21, 251–261, 1999.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 587
Parke, M., Green, J.C., Martin, I., Observations on the fine structure of Penhale, P.A., Research team focuses on environmental impact of an oil
zooids of the genus Phaeocystis (Haptophyceae), J. Mar. Biol. Ass. spill, Antarct. J. U.S., 24, 9–12, 1989.
U.K., 51, 927–932, 1992. Penhale, P.A., Coosen, J., Marschoff, E.R., The Bahia Paraiso: A case
Parkinson, C.L., Southern Ocean sea-ice distributions and extent, Philos. study in environmental impact, remediation and monitoring, in
Trans. R. Soc. Lond., Ser. B, 338, 241–256, 1992. Antarctic Communities: Species, Structure and Survival, Battaglia,
Parkinson, C.L., Southern Ocean sea-ice and its wider linkages: Insights B., Valencia, J., Walton, D.W.H., Eds., Cambridge University
revealed from models and observations, Antarct. Sci., 16(4), Press, Cambridge, UK, 1997, 437–444.
387–400, 2004. Penny, R.L., Lowry, G., Leopard seal predation on Adélie Penguins,
Parmelee, D.F., Banded South Polar skua found in Greenland, Antarct. Ecology, 48, 878–882, 1967.
J. U.S., 11, 111–117, 1976. Perissinotto, R., McQuaid, C.D., Land-based predator impact on
Parmelee, D.F., Parmelee, J.M., Revised penguin numbers and distri- vertically-migrating zooplankton and micronekton advected to a
bution for Anvers Island, Antarctica, Br. Antarct. Surv. Bull., 76, Southern Ocean archipelago, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 80, 15–27,
65–73, 1987. 1992.
Parry, G.D., The influence of the cost of growth in ectotherm meta- Perissinotto, R., Pakhomov, E.A., The trophic role of the tunicate Salpa
bolism, J. Theor. Biol., 101, 453–477, 1983. thompsoni in the Antarctic marine ecosystem, 17, 361–374 pp,
Parsons, T.R., LeBrasseur, R.J., Fulton, J.P., Some observations on the 1998.
dependence of zooplankton grazing on cell size and concentration Perissinotto, R., Duncombe, R.C.M., Boden, B.P., Allanson, B.R.,
of phytoplankton blooms, J. Oceanogr. Soc. Jap., 23, 10–17, 1967. Vertical stability as a controlling factor of marine phytoplankton
Paterson, R., Paterson, P., The status of the recovering stock of hump- production at the Prince Edward Archipelago (Southern Ocean),
back whales in east Australian waters, Biol. Conserv., 47, 33–48, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 60, 205–209, 1990.
1989. Perissinotto, R., Pakhomov, E.A., McQuaid, C.P., Froneman, P.W.,
Pauly, D., On the inter-relationship between natural mortality, growth In situ grazing rates and daily ration of Antarctic krill Euphausia
parameters, and mean environmental temperature in 175 fish superba feeding on phytoplankton at the Antarctic Polar Front and
stocks, Journal du Conseil, 39, 175–192, 1980. the Marginal Ice Zone, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 160, 77–91, 1997.
Pavlov, V. Ya., On the quantitative composition of food for Euphausia Perissinotto, R., Guruey, L., Pakhomov, E.A., Contribution of hetero-
Superba Dana, Trudy VNIRO, 86, 142, Translation Series of the trophic material to the diet and energy budget of Antarctic krill,
Fisheries Research Board of Canade, 1977, 1953, 42–54. Euphausia superba, Mar. Biol., 136, 129–135, 2000.
Pavlov, V.Ya., The feeding of krill and some features of its behaviour, Permitin, Yu.E., Fecundity and reproductive biology of icefish (Chan-
Trudy VNIRO, 66, 207–222, MAAF translation No. NS 94, 1969. nichthyidae), fish of the family Muraenolepidae, and dragonfish
Pawson, D.L., Holothuroidea, Antarctic Map Folio Series II, American (Bathydraconidae) of the Scotia Sea (Antarctica), J. Ichthyol., 13,
Geographical Society, Washington, DC, 36–38 pp, 1969a. 204–215, 1973.
Pawson, D.L., Echinoidea, Antarctic Map Folio Series II, American Permitin, Yu.E., Species composition and zoogeographical analysis of
Geographical Society, Washington, DC, 38–41 pp, 1969b. bottom fish of the Scotia Sea, Vopr. Ikhtiol., 17, 843–863, 1977.
Payne, M.R., Growth of a fur seal population, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Permitin, Yu.E., Sil’yanova, Z.S., New data on the reproductive biology
Lond. B Biol. Sci., 279, 67–79, 1977. and fecundity of fishes of the genus Notothenia (Richardson) in the
Payne, M.R., Population size and age determination in the Antarctic fur Scotia Sea (Antarctica), J. Ichthyol., 11, 693–705, 1971.
seal, Arctocephalus gazella, Mamm. Rev., 8, 67–73, 1978. Permitin, Yu.E., Traverdiyeva, M.I., The food of some Antarctic fish in
Payne, M.R., Growth of the Antarctic fur seal, Arctocephalus gazella, the South Georgia area, J. Ichthyol., 12, 104–114, 1978a.
J. Zool. (Lond.), 187, 1–20, 1979. Permitin, Yu.E., Traverdiyeva, M.I., Feeding of fishes of the families
Pearce, P.A., Wilson, W.H., Review of viruses in Antarctic ecosystems, Nototheniidae and Chaenichthyidae in the South Orkney Islands,
Antarct. Sci., 15, 319–331, 2003. Biol. Morya, 2, 75–81, 1978b. In Russian.
Pearcy, W.G., Seasonal and inshore/offshore variation in the standing Perrin, R.A., Lu, P., Marchant, H.J., Seasonal variation in marine
stock of micronekton and macrozooplankton off Oregon, Fish. phytoplankton and ice algae at a shallow coastal site, Hydrobio-
Bull. U. S., 74, 70–80, 1976. logia, 146, 33–46, 1987.
Pearse, J.S., Reproductive periodicities of Odontaster validus Koehler, a Peterson, B.J., Aquatic primary productivity and the 14CO2 method: A
common Antarctic asteroid, Antarc. Res. Ser. II, 5, 39–85, 1965. history of the productivity problem, Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst., 11,
Pearse, J.S., Giese, C., Food, reproduction, and organic constitution of 359–385, 1980.
the common Antarctic echinoid Sterechinus neumayeri (Meissner), Petit, J.R., Jouzel, J., Raynaud, D., Barkov, N.I., Barnola, J.-M., Basile,
Biol. Bull., 130, 387–401, 1966. I., Bender, M., Chappellaz, J., Davisk, M., Delaygue, G., Delmotte,
Pearse, D.A., Wilson, W.H., Review. Viruses in Antarctic ecosystems, M., Kotlyakov, V.M., Legrand, M., Lipenkov, V.Y., Lorius, C.,
Antarct. Sci., 15, 3198–3331, 2003. Pépin, L., Ritz, C., Saltzmank, E., Stievenard, M., Climate and
Pearse, J.S., Bosch, I., McClintock, J.B., Marinovic, B., Brittan, R., atmospheric history of the past 420,000 years from the Vostok ice
Contrasting tempos of reproduction by shallow-water animals in core, Antarctica, Nature (Lond.), 399, 429–436, 1999.
McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Antarct. J. U.S., 31, 182–184, 1986. Phillips, K.L., Jackson, G.D., Nichols, D.D., Predation on myctophids by
Peck, L.S., Temperature and basal metabolism in two Antarctic marine the squid Monoteuthis ingens around Macquarie and Heard
herbivores, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 127, 1–12, 1989. Islands: stomach contents and fatty acid analysis, Mar. Ecol.
Peck, L.S., Brockington, S., Vanhove, S., Beghyn, M., Community Prog. Ser., 215, 179–189, 2001.
recovery following catastrophic iceberg impacts in a soft-sediment Piakowski, U., Map of the geographical distribution of macrozoo-
shallow water site at Signy Island, Antarctica, Mar. Ecol. Prog. plankton in the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean, Ber.
Ser., 186, 1–8, 1999. Polarforsch., 30, 264–279, 1985a.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
588 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Piakowski, U., Distribution, abundance and diurnal migration of macro- Pomeroy, L.R., The ocean’s food web: A changing paradigm,
zooplankton in Antarctic surface waters, Meeresforschung, 20, BioScience, 24, 499–504, 1974.
264–279, 1985b. Pomeroy, L.R., Secondary production mechanisms of continental shelf
Piakowski, U., Rodhouse, P.G., White, M.G., Bone, D.G., Symon, C., communities, in Ecological Processes in Coastal and Marine
Nekton community of the Scotia Sea as sampled by RMT 25 Systems, Livingston, P.J., Ed., Plenum Press, New York, 1979,
during austral summer, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 112, 13–28, 1994. 163–182.
Piatkowski, U., Zoogeographische Untersuchungen und Germein schaft- Pomeroy, L.R., Diebel, D., Aggregation of organic matter by pelagic
sanalysen an antariktischen Makroplankton, Ber. Polarforsch., 34, tunicates, Limnol. Oceanogr., 25, 643–652, 1980.
1–150, 1987. Pomeroy, L.R., Diebel, D., Temperature regulation of bacterial activity
Picken, G.B., Non-pelagic reproduction of some Antarctic prosobranch during the spring bloom in Newfoundland coastal waters, Science,
gastropods from Signy Island, South Orkney Islands, Malacologia, 233, 359–361, 1986.
19, 109–128, 1978a. Pomeroy, L.R., Wiebe, W.J., Temperature and substrates: An interactive
Picken, G.B., Growth, production and biomass of the Antarctic gastro- limiting factor for marine heterotrophic bacteria, Aquat. Microb.
pod bivalve Laevikitorina antarctica Martin 1885, J. Exp. Mar.
Ecol., 23, 187–204, 2004.
Biol. Ecol., 40, 71–74, 1978b.
Pomeroy, I.R., Wiegert, W.J., Temperature and substrates an interactive
Picken, G.B., Reproductive adaptations of Antarctic benthic invert-
limiting factor for marine heterotrophic bacteria, Aquat. Microb.
ebrates, Biol. J. Linn. Soc., 14, 67–75, 1980.
Ecol., 23, 197–204, 2001.
Picken, G.B., Marine habitats—benthos, in Key Environments—
Pomeroy, L.R., Darley, W.M., Dunn, E.L., Gallagher, J.L.K., Haines,
Antarctica, Bonner, W.N., Walton, D.W.H., Eds., Pergamon
E.B., Whitney, D.M., Primary production, in The Ecology of a Salt
Press, Oxford, 1985a, 154–172.
Marsh, Pomeroy, L.R., Wiegert, R.G.W., Springer, Berlin, 1981,
Picken, G.B., Benthic research in Antarctica, in Marine Biology of Polar
39–67.
Regions and the Effect of Stress on Marine Organisms, Grey, J.S.,
Pomeroy, L.R., Hanson, R.B., McGillivary, P.A., Sherr, B.F., Kirchman,
Christiansen, M.E., Eds., Wiley, London, 1985b, 167–184.
Pimm, S.L., The complexity and stability of ecosystems, Nature (Lond.), D.L., Deibel, D. et al., Microbiology and chemistry of fecal
307, 321–326, 1984. products of pelagic tunicates: Rates and fates, Bull. Mar. Sci.,
Pingnee, R.D., Cyclonic eddies and cross frontal mixing, J. Mar. Biol. 35, 426–439, 1984.
Ass. U.K., 58, 955–963, 1978. Poncet, S., Poncet, J., Censuses of penguin population on the Antarctic
Platt, H.M., Ecology of King Edward Cove, South Georgia, I: Macro- Peninsula, Br. Antarct. Surv. Bull., 77, 109–129, 1987.
benthos and the benthic environment, Bull. Br. Antarc. Surv., 49, Pond, D., Watkins, J., Priddle, J., Sergent, J., Variation in lipid content
231–238, 1980. and composition of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, at South
Platt, T., Harrison, W.G., Biogenic fluxes of carbon and oxygen in the Georgia, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 117, 49–57, 1995.
ocean, Nature (Lond.), 318, 55–58, 1985. Pople, A., Simpson, R.D., Cairns, S.C., An incident of Southern Ocean
Platt, T., Harrison, W.G., Lewis, M.R., Li, W.K.W., Sathyendranath, S., oil pollution: Effects of a spillage of diesel fuel on the rocky shore
Smith, R.E., Vezina, A.F., Biological production of the oceans: the of Macquarie Island (sub-Antarctic), Aust. J. Mar. Freshwater
case for consensus, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 52, 77–88, 1989. Res., 41, 603–620, 1990.
Platt, T., Sabba Rao, D.V., Irwin, B., Photosynthesis of picoplankton in Porter, K.G., Sherr, E.B., Sherr, B.F., Pace, M., Sanders, R.W., Protozoa
the oligotrophic ocean, Nature (Lond.), 300, 702–704, 1993. in planktonic food webs, J. Protozool., 32, 409–415, 1985.
Plotz, J., Summer diet of Weddell Seals (Leptonychotes weddelli) in the Post, A., Paralepididae (Barracudinas), in Fishes of the Southern Ocean,
eastern and southern Weddell Sea, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 6, Gon, O., Heenstra, P.C.H., Eds., J.B.L. Smith Institute of
97–102, 1986. Ichthyology, Grahamstown, South Africa, 1990, 138–141.
Plotz, J., Weidel, H., Bersch, M., Winter aggregation of marine Poulet, S.A., Comparison between five coexisting species of copepods
mammals and birds in the north-eastern Weddell Sea pack ice, feeding on naturally-occurring particulate matter, Limnol. Ocea-
Polar Biol., 11, 305–309, 1991. nogr., 23, 1126–1143, 1978.
Plotz, J., Bornmann, H., Knust, R., Schroder, A., Bester, M., Foraging Poulet, S.A., Chanut, J.P., Nonselective feeding of Pseudocalanus,
behaviour of Weddell Seals and its ecological implications, Polar J. Fish. Res. Bd. Canada, 32, 706–713, 1975.
Biol., 24, 901–909, 2001. Powell, A.W.B., Mollusca of Antarctic and subantarctic seas, in
Pocklington, R., An oceanographic interpretation of seabird distributions Biogeography and Ecology in Antarctica, von Mieghan, J.,
in the Indian Ocean, Mar. Biol., 51, 9–21, 1979. van Oye, P., Eds., Dr. W. Junk, The Hague, 1965, 333–380.
Poisson, A., Metzl, N., Brunet, C., Schauer, B., Bres, B., Ruiz-Pino, D.,
Powell, W.M., Clarke, G.L., The reflection and absorption of daylight
Louanchi, F., Variability of sources and sinks of CO2 in the
at the surface of the ocean, Jour. Opt. Soc. Amer., 26, 111,
western Indian and Southern Oceans during the year 1991,
1936.
J. Geophys. Res., 8, 22759–22778, 1993.
Presler, P., Necrophagous invertebrates of Admiralty Bay of King
Poleck, T.P., Denys, C.J., Effects of temperature on the moulting,
George Island (South Shetland Islands), Pol. Polar Res., 7,
growth, and maturation of the Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba
25–61, 1986.
(Crustacea: Euphausiacea), under laboratory conditions, Mar.
Prévost, J., Ecology du Manchot Empereur, Hermann, Paris, 1961.
Biol., 70, 255–265, 1982.
Prévost, J., Population, biomass, and energy requirements of Antarctic
Pollard, P.C., Moriarty, D.J.W., Validity of titriated thymidine method
birds, in Biological Investigation of Antarctic Systems and Stocks
for estimating bacterial growth rates: Measurement of isotope
(BIOMASS Volume II), El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., SCAR, Cambrige, UK,
dilution during DNA synthesis, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 48,
1076–1083, 1984. 1981, 125–181.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 589
Prévost, J., Mougin, J.-L., Guide des oiseaux et mammiferes des terres Propp, M.V., The study of the bottom fauna at Halswell Islands by scuba
australes et Antarctiques Francaises. Neuchâtel, Delachaux et diving, in Antarctic Ecology, Volume I, Holdgate, M.W., Ed.,
Niestle, 1979. Academic Press, London, 1970, 239–241.
Prézelin, B.B., Aldridge, A.L., Primary production of marine snow Prut’ko, V.G., On the occurrence of the opah, Lampris guttatus
during and after an upwelling event, Limnol. Oceanogr., 28, (Osteichthyes: Lampridae), in the southern part of the Indian
1156–1167, 1983. Ocean, J. Ichthyol., 19, 140–141, 1979.
Prézelin, B.B., Ley, A.C., Photosynthesis and chlorophyll a fluorescence Pugh, P.R., Gelatinous zooplankton—the forgotten fauna, Progress in
rhythms in marine phytoplankton, Mar. Biol., 55, 295–307, 1980. Underwater Science, 14, 67–78, 1989.
Price, H.J., Swimming behaviour of krill in relation to algal patches: A Pugh, P.R., MacAlister, H.E., Acri of the subtropical zone on sub-
mesocosm study, Limnol. Oceanogr., 34, 649–659, 1989. Antarctic South Georgia, Pedobiologia, 38, 552–565, 1994.
Price, H.J., Boyd, K.R., Boyd, C.M., Omnivorous feeding behaviour of Purves, P.E., The wax plug in the external auditory meatus of the
the Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Mar. Biol., 97, 67–77, Mysticeti, Discov. Rep., 27, 293–302, 1955.
1988. Putz, K., The post-moult diet of emperor penguins (Aptenodytes forsteri)
in the eastern Weddell Sea, Polar Biol., 15, 457–463, 1995.
Priddle, J., Antarctic planktonic ecosystem, in Polar Marine Diatoms,
Pyke, G.H., Pulliam, H.R., Charnov, E.L., Optimal foraging: A selective
Mullins, B.W., Priddle, J., Eds., British Antarctic Survey, Natural
review of theory and tests, Quart. Rev. Biol., 52, 137–154, 1977.
Environment Research Council, Cambridge, UK, 1990, 47–51.
Pyle, J.A., Carriner, G., Grenfell, J.L., Kettleborough, J.A., Lary, D.J.,
Priddle, J., Hawes, I., Ellis-Evans, J.C., Antarctic aquatic ecosystems as
Ozone loss in Antarctica: Implications for global change, Philos.
habitats for phytoplankton, Biol. Rev., 61, 199–238, 1986a.
Trans. R. Soc. Lond., Ser. B, 338, 219–226, 1992.
Priddle, J., Heywood, R.B., Theriot, E., Some environmental factors
Quartino, M.L., Kloser, H., Schloss, I.R., Wiencke, C., Biomass and
influencing phytoplankton production in the Southern Ocean
associations of benthic marine macroalgae from inner Potter Cove
around South Georgia, Polar Biol., 5, 65–79, 1986b.
(King George Island, Antarctica) related to depth and substrate,
Priddle, J., Croxall, J.P., Everson, I., Heywood, R.B., Murphy, E.J.,
Polar Biol., 24, 349–355, 2001.
Prince, P.A., Sear, C.B. et al., Large-scale fluctuations in distri- Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., School composition of the Antarctic krill,
bution and abundance of krill—A discussion of possible causes, in Euphausia superba, in the waters west of the Antarctic Peninsula in
Antarctic Ocean and Resources Variability, Sahrhage, D. et al. the austral summer of 1982, J. Crust. Biol., 4(Special Issue No. 1),
Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1988, 169–182. 96–106, 1984.
Priddle, J., Watkins, J., Morris, D., Ricketts, C., Buchholz, F., Variation Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Feeding by Antarctic krill, Euphausia
of feeding in krill swarms, J. Plankton Res., 12, 1189–1205, 1990. superba: Does size matter?, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and
Priddle, J., Smetacek, V., Bathmann, U., Antarctic marine primary Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds.,
production, biochemical carbon cycles, and climate change, Springer, Berlin, 1985, 372–377.
Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. ,Ser. B, 338, 279–289, 1992. Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Effects of oxygen, temperature and age on the
Prince, P.A., The food and feeding ecology of blue petrel (Halobaena metabolic rate of the embryos and early larval stages of Antarctic
caerula) and dove prion (Pachyptila desolata), J. Zool. (Lond.), krill, Euphausia superba Dana, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 125,
190, 59–76, 1980a. 43–62, 1989.
Prince, P.A., The food and feeding ecology of grey-headed albatross, Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Behavioural and physiological characteristics
Diomedea chrysostoma, and black-browed albatross, D. melano- of the Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Am. Zool., 31, 49–63,
phris. Ibis, 122, 476–488, 1980b. 1991.
Prince, P.A., Population and energetic aspects of relationship between Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Factors affecting distribution and abundance
black-browed and grey-headed albatrosses and the Southern Ocean of zooplankton, with an emphasis on Antarctic krill, Euphausia
marine environment, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, superba, Antarc. Res. Ser., 70, 357–371, 1996.
Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Environmental variability and its impact on
1985, 473–477. the reproductive cycle of Antarctic krill, Am. Zool., 41, 74–89,
Prince, P.A., Payne, M.R., Current status of birds at South Georgia, Br. 2001.
Antarct. Surv. Bull., 48, 103–118, 1979. Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Episodic recruitment in Antarctic krill,
Priscu, J.C., Priscu, L.R., Palmisano, A.C., Sullivan, C.W., The effect of Euphausia superba, in the Palmer LTER study region, Mar.
temperature on inorganic nitrogen and carbon metabolism in sea- Ecol. Prog. Ser., 259, 185–200, 2003.
ice microalgae, Antarct. J. U.S., 20, 196–198, 1987. Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Clarke, A., Krill energetics: Seasonal and
environmental aspects of the physiology of Euphausia superba, in
Priscu, J.C., Downes, M.J., Priscu, R., Palmisano, A.C., Sullivan, C.W.,
Southern Ocean Ecology: The BIOMASS Perspective, El-Sayed,
Dynamics of ammonium oxidizer activity and nitrous oxide (N2O)
S.Z., Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1994,
within and beneath Antarctic sea ice, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 62,
165–184.
37–46, 1990.
Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Fraser, T.K., Haberman, K.L., Factors
Priscu, J.C., Lizotte, M.P., Cota, G.F., Palmisano, A.C., Sullivan, C.W.,
affecting distribution and abundance of zooplankton, with
Comparison of irradiance response of photosynthesis and nitrogen
emphasis on Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Antarct. Res.
uptake in sea-ice microalgae, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 70, 201–210,
Ser., 70, 113, 1996.
1991.
Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Fraser, T.K., Amsler, M.O., Wyatt-Evens, C.,
Probyn, T.A., Painting, S.J., Nitrogen uptake by size-fractionated
Oakes, S.A. et al., Growth of larval krill, Euphausia superba, in fall
phytoplankton populations in Antarctic surface waters, Limnol.
and winter west of the Antarctic Peninsula, Mar. Biol., 143,
Oceanogr., 30, 1327–1332, 1985. 833–843, 2003.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
590 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Quetin, L.B., Ross, R.M., Fraser, T.K., Haberman, K.L., Factors Rauchet, M., Ergebrisse der faunistichen Abeiten in Benthal von King
affecting distribution and abundance in macrozooplankton, with George Island (Südschtlandirodetn, Antarktis), Ber. Polarforsch.,
an emphasis on Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, in Foundations 76, 1–75, 1991.
for Ecological Research West of the Antarctic Peninsula, Antarctic Rauglin, A.G., Underwater observations of krill, Trudy, Vsessoyuznogo
Research Series Vol. 70, 357–371, 1996. Naucho-issledo-vatel’skogo Instituta Morskogo Rybnogo
Quuilty, P.G., Evolution of the modern glaciation of Antarctica, in Khozyaistiva i Okeanografi (VNIROTrudy VNIRO), 66, 231–234,
Impact of Climate Change on Antarctica–Australia, Australian 1969 (MAAF Translation No. NS 92).
Government Publishing Service, Canberra, 1992, 10–16. Rawlence, D.J., Ensor, P.H., Knox, G.A., Summer tide-crack phyto-
Racovitza, E.G., La vie des animaux et des plantes dans l’Antartique, plankton at White Island, McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, N.Z.
Bull. Soc. Roy. Belgique de Geographie (Brussels), 24, 177–230, J. Mar. Freshwat. Res., 21, 91–97, 1987.
1900. Ray, G.C., in Population Ecology of Antarctic Seals, Holdgate, M.W.,
Radok, U., Streten, N., Weller, G.E., Atmosphere and ice, Oceanus, Ed., Antarctic Ecology, Vol. 1, Academic Press, London, 1970,
18(4), 15–27, 1975. 389–414.
Radthe, R.L., Hourigan, T.F., Age and growth of the Antarctic fish Ray, G.C., Ross seal, in Handbook of Marine Mammals, Ridgway, S.H.,
Nototheniopsis nudifrons, Fish. Bull., 1990, 537–571. Harrison, R.J., Eds., Academic Press, London, 1981, 237–260.
Radthe, R.L., Targett, T.E., Rhythmic structure and chemical pattern in Raymond, J.A., DeVries, A.L., Adsorption inhibition as a mechanism of
otoliths of the Antarctic fish Notothenia larseni: Their application freezing resistance in polar fishes, Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 74,
to age determination, Polar Biol., 3, 203–210, 1984. 2589–2593, 1977.
Radthe, R.L., Targett, T.E., Kellerman, A., Bell, J.L., Hill, K.T., Raymont, J.E.C., Plankton and Productivity in the Oceans, 2nd edition,
Antarctic fish growth profile of Trematomus newnesi, Mar. Ecol. Pergamon Press, London, 1980.
Prog. Ser., 51, 103–117, 1989. Raytheon Service Company, Report on the McMurdo Sound Water
Ragulin, S.G., Underwater observations of krill, Trudy Vsecoiuznogo Quality Study. Unpublished Report to the U.S, Office of Polar
Nauche-assledovatel’skii Instit. Morskogo Rybnogo Koziaiskia i Programs, 1983.
Okeanographie (VNIROTrudy VNIRO) Moscow, 66, 231–234, Reay, D.S., Nedwell, D.B., Priddle, J., Ellis-Evans, J.C., Temperature
1969. dependence of inorganic nitrogen uptake reduced affinity for
Rakusa-Suszczewski, S., The biology of Paramoera walkeri Stebbing nitrate at subtropical temperatures in both algae and bacteria,
(Amphipoda) and the Antarctic sub-fast ice community, Pol. Arch. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 65, 2577–2584, 1999.
Hydrobiol., 19, 11–36, 1972. Reay, D.S. et al. Regulation of low temperature of phytoplankton growth
Rakusa-Suszczewski, S., Environmental conditions within krill swarms, and nutrient uptake in the Southern Ocean, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.,
Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol., 25, 585–587, 1978. 219, 51–64, 2001.
Rakusa-Suszczewski, S., Feeding of Euphausia superba Dana under Redvers, G., Dispersion and fate of sewage and wastewater components
from Scott Base, Antarctica, M.Sc. thesis, University of Auckland,
natural conditions, Pol. Polar Res., 3, 289–297, 1982.
Auckland, 2000.
Ralph, R., Maxwell, J.G.H., Growth of two Antarctic lamellibranches:
Reeburg, W.S., Fluxes associated with brine motion in growing sea ice,
Adamussium colbecki and Laternula elliptica, Mar. Biol., 42,
Polar Biol., 3, 29–33, 1984.
171–175, 1977.
Regan, C.T., Fishes, British Antarctic (“Terra Nova”) Expedition 1910,
Ralph, R., Maxwell, J.G.H., The oxygen consumption of the Antarctic
Natural History Reports, Zoology, 1, 1–54, 1914.
limpet Nacella (Patinigera) concinna, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 45,
Regel, J., Putz, K., Effect of human disturbance on body temperature
19–23, 1977b.
and energy expenditure in penguins, Polar Biol., 18, 246–253,
Ralph, R., Maxwell, J.G.H., The oxygen consumption of the Antarctic
1997.
lamellibranch Gaimardia trapesina in relation to cold adaptation in
Reichardt, W., Differential temperature effects on the efficiency of
polar invertebrates, Br. Antarc. Surv. Bull., 45, 41–46, 1977c.
carbon pathways in Antarctic marine benthos, Mar. Ecol. Prog.
Rassolzadegan, F., Sheldon, R.W., Predator-prey interactions of nano-
Ser., 40, 127–135, 1987.
zooplankton and bacterial in an oligotrophic marine environment,
Reid, B., An interpretation of the age structure and breeding status of an
Limnol. Oceanogr., 31, 1010–1029, 1986.
Adélie Penguin population, Notornis, 15(3), 193–197, 1968.
Rassoulzadegan, F., Laval-Pueto, M., Sheldon, R.W., Partition of the
Reid, F.M.H., Biomass estimation of components of marine nano-
food ration of marine ciliates between picoplankton and nano-
plankton and picoplankton by the Utermohl settling technique,
plankton, Hydrobiologia, 159, 75–88, 1988.
J. Plankton Res., 5, 235–252, 1983.
Rau, G.H., Low 15N/14N in hydrothermal vent animals: Ecological
Reid, K., Growth of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, at South
implications, Nature (Lond.), 289, 484–485, 1981.
Georgia, Mar. Biol., 138, 57–62, 2001.
Rau, G.H., Hopkins, H., Torres, J.J., 15N/14N and 13C/12C in Weddell Sea
Reid, K., Arnould, J.P.Y., The diet of Antarctic fur seals, Arctocephalus
invertebrates: Implications for feeding diversity, Mar. Ecol. Prog.
gazella, during the breeding season at South Georgia, Polar Biol.,
Ser., 77, 1–6, 1991a.
16, 105–114, 1996.
Rau, G.H., Sullivan, C.W., Gordon, J.J., 13C and 15C variations in Weddell
Reid, J.L., Nowlin, W.D., Jr., Patzert, W.C., On the characteristics and
Sea particulate organic matter, Mar. Chem., 35, 335–369, 1991b.
circulation of the southwestern Atlantic Ocean, J. Phys. Oceanogr.,
Rau, G.H., Ainley, D.G., Bengston, H., Torres, J.J., Hopkins, T.L.,
15 14
7, 62–91, 1977.
N/ N and 13C/12C in Weddell Sea birds, seals, and fish: Reid, K., Croxall, J.P., Prince, P.A., The fish diet of black-browed
Implications for diet and trophic structure, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., albatross (Diomedea melanophris) and grey-headed albatross
84(1), 1–8, 1992. (D. chryostoma) at South Georgia, Polar Biol., 16, 469–477, 1996.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 591
Reid, K., Croxall, J.P., Edwards, T.M., Interannual variation in the diet Riebesell, U., Schloss, I., Smetacek, V., Aggregation of algae released
of the Antarctic prion Pachyptila desolata at South Georgia, Emu, from melting sea ice: Implications for seeding and sedimentation,
97, 126–143, 1997. Polar Biol., 11, 239–248, 1991.
Reid, K., Barlow, K.E., Croxall, J.P., Taylor, R.I., Predicting changes in Riley, G.A., Theory of food chain relations in the ocean, in The Sea,
the Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, population at South Volume 2, Hill, M.N., Ed., Wiley Interscience, New York, 1963,
Georgia, Mar. Biol., 135, 647–652, 1999. 438–463.
Rembiszewski, J.M., Krzeptowski, M., Linkowski, T., Fishes (Pisces) Riseborough, R.W., Transfer of organochlorine pollutants to Antarctica,
as a by-catch in fisheries of krill, Euphausia superba in Adaptations within Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed.,
Dana (Euphausia: Crustacea), Pol. Arch. Hydrobiol., 25, Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC, 1977, 1203–1210.
677–695, 1971. Risebrough, R.W., Walker, H., Schmidt, T., de Lappe, B., Connors, C.W.,
Repenning, C.A., Peterson, R.S., Hubbs, C.L., Contribution to the Transfer of chloirinated biohenyls to Antarctica, Nature (Lond.),
systematics of southern fur seals, with particular reference to 264(5888), 738–739, 1976.
Rivkin, R.B., Seasonal pattern of planktonic production in McMurdo
Juan Fernandez and Galapagos species, in Antarctic pinnipedia,
Sound, Antarctica, Am. Zool., 31, 5–16, 1991.
Antarctic Research Series 18, Burt, W.H., Ed.,1971, 1–34.
Rivkin, R.B., Putt, M., Heterotrophy and photoheterotrophy by Antarctic
Retainal, M.A., Quintana, R., Neira, F., Analysis cauliy cuantitatiro de
microalgae: Light-dependent incorporation of amino acids and
las communidades benthonicus on Bahia Foster (Isla Deception)
glucose, J. Phycol., 23, 442–452, 1987.
(xxxv Expedition Antarctica Chileno, enero 1981), Publ. Inst. Ant.
Rivkin, R.B., Putt, M., Alexander, S.P., Meritt, D., Gander, L., Biomass
Chileno Ser. Cientifica, 29, 5–15, 1982.
and production of polar plankton and sea ice microbial commu-
Riaux-Gobin, C., Bourgoin, P., Microphytic standing stocks at
nities: A comparative study, Mar. Biol., 101(2), 273–283, 1989.
Kerguelen Islands (Subantarctic, Indian Ocean), annual variations
Rivkin, R.B., Anderson, M.R., Gustafson, D.E., Jr., Seasonal pattern of
to environmental factors, II: Intertidal and subtidal microphyto-
bacterial and net nano- and picophytoplankton in McMurdo Sound,
benthos, Polar Biol., 27, 133–141, 2001. Antarctica, Antarct. J. U.S., 25, 195–196, 1990.
Riaux-Gobin, C., Treguer, P., Poulton, M., Vetion, G., Nutrients, algal Robertson, A.I., On the relationship between annual production:
biomass, and communities in land-fast ice and seawater off Adélie Biomass ratios and life spans of marine invertebrates, Oecologia,
Land (Antarctica), Antarc. Sci., 12, 160–171, 2000. 38, 193–202, 1979.
Riaux-Gobin, C., Poulin, M., Prodon, R., Treguer, P., Land-fast ice Robertson, G., Gales, R., Eds., Albatross Biology and Conservation,
microalgae and phytoplanktonic communities (Adélie Land, Beatty and Sons, Surrey, Norton, Australia, 1998.
Antarctica) in relation to environmental factors during the ice Robertson, G., Williams, R., Green, K., Robertson, I., Diet composition
breakup, Antarc. Sci., 15, 353–364, 2003. of emperor penguin chicks, Aptenodytes forsteri, at two Mawson
Ribec, C.A., Ainley, D.G., Consistency of seabird assemblages: An coast colonies, Antarctica, Ibis, 136, 19–31, 1994.
exploratory look, Biol. Oceanogr., 6, 175–202, 1988. Robin, G.deQ., Antarctic ice sheet: Its history and response to sea-level
Ribec, C.A., Ainley, D.G., Fraser, W.R., Habitat selection by marine and climate changes over the past 100 million years, Palaeogeogr.,
mammals in the marginal ice zone, Antarc. Sci., 3(2), 181–186, Palaeoclimateol., Palaeoecol., 67, 31–50, 1988.
1991. Robinson, S.A., Hindell, M.A., Foraging ecology of gentoo penguins,
Richardson, M.D., Benthic studies in the Antarctic, Antarc. J. U.S., 7, Pygoscelis papua, at Macquarie Island during period of chick care,
185–186, 1972. Ibis, 138, 722–731, 1996.
Richardson, M.G., The dietary composition of some Antarctic fish, Br. Robinson, P.H., Kolber, Z., Sullivan, C.W., Photophysiology and
Antarc. Surv. Bull., 41/42, 113–120, 1979. photoacclimation in surface sea ice algae from McMurdo Sound,
Richardson, M.D., Hedgpeth, J.W., Antarctic soft-bottom macrobenthic Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 143, 243–256, 1997.
community adaptation to a cold, stable, highly productive, Robinson, C., Archer, S.D., Williams, P.T.leB., Microbial dynamics in
glacially-affected environment, in Adaptations within Antarctic coastal waters off East Antarctica: Plankton production and
Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smithsonian Institution, respiration, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 180, 23–26, 1999.
Washington, DC, 1977, 181–186. Rodhouse, P.G., Cephalopod fauna of the South Scotia Sea at South
Richardson, M.G., Whitaker, T.M., An Antarctic fast-ice food chain: Georgia: Potential for commercial exploitation and possible
Observations on the interaction of the amphipod Pontogeneia consequences, in Antarctic Ecosystems: Ecological Change and
antarctica Chevreux with ice-associated microalgae, Br. Antarc. Conservation, Kerry, K.R., Hempel, G., Eds., Springer, Berlin/
Heidelberg, 1990, 289–298.
Surv. Bull., 47, 107–115, 1979.
Rodhouse, P.G., Population structure of Martialia hyadesi (Cepha-
Richdale, L.E., Biology of the sooty shearwater, Puffinus griseus, Proc.
lopoda: Ommastrephidae) at the Antarctic Polar Front and the
Zool. Soc. Lond., 141, 1–117, 1963.
Patagonian Shelf, South Atlantic, Bull. Mar. Sci., 49, 404–418,
Ricker, W.E., Methods for Assessment of Fish Production in Fresh
1991.
Waters, IGP Handbook No. 3, 1968, 1–313.
Rodhouse, P.G., Prince, P.A., Cephalopod prey of the black-browed
Ridgeway, S.H., Harrison, R.J., Handbook of Marine Mammals,
albatross, Diomedea melanophrys, Polar Biol., 13, 373–376, 1993.
Volumes 1 and 2, Academic Press, London, 1981.
Rodhouse, P.G., Yeatman, J., Redescription of Martilia hyadesi Roch-
Ridoux, V., Offredo, C., The diets of five summer breeding seabirds in
brunne and Mabile, 1889 (Mollusca: Cephalopoda), Bull. Br.
Adélie Land, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 9, 137–145, 1989.
Museum Nat. His. (Zool.), 56, 135–140, 1990.
Riebesell, U., Comparison of sinking and sedimentation rate measure-
Rodhouse, P.G., Olsson, O., Anker-Nilsson, P., Murry, A.W.A., Cepha-
ments in a diatom winter/spring bloom, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 54,
lopod predation by the king penguin, Aptenodytes patagonicus,
109–119, 1989. from South Georgia, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 168, 13–19, 1987.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
592 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Rodhouse, P.G., Croxall, J.P., Prince, P.A., Towards an assessment of Rott, H., Skavarca, P., Nagler, T., Recent changes of Larsen Ice Shelf,
the stock of ommastrephid squid Martialia hyadesi in the Scotia Antarctic Peninsula, unveiled by ERS-1, Revista SELPER,
Sea: Data from predators, in Recent Advances in Cephalopod 11(1–2), 46–50, 1995.
Fishes Biology, Okutani, T., O’Dor, R.K., Kubodera, T., Eds., Rott, H., Rack, W., Naglaer, T., Skavarca, P., Climate-induced retreat
Tokai University Press, Tokyo, 1993, 433–440. and collapse of the Northern Larsen Ice Shelf (Antarctic Penin-
Rodhouse, P.G., Arnbom, T.R., Fedak, M.A., Yeatman, G.A., Murray, sula), Ann. Glaciol., 17, 628–632, 1998.
A.W.A., Cephalopod prey of the wandering albatross, Diomedea Rounesvell, D.E., Periodic eruption of itinerant leopard seals within the
exulans, Mar. Biol., 96, 1–10, 1997. Australian sector of the Southern Ocean, 1976–1986, Pap. Royal
Roe, H.S.J., Seasonal formation of laminae in the ear plug of the fin Society of Tasmania, 122, 189–191, 1988.
whale, Discov. Rep., 35, 1–36, 1967. Rounsevell, D.E., Eberhard, I., Leopard seals, Hydrurga leptonyx
Roed, L.P., O’Brien, J.J., A coupled ice-ocean model of upwelling in the (Pinnipedia), at Macquarie Island, Aust. J. Mar. Freshwat. Res.,
marginal ice zone, J. Geophys. Res., 88, 2863–2872, 1983. 7, 403–415, 1980.
Ronan, T.E., Jr., Lipps, J.A., Delaca, T.E., Sediments and life under the Rowedder, U., Feeding ecology of the myctophid Electrona antarctica
Ross Ice Shelf, Antarc. J. U.S., 13, 141–142, 1978. (Günther, 1878) (Teleostei), Meeresforschung, 27, 252–263,
Ronner, U., Sorenson, F., Holm-Hansen, O., Nitrogen assimilation by 1979a.
phytoplankton in the Scotia Sea, Polar Biol., 2, 137–147, 1983. Rowedder, U., Some aspects of the biology of Electrona antarctica
Roper, C.E.F., Systematics and zoogeography of the worldwide bath- (Günther 1878) (Family Myctophidae), Meeresforschung, 4,
ypelagic squid Bathyteuthis (Cephalopoda: Oregopsida), United 244–251, 1979b.
States National Museum Bulletin 291, Smithsonian Institution Rudd, J.T., On the biology of the Euphausiidae, Hvalradets Skr., 2,
Press, Washington, DC, 1969. 1–105, 1932.
Roper, C.E.F., Cephalopods of the Southern Ocean region: Potential Russek, J.T., Kaspryzk, Z., Szostak, S., Preliminary economic evaluation
resources and bibliography, in BIOMASS, Volume II, El-Sayed, of commercial kill catches, Stud. Mater. Morsk. Inst. Ryb. Gdynia,
S.Z., Ed., SCAR, SCOR, Scott Polar Research Institute, 42, 1981. In Polish.
Cambridge, UK, 1981, 99–105. Ryan, K.G., UV radiation and photosynthetic properties of sea ice
Roper, C.E.F., Systematics and zoogeography of the worldwide bath- microalgae, J. Photochem. Photobiol., 13, 25–31, 1992.
ypelagic squid Bathyteuthis (Cephalopoda: Oregopsida), United Ryan, K.G., Beaglehole, D., Ultraviolet radiation and bottom ice algae:
States National Museum Bulletin 291, Smithsonian Institution Laboratory and field studies from McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, in
Press, Washington, DC, 2001. Ultraviolet Radiation in Antarctica: Measurements and Environ-
Ropert-Condert, Y., Kato, A., Baudet, J., Bost, C.-A., Le Maho, Y., mental Effects, Antarctic Research Series 62, Weller, C.S., Penhale,
Naito, Y., Feeding strategies of free-ranging Adélie Penguins, P.A., Eds., American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, 1994,
Pygoscelis adeliae, analysed by multiple data recording, Polar 229–242.
Biol., 24(6), 460–466, 2001. Ryther, J.H., Photosynthesis and fish production in the sea, Science, 166,
Rosenberg, A.A., Beddington, J.R., Basson, M., Growth and longevity of 72–76, 1969.
krill during the first decade of pelagic whaling, Nature (Lond.), Sabourenkov, E., Mesopelagic fishes of the Southern Ocean—Summary
324, 152–153, 1986. results of recent Soviet studies, in Selected Scientific Papers,
Ross, R.M., Energetics of Euphausia pacifica: Complete carbon and Scientific Committee of CCAMLR, Commission for the Conserva-
nitrogen budgets at 88 and 128C throughout the life-span, Mar. tion of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 433–457 pp,
Biol., 68, 15–23, 1982. 1990.
Ross, R.M., Quetin, L.B., Euphausia superba: Fecundity and the Sadiq, M., Toxic Chemistry in Marine Environments, Marcel Dekker,
physiological ecology of its eggs and larvae, Antarc. J. U.S., 17, New York, 1992.
166–167, 1983. Sadlier, M.F.S., Lay, K.M., Foraging movements of Adélie Penguins
Ross, R.M., Quetin, L.B., Spawning frequency and fecundity of the (Pygoscelis adeliae) in McMurdo Sound, in Penguin Biology,
Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Mar. Biol., 77, 201–205, 1983. Davis, L.S., Darby, J.T., Eds., Academic Press, London, 1990,
Ross, R.M., Quetin, L.B., How productive are Antarctic krill?, 157–180.
BioScience, 36, 264–269, 1986. Saggiomo, V., Garrada, G.C., Magoni, O., Marino, D., Ribera d’Alcala,
Ross, R.M., Quetin, L.B., Ecological physiology of larval euphausiids, M., Ecological and physiological aspects of primary production in
Euphausia superba (Euphausiacea), Mem. Queensl. Mus., 31, the Ross Sea, in Ross Sea Ecology, Faranda, F.M., Guglielmo, L.,
321–333, 1991. Ianora, A., Eds., Springer, New York, 2000, 247–258.
Ross, R.M., Quetin, L.B., Amsler, M.O., Euphausia superba: A Sahrhage, D., Length-weight correlation in Antarctic krill Euphausia
preliminary report on three areas of investigation, Antarc. superba, Meeresforschung, 26, 47–49, 1978.
J. U.S., 19, 153–155, 1985. Sahrhage, D., Some indications for environmental and krill resources
Ross, R.M., Quetin, L.B., Baker, K.S., Vernet, M., Smith, R.C., Growth variability in the Southern Ocean, in Antarctic Ocean and Resources
limitation in young Euphausia superba under field conditions, Variability, Sahrhage, D., Ed., Springer, Berlin/ Heidelberg, 1988a,
Limnol. Oceanogr., 45, 31–43, 2000. 33–40.
Ross, R.M., Quetin, L.B., Newberger, T., Oakes, S.A., Growth and Sahrhage, D., Ed., Antarctic Ocean and Resources Variability, Springer,
behaviour of krill (Euphausia superba) under the ice in late winter Berlin/Heidelberg, 1988b.
