Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
CTSD Math Formulas PDF
Caricato da
AtulTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CTSD Math Formulas PDF
Caricato da
AtulCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Master List of Formulas and Symbology Descriptions
Video Camera Image Size
Disclaimer: Here are some common 𝐴
𝐼𝐼 = 2 ∗ 𝐷 ∗ tan � �
formulas; however this is not an 2
exhaustive list and you may not need all
Where IS is the image size
of them.
D is the distance from the lens to the subject
A is the lens angle of view
Projector Lumens Output
𝐿∗𝐶∗𝐴
𝑆𝑆 � �
𝐵𝐵𝐵𝐵ℎ𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡𝑡 =
𝐷𝐷
Where L is ambient light at screen location⋆
C is the desired contrast ratio
7:1 – Passive Viewing – television
15:1 – Basic Decision Making Presentations
50:1 – Analytical Decision Making – Art work, Medical
80:1 – Full Motion Video – Home Theater
A is the area of screen ⋆⋆
Sg is the gain of the screen. Assume a screen gain of 1 unless otherwise noted.
Dr is the projector derating value. Assume a derating value of 0.75 unless otherwise noted.
⋆ Light units are in either lux or footcandles
⋆⋆ area in square meters or square feet
Loudspeaker Coverage Pattern (Ceiling Mounted) Loudspeaker Spacing (Ceiling Mounted)
𝐶∠ 𝐷 =2∗𝑟 (Edge-to-edge)
𝐷 = 2 ∗ (𝐻 − ℎ) ∗ tan � �
2 𝐷 = 𝑟 ∗ √2 (Minimum overlap)
Where D is diameter of coverage circle at ear height
𝐷=𝑟 (Center-to-center)
H is overall ceiling height
h is height of the listener’s ears (48 inches) Where D is the distance between loudspeakers
C ∠ is off-axis coverage angle of polar pattern r is the radius of loudspeaker coverage circle
Wattage at the Loudspeaker
𝐷
𝐿𝑝 +𝐻−𝐿𝑠 +20log� 2 �
𝐷𝑟
� �
10
𝐸𝐸𝐸 = 10^ ∗ 𝑊𝑟𝑟𝑟
Where EPR is electrical power required at loudspeaker
L P is SPL required at distance D 2
H is required headroom
L S is loudspeaker sensitivity at 3.28 feet (1 m)
D 2 is distance from loudspeaker to listener
D r is distance reference value
W ref is the wattage reference value. Assume a wattage reference value of 1 unless otherwise noted.
© Copyright 2015 by InfoComm International® Page 1 of 3
Loudspeaker Impedance Ohm’s Law Related
1 𝑃
𝑍𝑇 = 𝐼=
1 1 1 1 𝑉
+ + …
𝑍1 𝑍2 𝑍3 𝑍𝑁
Where I is current
𝑍1 V is circuit voltage
𝑍𝑇 = P is power ⋆
𝑁
Where Z T is the total impedance of the loudspeaker
system
⋆ Look up amplifier power in owner’s manual before adding
Z 1 is the measured impedance of a to the other AV devices.
