Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
SCADA Reviews
Caricato da
Venkatesan NTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SCADA Reviews
Caricato da
Venkatesan NCopyright:
Formati disponibili
American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (8): 1418-1425, 2014
ISSN: 1546-9239
© 2014 A. Shahzad et al., This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution
(CC-BY) 3.0 license
doi:10.3844/ajassp.2014.1418.1425 Published Online 11 (8) 2014 (http://www.thescipub.com/ajas.toc)
THE SCADA REVIEW: SYSTEM COMPONENTS,
ARCHITECTURE, PROTOCOLS AND FUTURE SECURITY
TRENDS
1
Shahzad, A., 1S. Musa, 1A. Aborujilah and 2M. Irfan
1
Malaysian Institute of Information Technology (MIIT), University Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
2
Windfield College, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Received 2014-01-15; Revised 2014-05-13; Accepted 2014-05-27
ABSTRACT
The Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system has prominent place and play
important roles within real time industrial communication included “electric stations, oil stations and
water purification plants”. In this study; the SCADA System main components, architecture and
important protocols, which have been used in SCADA message transmission are reviewed. After
review, the current research changes the direction (Section: Future Work) to the security of SCADA
system and the existing methods or security methods that have been deployed within the SCADA
system. This review also gives directions to secure SCADA network communication.
Keywords: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) System, Protocols, Security Trends
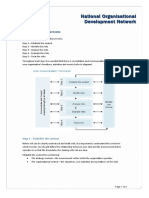
1. INTRODUCTION to Master Terminal Station (MTU) for monitoring and
controlling the entire SCADA system. Usually, SCADA
1.1. SCADA System Components system is divided into five main components/parts
(illustrated in Fig. 1) “included Master Terminal Unit
The SCADA system is based on hardware included (MTU), Remote Terminal Unit (RTU) and Human
“Master Terminal Unit (MTU), Remote Terminal Units Machine Interface (HMI) historian” and SCADA
(RTUs)” or/and actuators and sensors and software communication media or link (Stouffer and Kent, 2006;
included Human Machine Interface (HMI) or other user Musa et al., 2013b). More detail related with SCADA
software that provides communication interface between components is following below.
SCADA hardware and software. Human Machine
Interface (HMI) also provides facility to visualized entire 1.2. Master Terminal Unit (MTU)
SCADA communication included controlling and
The center controller or master terminal unit is may
monitoring. Master Terminal Unit (MTU) is located at
form of a server (computer) or/and group of sub servers
control center or perform the services of control station
and connected with one or more Remote Terminal Units connected directly or indirectly with main server,
(RTUs), that may geographically distributed over remote through communication link such as “Local Area
sites (wide area network) or within Local Area Network Network (LAN) or/and Wide Area Network (WAN)”.
(LAN) using communication link/media such as radio Human Machine Interface (HMI) is typically installed in
signals, telephone line, cable connection, satellite and Master Terminal Unit (MTU) or control center and
micro waves media. Typically, physical environment is provide facility to visualized the information coming
connected with actuators or/and sensors and from remote terminal units. The information is displayed
actuators/sensors are connected with Remote Terminal in understand able form such as in the form of textual
Units (RTUs). The RTUs have been collecting and graphical, that will easily understood able for
data/information from actuators/sensors and then process SCADA user/operators during communication.
Corresponding Author: Shahzad, A., Malaysian Institute of Information Technology (MIIT), University Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Science Publications 1418 AJAS
Shahzad, A. et al. / American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (8): 1418-1425, 2014
Fig. 1. SCADA communication component
So, each user terminals or sub terminals will visualize as home or office computer (Stouffer and Kent, 2006;
associated information on display screen by connected Musa et al., 2013b). Main services performed by
with main server through communication media. Master Terminal Unit (MTU) are follows below:
Few years before, SCADA system has many
• Monitor and control entire SCADA communication
incompatibilities in the terms of software/hardware
through communication link such as LAN/WAN
connectivity and information/data visualization, but
(radio signals, telephone line, cable connection,
with great revolution in DCS (distributed control
satellite and micro waves media)
system), now SCADA provides high resolution display
(screen). Therefore, SCADA operators can easy view • Using human machine software; visualized the
the site map or remote station operational view in high data/information related with SCADA
resolution and also successfully resolved the communication in the forms of text and graph
compatibilities issues during hardware/software • Send request data/message to RTUs included current
configuration and installation. So, any SCADA status of RTUs, information collection from RTUs,
software/hardware will easily install and operate, while check communication link and upon receiving
connecting with simple server (computer) included information/data from RTUs, perform acquisition
home computer or office computer having Microsoft
windows (XP, window 7 or 8).
