Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Baja 1
Caricato da
Ruddy ChoiruddynCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Baja 1
Caricato da
Ruddy ChoiruddynCopyright:
Formati disponibili
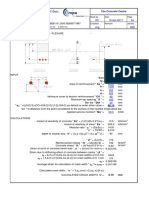
1.7.
Member Size and Check Stability
1.7.1 Purlin and Sagrod
1.7.1.1 Material Specification
Yield stress fy = 240 MPa
Ultimate stress fu = 370 MPa
Residual stress fr = 70 MPa
Modulus of elasticity E = 200,000 MPa
Poisson's ratio u = 0.3
1.7.1.2 Profile Specification
Lip Channel : C.150.50.20.2,3
ht = 150 mm
b = 50 mm
a = 20 mm
t = 2 mm
A = 632 mm2
Ix = 2,100,000 mm4
Iy = 219,000 mm4
Sx = 28,000 mm3
Sy = 6,330 mm3
rx = 63 mm
ry = 18.6 mm
c = 15.5 mm
Profile Weight, w = 5.0 kg/m
Strength reduction factor fb = 0.90
Shear reduction factor ff = 0.75
Sagrod diameter d = 10.00 mm
Slant distance between purlin s = 1,000 mm
Purlin length L1 = 6,000 mm
Distance between sagrod L2 = 2,000 mm
Roof angle a = 10 °
1.7.1.3 Section Properties
a. Shear modulus (G)
G = E / [ 2 * (1 + u) ]
= 76,923.08 Mpa
b. Profile clearence (h)
h₀ = ht - t
= 147.70 mm
c. Torsion constants (J)
J = 2 * 1/3 * b * t3 + 1/3 * (ht - 2 * t) * t3 + 2/3 * (a - t) * t3
= 1,138.83 mm4
d. Flection constants (Cw)
Cw = Iy * h2 / 4
1,194,387,128 mm6
e. Lateral torsional buckling moment coefficient
X1 = p/Sx * √ [ E * G * J * A/2 ]
= 8,350 Mpa
f. Lateral torsional buckling moment coefficient
X2 = 4 * [ Sx / (G * J) ] * Iw / Iy
2
= 0.00223 mm2/N2
g. Plastic section modulus of the X-axis
Zx = 1/4 * ht * t2 + a * t * (ht - a) + t * (b - 2 * t) * (ht - t)
= 21,601 mm3
h. Plastic section modulus of the Y-axis
Zy = ht*t*(c - t/2) + 2*a*t*(b - c - t/2) + t * (c - t)2 + t * (b - t - c)2
= 10,804 mm3
1.7.1.4 Purlin Load
a. Dead Load
Wide Q
Load Type Weight Unit
(m) (N/m)
Self weight 49.6 N/m 55.0
Roof weight 150.0 N/m2 1.2 180.0
Total Dead Load Q DL 235.0 N/m
b. Live Load
Uniform load (QLL)
Live loads due to rain water load equivalent to the load calculated height of 25
mm thick puddles.
Purlin distance (s) = 1 m
Water density = 1000 kg/m3 = 10 kN/m3
Wide Q
Load Type Weight Unit
(m) (N/m)
Rain load 250.0 N/m 250.0
Total Live Load QLL 250.0
Concentrated load (PLL)
Concentrated loads caused by workers or people = 1000 N
Wide P
Load Type Weight Unit
(m) (N)
Concentrated Load 1000 N 1000
Total Dead Load PLL 1000
1.7.1.5 Ultimate Load
a. Ultimate uniform load (Qu)
Qu = 1.2QDL + 1.6QLL
= 682 N/m
b. Ultimate concentrated load (Pu)
Pu = 1.6PLL
= 1,600 N/m
c. Roof angle (a)
a = 0.1745 rad
d. Uniform load on the X-axis (Qux)
Qux = Qu * cos a *10-3
= 0.6716 N/mm
e. Uniform load on the Y-axis (Qux)
Quy = Qu * sin a *10-3
= 0.1184 N/mm
f. Concentrated load on the X-axis (Pux)
Pux = Pu * cos a
= 1,575.69 N
g. Concentrated load on the Y-axis (Puy)
Puy = Pu * sin a
= 277.84 N
1.7.1.6 Moment and Shear Force due to Ultimate Loads
a. Purlin span length on the X-axis (Lx)
Lx = L1 = 6,000 mm
b. Purlin span length on the Y-axis (Ly)
Ly = L2 = 2,000 mm
Dimana
r²ts = √(Iy*Cw) /Sx
r²ts = 577.61
rts = 24.034
c. Moment due to ultimate loads to the X-axis (Mux)
Mux = 1/10 * Qux * Lx2 + 1/8 * Pux * Lx
= 3,599,669.30 Nmm
d. Moment at quarter span (MA)
MA = 2,699,751.97 Nmm
e. Moment at half span (MB)
MB = 3,599,669.30 Nmm
f. Moment at 3/4 span (MC)
MC = 2,699,751.97 Nmm
g. Moment due to ultimateoads to the Y-axis (Mux)
Muy = 1/10 * Quy * Ly2 + 1/8 * Puy * Ly
= 116,830.49 Nmm
h. Shear Force due to ultimate loads on the X-axis (Vux)
Vux = Qux * Lx + Pux
= 5,605.53 N
i. Shear Force due to ultimate loads on the Y-axis (Vuy)
Vuy = Quy * Ly + Puy
= 514.69 N
1.7.1.7 Nominal Effect of Local Buckling Moment
Effect of local buckling on flank :
a. Slenderness of The Flank Section
l = b/t
= 21.74
b. Maximum Slenderness Limits for Compact Cross-Section
lp = 0,38 * √(E/ fy ) ( SNI 2015 - B4.1b )
= 10.97
c. Maximum Slenderness Limits for Non=Compact Cross-Section
lr = 1,0 * √ (E / fy ) ( SNI 2015 - B4.1b )
= 28.87
d. Plastic Moment (Mp)
Mpx = fy * Zx
= 5,184,290.2 Nmm
e. Plastic Moment of The Y-axis (Mpy)
Mpy = fy * Zy
= 2,593,064.16 Nmm
f. Bending Moment on The X-axis Limits
Mrx = Sx * ( fy - fr )
= 4,760,000.0 Nmm
g. Bending Moment on The Y-axis Limits
Mry = Sy * ( fy - fr )
= 1,076,100.00 Nmm
Nominal cross-sectional moment conditions :
a. Compact cross section (l £ lp)
Mn = Mp
b. Non Compact cross section (lp < l £ lr)
Mn = Mp - (Mp - Mr) * ( l - lp) / ( lr - lp)
c. Sectional trim l > lr
Mn = Mr * ( lr / l )2
Of calculation obtained the following results :
