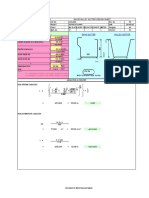
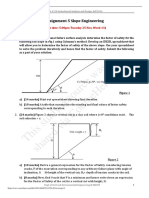
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sheikh Muhammad Waqar
Caricato da
Muhammad Sarmad0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
22 visualizzazioni3 pagineThis literature review discusses several studies on stabilizing problematic soils like clay and organic soils using lime and zeolite additives. Three key points:
1) Studies found that mixtures of cement, lime and zeolite can effectively reduce the swelling, shrinkage and permeability of clay soils, and increase their strength, especially with curing times of at least 90 days.
2) Replacing a portion of cement with zeolite in soil mixtures was also found to improve unconfined compressive strength and reduce permeability. The effectiveness increases with higher cement and zeolite contents.
3) Longer curing periods of 56 days or more led to higher strength gains in organic soils treated with lime and ze
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis literature review discusses several studies on stabilizing problematic soils like clay and organic soils using lime and zeolite additives. Three key points:
1) Studies found that mixtures of cement, lime and zeolite can effectively reduce the swelling, shrinkage and permeability of clay soils, and increase their strength, especially with curing times of at least 90 days.
2) Replacing a portion of cement with zeolite in soil mixtures was also found to improve unconfined compressive strength and reduce permeability. The effectiveness increases with higher cement and zeolite contents.
3) Longer curing periods of 56 days or more led to higher strength gains in organic soils treated with lime and ze
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
22 visualizzazioni3 pagineSheikh Muhammad Waqar
Caricato da
Muhammad SarmadThis literature review discusses several studies on stabilizing problematic soils like clay and organic soils using lime and zeolite additives. Three key points:
1) Studies found that mixtures of cement, lime and zeolite can effectively reduce the swelling, shrinkage and permeability of clay soils, and increase their strength, especially with curing times of at least 90 days.
2) Replacing a portion of cement with zeolite in soil mixtures was also found to improve unconfined compressive strength and reduce permeability. The effectiveness increases with higher cement and zeolite contents.
3) Longer curing periods of 56 days or more led to higher strength gains in organic soils treated with lime and ze
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 3
Literature Review
Stabilization of high plastic soil with lime and
zeolite.
Write a short title here describing your problem
statement concisely, in one brief sentence.
Sheikh Muhammad Waqar, F2019136012, MS Civil Engineering
landfill liner. Zeolite's preference is due to its high
PROBLEM STATEMENT adsorption potential for heavy metals as well as its
Clay soil in subgrade of road is a serious problem. pozzolanicity already well known. The results
The major problem of clay is the excessive indicated improved properties with curing when
settlements, lack of shear strength and less bearing using extensive soil to zeolite ratio of 0.5. Swell
capacity so for overcoming these problem we have capacity was observed to decrease by 85 percent
to stabilize the soil before construction of road over the 90 day healing period, while shrinking and
compressibility characteristics showed a 30-34
LITERATURE REVIEW percent decrease. Under all confining pressure
ranges tested, the hydraulic conductivity was found
Yadav and Kushwaha (2018) attributed It is well
to remain below the regulatory limit, given the
known that cement, stabilized sand is one of soil
curing time was at least 90 days. In addition, the
stabilization’s environmental and economic
mixture with time achieved enhanced strength
problems. Improving local cement and zeolite soils
characteristics and proved to be sustainable over the
can bring great benefits, including strength of the
period studied. Under all confining pressure ranges
slopes by problems of slope stability, stabilizing
tested, the hydraulic conductivity was found to
weak soils and stopping liquefaction of the soil.
remain below the regulatory limit, given the curing
Dosage methodologies for soil improvement are
time was at least 90 days. In addition, the mixture
being established recently on the basis of a logical
with time achieved enhanced strength characteristics
criteria as it exists in concrete engineering .The
and proved to be sustainable over the period studied.