1.3. Remote Terminal Unit (RTU)
With the SCADA advance software compatibilities Substations or Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) are act
and connectivity, open new ways to install SCADA as slave stations in SCADA architecture. Typically,
system applications included SCADA modeling and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) are connected with
simulation application, hydraulic modeling, physical environment through actuators or sensors. RTUs
geographical information system, drawing have been collecting real time information from sensors
applications and data bases within a single computer and transmit back to master terminal station, usually
Science Publications 1419 AJAS
Shahzad, A. et al. / American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (8): 1418-1425, 2014
depend upon the request send from master station. In few system design that compatible with hardware, while
cases, remote terminal station is also able to send request installation of new system (Stouffer and Kent, 2006;
to master station such as in case of disaster, disaster Musa et al., 2013b). Main services performed by
recovery, actuators or sensors functions off and other Human Machine Interface (HMI) are follows below:
critical issues. Main services performed by Remote
Terminal Unit (RTU) are follows below. • Provide interface for SCADA communication
Remote terminal stations are responsible to collect between hardware and software
information/data from sensors or actuators that are • Display all SCADA operational information such as
connected with physical environment and process controlling and monitoring and communication
information back to master station (depending on status between Master Terminal Unit (MTU) and
master request). Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) or/and Remote
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) are geographically Terminal Units (RTUs) and Master Terminal Unit
distributed over different sites, collecting and processing (MTU) in the form textual or graph or/and other
the real time information to master station using link human readable text
LAN/WAN (radio signals, telephone line, cable • Also provides conversion between several data types
connection, satellite and micro waves media,). Remote such as analog to digital, digital to analog,
Terminal Units (RTUs) are also responsible to deliver the digital/analog to human readable text and text to
current status information of physically devices connected digital/analog
with network included devices are configured properly and
working (operation) in right directions (Stouffer and Kent, Some of typical software's uses by SCADA system
2006; Musa et al., 2013b). (Stouffer and Kent, 2006) are following below:
1.4. Human Machine Interface (HMI) • “Master station (computer) operating node” is based
on UNIX platform and uses for controlling master
Human Machine Interface (HMI) or SCADA user station hardware
interface is most important part of SCADA system. • “Terminal station operating node” is uses for
This provides interface between hardware and controlling terminal station hardware and usually,
software within SCADA communication. SCADA master station operating node functionality is same
system deployment and performance are depending on as terminal station operating node
software (Human Machine Interface) specifications • “Master station software (Application)”; provides user
such as testing, checked and compatible with numbers interface or graphical user interface and operate/control
of nodes within SCADA network. Usually, Human “communication between master terminal unit (MTU)
Machine Interface (HMI) has been designed according and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) or/and Remote
to SCADA network structure needs and specification. Terminal Units (RTUs) and Master Terminal Unit
Some proprietary software’s are available (in market (MTU)”. At other side, “Terminal station software
(Application)”, is basically part of master station
or online) and uses for specific SCADA hardware
software and used to access information/data, that is
configuration. Often does not provide interface or
available on master station software (Application)
compatibilities for other vendors”hardware”.