loudspeaker
N is the quantity of loudspeakers in the
circuit
Needed Acoustic Gain Potential Acoustic Gain
𝐷0 ∗ 𝐷1
𝐷0 𝑃𝑃𝑃 = 20 log � �
𝑁𝑁𝑁 = 20 log � � 𝐷2 ∗ 𝐷𝑠
𝐸𝐸𝐸
Where PAG is Potential Acoustic Gain
Where NAG is Needed Acoustic Gain D 0 is distance from source to listener
D 0 is distance from source to listener D 1 is distance from loudspeaker to mic
EAD is Equivalent Acoustic Distance D 2 is distance from loudspeaker to listener
D S is distance from source to microphone
Audio System Stability (PAG NAG Complete Formula)
𝐷𝑂 𝐷0 𝐷1
20 log10 � � < 20 log10 � � − 10 log10 (𝑁𝑁𝑁) − 𝐹𝐹𝐹
𝐸𝐸𝐸 𝐷2 𝐷𝑆
Where NOM = Number of Open Microphones
FSM = Feedback Stability Margin
EAD = Equivalent Acoustic Distance
D 0 = the distance between the talker and the farthest listener
D 1 = the distance between the closest loudspeaker to the microphone and the microphone
D 2 = the distance between the loudspeaker closest to the farthest listener and the farthest listener
D s = the distance between the sound source (talker) and the microphone
Power Amplifier Wattage (Constant Voltage) Power Amplifier Heat Load
𝑊𝑡 = 𝑊 ∗ 𝑁 ∗ 1.5 𝑇𝑇𝑇𝑇𝑇 𝐵𝐵𝐵 = 𝑊 ∗ 3.4 ∗ (1 − 𝐸𝐷 )
Where W t is required wattage Where Total BTU is the total British Thermal Units released
W is watt tap used at individual loudspeaker W is the wattage of the amplifier
N is total number of loudspeakers E D is the efficiency of the device
1.5 is 50 percent amplifier headroom
© Copyright 2015 by InfoComm International® Page 2 of 3
Heat Load Jam Ratio
𝐼𝐼
𝑇𝑇𝑇𝑇𝑇 𝐵𝐵𝐵 = 𝑊𝐸 ∗ 3.4 𝐽𝐽𝐽 =
𝑂𝐷 + 𝑂𝐷2 + 𝑂𝐷3
� 1 3 �
Where Total BTU is the total British Thermal Units
released
W E is the total watts of equipment in the room
Where ID is the inner diameter of the conduit
OD is the outer diameter of each conductor
Conduit Capacity
𝑂𝑂2
Where ID is the inner diameter of the conduit
𝐼𝐼 > � One Cable
0.53
OD is outer diameter of each conductor
𝑂𝑂²+𝑂𝑂²
𝐼𝐼 > � Two Cables
0.31
𝑂𝑂²+𝑂𝑂²+𝑂𝑂²…
𝐼𝐼 > � 3+ Cables
0.40
Image Height to Farthest Viewer Distance Ratio
𝐼𝐻 𝐷𝑇 The relationship between image height, viewing task, and
= farthest viewer distance can also be represented as a
𝐼𝐷 𝑉𝑇 wheel:
Where I H = Image height
I D = Distance from the farthest viewer to
the image
V T = Viewing Task Ratio: distance
4 for Inspection Viewing Tasks
6 for Reading with Clues Viewing
Tasks
8 for General Viewing Tasks
D T = Viewing task: height ratio. This will
be 1.
Computer Video Signal Bandwidth Minimum Video System Bandwidth
𝐻𝑝𝑝𝑝 ∗ 𝑉𝑝𝑝𝑝 ∗ 𝑓𝑣 𝑆𝑆 = 𝐻𝐻 ∗ 2
𝐻𝐻 = ∗3
2 Where SF is the system frequency in Hertz
Where HF is the highest frequency in Hertz HF is the highest frequency in Hertz of the
H pix is the total number of horizontal pixels computer signal
V pix is the total number of vertical pixels
f v is the refresh rate
© Copyright 2015 by InfoComm International® Page 3 of 3
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 12th STD Business Math FormulaeDocumento12 pagine12th STD Business Math FormulaeSandhya BalakrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas For Prisms and PyramidsDocumento2 pagineFormulas For Prisms and PyramidsLady Muffins100% (1)
- Product: Formula For A ProportionDocumento12 pagineProduct: Formula For A ProportionJames ToledoNessuna valutazione finora
- GR1268 Full SolutionsDocumento66 pagineGR1268 Full SolutionsRGNessuna valutazione finora
- Advances in Database Querying: S. SudarshanDocumento86 pagineAdvances in Database Querying: S. SudarshanSambhaji BhosaleNessuna valutazione finora
- (DBA-403-M) DBA-403 SQLOS Memory Manager Changes in SQL Server 2012Documento32 pagine(DBA-403-M) DBA-403 SQLOS Memory Manager Changes in SQL Server 2012ebtrainNessuna valutazione finora