l > lp and l < lr
Based on the value of the slenderness of the flank, including the cross-section :
Non-Compact
Nominal moment cross the X-axis is calculated as follows:
Compact : Mn = Mp = - Nmm
Non-compact : Mn = Mp-(Mp - Mr)*( l - lp)/( lr - lp) = 4,928,986.9 Nmm
Sectional trim : Mn = Mr * ( lr / l )2 = - Nmm
Mnx = 4,928,986.9 Nmm
So the nominal moment cross the X-axis is equal to the Non-Compact
at : 4928986.85 Nmm
Nominal moment cross the Y-axis is calculated as follows:
Compact : Mn = Mp = - Nmm
Non-compact : Mn = Mp-(Mp - Mr)*( l - lp)/( lr - lp) = 1,680,278.52 Nmm
Sectional trim : Mn = Mr * ( lr / l )2 = - Nmm
Mny = 1,680,278.52 Nmm
So the nominal moment cross the Y-axis is equal to the Non-Compact
at : 1,680,278.52 Nmm
1.7.1.8 Nominal Effect of Lateral Buckling Moment
Nominal moment component structures with lateral buckling effect is calculated as
follows :
a. Short Span (L ≤ Lp)
Mn = Mp = fy * Zx
b. Medium Span (Lp ≤ L ≤ Lr)
Mn = Cb * [Mp-( Mp - 0,7fy*Sx ) * (L-Lp) / (Lr-Lp) ] ≤ Mp
c. Long Span (L > Lr)
Mn = Fcr * Sx ≤ Mp
Dimana :
Fcr = ( Cb*π²*E)/(L/rts)^2* √ 1 + 0,078*(Jc/(Sx*h₀))*(L/rts)²
= 346.81
d. The maximum span length of the beam is able to hold the plastic moment (Lp)
Lp = 1.76 * ry * √ ( E / fy )
= 945.01 mm
e. The difference between the yield stress and residual stress (fL)
fL = fy - fr
= 170 Mpa
f. Minimum length of span beam prisoners critical buckling moment determined by lateral
torsional (Lr)
Lr = 1,95rts*(E/0,7*fy)* √(Jc/Sx*h₀) + √(Jc/Sx*h₀)² + 6,76*(0,7fy/E)²
= 2776.56 mm
g. Lateral torsional buckling moment coefficient (Cb)
Cb = 12.5 * Mux / ( 2.5*Mux + 3*MA + 4*MB + 3*MC )
= 1.14
h. Plastic moment of the X-axis (Mpx)
Mpx = fy * Zx
= 5,184,290.2 Nmm
i. Plastic moment of the Y-axis (Mpy)
Mpy = fy * Zy
= 2,593,064.16 Nmm
j. Bending moment on the X-axis limits (Mrx)
Mrx = Sx * (fy - fr)
= 4,760,000.0 Nmm
k. Bending moment on the Y-axis limits (Mry)
Mry = Sy * (fy - fr)
= 1,076,100.00 Nmm
l. Span length of the Y-axis (distance lateral support), L = L2
L = 2,000.00 mm
Of calculation, obtained the following results :
L > Lp dan L < Lr
thus belongs to the category : medium span
Nominal moment on the X-axis is calculated as follows :
Mnx = Mpx = fy * Zx = - Nmm
Mnx =Cb * [Mpx-( Mpx - 0,7fy*Sx ) * (L-Lp) / (Lr-Lp) ] = 5,576,861.7 Nmm
Mnx = Fcr * Sx = - Nmm
Mnx = 5,576,861.7 Nmm
So the nominal moment on the X-axis for medium span structure is at 5,576,861.7
Nmm
Mnx > Mpx, so the nominal moment for the X-axis is used for 5,184,290.2
Nmm
Nominal moment on the Y-axis is calculated as follows :
Mny = Mpx = fy * Zy = - Nmm
Mny =Cb * [Mpy-( Mpy - 0,7fy*Sy ) * (L-Lp) / (Lr-Lp) ] = 1,945,438.24 Nmm
Mny = Fcr * Sy = - Nmm
Mny = 1,945,438.24 Nmm
So the nominal moment on the X-axis for medium span structure is at 1,945,438.24
Nmm
Mny < Mpy, so the nominal moment for the X-axis is used for 1,945,438.24
Nmm
1.7.1.9 Resistance Bending Moment
Nominal moment on the X-axis
a. By the influence of local buckling Mnx = 4,928,986.9 Nmm
b. By the influence of lateral buckling Mnx = 5,184,290.2 Nmm
c. Nominal moment to determine the smallest X-axis Mnx = 4,928,986.9 Nmm
d. Resistance bending moment on the X-axis = fb * Mnx = 4,436,088.2 Nmm
Nominal moment on the Y-axis
a. By the influence of local buckling Mny = 1,680,278.52 Nmm
b. By the influence of lateral buckling Mny = 1,945,438.24 Nmm
c. Nominal moment to determine the smallest X-axis Mny = 1,680,278.52 Nmm
d. Resistance bending moment on the X-axis = fb * Mny = 1,512,250.67 Nmm
Moment due to ultimate loads to the X-axis Mux = 3,599,669.30 Nmm
Moment due to ultimate loads to the Y-axis Muy = 116,830.49 Nmm
Mux / ( fb * Mnx ) = 0.8115
Muy / ( fb * Mny ) = 0.0773
Requirements that must be met are :
Mux / ( fb * Mnx ) + Muy / ( fb * Mny ) ≤ 1.0
0.8887 < 1.0 (SAFE)
1.7.1.10 Shear Resistance
Profile without stiffener plate thickness shall meet the following requirements :
h/t ≤ 2,24 * Ö ( E / fy )
64.22 < 64.66 Thickness profile qualify
a. Shear force due to ultimate loads on the X-axis (Vux)
Vux = 5,605.53 N
b. Cross-sectional area profile (Aw)
Aw = t * ht
= 345 mm2
c. Nominal shear resistance on the X-axis (Vnx)
Vnx = 0.60 * fy * Aw * Cv
= 49,680.00 N
d. Shear resistance of the X-axis
ff * Vnx = 37,260.00 N
e. Shear force due to ultimate loads on the Y-axis (Vuy)
Vuy = 514.69 N
f. Cross-sectional area profile (Af)
Af = 2*b*t
= 230 mm2
g. Nominal shear resistance on the X-axis (Vny)
Vny = 0.60 * fy * Aw * Cv
= 33,120.00 N
