Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lesson Plan
Caricato da
Dranlie LagdamenTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lesson Plan
Caricato da
Dranlie LagdamenCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Dranlie P.
Lagdamen BSN 2A January 24, 2020
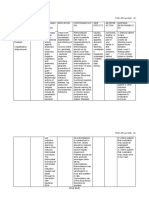
Ward Class (Lesson Plan)
Topic: Expanded Program on Immunization (EPI)
OBJECTIVES CONTENT AND TIME ALLOTMENT TEACHING REFERENCE
STRATEGIES AND
MATERIALS
After 20 minutes of - Active Reference:
Ward Class, I should
be able to : Discussion Webpages:
1.Discuss the I. 3 minutes - Reading DOH, (2019).
Rationale and the Expanded
Global Burden of the Rationale: The Expanded Program on Immunization (EPI) was established in 1976 to - Question program on
program. ensure that infants/children and mothers have access to routinely recommended Immunization
infant/childhood vaccines. Six vaccine-preventable diseases were initially included in the and Answer .Retrieved
EPI: tuberculosis, poliomyelitis, diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis and measles. In 1986, 21.3% January 24
“fully immunized” children less than fourteen months of age based on the EPI - 2020.https://
Comprehensive Program review. www.doh.gov
.ph/expanded
Global Burden: In 2002, WHO estimated that 1.4 million of deaths among children under -program-on-
5 years due to diseases that could have been prevented by routine vaccination. This immunization
represents 14% of global total mortality in children under 5 years of age.
2. Mention Goals of II. 2 minutes
the Program.
Over-all Goal: To reduce the morbidity and mortality among children against the most
common vaccine-preventable diseases.
Specific Goals:
1. To immunize all infants/children against the most common vaccine-preventable Materials:
diseases.
2. To sustain the polio-free status of the Philippines.
-Marker
3. To eliminate measles infection.
4. To eliminate maternal and neonatal tetanus -Manila
5. To control diphtheria, pertussis, hepatitis b and German measles.
Paper
6. To prevent extra pulmonary tuberculosis among children.
-Bond Paper
3. Tackle the III. 5 minutes
Mandates and
Strategies of the Mandates:
Program
Republic Act No. 10152 “Mandatory Infants and Children Health Immunization Act of 2011”
Signed by President Benigno Aquino III in July 26, 2010. The mandatory includes basic
immunization for children under 5 including other types that will be determined by the
Secretary of Health.
Strategies:
Conduct of Routine Immunization for Infants/Children/Women through
the Reaching Every Barangay (REB) strategy
REB strategy, an adaptation of the WHO-UNICEF Reaching Every District (RED),
was introduced in 2004 aimed to improve the access to routine immunization and reduce
drop-outs. There are 5 components of the strategy, namely: data analysis for action, re-
establish outreach services, strengthen links between the community and service,
supportive supervision and maximizing resources.
Supplemental Immunization Activity (SIA)
Supplementary immunization activities are used to reach children who have not been
vaccinated or have not developed sufficient immunity after previous vaccinations. It can be
conducted either national or sub-national –in selected areas.
Strengthening Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Surveillance
This is critical for the eradication/elimination efforts, especially in identifying true cases of
measles and indigenous wild polio virus
Procurement of adequate and potent vaccines and needles and syringes to all
health facilities nationwide
IV. 7 minutes
Measles Elimination
4. Discuss the
Accomplishments of Conducted 4 rounds of mass measles campaign: 1998, 2004, 2007 and 2011.
the program. Implemented the 2-dose measles-containing vaccine (MCV) in 2009
MCV1 (monovalent measles) at 9-11 months old
MCV2 (MMR) at 12-15 months old.
Implemented and strengthened the laboratory surveillance for confirmation of
measles. Blood samples are withdrawn from all measles suspect to confirm the
case as measles infection.
A supplemental immunization campaign for measles and rubella (German
measles) was done in 2011. This was dubbed as “Iligtas sa Tigdas ang Pinas”
15.6 million (84%) out of the 18.5 million children ages 9 months to 8 years old
were given 1 dose of the measles-rubella (MR) vaccine between April and June
2011.
Maternal and Neonatal Tetanus Elimination
Three (3) rounds of TT vaccination are currently on-going in the 10 highest risk
areas. An estimated 1,010,751 women age 15 - 40 year old women regardless of
their TT immunization will receive the vaccine during these rounds. This is funded
by the Kiwanis International through UNICEF and World Health Organization.