• “Protocol drivers” are usually situated in both master
Commercial “Off-The-Shelf (COTS) products are station and terminal station communication and used to
available and provide flexible and compatible control data translation and interpretation “between
interface between several types of SCADA hardware Master Terminal Unit (MTU) and Remote Terminal
and software. Usually, proprietary software’s are based Units (RTUs) or/and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs)
on SCADA processes and controlling operations, while and Master Terminal Unit (MTU)
software’s such as Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) • “Tool for network management” is used for
are based (focusing) on several types of SCADA SCADA network communication control and
compatible hardware’s or equipments and Instruments. monitoring purposes such as checking the network
Therfore, COTS are more flexible and reliable in performance results. At other side, “Automation
hardware compatibilities as comparison with tools for remote terminal station” is uses by
proprietary software. As conclusion; must be ensuring SCADA operators to make configuration and
that which of software is appropriate for SCADA maintain remote terminal station applications
Science Publications 1420 AJAS
Shahzad, A. et al. / American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (8): 1418-1425, 2014
1.5. Historian three main generations such as First Generation:
Monolithic, Second Generation: Distributed, Third
The term historian is used to store incoming and Generation: Networked. More detail related with
outgoing processing/processes from/to SCADA SCADA system generation is following:
control center. Historian is just same as database,
which is centralized located within SCADA server 2.1. First Generation: Monolithic
or/and as separate located server (database server). All
First generation of SCADA architecture
communication such as monitoring and control
development was based on idea similar with main
information “between Master Terminal Unit (MTU)
frame system. Mean that network communication was
and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) or/and Remote
not exit at all and each station was worked as single
Terminal Units (RTUs) and Master Terminal Unit
centralized station. More detail related with first
(MTU)” have been stored within historian. SCADA
generation of SCADA system is following below:
system will fetch information from historian
according to the requirements of process being
executed include information/data analysis, report • The concept of Wide Area Network (WAN), for
generationand time management of storage between connectivity between master station and remote
processes and query generation and execution, station was developed (concept based on remote
(Stouffer and Kent, 2006; Musa et al., 2013b). terminal communication in SCADA field only)
and WAN protocols (current protocols) were
1.6. SCADA Communication unknown in first generation
The communication network provides services for • Few proprietary protocols were developed for
communication between nodes in SCADA network SCADA communication with limited
system. Using transmission medium facility; functionalities; that don’t fulfill the requirements
data/message has been able to transmitted “between of communication such as infeasible for handling
Master Terminal Unit (MTU) and Remote Terminal several traffic communications with remote
Units (RTUs) or/and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) station over network
and Master Terminal Unit (MTU)” included radio • Field devices connectivity with the master station
signals, telephone line, cable connection, satellite and was fairly limited and deployed at bus level using
micro waves media. Cable connection is uses for small proprietary. Primary and backup systems were
type of networks usually, within industry or small used for the purposes of limited redundancy check
industry, because this connection is inconvenient for and monitoring and failure detection or event
large distance. With the growing demand of industry operations were performed by standby system
and larger connectivity of SCADA nodes with
LANs/WANs; based on network demands powerful 2.2. Second Generation: Distributed
radio signals, satellite and microwaves media have been
often used for SCADA communication. The significant improvements have been done in
Usually, SCADA system uses “point to point or PTP, second generation and several processes were distributed
point to multipoint or PTM” and multipoint to multipoint across stations within Local Area Network (LAN). Each
or MTM topologies and communication procedures station has specific operation/function and send/receive
included half-duplex and full-duplex for communication real time information/data between the stations
(Stouffer and Kent, 2006; Musa et al., 2013b). connected within LAN. More detail related with second
generation of SCADA system is following below:
2. SCADA COMMUNICATION
ARCHITECTURE • In distributed environment, some of stations are
uses for communication such as master station
Traditionally, SCADA systems have been communication with the remote stations and other
connected within limited networks but growing stations utilized as human machine interface or
demand of SCADA over the world and uses of HMI for monitoring and controlling purposes and
modern networks architectures, SCADA also replace remaining uses for database/historian storage
from Monolithic to Networked. SCADA • Usually, LAN protocols have been used for
communication architecture is usually divided into communication between the nodes within distributed
Science Publications 1421 AJAS
Shahzad, A. et al. / American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (8): 1418-1425, 2014
environment, where the functions have been stations. Few companies, also developing Remote
resisting as distribution of SCADA system function Terminal Units (RTUs) to communicate with master
across several multiple systems station through Ethernet.
• Distribution of SCADA functionalities across SCADA distribution system over WAN,
several systems connected within LAN, would functionalities also enhanced in this generation.
increase processing power and improve the system SCADA operations are distributed across several
redundancy and reliability physical stations through WAN for the purposes of
disaster issues handling and provides more reliability
• The system failure ratio in second generation will
and scalability. If any station crash or fail, this will
deceased while comparison with first generation. In
not effect on entire SCADA system because replicated
first generation; only one primary station was used copies are store over several locations. In second
but in second generation all stations are generation, SCADA processing were distributed
communicating simultaneously within LAN. If one across several systems within LAN for increases the
of system fails with network, then other stations are reliability in communication. But if master station
still in processing states fail/crash or/and LAN connectivity fail, this was
• Wide Area Network (WAN) technology has been affect the entire SCADA system. SCADA system
also deployed and used for “communication connectivity with several types of protocols and
between master station and remote station or/and networks over internet; make SCADA system more
remote station and master station” WAN vulnerable from several types of attacks and threads
communication is fairy same as current technology (Stouffer and Kent, 2006).