2001 west of the Antarctic Peninsula, Deep-Sea Res., 51, Saijo, Y., Kawashi, T., Primary production in the Antarctic Ocean,
2169–2184, 2004. J. Oceanogr. Soc. Jap., 19(4), 190–196, 1964.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 593
Sakshaug, E., Holm-Hansen, O., Factors governing pelagic production in SCAR/SCOR, First Meeting of the ad hoc Group on Squid Biology,
polar oceans, in Marine Phytoplankton and Productivity, Holm- BIOMASS Report Series No. 33, 1983b.
Hansen, O., Bolis, O.L., Gilles, R., Eds., Springer, Berling/ SC-CCAMLR, Report of the Seventh Meeting of the Scientific
Heidelberg, 1984, 1–18. Committee (SC-CAMLR-VII), Commission for the Conservation
Sakshaug, E., Holm-Hansen, O., Photoadaptation in Antarctic phyto- of Antarctic Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 1988.
plankton: Variations in growth rate, chemical composition, and SC-CCAMLR, Fish stock assessment—Report of the Working Group, in
P vs I curves, J. Plankton Res., 8, 459–573, 1986. Report of the Ninth Meeting of the Scientific Committee, Annex 6,
Sakshaug, E., Skjodal, H.R., Life at the ice edge, Ambio, 18, 60–67, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living
1989. Resources, Hobart, 1990a, 281–286.
Sakshaug, E., Slagstad, D., Light and productivity of phytoplankton in SC-CCAMLR, Report of the Ninth meeting of the Scientific Committee
polar marine systems: A physiological view, in Pro Mare Sym- (SC-CCAMLR-IX). Nitrogen assimilation by phytoplankton in the
posium on Polar Marine Ecology, Trondheim, Sakshaug, E., Scotia Sea, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine
Hopkins, C.C.E., Eds., Polar Research, 69–85, 1991. Living Resources, Hobart, 1990b.
Sampson, D.B., Pregnancy rates versus length in southern fin whales, Int. Schalk, R., Brey, T., Bathman, U., Arntz, W., Gerdes, D., Dieckmann,
Whaling Committee Rep., 20, 255–265, 1989. G., Ekau, W. et al., Towards a conceptual model for the Weddell
Samyshev, E.Z., Bacterioplankton of Antarctic coastal waters: Concen- Sea ecosystem, in Trophic Models of Aquatic Ecosystems,
tration, production and bacterial destruction, Oceanology, 26, Christense, V., Pauly, D. et al. Eds., International Center for
508–515, 1986. Living Aquatic Resources Management, Manila, 1993, 323–327.
Sanders, H.L., Benthic marine diversity and the stability-time Scheffer, V.B., Seals, Sea Lions and Walrusses: A Review of the
hypothesis: Diversity and stability in ecological systems, Proc. Pinnepedia, Stanford University Press, Stanford, CA, 1958.
Brookhaven Symp. Biol., 22, 71–81, 1969. Scheffer, M., Carpenter, S., Foley, J.A., Walker, B., Catastrophic shifts
Sanders, H.L., Evolutionary ecology and life-history patterns in the deep in ecosystems, Nature (Lond.), 413, 591–696, 2001.
sea, Sarsia, 64, 1–7, 1979. Schlosser, P., Helium: A new tracer in Antarctic oceanography, Nature
Sarmiento, J.L., Le Quéré, C., Oceanic carbon dioxide uptake in a model (Lond.), 321(6067), 233–235, 1986.
of century-scale global warming, Science, 274, 1346–1350, 1996. Schmitz, W.J., On the interbasin-scale thermohaline circulation, Rev.
Sasaki, H., Distribution of nano- and microplankton in the Indian Sector Geophys., 33, 151–173, 1995.
of the Southern Ocean, Mem. Natl Inst. Polar Res., Spec. Issue, 2, Schnack, S.B., A note on the sedimentation of particulate matter in
38–50, 1984. Antarctic waters during summer, Meeresforschung, 30, 306–315,
Sasaki, H., Hoshiai, T., Sedimentation of microalgae under Antarctic fast 1985a.
ice in summer, Mem. Natl Inst. Polar Res., Spe. Issue, 40, 45–55, Schnack, S.B., Feeding of Euphausia superba and copepod species in
1986. response to varying concentrations of phytoplankton, in Antarctic
Sasaki, H., Watanabe, K., Underwater observations of ice-algae in Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R.,
Lützow-Holm Bay, Antarctica, Antarc. Rec., 81, 1–8, 1984. Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985b, 311–323.
Sato, T., Hatanaka, H., A review of assessment of Japanese distant-water Schnack, S.B., Smetacek, V., von Bodungen, B., Utilization of phyto-
fisheries for cephalopods, in Advances in Assessment of World plankton by copepods in Antarctic waters during spring, in Marine
Cephalopod Resources, FAO Fisheries Technical Paper No. 231, Biology of Polar Regions and Effects of Stress on Marine
Caddy, J.F., Ed., FAO Fisheries, Rome, 1983, 145–203. Organisms, Gray, J.S., Christiansen, M.E., Eds., Wiley, Chichester,
Satoh, H., Watanabe, K., Kanda, H., Takahashi, E., Seasonal changes of 1985, 65–81.
chlorophyll a standing stocks and oceanographic conditions under Schnack-Schiel, S.B., The macrobiology of sea ice, in Sea Ice: An
fast ice near Syowa Station, Antarctica, Antarc. Rec., 30, 19–32, Introduction to its Physics, Biology and Geology, Thomas, D.N.,
1986. Dieckmann, G.S., Eds., Blackwell Science, Oxford, 2003, 211.
Satoh, H., Fukami, K., Watanabe, K., Takahashi, E., Seasonal changes in Schnack-Schiel, S.B., Hagen, W., Life cycle strategies and seasonal
heterotrophic bacteria under fast ice near Syowa Station, Antarc- variations in distribution and population structure of four dominant
tica, Can. J. Microbiol., 35, 329–333, 1989. copepod species in the easten Weddell Sea, Antarctica, J. Plankton
Savidge, G., Harbour, D., Gilpin, L.C., Boyd, P.W., Phytoplankton Res., 65, 1543–1552, 1994.
distribution and production in the Bellinghausen-Laurev Sea, Schnack-Schiel, S.B., Mujica, A., The zooplankton of the Antarctic
austral spring 1992, Deep-Sea Res., 42, 1201–1217, 1995. Peninsula, in Southern Ocean Ecology: The BIOMASS Perspec-
Savidge, G., Priddle, J., Gilpin, L.C., Bathmann, U., Murphy, E.J., tive, El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge,
Owens, N.J.P., Pollard, R.T., Turner, D.R., Veth, C., Boyd, UK, 1996, 79–92.
P.W., An assessment of the role of the marginal ice zone in the Schnack-Schiel, S.B., Dieckmann, G.S., Eicken, H., Weissenbeger, J.,
carbon cycle of the Southern Ocean, Antarc. Sci., 8, 349–358, Mizdalski, E., Beyer, K., Thomas, D., Gradinger, R., Spindler, M.,
1996. Life cycle strategy of the Antarctic calanoid copepod Stephos
Saville, A., Survey methods of appraising resources, FAO Fisheries longipes, Prog. Oceanogr., 36, 45–75, 1995.
Technical Paper, 1977, 171. Schnack-Schiel, S.B., Thomas, D., Dahms, H.-U., Haas, C., Mizdaski,
SCAR Bird Biology Subcommittee, Minutes of meeting 22 and 23 E., Copepods in Antarctic sea ice, Antarct. Rec. Ser., 73, 173–182,
August 1983, Hobart, Tasmania, Cormorant, 16, 138–145, 1983. 1998.
SCAR/SCOR, Meeting of the SCAR Group of Specialists of Southern Schnack-Schiel, S.B., Dieckmann, G.S., Gradinger, R., Melnikov, I.A.,
Ocean Ecosystems and Their Living Resources, BIOMASS Report Spindler, M., Thomas, D.N., Meiofauna in sea ice of the Weddell
Series No. 35, 1983a. Sea (Antarctica), Polar Biol., 24, 724–728, 2001.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:49—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
594 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Schneppenheim, R., Concentration of fluoride in Antarctic animals, Sheppard, D.S., Deely, J.M., Edgerley, W.H.L., Heavy metal content of
Meeresforschung, 28, 179–182, 1980. meltwater for the Ross Dependency, NZ J. Mar. Freshwat. Res.,
Schneppenheim, R., MacDonald, C.M., Genetic variation and population 31, 313–318, 1997.
structure of krill (Euphausia superba) in the Atlantic sector of Sherman, K., Ryan, A.F., Antarctic marine living resources, Oceanus,
Antarctic waters and off the Antarctic Peninsula, Polar Biol., 3, 31, 59–63, 1988.
19–28, 1984. Sherman, K., Jones, C., Sullivan, L., Smith, W., Berrien, P., Ejsymont,
Schröder, A., Lombarte, A., Olaso, I., Knust, R., Demersal fish fauna, L., Congruent shifts in sand eel abundance in western and eastern
Ber. Polarforsch., 301, 124–135, 1999. North Atlantic ecosystems, Nature (Lond.), 291, 486–489, 1981.
Schulenberger, E., Wormuth, J.H., Loeb, V.J., A large swarm of Sherr, B.F., Sherr, E.B., Role of heterotrophic protozoa in carbon and
Euphausia superba: Overview of patch structure and composition, energy flow in aquatic systems, in Current Perspectives in
J. Crust. Biol., 4, 75–95, 1984. Microbial Ecology, Klug, M.J., Reddy, C.A., Eds., American
Schwarzbacher, W., Die Fischfauna des östlichen und südlichen Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, 1984, 412–423.
Weddellmeers, Nahrung und trophrishe Stekkung, Fischarten, Sherr, E.B., Sherr, B.F., Fallon, R.D., Newell, S.Y., Small aloricate
Ber. Polarforsch., 54, 1084–1093, 1988. ciliates as a major component of the marine heterotrophic
Sciermammano, F., Jr., Observations of Antarctic polar front motions in nanoplankton, Limnol. Oceanogr., 31, 177–183, 1986.
a deep water expression, J. Phys. Oceanogr., 9, 221–226, 1989. Sherr, E.B., Rassoulzadegan, F., Sherr, B.F., Bacterivory by pelagic
Scolaro, J.A., Censo de elefantes marinos (Mirounga leonina L.) en el choreotrichous ciliates in coastal waters of the NW Mediterranean
territorio continental Argentino, Informes Técnicos del Centro Sea, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 55, 235–240, 1989.
Nacional Patagónico, 1.4.1, 1–12, 1976. Shevchenko, V., The nature of interrelationships between killer whales
Scott, F.J., Davidson, A.T., Marchant, H.J., Grazing by the Antarctic sea and other cetaceans. Fisheries and Marine Series Translation Series
ice ciliate Pseudocalanus embus, Polar Biol., 24, 127–131, 2001. No. 3839. Original title: Kharakter vzaimootnoshenii kasahiki i
Seddon, P.J., van Heezik, Y., Diving depths of the yellow-eyed penguin, drugikh kitoobraznykh, Morsk Mleikopitayushchie Chast, 23,
Megadyptes antipodes, Emu, 90, 53–57, 1990. 173–175, 1975.
Seebacher, F., Davison, W., Lowe, C.J., Franklin, C.E., A falsification of Shick, J., Dunlap, W., Mycosporine-like amino acids and related
the thermal specialization paradigm: Compensation for elevated gadusols: Biosynthesis, accumulation and UV-protective function
temperatures in Antarctic fishes, Biol. Lett., 1, 151–154, 2005. in aquatic organisms, Annu. Rev. Physiol., 54, 223–262, 2002.
Segawa, S., Kato, M., Murano, M., Growth, moult and filtering rate of Shick, J., Dunlop, W., Buettner, G., Ultraviolet (UV) protection in
krill in laboratory conditions, Mem. Natl Inst. Polar Res., Spec. marine organisms. II. Biosynthesis, accumulation, and sunscre-
Issue, 27, 93–103, 1983. ening function of micosporine-like amino acids, in Free Radicals
Selph, K.E., Landry, M.R., Allen, C.B., Calbet, A., Christensen, S., in Chemistry, Biology and Medicine, Yoshikawa, T., Toyokuri, S.,
Bidigare, R.R., Microbial community composition and growth Yamamoto, Y., Naito, Y., Eds., OICA International, London, 2000,
dynamics of the Antarctic polar front and seasonal ice zone 215–228.
during late spring, Deep-Sea Res., 48, 4059–4080, 2001. Shimadzu, Y, A brief summary of Japanese fishing activity in relation to
Seno, J., Komaki, Y., Takeda, A., Reports on the biology of the Umitaka- Antarctic krill, 1972/73 to 1982–83, in Selected Papers Presented
Maru expedition: Plankton collected by the Umitaka-Maru in the to the Scientific Committee of CCAMLR, 1982–1984: Part I,
Antarctic and adjacent water, with special reference to copepods, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living
J. Tokyo Univ. Fish., 49, 53–62, 1963. Resources, Hobart, 439–471 pp, 1984a.
Sergeant, D.E., Feeding rates of cetacea, Fiskeridirektorastets Skrifter Shimadzu, Y, A review of Antarctic ecosystem models, in Selected
Serie Havunderskelser, 15, 246–258, 1969. Papers Presented to the Scientific Committee of CCAMLR, 1982–
Sergeant, D.E., Feeding, growth and productivity of northwest Atlantic 1984: Part II, Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic
harp seals (Pagophilus groenlandicus), J. Fish. Res. Board Can., Marine Living Resources, Hobart, 221–246, 1984b.
30, 17–29, 1973. Shirakihara, K., Nakayama, K., Komaku, Y., Acoustic estimation of krill
Servais, P., Billen, G., Vives Rojo, J., Rate of bacterial mortality in biomass in R.V. Kaiyo-Maru SIBEX I Survey area (Indian Ocean
aquatic environments, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 40, 1440–1455, sector of the Southern Ocean), Mem. Natl Inst. Polar Res., Tokyo,
1985. 190, 140–152, 1986.
Seventy, D.L., The banding programme of Puffinus tenuirostris Shlibanov, V.I., Growth and natural mortality of Patagonian rock
(Temminck), CSIRO Wildl. Res., 6, 42–55, 1957. cod (Patagonotothen guntheri shagensis) from Shag Rocks,
Shabica, S.V., Tidal zone ecology at Palmer Station, Antarc. J. U.S., 7, SC-CAMLR Selected Scientific Papers, 1989, 1–11, 1990.
184–191, 1977. Showers, W.J., Jr., Daniels, R.A., Laine, D., Marine biology at Palmer
Shackleton, N.J., Kennett, J.P., Paleotemperature history of the Cenozoic Station, 1975 austral winter, Antarc. J. U.S., 12, 22–25, 1977.
and the initiation of Antarctic glaciation: Oxygen and carbon Shust, K.V., Visual observations on Antarctic krill made on board the
isotope analysis in DSDP sites 277, 279, and 281, Initial Rep. factory ship Akademik Knipovich, Trudy Vsesoyiuznogo Naucho-
Deep Sea Drilling Proj., 29, 743–755, 1975. issledovatel’skogo Instituta Morskogo Rybnogo Khnopvich (Trudy
Shaughnessy, P.D., Kerry, K.R., Crabeater seals (Lobodon carcino- VNIRO), 66, 223–250, 1969, MAAF Translation No. RTS 5588.
phagus) during the breeding season: Observations on five groups Shust, K.V., Brief communications on the distribution and biology of
near Enderby Land, Antarctica, Mar. Mamm. Sci., 5(1), 68–77, members of the genus Micromesistius (Family Gadidae),
1989. J. Ichthyol., 18, 490–492, 1978.
Shaw, E., Schooling fishes, Am. Sci., 66, 166–175, 1978. Sicrachi, M.E., Siebruth, J.McN., Sunlight-induced decay of planktonic
Sheldon, R.W., Prakash, A., Sutcliffe, W.H., Size distribution of marine bacteria in filtered seawater, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 33,
particles in the ocean, Limnol. Oceanogr., 17, 327–340, 1972. 19–27, 1986.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 595
Siebruth, J.McN., Microbiology of Antarctica, in Biogeography and Siegel, V., Loeb, V., Groger, J., Krill (Euphausia superba) density,
Ecology of Antarctica, van Miegham, J., van Oye, P., Eds., Dr. W. proportional and absolute recruitment and biomass in the Elephant
Junk, The Hague, 1967, 267–295. Island region (Antarctic Peninsula) during the period 1977 to 1997,
Siebruth, J.McN., Studies on algal substances in the sea. III. Glebstoff Polar Biol., 19, 393–398, 1998.
(humic material) in terrestrial and marine waters, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Siegel, V., Bergstrom, B., Muhlenherdt-Siegel, M., Demography of krill
Ecol., 2, 174–184, 1969. in the Elephant Island area during summer 2000 and its signi-
Siebruth, J.McN., Sea Microbes, Oxford University Press, New York, ficance for stock recruitment, Antarct. Sci., 14, 162–170, 2002.
1979. Siegfried, W.R., Birds and mammals—Oceanic birds of the Antarctic, in
Siebruth, J.McN., Grazing of bacteria by protozooplankton in pelagic Key Environments—Antarctica, Bonner, W.N., Walton, D.W.H.,
marine waters, in Heterotrophic Activity in the Sea, Hobbie, J., Eds., Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1985, 242–265.
Williams, A.J.LeB., Eds., Plenum Press, New York, 1984, Siegfried, W.R., Williams, A.J., Burger, A.E., Berruti, A., Mineral and
405–444. energy contributions of eggs of selected seabirds to the Marion
Siebruth, J.McN., Davis, P.G., The role of heterotrophic nanoplankton in Island terrestrial ecosystem, S. Afr. J. Antarc. Res., 8, 75–87, 1978.
the grazing of planktonic bacteria in the Sargasso and Caribbean Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Antarctic nutrient
Seas, Ann. Inst. Oceanogr., 58, 285–290, 1982. cycles and food webs, Symposium on Antarctic Biology, Wild-
Siebruth, J.McN., Smetacek, V., Lenza, J., Pelagic ecosystem structure: erness, South Africa 12–16 September 1983, Springer, Berlin,
Heterotrophic compartments and their relationship to plankton site 1985.
functions, Limnol. Oceanogr., 23, 1256–1263, 1978. Sievers, H.A., Nowlin, W.D., Jr., Upper ocean characteristics in Drake
Siegel, V., Relationships of various length measurements of Euphausia Passage and adjourning areas of the Southern Ocean, 398 W-958 W,
superba Dana, Meeresforschung, 29, 114–117, 1982. in Antarctic Ocean and Resources Variability, Sahrhage, D., Ed.,
Siegel, V., On the fecundity of the Antarctic krill Euphausia superba Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 1988, 57–80.
(Euphausiacea), Arch. Fischereiwiss., 36, 185–193, 1985. Silver, M.W., Alldredge, A.L., Bathypelagic marine snow: Deep sea
algal and detrital community, J. Mar. Res., 39, 501–530, 1981.
Siegel, V., Structure and composition of the Antarctic krill stock in the
Silver, M.W., Mitchell, J.G., Ringo, D.L., Siliceous nanoplankton, II.
Bransfield Strait (Antarctic Peninsula) during the Second Inter-
Newly discovered cysts and abundant choanoflagellates in the
national BIOMASS Experiment (SIBEX), Arch. Fischereiwiss.,
Weddell Sea, Antarctica, Mar. Biol., 58, 211–217, 1980.
37, 51–72, 1986a.
Silver, M.W., Gowing, M.M., Brownlee, D.C., Corless, J.O., Ciliated
Siegel, V., Untersuchungen zur Biologie des antarkischen Krill,
protozoa associated with oceanic sinking debris, Nature (Lond.),
Euphausia superba, im Bereich der Bransfield Strabe und angren-
309, 246–248, 1984.
zender Gebiete, Mitt. Inst. Seefischerei, Hamburg, 38, 1–224,
Simmonds, I., Modelling of the reaction of Antarctica to climate change
1986b.
at its periphery, in Impact of Climate Change on Antarctica-
Siegel, V., Age and growth of Antarctic Euphausiacea (Crustacea) under
Australia, Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra,
natural conditions, Mar. Biol., 96, 483, 1987.
1992, 16–23.
Siegel, V., Winter and spring distribution and status of the krill stock in
Simon, V., Sarano, F., Concentrations en sels nutritifs de l’eau de surface
Antarctic Peninsula waters, Arch. Fischereiwiss., 39, 45–72,
dans le secteur Indian de l’Ocean Austral (compagne Apsara II
1989.
Antipod III 1984), in Characteristiques biologiques, chemiques et
Siegel, V., Assessment of krill (Euphausia superba) spawning off the
sedimentalogiques du Secteur indian de l’Ocean Austral (Plateu
Antarctic Peninsula, Arch. Fischereiwiss., 41, 101–130, 1992.
des Kerguelen), Rapp. Comp. Mer. TAAF. 84-01, 8–103, 1978.
Siegel, V., Krill (Euphausiacea) life history and aspects of population
Simon, M., Glockner, F.O., Amann, R., Different community structure
dynamics, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 57(Supplement), 130–150,
and temperature optima of heterotrophic picoplankton in various
2000a. regions of the Southern Ocean, Aquat. Microb. Ecol., 68, 275–284,
Siegel, V., Krill (Euphausiacea) demography and variability in abun- 1999.
dance and distribution, Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 57(Supplement), Simpson, R.D., The shore environment of Macquarie Island, A.N.A.R.E.
151–167, 2000b. Report, Series B, 125(1), 1–41, 1976a.
Siegel, V., Distribution and population dynamics of Euphausia superba: Simpson, R.D., Physical and biotic factors limiting the distribution and
Summary of recent findings, Polar Biol., 29, 1–22, 2005. abundance of littoral molluscs on Macquarie Island (Sub-
Siegel, V., Kalinowski, J., Krill demography and small-scale processes: Antarctic), J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 21, 11–19, 1976b.
A review, in Southern Ocean Ecology: The BIOMASS Perspective, Simpson, R.D., The reproduction of some littoral molluscs from
El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, Macquarie Island, Mar. Biol., 44, 125–142, 1977.
1996, 145–163. Siniff, D.B., Seal population dynamics and ecology, J. Royal Soc. N. Z.,
Siegel, V., Loeb, V., Recruitment of Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, 11, 317–327, 1982.
and possible causes of its variability, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 123, Siniff, D.B., An overview of the ecology of Antarctic seals, Am. Zool.,
45–56, 1995. 31, 143–152, 1991.
Siegel, V., Bergstrom, B., Strobens, J.O., Schalk, P.H., Distribution, size Siniff, D.B., Bengtson, J.L., Observations and hypotheses concerning the
frequencies and maturity stages of krill, Euphausia superba, in interactions among crabeater seals, leopard seals, and killer
relation to sea-ice in the northern Weddell Sea, Polar Biol., 10, whales, J. Mammal., 58(3), 414–416, 1977.