Polio Eradication:
The Philippines has sustained its polio-free status since October 2000.
There is an on-going polio mass immunization to all children ages 6 weeks up
to 59 months old in the 10 highest risk areas for neonatal tetanus. These areas are
the following: Abra, Banguet, Isabela City and Basilan, Lanao Norte, Cotabato
City, Maguindanao, Lanao Sur, Marawi City and Sulu.
Hepatitis B Control
Republic Act No. 10152 has been signed. It is otherwise known as the
“Mandatory Infants and Children Health Immunization Act of 2011, which requires
that all children under five years old be given basic immunization against vaccine-
preventable diseases. Specifically, this bill provides for all infants to be given the
birth dose of the Hepatitis-B vaccine within 24 hours of birth.
Vaccines and cold chain management
Upgraded the cold chain equipment in the 80 provinces, 38 cities and 16
regions since 2003.
An effective vaccine management assessment was conducted last December
2011 and revealed cold chain capacity gaps from the national up to the
implementers level.
Introduction to New Vaccines
For 2012, Rotavirus and Pneumococcal vaccines will be introduced in the
national immunization program. Immunization will be prioritized among the infants
of families listed in the National Housing and Targeting System (NHTS) for Poverty
Reduction nationwide.
V. 3 minutes
Future Plan/ Action
5.Tackle the Future
Plan of the Program. Strengthening the Cold Chain to support the Immunization Program
Capacity Building for Health Workers for the Introduction of New Vaccines
Advocacy for the financial sustainability for the newly introduced vaccines for
expansion.
Development of the comprehensive multi-year plan for immunization program.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Journal Analysis-BALLON, Karlo CDocumento4 pagineJournal Analysis-BALLON, Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching PlanDocumento4 pagineTeaching PlanDickson,Emilia JadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 4.health Education PlanDocumento3 pagineActivity 4.health Education Planjoannamae molaga0% (1)
- Subjective: Goal: Dependent: Dependent:: Assessment Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineSubjective: Goal: Dependent: Dependent:: Assessment Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Cayabyab100% (1)
- Lesson Plan On HyperlipidemiaDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan On HyperlipidemiaBinita Shakya100% (1)
- Epi Brochure (Calalang)Documento2 pagineEpi Brochure (Calalang)Nickaela CalalangNessuna valutazione finora
- A Case Study In:: Hirschsprung DiseaseDocumento18 pagineA Case Study In:: Hirschsprung DiseaseJaimie La PenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 2 NCM 107Documento21 pagineWeek 2 NCM 107raise concern100% (1)
- Time Specific Objective Content Teachin G Learning Activity Av Aids EvaluationDocumento7 pagineTime Specific Objective Content Teachin G Learning Activity Av Aids Evaluationrittika dasNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP GrandcaseDocumento5 pagineNCP GrandcaseSaima BataloNessuna valutazione finora
- Gordons Assesment NarrativeDocumento9 pagineGordons Assesment NarrativeJeanelle DenostaNessuna valutazione finora
- FNCP FinalDocumento28 pagineFNCP FinalKristal Jane RuedasNessuna valutazione finora
- An Overview of Community Health Nursing Practice in The PhilippinesDocumento21 pagineAn Overview of Community Health Nursing Practice in The PhilippinesWilma BeraldeNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Risk For InjuryDocumento1 paginaNCP Risk For InjuryRenz Kier L. ComaNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Health NursingDocumento3 pagineFamily Health Nursingmarjo24100% (1)
- Community Health NurBBScN 23082012 1441Documento22 pagineCommunity Health NurBBScN 23082012 1441Aparna KinginiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Informatics in South AmericaDocumento28 pagineNursing Informatics in South AmericaJazkiNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Community Health Nursing 2Documento1 paginaWhat Is Community Health Nursing 2Soleil MaxwellNessuna valutazione finora
- Nurses Notes Soapie Day 2Documento3 pagineNurses Notes Soapie Day 2Sunny Al asadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Case Study-AbstractDocumento3 pagineFamily Case Study-AbstractKatherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 pagineHypertension Nursing Care PlanCj LowryNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocumento26 pagineFamily Nursing Care PlanAmira Fatmah QuilapioNessuna valutazione finora
