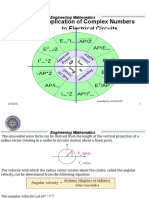
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Mar Ijamtes - 342
Caricato da
Optimas PrimeTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mar Ijamtes - 342
Caricato da
Optimas PrimeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
International Journal of Advanced in Management, Technology and Engineering Sciences ISSN NO : 2249-7455
Soft Start for 3-Phase-Induction Motor
Prof. Vinit V Patel1, Saurabh S. Kulkarni2, Rahul V. Shirsath3,
Kiran S. Patil4
1
Assistant Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering, R.C.Patel Institute of Technology, Shirpur
2,3,4
Final Year U.G. Student, Department of Electrical Engineering, R.C.Patel Institute of Technology,
Shirpur
1
vinitptl@gmail.com,2saurabhsk16@gmail.com, 3rahulshirsath1996@gmail.com,
4
kiran1234545@gmail.com
Abstract
The three-phase induction motor draws current more than its rated capacity during its starting
state which may lead to the damage of windings of the motor. In order to avoid this problem, for the
smooth and soft start of the induction motor (for safer operation), voltage is gradually applied from
lower to higher state.The main intention of this project is the designing of a smooth start process for
the three-phase induction motor by applying the delayed pulses to the motor through the SCR. The
motor thus starts slowly, and then picks-up full speed. The smooth starting of the induction motor is
achieved by the principle of SCR-firing-angle-control. This project consists of six-anti-parallel or
back to back SCRs connected in each series with an induction motor to the mains supply, wherein two
for each phase is used. Opto-coupler is connected to trigger the back-to-back SCRs with isolation
from the controlling section. During the start, the firing angle is heavily delayed by receiving delayed
triggering pulses from the operational amplifier.
Keywords: SCR triggering; IGBT; Firing angle delay; opto isolators; opto couplers; zero
voltage triggering ; motor current control
1. INTRODUCTION
The direct-on-line starting of induction motors produces troublesome torque and current
transients. Soft-starting techniques, which are commonly used with three-phase induction motors, lead
to more reliable operation and allow the reduction of the motor sizing: they limit the phase currents
during the starting transient in order to obtain a smooth connection to the power supply.
Unfortunately, little investigation has been made so far on the application of these techniques to
single-phase motors, even if they are widely used e.g. in households purpose and of course suffer of
the same troubles as in the three-phase motors.
Now a days, the present work can deals with various soft-starting techniques, implemented on a
simulation tool. Out of these some are almost based on the so-called point-on-wave technique of
switching, which is actually a delayed insertion, either simultaneous or independent, of both the main
and auxiliary phases to the main supply. In order to limit the total transient current within the allowed
maximum for household appliances, the gradual insertion of the motor's main phase, is also
investigated and discussed.
Volume 8, Issue III, MARCH/2018 1245 http://ijamtes.org/
International Journal of Advanced in Management, Technology and Engineering Sciences ISSN NO : 2249-7455
2. EXISTING SYSTEM
Soft starters of motors may offer a much variety of methods which are useful for controlling
motor starting. Every soft starting method uses a different primary control parameter.
Soft Start Method Parameter Performance Parameter
Controlled Influenced
Start current, Start torque,
Time Voltage Ramp Voltage
Acceleration
Constant Current Current Start current, Acceleration
Torque Control Torque Start current, Acceleration
Adaptive Acceleration
Acceleration Start current, Acceleration
Control
Best results are obtained by selecting the soft start method that directly controls the parameter of
most importance for the application. Typically soft starters are mainly used to limit motor starting
current or to control load acceleration and/or deceleration [4].
Timed Voltage Ramp (TVR) Starting
Timed voltage ramp (TVR) was the earliest form of soft starting. TVR slows the application of
voltage, which reduces the start current. This reduces start torque and slows the motor’s rate of
acceleration.
Current limit starting
With limiting of current of starting, the soft starter can delivers voltage to the motor so that it
reaches a specified current level, then pauses the voltage ramp. When the current drops, the voltage
ramp continues. This keeps start current within the required limit, although the motor’s actual current
level varies throughout the start. This can be useful for generator set applications where the supply is
limited.
Constant current
With constant current starting, the current is raised from zero to a specified level and keeps the
current stable at that level until the motor has accelerated. Constant current starting is very ideal for
all applications where the starting current must have to kept below a particular level.
Torque Control
Torque control is promoted as a method of providing a more linear speed ramp in soft starters.
By providing a constant acceleration torque, controlling of torque will allows the motor to speed to be
up or slow down in a linear fashion.
Adaptive Control for Starting
Adaptive Acceleration Control is a new intelligent motor control technique. In an adaptive nature
of control with soft start method, the soft starter are able adjusts the current value to start the motor
within a specified time and using a selected acceleration profile. Every application has a particular
starting profile, based on characteristics of the load and the motor. Adaptive Acceleration Control
offers three different starting profiles schemes, to be suit the requirements of various applications.