549–557, 1990. Siniff, D.B., Stone, S., The role of the leopard seal in the tropho-
Siegel, V., Shibowski, A., Harm, U., Community structure of the dynamics of the Antarctic marine ecosystem, in Antarctic Nutrient
epipelagic zooplankton community under the sea ice in the Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M.,
northern Weddell Sea, Polar Biol., 12, 15–24, 1992. Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 555–560.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
596 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Siniff, D.B., Cline, D.R., Erickson, A.W., Population densities of seals in Smetacek, V.S., Scharek, R., Gordon, L.I., Eicken, H., Fahrbach, E.,
the Weddell Sea, Antarctica, in 1968, in Antarctic Ecology, Rohardt, G., Moore, S., Early spring phytoplankton blooms in ice
Volume I, Holdgate, W.M., Ed., Academic Press, London, 1970, platelet layers of the southern Weddell Sea, Antarctica, Deep-Sea
377–394. Res., 39, 153–168, 1992.
Siniff, D.B., Tester, J.R., Kuechle, V.B., Some observations on the Smetacek, V.S., Scharek, R., Nöthig, E.-M., Seasonal and regional
activity patterns of Weddell seals as recorded by telemetry, in variation in the pelagial and its relationship to the life history
Antarctic Pinnipedia, Antarctic Research Series 18, Burt, W.H., cycle of krill, in Antarctic Ecosystems: Ecological Change
Ed., 1971, 173–180. and Conservation, Kerry, K.R., Hempel, G., Eds., Springer,
Siniff, D.B., DeMaster, D.P., Hofman, R.J., Eberhart, L.L., An analysis Berlin/Heidelberg, 1990, 103–114.
of the dynamics of a Weddell seal population, Ecol. Monogr., 47, Smetacek, V.S., Klaas, C., Menten-Deuers, S., Rynearson, T.A., Mesos-
319–335, 1977. cale distribution of dominant diatom species relative to the
Siniff, D.B., Stirling, I., Bengtson, J.L., Reichle, R.A., Biota of the hydrographic field along the Antarctic Polar Front, Deep-Sea
Antarctic pack ice: R/V Hero Cruise 1976–77, Antarc. J. U.S., 15, Res.II, 49/18, 3835–3848, 2002.
160–165, 1977. Smetacek, V.S., Assmy, P., Henjes, J., The role of grazing in structuring
Siniff, D.B., Stirling, I., Bengtson, J.L., Reichle, R.A., Social and Southern Ocean pelagic ecosystems and biogeochemical cycles,
reproductive behaviour of crabeater seals (Lobodon carcino- Antarc. Sci., 16(4), 541–558, 2004.
phagus) during austral spring, Can. J. Zool., 57, 2243–2256, 1979. Smith, M.S.R., Seasonal movements of the Weddell seal in McMurdo
Siniff, D.B., Stone, S., Reichle, D., Smith, T., Aspects of leopard seals Sound, Antarctica, J. Wildl. Manage., 29, 464–470, 1965.
(Hydrurga leptonyx) in the Antarctic Peninsula pack ice, Antarc. Smith, V.R., A quantitative description of energy flow and nutrient
J. U.S., 15, 160–161, 1980. cycling in the Marion Island terrestial ecosystem, Polar Rec., 18,
Sissenwinw, M.P., Modelling the application of a recent tool in Antarctic 361–370, 1977.
marine living resources, in Selected Papers Presented to the Smith, P.E., Biological effects of ocean variability: Time and space
Scientific Committee of CCAMLR, Part IV, CCAMLR, Hobart,
scales of biological response, Rapp. P. v. Reun. Cons. Int. Explor.
1985, 369–390.
Mer., 173, 117–122, 1978.
Skavarca, P., Fast recession of the northern Larsen ice Shelf monitored
Smith, W.O., Jr., Phytoplankton dynamics in marginal ice zones,
by space images, Ann. Glaciol., 17, 317–321, 1993.
Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Ann. Rev., 25, 1–38, 1990a.
Skavarca, P., Rack, W., Pott, H., Ibarzabal y Donangelo, T., Climatic
Smith, W.O., Jr., Ed., Polar Oceanography, Part A: Physical Science,
trend and the retreat and disintegration of ice shelves on the
Academic Press, London, 1990b.
Antarctic Peninsula: An overview, Polar Rec., 18, 151–157, 1999.
Smith, W.O., Jr., Ed., Polar Oceanography, Part B: Chemistry, Biology
Skottsberg, C.J.F., Communities of marine algae in subantarctic and
and Geology, Academic Press, London, 1990c.
Antarctic waters, Konglia svenska Veteetenskapsa kademions
Smith, R.C., Baker, K.S., Assessment of the influence of enhanced UV-B
Handlinger, 19(4), 1–92, 1941.
on marine primary productivity, in The Role of Ultraviolet
Skottsberg, C.J.F., Antarctic phycology, in Biologie Antarctique,
Radiation In Marine Ecosystems, Watkins, J., Ed., Plenum Press,
Carrick, R., Holdgate, M.W., Prevost, J., Eds., Herman, Paris,
New York, 1982, 509–537.
1964, 147–154.
Smith, E.A., Burton, R.W., Weddell seals of Signy Island, in Antarctic
Sladen, W.J.L., Menzie, C.M., Reichel, W.L. Nature (Lond.), 200, 670,
Ecology, Volume I, Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Academic Press,
1963.
London, 1970, 415–428.
Slattery, P.N., Oliver, J.S., Scavenging and other feeding habits of
Smith, W.O., Jr., Gordon, L.I., Hyperproductivity of the Ross Sea
lysanianassid amphipods (Orchomene spp.) from McMurdo
Sound, Polar Biol., 8, 181–190, 1986. (Antarctica) polyna during austral spring, Geophys. Res. Lett.,
Slawyk, G., 13C and 15N uptake by phytoplankton in the Antarctic 24, 233–236, 1997.
upwelling area: Results from the Antiopd 1 cruise in the Indian Smith, M.A.K., Haschemeyer, A.E.V., Protein metabolism and cold
Ocean sector, Aust. J. Mar. Freshwat. Res., 30, 431–448, 1979. adaptation in Antarctic fishes, Physiol. Zool., 53, 373–382, 1980.
Slijper, E.J., Whales, Hutchinson, London, 1982. Smith, W.O., Jr., Kettner, G., Inorganic nitrogen uptake by phyto-
Slosarczyk, W., Juvenile Trematomus bernacchii (Boulenger, 1982) and plankton in the marginal ice zone of the Fram Strait, Rapports et
Pagothenia brachysoma (Proppenheim, 1962) (Pisces: Notothe- Proces-Verbaux des Reuniones Conseil Permanent International
niidae) in krill concentrations off Balleney Island (Antarctica), Pol. pour l’Exploration de la Mer, 188, 90–97, 1989.
Polar Res., 4, 57–69, 1983. Smith, W.O., Jr., Lancelot, C., Bottom-up versus top-down control
Slosarczyk, W., Rembiszewski, J.M., The occurrence of juvenile in phytolankton of the Southern Ocean, Antarct. Sci., 16,
Notothenioidea (Pisces) within krill concentrations in the region 531–539, 2004.
of the Bransfield Strait and the southern Drake Passage, Pol. Polar Smith, W.O., Jr., Nelson, D.M., Phytoplankton biomass near a receding
Res., 4, 299–312, 1982. ice-edge in the Ross Sea, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food
Smetacek, V.S., The annual cycle of protozooplankton in the Kiel Bight, Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer,
Ophelia Suppl., 63, 1–11, 1980. Berlin, 1985a, 70–77.
Smetacek, V.S., Annual cycle of sedimentation in relation to plankton Smith, W.O., Jr., Nelson, D.M., Phytoplankton bloom produced by a
ecology in the western Kiel Bight, Ophelia Suppl., 1, 65–76, 1981a. receding ice edge in the Ross Sea: Spatial coherence with the
Smetacek, V.S., The annual cycle of protozooplankton in the Kiel Bight, density field, Science, 227, 163–166, 1985b.
Mar. Biol., 63, 1–11, 1981b. Smith, W.O., Jr., Nelson, D.M., The importance of ice edge phyto-
Smetacek, V.S., Passow, U., Spring bloom initiation and Sverdrup’s plankton production in the Southern Ocean, BioScience, 36,
critical-depth model, Limnol. Oceanogr., 35, 228–233, 1990. 251–257, 1986.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 597
Smith, W.O., Jr., Nelson, D.M., Phytoplankton growth and new pro- Snape, I., Cole, C.M., Riddle, M.J., Gore, D.G., Duquesne, S., Stark, J.S.,
duction in the Weddell Sea marginal ice zone during austral spring Management and remediation of contaminated sites at Casey
and autumn, Limnol. Oceanogr., 35, 909–921, 1990a. Station, Antarctica, Polar Rec., 37, 199–214, 2001.
Smith, W.O., Jr., Sakshaug, E., Polar phytoplankton, in Polar Ocean- Soevik, T., Braekholm, O.R., Fluoride in Antarctic krill (Euphausia
ography, Part B: Chemistry, Biology and Geology, Smith, W.O., superba) and the Atlantic krill (Meganyctiphanes norvegica),
Jr., Ed., Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 1995, 477–525. J. Fish. Res. Board of Can., 36, 1414–1416, 1979.
Smith, S.L., Schnack-Schiel, S.B., Polar zooplankton, in Polar Ocean- Solomon, S., Stratospheric ozone depletion: A review of concepts and
ography, Part B: Chemistry, Biology and Geology, Smith, W.O., history, Rev. Geophys., 17, 275–316, 1999.
Jr., Ed., Academic Press, London, 1990, 521–528. Solyanik, G.A., An interesting ichthyological find, Soviet Antarctic
Smith, J.M.B., Simpson, R.D., Biotic zonation on rocky shores of Heard Expedition Information Bulletin No. 42, 78–80, 1963.
Island, Polar Biol., 4, 89–94, 1985. Solyanik, G.A., Experiment in marking seals from small ships, Sov.
Smith, S.P.A., Simpson, R.D., Effect of the Nella Dan oil spill on the Antarc. Exped. Info. Bull., 5, 212–217, 1964.
fauna of Durvillaea antarctica holdfast, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., Solyanik, G.A., Distribution and nutrition of bathypelagic fish Notolepis
121, 73–89, 1995. coatsi (Paralepidae family), Sov. Antarct. Exped. Info. Bull., 5,
Smith, R.C., Stammerjohn, S.E., Variation of surface air temperarture 365–366, 1965.
and sea ice extent in the western Peninsula region, Ann. Glaciol., Solyanik, G.A., The food of the Antarctic fish (Electrona antarctica
33, 493–498, 2001. Günther), Sov. Antarc. Exped. Info. Bull., 6, 443–447, 1967.
Smith, V.R., Steenkamp, M., Climate change and its ecological impli- Somero, G.N., Enzyme mechanisms of temperature compensation:
cations at a subantarctic island, Oecologia, 85, 14–24, 1990. Immediate and evolutionary effects of temperature on enzymes
Smith, M.A.K., Mathews, R.W., Hudson, A.P., Haschemeyer, A.E.V., of aquatic poikilotherms, Am. Nat., 103, 517–530, 1969.
Protein metabolism of tropical reef and pelagic fish, Comp. Somero, G.N., Giese, A.C., Wohlschlag, D.E., Cold adaptation in the
Biochem. Physiol., 65B, 415–418, 1980. Antarctic fish Trematomus bernacchii, Comp. Biochem. Physiol.,
Smith, G.A., Nichols, P.D., White, D.C., Fatty acid composition and 26, 223–232, 1968.
Somero, G.N., Fields, P.A., Hofmann, C.E., Weinstein, R.B., Kawall, H.,
microbial activity of benthic marine sediment from McMurdo
Cold adaptation and stenothermy in Antarctic Notothenioid fishes:
Sound, Antarctica, FEMS Microb. Ecol., 38, 219–231, 1986.
What has been gained and what has been lost?, in Fishes of
Smith, W.O., Jr., Baunmann, M.E., Wilson, D.L., Aletsee, L., Phyto-
Antarctica: A Biological Overview, di Prisco, G., Pascano, E.,
plankton biomass and productivity in the marginal ice zone of the
Clarke, A., Eds., Springer, Milan, 1998, 98–109.
Fram Strait during summer 1984, J. Geophys. Res., 92, 6777–6786,
Sommer, U., Maximal growth rates of Antarctic phytoplankton: Only
1987.
weak dependence on cell size, Limnol. Oceanogr., 34, 1109–1112,
Smith, W.O., Jr., Keene, N.K., Comiso, J.C., Interannual variability in
1989.
estimated primary productivity of the Antarctic marginal ice zone,
SooHoo, J.B., Palmisano, A.C., Lizotte, M.P., Kottmeier, S.T., SooHoo,
in Antarctic Ocean and Resources Variability, Sahrhage, D., Ed.,
S.L., Sullivan, C.W., Spectral light absorption and quantum yield
Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 1988, 131–139.
of photosynthesis in sea ice microalgae and a bloom of Phaeocystis
Smith, G.A., Nichols, P.D., White, D.C., Benthic nearshore microbial
pouchetii from McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Mar. Ecol. Prog.
communities of McMurdo Sound. Paper presented at the Fifth
Ser., 39, 175–189, 1987.
SCAR Symposium on Antarctic Biology, Hobart, Australia, 29
Soot-Ryen, T., Antarctic pelecypods, Sci. Res. Norwegian Antarct.
August–3 September, 1988, 1989a.
Exped. 1927–1928, 3, 1–46, 1951.
Smith, G.A., Davis, J.D., Muscat, A.M., Moe, R.L., White, D.C., Lipid
Sorokin, Yu.I., Microheterotrophic organisms in marine ecosystems, in
composition and metabolic activities of benthic near-shore micro-
Analysis of Marine Ecosystems, Longhurst, A.R., Ed., Academic
bial communities of Arthur Harbour, Antarctic Peninsula: Press, New York, 1981, 293–342.
Comparisons with McMurdo Sound, Polar Biol., 9, 517–524, Sorokin, Yu.I., Federov, V.K., Classification of bacterioplankton in
1989. Antarctic waters, Trudy IOAN SSSR, 112, 69–75, 1978.
Smith, W.O., Jr., Kelly, H.P., Rich, J.H., Chlorophyll distribution and Sorokin, Yu.I., Kogelschatz, J.E., Analysis of heterotrophic micro-
primary production in the Ross Sea, austral summer, Antarct. plankton in an upwelling area, Hydrobiologia, 66, 195–208, 1979.
J. U.S., 25, 179–182, 1990. Sosinski, J., Kuranty, J., Morze Scotia-nowy nejon Polowow ryb
Smith, D.C., Steward, G.F., Azam, F., Virus and bacteria abundances in Polskiego Rybolowstwa, Technikai Gospodarka Morska, 12,
the Drake Passage during January and August 1991, Antarc. 23–29, 1979.
J. U.S., 27, 125–127, 1992. Sosinski, J., Sikora, K., Wyniki baden ichtiologicznych prowadzonych
Smith, R.C., Prézelin, B.B., Baker, K.S., Bidigare, R.R., Boucher, N.P., na MT Gemini w czasie II: Polskiej Ekspedycji Antarkycznei,
Coley, T., Karentz, D., Macintyre, S., Matlick, H.A., Menzies, D., Biuletyn Morskiego Institutu Rybackiago, 43, 23–29, 1977.
Ondrusek, M., Wan, Z., Waters, K.J., Ozone depletion—ultraviolet Soutar, A., Isaacs, J.D., Abundance of pelagic fish during the 19th and
radiation and phytoplankton biology in Antarctic waters, Science, 20th centuries as recorded in anaerobic sediments off California,
255, 952–959, 1992. Fish. Bull., NOAA/U.S. Dep. Commerce, 72, 257–273, 1974.
Smith, W.O., Jr., Nelson, D.M., Tullio, G.R., Leventer, A.R., Temporal South, G.R., Biogeography of benthic marine algae of the Southern
and spatial patterns in the Ross Sea: Phytoplankton biomass, Oceans, in Proceedings of the International Symposium on Marine
elemental composition, productivity and growth, J. Geophys. Biogeography and Evolution in the Southern Hemisphere: Volume I,
Res., 101, 18455–18465, 1996. N.Z. DSIR Information Series 137, Wellington, 85–108, 1979.
Smith, R.C., Ainley, D., Baker, K. et al. Marine ecosystem sensitivity to Southern Ocean Convention Workshop, Southern Ocean Convention
climate change, BioScience, 49, 393–404, 1999. Workshop on the Management of Antarctic Marine Living
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
598 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Resources 1980 Report and Recommendations, Centre for Stein, M, Variation of geostropic circulation off the Antarctic
Environmental Education—The Whale Protection Fund, Peninsula and in the southwest Scotia Sea, in Antarctic, Springer,
Washington, DC, 1980. Berlin/Heidelberg, 81 pp, 1988.
Spies, A., Growth rates of Antarctic marine phytoplankton in the Stein, M., Variability of local upwelling off the Antarctic Peninsula,
Weddell Sea, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 41, 267–274, 1987. 1986-1990, Arch. für Fischereiwiss., 41(2), 131–158, 1992.
Spindler, M., Dieckmann, G.S., Distribution and abundance of the Stein, M., Heywood, R.B., Antarctic environment—physical ocean-
planktic Foraminifera Neogloboquadrina pachyderma in sea ice ography: The Antarctic Peninsula and Southwest Atlantic region
of the Weddell Sea (Antarctica), Polar Biol., 5, 185–191, 1986. of the Southern Ocean, in Southern Ocean Ecology: The BIOMASS
Spindler, M., Dieckmann, G.S., Das Meeres ab Lebensraum, Spectrum Perspective, El-Sayed, S.Z., Ed., Cambridge University Press,
der Wissenschaft, 2/1991, 48, 1991. Cambridge, UK, 1994, 11–24.
Spindler, M., Dieckmann, G.S., Lange, M.A., Seasonal and geographic Stenton-Dozey, J., Griffiths, C.L., The fauna associated with kelp
variations in sea ice community structure of the Weddell stranded on a sandy beach, in Sandy Beaches as Ecosystems,
Sea, Antarctica, in Antarctic Ecosystems: Ecological Change McLachlan, A., Erasmus, T., Eds., Dr. W. Junk Publishers, The
and Conservation, Kerry, K.R., Hempel, G., Eds., Springer, Hague, 1983, 441–447.
Berlin/Heidelberg, 1990, 129–135. Stepnik, R., All-year population studies of Euphausiacea (Crustacea) in
Spiridonov, V.A., Gruzov, E.N., Pushkin, A.F., Issledovaniia stai Admiralty Bay (King George Island, South Shetland Islands,
antarkicheskoi Euphausia superba (Crustacea: Euphausiacea) Antarctica), Pol. Polar Res., 3, 49–68, 1982.
pod l’dom (Investigations of schools of Antarctic Euphausia Stewardson, C.L., Mammals of the Sea, Sedolna Publishing, Braddon,
superba under the ice), Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 64, 1655–1660, 1997.
1985. Stewart, B.S., Yochem, P.K., Gelatt, T.S., First-year movements of
Spurr, E.B., The breeding of the Adélie Penguin Pygoscelis adeliae at Weddell Seals (Leptonychotes weddellii) in the Ross Sea, Antarc-
Cape Bird, Ibis, 117, 324–338, 1975. tica, during the first year of life, N.Z. Nat. Sci., 23, 195, 2000.
Squire, V.A., The physical oceanography and sea ice characteristics of Stewart, B.S., Yochem, P.K., Gelatt, T.S., Siniff, D.B., The pack ice
the Southern Ocean, Primer Symposium Español de Estudios niche of Weddell seals in the Ross Sea, N.Z. Nat. Sci., 23(Supple-
Antarcticos, Pama de Mallorca, 30 June–July 1985, 1–2, 1987. ment), 114, 1998a.
Stachelin, J., Harris, N.R.P., Appenzeller, C., Eberhard, J., Ozone trends: Stewart, B.S., Yochem, P.K., Gelatt, T.S., Siniff, D.B., Dispersal and
A review, Rev. Geophys., 39, 231–290, 2001. habitat use of Weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddelli) in the Ross
Stahl, J.C., Jouventin, P., Mougin, J.L., Roux, J.P., Weimerskirch, H., Sea, Antarctica, during their first year of life, N.Z. Nat. Sci., 23,
The foraging zones of seabirds in the Crozet Islands sector of the 195–206, 1998b.
Southern Ocean, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Stewart, B.S., Yochem, P.K., Gelatt, T.S., Siniff, D.B., The pack ice
Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, niche of Weddell seals in the Ross Sea, in Antarctic Biology in a
1985, 478–486. Global Context, Huskies, A.H.L., Gieskes, W.W.C., Rozema, J.,
Stambler, N., Primary production, light absorption and quantum yields Schorno, R.M.L., van der Vies, S.M., Wolff, W.J., Eds., Backhuys
of phytoplankton from the Bellingshausen and Amundsen Seas Publishers, Leiden, The Netherlands, 2003, 224–229.
(Antarctica), Polar Biol., 26, 438–451, 2003. Steyeart, J., Distribution of planktonic diatoms along an African–
Stammerjohn, S.E., Smith, R.C., Spatial and temporal variability of outer Antarctic transect, Invest. Pesq., 37, 295–328, 1973.
Antarctic Peninsula ice coverage, Antarct. Res. Ser., 70, 81–104, Stirling, I., The seals at White Island: A hypothesis on their origin,
1996. Antarctica, 4, 310–313, 1965.
Stanwell-Smith, D.P., Barnes, P.K.A., Benthic community development Stirling, I., Ecology of the Weddell Seal in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica,
in Antarctica: recruitment and growth in settlement panels at Signy Ecology, 50, 573–586, 1969a.
Island, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 212, 61–79, 1997. Stirling, I., Tooth wear as a mortality factor in the Weddell seal
Stark, J.S., The distribution and abundance of soft-sediment macro- Leptonychotes weddelli, J. Mammal., 50, 559–565, 1969b.
benthos around Casey Station, East Antarctica, Polar Biol., 23, Stirling, I., Distribution and abundance of the Weddell seal in the
840–850, 2000. western Ross Sea, Antarctica, N.Z. J. Mar. Freshwat. Res., 3,
Stark, J.S., Riddle, M.J., Human impacts in marine benthic communities 191–200, 1969c.
at Casey Station: Description, determination and demonstration of Stirling, I., Population dynamics of the Weddell seal (Leptonychotes
impacts, in Antarctic Biology in a Global Context, Huiskes, weddelli) in McMurdo Sound, in Antarctic Pinnipedia, Antarctic
A.H.L., Gieskes, W.W.C., Rozema, J., Schorno, R.M.L., van der Research Series 18, Burt, W.H., Ed., American Geophysical
Vies, S.M., Wolff, W.J., Eds., Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, The Society, Washington, DC, 1971a, 141–161.