- FNCP Unplanned PregnancyDocumento1 paginaFNCP Unplanned PregnancyASTRA FAYE QUEENA DELENANessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For Client With Parent-Infant AttachmentDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan For Client With Parent-Infant AttachmentThe Right WayNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Plan For TBDocumento5 pagineTeaching Plan For TBakritiNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching Plan: Iron-Rich Foods BenefitsDocumento1 paginaHealth Teaching Plan: Iron-Rich Foods BenefitsJharene BasbañoNessuna valutazione finora
- A Descriptive Study To Assess The Knowledge Regarding Substance Abuse and Ill Effects Among P.U. Students in The Selected P.U. College of BagalkotDocumento3 pagineA Descriptive Study To Assess The Knowledge Regarding Substance Abuse and Ill Effects Among P.U. Students in The Selected P.U. College of BagalkotInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health Nursing by Maglaya PDFDocumento2 pagineCommunity Health Nursing by Maglaya PDFNicole Marie MartusNessuna valutazione finora
- Care of Mother, Child, and Adolescents (Well Clients) NCM - 107 Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Plan Intervention EvaluationDocumento4 pagineCare of Mother, Child, and Adolescents (Well Clients) NCM - 107 Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Plan Intervention EvaluationSophia Caisip100% (1)
- HypertensionDocumento3 pagineHypertensionCheryl Lim SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework 1: Developing A Health Teaching Program 1. What Insights and Reflections Do You Have Based On Your Understanding of The EssentialDocumento2 pagineHomework 1: Developing A Health Teaching Program 1. What Insights and Reflections Do You Have Based On Your Understanding of The EssentialRianne BaetiongNessuna valutazione finora
- FSPR Masalunga1Documento34 pagineFSPR Masalunga1Janela CaballesNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDocumento3 pagineRisk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPMarife Lipana Reyes100% (3)
- Labor Nursing Care Plan 1Documento4 pagineLabor Nursing Care Plan 1Anna Mae DollenteNessuna valutazione finora
- FNCP MumpsDocumento2 pagineFNCP MumpsCrizza JoyceNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Ethical Principles in NursingDocumento7 pagineUnderstanding Ethical Principles in NursingErica Bianca TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Nutrition Education for an Underweight InfantDocumento2 pagineNutrition Education for an Underweight InfantYzobel Phoebe ParoanNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Family-Nurse ContactDocumento6 pagineTypes of Family-Nurse ContactLYRIZZA LEA BHEA DESIATANessuna valutazione finora
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Actual NCPDocumento1 paginaTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Actual NCPDoreen ClaireNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions for HypertensionDocumento7 pagine5 Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions for Hypertensionmelerine16Nessuna valutazione finora
- Artillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaDocumento5 pagineArtillo NCP Renal Cell CarcinomaAl TheóNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Diseases Diabetes Mellitus Substance Abuse Hiv/Aids RH Sensitization AnemiaDocumento46 pagineHeart Diseases Diabetes Mellitus Substance Abuse Hiv/Aids RH Sensitization Anemiarevie67% (3)
- Criteria of A ProfessionDocumento3 pagineCriteria of A ProfessionDonnabell Dayuday100% (1)
- Buddy WorksDocumento3 pagineBuddy WorksJamaica Leslie NovenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminology CHNDocumento4 pagineTerminology CHNKailash NagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Measles Health TeachingDocumento2 pagineMeasles Health TeachingJune DumdumayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Family Nursing Care Plan CriteriaDocumento7 pagineFamily Nursing Care Plan CriteriaAnonymous K99UIf1Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHN Case Pres No Course in The Ward New 2 1 EmeDocumento33 pagineCHN Case Pres No Course in The Ward New 2 1 EmeJediah Rei TangonanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNessuna valutazione finora
- Standards of Public Health Nursing in The PhilippinesDocumento18 pagineStandards of Public Health Nursing in The PhilippinesWilma BeraldeNessuna valutazione finora
- RH Care, Women's Health, EquityDocumento28 pagineRH Care, Women's Health, EquitypriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Minimum Data Set SystemDocumento4 pagineNursing Minimum Data Set SystemHenry Roque Tagalag100% (3)
- Common Nursing Diagnosis Found in Nursing Care Plans For HypertensionDocumento2 pagineCommon Nursing Diagnosis Found in Nursing Care Plans For HypertensionRaveen mayiNessuna valutazione finora
