Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Assessment of The Peripheral Vascular System
Caricato da
Trisha Andrea DavaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Assessment of The Peripheral Vascular System
Caricato da
Trisha Andrea DavaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
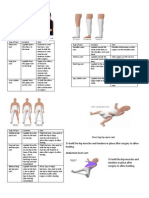
ASSESSING THE PHERIPHERAL VASCULAR SYSTEM INSPECTION
❶ Skin
- Skin color
o Normal:
No localized color changes
o Abnormal:
Pallor – Due to arterial obstruction
(obstructed blood vessel) which results to
low blood supply or less blood is going to the
leg; ISCHEMIA; Arterial insufficiency
Redness or brownish in color – due to
incompetent valves which causes the
backflow and accumulation of blood in the
veins of the lower extremities; Accumulation
of blood results in higher pressure in the
veins which causes it to distend. RBCs are
forced out of the vein [into the ISS], giving
the skin a flush of reddish color.
- Should be mobile and elastic and able to be pinched.
- Temperature should be equal.
- Extremities should be equal in size bilaterally
o Abnormal
Unilateral swelling / edema
- Veins should not be visible on the surface of the skin
o If visible, elevate lower extremities (LE).
Arteries & Veins If the veins and valves are not compromised,
the distended veins will disappear (due to
the incompetent valves)
If veins and valves are compromised, the
distended vein will remain
o Superficial veins – veins found beneath the skin
common veins on the LE: Greater
Saphenous, and Lesser Saphenous Vein—
dorsal.
Capillaries
- Very thin walls (one layer of tissue)
- Allows diffusion materials across capillary: O2, CO2, H2O, and Fluid
waste
Aneurysm
- For smokers, o Deep veins
o Nicotine causes vasoconstriction which results in Brachial artery – divides into radial and ulnar
increase of BP. arteries
- For patient’s that have Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA),
o Causes pulsations
When assessing, it should be on a supine
position and eye level.
When not seen, ultrasound is done.
Controlled by anti-hypertensive drug.
o AAA has more cases with 75%, whereas Thoracic Aortic
Aneurysm with 25%.
- Also related to chronic hypertension
- Obesity, pregnancy and ascites makes it hard to see pulsation.
Ultrasound is done.
Femoral artery – found in the groin area
Ascites
- It is the accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity— with plenty
visceral and subcutaneous fats.
Popliteal artery – at the dorsal side of the
knee → Buerger Test
- Position: supine and sitting
- (+) sign: 1-2 mins. before the color comes back (becomes blue then
red)
- Significance: poor arterial blood supply
- Procedure: elevate the leg at 45-degree for at least 3 minutes, foot
blanches. Position is then place at short-sitting
Dorsalis pedis – at the dorsal side of the foot
Inspect and palpate when leg
extremities are (+) pallor,
together with the posterior tibial
artery
❹ Spider Veins
- The valve is incompetent, weakened walls, and back flow of blood
- It will give you edema
❺ Varicose skin/Varicosity
- Distended vein that is greenish-bluish in color
- Damaged valves allow backflow of the blood
- This condition is hereditary
- Female are more susceptible due to the estrogen which weakens
the walls of the vein
❻ Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
- Reddish, hard and warm to touch, and swelling
- Those patients who are in supine position for more than 3 days are
more susceptible on having DVT
- No lesions visible o It is due to the blood that is stagnant allowing solid
o Abnormal if lesions don’t heal easily elements (platelets) to clump together which forms
o If there is a lesion, classify it: clotted blood thus, the blood does not go up
Petechiae— small red dots; common in - Should be suspected if there is:
dengue fever o Pain
Ecchymosis— bruise-like, larger than o Swelling
purpura o Tenderness over vein
Purpura— snake bites - Turn client side to side or perform compression stocking
❷ Hair - Observe the lower extremities for any manifestations of arterial
- Hair distribution insufficiency and obstruction
o If hair growth is evident, it should be equal in - A thrombus in the vein can dislodge (embolus) and will flow with
distribution bilaterally. the blood back to the superior or inferior vena cava to the heart
o Person with ischemia has less hair or no hair at all. and to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries, thus causing
Patient with arterial insufficiency will have PULMONARY EMBOLISM
hairless shiny skin on the legs
Due to lack of blood supply that ASSESSMENT TESTS
brings oxygen and nutrients to Trendelenburg Test
the hair follicles for hair growth. o Purpose: to assess the competence of the valves