Netherlands, 2003, 278–284. Stirling, I., Population aspects of Weddell seal harvesting at McMurdo
Starmans, A., Gutt, J., Arntz, W.E., Mega-epibenthic communities in Sound, Antarctica, Polar Rec., 15, 653–667, 1971b.
Arctic and Antarctic shelf areas, Polar Biol., 135, 269–280, 1999. Stirling, I., Regulation of numbers of an apparently isolated population
Steele, J.H., The Structure of Marine Ecosystems, Harvard University of Weddell seals (Leptonychotes weddelli), J. Mammal., 53,
Press, Cambridge, MA, 1974. 107–115, 1972.
Steeman-Nielsen, E., The use of radioactive carbon for measuring Stirling, I., Factors affecting the evolution of social behaviour in the
organic production in the sea, Journal du Conseil International pinnipedia, Rapports et Preces-Verbaux des Reunios Conseil
pour l’Exploration de la Mer, 18(2), 117–140, 1952. Permanent International pour l’Exploration de la Mer, 169,
Steen, J.B., Berg, T., The gills of two species of haemoglobin-free fishes 205–212, 1975.
compared to those of other teleosts—with a note on severe anaemia Stirling, I., The biological significance of polynas in the Canadian
in an eel, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 18, 517–526, 1966. Arctic, Arctic, 33, 303–312, 1980.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 599
Stirling, I., Cleator, H., Polynas in the Canadian Arctic, Canadian Sukuromato, K., Kato, H., Tanaka, S., A simulation study about several
Wildlife Service Occasional Paper No. 45, Canadian Wildlife factors influencing the estimates of a trend in age at sexual maturity
Service, Ottawa, 1981. of the Antarctic minke whale, Rep. Int. Whal. Commun., 35,
Stockner, J.G., Phototrophic picoplankton: an overview from marine 285–2990, 1985; 36, 231–235, 1980.
and freshwater ecosystems, Limnol. Oceanogr., 33, 765–775, Sullivan, C.W., Sea ice bacteria: Reciprocal interactions of the organ-
1988. isms and their environment, in Sea Ice Biota, Horner, R.A., Ed.,
Stockner, J.C., Anita, N.J., Algal picoplankton from marine and CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1985, 22–79.
freshwater systems: a multidisciplinary perspective, Can. J. Fish. Sullivan, C.W., Palmisano, A.C., Sea-ice microbial communities in
Aquat. Sci., 43, 2472–2503, 1986. McMurdo Sound, Antarc. J. U.S., 16, 128–130, 1981.
Stockton, W., An intertidal assemblage at Palmer Station, Antarc. Sullivan, C.W., Palmisano, A.C., Sea ice microbial communities:
J. U.S., 8, 305–307, 1973. Distribution, abundance and diversity of ice bacteria in
Stockton, W., The intertidal zone at Palmer Station, Anvers Island, McMurdo Sound, Antarctica in 1980, Appl. Environ. Microbiol.,
Antarctic Peninsula, in the wake of the Bahia Paraiso spill, Antarc. April 1984, 788–795, 1984.
J. U.S., 25, 203–207, 1990. Sullivan, C.W., Palmisano, A.C., Kottmeier, S., Moe, R., Development
Stoeckner, D.K., Michaels, E., Davis, L.H., Large proportion of marine of the sea ice microbial community in McMurdo Sound, Antarc.
planktonic ciliates found to contain functional chloroplasts, Nature J. U.S., 18, 155–157, 1982.
(Lond.), 326, 790–792, 1987. Sullivan, C.W., Palmisano, A.C., Soohoo, J.B., Influence of sea ice and
Stoeckner, D.K., Buck, H.R., Putt, M., A flagellate- and ciliate- sea ice biota on downwelling irradiance and spectral composition
dominated microbial community in the land-fast ice, Antarc. of light in McMurdo Sound, Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. Proc., 489, Ocean
J. U.S., 25, 197–199, 1990. Optics, 7, 159–165, 1984.
Stoeckner, D.K., Buck, H.R., Putt, M., Changes in the sea-ice brine Sullivan, C.W., Palmisano, A.C., Kottmeier, S., Grossi, S.McG., Moe,
community during spring–summer transition, McMurdo Sound, R., The influence of light on growth and development of the sea-ice
Antarctica. I. Photosynthetic protists, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 84, microbial community of McMurdo Sound, in Antarctic Nutrient
265–278, 1992. Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M.,
Stoeckner, D.K., Buck, H.R., Putt, M., Changes in sea-ice brine Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1985, 78–83.
community during the spring–summer transition in McMurdo Sullivan, C.W., McClain, C.R., Comiso, J.C., Smith, W.O., Jr., Phyto-
Sound, Antarctica. II. Phagotrophic protists, Mar. Ecol. Prog. plankton standing crops in an Antarctic ice edge assessed by
Ser., 95, 103–113, 1993. satellite remote sensing, J. Geophys. Res., 93, 12487–12498, 1988.
Stoeckner, D.K., Putt, M., Moisan, T., Nano- and microplankton Sullivan, C.W., Cota, G.F., Krempin, G.W., Smith, W.O., Jr., Distri-
dynamics during the spring Phaeocystis sp. bloom in bution and activity of bacterioplankton in the marginal ice zone of
McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K., 75, the Weddell-Scotia Sea during austral spring, Mar. Ecol. Prog.
815–832, 1995. Ser., 63, 239–252, 1990.
Stone, H.S., Siniff, D.B., Leopard seal feeding and food consumption in Sullivan, C.W., Arrigo, K.R., McLain, C.R., Comiso, J.C., Firestone, J.,
Antarctic spring and summer, in Proceedings of the Fourth Distribution of phytoplankton blooms in the Southern Ocean,
Biennial Conference on Biology of Marine Mammals, December Science, 262, 1832–1837, 1993.
14–18, 1983, 14–18, 1983. Sun, L.G., Liu, X.D., Yin, X.B., Zhu, R.B., Xie, Z.Q., Wang, Y.H., A
Stonehouse, B., Bird life, in Antarctic Research, Adie, R.J., Robin, 1500-year record of Antarctic seal populations in response to
G. deQ., Eds., Butterworth, London, 1964, 219–239. climate change, Polar Biol., 25, 495–501, 2004.
Stonehouse, B., The general ecology and thermal balance of penguins, Suskin, V.A., Planktonnye soobshcjestva antarkticheskoi chasti Atlan-
Adv. Ecol. Res., 4, 131–196, 1967. tiki, in Biologicheskie osnovy promyslovogo osvoeniia otkrytykh
Stonehouse, B., Adaptation in polar and subpolar penguins, in Antarctic rainov okeana, Vinogradov, M.E., Flint, M.V., Eds., Nauka,
Ecology, Volume I, Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Academic Press, Moscow, 1985, 29–39.
London, 1970, 526–541. Sverdrup, H.U., On conditions for the vernal blooming of phytoplankton,
Stonehouse, B., Birds and mammals—penguins, in Key Environments— Journal du Conseil, Conseil Permanent International pour
Antarctica, Bonner, W.W., Ed., Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1985, l’Exploration de la Mer, 18, 287–295, 1953.
223–241. Sverdrup, H.U., Johnson, M.W., Fleming, R.H., The Oceans: Their
Stonehouse, B., Monitoring shipborne visitors in Antarctica: A pre- Physics, Chemistry and General Biology, Prentice-Hall, Engle-
liminary field study, Polar Rec., 28, 213–218, 1992. wood Cliffs, NJ, 1942.
Stout, W.E., Shabica, S.V., Marine ecological studies at Palmer Station Svetlov, M.F., The porbeagle Lamma nasus in Atlantic waters,
and vicinity, Antarc. J. U.S., 5, 134–135, 1970. J. Ichthyol., 18, 850–851, 1978.
Strand, S.W., Hamner, W.M., Schooling behaviour of Antarctic krill Swadling, K.M., Population structure of two Antarctic ice-associated
(Euphausia superba) in laboratory aquaria: Reactions to chemical copepods, Drescheriella glacialis and Paralabidocera antarctica,
and visual stimuli, Mar. Biol., 105, 355–359, 1990. in winter sea ice, Mar. Biol., 139, 597–603, 2001.
Strange, I.J., The thin-billed prion, Pachyptila belcheri, at New Island, Swadling, K.M., Gibson, J.A.E., Ritz, D.A., Nichols, P.D., Horizontal
Falkland Islands, Gerfaut, 70, 411–445, 1980. patchiness in sympagic organisms of the Antarctic fast ice, Antarc.
Stretch, T.J., Hamner, P.P., Hamner, W.M., Michel, W.C., Cook, J., Sci., 9, 399–406, 1997.
Sullivan, C.W., Foraging behaviour of Antarctic krill Euphausia Swadling, K.M., Gibson, J.A.E., Ritz, D.A., Nichols, P.D., Grazing of
superba on sea-ice microalgae, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 44, 131–139, phytoplankton by protozoa in eastern Antarctic waters, Mar. Biol.,
1988. 128, 39–48, 1997.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
600 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Swithinbank, C., McClain, P., Little, P., Drift tracks of Antarctic Tanoue, E., Handa, N., Sakugawa, H., Difference of the chemical
icebergs, Polar Rec., 18, 495–561, 1977. composition of organic matter between fecal pellet of Euphausia
Takahasi, E., Loricate and scale-bearing protists from Lutzow–Holm superba and its feed, Dunaliella tertiolecta, Trans. Tokyo Univ.
Bay, Antarctica. I. Species of Acanthoecidae and Centrohelida Fish., 5, 189–196, 1982.
found at a site selected on fast ice, Antarct. Rec., 73, 1–22, 1981. Targett, T., Trophic ecology and structure of coastal Antarctic fish
Takahashi, M., Trophic ecology of demersal fish community north of the communities, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 4, 243–263, 1981.
South Shetland Islands, with note on the ecological role of krill, Tarling, G.A., Ward, P., Sheader, M., Williams, J.A., Symon, C.,
Mem. Natl Inst. Polar Res., Spec. Issue, 27, 183–192, 1983. Distribution patterns of macrozooplankton assemblages in the
Takahashi, E., Loricate and scale-bearing protists from Lützow-Holm Southwest Atlantic, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 120, 29–40, 1995.
Bay, Antarctica. II. Four marine species of Paraphysomonas Tarpy, C., Killer whale attack, Nat. Geograph. Mag., 155, 542–545,
(Chrysophyceae), including two new species from the fast-ice- 1979.
covered coastal area, Jap. J. Phycol., 35, 155–166, 1987. Tarverdiyera, M.I., The food consumption, daily ration and feeding
Takahashi, M., Bienfang, P.K., Size structure of phytoplankton in habits of the ice fish Champsocephalus gunnari Lönnberg of the
subtropical waters, Mar. Biol., 76, 203–211, 1983. South Orkneys, in Characteristics of the Pelagic Community from
Takahashi, M., Nemoto, T., Food of some Antarctic fish in the Western the Sea of Scotia and Adjacent Waters, Trudy VNIRO, Moscow,
Ross Sea in the summer of 1979, Polar Biol., 3, 237–239, 1984. 69–76 pp, 1982. In Russian.
Takeda, S., Influence of iron availability on nutrient consumption ratio of Tarverdiyera, M.I., Pinskaya, I.A., The feeding of fishes of the families
diatoms in oceanic waters, Nature (Lond.), 393, 774–777, 1998. Nototheniidae and Channichthyidae on the shelves of the Antarctic
Takeda, S., Watanabe, K., Growth response of Antarctic phytoplankton Peninsula and the South Shetland Islands, J. Ichthyol., 20, 50–69,
to iron enrichment, Proc. NIPR Symp. Antarct. Biol., 10, 14–24, 1980.
1997. Tatian, M., Sahade, R.T., Fuentes, V., Mecuri, G., Use of a wide
Taljaard, J.J., van Loon, H., Crutcher, H.L., Jenne, R.L., Climate of the spectrum of particle food by suspension feeders: Adaptation to
Upper Air. Part 1. Southern Hemisphere, U.S. National Center for low phytoplankton availability, IX SCAR Biol. Symp. Abstr., 63,
Atmospheric Research, Washington, DC, 1969, 140. 2005.
Tanabe, S., Tatsukawa, R., Chlorinated hydrocarbons in the Southern Taylor, G.T., The role of pelagic heterotrophic protozoa in nutrient
Ocean, in Proceedings of the BIOMASS Collection in 1982, cycling: A review, Ann. de l’Institut Oceanographique, 58,
Nemoto, T., Matsuda, T., Eds., National Institute for Polar 227–241, 1982.
Research, Tokyo, 1983, 64–76. Taylor, R.H., Wilson, P.R., Recent increase and southern expansion of
Tande, K.S., Bamstedt, U., On the trophic fate of Phaeocystis pouchetii. Adélie Penguin populations in the Ross Sea, Antarctica, related to
I. Copepod feeding rates on solitary cells and colonies of climate warming, N.Z. J. Ecol., 14, 25–29, 1990.
P. pouchetii, Sarsia, 72, 313–320, 1987. Taylor, G.T., Iturriaga, R., Sullivan, C.W., Interactions of bacterivorous
Taniguchi, A., Hamada, E., Okazaki, M., Naito, Y., Distribution of grazers and heterotrophic bacteria with dissolved organic matter,
phytoplankton chlorophyll continuously recorded in JARE-25 Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 23, 129–141, 1985.
cruise to Syowa Station, Antarctica (SIBEX I). Proceedings of Taylor, R.H., Wilson, P.R., Thomas, B.W., Status and trends of Adélie
the Eighth Symposium on Polar Biology, 1985, Mem. Natl Inst. Penguin populations in the Ross Sea Region, Polar Rec., 26,
Polar Res., Spe. Issue, 44, 3–14, 1986. 293–304, 1990.
Tanimura, A., Distribution of chlorophyll a along the course of the Fuji Tayor, R.J.F., An unusual record of three species of whale being
to and from Antarctica in 1979–1980, Antarct. Rec., 72, 35–48, restricted to pools in Antarctic sea ice, J. Zool., 129, 325–331,
1981. 1957.
Tanimura, A., Minoda, T., Fukuchi, M., Hoshiai, T., Ohtsuka, H., Swarm Tchernia, P., Etude de la derive antarctique Est-Quest au moyen
of Paralabidocera antarctica (Calanoida: Copepoda) under sea ice d’icebergs suivi par la satellite, Comptes Rendus Academie des
near Syowa Station, Antarctica, Antarc. Rec., 82, 12–19, 1984. Sciences (Paris), 278, 667–670, 1974.
Tanimura, A., Fukuchi, M., Hoshiai, T., Seasonal changes in the Tchernia, P., Descriptive Physical Oceanography, Pergamon Press,
abundance and species composition of copepods in the ice- Oxford, 1980.
covered sea near Syowa Station, Antarctica, Mem. Natl Inst. Tchernia, P., Jeannin, P.F., Circulation in Antarctic waters as revealed by
Polar Res., Spe. Issue, 40, 212–220, 1986. iceberg tracks, 1972–83, Polar Rec., 22, 263–269, 1984.
Tanimura, A., Hoshiai, T., Fukuchi, M., The life cycle of the ice- Tenaza, R., Behaviour and nesting success relative to nest location in
associated copepod Paralabidocera antarctica (Calanoida: Cope- Adélie Penguins (Pygoscelis adeliae), Condor, 73, 81–92, 1971.
poda) at Syowa Station, Antarctica, Antarc. Sci., 8, 257–266, 1996. Terazaki, M., Wada, M., Euphausiids collected from the Australian
Tanoue, E., Organic chemical composition of fecal pellet of the krill Sector of the Southern Ocean during BIOMASS SIBEX Cruise
Euphausia superba Dana, I: Lipid composition, Trans. Tokyo Univ. KH-83-4, Mem. Natl Inst. Polar Res., Spe. Issue, 40, 97–109, 1986.
Fish., 6, 43–57, 1985. Tererry, L.J., McMinn, A., Ryan, K.G., In situ oxygen microelectrode
Tanoue, E., Handa, N., Vertical transport of organic nutrients in the measurements of bottom ice algal production in McMurdo Sound,
northern Pacific as determined by sediment trap experiments, Part Antarctica, Polar Biol., 25, 72–80, 2002.
1: Fatty acid composition, J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan, 36, 231–245, Testa, J.W., Siniff, D.B., Population dynamics of Weddell seals
1980. (Leptonychotes weddelli) in McMurdo Sound, Ecol. Monogr., 57,
Tanoue, E., Hara, S., Ecological implications of fecal pellets produced 141–161, 1987.
by the Antarctic krill Euphausia superba in the Antarctic Ocean, Testa, J.W., Siniff, D.B., Ross, M.J., Winter, J.D., Dynamics of Weddell
Mar. Biol., 91, 359–369, 1986. seal/Antarctic cod interactions in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, in
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 601
Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs, Siegfried, W.R., Condy, Tikhomirov, E.A., Biology of the ice forms of seals in the Pacific section
P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin, Polar Biology 5, 1985, of the Antarctic, Rapports Proces-Verboux des Renunions Conceil
561. International Pour l’Exploration de la Mer, 169, 409–512, 1975.
Testa, J.W., Oehlert, G., Ainley, D.G., Bengtson, J.L., Siniff, D.B., Tilzer, M.M., Dubinsky, Z., Effects of temperature and day length on the
Laws, R.M., Rounsevelle, D., Temporal variability in Antarctic mass balance of Antarctic phytoplankton, Polar Biol., 7, 35–42,
marine ecosystems: Periodic fluctuations in the phocid seals, Can. 1987.
J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 48, 631–639, 1987. Tilzer, M.M., von Bodungen, B., Smetacek, V., Light-dependence of
Texido, N., Garrabau, J., Gutt, J., Arntz, W.E., Recovery in Antarctic photosynthesis in the Antarctic Ocean: Implications for regulatory
benthos after iceberg disturbance: Trends in benthic composition productivity, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs,
and growth forms, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 278, 1–16, 2004. Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer,
Theriot, F., Fryxell, G.A., Multivariate statistical analysis of net diatom Berlin, 1985, 61–69.
species distribution in the southwestern Atlantic and Indian Tilzer, M.M., Elbracher, M., Gieskes, W.W.C., Beeze, B., Light-
Oceans, Polar Biol., 5, 23–36, 1985. temperature interactions in the control of photosynthesis in
Thomas, G., The food and feeding ecology of the light-mantled sooty Antarctic phytoplankton, Polar Biol., 5, 105–111, 1986.
albatross at South Georgia, Emu, 82, 92–100, 1982. Timmermans, K.R., van Leeuwe, M.A., de Jong, J.T.M., McKay,
Thomas, D.N., Dieckmann, G.S., Antarctic sea ice: A habitat for extreme R.M.L., Nolting, R.P., Witte, H.J., van Ooyen, J., Swagerman,
places, Science, 295, 641–652, 2002. M.J.W., Kloosterhuis, H., de Baar, H.J.W., Iron stress in the Pacific
Thomas, D.M., Dieckman, G., Sea Ice: An Introduction to its Physics, region of the Southern Ocean: Evidence from enrichment bioas-
Chemistry, Biology and Geology, Blackwell Science, Oxford, says, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 166, 27–41, 1998.
2003. Timmermans, K.R., Garringa, L.T.A., de Baar, H.J.W., Vander Wagt,
Thomas, P.B., Green, K., Distribution of Euphausia crystallorophias B., Veldhuis, M.J.W., de Jong, J.T.M., Croot, P.L., Boye, M.,
within Prydz Bay and its importance to inshore the marine Growth rates of large and small Southern Ocean diatoms in relation
ecosystem, Polar Biol., 8, 327–331, 1988. to availability of iron in natural seawater, Limnol. Oceanogr., 46,
Thomas, P.B., Jiang, J., Epiphytic diatoms of the inshore marine areas 260–266, 2001.
near Davis Station, Hydrobiologia, 140, 193–198, 1986. Tizler, M.M., Gieskes, W.W.C., Heusel, R., Fenton, N., The impact of
Thomas, D.N., Baumann, M.E., Gleitz, M., Efficiency of carbon phytoplankton on the spectral water transparency in the Southern
assimilation and photoacclimation in Chaetoceros species from Ocean: Implications for primary production, Polar Biol., 14,
the Weddell Sea (Antarctica)—influence of temperature and 127–136, 1994.
irradiance, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 157, 195–209, 1992. Toharczyk, R., Annual cycle of chlorophyll a in Admiralty Bay 1981–
Thomas, D.N., Lara, R.J., Haas, C., Schnack-Schiel, S.B., Dieckmann, 1982 (King George Island, South Shetlands), Pol. Arch. Hydro-
G.S., Kattner, G., Nöthig, E.-M., Mizdalski, E., Biological soup biol., 33, 177–188, 1986.
within decaying summer sea ice in the Amundsen Sea, Antarctica, Tomlin, A.G., Cetacean Mammals of the USSR and Adjacent Countries,
in Antarctic Sea Ice: Biological Processes, Interactions and Isr. Prog. Sci. Transl., Jerusalem, 1967.
Variability, Antarctic Research Series 73, Lizotte, M., Arrigo, Torres, J.J., Somero, G.N., Metabolism, enzyme activities and cold
K., Eds., American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, 1998, adaptation in Antarctic mesopelagic fish, Mar. Biol., 98,
161–171. 169–180, 1988.
Thomas, D.N., Kattner, G., Engbrodt, R., Gannelli, V., Kennedy, H., Torres, J.J., Lancraft, T.M., Weigle, B.L., Hopkins, T.L., Distribution
Haas, C., Dieckmann, G.S., Dissolved organic matter in Antarctic and abundance of fishes and salps in relation to the marginal ice
sea ice, Ann. Glaciol., 33, 297–303, 2001. zone of the Scotia Sea, November and December 1983, Antarct.
Thomas, D.N., Kennedy, H., Kattner, G., Gerdes, D., Gough, C., J. U.S., 19(5), 117–119, 1984.
Dieckmann, G.S., Biogeochemistry of platelet ice: Influence on Torres, J.J., Aarset, A.V., Donnelly, J., Hopkins, T.L., Lancraft, T.M.,
particle flux under land-fast sea ice during summer at Drescher Ainley, D.G., Proximate composition and overwintering strategies
Inlet, Weddell Sea, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 24, 486–496, 2001. of Antarctic micronekton crustacea, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 113,
Thompson, R.B., Effects of human disturbance on an Adélie Penguin 221–232, 1994.
rookery and measures to control it, in Adaptations within Tortell, P.D., Evolutionary and ecological perspectives on carbon
Antarctic Ecosystems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smithsonian Institution, acquisition in phytoplankton, Limnol. Oceanogr., 45, 744–750,
Washington, DC, 1977, 1177–1180. 2000.