Volume 8, Issue III, MARCH/2018 1246 http://ijamtes.org/
International Journal of Advanced in Management, Technology and Engineering Sciences ISSN NO : 2249-7455
Selecting a profile that matches the inherent profile of the application can help smooth out
acceleration across the full start time. Selection of the dramatically different Adaptive Control profile
can somewhat able neutralize the inherent profile. The soft starter monitors the motor’s performance
during each start, to improve control for future soft starts.
COMPLETE BLOCK DIAGRAM
Fig 1: Soft Start for 3-Phase-Induction Motor
The block diagram shown in the fig 1 in this voltage is controlled by SCRs [3].
3. SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN
Regulated voltage supply
The 12V DC regulated voltage supply is achieved with the help of following circuit diagram.
The step down transformer (230V/12V AC) is used initially after that the bridge rectifier circuit is
used to convert ac supply to dc supply. By getting output of bridge rectifier circuit it is further fed to
regulating IC7812 to get positive 12V DC regulated supply. The LED used for indicating purpose.
Amplifier circuit
Initially at the time of switch on the base of transistor allows current flow from emitter to base
and charges the capacitor as well as current flows from emitter to collector and charges capacitor.
When capacitor is fully charged, the base becomes high due to which the current stops flowing from
emitter to base and collector. The positive terminal of capacitor is connected to the non-inverting pin
of LM324 comparator, the inverting terminal of comparator is fed from a fixed voltage. When the
capacitor is charging the voltage at non-inverting terminal is greater than the inverting terminal, hence
the output of comparator is high during this time. When the capacitor starts discharging the voltage at
the output of comparator also falls gradually because the voltage at non inverting terminal falls lower
slowly than the inverting terminal. Hence the level of the voltage is initially high and gradually falls
down, this level voltage L is fed to another comparator of Op-amp LM339 [2].
Volume 8, Issue III, MARCH/2018 1247 http://ijamtes.org/
International Journal of Advanced in Management, Technology and Engineering Sciences ISSN NO : 2249-7455
SCR power circuit
In this circuit antiparallel SCR’s are connected per phase. The 440 V, 3-phase, 50 Hz supply is
fed to SCR’s the opto-coupler circuit used in triggering for isolation purpose. The capacitors are used
in circuit for certain amount of voltage regulation. The cathode of SCR’s are connected to load
terminal of induction motor [5].
Fig 2: +12 V DC Regulated supply.
4. PROBLEM STATEMENT
Various studies have shown that nearly 91% of the motors employed or used in industrial
applications use no form of control other than simple electromechanical switching. This results in
increased machine wear as rapid acceleration causes damaging torque transients and high peak
currents. Soft starters able solve this problem by controlling the application of starting current during
acceleration and deceleration.
The purpose of this project is to give soft starting to the induction motor by controlling amount of
staring current with the help of thermistors. This method also covers some of the advanced
functionality that can be found in today’s modern soft starters as well as the considerations when
choosing and sizing soft starters.
Volume 8, Issue III, MARCH/2018 1248 http://ijamtes.org/
International Journal of Advanced in Management, Technology and Engineering Sciences ISSN NO : 2249-7455
5. MAJOR COMPONENTS
Resistors Capacitors Diodes Integrated circuits
560R 470uF/35V 1N4007 LM7812
1K 10uF/63V IN4148 LM339
2.2K 2.2uF/25V LM324
3.3K 0.47uF (470nF) Polyester MOC3021
4.7K 0.1uF/400V Polyester
10K
22K
27K
100K
2.2M
100R/2W
IC Base Transistors Miscellaneous
14-Pin Base BC558/BC557 Push Button 2-Pin
06-Pin Base BC547 Transformer 0-12V, 500
mA
LED-Red
LED-Yellow
LED-Green
Male Burge 2-Pin
Female Burge 2-Pin (For
Transformers)
Heat Sink
Screw Nut for Heat
SCR (TYN612 0R
TYN616)
PCB Connectors 3-Pin
Lamp
6. RESULT
This Method of soft starting initially after switching on the triggering is done and this implies the
on condition of SCR which are connected anti parallel in each phase. The triggering is done by
amplifier triggering method. The current limiting process in the soft starting method is very efficient
than that D.O.L. starter and star-delta starter. The amount of limiting current can be vary or adjusted
by changing the triggering angle for SCR’s.
7. CONCLUSION
The complete system is tested in power electronics laboratory. The experimental results obtained
using the designed three phase motor drive system are studied in two parts, namely, the control part
and the soft starter part. The controlling of the speed motor with almost an accuracy of ±10 rotation
per minute (r.p.m.) is achieved. The different pulse of gate and voltages are seen on oscilloscope. The
use of soft starter circuit suppressed the starting current very significantly. With this above project we
can conclude that by using the soft starter the starting losses will be reduced by 50%, so that heating
Volume 8, Issue III, MARCH/2018 1249 http://ijamtes.org/
International Journal of Advanced in Management, Technology and Engineering Sciences ISSN NO : 2249-7455
of the motor can be avoided and at the same time it will result in the increased life of the motor as
well as the efficiency of operation of motor gradually increases.
REFERENCES
[1] G. Bhuvaneswari, Charles. S and Manjula G. Nair.“Power Quality Studies on a Soft Start for an
Induction Motor”. 2008 IEEE.