❸ Nails o LE is elevated to allow venous blood to empty
- If the nails are dead / brittle, there is low blood supply which results o A tourniquet on the thigh will prevent backflow
to low oxygen and nutrients. o After 20 to 30 seconds, remove the tourniquet
o Competent valves – there will be a slow filling of blood
o Damaged valves – immediate filling of blood and veins
will distend (within 5 seconds)
o Tourniquet is applied to 1. Prevent backflow of blood,
and 2. To temporarily stop the blood flow
❸ Pitting edema
- Indentations
❼ Arterial occlusion
- Most common cause of occlusion is fats/lipids
Position Change Test
o Elevate the leg/s 12 in above the heart
o Dangle the leg beside the bed
o After 15 s, the leg/s should return into its normal pinkish
color – veins
o After 10s or less – artery
o If occlusion has been shown in developing, there will be
more likely conditions like the ff:
Muscle atrophy
Skin atrophy
Loss of hair growth
PALPATION
❶ Capillary Refill Time
- Normal
o Normal pinkish color will return after 1-3 seconds
- Abnormal
o More than 3 seconds (in people with Peripheral ❹ Bruit sound
Vascular Disease or PVD) - Done during hemodialysis
❷ Radial artery and Dorsalis pedis artery - Presence of arteriovenous fistula
- Most distal pulses
- Palpate using the 1st and 2nd finger pads
- AMPLITUDE
o Quality of pulse is the measurement of the force of
ventricular contraction that produces pulse wave
o Tests the integrity of the arterial wall
+3 Full/bounding pulse
+2 Expected
+1 Diminished/barely palpable
0 Absent pulse
Allen’s Test
o Assesses for the
Competency
Patency
Adequate collateral circulation of blood
o Radial artery
Supplies the thumb and the lateral side of ELDERLY
the index finger - Higher blood pressure due to blood vessels being LESS ELASTIC and
o Ulnar artery RIGID due to CALCIUM and FAT DEPOSITS
Supplies the remaining digits and the medial - Increase PERIPHERAL VASCULAR RESISTANCE
side of the index finger
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Complication of PregnancyDocumento44 pagineComplication of PregnancyJharaNessuna valutazione finora
- AnusRectumProstateExamDocumento24 pagineAnusRectumProstateExamLyn Mende100% (1)
- BPH Case HistoryDocumento4 pagineBPH Case HistoryChino Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional AssessmentDocumento33 pagineFunctional AssessmentGrace Sam100% (2)
- 9 Tips On How To Make A Good SOAPIEDocumento7 pagine9 Tips On How To Make A Good SOAPIEMagbanua Airene MarielNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To The Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento39 pagineIntroduction To The Musculoskeletal SystemdesyNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical PaperDocumento18 pagineClinical PaperlhhjklllNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Edited)Documento82 pagineComprehensive Edited)mikrobyo_ng_wmsuNessuna valutazione finora
- Process of ConceptionDocumento42 pagineProcess of ConceptionimnasNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care of The Child With Respiratory DysfunctionDocumento54 pagineNursing Care of The Child With Respiratory DysfunctionAlexis Coronado100% (1)
- ASSESSMENT OF MUSCULO-SKELETAL SYSTEMDocumento33 pagineASSESSMENT OF MUSCULO-SKELETAL SYSTEMRubin100% (1)
- Health Assessment: Nursing ProcessDocumento7 pagineHealth Assessment: Nursing ProcessAngelrica TumbadoNessuna valutazione finora
- FNCP EditedDocumento4 pagineFNCP EditedCRISTINE DE LOS REYESNessuna valutazione finora
- CastDocumento2 pagineCastpoppysmic11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Health: Health Assessment Lecture ReviewerDocumento22 pagineHealth: Health Assessment Lecture RevieweryanNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Analysis RLE MODULE TEMPLATE Nursery 1 (One)Documento7 pagineCase Analysis RLE MODULE TEMPLATE Nursery 1 (One)PanJan BalNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Skills ChecklistDocumento6 pagineNursing Skills Checklistapi-433883631Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Rubric 807Documento5 pagineNursing Care Plan Rubric 807KeishaAaliyah100% (1)
- 3c-Abas, Alexander Miguel M. (Ncm117 Rle - Self-Awareness Activity)Documento5 pagine3c-Abas, Alexander Miguel M. (Ncm117 Rle - Self-Awareness Activity)alexander abasNessuna valutazione finora
- Head To AssessmentDocumento10 pagineHead To AssessmentUtayde Cassey FaithNessuna valutazione finora
- C C C M MMMM MM M MMM 3mm MMMMM MM M MMMMMDocumento4 pagineC C C M MMMM MM M MMM 3mm MMMMM MM M MMMMMjohkieNessuna valutazione finora
- Skin - Hair.Nails Head & Neck Eyes. Ears. Nose. Sinuses Mouth. PharynxDocumento92 pagineSkin - Hair.Nails Head & Neck Eyes. Ears. Nose. Sinuses Mouth. PharynxAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAO100% (1)