Thompson, P.M., Ollason, J.C., Lagged effects of ocean climate change Totten, A.K., Siphonophora of the Indian Ocean, together with
on fulmar population dynamics, Nature (Lond.), 413, 417–420, systematic and biological notes on related species from other
2001. areas, Discov. Rep., 27, 1–162, 1954.
Thorson, G., Reproductive and larval ecology of marine bottom Townsend, C.H., The distribution of certain whales as shown by logbook
invertebrates, Biol. Rev., 25, 1–45, 1950. records of American whale ships, Zoologica (New York), 19(1),
Throndsen, J., Motility in some marine nanoplankton flagellates, 1–50, 1935.
Norwegian J. Zool., 21, 193–200, 1973. Tranter, D.J., Interlinking of physical and biological processes in the
Thurston, M.H., The Crustacean Amphipoda of Signy Island, South Antarctic Ocean, Oceanogr. Mar. Biol.: Ann. Rev., 20, 11–35,
Orkney Islands, Br. Antarct. Surv. Sci. Rep., 71, 1972. 1982.
Tickell, W.L.N., Movements of the black-browed and grey-headed Tratham, P.N., Croxall, J.P., Murphy, E.J., Dynamics of Antarctic
albatrosses in the South Atlantic, Emu, 66, 357–367, 1967. penguin populations in relation to interannual polar variability in
Tickell, W.L.N., Albatrosses, Pica Press, East Sussex, 2000. sea ice distribution, Polar Biol., 16, 321–330, 1996.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
602 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Tréguer, P., Silica and the cycle of carbon in the sea, Geoscience, 334, Truesdale, R.S., Kellog, T.B., Ross sea diatoms: Modern
2002. assemblage distributions and their relationship to ecologic, oceano-
Tréguer, P., Jacques, G., Dynamics of nutrient and phytoplankton and graphic, and sedimentary conditions, Mar. Micropaleontol., 4,
fluxes of carbon, nitrogen and silica in the Antarctic Ocean, Polar 13–31, 1979.
Biol., 12, 149–162, 1992. Tucker, M.J., Burton, H.R., Seasonal and spatial variations in the
Tréguer, P., van Bennekom, A.J., The annual production of biogenic zooplankton community of an eastern Antarctic coastal location,
silica in the Antarctic Ocean, Mar. Chem., 35, 477–487, 1991. Polar Biol., 10, 571–579, 1990.
Treguer, P., Gueneley, S., Zeyons, C., The distribution of biogenic and Tupas, L.M., Koike, I., Simultaneous uptake and regeneration of
lithogenic silica and the composition of particulate matter in the ammonium by mixed assemblages of heterotrophic bacteria,
Scotia Sea and Drake Passage during autumn, 1987, Deep-Sea Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 70, 273–282, 1991.
Res., 37, 783–791, 1990. Tupas, L.M., Koike, I., Karl, D.M., Holm-Hansen, O., Nitrogen meta-
Trehen, P., Vernon, P., Peuplement dipterologie d’une ı̂le subantarctique bolism by heterotrophic bacterial assemblages in Antarctic coastal
la Possession (418 S, 518 E, Îles Crozet), Rev. Ecol. Biol. Sol., 18, waters, Polar Biol., 14, 195–204, 1994.
105–120, 1982. Turbott, E.G., Seals of the southern ocean, in Antarctica Today,
Tremblay, Y., Cherel, Y., Benthic and pelagic dives: A new foraging Simpson, F.A., Ed., Reed, Wellington, 1952, 195–215.
behaviour in rockhopper penguins, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 204, Turkiewicz, M., Gales, E., Kalinowski, H., Collagenolytic activity of the
257–267, 2000. serine proteinase from Euphausia superba Dana. 19th FEBS
Tremblay, J.E., Lucas, M.I., Kattner, G., Pollard, R., Strauss, V.H., Meeting Rome, Abstracts, MO214, 1989.
Bathmann, U., Bracher, A., Significance of the Polar Frontal Zone Turner, J.T., Sinking rates of fecal pellets from marine copepod Pontella
for large sized diatoms and new production during summer in the meadii, Mar. Biol., 40, 249–259, 1977.
Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean, Deep-Sea Res. II, 49, Turner, J., The El Niño-Southern Oscillation and Antarctica, Int.
3793–3811, 2002.
J. Climatol., 24, 1–31, 2004.
Trenerry, L.J., McMinn, A., Ryan, K.G., In situ oxygen electrode
Twelves, E.L., Blood volumes of two Antarctic fishes, Br. Antarct. Surv.
measurements of bottom-ice algal production in McMurdo
Bull., 31, 85–92, 1960.
Sound, Polar Biol., 25, 72–80, 2002.
Tyler, J.C., Erythrocyte counts and haemoglobin determinations for two
Treshnikov, A.F., Alekseyev, G.V., Sarukanyan, E.I., Smirnov, N.P.,
Antarctic Nototheniid fishes, Stanford Ichthyol. Bull., 7, 199–201,
Water circulation in the southern Ocean, Trudy Arktichskii
1960.
Naucho-issle-dovatel’skii Institut, 345, English translation:
UNEP. Regionally-Based Assessment of Persistent Toxic Substances:
Scripton Publishing Co., Washington, DC, 21–35 pp, 1978.
Antarctic Regional Report. (2002), United Nations Environment
Tressler, W.L., Ommundsen, A.M., Seasonal oceanographic studies in
Programme, Geneva, 2002.
McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. U.S. Navy Hydrographic Office
Urban-Rich, J., Dagg, M.J., Peterson, T., Copepod grazing on phyto-
Technical Report, 1–141, 1962.
plankton in the Pacific sector of the Antarctic Polar Front, Deep-
Trillmich, F., Feeding territories and breeding success of South Polar
Sea Res., 48, 4223–4246, 2001.
skuas, The Auk, 95, 23–33, 1978.
Uribe, E., Influence of the phytoplankton and primary production of the
Trillimich, F., Oho, K.A., Pinnipeds and El Niño: Responses
Antarctic waters in relationships with the distribution and
to environmental stress, in Ecological Studies, Ed., Springer,
behaviour of krill, Serie Cientı́fico del Instituto Antártico
Berlin/Heidelberg, 1983, 1–62.
Chileno, 28, 147–163, 1982.
Trimble, A.M., Harris, G.P., Phytoplankton population dynamics of a
small reservoir: Use of sediment traps to quantify the loss of Ushakov, P.V., Quelques particularites de al bionomie benthique de
diatoms and recruitment of summer bloom-forming blue-green l’Antarctique del’Es, Cash. Biol. Mar., 4, 81–89, 1963.
algae, J. Plankton Res., 6, 897–917, 1984. van Aarde, R.J., Pascel, M., Marking southern elephant seals on Isles
Trivelpiece, W.Z., Fraser, W.R., The breeding biology and distribution Kerguelen, Polar Rec., 20, 62–65, 1980.
of Adélie Penguins: Adaptations to environmental variability, van Andel, T.H., Moore, T.C., Jr., Cenozoic calcium carbonate distri-
Antarct. Res. Ser., 70, 273–286, 1996. bution and calcite compensation depth in the central equatorial
Trivelpiece, W.Z., Volkman, N.J., Feeding strategies of sympatric polar Pacific ocean, Geology, 2, 87–92, 1974.
(Catharacta maccormicki) and brown skuas (C. lönnbergi), Ibis, van Franeker, J., Top predators as indicators for ecosystem events in the
124, 50–54, 1980. confluence zone and marginal ice zone of the Weddell and Scotia
Trivelpiece, W.Z., Butler, R.G., Volkman, N.J., Feeding territories of Seas, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 12, 93–102, 1992.
brown skuas (Catharacta lönnbergi), The Auk, 97, 669–676, 1980. van Loon, H., Shea, D.J., The Southern Oscillation, Part VI: Anomalies
Trivelpiece, W.Z., Bengtson, J.L., Trivelpiece, S.G., Volkman, N.J., of sea-level pressure on the southern Hemisphere and on Pacific
Foraging behaviour of Gentoo and Chinstrap Penguins as sea surface temperature during the development of Warm Event,
determined by radiotelemetry techniques, The Auk, 103, 777–781, Monthly Weather Review, 115, 370–379, 1987.
1986. van Woert, M.L., Wintertime expansion and contraction of the Terra
Trivelpiece, W.Z., Ainley, D.G., Fraser, W.R., Trivelpiece, S.G., Skua Nova Bay polyna, in Oceanography of the Ross Sea, Spezie, G.,
survival, Nature (Lond.), 345, 211, 1990. Manzella, G.M.R., Eds., Springer, Milan, 1999, 145–164.
Trivelpiece, W.Z., Trivelpiece, S.G., Guepel, G.R., Kjelmyr, J., Vanhoeffen, E., Van der deutschen Südpolar expedition Fischereiver-
Volkman, N.J., Adélie and Chinstrap Penguins: Their potential suche, Petermans geographische Mitteilungen Erganzungschaft,
as monitors of Southern Ocean marine ecosystems, in Antarctic 47, 19–20, 1902.
Ecosystems: Ecological Change and Conservation, Kerry, K.R., Vanhove, S., Wittoeck, J., Desmet, G., van den Berghe, B., Herman,
Hempel, G., Eds., Springer, Berlin, 1990, 191–202. R.L., Bak, R.P.M., Nieuwland, G., Vosjan, J.H., Boldrin, A.,
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 603
Rabitti, S., Vincx, M., Deep-sea meiofauna communities in Vincent, W.F., Ray, S., Solar ultraviolet-B radiation and aquatic primary
Antarctica: Structural analysis and relation with the environment, production: Damage protection and recovery, Environ. Rev., 1,
Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 127, 65–76, 1995. 1–12, 1993.
Vanhove, S., Lee, H.J., Beghyn, M., van Gansgeke, D., Brockington, S., Vincent, W.F., Belzile, C., Biological UV exposure in polar oceans:
Vincx, M., The metazoan meiofauna in its biochemical environ- Arctic–Antarctic comparisons, in Antarctic Biology in a Global
ment: The case of an Antarctic coastal sediment, J. Mar. Biol. Context, Huskies, A.H.L., Gieskes, W.W.C., Rozema, J., Schorno,
Assoc. U.K., 78, 411–434, 1998. R.M.L., van der Vies, S.M., Wolff, W.J., Eds., Backhuys
Vanhove, S., Beghyn, M., van Gansbehe, D., Bullough, L.W., Vinex, M., Publishers, Leiden, The Netherlands, 2003, 176–181.
A seasonally varying biotope at Signy Island, Antarctica: Impli- Vinex, M., Seasonal fluctuations and production of nematode commu-
cations for meiofaunal structure, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 201, nities in the Belgian coastal zone of the North Sea, in
13–25, 2000. Verhandelingen van het Symposium ‘Invertebraten van Belgie’,
Vanucci, S., Bruni, V., Ultraviolet phytoplankton community structure 25–28 Nov., 1988, Koninkhjk Belgisch Institut voor Naturwe-
in the Ross Sea during the Austral Spring 1994, in Ross Sea tenschappen, Brussels, 1989, 25–26.
Ecology, Faranda, F.M., Guglielmo, L., Ianora, A., Eds., Springer, Vinogradov, M.E., Naumov, A.G., Quantitative distribution of plankton
Berlin, 1998, 181. in Antarctic waters of the Indian and Pacific oceans, Inf. Bull.
Vaque, D., Durate, C.M., Marrasse, C., Phytoplankton colonization by Soviet Antarc. Exped., 1, 110–112, 1958.
bacteria; encounter probability as a limiting factor, Polar Biol., 5, Virtue, P., Nichols, P.D., Hosie, G., Reproductive trade-off in male
241–247, 1989. Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba, Mar. Biol., 126, 521–527,
Vargo, G.A., Fanning, K., Heil, C., Bell, L., Growth rates and the salinity 1996.
response on an Antarctic ice microflora community, Polar Biol., 5, Vo, J., Macrozoobenthos und Gemeinschaftsanlagse des östlichen
241–247, 1986. Weddellmeeres (Antarktis), Berichte zur Polarforschung, 39,
Veit, R.R., Braun, B.M., Hydrographic fronts and marine bird distri-
123, 1988.
bution in the Antarctic and sub-Antarctic, Antarct. J. U.S., 19,
Voisin, J.-F., Notes on the behaviour of the killer whale, Orcinus orca
165–167, 1984.
(L.), Nytt Magasin Zool., 20, 93–96, 1972.
Veith, C., Lancelot, C., Obst, S., On processes determining the
Voisin, J.-F., On the behaviour of the killer whale, Orcinus orca (L.),
vertical stability of surface waters in the marginal ice zone of
Nytt Magasin Zool, 24, 69–71, 1976.
the northwestern Weddell Sea and their relationship with
Volkman, N.J., Trivelpiece, W.Z., Nest-site selection among Adélie,
phytoplankton bloom development, Polar Biol., 12, 237–243,
chinstrap and gentoo penguins in mixed species rookeries, Wilson
1992.
Bulletin, 93(2), 243–248, 1981.
Veit-Köhler, G., Meiofauna study in Potter Cove: Sediment situation and
Volkman, N.J., Presler, P., Trivelpiece, W., Diets of pygoscelid penguins
resource availability for small crustaceans (Copepoda and Pera-
at King George Island, Antarctica, Condor, 82, 373–378, 1980.
carida), Berichte zur Polarforschung, 299, 132–136, 1998.
Volkovinskii, V.V., Studies on primary production in the waters of the
Veldhuis, M.J.W., Admiraal, W., Transfer of photosynthetic products in
Southern Ocean, Abstracts of Papers Presented at the Second
gelatinous colonies of Phaeocystis pouchetii (Haptophyceae) and
International Oceanology Congress (Moscow) 1966, 386–387,
its effect on the measurement of excretion rate, Mar. Ecol. Prog.
1966.
Ser., 26, 301–304, 1985.
von Bennekom, J., Burma, A., Geoyens, L., Linder, L., Morvan, J.,
Verity, P.G., Grazing of phytotrophic nanoplankton by microzoo-
Nöthig, R., Panouse, M., Sorensson, F., Treguer, P., Uptake and
plankton in Narragansett Bay, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 29,
regeneration of nitrogen, silica and phosphorus, Berichte zur
105–115, 1986.
Vernet, M., Brody, E.A., Holm-Hansen, O., Mitchell, B.G., The response Polarforschung, 65, 56–67, 1989.
of Antarctic phytoplankton to ultraviolet radiation: Absorption, von Bodungen, B., Phytoplankton growth and krill grazing during spring
photosynthesis, and taxonomic composition, in Ultraviolet Radi- in the Bransfield Strait, Antarctica—Implications for sediment trap
ation in Antarctica: Measurements and Biological Effects, collection, Polar Biol., 6, 153–161, 1986.
Antarctic Research Series 62, Weiler, C.S., Penhale, P.A., Eds., von Bodungen, B., von Brockel, K., Smetacek, V., Zeitzschel, B.,
American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, 1994, 143–158. Growth and sedimentation of the phytoplankton spring bloom in
Vervoot, W., Copepods from Antarctic and sub-Antarctic plankton the Bornholm Sea (Baltic Sea), Kieler Meeresforschung, Sond-
samples, Reports of the B.A.N.Z. Antar. Res. Exped., 3, 1–160, heim, 5, 49–60, 1981.
1957. von Bodungen, B., Smetacek, V.S., Tilzer, M.M., Zietschel, B., Primary
Villafãne, V.E., Helbling, E.W., Holm-Hansen, O., Phytoplankton production and sedimentation during the spring in the Antarctic
around Elephant Island, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 13, 183, 1993. Peninsula region, Deep-Sea Res., 33, 177–194, 1986.
Villafãne, V.E., Helbling, E.W., Holm-Hansen, O., Spatial and temporal von Bodungen, B., Fischer, G., Nöthig, E.-M., Wefer, G., Sedimentation
variability of phytoplankton biomass and taxonomic composition of krill faeces during spring development of phytoplankton in the
around Elephant Island, Antarctica, during summers of 1990– Bransfield Strait, Antarctica, in Particle Flux in the Ocean, Vol. 62,
1993, Mar. Biol., 123, 677–686, 1995. Degens, E.T., Honjo, S., Izdar, E., Eds., SCOPE UNEP Sonderband,
Villafãne, V.E., Helbling, E.W., Holm-Hansen, O., Distribution of Mitteilungen aus dem Geologisch-Palaeontologischen Institut der
phytoplankton organic carbon in the vicinity of Elephant Island, Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, 243–257 pp, 1987.
Antarctica, during the summers of 1990–1993, Antarct. Res. Ser., von Bodungen, B., Nöthig, E.-M., Sui, Q., New production of phyto-
7, 70–77, 1996. plankton and sedimentation during summer 1985 in the South
Vincent, W.F. Microbial Ecosystems of Antarctica, Cambridge Eastern Weddell Sea, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 90B, 475–487,
University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1988. 1988.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
604 Biology of the Southern Ocean
von Brockel, K., The importance of nanoplankton within the pelagic Waghorn, E.J., Knox, G.A., Summer tide-crack zooplankton at White
Antarctic ecosystem, Kieler Meeresforschung Sonderheft, 5, Island, McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, N.Z. J. Mar. Freshwat. Res.,
61–67, 1981. 22, 557–563, 1988.
von Brockel, K., Primary production data from the south-eastern Wagle, J.W., Buto, T.A., Die sublittorale Faun der maritimen Antartkis:
Weddell Sea, Polar Biol., 4, 75, 1985. Erste Unterwassenbeobachtungen in der Admiralitätsbacht, Nature
Voous, K.H., Antarctic birds, in Biogeography and Ecology in Antarc- Museum, 120, 269–282, 1990.
tica, van Meighem, J., van Oye, P., Eds., Dr. W. Junk, The Hague, Wakatsuchi, M., Seasonal variations in water structure under the fast ice
1965, 659–689. near Syowa Station, Antarct. Rec., 74, 85–105, 1982.
Vorinina, N.M., Distribution of zooplankton biomass in the Southern Walls, N.W., Bacteriology of Antarctic region waters and sediments,
Ocean, Oceanology, 6, 834–836, 1960. Antarct. J. U.S., 2, 192–193, 1967.
Vorinina, N.M., The distribution of zooplankton in the Southern Ocean Walsh, J.J., Relative importance of habitat variables in predicting the
and its dependence on the circulation of water, Sarsia, 34, distribution of phytoplankton at the ecotone of the Antarctic
277–283, 1968. upwelling ecosystem, Ecol. Monogr., 41, 291–309, 1971.
Vorinina, N.M., Seasonal cycles of some common Antarctic copepod Ward, P., Atkinson, A., Murray, A.W.A., Wood, A.G., Williams, R.,
species, in Antarctic Ecology, Volume 1, Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Poulet, S.A., The summer zooplankton community at South
Academic Press, London/New York, 1970, 162–172. Georgia: Biomass, vertical migration and grazing, Polar Biol.,
Vorinina, N.M., Annual cycle of Antarctic plankton, in Fundamentals of 15(3), 195–208, 1995.
the Biological Productivity of the Ocean and its Exploitation, Wassman, P., Vernet, M., Mitchell, B.G., Rey, F., Mass sedimentation of
Beklemishev, V., Ed., Nauka, Moscow, 1971, 64–71. In Russian. Phaeocystis pouchetii in the Barents Sea during spring, Mar. Ecol.
Vorinina, N.M., Vertical structure of a pelagic community in the Prog. Ser., 66, 183–195, 1990.
Antarctic, Oceanology (Okeanologiya), 12, 415–420, 1972. Watanabe, K., Centric diatom communities found in Antarctic sea ice,
Vorinina, N.M., An attempt at a functional analysis of the distributional Antarc. Rec., 74, 119–126, 1982.
range of Euphausia superba, Mar. Biol., 24, 347, 1974. Watanabe, K., Sub-ice microalgal strands in the Antarctic coastal fast ice
Vorinina, N.M., Variability of ecosystems, in Advances in Ocean- near Syowa Station, Jap. J. Phycol., 36, 221–229, 1988.
ography, Charnock, H., Deacon, G.E.R., Eds., Plenum Press, Watanabe, K., Nakajima, Y., Vertical distribution of chlorophyll a along
New York, 1978, 221–243. 458 E in the southern ocean, 1981, Mem. Natl Inst. Polar Res., Spe.
Voronina, N.M., Memshutkin, V.V., Tseytlin, V.B., Production of an Issue, 23, 73–86, 1982.
abundant species of copepod, Calanus acutus, Oceanology (Okea- Watanabe, K., Satoh, H., Seasonal variations of ice algal standing crop
nologiya), 20, 137, 1980. near Syowa Station, East Antarctica, in 1983/84, Bull. Plankton
Voronina, N.M., Memshutkin, V.V., Tseytlin, V.B., Model investi- Soc. J., 34, 143–164, 1987.
gations of an annual cycle of the abundant species Rhincalanus Watanabe, K., Nakajima, Y., Naito, Y., Higashi-Onguru-tô engan de no
gigas and an estimate of its production in the Antarctica, hyôka-sensui chôsa hôkoku (SCUBA ice diving along the coast of
Oceanology (Okeanologiya), 20, 709–713, 1980. East Ongul Island, Antarctica), Nankyoku Shiryô (Antarct. Rec.),
Voronina, N.M., Memshutkin, V.V., Tseytlin, V.B., Secondary pro- 75, 75–92, 1982. In Japanese with English abstract.
duction in the pelagic layer of the Antarctic, Oceanology Watanabe, K., Satoh, H., Hoshiai, T., Seasonal variation in ice algal
(Okeanologiya), 20, 714–715, 1981. assemblages in the fast ice near Syowa Station in 1983/84, in
Vosjan, J.H., Olaniczuk-Neyman, K.M., Influence of temperature on Antarctic Ecosystems: Ecological Change and Conservation,
respiration, ETS activity of micro-organisms from Admiralty Bay, Kerry, K.R., Hempel, G., Eds., Springer, Heidelberg, 1990,
King George Island, Antarctica, Neth. J. Sea Res., 28, 221–225, 136–142.
1991. Watanuki, Y., Kato, A., Naito, Y., Robertson, G., Robison, S., Diving
Voss, G.L., Cephalopod resources of the world, F.A.O. Fisheries and foraging behaviour of Adélie Penguins in areas with and
Circular, 149, 1973. without fast sea-ice, Polar Biol., 17, 296–304, 1997.
Voytek, M.A., Addressing the biological effects of decreased ozone on Waters, T.F., The turnover ratio in production ecology of freshwater
the Antarctic environment, Ambio, 19, 52–61, 1990. invertebrates, Am. Nat., 103, 173–185, 1969.
