Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Construction Safety Essentials
Caricato da
Ranji DhaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Construction Safety Essentials
Caricato da
Ranji DhaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
/ Essays / Construction
Disclaimer: This work has been submitted by a student. This is not an example of the work produced by our Essay Writing Service. You can v
Any opinions, ndings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily re ect th
Industrial safety refers to the condition of being protected from physical, chemical and biological hazards that are likely to occur in any industry
tolerance level that are recognised. These preventive measures minimises the economical losses as well as health losses to a maximum extend
TERMS RELATED TO SAFETY
Security: state of being free from danger or threat
Risk: (ISO 31000) the e ect of uncertainty on objectives, whether positive or negative
Failure: Lack of success
Damage: Physical harm caused to impair its value, usefulness, or normal function.
Error: state or condition of being wrong; mistake
Accidents: unplanned incident which positive or negative
Safety: Absence of risk
Near Miss: unplanned event that had a potential to cause damage
Order
O ers Support Noti cations Sign In +44 115 966 7955
Hazard: something that can cause harm if not controlled
Outcome: harm that results from an uncontrolled hazard
LIMITATIONS OF SAFETY
Safety can be brought to an extend on a relative basis rather than giving scent percentage assurance of its non occurrence. The surety of safety
economic value and standard and norms that the company follows. Hence safety is de ned as the situation where the injuries or damage mad
TYPES OF SAFETY
Normative safety: o ered to products that meet design standard and protection.
Substantive safety: also called objective safety, where protection is o ered whether standards are met or not.
Perceived safety: subjective safety where various methods are opted based on previous risks or accident met.
Get Help With Your E
If you need assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writin
Find out more
IMPORTANCE OF SAFETY
Taking into consideration the moral, legal and nancial criteria of an industry, its safety and protection are of greater importance. It is the respo
employees and personnel who are involved or a ected by the activities of an organization, which is de ned as duty of care of the organization.
moral duty of care where as compensation or preventive or punitive e ect of law is made in legal obligations. Every accident or damage is asso
ORGANIZATION FOR SAFETY STANDARDS
American Society of Safety Engineers
Board of Certi ed Safety Professionals
System Safety Society
The Safety and Reliability Society
Canadian Society of Safety Engineering
Consumer Product Safety Commission (USA)
Environmental Protection Agency or EPA (USA)
Fédération Internationale de l’Automobile or FIA (France)
Food and Drug Administration or FDA (USA)
Health and Safety Executive (UK)
National Highway Tra c Safety Administration (USA)
National Public Safety Commission (Japan)
National Transportation Safety Board or NTSB (USA)
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (USA)
Royal Society for the Prevention of Accidents (UK)
European Aviation Safety Agency or EASA (Europe)
Trading Standards Services (UK)
SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSYTEM
Various organizations were framed to assist and encourage industry for continual improvement in employee health and safety, achieved via a
evaluation, and action for improvement, all supported by constant auditing to determine the success of e ective actions. One such guideline is
Guidelines a on occupational safety and health management systems.
Get Help With Your E
If you need assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writin
Find out more
SAFETY POLICY
It is the basic safety policy of an organisation that no activity or duty is so important that an employee must violate a safety rule or take a risk o
comply with all safety rules and are encouraged to actively participate in identifying ways to make working environment a safer place to work. S
employees and as a part of daily duties must check the workplace for unsafe conditions, watch employees for unsafe actions and take prompt
SAFETY AND HEALTH RESPONSIBILITIES
The responsibilities are distributed among managers, supervisors and employee that are being planned, executed, evaluated and modi ed.
Manager Responsibilities
Ensures that safety authority committee is formed and requisite actions are taken such as su cient employee time, supervisor support and fu
Supervisors are evaluated on the basis of their e ciency in investigation and corrective action taken to prevent hazards condition and proper r
Supervisor Responsibility
Ensure that employees are competent and initial orientation is provided of which records are maintained for all the activities, so that any chang
communicated to higher authority and necessary actions taken. It is also the responsibility of supervisor to check whether all employee have re
safe and corrections are made then and there.
Get Help With Your E
If you need assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writin
Find out more
Employee Responsibility
Responsibility of employee is to strictly follow the safety rules framed and report the respective personnel about any unsafe conditions or actio
positive attitude towards safety among co-workers, and suggestions that would bring better safety conditions to higher level personnel.