(LAN/WAN), but communication functions were
limited for remote station protocols usage such as 3. SCADA COMMUNICATION
incompatible/unavailability for several network PROTOCOLS
traffic (Stouffer and Kent, 2006)
“The SCADA system communication between
2.3. Third Generation: Networked Master Terminal Unit (MTU) and Remote Terminal
Units (RTUs)” are implemented by uses of SCADA
Third generation of SCADA is approximately same protocols. Each SCADA protocol provides rules and
as second generation architecture but difference in procedures of communication between field devices
architecture uses. Current generation uses open and other functions included MTU/RTU command
architecture but second generation was based on generation, MTU/RTU status information,
proprietary architecture. More detail related with Third data/information accumulation, data presentation and
generation of SCADA systems is depicted below. conversation, assignment of MTU/RTU addresses,
Like second generation; master station is centralized system monitoring and controlling. Usually, each
and accessible from several remote stations, several SCADA protocol is proves two types of communication
networks are deployed for communication and single ways/sets. Fist communication set; is used by master
application functions are distributed/share between station, to initial the communication with allocated
several types of systems in SCADA network architecture Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and further response
and proprietary protocols are also used by remote back to Remote Terminal Units (RTUs). Second
stations to communication with master station. communication set; is used by remote station, to initial
Current generation has been deployed open the communication with allocated Master Terminal
architecture for SCADA communication across Unit (MTU) (in few critical cases, Remote Terminal
LANs/WANs by using several types of open standard Units (RTUs) are also able to send response or
protocols. These open standards completely minimize
unsolicited response to master station) (Reynders et al.,
the limitations suffered by SCADA communication in
2004; Krutz, 2005).
second generation and open new ways to connect
Some of most famous/popular protocols used
several types of input/output devices or off-the-shelf
systems with SCADA network. within SCADA communication (industrial
The main development done in third generation is communication) are following below.
uses of WAN technology for SCADA network using 3.1. Modbus Protocol
Internet Protocol (IP) or/and Transport Control Protocol
(TCP). SCADA uses TCP/IP for communication between SCADA system uses Modbus protocol for
the fields devices which are located across multiple application layer communication or real time
Science Publications 1422 AJAS
Shahzad, A. et al. / American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (8): 1418-1425, 2014
communication over OSI layer seven between field data/message to remote terminal station and remote
devices connected with several network lines. terminal station response according to master terminal
Basically; Modbus protocol has been provided station request. DNP protocol is used for serial or Internet
architecture of master station/remote station Protocol (IP) communication between master terminal
communication for the purposes of message/data station and remote terminal stations (Shahzad et al., 2014a).
request/response to/from master station and remote Using TCP/IP protocol, DNP3 provides communication
station. Modbus has been used four types of over internet between devices connected in Wide Area
communication modes between master station and Networks (WAN) and DNP3 protocol is situated
remote station communication such as request message above than TCP/IP protocol suite in communication
to master station, response message from master
hierarchy for fairly communication over internet
station, message/process acknowledgment or
(Reynders et al., 2004; Musa et al., 2013a; 2013b).
confirmation (upon message received by remote
station) and master station received request message 3.3. IEC 60870-5 Protocol
from remote station. Usually, Modbus protocol is
provides communication services “between Master In SCADA system, “Enhanced Performance
Terminal Unit (MTU) and Remote Terminal Units Architecture (EPA) model” is a simplified form of OSI
(RTUs) or/and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and seven layer model. The “International Electro
Master Terminal Unit (MTU)” or/and between fields Technical Commission (IEC)” has been developed the
devices and Human Machine Interface (HMI). EPA model and “IEC 60870-5-101 protocol” is also
In SCADA system, when remote station initial the based on EPA model. Usually, one special purpose
communication and send request message to master layer is added on the top of EPA model, known as
station Modbus protocol will assemble this message application layer. This user layer is specify the
(request) from remote station into Protocol Data Unit functions and operations related with telecontrol system
(PDU), usually PDU is combination of Function Code and provides interaction between SCADA field devices,
(FC) and data request, or by adding function code which are fully supported with telecontrol system.