effects of zeolite on the characteristics of cement
Mola-Abasi and Shooshpashaet. (2016) found that
treated sands were investigated in this analysis,
cemented sand is well known to be one of the
based on an al-program experiment. The effects of
financial and eco-friendly problems of soil
zeolite on the features of cement treated sands were
stabilization .In this situation, a mixture of sand,
investigated in this analysis, based on an al-program
cement and other materials such as carbon, glass,
experiment Portland cement and zeolite are included
nanoparticles and zeolite can be commercially
as a stabilizing agent. Results show that
available and can be used effectively in road
permeability is decreased as the content of cement
construction soil stabilization .Nevertheless,
increases. We add 4%, 6%, 8% and 10% cement by
zeolite's effect and effectiveness on the properties of
weight of sand, after which 10% cement add a
cemented sand classifications has not been fully
different percentage of zeolite by weight of cement
explored. In this study, based on a system of
By replacing the cement in the mixture and finding
experiments. To study the impact of zeolite on
permeability, permeability is also reduced here
cemented sand characteristics. The stabilizing agent
Furthermore, in the compaction test the peak value
includes Type II cement and zeolite from Portland.
of MDD is obtained at 10% cement by weight of
Results show improvements in the unconfined
sand with 50% Zeolite replacement by weight of
compressive test (UCT) and failure properties of
cement.
cemented sand when the cement is replaced by
Öncü (2017) attributed that experimental study
zeolite at an average 30%age after 28 days. The
evaluates the appropriateness of a local expensive
strength enhancement rate varies from about 20% to
soil mixed with zeolite readily obtained from
78%.With the increase in cement quantity and
turkey’s natural reserve to be proposed as semi-arid
porosity, the efficacy of using zeolite increases.
Eventually, it is demonstrated that a power function the healing time and improved properties with the
of the void-cement ratio and zeolite material is an mixture of cement and zeolite additives depending
suitable method for testing zeolite-cemented on the sodium adsorption ratio (SAR) and the
mixtures UCS. exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) of clay soil
Ling et.all. (2013) investigates organic soil content samples with various plasticity characteristics,
to prevent the development of lime-stabilizing dispersive and swelling properties. This research not
reaction products resulting in low strength gains in only demonstrated that a mixture of cement and
the treatment of organic soils. In this research, zeolite additives enhanced the dispersive and
zeolite, a form of pozzolan with high CEC strength, swelling properties of clay soil samples with four
is proposed to be used to improve the lime stability different plasticity characteristics, depending on
of organic soil. The efficiency of mixed lime zeolite their SAR and ESP values, but also observed
in organic soil stabilization was examined using two significant increases in strength values.
types of organic synthetic soil with predetermined DEMİRBAŞ (2009) attributed Expensive soils are
organic content. Through mixing inorganic soil a global problem that presents a number of
(commercial kaolin) with organic matter challenges for civil engineers. When they have
(commercial humic acid) at a particular ratio, access to water, these soils swell and shrink once
artificial organic soils are created Initial lime they dry out. The most common and cost-effective
consumption was estimated for organic soils to way to stabilize these soils is to use admixtures to
determine the minimum percentage of stabilizer prevent volume changes. This research explores the
required for each soil. Potential determining factors, impact of using Bigadic zeolite (boron by-product)
such as natural materials, stabilizer contents, and to reduce the potential for swelling. Through
healing cycles, have been identified. The study combining kaolinite and bentonite, the extensive soil
findings showed that high organic content and low is prepared in the laboratory. Bigadic zeolite (boron
lime content resulted in lower strength gains.. It is through-product) is applied by weight to the soil at
noticed, however, that a minor substitution of lime 0-25A portion of it. Distribution of grain size,
with zeolite works well with low organic soil at long Atterberg limits and percent swelling and mixture
healing times, resulting in the highest strength swelling level are calculated. Specimens are treated
among all the mixtures. Overall, longer periods of for 7 days and 28 days. As a result of the
healing would increase soil strength by 56 days > 28 experimental study, Bigadic zeolite (boron by-
days > 7 days. Nonetheless, the percentage of product) was introduced to decrease swelling
increase in strength during healing periods is linear potential and swelling level of the artificially
with the lime content, which has shown that lime is prepared expansive soil sample under laboratory
required for pozzolanic reaction. conditions. Healing positively influences the swell
Turkoz and Vural (2013) attributed that analysis of level and swell rate of the stabilized samples.
dispersive and extensive soils is considered
problematic and many construction systems have REFERENCES
serious problems with these soil properties. 1. Yadav, P. R. (2018).