- Preparing The Sterile Field PPT June 2011Documento61 paginePreparing The Sterile Field PPT June 2011gerard_xucnNessuna valutazione finora
- Activities Independence: (1 Point) NO Supervision, Direction or Personal Dependence: (0 Points) WithDocumento4 pagineActivities Independence: (1 Point) NO Supervision, Direction or Personal Dependence: (0 Points) WithLore Anne Mhae SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Informatics Competencies Self-Assessment and Plan of ActionDocumento2 pagineNursing Informatics Competencies Self-Assessment and Plan of Actionboxed juiceNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan2Documento3 pagineNursing Care Plan2gaeLtorvzNessuna valutazione finora
- TFN Bullets 2Documento13 pagineTFN Bullets 2Riam Carl AgunosNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal DisordersDocumento166 pagineMusculoskeletal DisordersTalosig Donaville50% (2)
- Assessment of The EYEDocumento8 pagineAssessment of The EYENins ArgallonNessuna valutazione finora
- FDARDocumento17 pagineFDARLylibette Anne CalimlimNessuna valutazione finora
- Proper Excreta Disposal, Food Safety and Environmental HealthDocumento15 pagineProper Excreta Disposal, Food Safety and Environmental HealthEden LacsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrocephalus and Spina Bifida: Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and ManagementDocumento63 pagineHydrocephalus and Spina Bifida: Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and ManagementAjeng Aristiany Rahawarin100% (2)
- Assessing The IntegumentaryDocumento73 pagineAssessing The IntegumentaryHelena Meurial HilkiahNessuna valutazione finora
- CASTING GUIDEDocumento16 pagineCASTING GUIDESheena Flores Abuga-a100% (1)
- Physical AssessmentDocumento3 paginePhysical AssessmentEjie Boy IsagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Leopold'S Maneuver: DefinitionDocumento3 pagineLeopold'S Maneuver: DefinitionJyra Mae TaganasNessuna valutazione finora
- Ear, Nose and Throat (Ent) AssessmentDocumento6 pagineEar, Nose and Throat (Ent) AssessmentObama kindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocumento34 pagineSexually Transmitted InfectionsMariana Creciun100% (1)
- HandwashingDocumento35 pagineHandwashingJoyce Catherine Buquing UysecoNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical Instruments: Grasping and Clamping Retracting Cutting and Dissecting Probing and DilatingDocumento55 pagineSurgical Instruments: Grasping and Clamping Retracting Cutting and Dissecting Probing and DilatingCathreen Agatha Fule100% (1)
- Fracture (Cast Care)Documento6 pagineFracture (Cast Care)Vane UcatNessuna valutazione finora
- Bag technique – essential public health toolDocumento5 pagineBag technique – essential public health toolblue14jojoNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical AssessmentDocumento90 paginePhysical AssessmentReann LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cultural Factor/ethnicity Such As Regard For Elders, Perception of HealthDocumento3 pagineCultural Factor/ethnicity Such As Regard For Elders, Perception of HealthQueency Jane Ursulum100% (1)
- Health Assessment and Physical ExaminationDocumento5 pagineHealth Assessment and Physical Examinationmrsfelic08Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of The BreastDocumento14 pagineAssessment of The BreastArlyn MendenillaNessuna valutazione finora
- TAHBSO Procedure ExplainedDocumento14 pagineTAHBSO Procedure ExplainedDafny CzarinaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Part 1Documento20 pagine01 Part 1api-3859513Nessuna valutazione finora
- III. Physical Assessment FindingsDocumento8 pagineIII. Physical Assessment FindingsBilly Joe SincoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 122 Ratio FinalsDocumento2 pagineNCM 122 Ratio FinalsLorenz Jude CańeteNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Nursing (Midterm Topic 1)Documento7 pagineFundamentals of Nursing (Midterm Topic 1)Manuel, Precious Marie B.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tinitti Balance Assessment ToolDocumento2 pagineTinitti Balance Assessment Toolcpradheep100% (2)
- Assessment of The Breast: Jonalyn Sotero Esco RN., MANDocumento41 pagineAssessment of The Breast: Jonalyn Sotero Esco RN., MANVan MaverickNessuna valutazione finora
- Breast AssessmentDocumento2 pagineBreast AssessmentTeanu Jose Gabrillo TamayoNessuna valutazione finora
