Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pathophysiology Ideal
Caricato da
Dranlie LagdamenCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pathophysiology Ideal
Caricato da
Dranlie LagdamenCopyright:
Formati disponibili
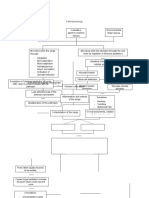
Pathophysiology
Personal Risk Causative Environmental
Factors agent’s virulence Risk Factors
factors
Microbes enter the lungs Microbes enter the stomach through the oral
through: route by ingestion of infected substance
- Inhalation
- Microaspiration Intestinal colonization and
- Macroaspiraton cellular adherance
- Hematogenous
- Direct inoculation
- Activation of Mucosal invasion Toxin release
dormant infection
Villous cell destuction Cytotoxin/enterotoxin
Production of Cytokines Interleukin 1B by the
Activation of defense mechanism
WBC when it comes in contact with the
pathogen Impaired sodium
Immune cells attack Stimulate chloride
absoprtion secretion
Loss effectiveness of the
defense mechanism
Inflammation and edema Symptoms:
of the lungs
- Diarrhea
Multiplication of the pathogen
- Vomitting
- Abdominal Pain
Consolidation of the lungs In viral pneumonia, ciliated
Fever which causes neurons
to be excited
Causes Hyperventilation increase
blood pH which excite neurons
more
Convulsions:
- Uncontrollable muscle
spasm
- Confusion
- Drooling No treatment of lifestyle
- Sudden shaking of the Treatment: changes Diagnostic tests:
body - Chest radiograph
- Adherence to prescribed - Blood culture
antimicrobial or antiviral - Sputum culture
medications - Polymerase chain
- Aspirin, Non-steroidal Worsening of signs and reactin
symptoms - Gram stain
Inflammatory drugs - Bronchoalveolar lavage
(NSAIDs), or - X-ray
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Cummins: ISX15 CM2250Documento17 pagineCummins: ISX15 CM2250haroun100% (4)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Fellows (Antiques)Documento90 pagineFellows (Antiques)messapos100% (1)
- Shelly Cashman Series Microsoft Office 365 Excel 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Freund Solutions ManualDocumento5 pagineShelly Cashman Series Microsoft Office 365 Excel 2016 Comprehensive 1st Edition Freund Solutions Manualjuanlucerofdqegwntai100% (10)
- All About TarlacDocumento12 pagineAll About TarlacAnonymous uLb5vOjXNessuna valutazione finora
- Coal Mining Technology and SafetyDocumento313 pagineCoal Mining Technology and Safetymuratandac3357Nessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Purlins: Try 75mm X 100mm: Case 1Documento12 pagineDesign of Purlins: Try 75mm X 100mm: Case 1Pamela Joanne Falo AndradeNessuna valutazione finora
- Amerex Ansul Badger Ul Catalogo Por PartesDocumento37 pagineAmerex Ansul Badger Ul Catalogo Por PartesPuma De La Torre ExtintoresNessuna valutazione finora
- Pcap - PathophysiologyDocumento4 paginePcap - PathophysiologyAyla Mar100% (1)
- Gordon's Functional Health Pattern For Adult (General)Documento8 pagineGordon's Functional Health Pattern For Adult (General)Dranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Notre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDocumento1 paginaNotre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Notre Dame of Dadiangas University College of Health Sciences BS Nursing ProgramDocumento2 pagineNotre Dame of Dadiangas University College of Health Sciences BS Nursing ProgramDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- DONNING and DOFFING PPEDocumento16 pagineDONNING and DOFFING PPEDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- TITLE: Relationship Between Malnutrition Risks and Functional Abilities of The ElderlyDocumento9 pagineTITLE: Relationship Between Malnutrition Risks and Functional Abilities of The ElderlyDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- TITLE: Cognitive Decline: Can Diet Be A Preventive or Treatment Option? AUTHOR: Nursing Older People (2014)Documento10 pagineTITLE: Cognitive Decline: Can Diet Be A Preventive or Treatment Option? AUTHOR: Nursing Older People (2014)Dranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- An Audiometer Gives A Precise Quantitative Measure of Hearing by Assessing The Person's Ability To Hear Sounds of Varying FrequencyDocumento5 pagineAn Audiometer Gives A Precise Quantitative Measure of Hearing by Assessing The Person's Ability To Hear Sounds of Varying FrequencyDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- TITLE: Considerations For The Development of Innovative Foods To Improve Nutrition inDocumento10 pagineTITLE: Considerations For The Development of Innovative Foods To Improve Nutrition inDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge PlanDocumento3 pagineDischarge PlanDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nursing Process Is A Modified Scientific Method. Nursing Practise Was First Described As A Four-Stage Nursing Process by Ida Jean Orlando in 1958Documento4 pagineThe Nursing Process Is A Modified Scientific Method. Nursing Practise Was First Described As A Four-Stage Nursing Process by Ida Jean Orlando in 1958Dranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- GANTTDocumento2 pagineGANTTDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- JMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Dadiangas University Marist Avenue, General Santos CityDocumento5 pagineJMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Dadiangas University Marist Avenue, General Santos CityDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Bibliography Gian NewDocumento2 pagineBibliography Gian NewDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Letter DistrictDocumento2 pagineLetter DistrictDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento14 pagineDrug StudyDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson PlanDocumento5 pagineLesson PlanDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Letter DistrictDocumento2 pagineLetter DistrictDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology IdealDocumento3 paginePathophysiology IdealDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- RESEARCHDocumento5 pagineRESEARCHroseve cabalunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sustainable Strategic Management BarbosaDocumento11 pagineSustainable Strategic Management BarbosapurwawardhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Anykycaccount Com Product Payoneer Bank Account PDFDocumento2 pagineAnykycaccount Com Product Payoneer Bank Account PDFAnykycaccountNessuna valutazione finora
- Nails Care: Word Search: Name: - DateDocumento1 paginaNails Care: Word Search: Name: - DateDeverly Hernandez Balba-AmplayoNessuna valutazione finora
- PretestDocumento8 paginePretestAlmonte Aira LynNessuna valutazione finora
- Zillah P. Curato: ObjectiveDocumento1 paginaZillah P. Curato: ObjectiveZillah CuratoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pot-Roasted Beef BrisketDocumento4 paginePot-Roasted Beef Brisketmarcelo nubileNessuna valutazione finora
- Icc Esr-2302 Kb3 ConcreteDocumento11 pagineIcc Esr-2302 Kb3 ConcretexpertsteelNessuna valutazione finora
- Pipe Freezing StudyDocumento8 paginePipe Freezing StudymirekwaznyNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of NABARD Grade ADocumento7 pagineStructure of NABARD Grade ARojalin PaniNessuna valutazione finora
- WoundVite®, The #1 Most Comprehensive Wound, Scar and Post-Surgical Repair Formula Receives Amazon's Choice High RatingsDocumento3 pagineWoundVite®, The #1 Most Comprehensive Wound, Scar and Post-Surgical Repair Formula Receives Amazon's Choice High RatingsPR.comNessuna valutazione finora
- 全新全真题库一 PDFDocumento36 pagine全新全真题库一 PDFTzarlene100% (1)
- Performance Task 2Documento3 paginePerformance Task 2Edrose WycocoNessuna valutazione finora
- Task of ProjectDocumento14 pagineTask of ProjectAbdul Wafiy NaqiuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- ANTINEOPLASTICSDocumento21 pagineANTINEOPLASTICSGunjan KalyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Speaking RubricDocumento1 paginaSpeaking RubricxespejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO LITERATUREDocumento4 pagineChapter 1 INTRODUCTION TO LITERATUREDominique TurlaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adolescents' Gender and Their Social Adjustment The Role of The Counsellor in NigeriaDocumento20 pagineAdolescents' Gender and Their Social Adjustment The Role of The Counsellor in NigeriaEfosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Batron: 29 5 MM Character Height LCD Modules 29Documento1 paginaBatron: 29 5 MM Character Height LCD Modules 29Diego OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- VTB Datasheet PDFDocumento24 pagineVTB Datasheet PDFNikola DulgiarovNessuna valutazione finora
- ManualDocumento24 pagineManualCristian ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Vocabulary of Latin Nouns and AdnounsDocumento129 pagineA Vocabulary of Latin Nouns and Adnounsthersitesslaughter-1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Calendar of Activities A.Y. 2015-2016: 12 Independence Day (Regular Holiday)Documento3 pagineCalendar of Activities A.Y. 2015-2016: 12 Independence Day (Regular Holiday)Beny TawanNessuna valutazione finora