h. Shear resistance of the X-axis
ff * Vnx = 24,840.00 N
Vux / ( ff * Vnx ) = 0.1504
Vuy / ( ff * Vny ) = 0.0207
Requirements that must be met are :
Vux / ( ff * Vnx ) + Vuy / ( ff * Vny ) ≤ 1.0
0.1712 < 1.0 (SAFE)
1.7.1.11 Shear and Bending Moment Interaction Control
Requirements that must be met for the shear and bending moment interaction is :
Mu / ( fb * Mn ) + 0.625 * Vu / ( ff * Vn ) £ 1.375
Mu / ( fb * Mn = Mux / ( fb * Mnx ) + Muy / ( fb * Mny )
= 0.8887
Vu/( ff * Vn ) = Vux / ( ff * Vnx ) + Vuy / ( ff * Vny )
= 0.1712
Mu / ( fb * Mn ) + 0.625 * Vu / ( ff * Vn ) = 0.996
0.996 < 1.375 SAFE
1.7.1.12 Sagrod Tensile Resistance
a. Ultimate uniform load on purlin (Quy)
Quy = 0.1184 N/mm
b. Ultimate concentrated load on purlin (Puy)
Puy = 277.84 N
c. Sagrod length (Ly)
Is equal to the distance between purlin
Ly = L2 = 2000 mm
d. Tensile force on sagrod due ultimate load (Tu)
Tu = Quy * Ly + Puy
= 514.69 N
e. Yield stress (fy) = 240 MPa
f. Ultimate stress (fu) = 370 MPa
g. Sagrod diameter (d)
d = 10 mm
h. Sagrod gross cross-sectional area (Ag)
Ag = p / 4 * d2
= 78.54 mm2
i. Sagrod effective cross-sectional area (Ae)
Ae = 0.9 * Ag
= 70.686 mm2
j. Sagrod tensile resistance by the gross cross-sectional area
f * Tn = 0.90 * Ag * fy
= 16,964.60 N
k. Sagrod tensile resistance by the effective cross-sectional area
f * Tn = 0.75 * Ae * fu
= 19,615.32 N
Use the smallest tensile resistance f * Tn = 16,964.60 N
Requirements that must be met are : Tu £ f * Tn
514.69 < 16,964.60 (SAFE)
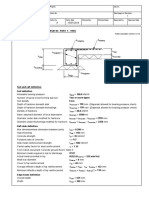
1.6.2 Beam Without Stiffenes
1.6.2.1 Material Specification
Yield stress fy = 240 MPa
Residual stress fr = 115 MPa
Modulus of elasticity E = 200,000 MPa
Poisson's ratio u = 0.3
1.6.2.2 Profile Specification
Wide flange : 400x200x8x13
ht = 400 mm
tf bf = 200 mm
tw = 8 mm
tw tf = 13 mm
h h2 ht r = 16 mm
A = 8,410 mm2
Ix = 237,000,000 mm4
r
h1 Iy = 17,400,000 mm4
bf rx = 168 mm
ry = 45.4 mm
Sx = 1,190,000 mm3
Sy = 174,000 mm3
Weight w= = 647 N/m
1.6.2.3 Beam Data
Length of the X-axis elements Lx = 8,000 mm
Length of the Y-axis elements (lateral support Ly = 4,000.00 mm
distance)
Maximum moment due to ultimate loads Mu = 160,000,000 Nmm
Moment at quarter span (MA) MA = 122,000,000 Nmm
Moment at half span (MB) MB = 146,000,000 Nmm
Moment at 3/4 span (MC) MC = 115,000,000 Nmm
Shear force due to ultimate loads Vu = 60,000 N
Strength reduction factor for bending moment fb = 0.90
Strength reduction factor for shear force ff = 0.75
1.6.2.4 Section Properties
a. Shear modulus (G)
G = E / [ 2 * (1 + u) ]
= 76,923.08 Mpa
b. Number of flange thickness and radius (h 1)
h1 = tf + r
= 29 mm
c. Profile clearence (h2)
h2 = ht - 2 * h1
= 342.00 mm
d. Center to center distance between the flange profile (h)
h = ht - tf
= 387.00 mm
e. Torsion constants (J)
= 2 * 1/3 * bf * tf + 1/3 * (ht - 2 * tf) * tw
3 3
J
= 356,762.67 mm4
f. Flection constants (Iw)
Iw = I y * h2 / 4
651,495,150,000 mm6
e. Lateral torsional buckling moment coefficient
X1 = p/Sx * √ [ E * G * J * A/2 ]
= 12,683 Mpa
f. Lateral torsional buckling moment coefficient
X2 = 4 * [ Sx / (G * J) ] * Iw / Iy
2
= 0.00028 mm2/N2
g. Plastic section modulus of the X-axis
Zx = tw * ht / 4 + ( bf - tw ) * ( ht - tf ) * tf
2
= 1,285,952 mm3
h. Plastic section modulus of the Y-axis
Zy = tf * bf / 2 + ( ht - 2 * tf ) * tw / 4
2 2
= 265,984 mm3
1.6.2.6 Local Buckling Effect on Nominal Moment
a. Slenderness of The flange Section
l = bf / t f
= 15.38
b. Maximum Slenderness Limits for Compact Cross-Section
lp = 170 / √ fy
= 10.97
c. Maximum Slenderness Limits for Non=Compact Cross-Section
lr = 370/ √ (fy - fr)
= 33.09
d. Plastic Moment (Mp)
Mp = f y * Zx
= 308,628,480 Nmm
f. Bending Moment (Mr)
Mr = Sx * ( fy - fr )
= 148,750,000 Nmm
Nominal cross-sectional moment conditions :
a. Compact cross section (l £
Mn Mp lp )
=
b. Non Compact cross section (l p < l £ lr)
Mn = Mp - (Mp - Mr) * ( l- - lp) / ( lr - l p)
c. Sectional trim l > lr
Mn = Mr * ( l r
/ l) ) 2
Of calculation obtained the following results :
l > lp and l < lr
Based on the value of the slenderness of the flange, including the cross-section :
Non-Compact
Nominal moment is calculated as follows:
Compact : Mn = Mp = - Nmm
Non-compact : Mn = Mp-(Mp - Mr)*( l- - l p)/( l r - l = 276,746,079 Nmm
Sectional trim : Mn = Mr * ( l r / l) )
2
= - Nmm
Mn = 276,746,079 Nmm
So the nominal moment cross section is equal to the Non-Compact at : 276,746,079
Nmm.
1.6.2.7 Nominal Moment On a Full-walled Beams