- EC-Networks-Basics-Old GATE QuestionsDocumento6 pagineEC-Networks-Basics-Old GATE QuestionsInstitute of Engineering Studies (IES)80% (5)
- Microsoft Math PowerpointDocumento31 pagineMicrosoft Math PowerpointA L Andriana SyaripNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Two Port NetworksDocumento14 pagine5 Two Port NetworksNitinNessuna valutazione finora
- DatabaseConcepts 01Documento120 pagineDatabaseConcepts 01Usha Datt100% (1)
- C# Questions1Documento11 pagineC# Questions1Sundari MuruganNessuna valutazione finora
- Mensuration FormulasDocumento6 pagineMensuration FormulasMahaveer SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Time MDX Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineTime MDX Cheat SheetSuman Kumar0% (1)
- Lesson One - Selecting Data From Oracle: Writing SELECT StatementsDocumento52 pagineLesson One - Selecting Data From Oracle: Writing SELECT Statementsblackwolf230% (1)
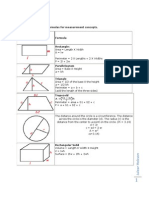
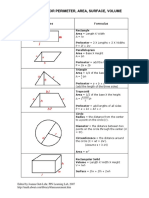
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeDocumento2 pagineGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeDavidson isaackNessuna valutazione finora
- GRE AverageDocumento23 pagineGRE AverageperwinsharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocumento2 pagineGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFGtech00Nessuna valutazione finora
- Multi-Criteria Decision Making: MCDM ApproachesDocumento21 pagineMulti-Criteria Decision Making: MCDM ApproachesKentDemeterioNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle 10g IMP Notes of DineshDocumento36 pagineOracle 10g IMP Notes of Dineshdinch100% (2)
- SQL Advance: The TOP ClauseDocumento43 pagineSQL Advance: The TOP ClausevrincNessuna valutazione finora
- SQL Query Interview QuestionsDocumento7 pagineSQL Query Interview QuestionsAmit KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz2 3510 Cheat-SheetDocumento4 pagineQuiz2 3510 Cheat-SheetKatherine Pham100% (1)
- Network Analysis & Synthesis (Book)Documento218 pagineNetwork Analysis & Synthesis (Book)hayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric Identities and FormulasDocumento6 pagineTrigonometric Identities and FormulasRajesh MauryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ssis Mock Test FDocumento7 pagineSsis Mock Test Fparashuram nNessuna valutazione finora
- Audioxpress Voice Coils A TutorialDocumento13 pagineAudioxpress Voice Coils A TutorialTiến Nam LêNessuna valutazione finora
- GATE Analog Circuits BookDocumento12 pagineGATE Analog Circuits BookFaniAli100% (1)
- Maths FormulasDocumento13 pagineMaths FormulasMadhu Pali100% (2)
- 01-Introduction To BIDocumento41 pagine01-Introduction To BIOssama AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Delft University of Technology: Design, Integration and Verification of The Delfi-n3Xt Reaction Wheel SystemDocumento292 pagineDelft University of Technology: Design, Integration and Verification of The Delfi-n3Xt Reaction Wheel SystemMaman de AnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Toad For Oracle 12 - 0 Vs SQL Developer Functional Matrix - FinalDocumento4 pagineToad For Oracle 12 - 0 Vs SQL Developer Functional Matrix - FinalAlex SiowNessuna valutazione finora
- 10th Class Math Formulas List and Important Formulas For Board ExamsDocumento4 pagine10th Class Math Formulas List and Important Formulas For Board ExamsShrey ShuklaNessuna valutazione finora