[2] Ahmed Riyaz, Atif Iqbal, Shaikh Moinoddin, SK.Moin Ahmed and Haitham Abu- Rub ”
Comparative Performance Analysis of Thyristor and IGBT based induction motor soft starters”.
International journal of engineering, Science and Technology Vol.1, No.1,2009, pp. 90-105.A. M.
[3] Eltamaly, A.I. Alolah and R. M. Hamouda“Performance Evaluation of Three Phase Induction
Motor under Different AC Voltage Control Strategies”. 2007 IEEE.
[4] Shihong Gan; Wei Gu; Jianxin Chu; Yuan Yu “Soft starting high voltage induction motors with
optimum performance”, Material for Renewable Energy & Environment (ICMREE), 2011
International conference, Vol-1, pp 665-659.
[5] Zhang Zili; Cui Xueshen; Zhao Haisen; Yang Yaping “Research on a novel star –delta soft start
method of three-phase induction motor” Power Electronics and Motion Control Conferences
(IPEMC), 2012 7th International, Vol.4, pp 2479-2483
Volume 8, Issue III, MARCH/2018 1250 http://ijamtes.org/
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Pw4 Series Resonance Circuit v1Documento6 paginePw4 Series Resonance Circuit v1Hairul Anuar MasrolNessuna valutazione finora
- ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT THEORY MCQs PDFDocumento9 pagineELECTRICAL CIRCUIT THEORY MCQs PDFYashNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheet 2 - SolutionDocumento7 pagineSheet 2 - SolutionSjf.vbg. hjNessuna valutazione finora
- E CircuitsDocumento34 pagineE CircuitsLazarevic_GoranNessuna valutazione finora
- SVERKER 750 - 780 Relay Test Unit. User S ManualDocumento76 pagineSVERKER 750 - 780 Relay Test Unit. User S ManualaleksandarlaskovNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Problem SolutionDocumento44 paginePractice Problem Solutionfalilv9580% (20)
- Principle of EE1: Lesson 3Documento88 paginePrinciple of EE1: Lesson 3Nguyễn Hoàng LânNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocumento12 pagineElectronic Devices and CircuitsAnandhi SrinivasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Theory Question Bank PDFDocumento14 pagineNetwork Theory Question Bank PDFmohammadmohisin134Nessuna valutazione finora
- BS-M101 MergedDocumento11 pagineBS-M101 MergedArkaprabha GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- EEEN221 Assignment 01 With Answers 01Documento15 pagineEEEN221 Assignment 01 With Answers 01Lame MorupisiNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Math 4Documento48 pagineEngineering Math 4Kaan AyyildizNessuna valutazione finora
- Aircraft Electrical and Ignition SystemDocumento34 pagineAircraft Electrical and Ignition SystemJohn RandelNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 08 en PG Fa SmallDocumento284 pagine2017 08 en PG Fa SmallNguyen QuocNessuna valutazione finora
- GaN Research PaperDocumento7 pagineGaN Research Papergurdiansky01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Express PCB Tutorial: Entering The Schematic Into ExpressschDocumento35 pagineExpress PCB Tutorial: Entering The Schematic Into Expressschgyuvaraj10100% (1)
- Diy Lithography 10micronDocumento11 pagineDiy Lithography 10micronMukund Srinivas100% (1)
- Network Theory - Coupled CircuitsDocumento6 pagineNetwork Theory - Coupled CircuitsHarsh GajjarNessuna valutazione finora
- Revenue Protection Issues of Tamper and Fraud: Drum - Training ProgramDocumento76 pagineRevenue Protection Issues of Tamper and Fraud: Drum - Training Programpawan kumar raiNessuna valutazione finora
- Inverter PDFDocumento84 pagineInverter PDFVenkedesh RNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet PDFDocumento20 pagineDatasheet PDFangel albertoNessuna valutazione finora
- CSE Syllebus of MBSTUDocumento41 pagineCSE Syllebus of MBSTUCSE 19015100% (1)
- Ujian 1 VRT 3033 - Razan Samhana Zaiedi D20182085643Documento5 pagineUjian 1 VRT 3033 - Razan Samhana Zaiedi D20182085643Razan SamhanaNessuna valutazione finora
- ATV320 Installation Manual EN NVE41289 07Documento166 pagineATV320 Installation Manual EN NVE41289 07KnezNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocumento2 pagineGujarat Technological UniversityAyush SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- UTM Course SynopsesDocumento14 pagineUTM Course SynopsesSaravanan KerishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Iot Based Transformer Monitoring System.Documento82 pagineIot Based Transformer Monitoring System.ra patNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter4 28wheatstonebridge 29Documento26 pagineChapter4 28wheatstonebridge 29Amirul SyazwanNessuna valutazione finora
- EL - 124 Electronic Devices & Circuits: Experiment # 04Documento6 pagineEL - 124 Electronic Devices & Circuits: Experiment # 04Jawwad IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepare A Chart of Electric Locomotive and Show The Various ComponentsDocumento14 paginePrepare A Chart of Electric Locomotive and Show The Various ComponentsViraj Tiware60% (5)