SAFETY COMMITTEE
A safety committee is formed to help employees and management work together to identify safety problems, develop solutions, review inciden
committee holds management-designated representatives and one employee-elected representative each from department, factory and outsi
themselves. If there is only one volunteer or nomination, the employees will approve the person by voice vote at a short meeting called for tha
being re-elected or replaced. In addition to the employee-elected representatives, management will designate no more than three representat
chairperson will be selected by majority vote of the committee members each year if any exception the same method will be used to select a re
RISK MANAGEMENT
It is the identi cation, assessment, and prioritization of risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, mo
maximize the realization of opportunities. The strategies to manage risk typically include avoiding the risk, transferring the risk to another part
or all of the potential or actual consequences of a particular risk.
Get Help With Your E
If you need assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writin
Find out more
The method opted are as follows:
identify, characterize hazards or threats
assess the vulnerability of critical assets to speci c threats
determine the risk
identify ways to tackle or prevent or reduce those risks
prioritize risk reduction measures based on a strategy
ANALYSIS TECHNIQUES
Analysis techniques are categorized into two: qualitative and quantitative methods. The main objective is to nd causal dependencies between
approaches focus on the cause of risk while quantitative methods aim at estimations about probabilities, rates and/or severity of consequence
expertise of the safety engineer that include failure mode and e ects analysis and fault tree analysis. In contrast model-based techniques try to
system.
HAZARD PREVENTION AND CONTROL
Eliminating Workplace Hazards
Basic Safety Rules
Job Related Safety Rules
Disciplinary Policy
Equipment Maintenance
Emergency Planning
Safety and Health Training and Education
MEASUREMENT AND EVALUATION
Monitoring and measurement – General
It should be made sure that they work, risk control measures need to be checked and criteria may include:
1. monitoring hazardous processes to ensure that implemented controls are e ective
2. inspection of plant, e.g. pressure vessels to ensure conformity with regulatory requirements
3. inspection and discussion in work areas where administrative controls are used
4. identi cation of necessary maintenance of buildings and facilities and
Get Help With Your E
If you need assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writin
Find out more
5. using equipment for monitoring and measurement of health and safety risks, that are identi ed, calibrated, maintained and stored in accord
Monitoring and measurement – Health surveillance
Monitoring the health of persons potentially exposed to hazardous substances and work environment hazards to detect adverse changes to he
This in turn help to evaluate the e ectiveness of risk controls and include the following:
1.biological testing, e.g. determination of the presence of substances or their metabolites in blood, urine or expired air
2.speci c medical tests, such as lung function tests
3. general medical examinations
4.hearing tests
Incident investigation and corrective action
It is important to report accidents and incidents so that an investigation can be carried out since hazards still exist and accidents and incidents
system. Corrective action is to be made to remove or minimise the hazard to prevent a recurrence. Basic elements that should be included are
1.identifying the cause of accidents
2.identifying and implementing the necessary corrective action
3. modifying controls necessary to avoid repetition of the incident
4. recording any changes in written procedures resulting from the corrective action.
Records and records management
It is necessary for an organization to keep records to demonstrate compliance with legislative requirements and conformance to health and sa
external ( legal) and internal (health and safety performance) requirements, health and safety management plans, hazard identi cation, risk as
employee quali cation information, information about process, product equipment, equipment inspection, maintenance and calibration recor
incidents, complaints and follow-up action, information of emergency preparedness and response, audit results and management reviews.
Get Help With Your E
If you need assistance with writing your essay, our professional essay writin
Find out more
Health and safety management-system audit
Auditing is a systematic and structured method of verifying that activities conform with planned arrangements and monitors their e ectivenes
e ectively, regular reviews must be undertaken. The audit program and procedures should cover the following:
1.the activities and areas to be evaluated in audits
2.the frequency of audits
3. the responsibilities associated with managing and conducting audits
4.the communication of audit ndings
5.auditor selection and competence
6. how audits will be conducted.