a. Slenderness of the web section
l = h/ tw
= 48.38
for section with dimension h/ tw > lr
nominal moment must be calculate with the following formula :
Mn = Kg * S * fcr
with, Kg = 1 - [ ar / (1200 + 300 * ar) ] * [ h / tw - 2550 / Ö fcr ]
for slenderness :
a. lG ≤ lp
fcr = fy
b. lp < l G ≤ lr
fcr = Cb * fy * [ 1 - ( lG - lp ) / ( 2 * ( lr - lp ) ) ] ≤ fy
c. lG > lr
fcr = fc * ( lr / lG )2 ≤ fy
for lateral torsional buckling :
fc = Cb * fy / 2 ≤ fy
for local buckling :
fc = fy / 2
Lateral torsional buckling moment coefficient calculated by the formula :
Cb = 12.5 * Mu / ( 2.5*Mu + 3*MA + 4*MB + 3*MC ) < 2.3
= 1.18 < 2.3
so taken value Cb = 1.18
Extensive comparison between the web and flange :
ar = h * t w / ( bf * t f )
= 1.19
Moment of Inertia (I1)
I1 = Iy / 2 - 1/12 * tw3 * 1/3 * h2
= 8,695,136 mm4
Sectional Area (A1)
A1 = A / 2 - 1/3 * tw * h2
= 3,293 mm2
The radius of gyration area a third of the flange plus web in compression is equal (r 1) :
r1 = Ö ( I1 / A1
= 51.39 mm
Nominal Moment Based on Lateral Torsional Buckling
a. Distance between the lateral bracing (L)
L = Ly
= 4,000 mm
b. Slenderness rate (lG)
lG = L / r1
= 77.84
c. Slenderness limit for the maximum cross-sectional
Compact cross section = lp = 1.76 * √ (E/fy)
= 50.807
Non-Compact cross section = lr = 4.40 * √ (E/fy)
= 127.02
d. Reference stress for lateral torsional buckling moment (f c)
fc = Cb * fy / 2
= 141.59 Mpa
fc < fy , so the value of fc is 141.59 Mpa
e. Cross-section critical stress is as follows:
If lG ≤ lp
fcr = fy = 240 Mpa
If lp < l G ≤ lr
fcr = Cb* fy*[ 1 - ( lG - lp) ( 2*( lr - lp)) ] = 232.96 Mpa
If lG > lr
fcr = fc * ( lr / lG )2 = - Mpa
so use the value of the critical stress cross-section is 240.00 Mpa
fcr < fy , so the value of fcr is 240 Mpa
f. Elastic section modulus (S)
S = Sx
= 1,190,000 mm
g. Walled full web coefficient (Kg)
Kg = 1 - [ ar / (1200 + 300 * ar) ] * [ h / tw - 2550 / Ö fcr ]
= 1.09
h. Cross sectional nominal moment (Mn)
Mn = Kg * S * fcr
= 310,982,774 Nmm
Nominal Moment Based by Local Buckling on Flange
a. Slenderness of the flange section (lG)
lG = bf / (2 * tf)
= 7.69
b. Web slenderness factor (ke)
ke = 4 / Ö ( h / tw )
= 0.575 < 0.763
be used for the value of ke = 0.5751
c. Slenderness limit for the maximum cross-sectional
Compact cross section = lp = 0.38 * √ (E/fy)
= 10.97
Non-Compact cross section = lr = 1.35 * √ (ke * E/fy)
= 29.55
lG < lp dan lG < lp
Based on flange slenderness value, cross section type is compact
d. Reference stress for local torsional buckling moment (f c)
fc = fy / 2
= 120.00 Mpa
fc < fy , so the value of fc is 120 Mpa
e. Cross-section critical stress is as follows:
If lG ≤ lp
fcr = fy = 240 Mpa
If lp < l G ≤ lr
fcr = Cb* fy*[ 1 - ( lG - lp) ( 2*( lr - lp)) ] = - Mpa
If lG > lr
fcr = fc * ( lr / lG )2 = - Mpa
so use the value of the critical stress cross-section is 240 Mpa
fcr < fy , so the value of fcr is 240 Mpa
f. Elastic section modulus (S)
S = Sx
= 1,190,000 mm
g. Walled full web coefficient (Kg)
Kg = 1 - [ ar / (1200 + 300 * ar) ] * [ h / tw - 2550 / Ö fcr ]
= 1.09
h. Cross sectional nominal moment (Mn)
Mn = Kg * S * fcr
= 310,982,774 Nmm
1.6.2.8 Lateral Buckling Effect on Nominal Moment
Nominal moment component structures with lateral buckling effect is calculated as
follows :
a. Short Span (L ≤ Lp)
Mn = Mp = f y * Zx
b. Medium Span (Lp ≤ L ≤ Lr)
Mn = Cb * [ Mr + ( Mp - Mr ) * ( Lr - L ) / ( Lr - Lp ) ] ≤ Mp
c. Long Span (L > Lr)
Mn = Cb * p/L*√ [E * Iy * G * J + (p * E/L )2 * Iy * Iw] ≤ Mp
d. The maximum span length of the beam is able to hold the plastic moment (Lp)
Lp = 1.76 * ry * √ ( E / fy )
= 2306.63 mm
e. The difference between the yield stress and residual stress (f L)
fL = fy - fr
= 125 Mpa
f. Minimum length of span beam durability critical buckling moment determined by lateral
torsional (Lr)
Lr = ry * X1 / fL * √ [ 1 + √ ( 1 + X2 * fL2 ) ]
= 8,398.14 mm
g. Lateral torsional buckling moment coefficient (C b)
Cb = 12.5 * Mux / ( 2.5*Mux + 3*MA + 4*MB + 3*MC )
= 1.18
h. Plastic moment (Mp)
Mp = f y * Zx
= 308,628,480 Nmm
i. Bending moment (Mr)
Mr = Sx * ( fy - fr )
= 148,750,000 Nmm
j. Distance between the lateral bracing (L)
L = Ly
= 4,000 mm
Of calculation, obtained the following results :
L > Lp dan L < Lr
thus belongs to the category : medium span
Nominal moment ois calculated as follows :
Mn = M p = f y * Zx = - Nmm
Mn = Cb * [ Mr + ( Mp - Mr ) * ( Lr - L )/( Lr - Lp ) ] = 311,721,646 Nmm
Mn = Cb*p/L* √[E*Iy*G*J + (p*E/L )2 * Iy * Iw ] = - Nmm