- Made Easy Ce Gate-2018 Sol Shift 2Documento41 pagineMade Easy Ce Gate-2018 Sol Shift 2Gaddam SudheerNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Theory QuestionsDocumento89 pagineNetwork Theory QuestionsRam Mohan Rao Makineni100% (1)
- Kreatryx Measurements PDFDocumento33 pagineKreatryx Measurements PDFKaushal DeshmukhNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions and Triggers PDFDocumento23 pagineFunctions and Triggers PDFXie PeiyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Alg1m3l2 - Writing Sequences With Recursive and Explicit Formulas 2Documento3 pagineAlg1m3l2 - Writing Sequences With Recursive and Explicit Formulas 2api-276774049Nessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 1 KeyDocumento5 pagineHomework 1 KeyveluarasuNessuna valutazione finora
- Msbi SQL QueriesDocumento88 pagineMsbi SQL QueriesraamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Audio EffectsDocumento111 pagineDigital Audio EffectsJosep M ComajuncosasNessuna valutazione finora
- Table of Math SymbolsDocumento16 pagineTable of Math SymbolsJohn LauNessuna valutazione finora
- System-Level ESD - EMI Protection GuideDocumento25 pagineSystem-Level ESD - EMI Protection GuideArvind SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigonometric FormulasDocumento2 pagineTrigonometric FormulasErik MierasNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure Query Language: by Prof - Manikandan QMC College, MedavakkamDocumento20 pagineStructure Query Language: by Prof - Manikandan QMC College, MedavakkamProf.ManikandanNessuna valutazione finora
- Math FormulasDocumento469 pagineMath Formulasm.jeevanNessuna valutazione finora
- WWWWWW WWWWWW WWWWWW WWWWWW WWWW WWWW WWWWWW: Data Transformation With DplyrDocumento2 pagineWWWWWW WWWWWW WWWWWW WWWWWW WWWW WWWW WWWWWW: Data Transformation With DplyrFelipe Balboa PolancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Circuit Frequency Considerations 12 Sept 2019Documento42 pagineChapter 2 Circuit Frequency Considerations 12 Sept 2019MaphikeNessuna valutazione finora
- (S (1) For (I 2 I N I++) D (I) C (1, I) For (I 1 I n-1 I++)Documento2 pagine(S (1) For (I 2 I N I++) D (I) C (1, I) For (I 1 I n-1 I++)bhariprasad_mscNessuna valutazione finora
- GMAT Math Formulas ListDocumento3 pagineGMAT Math Formulas ListOlzhas BolatbekulyNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Divider and CombinerDocumento28 paginePower Divider and Combinerkukumalu91Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaDocumento87 pagineChapter 1 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 - Operational AmplifierDocumento0 pagineChapter 5 - Operational AmplifierManiranjan RoutNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog ElectronicsDocumento390 pagineAnalog ElectronicsAnthony Robert XNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Physics Unit II NotesDocumento19 pagineEngineering Physics Unit II NotesFatherNessuna valutazione finora
- CTSD Math Formulas-20180501-FinalDocumento3 pagineCTSD Math Formulas-20180501-FinalMarcus YarboroughNessuna valutazione finora
- Slides Topic4-2Documento18 pagineSlides Topic4-2AbdulJawad Ibrahim ElmezoghiNessuna valutazione finora
- Antenna Lect 10 11Documento25 pagineAntenna Lect 10 11dilawar sumraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 Path LossDocumento32 pagineLecture 4 Path Losssaadi khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 2Documento24 pagineLec 2goraxi6015Nessuna valutazione finora
- Antennas For Communications Engineers Part IIDocumento22 pagineAntennas For Communications Engineers Part IIabdishNessuna valutazione finora
- PH Exporters ListDocumento77 paginePH Exporters ListHerbert Bactong100% (1)