with requested data, also known as Protocol Data Unit Several frame formats and services are specified
(PDU). By addiang fields at OSI layer 2, the for each layer in IEC 60870-5 protocol and several
constructed Protocol Data Unit (PDU) will convert functions are also defined for user program (layer),
into an Application Data Unit (ADU). Upon receiving, located between application layer (OSI model) and
master station will generate the request message and user interface. According to the needs of protocol
then send back to remote station. enhancement within SCADA industry, IEC 60870-5-
Traditionally, Modbus protocol is uses RS-232/485 101 protocol standards will also change from 60870-
or other modem for serial communication between 5-101 to 60870-5-104 or telecontrol standard profiles
master station and remote station, but uses of TCP/IP (such as T101, T102, T103, T104). Each protocol
standard define different specifications, data objects
protocol with modbus, a new layer has been established
and functions codes at application protocol level
for modbus message transmission (PDU encapsulation), within SCADA communication system.
over “transport control protocol/ internet protocol or International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
TCP/IP and Ethernet” (Reynders et al., 2004). has been developed first complete protocol known as
3.2. DNP3 Protocol 60870-5-101 for SCADA communication, that fulfill
the all necessary requirements, included define data
In terms of SCADA communication, “Enhanced objects and functions, across geographical area,
Performance Architecture (EPA) model is simplified through Wide Area Network (WAN) technology.
form of OSI seven layer “model”. The International 60870-5-101 protocol also specifies the basic
Electro Technical Commission (IEC) creates the EPA requirements such as generic data types and general
model and DNP protocol is based on EPA model. services for remote stations. Usually, standards
Distributed Network Protocol (DNP3) is one of 60870-5-101 to 60870-5-103 are uses for electrical
important open protocol has been used in SCADA industries operation, while standard 60870-5-104 also
communication between master terminal station and provides services for SCADA communication,
remote terminal stations or out stations. Usually master through Transport Control Protocol (TCP) and
terminal station initial the command or send Internet Protocol (IP) by adding two additional layers
Science Publications 1423 AJAS
Shahzad, A. et al. / American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (8): 1418-1425, 2014
such as transport and network layer of OSI seven layer within protocol stack and these all layers are based on
model (Reynders et al., 2004). OSI seven layer model, with extra layer on the top of
3.4. Profibus Protocol OSI model known as called user application layer.
Which provides specific (standard) user interface
Profibus is stand for “process field bus”. Profibus is between software and fields devices. Fieldbus has
network standard usually, uses within industrial control number of benefits/advantages, while connecting with
systems such as SCADA, DCS and PLC, Including modern or smart field devices and communication
Controlling, assembling and handling of field devices
networks, included easy processes integration, decrease
(ICS). Profibus has been mostly used in Europe and also
heavy wire cost,session minimized, enhancement in field
famous in other continent of world, included Asia,
America and Australia, Profibus is supported, devices control and monitoring, multifunctional devices,
communication between fields devices (with bus open standard and interoperability among vendors,
controller/access) or “between Master Terminal Unit enhancement in data integrity and availability.
(MTU) and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) or/and Another achievement of Fieldbus is HART (Highway
Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and Master Terminal Addressable Remote Transducer) Protocol, which is
Unit (MTU)”, with some specifications (requirements) supported both analog and digital communication of
such as connector type D, 127 point, 24 km distance industrial processing and automation. The most important
(supported), speed up to 12 Mbps and message size up to advantage of HART protocol is same existing wiring 4-20
244 bytes per node (Reynders et al., 2004). mA structure is used for receiving both analog and digital
Typically, Profibus protocol have three version such information on same cable (Reynders et al., 2004).