Vranken, G., Heip, C., The productivity of marine nematodes, Ophelia, Watkins, J.L., Variations in the size of Antarctic krill, Euphausia
26, 429–442, 1986. superba Dana, in small swarms, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 31,
Wada, E., Hatton, A., Nitrogen in the Sea: Abundance and Processes, 67–73, 1986.
CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1990. Watkins, J.L., A composite recruitment index to describe interannual
Wada, E., Tarazaki, M., Kabaya, Y., Nemoto, T., 15N and 13C abundance changes in the population structure of Antarctic krill at South
in the Antarctic Ocean, with emphasis on the biogeochemical Georgia, CCAMLR Science, 6, 71–84, 1999.
structure of the food web, Deep-Sea Res., 34, 829–841, 1987. Watkins, J.L., Murray, A.W.A., Layers of Antarctic krill, Euphausia
Wadhams, P., A mechanism for the formation of ice edge bands, superba: Are they just long krill swarms?, Mar. Biol., 131,
J. Geophys. Res., 88, 2813–2818, 1983. 237–247, 1998.
Wadhams, P., Ice in the Oceans, Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, Watkins, J.L., Morris, D.J., Rickets, C., Priddle, J., Differences between
London, 1992. swarms of Antarctic krill and some implications for sampling krill
Wadhams, P., Squire, V., An ice-water vortex at the edge of the East populations, Mar. Biol., 93, 137–146, 1986.
Greenland Current, J. Geophys. Res., 88, 2770–2780, 1983. Watkins, J.L., Morris, D.J., Ricketts, C., Priddle, J., Differences between
Waghorn, E.J., Two new species of copepoda from White Island, swarms of Antarctic krill and some implications for sampling krill
Antarctica, N.Z. J. Mar. Freshwat. Res., 13, 459–470, 1979. populations, Mar. Biol., 93, 137–146, 1986.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 605
Watkins, J.L., Morris, D.J., Ricketts, C., Murray, A.W.A., Sampling Wefer, G., Fischer, G., Futterer, D.K., Gersonde, R., Honjo, S.,
biological characteristics of krill: Effects of heterogeneous nature Osterman, D., Particle sedimentation and productivity in Antarctic
of krill swarms, Mar. Biol., 107, 409–415, 1990. waters of the Atlantic sector, in Geological History of Polar
Watkins, J.L., Buchholz, F., Priddle, J., Morris, D.J., Ricketts, C., Oceans: Arctic versus Antarctic, Bleil, U., Thiede, J., Eds.,
Variation in reproductive status of Antarctic krill swarms: Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, 1990, 363–379.
Evidence for a size-related sorting mechanism?, Mar. Ecol. Weimerskirch, H., La stratégie de reproduction de l’albatros fuligineux à
Prog. Ser., 82, 163–174, 1992. dos sombre, Comité National Français des Recherches Antarc-
Watson, G.E., Angle, J.P., Harper, P.C., Birds of the Antarctic and tique, 51, 437–447, 1982.
Subantarctic, Antarct. Res. Ser., 32, 1–12, 1971. Weimerskirch, H., Wilson, R.P., When do wandering albatrosses
Watson, R.T., Zinyowera, M.C., Moss, R.H., IPCC Special Report on the (Diomedea exulans) forage?, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser., 86, 297–300,
Regional Impacts of Climate Change: An assessment of Vulner- 1992.
ability, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Geneva, Weimerskirch, H., Mougey, T., Hindermeyer, X., Foraging and provi-
1997. sioning strategies of black-browed albatrosses in relation to
Watson, R.T., Zinyowera, M.C., Moss, R.H., IPPC Special Report on the requirements of chick: Natural variation and experimental study,
Regional Impacts of Climate Change: An Assessment of Vulner- Behav. Ecol., 8(6), 635–643, 1997.
ability, Intergovernment Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge Weimerskirch, H., Catard, A., Prince, P.A., Cherel, Y., Croxall, J.P.,
University Press, Cambridge, 2001. Foraging white-chinned petrels, Procellaria aequinoctialis, at risk
Waugh, S.M., Weimerskirch, H., Cherel, Y., Shankar, U., Prince, P.A., from the tropics to Antarctica, Biol. Conserv., 87, 273–275, 1999.
Sagar, P.M., Exploitation of the marine environment by two Weimerskirch, H., Inchausti, P., Guinet, C., Barbraud, C., Trends in bird
sympatric albatrosses in the Pacific Southern Ocean, Mar. Ecol. and seal populations as indicators of a system shift in the Southern
Prog. Ser., 177, 243–254, 1999. Ocean, Antarct. Sci., 15, 249–256, 2003.
Weber, L.H., Spatial variability of phytoplankton in relation to the
Weimerskirch, H., Jenouvrier, S., Barbraud, C., Climate and population
distributional patterns of krill (Euphausia superba), Ph.D. Thesis,
dynamics of Southern Ocean seabirds, Abstracts SCAR Science
Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, 1984.
Conference, Bremen, 2004, 2004, 130.
Weber, L.H., El-Sayed, S.Z., Spatial variability of phytoplankton and the
Weincke, C., Notes on the development of some benthic marine
distributions and abundance of krill in the Indian Sector of the
macroalgae of King George Island, Antarctica, Serie Cientı́fico
Southern Ocean, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs,
del Instituto Antártico Chileno, 37, 23–47, 1988.
Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin,
Weincke, C., Seasonality of brown macroalgae from Antarctica—a long-
1985, 284–293.
term culture study under fluctuating Antarctic daylengths, Polar
Weber, L.H., El-Sayed, S.Z., Size-fractionated phytoplankton standing
Biol., 10, 589–600, 1990.
crop and primary productivity in the west Indian sector of the
Weincke, C., Recent advances in the investigation of Antarctic macro-
Southern Ocean (R.S.S.A. Agulhas Cruise; February–March 1985),
algae, Polar Biol., 16, 231–240, 1996.
Technical Report, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX,
Weller, C.S., Penhale, P.A., Ultraviolet radiation and biological research
1986a.
in Antarctica, Antarct. Res. Ser., 62, 1–311, 1994.
Weber, L.H., El-Sayed, S.Z., Phytoplankton data from the November–
Wells, R.M.G., Respiration of Antarctic fishes from McMurdo Sound,
December 1984 cruise of the Polarstern to the Bransfield Strait/
Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 88, 417–424, 1987.
Elephant Island region of the Southern Ocean, Technical Report,
Wells, R.M.G., Ashby, M.D., Duncan, S.J., McDonald, J.A., Compara-
Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, 1986b.
tive study of the erythrocytes and haemoglobins in nototheniid
Weber, L.H., El-Sayed, S.Z., Contribution of net-, nano-, and pico-
plankton to the phytoplankton standing crop and primary fishes from Antarctica, Journal of Fish Biology, 17, 517–527,
productivity of the Southern Ocean, J. Plankton Res., 9, 1980.
973–994, 1987. Wells, R.M.G., MacDonald, J.A., Di Prisco, G., Thin-blooded Antarctic
Weber, L.H., El-Sayed, S.Z., Hampton, I., Variance spectra of phyto- fishes: A rheological comparison of the haemoglobin-free ice
plankton, krill and water temperature in the Atlantic Ocean south fishes Chionodraco kathbleenae and Cryodraco antarcticus with
of Africa, Deep-Sea Res., 33, 1327–1343, 1986. the red-blooded nototheniid Pagothenia bernacchii, J. Fish Biol.,
Weeks, W.F., Ackley, S.F., The growth, structure, and properties of sea 36, 595–609, 1990.
ice. CCREL Monograph 82-1, United States Army Cold Regions Wetzel, R.G., Detrital dissolved and particulate organic carbon functions
Research and Engineering Laboratory, Hanover, NH, 1982. in aquatic systems, Bull. Mar. Sci., 35, 503–509, 1984.
Weeks, W.F., Lee, O.S., The salinity distribution in young sea ice, Weyman, G., Wiencke, C., Seasonal photosynthetic performance of the
Arctic., 15, 92–109, 1982. endemic Antarctic alga Palmaria deicpiens (Reinsch) Ricker,
Wefer, G., Fischer, G., Annual primary production and export flux in the Polar Biol., 16, 357–361, 1996.
Southern Ocean sediment trap data, Mar. Chem., 35, 597–614, Whitaker, T.M., Sea ice habitats of Signy Island (South Orkneys) and
1991. their primary productivity, in Adaptations within Antarctic Ecosys-
Wefer, G., Suess, E., Balzer, W., Liebezeit, G., Müller, P.J., Ungerer, tems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC,
C.A., Zenk, W., Fluxes of biogenic components from sediment trap 1977a, 75–87.
deployment in circumpolar waters of the Drake Passage, Nature Whitaker, T.M., Plant production in inshore waters of Signy Island,
(Lond.), 299(5879), 145–147, 1982. Antarctica, Ph.D. thesis, University of London, 1977b.
Wefer, G., Fischer, G., Fuetterer, D., Gersonde, R., Seasonal particle flux Whitaker, T.M., Primary production of phytoplankton off Signy Island,
in the Bransfield Strait, Antarctica, Deep-Sea Res., 35, 891–898, South Orkneys, the Antarctic, Proc. Rl. Soc. Lond., B214,
1988. 169–189, 1982.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
606 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Whitaker, T.M., Richardson, M.G., Morphology and chemical compo- Wiencke, C., Gómez, I., Pakker, H., Flores-Moya, A., Altamirano, M.,
sition of a natural population of an ice-associated diatom, Navicula Hanelt, D., Bischof, K., Figueroa, F.L., Impacts of UV radiation on
glacei, J. Phycol., 16, 256–263, 1980. viability, photosynthetic characteristics and DNA of brown algal
White, M.G., Oxygen consumption and nitrogen excretion by the giant zoospores: Implications for depth zonation, Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser.,
Antarctic isopod Glyptonotus antarcticus Eights in relation to cold- 197, 217–229, 2000.
adapted metabolism in marine polar poikilotherms, Proceedings of Wigley, R.L., MacIntyre, A.D., Some quantitative comparisons of
the 9th European Marine Biology Symposium, 707–724, 1975. offshore meiobenthos and macrobenthos south of Martha’s Vine-
White, M.G., Ecological adaptations by Antarctic poikilotherms to the yard, Limnol. Oceanogr., 9, 485–493, 1964.
polar marine environment, in Adaptations within Antarctic Ecosys- Williams, P.J.LeB., in Biological and chemical aspects of dissolved
tems, Llano, G.A., Ed., Smithsonian Institution, Washington, DC, organic compounds in sea water, Riley, J.P., Shirrow, G., Eds. 2nd
1977, 197–208. edition Chemical Oceanography, Vol. 2, Academic Press, London,
White, M.G., Marine benthos, in Antarctic Ecology, Vol 2, Laws, R.M., 1975, 301–363.
Ed., Academic Press, London, 1984, 421–461. Williams, P.J.LeB., Incorporation of microheterotrophic processes into
White, M.G., Conroy, J.W.H., Aspects of competition between pygos- classical paradigm of the plankton food web, Kieler Meeres-
celid penguins at Signey Island, South Orkney Islands, Ibis, 117, forschung Sonderheft, 5, 1–28, 1981.
371–373, 1975. Williams, R., The inshore fishes of Heard and Macquarie Islands,
White, M.G., Robins, M.W., Biomass estimates from Borge Bay, South Southern Indian Ocean, J. Fish Biol., 23, 283–292, 1983.
Orkney Islands, Bull. Br. Antarct. Surv., 3, 45–56, 1972. Williams, A.J., The status and conservation of sea birds on some islands
White, M.G., North, A.W., Twelves, E.L., Jones, S., Early development in the African sector of the Southern Ocean, in The Status and
of Notothenia neglecta from the Scotia Sea, Antarctica, Cybium, 6, Conservation of the World’s Seabirds, ICBP Technical Publication
43–51, 1982. No. 2, Croxall, J.P., Evans, P.G.H., Schreiber, R.W., Eds.,
White, D.C., Smith, G.A., Stanton, G.R., Biomass community structure, International Council for Bird Preservation, Cambridge, UK,
and metabolic activity of the microbiota in benthic marine 627–636 pp, 1984.
Williams, R., Potential impact of a krill fishery upon pelagic fish in the
sediments and sponge spicule mats, Antarc. J. US, 19, 125–156,
Prydz Bay area of Antarctica, Polar Biol., 5, 1–4, 1985a.
1984.
Williams, R., Trophic relationships between pelagic fish and euphausiids
White, D.C., Smith, G.A., Nichols, P.D., Stanton, G.R., Palmisano, A.C.,
in Antarctic waters, in Antarctic Nutrient Cycles and Food Webs,
Lipid composition and microbial activity of selected recent
Siegfried, W.R., Condy, P.R., Laws, R.M., Eds., Springer, Berlin,
Antarctic benthic marine sediments and organisms: A mechanism
1985b, 452–459.
for monitoring and comparing microbial populations, Antarct.
Williams, A.J., Siegfried, W.R., Foraging ranges of krill-eating
J. U.S., 19, 130–132, 1985.
penguins, Polar Rec., 20, 159–162, 1980.
White, D.C., Smith, G.A., Guckert, T.B., Nichols, P.D., Nearshore
Williams, P.J.leB., Berman, T., Holm-Hansen, O., Amino acid uptake
benthic marine sediments, in Antarctic Microbiology, Friedman,
and respiration by marine heterotrophs, Mar. Biol., 35, 41–47,
E.I., Ed., Wiley-Liss, New York, 1993, 235–240.
1976.
Whitehead, M.D., Johnstone, G.W., Burton, H.R., Annual fluctuations in
Williams, A.J., Siegfried, W.R., Berger, A.E., Berruti, A., The Prince
productivity and breeding success of Adélie Penguins and
Edward Islands: A sanctuary for seabirds in the Southern Ocean,
fulmarine petrels in Prydz Bay, East Antarctica, in Antarctic
Biological Conservation, 15, 59–71, 1979.
Ecosystems: Ecological Change and Conservation, Kerry, K.R.,
Williams, R., Kirkwood, J.M., O’Sullivan, D., FIBEX cruise
Hempel, G., Eds., Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 1990, 214–223.
zooplankton data, Aust. Natl Antarc. Res. Exped. Notes, 7,
Whitehouse, M.J., Veit, R.R., Distribution and abundance of seabirds
1–163, 1983.
and fur seals near the Antarctic Peninsula during the austral winter, Williams, R., Kirkwood, J.M., O’Sullivan, D., AbdEX 1 cruise
1986, Polar Biol., 14, 325–330, 1994. zooplankton data, Aust. Natl Antarc. Res. Exped. Notes, 31, 1–9,
Whitehouse, M.J., Priddle, J.P., Symon, C., Seasonal and annual changes 1986.
in seawater, temperature, salinity, nutrient and chlorophyll a Williamson, G.R., Minke whales off Brazil, Sci. Rep. Whales Res. Inst.
distribution around South Georgia, CCAMLR Science, 6, 71–79, Tokyo, 27, 37–59, 1975.
1996. Wilson, E.A., Stenorhincus leptonyx, the sea leopard, National Antarctic
Wiebe, W.J., Pomeroy, L.R., Microorganisms and their association with Expedition, 1901–1904, Natural History and Zoology, 2, 26–30,
aggregates and detritus in the sea: A microscopic study, Memories 1907.
de l’Institut Italiano di Idriobiologia, 24(Suppl.), 325–352, 1972. Wilson, G.J., Distribution and abundance of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic
Wiencke, C., Stolpe, U., Lehmann, H., Morphogenesis of the brown alga penguins: a synthesis of current knowledge, BIOMASS Sci. Ser. 4,
Desmarestia antarctica cultivated under seasonally fluctuating 1981.
daylengths, Serie Cientı́fico del Instituto Antártico Chileno, 41, Wilson, K.J., Fluctuations in populations of Adélie Penguins at Cape
65–78, 1991. Bird, Antarctica, Polar Rec., 26, 305–308, 1990.
Wiencke, C., Rahmel, J., Karsten, U., Weykam, G., Kirst, G.O., Wilson, R.P., Preliminary assessment of depth utilization by Adélie and
Photosynthesis of marine macroalgae from Antarctica: Light and Gentoo Penguins at Esperanza, Antarctica. Cormorant 17, 1–8, 19.
temperature requirements, Botanica Acta, 106, 78–87, 1993. Wilson, E.O., Bossert, W.H. A Primer of Population Biology, Sinauer
Wiencke, C., Bartsch, I., Bishoff, B., Peters, A.F., Breeman, A.M., Associates, Sunderland, MA, 1971.
Temperature requirements and biogeography of Antarctic, Arctic Wilson, W.H., Mann, N.H., Lysogenic and lyric viral production in
and amphiequatorial seaweeds, Botanica Marina, 37, 247–259, marine microbial communities, Aquat. Microbial Ecol., 13,
1994. 95–103, 1997.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
References 607
Wilson, D.L., Smith, W.O., Jr., Nelson, D.M., Phytoplankton bloom Woehler, E.J., Cooper, J., Croxall, J.P., Fraser, W.R., Kooyman, G.L.,
dynamics of the western Ross Sea ice edge, I: Primary productivity Miller, G.D., Nel, D.C., Patterson, D.L., Peter, H.-U., Ribic, C.A.,
and species-specific production, Deep-Sea Res., 33, 1375–1387, Salwicka, K., Trivelpiece, W.Z., Weimerskirch, H., A statistical
1986. assessment of the status and trends of Antarctic and subantarctic
Wilson, K.J., Taylor, R.H., Barton, K.H., The impact of man on Adélie seabirds, SCAR, NSF, CCAMLR 2001.
Penguins at Cape Hallett, Antarctica, in Antarctic Ecosystems: Wohlschlag, D.E., Respiratory metabolism and ecological charac-
Ecological Change and Conservation, Kerry, K.R., Hempel, G., teristics of some fishes in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica, Antarct.
Eds., Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 1990, 183–190. Res. Ser., 1, 11–62, 1964.
Wilson, R.P., Culik, B.M., Darnfield, R., Adelung, D., People in Wohrmann, A.P.A., Freezing resistance in Antarctic fish, in Antarctic
Antarctica: How much do Adélie Penguins (Pygoscelis adeliae) Communities: Species, Structures and Survival, Valencia, J.,
care?, Polar Biol., 11, 363–470, 1991. Walton, D.W.H., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge,
Wilson, R.P., Pútz, K., Grémillet, D., Culik, B.M., Kierspel, M., UK, 1997, 209–211.
Regel, M., Bost, J., Lage, C.A., Cooper, J., Reliability of Wolnomiejski, N., Chlapowski, K., Porebski, J., Gorbacik-Wesolowka,
stomach temperature changes in determining feeding charac- A., Obserwacje nad ekologia antarktyczrego kryala (Euphausia
teristics of seabirds, J. Exp. Biol., 198, 1115–1135, 1995. superba Dana), Studi i Materialy MIR, Gdynia, A23, 1978. In
Wilson, R.P., Ainley, D.G., Nur, N. et al., Adélie Penguin population Polish.
changes in the Pacific sector of Antarctica: Relation to sea-ice Wommack, K.E., Colwell, R.R., Viroplankton: Viruses in aquatic
extent and the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, Mar. Ecol. Prog. ecosystems, Microbiology and Molecular Biology Review, 64,
Ser., 213, 301–318, 2001. 69–114, 2000.
Witek, Z., Koronkeiwicz, A., Soszka, G.J., Certain aspects of the early Woodley, J.D., Chornesky, E.A., Clifford, P.A., Jackson, J.B.C.,
life history of krill, Euphausia superba Dana (Crustacea), Pol. Kaufman, L.S., Knowlton, N., Lang, J.C., Pearson, M.P., Porter,
Polar Res., 1, 97–115, 1980. J.W., Rooney, M.C., Rylaarsdam, K.W., Tunnicliffe, V.J., Wahle,
Witek, Z., Grelowski, A., Wolnomiejski, N., Studies in aggregations of C.M., Wulff, J.L., Curtis, A.S.G., Dallmeyer, M.D., Jupp, B.P.,
krill (Euphausia superba), Meeresforschung, 28, 228–243, 1981. Koehl, M.A.R., Neigel, J., Sides, E.M., Hurricane Allen’s impact
Witek, Z., Pastuzak, M., Grelowski, A., Net-phytoplankton abundance in on Jamaican coral reefs, Science, 214, 749–755, 1991.
western Antarctic and its relationship to environmental conditions, Wormuth, J.H., Interannual variability in Antarctic zooplankton popu-
Meeresforschung, 29, 166–180, 1982a. lations round the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula (abstract),
Witek, Z., Grelowski, A., Kalinowsky, J., Formation of Antarctic krill Intergovernmental Oceanographical Committee Reports, 50,
concentrations in relation to hydrodynamic processes and social 10–19, 1987.
behaviour, ICES CM 1982/L, 59, 16–22, 1982b. Worrest, R.C., Wolniaowski, K.U., Scott, J.D., Brooker, D.L., Thomson,
Witek, Z., Kittel, W., Czkieta, H., Zmijewoska, M.I., Presler, E., B.E., van Dyke, H., Sensitivity of marine phytoplankton to UV-B
Macrozooplankton in the Southern Drake Passage and the Brans- radiation: Impact upon a model ecosystem, Photochem. Photobiol.,
field Strait during BIOMASS-SIBEX (December 1983–January 33, 223–227, 1981.
1984), Pol. Polar Res., 6, 95–115, 1985. Wright, R.T., Coffin, R.B., Measuring microzooplankton grazing on
Witek, Z., Kalinowski, J., Grelowski, A., Formation of Antarctic krill planktonic marine bacteria by its impact on bacterial production,
concentrations in relation to hydrodynamic processes and social Microbial Ecol., 10, 137–149, 1984.
behaviour, in Antarctic Ocean and Resources Variability, Wyanski, D.M., Targett, T.E., Feeding biology of fishes in the endemic
Sahrhage, D., Ed., Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, 1988, 237–244. Antarctic Harpagiferidae, Copeia, 3, 686–693, 1981.
Woehler, E.J., The Distribution and Abundance of Antarctic and Xavier, J.C., Croxall, J.P., Tratham, P.N., Rodhouse, G.R., Inter-annual
Subantarctic Penguins, Scientific Committee for Antarctic variability in the cephalopod component of the diet of wandering
Research, Cambridge, UK, 1993. albatross, Diomedea exulans, breeding at Bird Island, South
Woehler, E.J., Concurrent decreases in five species of Southern Ocean Georgia, Mar. Biol., 142, 611, 2003.
seabirds in Prydz Bay, Polar Biol., 16, 379–382, 1995. Xiuren, N., Zilin, L., Genhai, Z., Junxian, S., Size-fractionated biomass
Woehler, E.J., Seabird abundance, biomass and energy consumption and productivity of phytoplankton and particulate organic carbon
within Prydz Bay, Antarctica, 1980/81–1992/93, Polar Biol., 17, in the Southern Ocean, Polar Biol., 16, 1–11, 1996.