Comprehensive studies have been conducted for Effect of addition of zeolite and cement on soil g
many years with the goal of improving soil swelling eotechnical properties. International Research
and dispersive properties through the use of Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET),
additives. That function associated with enhancing 851-856..
the dispersive and swell properties of clay soil with 2. Öncü, Ş., & Bilsel, H. (2017). Effect of
additives has been evaluated separately in the zeolite utilization on volume change and strength
literature. The effect of cement and natural zeolite properties of expansive soil as landfill
additives on the dispersibility characteristics and barrier. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 54(9),
swelling ability of clay soils was investigated in this 1320-1330.
study. A fixed percentage of cement (3%) plus 3. Mola-Abasi, H., & Shooshpasha, I. (2016).
various percentages of natural zeolite (1%, 3%, 6%, Influence of zeolite and cement additions on
10%, 15% and 20%) was combined with four mechanical behavior of sandy soil. Journal of Rock
different samples of clay soil. Next, the physical and Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 8(5),
chemical properties of the soil samples have been 746-752.
calculated in this context. Next, the swelling 4. Ling, F. N. L., Kassim, K. A., Karim, A.,
percentage, swelling pressure, crumb, pinhole and Tarmizi, A., & Chan, T. W. (2013). Stabilization of
unconfined compressive strength tests were artificial organic soil at room temperature using
performed on samples with and without the additive blended lime zeolite. In Advanced materials
research (Vol. 723, pp. 985-992). Trans Tech
to achieve specific compaction characteristics.
Publications.
Significant improvements in strength depended on
5. Turkoz, M., & Vural, P. (2013). The effects of
cement and natural zeolite additives on problematic
clay soils. Science and Engineering of Composite
Materials, 20(4), 395-405.
6. Shi, J. X. (2013). The applications of zeolite
in sustainable binders for soil stabilization.
In Applied Mechanics and Materials (Vol. 256, pp.
112-115). Trans Tech Publications.
7. GÜNEŞDEMİRBAŞ. (2009). Stabilization of
Expansive Soils using Bigadic Zeolite. Middle East
Technical University.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Eave Valley Gutter Design SheetDocumento1 paginaEave Valley Gutter Design SheetIshaan AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Aashto-H20, Hs20 & Hl93 LoadingDocumento5 pagineAashto-H20, Hs20 & Hl93 Loadingsmartman35100% (3)
- Bearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationDocumento49 pagineBearing Capacity of Shallow FoundationMuhammad Faisal Habib JanjuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 4 Cable Size and Wiring MethodDocumento64 pagineTopic 4 Cable Size and Wiring MethodYuen Chan100% (1)
- Soil StabilizationDocumento35 pagineSoil StabilizationVaish Navi100% (1)
- Architect's Guide To FLS (NFPA)Documento29 pagineArchitect's Guide To FLS (NFPA)N V Sumanth Vallabhaneni100% (1)
- Cofferdam ProcessDocumento208 pagineCofferdam ProcessErikGrobler100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Davit Cal 2251B Davit Arm CalculationDocumento4 pagineDavit Cal 2251B Davit Arm CalculationKarina RoquelNessuna valutazione finora
- Strength, Durability and Shrinkage Characteristics of Cement Stabilised Soil BlocksDocumento10 pagineStrength, Durability and Shrinkage Characteristics of Cement Stabilised Soil BlocksSam ChongNessuna valutazione finora
- EC3 - Tension Member - 2021Documento27 pagineEC3 - Tension Member - 2021MUHAMMAD AMIRUL ASYRAF BIN MOHD RANINessuna valutazione finora
- The Electricians Guide To The Building Regulations Part PDocumento1 paginaThe Electricians Guide To The Building Regulations Part PSangar KarimNessuna valutazione finora
- In Construction: Waterproofing Is The Process of Making An Object or Structure Waterproof or Water-Resistant SoDocumento63 pagineIn Construction: Waterproofing Is The Process of Making An Object or Structure Waterproof or Water-Resistant SoSuhaimi BohariNessuna valutazione finora
- DME-Online Class Sep2020-Module 2-PartB PDFDocumento37 pagineDME-Online Class Sep2020-Module 2-PartB PDFMathew John100% (1)