as Distributed Peripheral (DP), Field bus Message
Specification (FMS) and PA. More detail is given below. 3.6. Modbus Plus Protocol
In Distributed Peripheral (DP), master station takes
request message (read input) from remote station and Modbus plus Protocol is based on standard Modbus
then generate response message (write information) back protocol limitation. Modbus plus protocol (not open
to remote station. Distributed Peripheral (DP) is also standard) is designed to overcome the master station
supported, more than one master station (multiply limitation over modbus protocol, such that field devices
stations) read information/data from field devices and connectivity with master station through several modbus
then main controller (master) will able to send response networks or networks. Modbus plus is “token” base
back to remote station. protocol and allow the field devices to exchange
Field bus Message Specification (FMS), only information/data from master station and master station
support peer-to-peer communication between master is also able to control and monitor all communication at
stations; such that each master station is authorized to
remote site. The network addresses range 1--64 are
send/receive message from other master stations
within communication system. FMS communication utilized and each field device has its own unique
(message) has contained more loads as comparison address. Each field device is able to communicate with
with DP communication. other device in network, with specified route as
When FMS and DP versions are used simultaneously information inside message. Mostly, Modbus II is not
within one network, than called COMBI mode. The PA used within real time communication, because of extra
protocol working is same as Distributed Peripheral (DP), wire (cable) and other difficulties related with
only has difference in voltage level. communication (Reynders et al., 2004).
Profibus protocol is also based on OSI model
seven layer, with extra layer on the top of OSI model, 3.7. Data Highway Plus/Dh-485 Protocol
known as called application layer. Data link layer has Allen Bradley uses three main protocol standards
same specification for FMS, DP and PA (Profibus such as the highway protocol, the highway plus
variations), while IEC 61158-2 standard is uses by PA protocol and DH-485 for communication. The
and RS-485 is uses by DP and PA as physical layer highway protocol provides peer-to-peer half duplex
implementation (Reynders et al., 2004). communication within Local Area Network (LAN)
and systems range and data rate are up to 64 nodes
3.5. Foundation Fieldbus
and 56.7 Kbaud.
Foundation Fieldbus has four layers such as “user The highway plus protocol communication is same
layer, application layer, data link layer, physical layer” as the highway protocol, with limitation of systems and
Science Publications 1424 AJAS
Shahzad, A. et al. / American Journal of Applied Sciences 11 (8): 1418-1425, 2014
utilization of token system, also called floating master. 7. REFERENCES
The highway plus protocol also utilize three layers such
as application layer, data link layer, physical layer) of Krutz, R.L., 2005. Securing SCADA Systems. 1st Edn.,
OSI model. DH-485 is a proprietary protocol and illustrated, Hoboken, John Wiley Publishing,
provides communication between system (computer) ISBN-10: 047178768X, pp: 218.
and field devices within local area network, with RS- Musa, A.S., A. Shahzad and A. Aborujilah, 2013a.
485 support medium (Reynders et al., 2004). Simulation base implementation for placement of
security services in real time environment.
4. CONCLUSION Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on
Ubiquitous Information, (CUI’ 13), New York,
In this study, the SCADA system details included the
USA, DOI: 10.1145/2448556.2448587
components “such as Master Terminal Unit or MTU,
Musa, A.S., A. Shahzad and A. Aborujilah, 2013b.
Remote Terminal Unit or RTU, Human Machine
Secure security model implementation for security
Interface or HMI, Historian and SCADA
services and related attacks base on end-to-end,
Communication”, the architecture “such as First
application layer and data link layer security.
Generation: Monolithic; Second Generation: Distributed;
Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on
and Third Generation: Networked” and the important
Ubiquitous Information Management and
protocols “such as Modbus Protocol, DNP3 Protocol,
Communication, (IMC’ 13).
IEC 60870-5 Protocol, Profibus Protocol, Foundation
DOI:10.1145/2448556.2448588
Fieldbus, Modbus Plus Protocol and Data Highway
Reynders, D., S. Mackay and E. Wright, 2004. Practical
Plus/DH-485 Protocol” with their specifications, which
Industrial Data Communications: Best Practice
are using in current age, have been reviewed.
Techniques. 1st Edn., Butterworth-Heinemann,
Elsevier, ISBN-10: 0080480136, pp: 432.