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Is Family-Centered Assessment DataDocumento5 pagineMaternal and Child Health Nursing Is Family-Centered Assessment DataWendell Gian GolezNessuna valutazione finora
- BSN II-A Student Clinical Report on Leopold's Maneuver and Newborn CareDocumento2 pagineBSN II-A Student Clinical Report on Leopold's Maneuver and Newborn CarePauPauNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionVincent Paul SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Community Health NursingDocumento11 pagineCommunity Health NursingIligan, JamaicahNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching PlanDocumento11 pagineHealth Teaching PlanVic Intia Paa100% (1)
- EPI and HIV 1Documento5 pagineEPI and HIV 1April Ivonne Claire BatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Doh Programs Related To Family HealthDocumento31 pagineDoh Programs Related To Family Healthamal abdulrahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Notre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDocumento1 paginaNotre Dame of Dadiangas UniversityDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Notre Dame of Dadiangas University College of Health Sciences BS Nursing ProgramDocumento2 pagineNotre Dame of Dadiangas University College of Health Sciences BS Nursing ProgramDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- DONNING and DOFFING PPEDocumento16 pagineDONNING and DOFFING PPEDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- TITLE: Relationship Between Malnutrition Risks and Functional Abilities of The ElderlyDocumento9 pagineTITLE: Relationship Between Malnutrition Risks and Functional Abilities of The ElderlyDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- TITLE: Cognitive Decline: Can Diet Be A Preventive or Treatment Option? AUTHOR: Nursing Older People (2014)Documento10 pagineTITLE: Cognitive Decline: Can Diet Be A Preventive or Treatment Option? AUTHOR: Nursing Older People (2014)Dranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Gordon's Functional Health Pattern For Adult (General)Documento8 pagineGordon's Functional Health Pattern For Adult (General)Dranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- TITLE: Considerations For The Development of Innovative Foods To Improve Nutrition inDocumento10 pagineTITLE: Considerations For The Development of Innovative Foods To Improve Nutrition inDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nursing Process Is A Modified Scientific Method. Nursing Practise Was First Described As A Four-Stage Nursing Process by Ida Jean Orlando in 1958Documento4 pagineThe Nursing Process Is A Modified Scientific Method. Nursing Practise Was First Described As A Four-Stage Nursing Process by Ida Jean Orlando in 1958Dranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- JMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Dadiangas University Marist Avenue, General Santos CityDocumento5 pagineJMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Dadiangas University Marist Avenue, General Santos CityDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge PlanDocumento3 pagineDischarge PlanDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- An Audiometer Gives A Precise Quantitative Measure of Hearing by Assessing The Person's Ability To Hear Sounds of Varying FrequencyDocumento5 pagineAn Audiometer Gives A Precise Quantitative Measure of Hearing by Assessing The Person's Ability To Hear Sounds of Varying FrequencyDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento14 pagineDrug StudyDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Bibliography Gian NewDocumento2 pagineBibliography Gian NewDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Pcap - PathophysiologyDocumento4 paginePcap - PathophysiologyAyla Mar100% (1)
- Pathophysiology IdealDocumento3 paginePathophysiology IdealDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology IdealDocumento3 paginePathophysiology IdealDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Letter DistrictDocumento2 pagineLetter DistrictDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- Letter DistrictDocumento2 pagineLetter DistrictDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- GANTTDocumento2 pagineGANTTDranlie LagdamenNessuna valutazione finora
- P.2 Literacy T2 EXAM - TEACHER - ACDocumento37 pagineP.2 Literacy T2 EXAM - TEACHER - ACNamusoke MariamNessuna valutazione finora
- The Protective Role of Maternal Immunization in Early LifeDocumento15 pagineThe Protective Role of Maternal Immunization in Early LifeYasminNessuna valutazione finora