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Template: SBAR - Postpartum Care SDocumento2 pagineThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Template: SBAR - Postpartum Care SAira Leigh MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Malaria PosterDocumento1 paginaMalaria PosterTommaso ForzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cues Problem Physiologic Behavioral: Date Identified: July 19, 2016 Subjective CuesDocumento2 pagineCues Problem Physiologic Behavioral: Date Identified: July 19, 2016 Subjective CuesitsmeayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Progress RecordDocumento3 pagineFamily Progress RecordMary SutingcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebstein Anomaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDa EverandEbstein Anomaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Superficial Vein Thrombosis - 29aug2020Documento5 pagineSuperficial Vein Thrombosis - 29aug2020Luis octavio carranzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Varicose VeinDocumento22 pagineVaricose VeinArslan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- European Guidelines On Perioperative Venous.4Documento6 pagineEuropean Guidelines On Perioperative Venous.4Mihai stancaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nizatul Mumtazah - 1706013371 - Remedial Jurnal DVTDocumento13 pagineNizatul Mumtazah - 1706013371 - Remedial Jurnal DVTnizaNessuna valutazione finora
- A study on prevention of deep vein thrombosis among high risk hospitalized clientsDocumento29 pagineA study on prevention of deep vein thrombosis among high risk hospitalized clientssr.kumariNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pre-Travel Consultation: An OverviewDocumento4 pagineThe Pre-Travel Consultation: An OverviewintanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anticoagulant BookletDocumento69 pagineAnticoagulant BookletTarek SameerNessuna valutazione finora
- Emergency in Vascular SurgeryDocumento74 pagineEmergency in Vascular Surgerysteven andreanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pub 004721 PDFDocumento42 paginePub 004721 PDFRenee Jessee Anthony LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Mayo ClinicDocumento338 pagineMayo Clinicrajkumarss87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Thrombophlebitis 1Documento8 pagineThrombophlebitis 1Aya Rugaiyah AlkaffNessuna valutazione finora
- EdemaDocumento13 pagineEdemaNUR ZAMZAM AZIZAHNessuna valutazione finora
- Fondaparinux Guidelines 1Documento2 pagineFondaparinux Guidelines 1Tri Purma SariNessuna valutazione finora
- Patofisiologi SN Tromboembolic DiseaseDocumento8 paginePatofisiologi SN Tromboembolic DiseaseMulyono Aba AthiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Postpartum Head To Toe Assessment/ Bubble HeDocumento2 paginePostpartum Head To Toe Assessment/ Bubble HeJariel CatacutanNessuna valutazione finora
- Thrombosis Risk Factor Assessment FormDocumento3 pagineThrombosis Risk Factor Assessment Formpanel.anuphospitalNessuna valutazione finora
- Complications of Ischemic StrokeDocumento40 pagineComplications of Ischemic StrokeVitas HaryantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Stroke: Prsented By-Raymol Dagani (Iv) Yearbpth Stefee Gomes (Iv) YearbpthDocumento20 pagineStroke: Prsented By-Raymol Dagani (Iv) Yearbpth Stefee Gomes (Iv) YearbpthShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Care Goals and ObjectivesDocumento28 pagineCritical Care Goals and ObjectivesjyothiNessuna valutazione finora
- Thrombosis Prevention by SlidesgoDocumento67 pagineThrombosis Prevention by SlidesgoRohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Isometric Exercise of Quadriceps and Gluteal Muscle in Patient With Close Femur FractureDocumento8 pagineIsometric Exercise of Quadriceps and Gluteal Muscle in Patient With Close Femur FractureSyamsu RizaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Mrcs SyllabusDocumento55 pagineMrcs Syllabussamuelfernando123100% (2)
- DVT Case StudyDocumento2 pagineDVT Case StudyCrystal B Costa78Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abbreviation NursingDocumento16 pagineAbbreviation NursingPeter Lucky Turiano100% (1)
- Ack Medikal Ortopedi KataloğDocumento220 pagineAck Medikal Ortopedi KataloğTCRemziCelikNessuna valutazione finora
- 114 Final Brain Dump Part 2Documento8 pagine114 Final Brain Dump Part 2kelsey jacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- Approach to Leg Edema DiagnosisDocumento4 pagineApproach to Leg Edema DiagnosisMarco Paulo Reyes NaoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Bjsports 2023 106931.fullDocumento8 pagineBjsports 2023 106931.fullDevi SiswaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions For UNSW Mock Biomed VivaDocumento67 pagineQuestions For UNSW Mock Biomed VivaReuben TangNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEST Releases New Guidelines For Antithrombotic Therapy For VTE DiseaseDocumento2 pagineCHEST Releases New Guidelines For Antithrombotic Therapy For VTE DiseaseИгорь БалдинNessuna valutazione finora