- Development of High Strength Concrete From Recycled Aggregate Concrete.Documento94 pagineDevelopment of High Strength Concrete From Recycled Aggregate Concrete.Micah GentleNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Stabilization Using Geopolymer and Biopolymer 2Documento10 pagineSoil Stabilization Using Geopolymer and Biopolymer 2Chisomo Henry ChuluNessuna valutazione finora
- Influence of Geopolymers in The Stabilization of Clay SoilDocumento13 pagineInfluence of Geopolymers in The Stabilization of Clay SoilAmmar AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Stabilization of Clayey Soil by Lime & Coir: Shreyas.KDocumento22 pagineStabilization of Clayey Soil by Lime & Coir: Shreyas.KAli Saleh Saad ALiSAWiNessuna valutazione finora
- Report AbhiDocumento14 pagineReport AbhiAshique PNessuna valutazione finora
- Expansive Soil Stabilization Using Industrial Solid Wastes A ReviewDocumento11 pagineExpansive Soil Stabilization Using Industrial Solid Wastes A ReviewTIZA MICHAEL B.Engr., BBS, MBA, Aff. M. ASCE, ASS.M. UACSE, M. IAENG. M.ITE.100% (1)
- Experimental Study of Silty Clay StabilizationDocumento6 pagineExperimental Study of Silty Clay StabilizationTanveer KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Settlement Behaviour of A Cement-Stabilised Malaysian ClayDocumento7 pagineSettlement Behaviour of A Cement-Stabilised Malaysian ClaysyahirabdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Resin As A Soil Stabilizer - Formatted PaperDocumento5 pagineResin As A Soil Stabilizer - Formatted PaperAbass AbdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Amini 2019Documento12 pagineAmini 2019OM YeimyNessuna valutazione finora
- Strength Characteristics of Expansive Soils Using Epoxy Resin and Silty SoilDocumento4 pagineStrength Characteristics of Expansive Soils Using Epoxy Resin and Silty SoilsonofalexanderNessuna valutazione finora
- S0165232X21001397Documento15 pagineS0165232X21001397Abbas AyadNessuna valutazione finora
- 48 55 1951 Ahmed April 2022 921Documento9 pagine48 55 1951 Ahmed April 2022 921Ahmed.S.AbdulrasoolNessuna valutazione finora
- An Experimental Study of Soil Stabilization Using Marble DustDocumento6 pagineAn Experimental Study of Soil Stabilization Using Marble DustnidsNessuna valutazione finora
- Stabilization of Pavement Subgrade by Using Fly Ash Activated by CementDocumento8 pagineStabilization of Pavement Subgrade by Using Fly Ash Activated by CementNandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Strength Behavior of Enzymatic Cement Treated Clay: International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering June 2019Documento16 pagineStrength Behavior of Enzymatic Cement Treated Clay: International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering June 2019veenau 1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2012 USA, Mejora de Las Características de Los Suelos Expansivos de Suelos Expansivos Utilizando Cal y Cenizas VolantesDocumento6 pagine2012 USA, Mejora de Las Características de Los Suelos Expansivos de Suelos Expansivos Utilizando Cal y Cenizas VolantesEder RuizNessuna valutazione finora
- Ud SSC 81580542567Documento6 pagineUd SSC 81580542567Ali Saleh Saad ALiSAWiNessuna valutazione finora
- Report ChartsDocumento10 pagineReport Chartskranthi bhushan02Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geomechanical Behaviour of Clay Stabilised With FlyAshBased Geopolymer For Deep MixingGeosciences SwitzerlandDocumento15 pagineGeomechanical Behaviour of Clay Stabilised With FlyAshBased Geopolymer For Deep MixingGeosciences SwitzerlandIvan Lee Lozano TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Improvement of Soft Clay Soil Using Different Types of AdditivesDocumento9 pagineImprovement of Soft Clay Soil Using Different Types of AdditivesWilson Rojas CamayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Stabilization of Expansive Soils Derived From Enugu Shale in Enugu Area, Southeastern Nigeria Using Lime, Cement and Coal Fly Ash AdmixturesDocumento14 pagineStabilization of Expansive Soils Derived From Enugu Shale in Enugu Area, Southeastern Nigeria Using Lime, Cement and Coal Fly Ash AdmixturesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimizing Micaceous Soil Stabilization - 2021 - Journal of Rock Mechanics andDocumento9 pagineOptimizing Micaceous Soil Stabilization - 2021 - Journal of Rock Mechanics andsidabutarwelsin98Nessuna valutazione finora