- Compare These Two SentencesDocumento1 paginaCompare These Two SentencesDevi SitepuNessuna valutazione finora
- XyzDocumento2 pagineXyzrijusmitasaikiaNessuna valutazione finora
- DSC-T1 Level 3Documento33 pagineDSC-T1 Level 3Anonymous Lfgk6vygNessuna valutazione finora
- The Meso American CivilizationDocumento40 pagineThe Meso American Civilizationsami karemNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparatives and SuperlativesDocumento3 pagineComparatives and SuperlativesΜαριάννα100% (1)
- Cally Banham, 2018Documento7 pagineCally Banham, 2018ValNessuna valutazione finora
- FREE Music Lessons From Berklee College of Music: A Modern Method For GuitarDocumento4 pagineFREE Music Lessons From Berklee College of Music: A Modern Method For Guitarbgiangre8372Nessuna valutazione finora
- Manual CorporativoDocumento13 pagineManual CorporativoMariana Fierro100% (1)
- Architectural Working DrawingsDocumento62 pagineArchitectural Working DrawingsDondie Porcil CorduwaNessuna valutazione finora
- MetMuseumOfArt - The Emperor's Album PDFDocumento320 pagineMetMuseumOfArt - The Emperor's Album PDFben100% (2)
- Cendrillon 17-18 Guide PDFDocumento41 pagineCendrillon 17-18 Guide PDFKenneth PlasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advertising LCD DisplayDocumento32 pagineAdvertising LCD DisplayDramane BonkoungouNessuna valutazione finora
- Living-in-Christ - Billy Graham PDFDocumento27 pagineLiving-in-Christ - Billy Graham PDFPrecious Udoada75% (8)
- First Paulinian Prayer CongressDocumento3 pagineFirst Paulinian Prayer CongressDeziree Vera CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethnomedical Profile of The Hos PDFDocumento317 pagineEthnomedical Profile of The Hos PDFDarshan KanganeNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar Revision Answer Key1Documento7 pagineGrammar Revision Answer Key1AlinnNessuna valutazione finora
- Times-NIE-11th May To 16th May 2020Documento11 pagineTimes-NIE-11th May To 16th May 2020pankarvi6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Movie ReviewDocumento1 paginaMovie ReviewRohzmeen MalilayNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 A Dream Deferred WorkDocumento4 pagine2017 A Dream Deferred WorkCarolina Malfettano100% (1)
- Brand Personality of KHAADIDocumento17 pagineBrand Personality of KHAADIBusteD WorlDNessuna valutazione finora
- An Overview of Silicone SoftenerDocumento3 pagineAn Overview of Silicone SoftenersiliconemanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mahesh Dattanis A Muggy Night in MumbaiDocumento12 pagineMahesh Dattanis A Muggy Night in MumbaiPratyashNessuna valutazione finora
- TT CB 5 1 50 CF: Peak Design Travel TripodDocumento1 paginaTT CB 5 1 50 CF: Peak Design Travel TripodJuliNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On The Six Obstacle Removing Mantras in Parasurama Kalpa SutraDocumento5 pagineA Study On The Six Obstacle Removing Mantras in Parasurama Kalpa SutraKutticad Ramesh100% (9)
- Desoeuvrement in Understanding BlanchotDocumento3 pagineDesoeuvrement in Understanding Blanchotmadequal2658Nessuna valutazione finora
- Perfect Espresso:: The First Step To Make ADocumento3 paginePerfect Espresso:: The First Step To Make AAlyHDNessuna valutazione finora
- Athena Patterson-Orazem Dreams in VodouDocumento4 pagineAthena Patterson-Orazem Dreams in VodouRob ThuhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Put The Verbs Into The Correct Tense2Documento2 paginePut The Verbs Into The Correct Tense2auroramartinescuNessuna valutazione finora
- LABREPORT#3Documento2 pagineLABREPORT#3reasonbmor69Nessuna valutazione finora