5. FUTURE WORK
Shahzad, S., A. Aborujilah, M.N. Ismail and M. Irfan,
Several generic security solutions included 2013. Conceptual model of real time infrastructure
SSL/TSL, TCP, IPSec, security pattern and most within cloud computing environment. Int. J.
important cryptography have been deployed in the Comput. Networks, 5: 18-24.
area of Industrial control systems or ICSs security and Shahzad, S., A. Aborujilah, S. Musa and M. Irfan, 2014a.
implementation. Almost, all solutions are based on Industrial Control Systems (ICSs) vulnerabilities
end-to-end communication and provide security analysis and SCADA security enhancement using
mechanisms for SCADA system protection are also testbed encryption. Proceedings of the 8th
based on end-to-end. International Conference on Ubiquitous Information
After conducting and analyzed; the detail literature Management and Communication, (IMC’ 14), New
survey on SCADA/protocols security issues and its York, USA. DOI: 10.1145/2557977.2558061
potential vulnerabilities (Shahzad et al., 2013; 2014b; Shahzad, S., A. Aborujilah, S. Musa and M. Irfan,
Musa et al., 2013a), a solution has been proposed to 2014b. A new cloud based supervisory control and
secure the SCADA communication, by deploying data acquisition implementation to enhance the level
cryptography solution within Distributed Network of security using testbed. J. Comput. Sci., 10: 652-
Protocol version 3 (DNP3) and/or other SCADA 659. DOI: 10.3844/jcssp.2014.652.659
protocols as part of Industrial Control Systems (ICSs). Stouffer, J. and K. Kent, 2006. Guide to Supervisory
Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) and
6. ACKNOWLEDGMENT industrial control systems security.
Recommendations of the National Institute of
I would like to thank to my parents and my friend, M. Standards and Technology.
Irfan boosted me morally and provided me great
information resources.
Science Publications 1425 AJAS
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- VOITH Variable Speed Fluid CouplingsDocumento20 pagineVOITH Variable Speed Fluid CouplingsChristian AlmengorNessuna valutazione finora
- Turbine Governing System - Electro Hydraulic Controller (Ehc)Documento5 pagineTurbine Governing System - Electro Hydraulic Controller (Ehc)Venkatesan NNessuna valutazione finora
- Supercritical Boiler Technology PDFDocumento16 pagineSupercritical Boiler Technology PDFNazim SalehNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrumentation Documents Basic PDFDocumento32 pagineInstrumentation Documents Basic PDFVenkatesan NNessuna valutazione finora
- Field Bus CompDocumento1 paginaField Bus CompArun BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- ATEX Rating ChartDocumento1 paginaATEX Rating ChartAshish Joshi67% (3)
- Actuator&Thermal Relief ValveDocumento21 pagineActuator&Thermal Relief ValveVenkatesan NNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Lect. 8Documento7 pagineElectrical Lect. 8Yogesh BadheNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Management ProcessDocumento6 pagineRisk Management ProcessVenkatesan NNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrument Air Consumption CalculationDocumento3 pagineInstrument Air Consumption CalculationVenkatesan N0% (1)
- Taking Overfill Prevention To The Next LevelDocumento3 pagineTaking Overfill Prevention To The Next LevelVenkatesan NNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To S88Documento56 pagineIntroduction To S88Jennifer MatthewsNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC'S) : Industrial Control Systems Fall 2006Documento47 pagineIntroduction To Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC'S) : Industrial Control Systems Fall 2006Hamidreza MoaddeliNessuna valutazione finora
- MFM Spec EilDocumento274 pagineMFM Spec EilVenkatesan NNessuna valutazione finora
- Osmr®: Liquefaction Process For LNG ProjectsDocumento17 pagineOsmr®: Liquefaction Process For LNG ProjectsVenkatesan NNessuna valutazione finora
- Terminal Automation SystemDocumento18 pagineTerminal Automation SystemVenkatesan N100% (2)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- HNS Level III COC Knowledge TestDocumento3 pagineHNS Level III COC Knowledge TestAlem Girma100% (10)