- Properties Concrete Dune SandDocumento6 pagineProperties Concrete Dune SandAlanSamNessuna valutazione finora
- Naga 1Documento31 pagineNaga 1Siddharth RavuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Stone Dust On Geotechnical Parameter of Fine Grained SoilDocumento7 pagineEffect of Stone Dust On Geotechnical Parameter of Fine Grained SoilAmanulla KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Two Literature ReviewDocumento19 pagineChapter Two Literature ReviewVictor ImehNessuna valutazione finora
- IJRESTS Published Paper PDFDocumento5 pagineIJRESTS Published Paper PDFEr Sufyan AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Strain Rate On The Strength CharacteristicsDocumento11 pagineEffect of Strain Rate On The Strength Characteristicskamrul_07Nessuna valutazione finora
- Improvement of Clayey Soil With Lime and Industrial SludgeDocumento10 pagineImprovement of Clayey Soil With Lime and Industrial SludgeJPDGLNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017GAE1255XanthanOmandesert Qureshietal 2Documento17 pagine2017GAE1255XanthanOmandesert Qureshietal 2SaiFunNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of Powdered Golden Apple Snail Shells As A Stabilizing Agent To Sandy Clay Loam SoilsDocumento7 pagineEvaluation of Powdered Golden Apple Snail Shells As A Stabilizing Agent To Sandy Clay Loam SoilsMARK KEVIN GUTIERREZNessuna valutazione finora
- Wakchaure Presentation ProjectDocumento16 pagineWakchaure Presentation ProjectMayur Madhukar MankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ijs DR 2009016Documento6 pagineIjs DR 2009016عبدالرحمن العليميNessuna valutazione finora
- Super Plasticizer ConcreteDocumento43 pagineSuper Plasticizer ConcretelazamNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 2017, 4 (9) :228-237Documento10 pagineJournal of Scientific and Engineering Research, 2017, 4 (9) :228-237Basha FayissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdulrahman Et Al. - The Autoclaved Concrete Industry-An Easy To Follow Method For Optimization and TestingDocumento10 pagineAbdulrahman Et Al. - The Autoclaved Concrete Industry-An Easy To Follow Method For Optimization and TestingAlex BritoNessuna valutazione finora
- GeopolymerDocumento3 pagineGeopolymerSange SherpaNessuna valutazione finora
- Swell and ComprexibilityDocumento5 pagineSwell and ComprexibilityDylan SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lime StabilizationDocumento4 pagineLime StabilizationKshitija NadgoudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Cement-Zeolite Grouts On The Durability of Stabilised Clays Effet Des Mortiers Béton-Zéolite Sur La Durabilité Des Argiles StabilisésDocumento4 pagineEffect of Cement-Zeolite Grouts On The Durability of Stabilised Clays Effet Des Mortiers Béton-Zéolite Sur La Durabilité Des Argiles StabilisésrasnarockNessuna valutazione finora
- Use of Quick and Hydrated Lime in Stabilization of Lateritic Soil: Comparative Analysis of Laboratory DataDocumento13 pagineUse of Quick and Hydrated Lime in Stabilization of Lateritic Soil: Comparative Analysis of Laboratory DataCarlos CabanasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1 1.1.1 GENERALDocumento45 pagineChapter-1 1.1.1 GENERALVishNessuna valutazione finora
- Cement Soil Stabilization As An Improvement Technique For Rail Track Subgrade and Highway Subbase and Base Courses A RevDocumento6 pagineCement Soil Stabilization As An Improvement Technique For Rail Track Subgrade and Highway Subbase and Base Courses A RevHyukLadezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abstract.: Article Available at orDocumento8 pagineAbstract.: Article Available at orSERBAH BoumedieneNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Hadi Bahadori, Hooman Motamedi, Araz Hasheminezhad, Ramin MotamedDocumento13 pagineSoil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering: Hadi Bahadori, Hooman Motamedi, Araz Hasheminezhad, Ramin MotamedRobert MerinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Geotextiles and Geomembranes: Arvind Kumar, Deepak GuptaDocumento9 pagineGeotextiles and Geomembranes: Arvind Kumar, Deepak GuptaRithYNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Polypropylene Fibers, Lime and Ceramic Additives On The Compressibility of Silty-Clay SoilDocumento11 pagineEffect of Polypropylene Fibers, Lime and Ceramic Additives On The Compressibility of Silty-Clay SoilAsad HafudhNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S1674775516302736 MainDocumento11 pagine1 s2.0 S1674775516302736 MainAdrián AhumadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ghobadi, M. H. Abdilor, Y. Babazadeh, R.Documento9 pagineGhobadi, M. H. Abdilor, Y. Babazadeh, R.BRUNO KARASIAKNessuna valutazione finora