/ Essays / Construction
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Safety Management Unit - 1Documento24 pagineSafety Management Unit - 1Abdul LathifNessuna valutazione finora
- Workplace Security Playbook: The New Manager's Guide to Security RiskDa EverandWorkplace Security Playbook: The New Manager's Guide to Security RiskNessuna valutazione finora
- WINSEM2022-23 MEE3502 ETH VL2022230500781 2023-02-22 Reference-Material-IIDocumento18 pagineWINSEM2022-23 MEE3502 ETH VL2022230500781 2023-02-22 Reference-Material-IIwewewewNessuna valutazione finora
- Duke Paints Safety Program ManualDocumento11 pagineDuke Paints Safety Program ManualMzt Duke AmosNessuna valutazione finora
- Management & SafetyDocumento25 pagineManagement & SafetyJawad Ahmad Bin KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ok - Sigay (Dandin)Documento45 pagineOk - Sigay (Dandin)Christ Archer SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Safety and HealthDocumento6 pagineManaging Safety and HealthLexter CEmpronNessuna valutazione finora
- BESS Project Behavioral Based Safety TrainingDocumento74 pagineBESS Project Behavioral Based Safety Trainingarnold arayataNessuna valutazione finora
- Report 2.safety and HealthDocumento26 pagineReport 2.safety and HealthJoseph Nathan Marquez100% (1)
- OSHA and You As A SupervisorDocumento28 pagineOSHA and You As A Supervisorfgdgrte gdfsgdNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 500 – SAFETY ENGINEERING QUIZ 2Documento4 pagineME 500 – SAFETY ENGINEERING QUIZ 2Emilio Joaquin FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Nine Practices of the Successful Security Leader: Research ReportDa EverandNine Practices of the Successful Security Leader: Research ReportNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of HSEDocumento19 pagineFundamentals of HSEJuliet EtingeNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety and RiskDocumento16 pagineSafety and RiskVidula KNessuna valutazione finora
- HIRA. 1pptDocumento46 pagineHIRA. 1pptnvaradharajan1971Nessuna valutazione finora
- Protecting Health and The Environment Is Everyone's JobDocumento50 pagineProtecting Health and The Environment Is Everyone's JobAli Akbar100% (1)
- HSE Interview Q&ADocumento20 pagineHSE Interview Q&ANaveed AkramNessuna valutazione finora
- The Real Product Safety Guide: Reducing the Risk of Product Safety Alerts and RecallsDa EverandThe Real Product Safety Guide: Reducing the Risk of Product Safety Alerts and RecallsNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Risk MGT Policy and ProcedureDocumento18 pagineSample Risk MGT Policy and ProcedurerabiulfNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk, Safety and LiabilityDocumento12 pagineRisk, Safety and LiabilityNuuradiin Xasan DhaqaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Safety ManagementDocumento9 pagineFundamentals of Safety Managementprecious maningasNessuna valutazione finora
- Techniques of Construction Safety ManagementDocumento9 pagineTechniques of Construction Safety Managementkhrizel lee tuazonNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Overview of Health and SafetyDocumento43 pagine1 - Overview of Health and SafetyJustine jerome FloranteNessuna valutazione finora
- Reporting Hazards and WHS Procedures < 40Documento15 pagineReporting Hazards and WHS Procedures < 40Ivan LisdiyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Audit CourseDocumento18 pagineAudit CourseVrushabh NikamNessuna valutazione finora
- 32Documento1 pagina32Rohan ShresthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 1 M11 OOS 2018Documento118 pagineDay 1 M11 OOS 2018AbdulslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Improving safety performance through behavioural approachesDocumento16 pagineImproving safety performance through behavioural approachesKhalid Mahmood AwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Keselamatan & Pengurusan Bengkel SHPE 1033: Introduction To The CourseDocumento15 pagineKeselamatan & Pengurusan Bengkel SHPE 1033: Introduction To The CourseNava Mathi SelvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Behaviouralsafetyf PDFDocumento14 pagineBehaviouralsafetyf PDFAntony JebarajNessuna valutazione finora