- Meryl Dorey 2004Documento25 pagineMeryl Dorey 2004Kate SquiresNessuna valutazione finora
- Sokoto, NigeriaDocumento7 pagineSokoto, NigeriakrishnasreeNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding the Complex Factors Driving Vaccine Hesitancy in 40 CharactersDocumento6 pagineUnderstanding the Complex Factors Driving Vaccine Hesitancy in 40 CharactersAlexandra Mae D. MiguelNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Answers: Chapter 11 Immunity in HumansDocumento3 pagineModel Answers: Chapter 11 Immunity in HumansLaff IzzatulNessuna valutazione finora
- Smith Adam Edi Ielts Writing Task 2Documento130 pagineSmith Adam Edi Ielts Writing Task 2Nhung Le85% (34)
- National Immunization Program: Manual of Procedures Booklet 8Documento28 pagineNational Immunization Program: Manual of Procedures Booklet 8Blue PielagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of The Implementation of Expanded Program On Immunization in Barangay Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del Norte From 2014-2018Documento15 pagineAssessment of The Implementation of Expanded Program On Immunization in Barangay Maranding, Lala, Lanao Del Norte From 2014-2018Diana Grace ViñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laporan Data Kesakitan (Lb1) : Kode Unit: Kabupaten: Puskesmas: Subunit: LaporanDocumento24 pagineLaporan Data Kesakitan (Lb1) : Kode Unit: Kabupaten: Puskesmas: Subunit: Laporanpitikku_Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9 - Hepatitis B VaccineDocumento1 pagina9 - Hepatitis B VaccineabhivnairNessuna valutazione finora
- ĐỀ THI HSG LỚP 12 TỈNH BẮC NINH NĂM HỌC 2020-2021Documento8 pagineĐỀ THI HSG LỚP 12 TỈNH BẮC NINH NĂM HỌC 2020-2021Fam DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Childhood Immunization & Catch Up Immunization-2Documento53 pagineChildhood Immunization & Catch Up Immunization-2Haters ExterminatorNessuna valutazione finora
- How Soon Can You Drink Alcohol After Getting Your Covid-19 Vaccine - SA Corona Virus Online PortalDocumento1 paginaHow Soon Can You Drink Alcohol After Getting Your Covid-19 Vaccine - SA Corona Virus Online PortalArjay GudoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetanus in Farm AnimalsDocumento7 pagineTetanus in Farm AnimalsIsrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 15Documento40 pagineChap 15Koby100% (4)
- Why Do We Fall Ill Lesson PlanDocumento7 pagineWhy Do We Fall Ill Lesson Planvijos16655Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mode of TransmissionDocumento50 pagineMode of TransmissionHairul AnuarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1970 US Army Vietnam Field Hygiene and Sanitation 90p.Documento96 pagine1970 US Army Vietnam Field Hygiene and Sanitation 90p.macioman8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Immunization SchedulesDocumento12 pagineImmunization SchedulesAnjali ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Links and Ideas Regarding Vaccine and Religion:: Vaccination Liberation - InformationDocumento9 pagineLinks and Ideas Regarding Vaccine and Religion:: Vaccination Liberation - Informationdeejaylivz50% (2)
- BHW TRAINING Neonate and Infant HealthDocumento24 pagineBHW TRAINING Neonate and Infant HealthWilma BeraldeNessuna valutazione finora
- Indicator Reference Guide Final FINAL July242018Documento147 pagineIndicator Reference Guide Final FINAL July242018Amenti TekaNessuna valutazione finora
- Parents ' Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Towards Children 'S Vaccination in Lebanon: Role of The Parent-Physician CommunicationDocumento9 pagineParents ' Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Towards Children 'S Vaccination in Lebanon: Role of The Parent-Physician CommunicationPutri Raudatul JannahNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 Primary One Registration Exercise Application Form: Phase 1Documento1 pagina2020 Primary One Registration Exercise Application Form: Phase 1Suresh ThevanindrianNessuna valutazione finora
- Varicella Immunization CertDocumento2 pagineVaricella Immunization CertShaikahamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Argumentative Essay 4 VaccinesDocumento9 pagineArgumentative Essay 4 Vaccinesapi-30225964750% (8)
- How Vaccinosis Was Recognized as a Distinct Disease State in the 1800sDocumento20 pagineHow Vaccinosis Was Recognized as a Distinct Disease State in the 1800sCharlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Philippines Microplanning Guide: Reaching Every Purok Measles EliminationDocumento30 paginePhilippines Microplanning Guide: Reaching Every Purok Measles EliminationBe NjNessuna valutazione finora
- Argument Article Elc 231Documento1 paginaArgument Article Elc 231izzahNessuna valutazione finora