Mn = 311,721,646 Nmm
So the nominal moment of medium span structure is at 311,721,646 Nmm
Mnx > Mpx, so the nominal moment for this case is used for 308,628,480
Nmm
1.6.2.10 Bending Moment Durability
a. Nominal moment due to local buckling = 276,746,079 Nmm
b. Nominal Moment On a Full-walled Beams
Nominal Moment due to Lateral Torsional Buckling = 310,982,774 Nmm
Nominal Moment due to Local Buckling on Flange = 310,982,774 Nmm
c. Lateral Buckling Effect on Nominal Moment = 308,628,480 Nmm
The smallest Mn value is taken from the whole calculation, and the result is :
Mn = 308,628,480 Nmm
Bending moment durability = fb * Mn
= 277,765,632 Nmm
Safety control : Mu £ f b * Mn
160,000,000 < 277,765,632 (SAFE)
Mu / ( f b * M n ) = 0.576 < 1.0 (OK)
1.6.2.15 Shear Durability
Web plate thickness without stiffenes must be qualified with the following condition :
h2/tw £ 6.36 * Ö ( E / fy )
42.75 < 183.6 (Qualified)
a. Cross sectional area (Aw)
Aw = tw * ht
= 3200 mm2
b. Nominal shear force durability
Vn = 0.60 * fy * Aw
= 460800 N
c. Shear force durability
ff * Vn = 345600 N
Control : Vu ≤ ff * Vn
60,000 > 345,600 (SAFE)
Vu / ff * Vn = 0.174 < 1.0 (OK)
1.6.2.16 Interaction of Shear and Bending Moment
Elements that carry a combination of shear and bending should be controlled with the
following requirements :
Mu / ( fb * Mn ) + 0.625 * Vu / ( ff * Vn ) ≤ 1.375
0.685 < 1.375 (SAFE)
SIZE
NO SIZE A B C
mm in mm in mm
1 C.200.75.20.3,2 200 7.874 75 2.953 20
2 C.150.75.20.4,5 150 5.906 75 2.953 20
3 C.150.65.20.3,2 150 5.906 65 2.559 20
4 C.150.50.20.4,5 150 5.906 50 1.969 20
5 C.150.50.20.3,2 150 5.906 50 1.969 20
6 C.150.50.20.2,3 150 5.906 50 1.969 20
7 C.125.50.20.4,5 125 4.921 50 1.969 20
8 C.125.50.20.4,0 125 4.921 50 1.969 20
9 C.125.50.20.3,2 125 4.921 50 1.969 20
10 C.125.50.20.2,3 125 4.921 50 1.969 20
11 C.100.50.20.4,5 100 3.937 50 1.969 20
12 C.100.50.20.4,0 100 3.937 50 1.969 20
13 C.100.50.20.3,2 100 3.937 50 1.969 20
14 C.100.50.20.2,6 100 3.937 50 1.969 20
15 C.100.50.20.2,3 100 3.937 50 1.969 20
16 C.100.50.20.1,6 100 3.937 50 1.969 20
17 C.75.45.15.2,3 75 2.953 45 1.772 15
18 C.75.45.15.1,6 75 2.953 45 1.772 15
19 C.60.30.10.2,3 60 2.362 30 1.181 10
20 C.60.30.10.1,6 60 236.200 30 1.181 10
ZE CENTER OF
SECTION AREA WEIGHT
C t Cx
in mm in cm² in² kg/m kg/ft lb/ft cm
0.787 3.2 0.126 11.810 1.831 9.270 2.824 6.229 0
0.787 4.5 0.177 13.970 2.165 11.000 3.351 7.392 0
0.787 3.2 0.126 9.567 1.483 7.510 2.288 5.047 0
0.787 4.5 0.177 11.720 1.817 9.200 2.802 6.182 0
0.787 3.2 0.126 8.607 0.207 6.760 2.059 4.543 0
0.787 2.3 0.150 6.322 0.980 4.960 1.511 3.333 0
0.787 4.5 0.177 10.590 1.641 8.320 2.534 5.591 0
0.787 4 0.157 9.548 1.480 7.500 2.285 5.040 0
0.787 3.2 0.126 7.807 1.210 6.130 1.867 4.119 0
0.787 2.3 0.150 5.747 0.891 4.510 1.374 3.031 0
0.787 4.5 0.177 9.469 1.468 7.430 2.263 4.993 0
0.787 4 0.167 8.548 1.325 6.710 2.044 4.509 0
0.787 3.2 0.126 7.007 1.086 5.500 1.675 3.696 0
0.787 2.6 0.102 5.796 0.898 4.550 1.386 3.057 0
0.787 2.3 0.091 5.172 0.802 4.060 1.237 2.728 0
0.787 1.6 0.063 3.672 0.569 2.880 0.877 1.935 0
0.591 2.3 0.091 1.170 0.641 3.250 0.990 2.184 0
0.591 1.6 0.063 2.952 0.458 2.320 0.707 1.559 0
0.394 2.3 0.091 2.872 0.445 2.250 0.685 1.512 0
0.394 1.6 0.063 2.072 0.321 1.630 0.496 1.095 0
CENTER OF GRAVITY MOMENT OF INERTIA RADIUS OF GYRATION
Cx Cy Ix Iy ix
in cm in cm4 in4 cm4 in4 cm in
0 2.270 0.894 721.000 17.320 87.500 2.102 7.770 3.059
0 2.500 0.984 489.000 11.750 99.200 2.383 5.920 2.331
0 2.110 0.131 332.000 7.976 53.800 1.293 5.890 2.319
0 1.540 0.604 368.000 8.841 35.700 0.858 5.600 2.205
0 1.540 0.604 280.000 6.727 28.300 0.680 5.710 2.248
0 1.550 0.610 210.000 5.045 21.900 0.526 5.770 2.272
0 1.680 0.661 238.000 5.718 33.500 0.805 4.740 1.866
0 1.680 0.661 217.000 5.213 33.100 0.795 4.770 1.878
0 1.680 0.661 181.000 4.349 26.600 0.639 4.820 1.898
0 1.690 0.665 137.000 3.291 20.600 0.495 4.880 1.921
0 1.860 0.732 139.000 3.339 30.900 0.742 3.820 1.504
0 1.860 0.732 127.000 3.051 28.700 0.690 3.850 1.516
0 1.860 0.732 107.000 2.571 24.500 0.589 3.900 1.535
0 1.860 0.732 89.700 2.155 21.000 0.509 3.930 1.547
0 1.860 0.732 80.700 1.939 19.000 0.456 3.950 1.555
0 1.870 0.736 58.400 1.403 14.000 0.336 3.990 1.571
0 1.720 0.677 37.100 0.891 11.800 0.283 3.000 1.181
0 1.720 0.677 27.100 0.651 8.710 0.209 3.030 1.193
0 1.060 0.417 15.600 0.375 3.320 0.080 2.330 0.917
0 1.060 0.417 11.600 0.279 2.560 0.062 2.370 0.933
ADIUS OF GYRATION SECTION MODULUS