371–383, 1997. Yamada, S., Kawamura, A., Some characteristics of the zooplankton
Woehler, E.J., Bergstrom, D., The impacts of climate change on Heard distribution in the Prydz Bay region of the Indian sector of the
Island during the 20th century, Abstracts of the SCAR Science Antarctic Ocean in the summer of 1983/84, Mem. Natl. Inst Polar
Conference, Bremen, 95, 2004. Res., 44, 86–95, 1986.
Woehler, E.J., Green, K., Consumption of marine resources by seabirds Yamaguchi, Y., Shibata, Y., Standing stock and distribution of phyto-
and seals at Heard Island and the McDonald Islands, Polar Biol., plankton chlorophyll in the Southern Ocean south of Australia,
12, 659–665, 1992. Trans. Tokyo Univ. Fish., 5, 111–128, 1982.
Woehler, E.J., Perry, R.L., Creet, S.M., Burton, H.R., Impacts of human Yamanaka, I., Interaction among krill, whales and other mammals in the
visitors on breeding success and long-term population trends in Antarctic ecosystem, Mem. Natl Inst. Polar Res., Spe. Issue, 27,
Adélie Penguins at Casey, Antarctica, Polar Biol., 14, 269–274, 220–232, 1983.
1994. Yeates, G.W., Studies on the Adélie Penguin at Cape Royds, 1964–65
Woehler, E.J., Slip, D.J., Robertson, L.M., Fullabar, P.J., Burton, H.R., and 1965–66, N.Z. J. Mar. Freshwat. Res., 2, 472–496, 1968.
The distribution, abundance and status of Adélie Penguins (Pygos- Yeates, G.W., Microclimate, climate and breeding success in Antarctic
celis adeliae) in the Windmill Islands, Wilkes Land, Antarctica, penguins, in The Biology of Penguins, Stonehouse, B., Ed.,
Mar. Ornithol., 19, 1–18, 1997. MacMillan, London, 1975, 397–409.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:50—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
608 Biology of the Southern Ocean
Young, E.C., The breeding behaviour of the South Polar skua, Cathar- Zinova, A.D., Composition and character of the algal flora near the
acta maccormicki, Ibis, 105, 205–232, 1963. shores of the Antarctic Continent in the vicinity of Kerguelen
Young, E.C., Feeding habits of the South Polar skua, Catharacta and Macquarie Islands, Inf. Bull. Soviet Antarc. Exped., 3, 47–49,
maccormicki, Ibis, 105, 301–318, 1963. 1958.
Yukov, V.I., The Antarctic Toothfish, Nauka, Moscow, 1982. Zmijewska, M.I., Copepoda in the southern part of the Drake Passage
Zacher, K., Wulff, A., Hanelt, D., Wiencke, C., Campana, G., Quartino, and in Bransfield Strait during early summer 1983–1984
L., Impact of UV radiation on succession of benthic primary (BIOMASS-SIBEX, December–January), Pol. Polar Res., 6,
producers in Antarctica, Information Leaflet, Alfred 79–83, 1985.
Wegner Institute for Polar and Marine Research, Bremerhaven, Zmijewska, M.I., Yen, J., Seasonal and diel changes in the abundance
and vertical distribution of Antarctic copepod species Calanoides
2005.
acutus, Calanus propinquus, Rhincalanus gigas, Metridia gerla-
Zaneveld, J.S., The occurrence of benthic marine algae under shore-fast
chei and Euchaeta antarctica (Calanoida) in Croker Passage
ice in the western Ross Sea, Antarctica, Proceedings of the 5th
(Antarctic Peninsula), Oceanology, 35, 73–100, 1993.
International Seaweed Symposium, Halifax, 1965, Pergamon
Zumberge, J.H., Swithinbank, C., The dynamics of ice shelves, Antarc.
Press, London, 217–231, 1966a.
Res., Geophys. Monogr., 7, 197–218, 1962.
Zaneveld, J.S., Vertical zonation of Antarctic and sub-Antarctic benthic
Zurr, R., The age and growth of Trematomus bernacchi and Trematomus
marine algae, Antarct. J. U.S., 1, 211–213, 1966.
centronotus at White Island, Antarctica, B.Sc. (Hons) thesis in
Zaneveld, J.S., Benthic marine algae, Ross Island, Antarctic Map Folio Zoology, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, 1977.
Series, Vol. 10, American Geographical Society, Washington, DC, Zvreva, Zh. A., Ed., Seasonal changes of Antarctic plankton in the
9–10 pp, 1968. Molodezhnaya and Mirny region. Geographical and seasonal
Zemsky, V.A., Whales of the Antarctic, Karlingrad, 1962. In Russian. variations of marine plankton, Explor. Mar. Fauna 12, 248–262,
Zenkovitch, B.A., Whales and plankton, in Food and Feeding Behaviour 1975.
of Whales, Asenev, V.A., Zenkovich, B.A., Chalskii, K.K., Eds., Zwally, H.T., Comiso, J.C., Parkinson, C.L., Campbell, W.J., Carsey,
Izdatel’stro Nauka, Moscow, 1969, 150–152. In Russian. F.D., Gleorsen, P., Antarctic sea ice, 1973–1976: Satellite passive-
Zenkovitch, B.A., Whales and plankton in Antarctic waters, in Antarctic microwave observations. NASA Special Publication SP 459,
Ecology, Volume 1, Holdgate, M.W., Ed., Academic Press, 1983a.
London, 1970, 183–185. Zwally, H.J., Parkinson, C.L., Comiso, J.C., Variability of Antarctic sea
Zielinski, K., Bottom macrobenthic of the Admiralty bay (King George ice and changes in carbon dioxide, Science, 220, 1005–1012,
Island, South Shetland Islands, Antarctica), Pol. Polar Res., 11, 1983b.
95–131, 1990. Zwally, H.T., Comiso, K., Gordon, A.L., Antarctic offshore leads and
Zink, M., Observations of seabirds during a cruise from Ross Island to polynas and oceanographic effects, Antarc. Res. Ser., 43, 203–226,
Anvers Island, Antarctica, Wilson Bulletin, 93, 1–20, 1977. 1985.
3394—CHAPTER —26/10/2006—13:51—GOVIND—XML MODEL C – pp. 533–608
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Antarctic Marine BiologyDocumento622 pagineAntarctic Marine Biologysyamsul hidayat100% (1)
- Maps of The World North AmericaDocumento1 paginaMaps of The World North AmericaΔημητριος ΣταθηςNessuna valutazione finora
- General - Australia AustraliaDocumento116 pagineGeneral - Australia AustraliaВаня СемчёнокNessuna valutazione finora
- Au 01 PlanDocumento123 pagineAu 01 Planwaleed yehiaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Penguin Paradise and Exceptional Wetland AreaDocumento8 pagineA Penguin Paradise and Exceptional Wetland AreaSreeambujavalliVaraaha Charan Tejj SrinivasNessuna valutazione finora
- Discover Sea Lion Island's Diverse WildlifeDocumento8 pagineDiscover Sea Lion Island's Diverse WildlifeSreeambujavalliVaraaha Charan Tejj SrinivasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ohio State Parks BrochureDocumento2 pagineOhio State Parks Brochurechen4567Nessuna valutazione finora
- Counting The Continents - Ellen Mitten - 2009 - Rourke Educational Media - 9781606945384 - Anna's ArchiveDocumento28 pagineCounting The Continents - Ellen Mitten - 2009 - Rourke Educational Media - 9781606945384 - Anna's ArchiveCecilia DaoNessuna valutazione finora
- FK 01 PlanDocumento2 pagineFK 01 Planwaleed yehiaNessuna valutazione finora
- 605 Antarc DWDocumento1 pagina605 Antarc DWReyNessuna valutazione finora
- Noaa 17743 DS1Documento367 pagineNoaa 17743 DS1angel_blitz121022Nessuna valutazione finora
- Canada Carte Des Parcs NationauxDocumento1 paginaCanada Carte Des Parcs NationauxPasymal Pas Si MalNessuna valutazione finora
- 614 Canada DWDocumento1 pagina614 Canada DWReyNessuna valutazione finora
- Canada MapDocumento3 pagineCanada MapEdgardo LamadridNessuna valutazione finora
- Asia Political MapDocumento2 pagineAsia Political Mapabuobyda3242Nessuna valutazione finora
- Papua New Guinea Future ClimateDocumento8 paginePapua New Guinea Future ClimateRon BurgundyNessuna valutazione finora
- ILLINOIS - Counties: WinnebagoDocumento1 paginaILLINOIS - Counties: WinnebagoKelly ClaytonNessuna valutazione finora
- Canada: Slide 1 Land and Text Slide 2 Land Only Slide 3 Text OnlyDocumento5 pagineCanada: Slide 1 Land and Text Slide 2 Land Only Slide 3 Text OnlyRobertoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 14Documento6 pagineChapter 14Konul AlizadehNessuna valutazione finora
- General - Iceland IcelandDocumento8 pagineGeneral - Iceland Icelandwaleed yehiaNessuna valutazione finora
- AEF2e Maps North AmericaDocumento1 paginaAEF2e Maps North AmericaJAVIER MURILLO GONZALEZNessuna valutazione finora
- Worldwide Operations and Locations: North AmericaDocumento1 paginaWorldwide Operations and Locations: North AmericaLucas MeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Aritime Maps: Asia Europe Orth MericaDocumento1 paginaAritime Maps: Asia Europe Orth MericaEvgeniiNessuna valutazione finora
- AmericasDocumento1 paginaAmericasRichard ZuñigaNessuna valutazione finora
- World MapDocumento1 paginaWorld MapMd Zakaria IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Map of The WorldDocumento1 paginaMap of The WorldWaniya Sakib StudentNessuna valutazione finora
- Noamer 072838Documento1 paginaNoamer 072838Elaina MominNessuna valutazione finora
- North America Pol 2012Documento1 paginaNorth America Pol 2012TsantNessuna valutazione finora
- ForecastDocumento1 paginaForecastMichael AllenNessuna valutazione finora
- ACE Brochure Web PDFDocumento32 pagineACE Brochure Web PDFSam CarrNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To The Presentation: Page 1Documento30 pagineWelcome To The Presentation: Page 1balakumaranarchNessuna valutazione finora
- General - Estonia EstoniaDocumento6 pagineGeneral - Estonia Estoniawaleed yehiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hinschberger Et Al 2001 Tectonophysics PDFDocumento13 pagineHinschberger Et Al 2001 Tectonophysics PDFDimas PramuditoNessuna valutazione finora
- Australia: Pacific OceanDocumento5 pagineAustralia: Pacific Oceanpepe1bmNessuna valutazione finora
- 2021-11-01 Australian GeographicDocumento134 pagine2021-11-01 Australian GeographicIstvan Daniel100% (2)
- Americas PhysDocumento1 paginaAmericas Physvenkatesh286Nessuna valutazione finora
- Map of The British IslesDocumento2 pagineMap of The British IslesdecarvalhothiNessuna valutazione finora
- Wale'S: ScotlandDocumento1 paginaWale'S: ScotlandNnekaNessuna valutazione finora
- 609 Oceani DWDocumento1 pagina609 Oceani DWReyNessuna valutazione finora
- General - Guam Guam: Cabras Island Power PlantDocumento3 pagineGeneral - Guam Guam: Cabras Island Power Plantwaleed yehiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Europe: North North Atlantic Atlantic Ocean OceanDocumento1 paginaEurope: North North Atlantic Atlantic Ocean OceanRamon SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Navtex Stations: Xviii Xvii XIX XX XXIDocumento1 paginaNavtex Stations: Xviii Xvii XIX XX XXIBill DjadNessuna valutazione finora
- Europe Ref 2010Documento1 paginaEurope Ref 2010Bogdan WhiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Ocean Currents - Shortcut Method by To Learn FasterDocumento12 pagineOcean Currents - Shortcut Method by To Learn Fastermydevacc03Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bering Sea Bering Sea: A OC RCC TIDocumento1 paginaBering Sea Bering Sea: A OC RCC TIEvgeniiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - UK Physical Geography Worksheet Home StudyDocumento3 pagine1 - UK Physical Geography Worksheet Home StudyAndreea ŞerbanoiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Central America and the Caribbean islands mapDocumento1 paginaCentral America and the Caribbean islands mapzNessuna valutazione finora
- A Savage History: Whaling in the Pacific and Southern OceansDa EverandA Savage History: Whaling in the Pacific and Southern OceansNessuna valutazione finora
- North Pacific Ocean North Pacific OceanDocumento1 paginaNorth Pacific Ocean North Pacific OceanHorobets DmytroNessuna valutazione finora
- Latinoamerica (3 3)Documento1 paginaLatinoamerica (3 3)Diego Leon GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Portfolio Management in An Upstream Oil & Gas OrganizationDocumento25 paginePortfolio Management in An Upstream Oil & Gas OrganizationMazSkafNessuna valutazione finora
- Ha-America_Mapes s15-s19 (Cespedes; Lockhart; Et Al) 264pDocumento264 pagineHa-America_Mapes s15-s19 (Cespedes; Lockhart; Et Al) 264p4 5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ward VI - Registered Neighborhood Associations: LegendDocumento1 paginaWard VI - Registered Neighborhood Associations: LegendKOLD News 13Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Fens: An Abundant and Dangerous IntersectionDocumento23 pagineThe Fens: An Abundant and Dangerous IntersectionOGI ConstructNessuna valutazione finora
- Coral Reefs of The Andaman Sea - An Integrated Perspective: Oceanography and Marine Biology June 2007Documento23 pagineCoral Reefs of The Andaman Sea - An Integrated Perspective: Oceanography and Marine Biology June 2007Tyata SamratNessuna valutazione finora
- IMO Maritime SAR RegionsDocumento19 pagineIMO Maritime SAR RegionsJavier Quintero SaavedraNessuna valutazione finora
- WEM Plate Tectonics WorksheetDocumento2 pagineWEM Plate Tectonics WorksheetmarcosNessuna valutazione finora
- HHT DirectionsDocumento1 paginaHHT DirectionsschurulzNessuna valutazione finora
- Yoshiaki Nishida, Ann Waswo - Farmers-and-Village-Life-in-JapanDocumento309 pagineYoshiaki Nishida, Ann Waswo - Farmers-and-Village-Life-in-JapanEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix V: Major Tropical Soils and Their Susceptibility To Land DegradationDocumento2 pagineAppendix V: Major Tropical Soils and Their Susceptibility To Land Degradationashe zinabNessuna valutazione finora
- Shiretoko Parcul Național Din Hokkaidō Parte A Patrimoniului Mondial UNESCODocumento2 pagineShiretoko Parcul Național Din Hokkaidō Parte A Patrimoniului Mondial UNESCOEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prevatt2012 PDFDocumento63 paginePrevatt2012 PDFEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Biology of the Southern OceanDocumento107 pagineThe Biology of the Southern OceanEllie M.100% (1)
- Great Pacific Garbage Patch ExplainedDocumento3 pagineGreat Pacific Garbage Patch ExplainedEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Antarctic Notothenioid Fishes As Subjects For Research in Evolutionary BiologyDocumento13 pagineAntarctic Notothenioid Fishes As Subjects For Research in Evolutionary BiologyEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dunn - WIND FARMS PDFDocumento172 pagineDunn - WIND FARMS PDFEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Biology of the Southern OceanDocumento107 pagineThe Biology of the Southern OceanEllie M.100% (1)
- Dunn - WIND FARMS PDFDocumento172 pagineDunn - WIND FARMS PDFEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Routledge Handbook of South Asian Politics India Pakistan Bangladesh Sri Lanka and Nepal PDFDocumento481 pagineRoutledge Handbook of South Asian Politics India Pakistan Bangladesh Sri Lanka and Nepal PDFEllie M.100% (1)
- Alpine PDFDocumento16 pagineAlpine PDFEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mountain Resorts PDFDocumento491 pagineMountain Resorts PDFEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Competencies Higher Education and Career in JapanDocumento270 pagineCompetencies Higher Education and Career in JapanEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Rise of A Middle Class and The Changing Concept of Equity in IndonesiaDocumento23 pagineThe Rise of A Middle Class and The Changing Concept of Equity in IndonesiaEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brendan F.D. Barrett - Ecological-Modernisation-and-JapanDocumento241 pagineBrendan F.D. Barrett - Ecological-Modernisation-and-JapanEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brendan F.D. Barrett - Ecological-Modernisation-and-JapanDocumento241 pagineBrendan F.D. Barrett - Ecological-Modernisation-and-JapanEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Yuji Honjo - Competition-Innovation-and-Growth-in-JapanDocumento269 pagineYuji Honjo - Competition-Innovation-and-Growth-in-JapanEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mikael Adolphson and Kames Edward and Stacie Matsumoto and Edward Kamens - Heian-Japan-Centers-And-Peripheries PDFDocumento465 pagineMikael Adolphson and Kames Edward and Stacie Matsumoto and Edward Kamens - Heian-Japan-Centers-And-Peripheries PDFEllie M.100% (1)
- S. Javed Maswood - Japan in CrisisDocumento191 pagineS. Javed Maswood - Japan in CrisisEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mountain Resorts PDFDocumento491 pagineMountain Resorts PDFEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bub GB p4lBAAAAIAAJ PDFDocumento344 pagineBub GB p4lBAAAAIAAJ PDFEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mikael Adolphson and Kames Edward and Stacie Matsumoto and Edward Kamens - Heian-Japan-Centers-And-Peripheries PDFDocumento465 pagineMikael Adolphson and Kames Edward and Stacie Matsumoto and Edward Kamens - Heian-Japan-Centers-And-Peripheries PDFEllie M.100% (1)
- Mikael Adolphson and Kames Edward and Stacie Matsumoto and Edward Kamens - Heian-Japan-Centers-And-Peripheries PDFDocumento465 pagineMikael Adolphson and Kames Edward and Stacie Matsumoto and Edward Kamens - Heian-Japan-Centers-And-Peripheries PDFEllie M.100% (1)
- The Changing Geography of AsiaDocumento284 pagineThe Changing Geography of AsiaEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Neil Gordon Munro, Sam Sloan - Coins of Japan PDFDocumento413 pagineNeil Gordon Munro, Sam Sloan - Coins of Japan PDFEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Competencies Higher Education and Career in JapanDocumento270 pagineCompetencies Higher Education and Career in JapanEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Williams - Japan Beyond The End of HistoryDocumento261 pagineWilliams - Japan Beyond The End of HistoryEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mountains and ValleysDocumento113 pagineMountains and ValleysEllie M.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Earth-Science Cheat SheetDocumento13 pagineEarth-Science Cheat SheetLeizel TicoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Wilo General Overview 201: Efficient Solutions - 50 HZDocumento72 pagineWilo General Overview 201: Efficient Solutions - 50 HZJustin ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- PROJECTWISE PROVISIONS UNDER WATER RESOURCES DEPARTMENTDocumento76 paginePROJECTWISE PROVISIONS UNDER WATER RESOURCES DEPARTMENTGiridhari ChandrabansiNessuna valutazione finora
- Model 4 Operating and Maintenance ManualDocumento164 pagineModel 4 Operating and Maintenance Manualfauzi endraNessuna valutazione finora
- EssayDocumento19 pagineEssayBarocio Azpeitia Aldo RobertoNessuna valutazione finora
- BioSystems A-15 Analyzer - Maintenance Manual PDFDocumento23 pagineBioSystems A-15 Analyzer - Maintenance Manual PDFGarcía XavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Ufc 4 832 01nDocumento245 pagineUfc 4 832 01nsfadhilah_6Nessuna valutazione finora
- FeaturesDocumento8 pagineFeaturesankit rajNessuna valutazione finora
- Fouad A. Ahmed, Rehals F. M. Ali, 2013 - Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Fresh and Processed White Cauliflower PDFDocumento10 pagineFouad A. Ahmed, Rehals F. M. Ali, 2013 - Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Fresh and Processed White Cauliflower PDFGabitzzu AnonimNessuna valutazione finora
- Environment DefinitionsDocumento4 pagineEnvironment DefinitionsNancy Cárdenas100% (1)
- Articol GEOMAT Dec 2018-Simulare 2dDocumento7 pagineArticol GEOMAT Dec 2018-Simulare 2dIsabela BalanNessuna valutazione finora
- SAFETY DATA SHEET Shell Rimula R5 LE 10W-40.PDocumento15 pagineSAFETY DATA SHEET Shell Rimula R5 LE 10W-40.PChristian MontañoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Sea Solution BenefitsDocumento3 pagineBio Sea Solution BenefitsClaudio Santellanes100% (1)
- ChlorinationDocumento1 paginaChlorinationCindy GallosNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Survey: ART 403 Introduction To Planning Assignment - 9Documento2 pagineTypes of Survey: ART 403 Introduction To Planning Assignment - 9Ritu ChoudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- CEP v.107 n.4 2011Documento3 pagineCEP v.107 n.4 2011Chava TututiNessuna valutazione finora
- BCA Green Mark Certification Standards - 2010Documento204 pagineBCA Green Mark Certification Standards - 2010Carrie BradleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Waste Water Treatment Project ReportDocumento4 pagineWaste Water Treatment Project ReportMordhwaj Singh TomarNessuna valutazione finora
- Permionics Membrane CodingDocumento5 paginePermionics Membrane CodingPermionics IndiaNessuna valutazione finora
- TES 5 KKI SIMAK UI Landscape FeaturesDocumento3 pagineTES 5 KKI SIMAK UI Landscape FeaturesPA P ClassNessuna valutazione finora
- CBN MagazineDocumento61 pagineCBN MagazineUrooj Fatima100% (1)
- Enmax Cprs Case StudiesDocumento51 pagineEnmax Cprs Case StudiesleoarzuzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Utilizing food waste to reduce pollutionDocumento16 pagineUtilizing food waste to reduce pollutionHamza RafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Gravity Dam - Y910026Documento17 pagineGravity Dam - Y910026Ashish Sanghavi100% (27)
- MSDS Vactra Oil No 4Documento10 pagineMSDS Vactra Oil No 4Distributor Oli SpecialtiesNessuna valutazione finora
- Seboclear DB Sds v402 enDocumento7 pagineSeboclear DB Sds v402 enAchwan FebNessuna valutazione finora
- Bath Room TileDocumento28 pagineBath Room TileStephanie MYNessuna valutazione finora
- Analisis Kualitas Sub DAS Citarum Hulu: Astri Mutia Ekasari, Hani Burhanudin, Irland FardaniDocumento1 paginaAnalisis Kualitas Sub DAS Citarum Hulu: Astri Mutia Ekasari, Hani Burhanudin, Irland FardaniabahaangNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Lab Flash PointDocumento5 paginePre-Lab Flash PointJona Nichole LovinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cycles of Matter: Lesson ObjectivesDocumento6 pagineCycles of Matter: Lesson Objectivesapi-593653104Nessuna valutazione finora