- Irjet V7i11143Documento6 pagineIrjet V7i11143OwaisNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S2214509522001206 MainDocumento16 pagine1 s2.0 S2214509522001206 MainMALIKNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Stabilization Using Vertical ColumnsDocumento10 pagineSoil Stabilization Using Vertical Columnshareesh vinodNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 17341-Gazimmfd 488720-889218Documento13 pagine10 17341-Gazimmfd 488720-889218Sumit BhavsarNessuna valutazione finora
- Irjet V4i6529 PDFDocumento3 pagineIrjet V4i6529 PDFShankar Dev GourNessuna valutazione finora
- Clayey Soil Stabilization Using Alkali-Activated Cementitious MaterialsDocumento12 pagineClayey Soil Stabilization Using Alkali-Activated Cementitious MaterialsNicolasNessuna valutazione finora
- 21pce023 Bishal Roy SarkarDocumento18 pagine21pce023 Bishal Roy SarkarBishal Roy SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture Toughness: A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture ToughnessDa EverandA Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture Toughness: A Comparative Study of Mechanical Properties of Zinc Acrylate Epoxy nanocomposites Reinforced by AL2O3 and Cloisite®30B and Their Mixture: Tensile Strength and Fracture ToughnessNessuna valutazione finora
- LWM - MEP-ProgramDocumento2 pagineLWM - MEP-ProgramAburvarajNessuna valutazione finora
- FHWA Geotechnical Aspects of Pavements Reference Manual: Chapter 5.0 Geotechnical Inputs For Pavement Design (Continued)Documento1 paginaFHWA Geotechnical Aspects of Pavements Reference Manual: Chapter 5.0 Geotechnical Inputs For Pavement Design (Continued)Erasmo AlexanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Tunnelling - 3Documento14 pagineIntroduction To Tunnelling - 3Kiprono VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 13 13 - Wet Pipe Sprinkler SystemsDocumento7 pagine21 13 13 - Wet Pipe Sprinkler SystemsLangzkie NalipaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure Loss in Schedule 40 Steel PipesDocumento11 paginePressure Loss in Schedule 40 Steel PipesAnonymous qrSsYuxyoYNessuna valutazione finora
- RCP 24 Inch Class 2Documento5 pagineRCP 24 Inch Class 2noto.sugiartoNessuna valutazione finora
- Physicschapter 6Documento14 paginePhysicschapter 6Owais FarooqNessuna valutazione finora
- Kamus Data GDC-JPS Rev11Documento147 pagineKamus Data GDC-JPS Rev11omkjp 01Nessuna valutazione finora
- CIVL4720 2014 Assign 5Documento4 pagineCIVL4720 2014 Assign 5rivai sargawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Anexo A - Magnesium Elektron Elektron® ZRE1 Magnesium Alloy, UNS M12330 - DatasheetDocumento3 pagineAnexo A - Magnesium Elektron Elektron® ZRE1 Magnesium Alloy, UNS M12330 - DatasheetAmilton CardosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Walkway Truss Design: MEMB123 SEM 2 16/17Documento19 pagineWalkway Truss Design: MEMB123 SEM 2 16/17Darwish Akmal LikeaBossNessuna valutazione finora
- Machine Chapt5 Pressure VesselDocumento10 pagineMachine Chapt5 Pressure VesselHelen AdugnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sheel Roof: Vaibhav.b.p 3PD14AT034Documento1 paginaSheel Roof: Vaibhav.b.p 3PD14AT034vaibhavNessuna valutazione finora
- 23-Article Text-53-1-10-20220731Documento6 pagine23-Article Text-53-1-10-20220731Way ReyNessuna valutazione finora
- Utilities Pugeda Quiz 1Documento5 pagineUtilities Pugeda Quiz 1Donna Andrea DesembranaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana, 2016-17: Cost Estimate For Road WorksDocumento6 paginePradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana, 2016-17: Cost Estimate For Road WorksHoque joynul100% (1)
- Ensign Cast Iron Pipes Dec2009Documento92 pagineEnsign Cast Iron Pipes Dec2009Kkrkollam KrishnaKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Postensioned Bridge Plate 4Documento1 paginaPostensioned Bridge Plate 4John Emerald GoloNessuna valutazione finora