iy Zx Zy
cm in cm³ in³ cm³ in³
2.710 1.067 72.100 4.400 16.800 1.025
2.660 1.047 65.200 3.979 19.800 1.208
2.370 0.933 44.300 2.703 12.200 0.744
1.750 0.689 49.000 2.990 10.500 0.641
1.810 0.713 37.400 2.282 8.190 0.031
1.860 0.772 28.000 1.709 6.330 0.513
1.780 0.701 38.000 2.319 10.100 0.616
1.810 0.713 34.700 2.117 9.380 0.572
1.850 0.728 29.000 1.770 8.020 0.489
1.890 0.783 21.900 1.336 6.220 0.520
1.810 0.713 27.700 1.690 5.820 0.599
1.830 0.720 25.400 1.550 9.130 0.557
1.870 0.736 21.300 1.300 7.810 0.477
1.900 0.748 17.900 1.092 6.680 0.408
1.920 0.756 16.100 0.982 6.060 0.370
1.950 0.768 11.700 0.714 4.470 0.273
1.090 0.665 9.900 0.604 4.240 0.259
1.720 0.677 7.240 0.442 3.130 0.191
1.070 0.421 5.200 0.317 1.710 0.104
1.110 0.437 3.880 0.237 1.320 0.081
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- N12192.1a-C-0-000-1-01-0 Civil Design Basis Rev-0Documento18 pagineN12192.1a-C-0-000-1-01-0 Civil Design Basis Rev-0Anonymous 3kDy7eNessuna valutazione finora
- Show Section PropertiesDocumento3 pagineShow Section PropertiesCon Can100% (1)
- Structures of Gas Station in Saint PetersburgDocumento97 pagineStructures of Gas Station in Saint PetersburgassdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anchor Bolt Design (AISC) - Tt100Documento2 pagineAnchor Bolt Design (AISC) - Tt100Jennifer HudsonNessuna valutazione finora
- 16MST0038 Thesis Final PDFDocumento54 pagine16MST0038 Thesis Final PDFSrivatsanHariharanNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Aids of Flexural Members and Beam Columns Based On Limit State Method PDFDocumento16 pagineDesign Aids of Flexural Members and Beam Columns Based On Limit State Method PDFscshekarNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Material 8.8: (Table J3.2)Documento4 pagineI. Material 8.8: (Table J3.2)Anh KyNessuna valutazione finora
- Repport Steel Structure PDFDocumento111 pagineRepport Steel Structure PDFAnonymous fxqnhfKNessuna valutazione finora
- Tubular Profiles For Telecom Structures PDFDocumento8 pagineTubular Profiles For Telecom Structures PDFJitendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Design of Box CulvertsDocumento24 pagineStructural Design of Box Culvertsdanilo m.sampagaNessuna valutazione finora
- RCC14 Crack Width PDFDocumento1 paginaRCC14 Crack Width PDFmdelacua2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Description of Problem Values Units: Infomile SolutionsDocumento3 pagineReference Description of Problem Values Units: Infomile SolutionsdhawanaxitNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Well Staircase Design Excel SheetDocumento5 pagineOpen Well Staircase Design Excel SheetPeter KinyanjuiNessuna valutazione finora
- Shear Lug Verification Example 2Documento1 paginaShear Lug Verification Example 2Nasrul AdliNessuna valutazione finora
- Frame Analysis Moment Distribution MethodDocumento49 pagineFrame Analysis Moment Distribution MethodJuNe RaMos JavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Circular Wall (Tank Wall) : Case: 1 Only Water From InsideDocumento6 pagineDesign of Circular Wall (Tank Wall) : Case: 1 Only Water From InsidecivilceejiNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Primary Beam Is Rested On Secondary Beam How To Define in Staad ProDocumento4 pagineHow To Primary Beam Is Rested On Secondary Beam How To Define in Staad ProseshukvsNessuna valutazione finora
- F3-Piperack Footing DesignDocumento6 pagineF3-Piperack Footing DesignRahul PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Slab Foundation Design 1Documento6 pagineSlab Foundation Design 1Renato ZanescoNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophy of Limit State Design and Classification of SectionsDocumento96 paginePhilosophy of Limit State Design and Classification of Sectionsybm987100% (1)
- Nib CalculationDocumento1 paginaNib CalculationKen LuuNessuna valutazione finora
- Staad PRODocumento7 pagineStaad PROThomas John Doblas AgrabioNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Story Drift in ETABS PDFDocumento10 pagineBuilding Story Drift in ETABS PDFntirugiribambeNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthquake Resistant StructuresDocumento6 pagineEarthquake Resistant StructuresAmith KeshvtakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Seismic Response of Elevated Water Tanks An OverviewDocumento5 pagineSeismic Response of Elevated Water Tanks An OverviewRaeghoNessuna valutazione finora