- Fibre Channel TutorialDocumento16 pagineFibre Channel TutorialvirtualkiranrajNessuna valutazione finora
- Isa 100.11a-2009Documento819 pagineIsa 100.11a-2009haroldalconzNessuna valutazione finora
- ABB Communicator 691HTDocumento60 pagineABB Communicator 691HTM Jawad AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethics Award Nomination DeaneDocumento17 pagineEthics Award Nomination DeaneAndrew MoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- HCL Industrial Training ReportDocumento40 pagineHCL Industrial Training ReportBirjesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Communication Part B Question BankDocumento2 pagineComputer Communication Part B Question BankNagineni VenkatesNessuna valutazione finora
- Auditing Routers, Switches, and FirewallsDocumento14 pagineAuditing Routers, Switches, and FirewallsTrafalgar S Topan0% (1)
- Hcia - Routing and Switching Mock ExamDocumento187 pagineHcia - Routing and Switching Mock ExamAbdelmoumen Achache78% (9)
- SCADA Deep Inside Protocols and Security MechanismsDocumento83 pagineSCADA Deep Inside Protocols and Security Mechanismsvarg7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Normas Iso PublicadasDocumento104 pagineNormas Iso Publicadasflorin_nite2750100% (1)
- Introduction To Data Communication & Networking: Anjan MahantaDocumento108 pagineIntroduction To Data Communication & Networking: Anjan MahantaAdipNessuna valutazione finora
- HEC MS Computer Science CurriculumDocumento215 pagineHEC MS Computer Science Curriculumadnan0% (1)
- Instructor Materials Chapter 3: Network Protocols and CommunicationsDocumento17 pagineInstructor Materials Chapter 3: Network Protocols and CommunicationsAniket SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Decentralization With Profibus DP DPV1 2ed-07-2003 eDocumento11 pagineDecentralization With Profibus DP DPV1 2ed-07-2003 eNguyễn Anh TúNessuna valutazione finora
- Is-Is: Intermediate System-to-Intermediate SystemDocumento81 pagineIs-Is: Intermediate System-to-Intermediate SystemLoop AvoidanceNessuna valutazione finora
- SIMATIC S7-1200 CP 1243-1 V3.2 CP 1243-7 LTE V3.3 CP 1243-8 IRC V3.2 Protocol IEC 60870-5-104 Interoperability List V3.3Documento17 pagineSIMATIC S7-1200 CP 1243-1 V3.2 CP 1243-7 LTE V3.3 CP 1243-8 IRC V3.2 Protocol IEC 60870-5-104 Interoperability List V3.3Florin Marian MoiseNessuna valutazione finora
- Comptia Network Certification All in One Exam Guide Eighth Edition Exam N10 008 8Th Edition Mike Meyers Full ChapterDocumento56 pagineComptia Network Certification All in One Exam Guide Eighth Edition Exam N10 008 8Th Edition Mike Meyers Full Chaptersherman.prichard680100% (4)
- GSM Chap1 - 8th ECE - VTU - GSM Architectrue and Interfaces2-RamisuniverseDocumento15 pagineGSM Chap1 - 8th ECE - VTU - GSM Architectrue and Interfaces2-Ramisuniverseramisuniverse2100% (1)
- ADC&N Chapter 1 PPTDocumento88 pagineADC&N Chapter 1 PPTBerhane KifleNessuna valutazione finora
- TEMS Layer3 Messages Analysis V2Documento56 pagineTEMS Layer3 Messages Analysis V2siasingle100% (2)
- 100 CiscoDocumento93 pagine100 CiscoulugbekNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Year COMPUTER CH Wise 2021 by 786 AcademyDocumento10 pagine1st Year COMPUTER CH Wise 2021 by 786 AcademySindhu Jatt100% (1)
- HCF Spec 190 1.0 PDFDocumento31 pagineHCF Spec 190 1.0 PDFvikulovNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ExamDocumento36 pagineFinal Examramzy athayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tryhorn 等 - 2023 - Modeling fog of war effects in AFSIMDocumento16 pagineTryhorn 等 - 2023 - Modeling fog of war effects in AFSIMingoreallNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Science Syllabus Pondicherry UniversityDocumento51 pagineComputer Science Syllabus Pondicherry UniversityBalayogi G0% (1)
- Mcqs of Chapter 1: C. MessageDocumento42 pagineMcqs of Chapter 1: C. MessageMuhammad Waseem Anjum Muhammad Waseem AnjumNessuna valutazione finora
- Process-to-Process Delivery: Udp, TCP, and SCTPDocumento89 pagineProcess-to-Process Delivery: Udp, TCP, and SCTPPrafulla Durgadhar GawandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ism Cat 1Documento88 pagineIsm Cat 1AAKASH GOPALNessuna valutazione finora