- Bsbwhs401summative 1 2020Documento3 pagineBsbwhs401summative 1 2020LAN LNessuna valutazione finora
- Dimensions of The Architecture of Safety ExcellenceDocumento6 pagineDimensions of The Architecture of Safety ExcellenceGissmo100% (1)
- BSBWHS401 Implement and Monitor WHS Policies, Procedures and Programs To Meet Legislative Requirements (Assessment 1 - 4)Documento19 pagineBSBWHS401 Implement and Monitor WHS Policies, Procedures and Programs To Meet Legislative Requirements (Assessment 1 - 4)annwong85Nessuna valutazione finora
- SITXWHS003 Online Learning Activity BookDocumento18 pagineSITXWHS003 Online Learning Activity Bookadnan malikNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety PolicyDocumento4 pagineSafety Policypco.safety2023Nessuna valutazione finora
- Five TIPS TO MANAGE EMPLOYEE RISKDocumento4 pagineFive TIPS TO MANAGE EMPLOYEE RISKaswin albertNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Osh Program PDFDocumento30 pagine2 Osh Program PDFAlessandra SisonNessuna valutazione finora
- A Guide For Safety RepresentativesDocumento16 pagineA Guide For Safety RepresentativesJose Barbosa Reis Jr.100% (2)
- Seemon FinalDocumento101 pagineSeemon FinalanujNessuna valutazione finora
- Security Careers: Skills, Compensation, and Career PathsDa EverandSecurity Careers: Skills, Compensation, and Career PathsNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Safety and HealthDocumento7 pagineManaging Safety and Healthtsega-alem berihuNessuna valutazione finora
- Hazard Assessment Program PDFDocumento10 pagineHazard Assessment Program PDFHassan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- BoshDocumento43 pagineBoshPrinze CalajateNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Safety FundamentalsDocumento184 pagineIndustrial Safety FundamentalsAkash TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial SafetyDocumento10 pagineIndustrial Safetywasi_bhutto100% (9)
- The Art of Risk Management: Learn to Manage Risks Like a ProDa EverandThe Art of Risk Management: Learn to Manage Risks Like a ProValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Industrial SafetyDocumento7 pagineIndustrial SafetyAhsan JalalNessuna valutazione finora
- Duties of Safety OfficerDocumento5 pagineDuties of Safety Officerjio4g1941Nessuna valutazione finora
- SST CompanyName EHS ProgramsDocumento9 pagineSST CompanyName EHS ProgramsRaymond TuazonNessuna valutazione finora
- D2. Fundamental Concepts Terms 1Documento17 pagineD2. Fundamental Concepts Terms 1Vicente Alberm F. CRUZ-AMNessuna valutazione finora
- OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM GUIDEDocumento81 pagineOCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM GUIDEmohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Institute of Technology Division of Civil Eng. Safety and Environment Protection Management BDC 323 2 CRHDocumento81 pagineInstitute of Technology Division of Civil Eng. Safety and Environment Protection Management BDC 323 2 CRHKinfe Dufera Gonfa100% (1)
- Nicollet AWAIR PlansDocumento11 pagineNicollet AWAIR PlansidahssNessuna valutazione finora
- OHS Management SystemDocumento33 pagineOHS Management Systems_pamungkasNessuna valutazione finora
- Roles of Safey OfficerDocumento9 pagineRoles of Safey OfficerLorie Jean Caliboso Pacion100% (1)
- People Workforce Health SafetyDocumento7 paginePeople Workforce Health SafetydakidofdaboomNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavior-Based Safety Training For SupervisorsDocumento67 pagineBehavior-Based Safety Training For Supervisorsroy wilsonNessuna valutazione finora
- AIS Risk Management and Risk AssessmentDocumento6 pagineAIS Risk Management and Risk AssessmentavsecNessuna valutazione finora
- Prevention of Accident and Safety Provision - 4thunit - PrintDocumento7 paginePrevention of Accident and Safety Provision - 4thunit - Printthilaga2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nathaniel Lichfield - Community Impact Evaluation - Principles and Practice-Routledge (1996)Documento342 pagineNathaniel Lichfield - Community Impact Evaluation - Principles and Practice-Routledge (1996)Michael González VásquezNessuna valutazione finora