- Providing and Fixing Noise Barriers on Flyovers in MumbaiDocumento113 pagineProviding and Fixing Noise Barriers on Flyovers in MumbairohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Truss Tower R2 PDFDocumento41 pagineDesign Truss Tower R2 PDFPrashant HuddarNessuna valutazione finora
- IS 875 1987 Part-3 PDFDocumento63 pagineIS 875 1987 Part-3 PDFPrabesh Kc100% (2)
- Crack Width Calculation for Bottom Slab SectionDocumento2 pagineCrack Width Calculation for Bottom Slab SectionPitolwala ZuzarNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.5 Design of Precast Protection Slab 6.5.1 Materials: Job: Made by Sheet No. Total Sh. Set No. Date Rev. No. Job NoDocumento47 pagine6.5 Design of Precast Protection Slab 6.5.1 Materials: Job: Made by Sheet No. Total Sh. Set No. Date Rev. No. Job NobalaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Cable Trench Installation GuideDocumento12 pagineCable Trench Installation GuideTimothy LeonardNessuna valutazione finora
- Plate Girders with Corrugated Webs AnalysisDocumento6 paginePlate Girders with Corrugated Webs AnalysisLệnh BùiNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Appraisal of Existing 90m Lattice TowerDocumento28 pagineStructural Appraisal of Existing 90m Lattice TowerEngr Kelechi EthelNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Interaction of Machine FoundationsDocumento262 pagineDynamic Interaction of Machine FoundationsSayed ElarabyNessuna valutazione finora
- Load Combination For Steel Design Per BS en 1990 EditionDocumento2 pagineLoad Combination For Steel Design Per BS en 1990 EditionAsaru Deen100% (1)
- Flat Slab Punching Shear Check r1Documento5 pagineFlat Slab Punching Shear Check r1Usama ChauguleNessuna valutazione finora
- Dimensional Solutions Mat3DDocumento69 pagineDimensional Solutions Mat3DTimothy HancockNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Tube End Plate Calculation PDFDocumento4 pagineCircular Tube End Plate Calculation PDFALPHYL BALASABASNessuna valutazione finora
- Skylight StructureDocumento16 pagineSkylight Structuremsiddiq1Nessuna valutazione finora
- DG FoundationDocumento1 paginaDG FoundationVysakh RNessuna valutazione finora
- CE8501 Notes PDFDocumento53 pagineCE8501 Notes PDFprem rajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bs5950 Calculation Decking SheetDocumento6 pagineBs5950 Calculation Decking SheetKho C Ahl100% (1)
- Concrete Foundation DesignDocumento3 pagineConcrete Foundation DesignPradeep Kumar SukumaranNessuna valutazione finora
- New Doha International Airport GSE Vehicle Washing Bay Design CalculationsDocumento182 pagineNew Doha International Airport GSE Vehicle Washing Bay Design CalculationsHema Chandra IndlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Calcualtion of Tower Foundation - 24.12.18Documento14 pagineDesign Calcualtion of Tower Foundation - 24.12.18Sougata DuttaNessuna valutazione finora
- Section A-A: Wall Cheq'D PlateDocumento1 paginaSection A-A: Wall Cheq'D PlateAL BASTAKI CONTRACTING L.L.C.50% (2)
- Laboratory Test Frequency LGEDDocumento6 pagineLaboratory Test Frequency LGEDmohammed nusrot hossanNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation Note of Coulmn 162Documento18 pagineCalculation Note of Coulmn 162Der3'am Al m7armehNessuna valutazione finora
- Offshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsDa EverandOffshore Mechanics: Structural and Fluid Dynamics for Recent ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Member Size Check StabilityDocumento66 pagineMember Size Check StabilityUp RianNessuna valutazione finora
- Gording & TreckstangDocumento10 pagineGording & TreckstangHendra CenNessuna valutazione finora
- Annexure-2 (Section Design Calcs)Documento107 pagineAnnexure-2 (Section Design Calcs)blisscutest beagleNessuna valutazione finora
- Busugan Part 2 Design BSDSDocumento257 pagineBusugan Part 2 Design BSDSmarco miguelNessuna valutazione finora
- Stair KagiggrDocumento8 pagineStair KagiggrRabin BhattaraiNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculate Strength of Roof GirderDocumento11 pagineCalculate Strength of Roof Girdervicky kakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Camber by Coefficients of Pci-Bridge Design ManualDocumento4 pagineCamber by Coefficients of Pci-Bridge Design ManualFAIZAN AHMED100% (1)
- Calculation - Pierhead - Jembatan KIT BatangDocumento9 pagineCalculation - Pierhead - Jembatan KIT Batanghanif ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of PurlinsDocumento10 pagineDesign of PurlinsFranklyn GenoveNessuna valutazione finora