- KSH13007 KSH13007: SEMIHOW REV.A1, Oct 2007Documento6 pagineKSH13007 KSH13007: SEMIHOW REV.A1, Oct 2007Manolo DoperNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 9 - Curvature and Refraction, Measuring Vertical DistancesDocumento11 pagineLesson 9 - Curvature and Refraction, Measuring Vertical DistancesJohn Andrei PorrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Dinosaur Lesson by SlidesgoDocumento41 pagineDinosaur Lesson by SlidesgoDonalyn PaderesNessuna valutazione finora
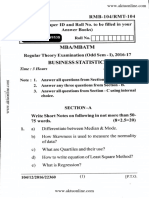
- Mba-1-Sem-Business-Statistics-Mba-Aktu-Previous Year PaperDocumento7 pagineMba-1-Sem-Business-Statistics-Mba-Aktu-Previous Year PaperNishant TripathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Medica2023 ExhibitorsDocumento288 pagineMedica2023 ExhibitorsHamza BadraneNessuna valutazione finora
- PH102 LabDocumento10 paginePH102 LabPeggy CockerNessuna valutazione finora
- ADB Procurement Framework UpdateDocumento59 pagineADB Procurement Framework UpdateAvisheak PalNessuna valutazione finora
- There Is No A.I. - The New YorkerDocumento8 pagineThere Is No A.I. - The New YorkerNoam NorkhatNessuna valutazione finora
- Stripline 41 HoDocumento2 pagineStripline 41 Howaheed babarNessuna valutazione finora
- Business 71 PDFDocumento1 paginaBusiness 71 PDFLissa Montiel0% (1)
- TERMINOLOGI HUKUM-1st LectureDocumento15 pagineTERMINOLOGI HUKUM-1st LectureAal Lukmanul HakimNessuna valutazione finora
- Astronomical Distance, Mass and Time ScalesDocumento11 pagineAstronomical Distance, Mass and Time ScalesHARENDRA RANJANNessuna valutazione finora
- A Letter To BenefactorDocumento2 pagineA Letter To BenefactorJeremy JM88% (8)
- Population Growth: SC.912.L.17.5 Analyze How Population Size Is Determined by Births, Deaths, ImmigrationDocumento14 paginePopulation Growth: SC.912.L.17.5 Analyze How Population Size Is Determined by Births, Deaths, ImmigrationBrianna DominguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Statement of Purpose or Motivation LetterDocumento2 pagineStatement of Purpose or Motivation LettersalequeNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.my Feelings ADocumento2 pagine1.my Feelings ACath TempestNessuna valutazione finora
- Conclusion and RecommendationDocumento6 pagineConclusion and Recommendationapril rose soleraNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophy and The Hitchhiker's: Guide To The GalaxyDocumento4 paginePhilosophy and The Hitchhiker's: Guide To The GalaxyAggelou MayaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Building Sustainability Assessment System (BSAS) For Least DevDocumento9 pagineA Building Sustainability Assessment System (BSAS) For Least DevGibidaws HapNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Tutorial Pressure Sept19Documento7 pagine2 Tutorial Pressure Sept19hairinnisaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Stage of Bearing FailureDocumento3 pagine4 Stage of Bearing Failure2003vinayNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Handout For Masters (Text Book Two)Documento177 pagineProject Handout For Masters (Text Book Two)Hamse HusseinNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet 14 - Hybridization: 2 The Other SP Orbitals Hold The Oxygen Lone PairsDocumento5 pagineWorksheet 14 - Hybridization: 2 The Other SP Orbitals Hold The Oxygen Lone PairsKosmos100% (1)
- Formation Damage Cuased by A Water Blockage Chemical SPE-00073790Documento12 pagineFormation Damage Cuased by A Water Blockage Chemical SPE-00073790Oscar Mauricio TellezNessuna valutazione finora
- Epsy For Edpm Chapter 3,4 &5Documento22 pagineEpsy For Edpm Chapter 3,4 &5mekit bekeleNessuna valutazione finora
- Nature and Scope of EconomicsDocumento6 pagineNature and Scope of EconomicsRenu AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pointers in Grade 6.Documento4 paginePointers in Grade 6.Jobert SimoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Units 1-5 Progress Test A: Macmillan Education Pobrano Przez Użytkownika Iwona Szulik 140979Documento4 pagineUnits 1-5 Progress Test A: Macmillan Education Pobrano Przez Użytkownika Iwona Szulik 140979Łukasz KaczkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthony J Jakeman Et. Al. - Integrated Groundwater ManagementDocumento756 pagineAnthony J Jakeman Et. Al. - Integrated Groundwater ManagementPaul Kevin Bautista PalaciosNessuna valutazione finora