- Plat Bawah: Perhitungan Gorong-GorongDocumento16 paginePlat Bawah: Perhitungan Gorong-GorongTombakNessuna valutazione finora
- Schmid - Stability and Transition in Shear Flows PDFDocumento561 pagineSchmid - Stability and Transition in Shear Flows PDFBrenda GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepared By: Mr. Harsh PanchalDocumento46 paginePrepared By: Mr. Harsh PanchalKáûshàl PãtëlNessuna valutazione finora
- Form No.2Documento4 pagineForm No.2sibasish patelNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Clauses Reconsidered: Not So Small and Not All Alike: Barbara CitkoDocumento35 pagineSmall Clauses Reconsidered: Not So Small and Not All Alike: Barbara CitkoEl imam Zine-eddineNessuna valutazione finora
- Artemis Validation v8p4Documento35 pagineArtemis Validation v8p4De Jesus, AlexanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Asphalt Temperature Test ReportDocumento21 pagineAsphalt Temperature Test ReportDede NurcahyadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Afd Aa 2020Documento51 pagineAfd Aa 2020Nguyen Co ThachNessuna valutazione finora
- Manar Steel Waler SystemDocumento56 pagineManar Steel Waler Systemtarek.fileNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.3.5 PreHeat TrainDocumento20 pagine1.3.5 PreHeat TrainflowealthNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelton Turbine ExperimentDocumento6 paginePelton Turbine ExperimentvedNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Conductors and Insulators?Documento14 pagineWhat Are Conductors and Insulators?maria esperanza quilaNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2022 Paper 3Documento48 pagineJune 2022 Paper 3Charbel El habrNessuna valutazione finora
- Second-Order RLC Circuits ExplainedDocumento5 pagineSecond-Order RLC Circuits ExplainedAmiel Hana Lem ManaloNessuna valutazione finora
- S1 - Lesson 6 (Context Clues) - QDocumento6 pagineS1 - Lesson 6 (Context Clues) - QMuhammad Harist MurdaniNessuna valutazione finora
- DCM Jhs 8scienceDocumento12 pagineDCM Jhs 8scienceJogil ParaguaNessuna valutazione finora
- Leaf Area Estimation of Anacardium HumileDocumento8 pagineLeaf Area Estimation of Anacardium HumileAngelita SoaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Sound SummaryDocumento2 pagineSound Summaryhweta173Nessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study of A 13-Year-Old Boy Suffering From DepressionDocumento66 pagineCase Study of A 13-Year-Old Boy Suffering From Depressionvamp blackroseNessuna valutazione finora
- Patterns and Numbers in NatureDocumento5 paginePatterns and Numbers in NatureAlethea PayabyabNessuna valutazione finora
- Guided Wave Radar in Steam Boiler Service: Measuring Water Level Accurately Despite ChallengesDocumento14 pagineGuided Wave Radar in Steam Boiler Service: Measuring Water Level Accurately Despite ChallengesRoger SeaverNessuna valutazione finora
- Solved Problems - Design of Cam Clutches and BrakesDocumento9 pagineSolved Problems - Design of Cam Clutches and BrakesSashankNiroulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Perubahan EnthalpiDocumento1 paginaPerubahan EnthalpiTetty Arsety GuluhNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento60 pagineChapter 2Fatih İnalNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Electric Charges and ForcesDocumento20 pagineUnderstanding Electric Charges and Forcesnouf AldosareNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading Comprehension Worksheet Albert EinsteinDocumento3 pagineReading Comprehension Worksheet Albert EinsteinAnacel Faustino100% (3)
- Grade: 6 - Mathematics Olympiad Qualifier - Set: 2Documento6 pagineGrade: 6 - Mathematics Olympiad Qualifier - Set: 2S dasNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of vertical load-bearing capacity of a single pile using GEO 5 - PILESDocumento12 pagineAnalysis of vertical load-bearing capacity of a single pile using GEO 5 - PILESjasamnajNessuna valutazione finora
- AHS Self DualityDocumento37 pagineAHS Self DualityTimothy PonepalNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper - Study Kasus Pada Sistem FlareDocumento4 paginePaper - Study Kasus Pada Sistem FlareTeknologi TermutakhirNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Physics Notes (General Properties of Waves)Documento4 pagineIGCSE Physics Notes (General Properties of Waves)Tejas RajeshNessuna valutazione finora